Short term plan
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 1 |
School: S. Yerubayev |
||
|
Date: 02.09.2024 |
Teacher name: S. Murataliyeva |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Attributes and personality |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics; 9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; 9.6.15.1 use infinitive forms after a growing number of adjectives and verbs, use gerund forms after a growing variety of verbs and prepositions, use an increased variety of prepositional verbs and phrasal verbs on a range of familiar general and curricular topics; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
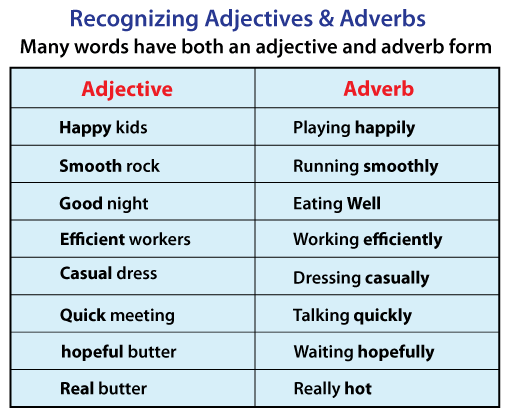
Learners will be able to: - Recognize and use nouns and adjectives of attributes and personality. - Make adverbs from adjectives. - Construct the sentences using comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs with some support |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Creativity and innovation The Education Day! "School is a place of kindness!" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, ask: How would you describe your personality? Elicit a few ideas from individual students. • Put students into pairs to write down as many words they can think of associated with personality. • Write attributes on the board and ask students if they think people with certain attributes are suited to particular hobbies. Ask: What kind of people are suited to playing chess? Accept all answers. T: What do you think about today’s theme? Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. Learners fill the sheets of papers by classifying hobbies in together |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/i2kwjRagkf6dqBDG6
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P:8 In a weaker class, ask for translations. In a stronger class, encourage students to put the words into sentences to show understanding. Differentiation with individual need learners: * Translate in L1 adjectives of the hobbies. |
Learners complete the table. Which adjectives are negative? ANSWERS 1 generous 2 passion 3 moody 4 anxious 5 pessimistic 6 optimism 7 responsibility 8 respect 9 enthusiasm 10 confidence 11 frustrated Negative adjectives: moody, anxious, pessimistic, frustrated |
T’s feedback
Descriptor: - complete the table. Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P:8 In a weaker class, you could help students to prepare for the task by deciding together whether the missing words are adjectives or nouns. In a stronger class, ask students to give reasons and justify their opinion. Ask some students to compare their answers and report back to the class on how similar or different they and their partner are. A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners complete the sentences with your own ideas using words in exercise 1. ANSWERS Student’s own answer |
Self -assessment T’s CCQs
Descriptor: - complete the sentences - using words in exercise 1 Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Stickers |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P:8 Students do the Hobbies questionnaire, then compare their answers in pairs. Do they have similar views on hobbies? Ask them to discuss what hobbies they do and what attributes help with that hobby. T asks some CCQs:
|
Learners complete the Hobbies questionnaire. Then compare your answers with a partner. Do you have the same attitude to hobbies? How are you the same and different? ANSWERS Student’s own answer Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS -No -Yes -Yes |
T’s feedback
Descriptor: - complete the Hobbies questionnaire - answer the question Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Pictures Worksheet |
|
End 5 min |
“Finger” method is used to find out was the lesson clear or not. 5 fingers- I understood 4 fingers -I have some questions 2 fingers-I need a help Ex: P: Home task |
Ss show their knowledge according to the lesson Ss evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: W |
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 2 |
School: S. Yerubayev |
||
|
Date: o5.09.2024 |
Teacher name: S. Murataliyeva |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Compare people and the things they do. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; 9. 6. 12. 1 use different comparative forms of regular and irregular adverbs on many familiar general and educational topics, use many types of adverbs that come before the verb, after the verb and at the end of the verb; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Construct the sentences using comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs with some support - Comprehend comparisons to compare and contrast people and the things they do. - Produce a clear, coherent description of a person they know. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Independence and Patriotism Day of the Languages of the People of Kazakhstan |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: Pantomime: 'What do you like? Play the game in 2 groups. One pupil from each group comes to the board and mimes a hobby. The other group tries to guess the hobby. If they guess correctly, they win one point. At the end of the game, the group with the most points is the winner. T: What do you think about today’s theme? Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/i2g4PSk1aFJaj5G69
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 4 P: 9 Write on the board: In life, it’s best not to act too … Elicit possible endings for the sentence (quickly, carefully, etc.). Write the adverbs successfully, generously, anxiously, and confidently on the board and underline them. Elicit that they are adverbs, they end in -ly, and they are formed from the adjectives in exercise 1. Check that students understand the difference between adjectives and adverbs. Write on the board: Petra is a good singer. Petra sings well. Underline good and well. Explain or elicit that adjectives modify nouns and adverbs modify verbs. Point out that well is irregular. Ask students to look back at exercise 1 and make adverbs out of the remaining adjectives.. Differentiation with individual need learners: Learners understand the difference between adjectives and adverbs. Less motivated learner do the task with support. |
Learners complete the examples and the rules in the table ANSWERS 1 -ly 2 firmly 3 -ily 4 angrily 5 -ally 6 optimistic 7 fast 8 hard Adverbs from adjectives in exercise 1: successfully, generously, passionately, moodily, anxiously, pessimistically, optimistically, responsibly, enthusiastically, confidently, frustratingly |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - complete the examples -make adverbs from adjectives Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 5 P: 9 Ask some students to write some of their sentences on the board. Discuss if they are logical and correctly formed. A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. Less motivated learner work in pairs to write their sentences. |
Students write six sentences describing how you do different things. Use the verbs in the first box and adverbs formed from the adjectives in the second box. ANSWERS Student’s own answer |
Self -assessment
Descriptor: - write six sentences - use the verbs Total: 2 point |
Worksheets |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 6 P: 9 • Focus on the example and elicit one or two more examples from the class. Check answers. Make sure students understand we use less, the least, more, the most to form comparative and superlative forms of adverbs A learner with individual needs: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use simple, basic statements in his discussion. |
Learners study sentences 1–5. How do we form the comparative and superlative forms of adverbs? Complete the table with the words in blue ANSWERS We use less and more to form comparative adjectives. We use the least and the most to form superlatives. Comparative adjectives: meaner, more comfortable, less stressful Comparative adverbs: less seriously, more positively, more happily Superlative adjectives: the most selfish, the least successful, the most optimistic, the richest Superlative adverbs: the least generously, the most rudely |
T’s feedback
Descriptor: - complete the table Total: 2 point |
Pictures Worksheet |
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 7 P: 9 Focus on the first sentence and elicit that the missing word is an adverb and a superlative. Elicit the answer (the most successfully). In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs. In a stronger class, ask students to complete the sentences individually, but allow them to check their answers in pairs before you check with the class Differentiation with individual need learners: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to complete the sentences with. |
Learners complete the sentences with the comparative or superlative form of an adjective or adverb. Use more / less and the most / the least ANSWERS 1 the most successfully 2 less pessimistically 3 more carefully 4 less noisy 5 more slowly 6 the least sensitive |
Self -assessment T s feedback Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Home task Ex: P: |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 3 |
School: S. Yerubayev |
||
|
Date: 06.09.2024 |
Teacher name: S. Muratalyeva |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Comparing generations |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; 9. 6. 12. 1 use different comparative forms of regular and irregular adverbs on many familiar general and educational topics, use many types of adverbs that come before the verb, after the verb and at the end of the verb; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Synthesize information from the reading passage about life in the 1950s. - Demonstrate the correct use of adjectives + prepositions. - Interpret a text comparing past and present generations. - Express their opinions about different generations building extended sentences. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Independence and Patriotism to make students understand the value of three languages |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, ask students if they have seen photographs of their parents and grandparents when they were young. Ask: What were their clothes like? What were their hairstyles like? Ask: What do you think life was like in the 1950s? Elicit a range of ideas, but don’t confirm or reject any at this stage. T: What do you think about today’s theme? Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/Ce8ZAnooSXd3PnA5A
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 10 • Read through the items in the list with the class and check that students understand them. In a weaker class, allow students to use dictionaries or pre-teach ballroom (a place where people used to go to dance) and big band (a style of jazz music played by a group of twelve to fifteen musicians). In a stronger class, elicit suggestions and guesses for unfamiliar vocabulary, and then discuss again after the first reading, encouraging students to use context to work out the meaning. In pairs, or as a group, discuss the questions. Then let students listen and read, and check their answers. Differentiation with individual need learners: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use dictionaries or pre-teach ballroom |
Learners which of these things do you think were common in the 1950s? Which are common now? Read, listen and compare your answers with the text. ANSWERS More common in the 1950s ballrooms, big bands, black-and-white TV More common now mobile phones, computers, jobs for women, discos, bad language |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - read the text - listen and compare your answers Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 10 In a weaker class, encourage students to underline the parts of the text where they found the answers. In a stronger class, encourage students to identify the false sentences and correct them from memory. Then they should read again and confirm. T asks some CCQs:
|
Learners read the text again. Write true or false. Correct the false sentences. ANSWERS 1 False. The cinema was popular in the fifties. 2 False. A family in her street bought a TV. 3 True. 4 False. She really likes the fashions. 5 True. 6 True. 7 False. People wait longer these days. 8 True Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS - Yes - No - Not |
Self -assessment
Descriptor: - read the text again - write true or false. Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Worksheets |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 10 • In a weaker class, explain that prepositions are words like in, from, to, in front of, at and on, which are usually used before a noun or pronoun to show place (He lives in Paris.), position (The book is on the table.), time (The film starts at nine o’clock.) or method (Shall we walk or go by bus?). In a stronger class, ask students what prepositions are and elicit examples. Explain that many adjectives are followed by particular prepositions. A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners complete the sentences with prepositions. Then check your answers in the text ANSWERS 1 on 2 by 3 about 4 in 5 to 6 for 7 about |
T’s comment Descriptor: - complete the sentences - check your answers Total: 2 point |
Pictures Worksheet |
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 10 In a weaker class, ask students to choose the correct prepositions first. Check the answers with the class, then tell students to complete the sentences with their own ideas. In a stronger class, ask students to look at the sentences in exercise 3 again and tell you what part of speech usually follows the preposition (noun). Write on the board: She’s keen on playing tennis. Are you interested in joining the drama club? Ask students what part of speech are the words after on and in (verb). |
Learners complete the sentences with the prepositions in the box and your own ideas ANSWERS 1 of + students’ own answers 2 with + students’ own answers 3 about + students’ own answers 4 at + students’ own answers 5 for + students’ own answers 6 from + students’ own answers |
Self assessment
Descriptor: - complete the sentences -use prepositions in the box Total: 2 point |
Pictures |
|
|
Task. V Ex: 5 P: 10 You may want students to prepare the answers for this activity as homework so they can ask older family members for their opinions. Read through the questions with the class and make sure that students understand everything. Ask students to prepare their answers to the questions individually. Students can ask and answer the questions in pairs. |
Learners ask and answer the questions. ANSWERS |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - ask and answer Total: 2 point |
Pictures |
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 4 |
School: |
||
|
Date: 09.09.2024 |
Teacher name: Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talk about events at different times in the past. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics; 9. 5. 1. 1 plan, write, correct and check text-level works on general and academic topics without the support of the teacher; 9.6.9.1 use appropriately an increased variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Identify the difference between the past perfect and past simple. - Construct the sentences using past perfect and past simple with support. - Construct the sentences using past perfect and past simple with minimal support. - Apply past perfect and past simple to talk about events at different times in the past without support. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Family day! "Family is the golden cradle of education" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, ask the students what they remember about the reading text from last lesson. Write on the board the example I visited my gran last weekend and she’d found some of her old photos. Underline she’d found. Ask: When did I visit my gran? (last weekend) When did she find the photos, before or after I visited? (before I visited) Elicit the full form of the contraction (had found). Tell students that this tense is called the past perfect. There are six chairs in the classroom. Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/8kkaLWk3uKKj8cNN6
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 11 Ask students to open their books and look at the timeline. Tell them to read the sentence again and match the events to the diagram. Ask students to translate the examples into their own language. Discuss how the equivalent tense is formed in the students’ own language, and whether this is similar to English Differentiation with individual need learners: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to write the events in the correct place on the timeline |
Learners study the timeline and the sentence. Write the events in the correct place on the timeline. Then choose the correct words in the rules ANSWERS Recent past: I visited my gran Earlier past: she’d found some of her old photos Rules: a before b past simple c had |
T’s feedback Descriptor: - study the timeline - write the events in the correct place Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 11 Read the example with the class and ask: Which action happened first? (I saw the film) Focus on the next sentence and ask Which action happened first? (Alice didn’t have many hobbies when she was a child). Elicit which verb should be in the past perfect (have) and which in the past simple (tell). Remind students that some irregular verbs have the same form for the past tense and past participle, but others have different forms. Tell students to use the irregular verbs list on page 126 of the Student’s Book. Differentiation: A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners complete the sentences. Use the past perfect and the past simple in each sentence. ANSWERS 1 told, hadn’t had 4 was, had left, had found 2 got, went, hadn’t seen 5 hadn’t started, arrived 3 hadn’t invented, was 6 wanted, had had |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - complete the sentences - use the past perfect and the past simple Total: 2 point |
Worksheets |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 11 Make sure students understand the logical order of events. In the example, one fact is a consequence of the other. Remind them to use context and to look out for time markers, e.g. when, by the time, after in the prompts |
Students complete the sentences using the past perfect and your own ideas ANSWERS Students’ own answers |
T’s comment Descriptor: - complete the sentences - use the past perfect Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 5 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
People talking about their memories |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 2. 1 understand on their own some specific information on general and learning topics without support in a wide-ranging extended conversation 9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
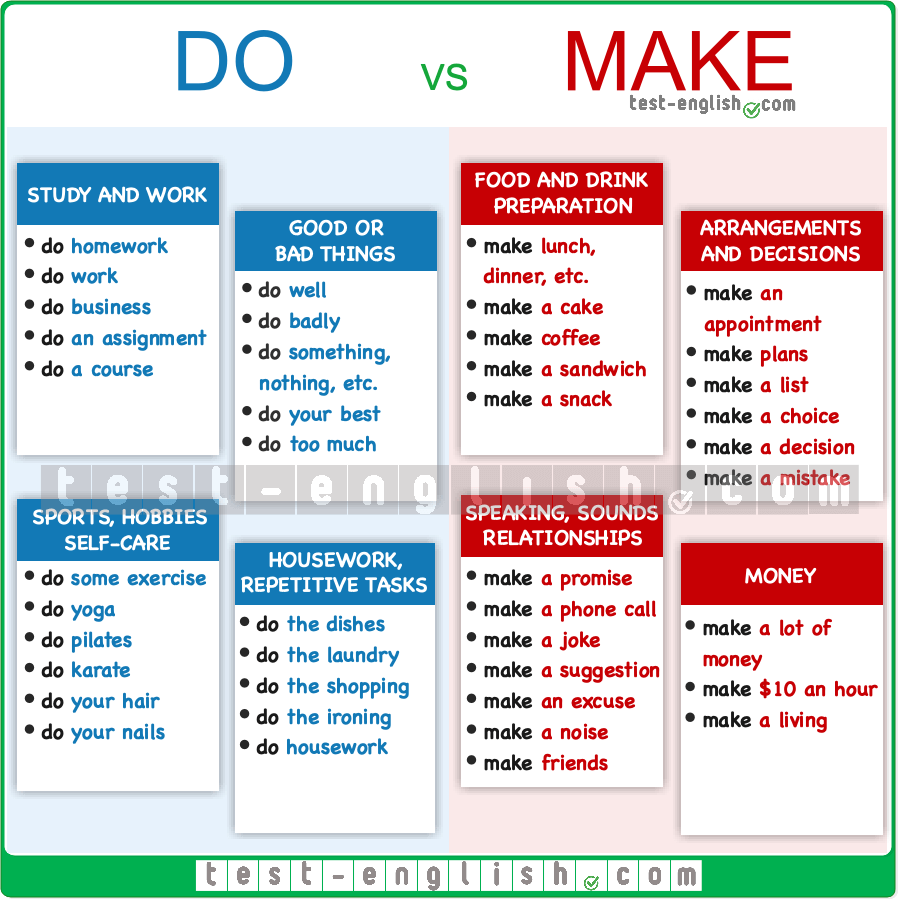
Learners will be able to: - Ask and answer the questions using collocations with make, do, collect and write. - Identify the meaning of the dialogues "People talking about the past". |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Independence and Patriotism to make students understand the value of three languages |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: Write make, do, collect and write on the board as headings. With books closed, students work in pairs and brainstorm words you use with each Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/RT9tFY74hZ1ffEbw6
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 12 In a weaker class, elicit translations of the collocations and make example sentences as a class. In a stronger class, encourage students to record the new phrases in their own example sentences. Point out that students can use diagrams like these to record other collocations. They could also turn the diagrams into spider grams if they prefer. Differentiation with individual need learners: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to translate collocations and make example sentences as a class |
Learners complete the diagram with the words in the box ANSWERS 1 model planes 2 clothes 3 music 4 puzzles 5 woodwork 6 sports 7 badges 8 stamps 9 football cards 10 blogs 11 poetry 12 short stories |
T’s feedback
Descriptor: - complete the diagram - use the words in the box Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 12 Students complete the questions individually. Check answers, then put students into pairs to ask and answer the questions. Ask some students to report back on what they learnt about their partner. |
Learners choose the correct words to complete the questions. Then ask and answer in pairs. ANSWERS 1collect 2 write 3 make 4 make 5 written 6 do 7 do, make Students’ own answers. |
Self -assessment
Descriptor: - choose the correct words - ask and answer in pairs Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 12 • Focus on the photos and elicit what they show. Elicit whether they are modern or old photos (old). Tell students they are going to hear people talking about the past. Allow students time to read through the words in the box. Students listen and match the words with the people. A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. TRANSCRIPT 1 M1 I got my driving licence when I was seventeen. I had saved and saved for this car, so when I passed the test my dad gave me the rest of the money I needed. I went to a garage and bought it immediately. When I got to school the next day, I showed it to all my friends. I was so proud. For the first week I used to look at it every ten minutes. I couldn’t believe it was my car. 2 M2 Well, I was OK when I got up, but as the time got nearer, I was watching the clock and I was getting more and more upset. When I finally got to school, I was crying and crying. My uniform was much too big, the place seemed big, in fact it was all big – my bag, my teacher, everything. I hated it. Of course, I didn’t want to go back the next day. At breakfast I was crying again and my mum was getting upset, too. Then mum started crying, so dad had to take me! But by the end of the week I’d made some friends, so things got better. 3 G This music’s good. C Yes, I love reggae. I first heard it when I was at a party. I was dancing with a boy called Dave. I loved it. A few weeks later I was sixteen, so I had a party at my place. I invited Dave and he got me a Bob Marley record for my birthday. G That was nice of him. C Yes. We started going out together after that. G Isn’t your husband called Dave? C Yes, we got married! That record is still one of our favourites. It gets better each time I hear it. 4 J I won some tickets to a football match once. B You won tickets? J Yeah, to my first football match. It was Manchester United against Everton. I gave my uncle a ticket because he was a Man United fan. Their best player was called George Best, and he got three goals, but I didn’t see two of them. B You missed two goals? J Yes, I was talking to my uncle when he scored! B Oh no! J My uncle missed them, too and he’s never forgotten it. He still talks about those goals today and he’s eighty-two! |
Learners listen to the dialogues. Match two words with each of the people in the photos 1–4 ANSWERS 1 Michael: money, test 2 Maxine: uniform, upset 3 Clare: party, married 4 Joey: uncle, tickets |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - listen to the dialogues - match two words Total: 2 point |
Pictures Worksheet |
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 12 Check that students understand the meaning of positive and negative. Write a plus and minus symbol on the board to help explain the meaning (or a happy and sad face). When students have finished, ask them to compare their answers with a partner. Then, ask individual students to come to the board and write the phrases in the correct list. Ask them to read the phrases and help with pronunciation |
Learners listen again and choose the correct answers. ANSWERS 1 c 2 a 3 b 4 c 5 a |
T’s feedback
Descriptor: - listen again - choose the correct answers Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 6 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talk about past events and memories |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 1. 1 unsupported understanding of general and main points of study topics with long conversations; 9. 3. 6. 1 in pair, group and whole class work to explain what others said in sentences or reasoning with a certain level of flexibility; 9.6.10.1 use present continuous forms and past continuous, including a growing variety of passive forms, on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Read about people’s hobbies. - Learn expressions for talking about your interests and hobbies. - Write about your interests and hobbies. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Family day! "Family is the golden cradle of education" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: Refer students back to the photos on page 12. Ask What was Clare doing when she first heard the music? • Elicit the answer (she was dancing) and write the sentence on the board: She was dancing when she heard the music. • Underline the verbs and elicit that they are in the past continuous and past simple. • Ask: Which action happened first? (she was dancing); Did she continue dancing when she heard it? (yes) Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/H5FuapmFSi4DHZnDA
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 13 Students work in pairs to study the sentences and match them to the descriptions. Check answers with the class. Elicit which tenses are used. |
Learners look at the photos and about their hobbies. ANSWERS 1 b (past continuous) 2 c (past continuous and past simple) 3 a (past simple) |
T’s feedback Descriptor: - look at the photos - guess three people’s interests are Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 13 Students copy the sentences from exercise 4 and highlight or underline the tenses. • Tell students to use different colours to indicate different tenses. • Discuss as a class how this technique might be helpful, for example by giving students memorable examples of tenses that they can remember easily. In a stronger class, write on the board: When I arrived, she had made a cake. When I arrived, she was making a cake. and When I arrived, she made a cake. Ask students to underline or highlight the verbs in the sentences, then identify the tenses and explain the difference in meaning |
Learners read and listen to the text. Check your answers. ANSWERS Student’s own answer |
Pair -assessment
Descriptor: - read and listen - check your answers Total: 2 point |
Worksheets |
|
|
Task. III (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 3 P: 13 Focus on the example and ask: Which action was in progress? (he was competing) Which action is finished? (he won). In a weaker class, do another together. Focus on the first question and elicit which action was in progress (using) and which finished (said). Elicit the correct verb forms from the class. In a stronger class, one example should be enough. • Students continue writing their questions individually. Check answers as a class. • Put students into pairs to answer the questions. Listen and check answers to the quiz questions. Ask students how many they got right. Differentiation with individual need learners: will be do another easy task. Choose the correct answer.
|
Learners read the text again and choose the correct answers. ANSWERS 1 What new invention was Alexander Bell using when he said, ‘Mr Watson, come here. I want to see you’? (the telephone) 2 When Titanic hit an iceberg in 1912, where was it travelling to? (New York) 3 When Neil Armstrong said, ‘That’s one small step for man; one giant leap for mankind’, where was he standing? (on the moon) 4 Where was Isaac Newton sitting when he discovered gravity? (under a tree) 5 Where was Mark Zuckerberg studying when he invented Facebook? (Harvard University) 6 Where were people celebrating the new millennium when they took this picture? (Sydney, Australia) |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - read the text - choose the correct answers. Total: 2 point |
Student’s book Worksheets https://images.app.goo.gl/sCPKnucNBHVijzHU9 |
|
|
Task. IV (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 4 P: 13 Point out the blue phrases in the text, and explain that these are key vocabulary items. Ask students to look at the gapped sentences 1–6. Explain that they should find the complete sentences in the texts and write the missing blue words. Check understanding of the words and expressions, for example by asking students to translate them |
Learners find these sentences in the text. Then complete the sentences with the words in blue. ANSWERS 1 not mad about 2 prefer 3 especially 4 a … fan 5 good at 6 can’t stand |
Self assessment Descriptor: - find these sentences - complete the sentences Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. V (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 5 P: 13 Ask students to compare their answers in pairs. Ask some students to read their sentences to the class. |
Learners complete the sentences and compare your answers with a partner. ANSWERS |
Pair assessment Descriptor: - work in pairs - complete the sentences Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 7 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talking about past events |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 1. 1 unsupported understanding of general and main points of study topics with long conversations; 9. 3. 6. 1 in pair, group and whole class work to explain what others said in sentences or reasoning with a certain level of flexibility; 9. 4. 4. 1 reading long texts in fiction and non-fiction literature within familiar and some unfamiliar general and educational topics; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Develop their listening skills for gist and specific information in the context of talking about past events. - Recognize and use key phrases for talking about events in the past.. - Perform situations talking about events in the past without support |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Mother's Day! "Family is the golden cradle of education" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, ask students what important days they can remember from the past. Elicit some answers, e.g. the first day at a new school, a holiday, Christmas day, etc. Ask students to describe what they remember and how they felt Did you celebrate the Nauryz last year? Did you remember the first day at school? Did you spend your holiday at the beach? Setting the aim of the lesson. |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 14 Draw students’ attention to the photo and elicit a description. In a weaker class, encourage students to participate by accepting factual descriptions. In a stronger class, ask students to speculate about the answers to the questions and explain their answers. Differentiation: Learners will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners complete the sentences from the text. Then complete rules. ANSWERS Student’s own answer |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - complete the sentences - complete rules Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 14 Tell students they are going to listen to a conversation between the man and the boy. They should listen for general understanding and to find the answer to the question. (Colin is Dean’s grandfather.) After listening once, ask which part of the festival Colin enjoyed most. T asks some CCQs:
|
Learners listen to the dialogue. Which part of the festival did Colin enjoy most? ANSWERS The end of the last day. Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS - No - Yes - No |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - listen to the dialogue - answer to the question Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 14 Students work in pairs to complete the key phrases. In a stronger class, tell them to cover the dialogue and try to do it from memory. Students listen again to check their answers. Tell them to listen to the intonation of the phrases, as well as the words. Students practise the dialogue in pairs Differentiation: A less motivated learner work in pairs, and do the example with support. |
Learners complete the key phrases. Then listen and check your answers. Practise the dialogue with a partner ANSWERS 1 ever 2 was 3 ago 4 have 5 bit 6 happened |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - complete the key phrases - practise the dialogue Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 14 Tell students they are going to hear parts of a dialogue, and they must choose the most appropriate responses. Students listen and answer individually. Play the CD again and elicit the answers |
Learners listen and choose the correct answers ANSWERS 1 b 2 b 3 a 4 b |
T’s comment Descriptor: - choose the correct answers Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. V Ex: 5 P: 14 Students complete the key phrases and compare answers in pairs before checking as a class. Individually students rewrite the mini-dialogue by changing the blue words. Then students read their new dialogues in pairs. Differentiation: Learners will be supported by teacher and by helpers. |
Learners complete the mini-dialogue with the key phrases. Then change the words in blue and practise the new minidialogue. ANSWERS 1 tell 4 Did 2 when 5 best 3 around 6 What |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: -. complete the mini-dialogue - practise the new minidialogue Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 8 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Describing a decade |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics 9. 4. 6. 1 determine the author's opinion or point of view in long texts in the context of general and study topics 9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Study a model account of a decade. - Learn key phrases for writing about a decade. - Learn about giving examples. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Mother's Day! "Family is the golden cradle of education" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: Ask students what they think all these events have in common. If necessary, tell them that they all happened in the same decade and invite students to guess which one. Confirm that it is the 1960s • Ask: What else do you know about the 1960s? Elicit ideas, and write useful vocabulary on the board. Setting the aim of the lesson. Answer the questions What do you know about the sixties? It was an era of memorable events, for example, the moon landing in July 1969 Many people remember exciting events such as England’s World Cup win Some bands became incredibly successful, The Beatles, for instance. |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 15 Read through the questions and make sure everyone understands. In a weaker class, students can compare answers in pairs before checking as a class. In a stronger class, set a short time limit and tell students to skim read the text for the information in the questions. T asks some CCQs:
|
Learners read the model text and answer the questions. ANSWERS 1 a 2 Paragraph 2 3 Paragraph 4 Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS - Yes - Yes - No |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - read the model text - answer the questions Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 15 Read through the key phrases with the class. Ask students to find the key phrases in the model text and translate them into their own language |
Learners study the key phrases. Which phrases introduce the paragraphs in the text? ANSWERS Paragraph 1: The … was a decade which … Paragraph 2: In the world of fashion … Paragraph 3: One of the most memorable … Paragraph 5: By the end of the decade.. |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - study the key phrases - to find the key phrases Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 15 Look at the words in blue in the model text. Elicit what their role is (to introduce examples). • Point out the use of commas with for instance and for example. • Students complete sentences 1–4 individually with their own ideas. • Ask some students to read their sentences to the class. Differentiation: A less motivated learner translate the sentences with by helpers |
Learners study the words in blue in the model text. Then complete sentences with these words and your own ideas ANSWERS Student’s own answer |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - study the words in blue - complete sentences Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 9 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Comparing generations |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 1. 1 unsupported understanding of general and main points of study topics with long conversations; 9. 3. 6. 1 in pair, group and whole class work to explain what others said in sentences or reasoning with a certain level of flexibility; 9. 4. 2. 1 understand specific information in texts within the context of familiar general and reading topics, including some longer texts; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Study a text written by a grandfather and his granddaughter about their different experiences and hobbies as teenagers. - Learn compound adjectives connected with people’s attributes - Review talking about the past using used to. Talk about hobbies and interests students used to have |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Labor day! Be Honesty and justice |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: • Ask students to work in pairs and talk about what they know about their grandparents as young people. What jobs did they do and what did they do in their free time? • When they have finished, they join a second pair and tell each other what they’ve found out about their partner’s grandparents. Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 16 Draw students’ attention to the photos and ask them what they know about the people’s hobbies from the photos. Encourage students to describe the photos using the present continuous. |
Learners look at the photos. What are the people doing? What do you think their hobbies are? ANSWERS Grandpa Sansizbay is playing a dobra and his granddaughter is drawing in the mountains |
Pair assessment Descriptor: - look at the photos. - describe the photos - use the present continuous. Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 16 Before reading and listening students look at the true / false questions and guess the answers. Ask them to discuss the reason for their decisions in pairs. Students listen and answer individually. Give students a few minutes after the audio ends for them to complete the exercise Differentiation with individual need learners: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to discuss the reason for their decisions in pairs. |
Learners read and listen to the text. Are the sentences true or false? ANSWERS 1 True. 2 False. There were no buses then. 3 False. He thinks most teenagers are like his granddaughter: hardworking and open-minded. 4 False. She’s not really into sport. 5 True. 6 True |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - read the text - write true or false Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 16 Students look through the text and complete the exercise. • Encourage them to use their dictionaries to find the meaning of any adjectives they don’t understand. Check the meanings in translation. • As a follow-up, ask students in a stronger class to write sentences using the adjectives. In a weaker class, put the translations on the board for students to copy |
Learners match the words to make compound adjectives. ANSWERS 1 b 2 d 3 f 4 a 5 c 6 e |
Self assessment Descriptor: - match the words - make compound adjectives. Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV (Task for understanding) Ex: 4 P: 16 • Allow students time to think about the adjectives in relation to the people listed. • Encourage them to write two sentences, then in pairs to describe the people. In a stronger class, encourage them to give examples demonstrating the attribute described by the adjective. |
Learners choose two of the adjectives in exercise 3 to describe each of these people ANSWERS Students’ own answers. |
Pair asessment
Descriptor: - choose two of the adjectives - describe the people Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. V (Task for understanding) Ex: 5 P: 16 • Draw students’ attention to the example sentences. Ask students how you could give the same information without used to. (I had long hair. I didn’t like skiing. Did you live in Zyryan?) • Students work individually. Then compare their answers before you go through them with class. • Give students the following two sentences: I used to go swimming every weekend. I used to go swimming last Saturday. Ask them which one is grammatically correct, to check they understand how used to is used. • Draw students’ attention to the form in negative sentences and questions. Ask them what they notice. (Used to becomes use to after Did / Didn’t.) |
Learners study the sentences below and find seven more examples of used to in the text. Choose the correct words to complete the rules ANSWERS 1 past 2 habits and states 3 did |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - work individually - choose the correct words Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. VI (Task for understanding) Ex: 6 P: 16 Students work individually to complete the exercise. |
Learners complete the sentences with the correct form of used to and the words in brackets ANSWERS 1 used to go 2 didn’t use to listen 3 didn’t use to play 4 Did you use to have 5 used to cycle |
T’s comment Descriptor: - complete the sentences - use the words in brackets Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 10 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. The British sense of humour |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 2. 1 understand on their own some specific information on general and learning topics without support in a wide-ranging extended conversation 9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics 9. 4. 2. 1 understand specific information in texts within the context of familiar general and reading topics, including some longer texts; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Recognize and use vocabulary to do with humour. - Identify the meaning of the text about the British sense of humour. - Talk about the sense of humour in your country. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Labor day! Be Honesty and justice |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, ask students what makes them laugh. Elicit ideas about films, books, TV programmes, etc. and encourage students to express their opinions. Ask students if they know the character Mr Bean. Ask: Do you find him funny? Elicit a range of answers Did you watch film about Mr Bean? What does Mr Bean carry with him?
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/yGQ8zRcuyVuK3LwU7
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 17 In a weaker class, remind students to note the part of speech as well as the meaning for the words. In a stronger class, check understanding of the new words by eliciting example sentences. Pay particular attention to make fun of and make sure students are formulating it correctly. Don’t check answers at this stage. T asks some CCQs:
|
Learners сheck the meaning of the words and phrases in the box. Then complete the text. ANSWERS Student’s own answer Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS - Yes - No - Yes |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - сheck the meaning of the words - complete the text Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 17 Students listen, read and check their answers to exercise 1 A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners read and listen to the text. Check your answers to exercise 1. ANSWERS 1 good sense of humour 2 comedians 3 laughter 4 sarcasm 5 make fun of 6 bizarre |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - listen to the text - check your answers Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 17 Allow students time to compare their answers in pairs and discuss any differences before you check with the class. As usual, in a stronger class, encourage full, complete answers in the students’ own words |
Learners read the text again and answer the questions. ANSWERS 1 a good sense of humour, good looks and money are important qualities when choosing a partner 2 people feel happier, healthier and more optimistic when they lough because laughing releases hormones which have this effect. 3 Sunny weather has a similar effect on people to laughing, so the writer suggests that British people need to laugh because their weather is so bad. 4 British musicians are popular in other countries whereas British comedians usually aren’t. 5 People in British comedy shows aren’t always polite to each other because part of the humour is based on them being unkind and rude. 6 We know Mr Bean is popular around the world because his shows and films have been seen in more than 200 countries over the last twenty years 7 People like Mr Bean because he does everyday things in a bizarre way and because they like his eccentricity. |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - read the text - answer the questions Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV (Task for understanding) Ex: 4 P: 17 In a weaker class, do the whole task together, encouraging as many students as possible to join in. In a stronger class, ask students to translate a joke into English and see how many work in translation Differentiation: A less motivated learner , do the whole task together with support |
Learners answer the questions. ANSWERS Student’s own answer |
Self assessment Descriptor: - complete the task - answer the question Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1 Hobbies and qualities lesson 11 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review. Unit 1. Summative Assessment for the unit «Hobbies and Qualities» |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 7. 1 use subject-specific vocabulary and syntax within the framework of unlimited general and study topics; 9. 5. 1. 1 plan, write, correct and check text-level works on general and academic topics without the support of the teacher; 9.6.12.1 use an increased variety of comparative degree adverb structures with regular and irregular adverbs, use a variety of preverbal, post-verbal and end-position adverbs on a range of familiar general and curricular topics; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - make adverbs from adjectives. - ask and answer the questions using collocations with make, do, collect and write. - construct the sentences using past simple and continuous with support. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Labor day! Be Honesty and justice |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: Ask students to work in pairs and talk about what they know about their grandparents as young people. What jobs did they do and what did they do in their free time? Setting the aim of the lesson. |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 18 Write the adverbs for these adjectives |
Learners write the adverbs for these adjectives ANSWERS 1 angrily 4 politely 2 well 5 optimistically 3 carefully 6 firmly |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - write the adverbs - complete the task Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 18 Exercise 2 Allow students to work in pairs. In a stronger class, ask students to complete the sentences individually, but allow them to check their answers in pairs before you check with the class Differentiation: A less motivated learner to choose the correct words with support by helpers |
Students choose the correct words. ANSWERS 1 beautifully 2 the hardest, 3 noisily, happily 4 optimistic successful 5 well, best |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - work in pairs - choose the correct words Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 18 Students complete the questions individually. Check answers, then put students into pairs to ask and answer the questions. Ask some students to report back on what they learnt about their partner Complete the sentences with correct tense of the words in the box. |
Learners complete the sentences with correct tense of the words in the box. ANSWERS 1 collected 2 writing 3 make 4 do 5 make 6 do |
Pair assessment
- complete the sentences Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 18 Remind students to use the both the positive and the negative – to talk about things they had and had not done. In a weaker class, allow students time to do the task Summative Assessment for the unit «Hobbies and Qualities» |
Learners choose the correct words ANSWERS 1 ’d forgotten 2 got 3 hadn’t seen 4 hadn’t eaten 5 ’d cut
|
Descriptor: - choose the correct words - complete the task Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1 Hobbies and qualities lesson 12 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project. An interview summary: teenage years |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 4. 6. 1 determine the author's opinion or point of view in long texts in the context of general and study topics 9. 5. 6. 1 write texts related to general familiar and learning topics using different connectives |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Read a summary of an interview with a family member. - Interview an older person about their teenage years and their generation. - Write a summary of your interview about an older person’s youth |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Labor day! Be Honesty and justice |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, write My teenage years on the board and elicit or explain the meaning If students are struggling, give them some categories and decades and brainstorm associations, for example, fashion and hair styles in the 1980s, music in the 1960s, exciting new technology in the 1990s Setting the aim of the lesson. The word teenager to describe a person between the ages of 13–19 originated in the 1950s. Prior to that, this age group was not a clearly defined demographic grouping. In the 1950s adolescents began to stand out as a group of people for whom modern music, fashions and trends were very important. |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 19 Look at the photographs and elicit what they show. Ask students to guess the decade, then read the text quickly and check their guesses. Students work individually to read the paragraphs and match them to the questions. Check answers |
Learners read the interview summary. Match paragraphs A–E with interview questions ANSWERS: 1 E 2 A 3 D 4 B 5 C |
Pair assessment Descriptor: - read the interview - match paragraphs Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 19 Read through the project checklist with the class. In a weaker class, brainstorm other questions or topics that students could ask about. Tell them to choose five questions and point out or elicit that this means their summary will have five paragraphs. Remind students that to write a whole paragraph, they will need to get detailed answers, so it might be a good idea to prepare some follow-up questions. Ask students to write their summaries for homework |
Learners write about an older person’s teenage years. Follow the steps in the project checklist. ANSWERS |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - write about an older person’s teenage years Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 19 Collect in the summaries and arrange them on desks around the class for students to look at. Find out which generation was the most researched and whether people had the same experiences. Ask students whether they would rather be teenagers now, or in another decade. Have a vote for the most popular decade |
Learners share your interview summary with the rest of the class. Did any other students find out similar information? ANSWERS |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - share your interview - find out similar information Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 13 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Medical science |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 4. 6. 1 determine the author's opinion or point of view in long texts in the context of general and study topics 9. 5. 6. 1 write texts related to general familiar and learning topics using different connectives |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Learn nouns and verbs related to the health benefits of exercise. - Do a health and exercise quiz. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Unity and solidarity International Day of the Elderly! |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, write health and exercise on the board and elicit the connection between the two. Ask: Can you be healthy without doing exercise? Setting the aim of the lesson. 1 Why are team sports good for you? 2 What are the health benefits of sport and exercise? 3 What are the secrets of a long life?
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/WFW4ZRoifs8i95fPA
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 20 Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the nouns in the quiz. If you want to speed this up, put them in pairs and ask each student to find half the words. Point out that some of the nouns are used to talk about mental attitude and some are used to talk about physical health. In pairs, students decide which words fall in the two categories. Differentiation: A less motivated learner use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the nouns and categorise the nouns in the two categories. |
Learners check the meaning of the nouns in blue in the Health and exercise quiz. Which words are about mental attitude, and which are about physical health? ANSWERS: Mental attitude: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 Physical health: 6, 10, 11, 12 |
Pair assessment Descriptor: - check the meaning of the nouns in blue - find half the words Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 20 Focus students’ attention on the table and ask students what the verb for commitment is to elicit have commitment. Point out that not all nouns have a single word equivalent, because they are things you have or states. Tell students to look at the text and find the verbs that are used with the nouns in the text and write the nouns and the related verb phrase |
Learners read the text again and complete the table with nouns 1–12 from exercise 1 and the verbs used with them ANSWERS 1 have commitment 2 build self-esteem 3 have determination 4 develop self-reliance 5 have discipline 6 improve stamina 7 involve team work 8 improve concentration 9 boost (your) mood 10 increase endorphins 11 increase (your) energy 12 raise (your) blood pressure |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - read the text again - complete the table with nouns Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III Ex: 3 P: 20 • Put students into pairs to read the sentences in the Health and exercise quiz and decide whether they are true or false. If there seems to be a lot of disagreement, briefly discuss the questions as a class, and share knowledge and opinions before playing the CD to check the answers. Find out who got the most answers right. Were there any answers that really surprised students? TRANSCRIPT 1 True. Exercising regularly not only increases physical stamina, the ability to do things for a long time, but it also increases your mental stamina. This means you can concentrate on things for longer. 2 True. In team sports you have to learn how to be part of a group. To win a competition, you have to work as a team and create chances for other players. You can’t compete with your own team. Once you understand the importance of groups in sport, it is easier to see their importance in other areas of life. 3 False. Both team and individual sports help people feel better about themselves and find ways of overcoming problems, but in individual sports the effect is even greater as there are no team mates to help you when your energy falls, or you miss the ball. 4 False. Yoga is not only good for flexibility. In yoga, you often have to hold difficult positions while breathing calmly and deeply. This combination of physical difficulty and a calm mind is good for controlling stress. As a result, researchers have found people who do yoga have higher levels of endorphins and feel less depressed. 5 True. It takes around sixty-six days for a routine to become a habit, so it’s important to be determined and committed for those first two months. After that, it becomes easier. 6 True. Exercise increases your energy levels. You will probably find that you won’t be able to run very far or play for very long the first time you do a new sport, but after a few weeks, you’ll be able to exercise for much longer without feeling tired. 7 False. Exercise does increase your blood pressure, but in people who exercise it falls quickly when they stop and people who exercise regularly have lower blood pressure than those who don’t. 8 False. People with not much self-discipline can find a new routine difficult to begin with, but self-discipline can be learned. When you start doing a new sport, it’s best to try and do it bit by bit. Decide to take a twenty minute walk a day and keep to this before you decide to train for a marathon. 9 False. Some people think that there will soon be a pill for everything, but a pill won’t be able to replace exercise because it is necessary for so many things, such as strength, stamina, a positive mood, a healthy heart, low blood pressure and much more. |
Learners do the Health and exercise quiz. Decide if the sentences are true or false. Then listen and check. ANSWERS : 1 True. 2 True 3 False. Both team and individual sports help. 4 False. People who do yoga have higher levels of endorphins and feel less stressed. 5 True. 6 True. 7 False. People who exercise regularly have lower blood pressure than those who don’t. 8 False. Self-discipline can be learned. 9 False. Exercise is necessary for stamina, a positive mood, a healthy heart, low blood pressure, etc. |
Teacher’s comment Descriptor: - do the Health and exercise quiz. - write true or false Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 14 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
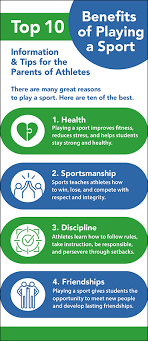
Benefits of doing sport |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 7. 1 use subject-specific vocabulary and syntax within the framework of unlimited general and study topics; 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Talk about the benefits of doing sport and exercise. - Learn the use of could, can and will be able to. - Practise using could, can and will be able to to talk about ability in the past, present and future |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Unity and solidarity Let's protect our old people |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, write health and exercise on the board and elicit the connection between the two. Ask: Can you be healthy without doing exercise? Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/1TXFgYbVWapQAXiv9 |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 4 P: 21 Check answers and discuss the questions. If possible, ask the students to research some of the benefits of these sports for homework, and report back in a future lesson |
Learners look at Benefits of doing sport. In pairs, match the benefits with the sports in the box. Discuss your reasons for choosing the sports. Which benefits do you think are the most and least important? ANSWERS: Student’s own answer |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - answers and discuss the questions - match the benefits with the sports Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 5 P: 21 Ask students to look at the quiz again and find an example of can and will be able to. Ask what are they used to express (ability). Play the audio again and ask students to listen for examples of can, could and will be able to in the affirmative and negative. Pause when you hear each example and ask students when the speaker is referring to – past, present or future. Students complete the sentences. Tell them to think of the tense they need for each sentence A learner with individual needs: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use simple, basic statements in his discussion. |
Learners look at the sentences from the quiz and the listening. Complete them with can / can’t or will / won’t be able to ANSWERS 1 will be able to 2 can’t 3 won’t be able to 4 will be able to 5 won’t be able to |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - look at the quiz - complete the sentences Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 6 P: 21 Ask students to read the text through quickly, ignoring the gaps. Ask: What problem did Jed have? (He fell down a hole and damaged his feet and knees.) Ask students if they have ever had physiotherapy. Ask what they couldn’t do before they had it and what they can do now Differentiation with individual need learners: *Define the rules and complete the text with the affirmative and negative forms |
Learners complete the text with the affirmative and negative forms of can, could and will be able to ANSWERS : 1 can’t 5 will be able to 2 couldn’t 6 will be able to 3 couldn’t 7 won’t be able to 4 can |
Teacher’s comment Descriptor: - complete the text with the affirmative and negative forms Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 7 P: 21 Ask two students to read out the example dialogue. Make sure students understand what they have to do. If necessary, do the first sentence as an example. Students write their sentences individually and then compare their answers in pairs. Ask some students to read their sentences to the class |
Learners make sentences using the phrases in the table and affirmative and negative forms of can, could and will be able to. Then interview your partner about their ideas ANSWERS : Student’s own answer |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - make sentences - use the phrases in the table Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 15 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Alternative therapy |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics; 9. 4. 2. 1 understand specific information in texts within the context of familiar general and reading topics, including some longer texts; 9. 5. 3. 1 write familiar general and study topics with uniform grammatical competence; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Read about exercise as a cure. - Read for general meaning and specific information. - Express your own opinions on exercise as an alternative medical treatment. - Learn about and practise noun suffixes |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Diligence and Professional Qualification! Teachers' Day |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, write the quote from Hippocrates Walking is man’s best medicine on the board and ask students what they think it means. Elicit or explain that it probably means that keeping active improves your health Setting the aim of the lesson. Hippocrates lived between 460–370 BCE and was possibly the first person to think disease and illness was the result of natural causes and not a punishment from the gods. He believed lifestyle, diet and environment all had a part in people’ s health and that health could be improved by improving these factors |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 22 Draw students’ attention to the photos and elicit a description. In a weaker class, encourage students to participate by accepting factual descriptions. In a stronger class, ask students to speculate about and explain their answers. Students discuss the questions in pairs, then ask them to read the text quickly to find the answers. T asks some CCQs:
|
Learners look at the photos and the title of the text, and answer the questions. Then read the text and check your answers. ANSWERS: Exercise reduces pain, helps people with depression and reduces loneliness Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS - No - Yes - No |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - look at the photos and the title - answer the questions Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 22 Read the instructions and make sure students understand what they have to do. Tell them to use context and meaning, but also to look at structural elements like tenses or words such as however A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners complete the text with sentences a–e. Listen and check your answers ANSWERS: 1 b 2 d 3 c 4 e 5 c |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - complete the text - check your answers Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III Ex: 3 P: 22 In a stronger class, ask students to predict or guess the noun form and share ideas as a class. Elicit the suffix that is used in each case to turn the verb or adjective into a noun. Elicit any other examples that students are familiar with A learner with individual needs: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use simple, basic statements in his discussion. |
Learners complete the table with words from the text. What suffixes are used to form the nouns? ANSWERS: 1 medication 2 treatment 3 infection 4 illness 5 reduction 6 depression 7 loneliness |
Descriptor: - complete the table - predict or guess the noun Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 22 Do the first sentence with the class as an example. |
Learners complete the sentences with a noun formed from the words in brackets. Use the suffixes in the box ANSWERS: 1 sadness 2 intelligence 3 enjoyment 4 connection 5 receptionist |
Descriptor: - complete the sentences - use the suffixes in the box Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 16 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talk about things that are possible or certain |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics; 9. 5. 3. 1 write familiar general and study topics with uniform grammatical competence; 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Learn the use of may, might, could, must and can’t for possibility and certainty. - Practise using may, might, could, must and can’t to express possibility and certainty in opinions. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Low and Order "Victim in the life of a child" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: Refer students back to the text on pages 22–23 and ask: Do you think that swimming in cold water helps depression? Elicit a range of ideas, including the idea that it is possible it works. • Write on the board: Swimming in cold water might help depression and underline might. Elicit or explain the meaning (it is possible that it works). • Tell students they are going to learn some other ways of expressing possibility and certainty. Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/q8MYHwfKCsvZukWF9
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 23 • Students study the examples in pairs and complete the rules. • Check answers with the class. • Point out that we don’t usually use can to express possibility. • Ask students how they would express these ideas in their own language. |
Learners study the modal forms in blue in sentences 1–5. Then choose the correct options in the rules. ANSWERS: a possibility b are c don’t |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - study the modal forms - choose the correct options Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 23 Allow students time to compare their answers in pairs before you check with the class. Discuss what helped students make their choices A learner with individual needs: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use simple, basic statements in his discussion. |
Learners сhoose the correct words ANSWERS : 1 might 2 can’t 3 may 4 must 5 might 6 might |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - сhoose the correct words Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 23 • In a weaker class, do a few examples and discuss them before students continue in pairs. In a stronger class, ask students to provide not just one sentence for each item, but all the possible sentences for each item. • Allow students to compare their answers in pairs before you check with the class. • If your students need extra practice, you may want to do the activities on page 15 of the Workbook in class. Exercise 3 could be done individually or in pairs. Exercise 4 could be done orally in class, and students could write it up for homework. A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners make sentences using the modal verbs in exercise 1 and the words in brackets ANSWERS : 1 He / She may / might / could have flu. 2 He must be tired. 3 They may / might / could be Mexican. 4 He / She can’t be angry. 5 She must be ill. 6 He may / might / could be a surgeon |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - make sentences - use the modal verbs Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 23 • Read through all the vocabulary with the class and make sure that students understand it. • Read the example opinions and then elicit some more opinions about acupuncture. • In pairs, students discuss the topics. • Ask some students to report back to the class on what they and their partner agreed and disagreed about |
Learners exchange opinions about topics 1–6 using the phrases in the box and the modal verbs in exercise 1. ANSWERS : Student’s own answer |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - exchange opinions - use the phrases in the box Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 17 |
School: Teacher name: |
||
|
Date: |
|||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talk about a healthy lifestyle |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 2. 1 independently understand more specific information on general and educational topics without support in a wide-ranging extended conversation; 9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics; 9. 4. 2. 1 understand specific information in texts within the context of familiar general and reading topics, including some longer texts; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Learn phrasal verbs about health and lifestyle. - Read an eight-point health plan. - Listen to a conversation about living longer |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Low and Order "Victim in the life of a child" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: • With books closed, write health and lifestyle on the board and elicit or teach the meaning. • Ask: How can your lifestyle affect your health? Elicit some ideas. • Ask: How can you change your lifestyle to make you healthier? Elicit a range of ideas Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/tEhWUiEskcoABNct7
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 24 Read the eight-point health plan together and see if any of the students’ ideas from the warm-up are mentioned. • Students match the phrasal verbs with their synonyms. |
Learners match the phrasal verbs in blue in The eight-point health plan with synonyms ANSWERS: 1 h 2 c 3 g 4 a 5 d 6 f 7 b 8 e |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - discuss about Almaty Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 24 Elicit any strategies students have for doing listening activities. • As a class, read through the study strategy tip. Ask if anyone prepares for listening in this way. Emphasize that preparing to listen can make the task significantly easier, as it helps to predict the types of information you need. • Elicit the task type for which students have to be particularly careful (true / false) and ask why (some of the statements are false, so students may not hear these words or ideas in the recording). Point out that the ideas in the statements might not be expressed in the same way as those in the recording. Differentiation with individual need learners: Define that the words for languages are often the same as those for nationalities. |
Learners before you listen, read exercises 3 and 4 carefully and underline key words. This will help you to understand the dialogue more easily. It will also help you to focus on the answers while you are listening ANSWERS: |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - read the text - answer the question Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 24 Focus on the photos and the title Live longer, live better. Ask How old do you think the people are? What are they doing? • Ask students to read the introduction to the article. Elicit suggestions as to what a centenarian might be. Remind students to listen for general understanding, and to pick out the meaning of the word. TRANSCRIPT J Hi, Chloe. What are you reading? C Oh, hi James. It’s an article called ‘Live longer, live better’. It’s about people in some parts of the world who live much longer than other people. This lady in Japan is a centenarian and she’s still working. J You’re kidding! She must have had a healthy lifestyle. C Yes. And this man on the waterskis is a hundred, too. J Wow! So I have to take up waterskiing to live to a hundred? Is that the secret? C No, actually most of the advice is obvious – for example, you shouldn’t smoke. None of these people smoke. J Obviously. C And they have a very healthy diet. It says most of us must cut down on fatty foods and sugar. Our bodies don’t need much sugar. J Do I have to give up chocolate? C No, you don’t have to give up all chocolate – just cut down a bit. We all eat too much. J Mmm. What else? C Well, all of these people are pretty active, you know – lots of work, and exercise. J Lots of work? That’s bad news … C Well, work and activities. They spend a lot of time outside. Maybe you should turn off your computer occasionally. You shouldn’t stay in your room all day. J I suppose so. C But there are two things that all of these people have got in common, right. Firstly, they often call on their families and friends. They chat about problems and their friends and family help them. Friends and family make you feel good. J And the second thing? C The second thing is the most important. It says that they’re all very positive. Happiness is the secret ingredient. J Happiness? C Happiness. ‘Smile and the world smiles with you,’ they said. J OK, I’ll try that. Thanks, Chloe. T asks some CCQs:
|
Learners read the introduction to the Live longer, live better article. Then listen. What is a centenarian? ANSWERS: A centenarian is a person who is over a hundred years old. Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS -Yes - No - Yes |
Teacher’s comment Descriptor: - read the text - choose the correct answers Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 24 Look at the statements and tell students they should prepare to listen by following the advice in the study strategy. Give them some time to read the statements and underline key words. Compare key words as a class and discuss the students’ suggestions. In a weaker class, draw attention to words like all and negative statements, and make sure students have read and understood each complete statement, as well as identifying the key words. |
Learners listen again and write true or false. ANSWERS: 1 True. 2 False. 3 False. 4 False. 5 True. 6 True |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - write the plural form - find in the text. Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 18 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Speculate about the past. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 6. 1 in pair, group and whole class work to explain what others said in sentences or reasoning with a certain level of flexibility; 9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
|
Learners will be able to: - Learn the use of must have, can’t have, could have and might have to speculate about the past. - Practise speculating about the past using past modals. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Diligence and Professional Qualification! Day of librarians |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, ask students to remember how we express possibility in the present. Give them some scenarios and elicit sentences using may, might, could and must, can’t. For example, say: Joe’s doing his driving test after only three lessons. (He can’t be ready / must be very confident.) Look, it’s getting cloudy. (It may / might rain this afternoon.), etc T: What do you think about today’s theme? |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 25 Students read the sentences and answer the questions. • Check answers and remind students what past participles are.
|
Learners study the modal forms in blue in sentences. Then answer questions a and b ANSWERS: a must, can’t, could / might b have |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - study the modal forms in blue - answer questions a and b Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 25 Remind students that some verbs have irregular past participles. Tell them to look up any they are not sure of in the irregular verbs list on page 126 of the Student’s Book. • Allow students time to compare their answers in pairs before you check with the class A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners rewrite the sentences in the past form ANSWERS : 1 They could have been seventy years old. 2 He can’t have been a hundred years old. He was still working. 3 She might have cut down on chocolate. 4 He must have worked out a lot. 5 She could have gone without dessert. 6 They might have taken up basketball |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - rewrite the sentences Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 25 Students complete the sentences with the correct modals. Check answers by asking some students to read out their sentences and asking the class to say whether they are correct or not. Differentiation with individual need learners For the general comprehension Teacher explain the task and less able learners complete the sentences as possible, more able learners complete the sentences correctly. |
Learners choose the correct words. ANSWERS : 1 might 2 must 3 could 4 can’t 5 must 6 can’t |
Teacher’s comment Descriptor: - complete the sentences - choose the correct words Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 25 • Read the example as a class. Then put students in pairs to speculate about the situations. In a weaker class, do a few more together and discuss them first. Establish that might, could and must are largely interchangeable; it depends on your level of certainty. |
Learners work in pairs. Take turns reading and responding to situations 1–6 using past modals and the words in brackets ANSWERS : 1 She might / could / must have been ill. 2 He might / could / must have received some good news. 3 He might / could / must have taken up tennis. 4 He might / could / must have had an operation. 5 He might / could / must have cut down on sugar. 6 She might / could / must have given up smoking. |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - work in pairs - use past modals Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. V Ex: 5 P: 25 Read the instructions and check that students understand. Play the first dialogue for students to listen, then pause and elicit speculation from the class. • In a weaker class, pause after each one and speculate together. In a stronger class, play the other dialogues and encourage students to discuss in pairs before sharing with the group |
Learners listen to five dialogues and speculate about what has happened. Use past modals to give your reasons ANSWERS : 1 They must have been burgled. 2 They must have been on holiday. 3 He could have left his essay on the bus. 4 He must have hit the man. 5 She must have got a part in a play. |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - listen to five dialogues - use past modals Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 19 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Exchanging opinions |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 7. 1 to determine the characteristic features of most oral genres at the word, sentence and text level 9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: -Listen to a conversation in which people exchange opinions. - Learn key phrases for exchanging opinions. - Learn how to use should, must, have to - Practise exchanging opinions. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Low and Order "Victim in the life of a child" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, see how many suggestions for a healthy lifestyle students can remember from the eight point health plan on page 24. • Ask where students come across advice about health. Elicit suggestions for how the government and schools can communicate with young people about health issues, e.g. TV advertising and posters. T: What do you think about today’s theme? Why do people use drugs in sports? What health damage can performance drugs cause?
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/9KtxQm7msnZZgxr5A
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 26 Focus on the photo. Ask: What are Marie and Dean looking at? What do the posters show? Elicit ideas and then ask: Which poster do you prefer? Why? Elicit a range of opinions |
Learners look at the posters. What are they campaigning against? ANSWERS: They are campaigning against drugs. |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - look at the posters. - answer the question Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 26 In a stronger class, tell students to cover the dialogue and just listen. Play the CD once and ask whether Marie and Dean agree about the posters. A learner with individual needs: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use simple, basic statements in his discussion. |
Learners listen to the dialogue. Which poster has got the clearest message? ANSWERS: Marie thinks the poster with the photo has a clearer message, but Dean prefers the poster with a more positive message |
T’s ffedback Descriptor: - listen to the dialogue Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 26 Play the CD and ask students to listen to the intonation, and try to copy it when they practise the dialogue themselves. • Ask students to find the key phrases in the dialogue and translate them into their own language. • Students practise the dialogue in pairs |
Learners listen to the key phrases. Which phrase expresses a strong opinion? Practise the dialogue ANSWERS: It should definitely … expresses a strong opinion |
Teacher’s comment Descriptor: - listen to the key phrases - practise the dialogue Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 26 Read the sentences and the rules with the class. Make sure that students understand advice (a suggestion about what somebody should do in a particular situation), obligation (something you must do because you have promised, because of a law or a rule) and prohibition (a law or a rule that stops something being done or used). • In a weaker class, ask students to work in pairs to create new sentences. Differentiation: All learners understand and complete not all sentences and more able Ss complete and read the correct sentences to the class. |
Learners look at sentences and read the rules. Then change the words in blue using your own ideas ANSWERS : 1 six 2 factory 3 six 4 5.30 5 20 6 sleeps |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - look at sentences - read the rules Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. V Ex: 5 P: 26 Read the four statements with the class. Elicit opinions about the first statement, and encourage students to use key phrases from exercise 3. • Ask some students to report back on whether they and their partner agreed or disagreed. |
Learners work in pairs. Talk about opinions. Use the key phrases in exercise 3. ANSWERS : |
Self assessment
Descriptor: - work in pairs - use the key phrases Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 20 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A discussion essay Summative assessment for the unit «Exercise and Sport» |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 7. 1 use subject-specific vocabulary and syntax within the framework of unlimited general and study topics; 9. 4. 6. 1 determine the author's opinion or point of view in long texts within the framework of general and educational topics; 9. 5. 5. 1 teacher-supported use of arguments in endlessly familiar general and educational topics with examples and justifications; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary to do with nutrition and healthy eating. • Read a text about healthy eating. • Talk about diet and ways it could be improved. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Diligence and Professional Qualification! Labor in human life, family, society understand the value |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, write footballers’ salaries on the board and elicit the meaning. Ask: Do you think footballers should be paid a lot of money for what they do? Elicit some opinions. • Write For and Against on the board and list arguments under the two headings as students give them. • Tell students they are going to learn how to present arguments for and against in a discussion essay. T: What do you think about today’s theme? |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 27 Students read the model text and answer the questions. T shows on the reading text on the smart board and asks some CCQs:
|
Learners read the model text and answer the questions. ANSWERS: 1 The writer is against footballers getting enormous salaries, but thinks they should be paid well. 2 Yes, the writer gives both sides of the argument. 3 For high salaries: need to pay high salaries to get good players; TV advertising attracts a large amount of money to clubs and football players should get some of this money. 4 The writer’s opinions are in the last paragraph. Footballers should be paid well, but they could earn half of their current salaries and still be well paid. Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS -No - Yes - Yes |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - read the model text - answer the questions Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 27 In a weaker class, allow students to find the key phrases in the text. In a stronger class, encourage students to complete them from memory. • If necessary, ask students to translate the phrases into their own language. |
Learners complete the key phrases. Then read the model text and check. ANSWERS : 1 for 2 against 3 arguments 4 other 5 in 6 favour |
T’s ffedback Descriptor: - complete the key phrases - read the model text Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 27 Focus on the table and words in the box to make sure that students understand everything. Elicit an example of one contrasting discourse maker and one summarizing. • Students copy and complete the table. • Check answers |
Learners which words or phrases in the box can you use to replace the phrases in blue in the text? Complete the table ANSWERS Adding: in addition, furthermore, also, what’s more Contrasting: although, but, however, on the other hand, even though Summarizing: all in all, to sum up, in conclusion |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - use to replace the phrases - complete the table Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 27 • Students can work in pairs to choose the correct words in sentences 1–6. A learner with individual needs: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use simple, basic statements in his discussion. |
Learners choose the correct words. ANSWERS 1 In addition 2 Although 3 What’s more 4 However 5 On the other hand 6 all in all |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - work in pairs . - choose the correct words Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 21 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country. Exercise and sport |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 2. 1 independently understand more specific information on general and educational topics without support in a wide-ranging extended conversation; 9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics; 9.4.9.1 recognise inconsistencies in argument in extended texts on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Read a text about Kazakh sports stars. - Learn vocabulary connected to success in sports. - Learn the difference between could, was / were able to and managed to. - Write sentences about famous sportspeople in Kazakhstan. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Independence and Patriotism National interest: expanding the scope of the Kazakh language |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: • Have a race to find which group can list the most Kazakh sportspeople in two minutes. • After two minutes, find out which group had the longest list and declare them the winner. • Ask that pair for their answers and write them on the board. • Ask other groups to contribute more names if they have them T: What do you think about today’s theme?
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/rsA7X17GEinNuoou9
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 28 • Draw students’ attention to the photos. Ask them if they can identify who they are. • In pairs, students discuss what they know about the sportspeople. T shows on the reading text on the smart board and asks some CCQs:
|
Learner look at the photos. Who are these people? What do you know about them? ANSWERS: Kazhymukan Munaitpasov Denis Ten Zarina Diyas Students’ own answers Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS -Yes -Yes -No |
Pair assessment Descriptor: - look at the photos. - answer the question Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 28 Tell students to listen to and read the text and see if it contains the information they talked about. • In a stronger class, play the recording with books closed to see how much they understand and for them to check whether the information they talked about is mentioned. • Students read the sentences. • Play the recording again while students read the text on the page. • Give them extra time at the end to complete the sentences Differentiation with individual need learners: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use simple, basic statements in his discussion. |
Learners read and listen to the text. Complete the sentences with the names of the people ANSWERS : 1 Zarina Diyas (Czech Republic) 2 Kazhymukan Munaitpasov 3 Denis Ten (shopping mall) 4 Kazhymukan Munaitpasov 5 Denis Ten 6 Zarina Diyas |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - read the text - complete the sentences Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 28 Focus students’ attention on the verbs. • Ask students to note down what they think the nouns are. •Then tell them to check their answers in the text and correct any they have got wrong. • Students underline the suffixes. • Check answers as a class. |
Learners complete the table with nouns from the text. What suffixes are used to form the nouns? What other noun suffixes do you know? ANSWERS: 1 wrestling 2 performance 3 failure 4 achievement 5 competition 6 injury |
Teacher’s comment Descriptor: - complete the table - underline the suffixes Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 28 Write on the board: I can speak English. Then add when I was ten years old. Ask students if the sentence is correct. Ask them to correct it to elicit could. • Write could, was / were able to and managed to on the board and ask students to look at the text again and see the different ways they are used. • Elicit the difference between could (ability), was / were able to (ability and for describing being successful after trying to do something, e.g. He was able to escape after a few hours.) and managed to (only for being successful after trying to do something). |
Learners look at the words in blue in the text. Then complete the rule ANSWERS: was able to, managed to |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - look at the words in blue - complete the rule Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. V Ex: 5 P: 28 Students now to put this information into practice. • Students check their answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class and explain further if students have difficulty with understanding the differences between the words. A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners complete the sentences. Write one word in each gap. ANSWERS: 1 could 2 able 3 managed 4 were 5 manage |
Self assessment Descriptor: - ask and answer questions Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 22 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Healthy eating |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 4. 9. 1 identify inconsistencies in evidence presented in long texts on a variety of general and academic topics 9. 5. 5. 1 teacher-supported use of arguments in endlessly familiar general and educational topics with examples and justifications; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Learn vocabulary to do with nutrition and healthy eating. - Read a text about healthy eating. - Talk about diet and ways it could be improved |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Independence and Patriotism National interest: expanding the scope of the Kazakh language |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, write An apple a day keeps the doctor away on the board. Explain that this is an old proverb and ask students what it means. • Elicit that the proverb is not meant literally, but suggests that if we eat healthy foods, like fruit, we will not get ill. • Ask students whether they think their diets are healthy. Do they think about what they eat? • Elicit examples of healthy and unhealthy foods. T: What do you think about today’s theme?
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 29 • Students match the definitions with the blue words. Allow students to use their dictionaries if necessary. • Check answers with the class. |
Learners match definitions with the words in blue in the text. ANSWERS: 1 dairy 2 processed 3 tissues 4 evidence 5 fibre |
Pair assessment Descriptor: - match definitions - use their dictionaries Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 29 Students listen and read. Ask the question to the whole class. Differentiation Learners will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners read and listen to the text. How does healthy eating affect our lives? ANSWERS: Healthy eating affects our physical and mental health. It can reduce the risk of serious illnesses such as heart disease, diabetes and possibly also mental illness, like depression. Eating regular meals can help with energy, as well as mood and memory. |
T’s ffedback Descriptor: - read the text - answer the question Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 29 • Tell students to read the questions and multiple-choice answers. • In a weaker class, encourage students to reread the text carefully and underline the parts of the text that contain the answers, so that they can find them again easily. When comparing answers with a partner, they can refer back to the text extracts, and check that they have understood the question and the text correctly. • In a stronger class, they can make notes based on their first reading of the text. Then they read the text again, and confirm or correct their answers. • Remind students to look carefully at the whole question, and watch out for little words or negatives that change the meaning of the sentences, e.g. question 5 (Which fats are not good for us?). • Students read the text again and answer the questions T shows on the reading text on the smart board and asks some CCQs:
|
Learners read the text again and choose the correct answers. ANSWERS : 1 a 2 c 3 b 4 b 5 a 6 b Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS -Yes -Yes -No |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - read the text - choose the correct answers Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 29 In a weaker class, read the sentences together and establish the type of words that are required (foods, number, adverb of frequency). • Students complete the sentences individually, before comparing answers and discussing the questions with a partner. In a stronger class, encourage students to give reasons for their answers and examples where possible. • Ask some students to report back to the class on whether they think their diet is healthy. Share suggestions for things students can do to improve their eating habits Differentiation with individual need learners: Allow students time to complete the sentences about your diet. |
Learners complete the sentences about your diet. Discuss how healthy or unhealthy your diet is. What should you change? ANSWERS : Student’s own answer |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - complete the sentences - discuss about diet Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 23 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative control work for the 1st term |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 2. 1 independently understand more specific information on general and educational topics without support in a wide-ranging extended conversation; 9. 3. 7. 1 use subject-specific vocabulary and syntax within the framework of unlimited general and study topics; 9.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: -understand more complex supported questions on a growing range of general and curricular topics; -recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level in a range of written genres; -write with some support topics with some paragraphs to give basic personal information; |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Independence and Patriotism Republic Day! |
||
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 24 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review. Unit 2 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 2. 1 ask complex questions to obtain information within general and educational topics; 9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Use nouns and verbs related to the health benefits of exercise. - Practise using may, might, could, must and can’t to express possibility and certainty in opinions |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Independence and Patriotism National interest: expanding the scope of the Kazakh language |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: Ask students to work in pairs and talk about what they know about their grandparents as young people. What jobs did they do and what did they do in their free time? Setting the aim of the lesson. |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 30 Allow students to work in pairs. Ask students to complete the sentences individually, but allow them to check their answers in pairs before you check with the class |
Learners complete the sentences with the correct form of the verbs in the box ANSWERS 1 boost 2 raise 3 have 4 build 5 increase 6 involves 7 improve |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - complete the sentences - use the verbs in the box Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 30 Allow students to work in pairs. In a stronger class, ask students to write the nouns for these words and check their answers in pairs Differentiation: A less motivated learner to choose the correct words with support by helpers |
Students write the nouns for these words. ANSWERS 1 loneliness 2 infection 3 medication 4 depression 5 illness 6 reduction 7 commitment 8 intelligence |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - work in pairs - write the nouns Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 30 Ask students to work in pairs. Ask students to complete the sentences individually, but allow them to check their answers in pairs Complete the sentences with correct tense of the words in the box. |
Learners complete the sentences with the words in the box. ANSWERS 1 down 4 up 2 without 5 off 3 up 6 on |
Pair assessment
- complete the sentences - use the words in the box Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 30 Ask students to complete the sentences with the affirmative or negative form of could, can and will be able to. |
Learners complete the sentences with the affirmative or negative form of could, can and will be able to. ANSWERS 1will be able to 2 couldn’t, can 3 can’t 4 couldn’t 5 could 6 won’t be able to |
Descriptor: - choose the correct words - complete the task Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
Lesson plans English plus Grade 9
Lesson plans English plus Grade 9
Short term plan
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 1 |
School: S. Yerubayev |
||
|
Date: 02.09.2024 |
Teacher name: S. Murataliyeva |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Attributes and personality |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics; 9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; 9.6.15.1 use infinitive forms after a growing number of adjectives and verbs, use gerund forms after a growing variety of verbs and prepositions, use an increased variety of prepositional verbs and phrasal verbs on a range of familiar general and curricular topics; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Recognize and use nouns and adjectives of attributes and personality. - Make adverbs from adjectives. - Construct the sentences using comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs with some support |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Creativity and innovation The Education Day! "School is a place of kindness!" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, ask: How would you describe your personality? Elicit a few ideas from individual students. • Put students into pairs to write down as many words they can think of associated with personality. • Write attributes on the board and ask students if they think people with certain attributes are suited to particular hobbies. Ask: What kind of people are suited to playing chess? Accept all answers. T: What do you think about today’s theme? Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. Learners fill the sheets of papers by classifying hobbies in together |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/i2kwjRagkf6dqBDG6
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P:8 In a weaker class, ask for translations. In a stronger class, encourage students to put the words into sentences to show understanding. Differentiation with individual need learners: * Translate in L1 adjectives of the hobbies. |
Learners complete the table. Which adjectives are negative? ANSWERS 1 generous 2 passion 3 moody 4 anxious 5 pessimistic 6 optimism 7 responsibility 8 respect 9 enthusiasm 10 confidence 11 frustrated Negative adjectives: moody, anxious, pessimistic, frustrated |
T’s feedback
Descriptor: - complete the table. Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P:8 In a weaker class, you could help students to prepare for the task by deciding together whether the missing words are adjectives or nouns. In a stronger class, ask students to give reasons and justify their opinion. Ask some students to compare their answers and report back to the class on how similar or different they and their partner are. A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners complete the sentences with your own ideas using words in exercise 1. ANSWERS Student’s own answer |
Self -assessment T’s CCQs
Descriptor: - complete the sentences - using words in exercise 1 Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Stickers |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P:8 Students do the Hobbies questionnaire, then compare their answers in pairs. Do they have similar views on hobbies? Ask them to discuss what hobbies they do and what attributes help with that hobby. T asks some CCQs:
|
Learners complete the Hobbies questionnaire. Then compare your answers with a partner. Do you have the same attitude to hobbies? How are you the same and different? ANSWERS Student’s own answer Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS -No -Yes -Yes |
T’s feedback
Descriptor: - complete the Hobbies questionnaire - answer the question Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Pictures Worksheet |
|
End 5 min |
“Finger” method is used to find out was the lesson clear or not. 5 fingers- I understood 4 fingers -I have some questions 2 fingers-I need a help Ex: P: Home task |
Ss show their knowledge according to the lesson Ss evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: W |
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 2 |
School: S. Yerubayev |
||
|
Date: o5.09.2024 |
Teacher name: S. Murataliyeva |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Compare people and the things they do. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; 9. 6. 12. 1 use different comparative forms of regular and irregular adverbs on many familiar general and educational topics, use many types of adverbs that come before the verb, after the verb and at the end of the verb; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Construct the sentences using comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs with some support - Comprehend comparisons to compare and contrast people and the things they do. - Produce a clear, coherent description of a person they know. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Independence and Patriotism Day of the Languages of the People of Kazakhstan |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: Pantomime: 'What do you like? Play the game in 2 groups. One pupil from each group comes to the board and mimes a hobby. The other group tries to guess the hobby. If they guess correctly, they win one point. At the end of the game, the group with the most points is the winner. T: What do you think about today’s theme? Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/i2g4PSk1aFJaj5G69
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 4 P: 9 Write on the board: In life, it’s best not to act too … Elicit possible endings for the sentence (quickly, carefully, etc.). Write the adverbs successfully, generously, anxiously, and confidently on the board and underline them. Elicit that they are adverbs, they end in -ly, and they are formed from the adjectives in exercise 1. Check that students understand the difference between adjectives and adverbs. Write on the board: Petra is a good singer. Petra sings well. Underline good and well. Explain or elicit that adjectives modify nouns and adverbs modify verbs. Point out that well is irregular. Ask students to look back at exercise 1 and make adverbs out of the remaining adjectives.. Differentiation with individual need learners: Learners understand the difference between adjectives and adverbs. Less motivated learner do the task with support. |
Learners complete the examples and the rules in the table ANSWERS 1 -ly 2 firmly 3 -ily 4 angrily 5 -ally 6 optimistic 7 fast 8 hard Adverbs from adjectives in exercise 1: successfully, generously, passionately, moodily, anxiously, pessimistically, optimistically, responsibly, enthusiastically, confidently, frustratingly |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - complete the examples -make adverbs from adjectives Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 5 P: 9 Ask some students to write some of their sentences on the board. Discuss if they are logical and correctly formed. A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. Less motivated learner work in pairs to write their sentences. |
Students write six sentences describing how you do different things. Use the verbs in the first box and adverbs formed from the adjectives in the second box. ANSWERS Student’s own answer |
Self -assessment
Descriptor: - write six sentences - use the verbs Total: 2 point |
Worksheets |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 6 P: 9 • Focus on the example and elicit one or two more examples from the class. Check answers. Make sure students understand we use less, the least, more, the most to form comparative and superlative forms of adverbs A learner with individual needs: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use simple, basic statements in his discussion. |
Learners study sentences 1–5. How do we form the comparative and superlative forms of adverbs? Complete the table with the words in blue ANSWERS We use less and more to form comparative adjectives. We use the least and the most to form superlatives. Comparative adjectives: meaner, more comfortable, less stressful Comparative adverbs: less seriously, more positively, more happily Superlative adjectives: the most selfish, the least successful, the most optimistic, the richest Superlative adverbs: the least generously, the most rudely |
T’s feedback
Descriptor: - complete the table Total: 2 point |
Pictures Worksheet |
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 7 P: 9 Focus on the first sentence and elicit that the missing word is an adverb and a superlative. Elicit the answer (the most successfully). In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs. In a stronger class, ask students to complete the sentences individually, but allow them to check their answers in pairs before you check with the class Differentiation with individual need learners: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to complete the sentences with. |
Learners complete the sentences with the comparative or superlative form of an adjective or adverb. Use more / less and the most / the least ANSWERS 1 the most successfully 2 less pessimistically 3 more carefully 4 less noisy 5 more slowly 6 the least sensitive |
Self -assessment T s feedback Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Home task Ex: P: |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 3 |
School: S. Yerubayev |
||
|
Date: 06.09.2024 |
Teacher name: S. Muratalyeva |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Comparing generations |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; 9. 6. 12. 1 use different comparative forms of regular and irregular adverbs on many familiar general and educational topics, use many types of adverbs that come before the verb, after the verb and at the end of the verb; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Synthesize information from the reading passage about life in the 1950s. - Demonstrate the correct use of adjectives + prepositions. - Interpret a text comparing past and present generations. - Express their opinions about different generations building extended sentences. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Independence and Patriotism to make students understand the value of three languages |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, ask students if they have seen photographs of their parents and grandparents when they were young. Ask: What were their clothes like? What were their hairstyles like? Ask: What do you think life was like in the 1950s? Elicit a range of ideas, but don’t confirm or reject any at this stage. T: What do you think about today’s theme? Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/Ce8ZAnooSXd3PnA5A
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 10 • Read through the items in the list with the class and check that students understand them. In a weaker class, allow students to use dictionaries or pre-teach ballroom (a place where people used to go to dance) and big band (a style of jazz music played by a group of twelve to fifteen musicians). In a stronger class, elicit suggestions and guesses for unfamiliar vocabulary, and then discuss again after the first reading, encouraging students to use context to work out the meaning. In pairs, or as a group, discuss the questions. Then let students listen and read, and check their answers. Differentiation with individual need learners: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use dictionaries or pre-teach ballroom |
Learners which of these things do you think were common in the 1950s? Which are common now? Read, listen and compare your answers with the text. ANSWERS More common in the 1950s ballrooms, big bands, black-and-white TV More common now mobile phones, computers, jobs for women, discos, bad language |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - read the text - listen and compare your answers Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 10 In a weaker class, encourage students to underline the parts of the text where they found the answers. In a stronger class, encourage students to identify the false sentences and correct them from memory. Then they should read again and confirm. T asks some CCQs:
|
Learners read the text again. Write true or false. Correct the false sentences. ANSWERS 1 False. The cinema was popular in the fifties. 2 False. A family in her street bought a TV. 3 True. 4 False. She really likes the fashions. 5 True. 6 True. 7 False. People wait longer these days. 8 True Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS - Yes - No - Not |
Self -assessment
Descriptor: - read the text again - write true or false. Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Worksheets |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 10 • In a weaker class, explain that prepositions are words like in, from, to, in front of, at and on, which are usually used before a noun or pronoun to show place (He lives in Paris.), position (The book is on the table.), time (The film starts at nine o’clock.) or method (Shall we walk or go by bus?). In a stronger class, ask students what prepositions are and elicit examples. Explain that many adjectives are followed by particular prepositions. A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners complete the sentences with prepositions. Then check your answers in the text ANSWERS 1 on 2 by 3 about 4 in 5 to 6 for 7 about |
T’s comment Descriptor: - complete the sentences - check your answers Total: 2 point |
Pictures Worksheet |
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 10 In a weaker class, ask students to choose the correct prepositions first. Check the answers with the class, then tell students to complete the sentences with their own ideas. In a stronger class, ask students to look at the sentences in exercise 3 again and tell you what part of speech usually follows the preposition (noun). Write on the board: She’s keen on playing tennis. Are you interested in joining the drama club? Ask students what part of speech are the words after on and in (verb). |
Learners complete the sentences with the prepositions in the box and your own ideas ANSWERS 1 of + students’ own answers 2 with + students’ own answers 3 about + students’ own answers 4 at + students’ own answers 5 for + students’ own answers 6 from + students’ own answers |
Self assessment
Descriptor: - complete the sentences -use prepositions in the box Total: 2 point |
Pictures |
|
|
Task. V Ex: 5 P: 10 You may want students to prepare the answers for this activity as homework so they can ask older family members for their opinions. Read through the questions with the class and make sure that students understand everything. Ask students to prepare their answers to the questions individually. Students can ask and answer the questions in pairs. |
Learners ask and answer the questions. ANSWERS |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - ask and answer Total: 2 point |
Pictures |
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 4 |
School: |
||
|
Date: 09.09.2024 |
Teacher name: Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talk about events at different times in the past. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics; 9. 5. 1. 1 plan, write, correct and check text-level works on general and academic topics without the support of the teacher; 9.6.9.1 use appropriately an increased variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Identify the difference between the past perfect and past simple. - Construct the sentences using past perfect and past simple with support. - Construct the sentences using past perfect and past simple with minimal support. - Apply past perfect and past simple to talk about events at different times in the past without support. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Family day! "Family is the golden cradle of education" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, ask the students what they remember about the reading text from last lesson. Write on the board the example I visited my gran last weekend and she’d found some of her old photos. Underline she’d found. Ask: When did I visit my gran? (last weekend) When did she find the photos, before or after I visited? (before I visited) Elicit the full form of the contraction (had found). Tell students that this tense is called the past perfect. There are six chairs in the classroom. Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/8kkaLWk3uKKj8cNN6
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 11 Ask students to open their books and look at the timeline. Tell them to read the sentence again and match the events to the diagram. Ask students to translate the examples into their own language. Discuss how the equivalent tense is formed in the students’ own language, and whether this is similar to English Differentiation with individual need learners: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to write the events in the correct place on the timeline |
Learners study the timeline and the sentence. Write the events in the correct place on the timeline. Then choose the correct words in the rules ANSWERS Recent past: I visited my gran Earlier past: she’d found some of her old photos Rules: a before b past simple c had |
T’s feedback Descriptor: - study the timeline - write the events in the correct place Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 11 Read the example with the class and ask: Which action happened first? (I saw the film) Focus on the next sentence and ask Which action happened first? (Alice didn’t have many hobbies when she was a child). Elicit which verb should be in the past perfect (have) and which in the past simple (tell). Remind students that some irregular verbs have the same form for the past tense and past participle, but others have different forms. Tell students to use the irregular verbs list on page 126 of the Student’s Book. Differentiation: A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners complete the sentences. Use the past perfect and the past simple in each sentence. ANSWERS 1 told, hadn’t had 4 was, had left, had found 2 got, went, hadn’t seen 5 hadn’t started, arrived 3 hadn’t invented, was 6 wanted, had had |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - complete the sentences - use the past perfect and the past simple Total: 2 point |
Worksheets |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 11 Make sure students understand the logical order of events. In the example, one fact is a consequence of the other. Remind them to use context and to look out for time markers, e.g. when, by the time, after in the prompts |
Students complete the sentences using the past perfect and your own ideas ANSWERS Students’ own answers |
T’s comment Descriptor: - complete the sentences - use the past perfect Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 5 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
People talking about their memories |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 2. 1 understand on their own some specific information on general and learning topics without support in a wide-ranging extended conversation 9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Ask and answer the questions using collocations with make, do, collect and write. - Identify the meaning of the dialogues "People talking about the past". |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Independence and Patriotism to make students understand the value of three languages |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: Write make, do, collect and write on the board as headings. With books closed, students work in pairs and brainstorm words you use with each Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/RT9tFY74hZ1ffEbw6
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 12 In a weaker class, elicit translations of the collocations and make example sentences as a class. In a stronger class, encourage students to record the new phrases in their own example sentences. Point out that students can use diagrams like these to record other collocations. They could also turn the diagrams into spider grams if they prefer. Differentiation with individual need learners: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to translate collocations and make example sentences as a class |
Learners complete the diagram with the words in the box ANSWERS 1 model planes 2 clothes 3 music 4 puzzles 5 woodwork 6 sports 7 badges 8 stamps 9 football cards 10 blogs 11 poetry 12 short stories |
T’s feedback
Descriptor: - complete the diagram - use the words in the box Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 12 Students complete the questions individually. Check answers, then put students into pairs to ask and answer the questions. Ask some students to report back on what they learnt about their partner. |
Learners choose the correct words to complete the questions. Then ask and answer in pairs. ANSWERS 1collect 2 write 3 make 4 make 5 written 6 do 7 do, make Students’ own answers. |
Self -assessment
Descriptor: - choose the correct words - ask and answer in pairs Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 12 • Focus on the photos and elicit what they show. Elicit whether they are modern or old photos (old). Tell students they are going to hear people talking about the past. Allow students time to read through the words in the box. Students listen and match the words with the people. A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. TRANSCRIPT 1 M1 I got my driving licence when I was seventeen. I had saved and saved for this car, so when I passed the test my dad gave me the rest of the money I needed. I went to a garage and bought it immediately. When I got to school the next day, I showed it to all my friends. I was so proud. For the first week I used to look at it every ten minutes. I couldn’t believe it was my car. 2 M2 Well, I was OK when I got up, but as the time got nearer, I was watching the clock and I was getting more and more upset. When I finally got to school, I was crying and crying. My uniform was much too big, the place seemed big, in fact it was all big – my bag, my teacher, everything. I hated it. Of course, I didn’t want to go back the next day. At breakfast I was crying again and my mum was getting upset, too. Then mum started crying, so dad had to take me! But by the end of the week I’d made some friends, so things got better. 3 G This music’s good. C Yes, I love reggae. I first heard it when I was at a party. I was dancing with a boy called Dave. I loved it. A few weeks later I was sixteen, so I had a party at my place. I invited Dave and he got me a Bob Marley record for my birthday. G That was nice of him. C Yes. We started going out together after that. G Isn’t your husband called Dave? C Yes, we got married! That record is still one of our favourites. It gets better each time I hear it. 4 J I won some tickets to a football match once. B You won tickets? J Yeah, to my first football match. It was Manchester United against Everton. I gave my uncle a ticket because he was a Man United fan. Their best player was called George Best, and he got three goals, but I didn’t see two of them. B You missed two goals? J Yes, I was talking to my uncle when he scored! B Oh no! J My uncle missed them, too and he’s never forgotten it. He still talks about those goals today and he’s eighty-two! |
Learners listen to the dialogues. Match two words with each of the people in the photos 1–4 ANSWERS 1 Michael: money, test 2 Maxine: uniform, upset 3 Clare: party, married 4 Joey: uncle, tickets |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - listen to the dialogues - match two words Total: 2 point |
Pictures Worksheet |
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 12 Check that students understand the meaning of positive and negative. Write a plus and minus symbol on the board to help explain the meaning (or a happy and sad face). When students have finished, ask them to compare their answers with a partner. Then, ask individual students to come to the board and write the phrases in the correct list. Ask them to read the phrases and help with pronunciation |
Learners listen again and choose the correct answers. ANSWERS 1 c 2 a 3 b 4 c 5 a |
T’s feedback
Descriptor: - listen again - choose the correct answers Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 6 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talk about past events and memories |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 1. 1 unsupported understanding of general and main points of study topics with long conversations; 9. 3. 6. 1 in pair, group and whole class work to explain what others said in sentences or reasoning with a certain level of flexibility; 9.6.10.1 use present continuous forms and past continuous, including a growing variety of passive forms, on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Read about people’s hobbies. - Learn expressions for talking about your interests and hobbies. - Write about your interests and hobbies. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Family day! "Family is the golden cradle of education" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: Refer students back to the photos on page 12. Ask What was Clare doing when she first heard the music? • Elicit the answer (she was dancing) and write the sentence on the board: She was dancing when she heard the music. • Underline the verbs and elicit that they are in the past continuous and past simple. • Ask: Which action happened first? (she was dancing); Did she continue dancing when she heard it? (yes) Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/H5FuapmFSi4DHZnDA
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 13 Students work in pairs to study the sentences and match them to the descriptions. Check answers with the class. Elicit which tenses are used. |
Learners look at the photos and about their hobbies. ANSWERS 1 b (past continuous) 2 c (past continuous and past simple) 3 a (past simple) |
T’s feedback Descriptor: - look at the photos - guess three people’s interests are Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 13 Students copy the sentences from exercise 4 and highlight or underline the tenses. • Tell students to use different colours to indicate different tenses. • Discuss as a class how this technique might be helpful, for example by giving students memorable examples of tenses that they can remember easily. In a stronger class, write on the board: When I arrived, she had made a cake. When I arrived, she was making a cake. and When I arrived, she made a cake. Ask students to underline or highlight the verbs in the sentences, then identify the tenses and explain the difference in meaning |
Learners read and listen to the text. Check your answers. ANSWERS Student’s own answer |
Pair -assessment
Descriptor: - read and listen - check your answers Total: 2 point |
Worksheets |
|
|
Task. III (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 3 P: 13 Focus on the example and ask: Which action was in progress? (he was competing) Which action is finished? (he won). In a weaker class, do another together. Focus on the first question and elicit which action was in progress (using) and which finished (said). Elicit the correct verb forms from the class. In a stronger class, one example should be enough. • Students continue writing their questions individually. Check answers as a class. • Put students into pairs to answer the questions. Listen and check answers to the quiz questions. Ask students how many they got right. Differentiation with individual need learners: will be do another easy task. Choose the correct answer.
|
Learners read the text again and choose the correct answers. ANSWERS 1 What new invention was Alexander Bell using when he said, ‘Mr Watson, come here. I want to see you’? (the telephone) 2 When Titanic hit an iceberg in 1912, where was it travelling to? (New York) 3 When Neil Armstrong said, ‘That’s one small step for man; one giant leap for mankind’, where was he standing? (on the moon) 4 Where was Isaac Newton sitting when he discovered gravity? (under a tree) 5 Where was Mark Zuckerberg studying when he invented Facebook? (Harvard University) 6 Where were people celebrating the new millennium when they took this picture? (Sydney, Australia) |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - read the text - choose the correct answers. Total: 2 point |
Student’s book Worksheets https://images.app.goo.gl/sCPKnucNBHVijzHU9 |
|
|
Task. IV (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 4 P: 13 Point out the blue phrases in the text, and explain that these are key vocabulary items. Ask students to look at the gapped sentences 1–6. Explain that they should find the complete sentences in the texts and write the missing blue words. Check understanding of the words and expressions, for example by asking students to translate them |
Learners find these sentences in the text. Then complete the sentences with the words in blue. ANSWERS 1 not mad about 2 prefer 3 especially 4 a … fan 5 good at 6 can’t stand |
Self assessment Descriptor: - find these sentences - complete the sentences Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. V (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 5 P: 13 Ask students to compare their answers in pairs. Ask some students to read their sentences to the class. |
Learners complete the sentences and compare your answers with a partner. ANSWERS |
Pair assessment Descriptor: - work in pairs - complete the sentences Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 7 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talking about past events |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 1. 1 unsupported understanding of general and main points of study topics with long conversations; 9. 3. 6. 1 in pair, group and whole class work to explain what others said in sentences or reasoning with a certain level of flexibility; 9. 4. 4. 1 reading long texts in fiction and non-fiction literature within familiar and some unfamiliar general and educational topics; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Develop their listening skills for gist and specific information in the context of talking about past events. - Recognize and use key phrases for talking about events in the past.. - Perform situations talking about events in the past without support |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Mother's Day! "Family is the golden cradle of education" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, ask students what important days they can remember from the past. Elicit some answers, e.g. the first day at a new school, a holiday, Christmas day, etc. Ask students to describe what they remember and how they felt Did you celebrate the Nauryz last year? Did you remember the first day at school? Did you spend your holiday at the beach? Setting the aim of the lesson. |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 14 Draw students’ attention to the photo and elicit a description. In a weaker class, encourage students to participate by accepting factual descriptions. In a stronger class, ask students to speculate about the answers to the questions and explain their answers. Differentiation: Learners will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners complete the sentences from the text. Then complete rules. ANSWERS Student’s own answer |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - complete the sentences - complete rules Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 14 Tell students they are going to listen to a conversation between the man and the boy. They should listen for general understanding and to find the answer to the question. (Colin is Dean’s grandfather.) After listening once, ask which part of the festival Colin enjoyed most. T asks some CCQs:
|
Learners listen to the dialogue. Which part of the festival did Colin enjoy most? ANSWERS The end of the last day. Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS - No - Yes - No |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - listen to the dialogue - answer to the question Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 14 Students work in pairs to complete the key phrases. In a stronger class, tell them to cover the dialogue and try to do it from memory. Students listen again to check their answers. Tell them to listen to the intonation of the phrases, as well as the words. Students practise the dialogue in pairs Differentiation: A less motivated learner work in pairs, and do the example with support. |
Learners complete the key phrases. Then listen and check your answers. Practise the dialogue with a partner ANSWERS 1 ever 2 was 3 ago 4 have 5 bit 6 happened |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - complete the key phrases - practise the dialogue Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 14 Tell students they are going to hear parts of a dialogue, and they must choose the most appropriate responses. Students listen and answer individually. Play the CD again and elicit the answers |
Learners listen and choose the correct answers ANSWERS 1 b 2 b 3 a 4 b |
T’s comment Descriptor: - choose the correct answers Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. V Ex: 5 P: 14 Students complete the key phrases and compare answers in pairs before checking as a class. Individually students rewrite the mini-dialogue by changing the blue words. Then students read their new dialogues in pairs. Differentiation: Learners will be supported by teacher and by helpers. |
Learners complete the mini-dialogue with the key phrases. Then change the words in blue and practise the new minidialogue. ANSWERS 1 tell 4 Did 2 when 5 best 3 around 6 What |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: -. complete the mini-dialogue - practise the new minidialogue Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 8 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Describing a decade |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics 9. 4. 6. 1 determine the author's opinion or point of view in long texts in the context of general and study topics 9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Study a model account of a decade. - Learn key phrases for writing about a decade. - Learn about giving examples. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Mother's Day! "Family is the golden cradle of education" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: Ask students what they think all these events have in common. If necessary, tell them that they all happened in the same decade and invite students to guess which one. Confirm that it is the 1960s • Ask: What else do you know about the 1960s? Elicit ideas, and write useful vocabulary on the board. Setting the aim of the lesson. Answer the questions What do you know about the sixties? It was an era of memorable events, for example, the moon landing in July 1969 Many people remember exciting events such as England’s World Cup win Some bands became incredibly successful, The Beatles, for instance. |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 15 Read through the questions and make sure everyone understands. In a weaker class, students can compare answers in pairs before checking as a class. In a stronger class, set a short time limit and tell students to skim read the text for the information in the questions. T asks some CCQs:
|
Learners read the model text and answer the questions. ANSWERS 1 a 2 Paragraph 2 3 Paragraph 4 Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS - Yes - Yes - No |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - read the model text - answer the questions Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 15 Read through the key phrases with the class. Ask students to find the key phrases in the model text and translate them into their own language |
Learners study the key phrases. Which phrases introduce the paragraphs in the text? ANSWERS Paragraph 1: The … was a decade which … Paragraph 2: In the world of fashion … Paragraph 3: One of the most memorable … Paragraph 5: By the end of the decade.. |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - study the key phrases - to find the key phrases Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 15 Look at the words in blue in the model text. Elicit what their role is (to introduce examples). • Point out the use of commas with for instance and for example. • Students complete sentences 1–4 individually with their own ideas. • Ask some students to read their sentences to the class. Differentiation: A less motivated learner translate the sentences with by helpers |
Learners study the words in blue in the model text. Then complete sentences with these words and your own ideas ANSWERS Student’s own answer |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - study the words in blue - complete sentences Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 9 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Comparing generations |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 1. 1 unsupported understanding of general and main points of study topics with long conversations; 9. 3. 6. 1 in pair, group and whole class work to explain what others said in sentences or reasoning with a certain level of flexibility; 9. 4. 2. 1 understand specific information in texts within the context of familiar general and reading topics, including some longer texts; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Study a text written by a grandfather and his granddaughter about their different experiences and hobbies as teenagers. - Learn compound adjectives connected with people’s attributes - Review talking about the past using used to. Talk about hobbies and interests students used to have |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Labor day! Be Honesty and justice |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: • Ask students to work in pairs and talk about what they know about their grandparents as young people. What jobs did they do and what did they do in their free time? • When they have finished, they join a second pair and tell each other what they’ve found out about their partner’s grandparents. Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 16 Draw students’ attention to the photos and ask them what they know about the people’s hobbies from the photos. Encourage students to describe the photos using the present continuous. |
Learners look at the photos. What are the people doing? What do you think their hobbies are? ANSWERS Grandpa Sansizbay is playing a dobra and his granddaughter is drawing in the mountains |
Pair assessment Descriptor: - look at the photos. - describe the photos - use the present continuous. Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 16 Before reading and listening students look at the true / false questions and guess the answers. Ask them to discuss the reason for their decisions in pairs. Students listen and answer individually. Give students a few minutes after the audio ends for them to complete the exercise Differentiation with individual need learners: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to discuss the reason for their decisions in pairs. |
Learners read and listen to the text. Are the sentences true or false? ANSWERS 1 True. 2 False. There were no buses then. 3 False. He thinks most teenagers are like his granddaughter: hardworking and open-minded. 4 False. She’s not really into sport. 5 True. 6 True |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - read the text - write true or false Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 16 Students look through the text and complete the exercise. • Encourage them to use their dictionaries to find the meaning of any adjectives they don’t understand. Check the meanings in translation. • As a follow-up, ask students in a stronger class to write sentences using the adjectives. In a weaker class, put the translations on the board for students to copy |
Learners match the words to make compound adjectives. ANSWERS 1 b 2 d 3 f 4 a 5 c 6 e |
Self assessment Descriptor: - match the words - make compound adjectives. Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV (Task for understanding) Ex: 4 P: 16 • Allow students time to think about the adjectives in relation to the people listed. • Encourage them to write two sentences, then in pairs to describe the people. In a stronger class, encourage them to give examples demonstrating the attribute described by the adjective. |
Learners choose two of the adjectives in exercise 3 to describe each of these people ANSWERS Students’ own answers. |
Pair asessment
Descriptor: - choose two of the adjectives - describe the people Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. V (Task for understanding) Ex: 5 P: 16 • Draw students’ attention to the example sentences. Ask students how you could give the same information without used to. (I had long hair. I didn’t like skiing. Did you live in Zyryan?) • Students work individually. Then compare their answers before you go through them with class. • Give students the following two sentences: I used to go swimming every weekend. I used to go swimming last Saturday. Ask them which one is grammatically correct, to check they understand how used to is used. • Draw students’ attention to the form in negative sentences and questions. Ask them what they notice. (Used to becomes use to after Did / Didn’t.) |
Learners study the sentences below and find seven more examples of used to in the text. Choose the correct words to complete the rules ANSWERS 1 past 2 habits and states 3 did |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - work individually - choose the correct words Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. VI (Task for understanding) Ex: 6 P: 16 Students work individually to complete the exercise. |
Learners complete the sentences with the correct form of used to and the words in brackets ANSWERS 1 used to go 2 didn’t use to listen 3 didn’t use to play 4 Did you use to have 5 used to cycle |
T’s comment Descriptor: - complete the sentences - use the words in brackets Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Hobbies and qualities lesson 10 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. The British sense of humour |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 2. 1 understand on their own some specific information on general and learning topics without support in a wide-ranging extended conversation 9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics 9. 4. 2. 1 understand specific information in texts within the context of familiar general and reading topics, including some longer texts; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Recognize and use vocabulary to do with humour. - Identify the meaning of the text about the British sense of humour. - Talk about the sense of humour in your country. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Labor day! Be Honesty and justice |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, ask students what makes them laugh. Elicit ideas about films, books, TV programmes, etc. and encourage students to express their opinions. Ask students if they know the character Mr Bean. Ask: Do you find him funny? Elicit a range of answers Did you watch film about Mr Bean? What does Mr Bean carry with him?
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/yGQ8zRcuyVuK3LwU7
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 17 In a weaker class, remind students to note the part of speech as well as the meaning for the words. In a stronger class, check understanding of the new words by eliciting example sentences. Pay particular attention to make fun of and make sure students are formulating it correctly. Don’t check answers at this stage. T asks some CCQs:
|
Learners сheck the meaning of the words and phrases in the box. Then complete the text. ANSWERS Student’s own answer Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS - Yes - No - Yes |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - сheck the meaning of the words - complete the text Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 17 Students listen, read and check their answers to exercise 1 A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners read and listen to the text. Check your answers to exercise 1. ANSWERS 1 good sense of humour 2 comedians 3 laughter 4 sarcasm 5 make fun of 6 bizarre |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - listen to the text - check your answers Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 17 Allow students time to compare their answers in pairs and discuss any differences before you check with the class. As usual, in a stronger class, encourage full, complete answers in the students’ own words |
Learners read the text again and answer the questions. ANSWERS 1 a good sense of humour, good looks and money are important qualities when choosing a partner 2 people feel happier, healthier and more optimistic when they lough because laughing releases hormones which have this effect. 3 Sunny weather has a similar effect on people to laughing, so the writer suggests that British people need to laugh because their weather is so bad. 4 British musicians are popular in other countries whereas British comedians usually aren’t. 5 People in British comedy shows aren’t always polite to each other because part of the humour is based on them being unkind and rude. 6 We know Mr Bean is popular around the world because his shows and films have been seen in more than 200 countries over the last twenty years 7 People like Mr Bean because he does everyday things in a bizarre way and because they like his eccentricity. |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - read the text - answer the questions Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV (Task for understanding) Ex: 4 P: 17 In a weaker class, do the whole task together, encouraging as many students as possible to join in. In a stronger class, ask students to translate a joke into English and see how many work in translation Differentiation: A less motivated learner , do the whole task together with support |
Learners answer the questions. ANSWERS Student’s own answer |
Self assessment Descriptor: - complete the task - answer the question Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1 Hobbies and qualities lesson 11 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review. Unit 1. Summative Assessment for the unit «Hobbies and Qualities» |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 7. 1 use subject-specific vocabulary and syntax within the framework of unlimited general and study topics; 9. 5. 1. 1 plan, write, correct and check text-level works on general and academic topics without the support of the teacher; 9.6.12.1 use an increased variety of comparative degree adverb structures with regular and irregular adverbs, use a variety of preverbal, post-verbal and end-position adverbs on a range of familiar general and curricular topics; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - make adverbs from adjectives. - ask and answer the questions using collocations with make, do, collect and write. - construct the sentences using past simple and continuous with support. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Labor day! Be Honesty and justice |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: Ask students to work in pairs and talk about what they know about their grandparents as young people. What jobs did they do and what did they do in their free time? Setting the aim of the lesson. |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 18 Write the adverbs for these adjectives |
Learners write the adverbs for these adjectives ANSWERS 1 angrily 4 politely 2 well 5 optimistically 3 carefully 6 firmly |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - write the adverbs - complete the task Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 18 Exercise 2 Allow students to work in pairs. In a stronger class, ask students to complete the sentences individually, but allow them to check their answers in pairs before you check with the class Differentiation: A less motivated learner to choose the correct words with support by helpers |
Students choose the correct words. ANSWERS 1 beautifully 2 the hardest, 3 noisily, happily 4 optimistic successful 5 well, best |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - work in pairs - choose the correct words Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 18 Students complete the questions individually. Check answers, then put students into pairs to ask and answer the questions. Ask some students to report back on what they learnt about their partner Complete the sentences with correct tense of the words in the box. |
Learners complete the sentences with correct tense of the words in the box. ANSWERS 1 collected 2 writing 3 make 4 do 5 make 6 do |
Pair assessment
- complete the sentences Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 18 Remind students to use the both the positive and the negative – to talk about things they had and had not done. In a weaker class, allow students time to do the task Summative Assessment for the unit «Hobbies and Qualities» |
Learners choose the correct words ANSWERS 1 ’d forgotten 2 got 3 hadn’t seen 4 hadn’t eaten 5 ’d cut
|
Descriptor: - choose the correct words - complete the task Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1 Hobbies and qualities lesson 12 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project. An interview summary: teenage years |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 4. 6. 1 determine the author's opinion or point of view in long texts in the context of general and study topics 9. 5. 6. 1 write texts related to general familiar and learning topics using different connectives |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Read a summary of an interview with a family member. - Interview an older person about their teenage years and their generation. - Write a summary of your interview about an older person’s youth |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Justice and Responsibility Labor day! Be Honesty and justice |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, write My teenage years on the board and elicit or explain the meaning If students are struggling, give them some categories and decades and brainstorm associations, for example, fashion and hair styles in the 1980s, music in the 1960s, exciting new technology in the 1990s Setting the aim of the lesson. The word teenager to describe a person between the ages of 13–19 originated in the 1950s. Prior to that, this age group was not a clearly defined demographic grouping. In the 1950s adolescents began to stand out as a group of people for whom modern music, fashions and trends were very important. |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 19 Look at the photographs and elicit what they show. Ask students to guess the decade, then read the text quickly and check their guesses. Students work individually to read the paragraphs and match them to the questions. Check answers |
Learners read the interview summary. Match paragraphs A–E with interview questions ANSWERS: 1 E 2 A 3 D 4 B 5 C |
Pair assessment Descriptor: - read the interview - match paragraphs Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 19 Read through the project checklist with the class. In a weaker class, brainstorm other questions or topics that students could ask about. Tell them to choose five questions and point out or elicit that this means their summary will have five paragraphs. Remind students that to write a whole paragraph, they will need to get detailed answers, so it might be a good idea to prepare some follow-up questions. Ask students to write their summaries for homework |
Learners write about an older person’s teenage years. Follow the steps in the project checklist. ANSWERS |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - write about an older person’s teenage years Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 19 Collect in the summaries and arrange them on desks around the class for students to look at. Find out which generation was the most researched and whether people had the same experiences. Ask students whether they would rather be teenagers now, or in another decade. Have a vote for the most popular decade |
Learners share your interview summary with the rest of the class. Did any other students find out similar information? ANSWERS |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - share your interview - find out similar information Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 13 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Medical science |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 4. 6. 1 determine the author's opinion or point of view in long texts in the context of general and study topics 9. 5. 6. 1 write texts related to general familiar and learning topics using different connectives |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Learn nouns and verbs related to the health benefits of exercise. - Do a health and exercise quiz. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Unity and solidarity International Day of the Elderly! |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, write health and exercise on the board and elicit the connection between the two. Ask: Can you be healthy without doing exercise? Setting the aim of the lesson. 1 Why are team sports good for you? 2 What are the health benefits of sport and exercise? 3 What are the secrets of a long life?
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/WFW4ZRoifs8i95fPA
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 20 Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the nouns in the quiz. If you want to speed this up, put them in pairs and ask each student to find half the words. Point out that some of the nouns are used to talk about mental attitude and some are used to talk about physical health. In pairs, students decide which words fall in the two categories. Differentiation: A less motivated learner use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the nouns and categorise the nouns in the two categories. |
Learners check the meaning of the nouns in blue in the Health and exercise quiz. Which words are about mental attitude, and which are about physical health? ANSWERS: Mental attitude: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 Physical health: 6, 10, 11, 12 |
Pair assessment Descriptor: - check the meaning of the nouns in blue - find half the words Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 20 Focus students’ attention on the table and ask students what the verb for commitment is to elicit have commitment. Point out that not all nouns have a single word equivalent, because they are things you have or states. Tell students to look at the text and find the verbs that are used with the nouns in the text and write the nouns and the related verb phrase |
Learners read the text again and complete the table with nouns 1–12 from exercise 1 and the verbs used with them ANSWERS 1 have commitment 2 build self-esteem 3 have determination 4 develop self-reliance 5 have discipline 6 improve stamina 7 involve team work 8 improve concentration 9 boost (your) mood 10 increase endorphins 11 increase (your) energy 12 raise (your) blood pressure |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - read the text again - complete the table with nouns Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III Ex: 3 P: 20 • Put students into pairs to read the sentences in the Health and exercise quiz and decide whether they are true or false. If there seems to be a lot of disagreement, briefly discuss the questions as a class, and share knowledge and opinions before playing the CD to check the answers. Find out who got the most answers right. Were there any answers that really surprised students? TRANSCRIPT 1 True. Exercising regularly not only increases physical stamina, the ability to do things for a long time, but it also increases your mental stamina. This means you can concentrate on things for longer. 2 True. In team sports you have to learn how to be part of a group. To win a competition, you have to work as a team and create chances for other players. You can’t compete with your own team. Once you understand the importance of groups in sport, it is easier to see their importance in other areas of life. 3 False. Both team and individual sports help people feel better about themselves and find ways of overcoming problems, but in individual sports the effect is even greater as there are no team mates to help you when your energy falls, or you miss the ball. 4 False. Yoga is not only good for flexibility. In yoga, you often have to hold difficult positions while breathing calmly and deeply. This combination of physical difficulty and a calm mind is good for controlling stress. As a result, researchers have found people who do yoga have higher levels of endorphins and feel less depressed. 5 True. It takes around sixty-six days for a routine to become a habit, so it’s important to be determined and committed for those first two months. After that, it becomes easier. 6 True. Exercise increases your energy levels. You will probably find that you won’t be able to run very far or play for very long the first time you do a new sport, but after a few weeks, you’ll be able to exercise for much longer without feeling tired. 7 False. Exercise does increase your blood pressure, but in people who exercise it falls quickly when they stop and people who exercise regularly have lower blood pressure than those who don’t. 8 False. People with not much self-discipline can find a new routine difficult to begin with, but self-discipline can be learned. When you start doing a new sport, it’s best to try and do it bit by bit. Decide to take a twenty minute walk a day and keep to this before you decide to train for a marathon. 9 False. Some people think that there will soon be a pill for everything, but a pill won’t be able to replace exercise because it is necessary for so many things, such as strength, stamina, a positive mood, a healthy heart, low blood pressure and much more. |
Learners do the Health and exercise quiz. Decide if the sentences are true or false. Then listen and check. ANSWERS : 1 True. 2 True 3 False. Both team and individual sports help. 4 False. People who do yoga have higher levels of endorphins and feel less stressed. 5 True. 6 True. 7 False. People who exercise regularly have lower blood pressure than those who don’t. 8 False. Self-discipline can be learned. 9 False. Exercise is necessary for stamina, a positive mood, a healthy heart, low blood pressure, etc. |
Teacher’s comment Descriptor: - do the Health and exercise quiz. - write true or false Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 14 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Benefits of doing sport |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 7. 1 use subject-specific vocabulary and syntax within the framework of unlimited general and study topics; 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Talk about the benefits of doing sport and exercise. - Learn the use of could, can and will be able to. - Practise using could, can and will be able to to talk about ability in the past, present and future |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Unity and solidarity Let's protect our old people |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, write health and exercise on the board and elicit the connection between the two. Ask: Can you be healthy without doing exercise? Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/1TXFgYbVWapQAXiv9 |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 4 P: 21 Check answers and discuss the questions. If possible, ask the students to research some of the benefits of these sports for homework, and report back in a future lesson |
Learners look at Benefits of doing sport. In pairs, match the benefits with the sports in the box. Discuss your reasons for choosing the sports. Which benefits do you think are the most and least important? ANSWERS: Student’s own answer |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - answers and discuss the questions - match the benefits with the sports Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 5 P: 21 Ask students to look at the quiz again and find an example of can and will be able to. Ask what are they used to express (ability). Play the audio again and ask students to listen for examples of can, could and will be able to in the affirmative and negative. Pause when you hear each example and ask students when the speaker is referring to – past, present or future. Students complete the sentences. Tell them to think of the tense they need for each sentence A learner with individual needs: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use simple, basic statements in his discussion. |
Learners look at the sentences from the quiz and the listening. Complete them with can / can’t or will / won’t be able to ANSWERS 1 will be able to 2 can’t 3 won’t be able to 4 will be able to 5 won’t be able to |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - look at the quiz - complete the sentences Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 6 P: 21 Ask students to read the text through quickly, ignoring the gaps. Ask: What problem did Jed have? (He fell down a hole and damaged his feet and knees.) Ask students if they have ever had physiotherapy. Ask what they couldn’t do before they had it and what they can do now Differentiation with individual need learners: *Define the rules and complete the text with the affirmative and negative forms |
Learners complete the text with the affirmative and negative forms of can, could and will be able to ANSWERS : 1 can’t 5 will be able to 2 couldn’t 6 will be able to 3 couldn’t 7 won’t be able to 4 can |
Teacher’s comment Descriptor: - complete the text with the affirmative and negative forms Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 7 P: 21 Ask two students to read out the example dialogue. Make sure students understand what they have to do. If necessary, do the first sentence as an example. Students write their sentences individually and then compare their answers in pairs. Ask some students to read their sentences to the class |
Learners make sentences using the phrases in the table and affirmative and negative forms of can, could and will be able to. Then interview your partner about their ideas ANSWERS : Student’s own answer |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - make sentences - use the phrases in the table Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 15 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Alternative therapy |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics; 9. 4. 2. 1 understand specific information in texts within the context of familiar general and reading topics, including some longer texts; 9. 5. 3. 1 write familiar general and study topics with uniform grammatical competence; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Read about exercise as a cure. - Read for general meaning and specific information. - Express your own opinions on exercise as an alternative medical treatment. - Learn about and practise noun suffixes |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Diligence and Professional Qualification! Teachers' Day |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, write the quote from Hippocrates Walking is man’s best medicine on the board and ask students what they think it means. Elicit or explain that it probably means that keeping active improves your health Setting the aim of the lesson. Hippocrates lived between 460–370 BCE and was possibly the first person to think disease and illness was the result of natural causes and not a punishment from the gods. He believed lifestyle, diet and environment all had a part in people’ s health and that health could be improved by improving these factors |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 22 Draw students’ attention to the photos and elicit a description. In a weaker class, encourage students to participate by accepting factual descriptions. In a stronger class, ask students to speculate about and explain their answers. Students discuss the questions in pairs, then ask them to read the text quickly to find the answers. T asks some CCQs:
|
Learners look at the photos and the title of the text, and answer the questions. Then read the text and check your answers. ANSWERS: Exercise reduces pain, helps people with depression and reduces loneliness Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS - No - Yes - No |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - look at the photos and the title - answer the questions Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 22 Read the instructions and make sure students understand what they have to do. Tell them to use context and meaning, but also to look at structural elements like tenses or words such as however A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners complete the text with sentences a–e. Listen and check your answers ANSWERS: 1 b 2 d 3 c 4 e 5 c |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - complete the text - check your answers Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III Ex: 3 P: 22 In a stronger class, ask students to predict or guess the noun form and share ideas as a class. Elicit the suffix that is used in each case to turn the verb or adjective into a noun. Elicit any other examples that students are familiar with A learner with individual needs: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use simple, basic statements in his discussion. |
Learners complete the table with words from the text. What suffixes are used to form the nouns? ANSWERS: 1 medication 2 treatment 3 infection 4 illness 5 reduction 6 depression 7 loneliness |
Descriptor: - complete the table - predict or guess the noun Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 22 Do the first sentence with the class as an example. |
Learners complete the sentences with a noun formed from the words in brackets. Use the suffixes in the box ANSWERS: 1 sadness 2 intelligence 3 enjoyment 4 connection 5 receptionist |
Descriptor: - complete the sentences - use the suffixes in the box Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 16 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talk about things that are possible or certain |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics; 9. 5. 3. 1 write familiar general and study topics with uniform grammatical competence; 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Learn the use of may, might, could, must and can’t for possibility and certainty. - Practise using may, might, could, must and can’t to express possibility and certainty in opinions. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Low and Order "Victim in the life of a child" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: Refer students back to the text on pages 22–23 and ask: Do you think that swimming in cold water helps depression? Elicit a range of ideas, including the idea that it is possible it works. • Write on the board: Swimming in cold water might help depression and underline might. Elicit or explain the meaning (it is possible that it works). • Tell students they are going to learn some other ways of expressing possibility and certainty. Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/q8MYHwfKCsvZukWF9
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 23 • Students study the examples in pairs and complete the rules. • Check answers with the class. • Point out that we don’t usually use can to express possibility. • Ask students how they would express these ideas in their own language. |
Learners study the modal forms in blue in sentences 1–5. Then choose the correct options in the rules. ANSWERS: a possibility b are c don’t |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - study the modal forms - choose the correct options Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 23 Allow students time to compare their answers in pairs before you check with the class. Discuss what helped students make their choices A learner with individual needs: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use simple, basic statements in his discussion. |
Learners сhoose the correct words ANSWERS : 1 might 2 can’t 3 may 4 must 5 might 6 might |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - сhoose the correct words Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 23 • In a weaker class, do a few examples and discuss them before students continue in pairs. In a stronger class, ask students to provide not just one sentence for each item, but all the possible sentences for each item. • Allow students to compare their answers in pairs before you check with the class. • If your students need extra practice, you may want to do the activities on page 15 of the Workbook in class. Exercise 3 could be done individually or in pairs. Exercise 4 could be done orally in class, and students could write it up for homework. A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners make sentences using the modal verbs in exercise 1 and the words in brackets ANSWERS : 1 He / She may / might / could have flu. 2 He must be tired. 3 They may / might / could be Mexican. 4 He / She can’t be angry. 5 She must be ill. 6 He may / might / could be a surgeon |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - make sentences - use the modal verbs Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 23 • Read through all the vocabulary with the class and make sure that students understand it. • Read the example opinions and then elicit some more opinions about acupuncture. • In pairs, students discuss the topics. • Ask some students to report back to the class on what they and their partner agreed and disagreed about |
Learners exchange opinions about topics 1–6 using the phrases in the box and the modal verbs in exercise 1. ANSWERS : Student’s own answer |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - exchange opinions - use the phrases in the box Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 17 |
School: Teacher name: |
||
|
Date: |
|||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talk about a healthy lifestyle |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 2. 1 independently understand more specific information on general and educational topics without support in a wide-ranging extended conversation; 9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics; 9. 4. 2. 1 understand specific information in texts within the context of familiar general and reading topics, including some longer texts; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Learn phrasal verbs about health and lifestyle. - Read an eight-point health plan. - Listen to a conversation about living longer |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Low and Order "Victim in the life of a child" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: • With books closed, write health and lifestyle on the board and elicit or teach the meaning. • Ask: How can your lifestyle affect your health? Elicit some ideas. • Ask: How can you change your lifestyle to make you healthier? Elicit a range of ideas Setting the aim of the lesson.
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/tEhWUiEskcoABNct7
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 24 Read the eight-point health plan together and see if any of the students’ ideas from the warm-up are mentioned. • Students match the phrasal verbs with their synonyms. |
Learners match the phrasal verbs in blue in The eight-point health plan with synonyms ANSWERS: 1 h 2 c 3 g 4 a 5 d 6 f 7 b 8 e |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - discuss about Almaty Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 24 Elicit any strategies students have for doing listening activities. • As a class, read through the study strategy tip. Ask if anyone prepares for listening in this way. Emphasize that preparing to listen can make the task significantly easier, as it helps to predict the types of information you need. • Elicit the task type for which students have to be particularly careful (true / false) and ask why (some of the statements are false, so students may not hear these words or ideas in the recording). Point out that the ideas in the statements might not be expressed in the same way as those in the recording. Differentiation with individual need learners: Define that the words for languages are often the same as those for nationalities. |
Learners before you listen, read exercises 3 and 4 carefully and underline key words. This will help you to understand the dialogue more easily. It will also help you to focus on the answers while you are listening ANSWERS: |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - read the text - answer the question Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 24 Focus on the photos and the title Live longer, live better. Ask How old do you think the people are? What are they doing? • Ask students to read the introduction to the article. Elicit suggestions as to what a centenarian might be. Remind students to listen for general understanding, and to pick out the meaning of the word. TRANSCRIPT J Hi, Chloe. What are you reading? C Oh, hi James. It’s an article called ‘Live longer, live better’. It’s about people in some parts of the world who live much longer than other people. This lady in Japan is a centenarian and she’s still working. J You’re kidding! She must have had a healthy lifestyle. C Yes. And this man on the waterskis is a hundred, too. J Wow! So I have to take up waterskiing to live to a hundred? Is that the secret? C No, actually most of the advice is obvious – for example, you shouldn’t smoke. None of these people smoke. J Obviously. C And they have a very healthy diet. It says most of us must cut down on fatty foods and sugar. Our bodies don’t need much sugar. J Do I have to give up chocolate? C No, you don’t have to give up all chocolate – just cut down a bit. We all eat too much. J Mmm. What else? C Well, all of these people are pretty active, you know – lots of work, and exercise. J Lots of work? That’s bad news … C Well, work and activities. They spend a lot of time outside. Maybe you should turn off your computer occasionally. You shouldn’t stay in your room all day. J I suppose so. C But there are two things that all of these people have got in common, right. Firstly, they often call on their families and friends. They chat about problems and their friends and family help them. Friends and family make you feel good. J And the second thing? C The second thing is the most important. It says that they’re all very positive. Happiness is the secret ingredient. J Happiness? C Happiness. ‘Smile and the world smiles with you,’ they said. J OK, I’ll try that. Thanks, Chloe. T asks some CCQs:
|
Learners read the introduction to the Live longer, live better article. Then listen. What is a centenarian? ANSWERS: A centenarian is a person who is over a hundred years old. Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS -Yes - No - Yes |
Teacher’s comment Descriptor: - read the text - choose the correct answers Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 24 Look at the statements and tell students they should prepare to listen by following the advice in the study strategy. Give them some time to read the statements and underline key words. Compare key words as a class and discuss the students’ suggestions. In a weaker class, draw attention to words like all and negative statements, and make sure students have read and understood each complete statement, as well as identifying the key words. |
Learners listen again and write true or false. ANSWERS: 1 True. 2 False. 3 False. 4 False. 5 True. 6 True |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - write the plural form - find in the text. Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 18 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Speculate about the past. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 6. 1 in pair, group and whole class work to explain what others said in sentences or reasoning with a certain level of flexibility; 9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
|
Learners will be able to: - Learn the use of must have, can’t have, could have and might have to speculate about the past. - Practise speculating about the past using past modals. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Diligence and Professional Qualification! Day of librarians |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, ask students to remember how we express possibility in the present. Give them some scenarios and elicit sentences using may, might, could and must, can’t. For example, say: Joe’s doing his driving test after only three lessons. (He can’t be ready / must be very confident.) Look, it’s getting cloudy. (It may / might rain this afternoon.), etc T: What do you think about today’s theme? |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 25 Students read the sentences and answer the questions. • Check answers and remind students what past participles are.
|
Learners study the modal forms in blue in sentences. Then answer questions a and b ANSWERS: a must, can’t, could / might b have |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - study the modal forms in blue - answer questions a and b Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 25 Remind students that some verbs have irregular past participles. Tell them to look up any they are not sure of in the irregular verbs list on page 126 of the Student’s Book. • Allow students time to compare their answers in pairs before you check with the class A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners rewrite the sentences in the past form ANSWERS : 1 They could have been seventy years old. 2 He can’t have been a hundred years old. He was still working. 3 She might have cut down on chocolate. 4 He must have worked out a lot. 5 She could have gone without dessert. 6 They might have taken up basketball |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - rewrite the sentences Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 25 Students complete the sentences with the correct modals. Check answers by asking some students to read out their sentences and asking the class to say whether they are correct or not. Differentiation with individual need learners For the general comprehension Teacher explain the task and less able learners complete the sentences as possible, more able learners complete the sentences correctly. |
Learners choose the correct words. ANSWERS : 1 might 2 must 3 could 4 can’t 5 must 6 can’t |
Teacher’s comment Descriptor: - complete the sentences - choose the correct words Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 25 • Read the example as a class. Then put students in pairs to speculate about the situations. In a weaker class, do a few more together and discuss them first. Establish that might, could and must are largely interchangeable; it depends on your level of certainty. |
Learners work in pairs. Take turns reading and responding to situations 1–6 using past modals and the words in brackets ANSWERS : 1 She might / could / must have been ill. 2 He might / could / must have received some good news. 3 He might / could / must have taken up tennis. 4 He might / could / must have had an operation. 5 He might / could / must have cut down on sugar. 6 She might / could / must have given up smoking. |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - work in pairs - use past modals Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. V Ex: 5 P: 25 Read the instructions and check that students understand. Play the first dialogue for students to listen, then pause and elicit speculation from the class. • In a weaker class, pause after each one and speculate together. In a stronger class, play the other dialogues and encourage students to discuss in pairs before sharing with the group |
Learners listen to five dialogues and speculate about what has happened. Use past modals to give your reasons ANSWERS : 1 They must have been burgled. 2 They must have been on holiday. 3 He could have left his essay on the bus. 4 He must have hit the man. 5 She must have got a part in a play. |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - listen to five dialogues - use past modals Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 19 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Exchanging opinions |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 7. 1 to determine the characteristic features of most oral genres at the word, sentence and text level 9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: -Listen to a conversation in which people exchange opinions. - Learn key phrases for exchanging opinions. - Learn how to use should, must, have to - Practise exchanging opinions. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Low and Order "Victim in the life of a child" |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, see how many suggestions for a healthy lifestyle students can remember from the eight point health plan on page 24. • Ask where students come across advice about health. Elicit suggestions for how the government and schools can communicate with young people about health issues, e.g. TV advertising and posters. T: What do you think about today’s theme? Why do people use drugs in sports? What health damage can performance drugs cause?
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/9KtxQm7msnZZgxr5A
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 26 Focus on the photo. Ask: What are Marie and Dean looking at? What do the posters show? Elicit ideas and then ask: Which poster do you prefer? Why? Elicit a range of opinions |
Learners look at the posters. What are they campaigning against? ANSWERS: They are campaigning against drugs. |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - look at the posters. - answer the question Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 26 In a stronger class, tell students to cover the dialogue and just listen. Play the CD once and ask whether Marie and Dean agree about the posters. A learner with individual needs: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use simple, basic statements in his discussion. |
Learners listen to the dialogue. Which poster has got the clearest message? ANSWERS: Marie thinks the poster with the photo has a clearer message, but Dean prefers the poster with a more positive message |
T’s ffedback Descriptor: - listen to the dialogue Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 26 Play the CD and ask students to listen to the intonation, and try to copy it when they practise the dialogue themselves. • Ask students to find the key phrases in the dialogue and translate them into their own language. • Students practise the dialogue in pairs |
Learners listen to the key phrases. Which phrase expresses a strong opinion? Practise the dialogue ANSWERS: It should definitely … expresses a strong opinion |
Teacher’s comment Descriptor: - listen to the key phrases - practise the dialogue Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 26 Read the sentences and the rules with the class. Make sure that students understand advice (a suggestion about what somebody should do in a particular situation), obligation (something you must do because you have promised, because of a law or a rule) and prohibition (a law or a rule that stops something being done or used). • In a weaker class, ask students to work in pairs to create new sentences. Differentiation: All learners understand and complete not all sentences and more able Ss complete and read the correct sentences to the class. |
Learners look at sentences and read the rules. Then change the words in blue using your own ideas ANSWERS : 1 six 2 factory 3 six 4 5.30 5 20 6 sleeps |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - look at sentences - read the rules Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. V Ex: 5 P: 26 Read the four statements with the class. Elicit opinions about the first statement, and encourage students to use key phrases from exercise 3. • Ask some students to report back on whether they and their partner agreed or disagreed. |
Learners work in pairs. Talk about opinions. Use the key phrases in exercise 3. ANSWERS : |
Self assessment
Descriptor: - work in pairs - use the key phrases Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 20 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A discussion essay Summative assessment for the unit «Exercise and Sport» |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 7. 1 use subject-specific vocabulary and syntax within the framework of unlimited general and study topics; 9. 4. 6. 1 determine the author's opinion or point of view in long texts within the framework of general and educational topics; 9. 5. 5. 1 teacher-supported use of arguments in endlessly familiar general and educational topics with examples and justifications; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary to do with nutrition and healthy eating. • Read a text about healthy eating. • Talk about diet and ways it could be improved. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Diligence and Professional Qualification! Labor in human life, family, society understand the value |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, write footballers’ salaries on the board and elicit the meaning. Ask: Do you think footballers should be paid a lot of money for what they do? Elicit some opinions. • Write For and Against on the board and list arguments under the two headings as students give them. • Tell students they are going to learn how to present arguments for and against in a discussion essay. T: What do you think about today’s theme? |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 27 Students read the model text and answer the questions. T shows on the reading text on the smart board and asks some CCQs:
|
Learners read the model text and answer the questions. ANSWERS: 1 The writer is against footballers getting enormous salaries, but thinks they should be paid well. 2 Yes, the writer gives both sides of the argument. 3 For high salaries: need to pay high salaries to get good players; TV advertising attracts a large amount of money to clubs and football players should get some of this money. 4 The writer’s opinions are in the last paragraph. Footballers should be paid well, but they could earn half of their current salaries and still be well paid. Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS -No - Yes - Yes |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - read the model text - answer the questions Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 27 In a weaker class, allow students to find the key phrases in the text. In a stronger class, encourage students to complete them from memory. • If necessary, ask students to translate the phrases into their own language. |
Learners complete the key phrases. Then read the model text and check. ANSWERS : 1 for 2 against 3 arguments 4 other 5 in 6 favour |
T’s ffedback Descriptor: - complete the key phrases - read the model text Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 27 Focus on the table and words in the box to make sure that students understand everything. Elicit an example of one contrasting discourse maker and one summarizing. • Students copy and complete the table. • Check answers |
Learners which words or phrases in the box can you use to replace the phrases in blue in the text? Complete the table ANSWERS Adding: in addition, furthermore, also, what’s more Contrasting: although, but, however, on the other hand, even though Summarizing: all in all, to sum up, in conclusion |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - use to replace the phrases - complete the table Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 27 • Students can work in pairs to choose the correct words in sentences 1–6. A learner with individual needs: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use simple, basic statements in his discussion. |
Learners choose the correct words. ANSWERS 1 In addition 2 Although 3 What’s more 4 However 5 On the other hand 6 all in all |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - work in pairs . - choose the correct words Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 21 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country. Exercise and sport |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 2. 1 independently understand more specific information on general and educational topics without support in a wide-ranging extended conversation; 9. 3. 3. 1 explain and justify their point of view on general and educational topics; 9.4.9.1 recognise inconsistencies in argument in extended texts on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Read a text about Kazakh sports stars. - Learn vocabulary connected to success in sports. - Learn the difference between could, was / were able to and managed to. - Write sentences about famous sportspeople in Kazakhstan. |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Independence and Patriotism National interest: expanding the scope of the Kazakh language |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: • Have a race to find which group can list the most Kazakh sportspeople in two minutes. • After two minutes, find out which group had the longest list and declare them the winner. • Ask that pair for their answers and write them on the board. • Ask other groups to contribute more names if they have them T: What do you think about today’s theme?
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
https://images.app.goo.gl/rsA7X17GEinNuoou9
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 28 • Draw students’ attention to the photos. Ask them if they can identify who they are. • In pairs, students discuss what they know about the sportspeople. T shows on the reading text on the smart board and asks some CCQs:
|
Learner look at the photos. Who are these people? What do you know about them? ANSWERS: Kazhymukan Munaitpasov Denis Ten Zarina Diyas Students’ own answers Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS -Yes -Yes -No |
Pair assessment Descriptor: - look at the photos. - answer the question Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 28 Tell students to listen to and read the text and see if it contains the information they talked about. • In a stronger class, play the recording with books closed to see how much they understand and for them to check whether the information they talked about is mentioned. • Students read the sentences. • Play the recording again while students read the text on the page. • Give them extra time at the end to complete the sentences Differentiation with individual need learners: will be paired with helpers and teacher allows him to use simple, basic statements in his discussion. |
Learners read and listen to the text. Complete the sentences with the names of the people ANSWERS : 1 Zarina Diyas (Czech Republic) 2 Kazhymukan Munaitpasov 3 Denis Ten (shopping mall) 4 Kazhymukan Munaitpasov 5 Denis Ten 6 Zarina Diyas |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - read the text - complete the sentences Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 28 Focus students’ attention on the verbs. • Ask students to note down what they think the nouns are. •Then tell them to check their answers in the text and correct any they have got wrong. • Students underline the suffixes. • Check answers as a class. |
Learners complete the table with nouns from the text. What suffixes are used to form the nouns? What other noun suffixes do you know? ANSWERS: 1 wrestling 2 performance 3 failure 4 achievement 5 competition 6 injury |
Teacher’s comment Descriptor: - complete the table - underline the suffixes Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 28 Write on the board: I can speak English. Then add when I was ten years old. Ask students if the sentence is correct. Ask them to correct it to elicit could. • Write could, was / were able to and managed to on the board and ask students to look at the text again and see the different ways they are used. • Elicit the difference between could (ability), was / were able to (ability and for describing being successful after trying to do something, e.g. He was able to escape after a few hours.) and managed to (only for being successful after trying to do something). |
Learners look at the words in blue in the text. Then complete the rule ANSWERS: was able to, managed to |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - look at the words in blue - complete the rule Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. V Ex: 5 P: 28 Students now to put this information into practice. • Students check their answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class and explain further if students have difficulty with understanding the differences between the words. A learner with individual needs: will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners complete the sentences. Write one word in each gap. ANSWERS: 1 could 2 able 3 managed 4 were 5 manage |
Self assessment Descriptor: - ask and answer questions Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 22 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Healthy eating |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 4. 9. 1 identify inconsistencies in evidence presented in long texts on a variety of general and academic topics 9. 5. 5. 1 teacher-supported use of arguments in endlessly familiar general and educational topics with examples and justifications; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Learn vocabulary to do with nutrition and healthy eating. - Read a text about healthy eating. - Talk about diet and ways it could be improved |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Independence and Patriotism National interest: expanding the scope of the Kazakh language |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: With books closed, write An apple a day keeps the doctor away on the board. Explain that this is an old proverb and ask students what it means. • Elicit that the proverb is not meant literally, but suggests that if we eat healthy foods, like fruit, we will not get ill. • Ask students whether they think their diets are healthy. Do they think about what they eat? • Elicit examples of healthy and unhealthy foods. T: What do you think about today’s theme?
|
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
|
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be
|
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 29 • Students match the definitions with the blue words. Allow students to use their dictionaries if necessary. • Check answers with the class. |
Learners match definitions with the words in blue in the text. ANSWERS: 1 dairy 2 processed 3 tissues 4 evidence 5 fibre |
Pair assessment Descriptor: - match definitions - use their dictionaries Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 29 Students listen and read. Ask the question to the whole class. Differentiation Learners will be supported by teacher and by helpers from his class. |
Learners read and listen to the text. How does healthy eating affect our lives? ANSWERS: Healthy eating affects our physical and mental health. It can reduce the risk of serious illnesses such as heart disease, diabetes and possibly also mental illness, like depression. Eating regular meals can help with energy, as well as mood and memory. |
T’s ffedback Descriptor: - read the text - answer the question Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 29 • Tell students to read the questions and multiple-choice answers. • In a weaker class, encourage students to reread the text carefully and underline the parts of the text that contain the answers, so that they can find them again easily. When comparing answers with a partner, they can refer back to the text extracts, and check that they have understood the question and the text correctly. • In a stronger class, they can make notes based on their first reading of the text. Then they read the text again, and confirm or correct their answers. • Remind students to look carefully at the whole question, and watch out for little words or negatives that change the meaning of the sentences, e.g. question 5 (Which fats are not good for us?). • Students read the text again and answer the questions T shows on the reading text on the smart board and asks some CCQs:
|
Learners read the text again and choose the correct answers. ANSWERS : 1 a 2 c 3 b 4 b 5 a 6 b Learners answers Yes or No in CCQ ANSWERS -Yes -Yes -No |
Feedback: “Thumbs up, thumbs down” After correct answer teacher shows thumbs up, if there are some mistakes thumbs down with comments Descriptor: - read the text - choose the correct answers Total: 2 point Descriptor: - answers Yes or No |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 29 In a weaker class, read the sentences together and establish the type of words that are required (foods, number, adverb of frequency). • Students complete the sentences individually, before comparing answers and discussing the questions with a partner. In a stronger class, encourage students to give reasons for their answers and examples where possible. • Ask some students to report back to the class on whether they think their diet is healthy. Share suggestions for things students can do to improve their eating habits Differentiation with individual need learners: Allow students time to complete the sentences about your diet. |
Learners complete the sentences about your diet. Discuss how healthy or unhealthy your diet is. What should you change? ANSWERS : Student’s own answer |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - complete the sentences - discuss about diet Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 23 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative control work for the 1st term |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 2. 2. 1 independently understand more specific information on general and educational topics without support in a wide-ranging extended conversation; 9. 3. 7. 1 use subject-specific vocabulary and syntax within the framework of unlimited general and study topics; 9.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: -understand more complex supported questions on a growing range of general and curricular topics; -recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level in a range of written genres; -write with some support topics with some paragraphs to give basic personal information; |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Independence and Patriotism Republic Day! |
||
Short term plan
|
Unit 2 Exercise and sport lesson 24 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review. Unit 2 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9. 3. 2. 1 ask complex questions to obtain information within general and educational topics; 9. 5. 2. 1 to write on one's own past experience or true events, actions on familiar general and educational topics; |
||
|
Learning objectives (assessment criteria) |
Learners will be able to: - Use nouns and verbs related to the health benefits of exercise. - Practise using may, might, could, must and can’t to express possibility and certainty in opinions |
||
|
Values and its purpose: |
Independence and Patriotism National interest: expanding the scope of the Kazakh language |
||
|
Stages/ Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
|
Beginning 5 min |
Greeting. (Whale class, Individually) T tells the class to make groups of 2. Warm up: Ask students to work in pairs and talk about what they know about their grandparents as young people. What jobs did they do and what did they do in their free time? Setting the aim of the lesson. |
Learners read the given sentences on the board and guess the topic and share with their ideas. Remember and recognize the main vocabulary. |
Teacher controles the process, gives feedback and asks additional questions if it’s nessasery. Teacher evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment |
Sheets of peppers Pictures of to be |
|
Middle 30 min |
Task. I (Wh, I) (pair dicsussion) Ex: 1 P: 30 Allow students to work in pairs. Ask students to complete the sentences individually, but allow them to check their answers in pairs before you check with the class |
Learners complete the sentences with the correct form of the verbs in the box ANSWERS 1 boost 2 raise 3 have 4 build 5 increase 6 involves 7 improve |
Pair assessment
Descriptor: - complete the sentences - use the verbs in the box Total: 2 point |
Student’s book |
|
|
Task. II (Wh, I) (Task for location) Ex: 2 P: 30 Allow students to work in pairs. In a stronger class, ask students to write the nouns for these words and check their answers in pairs Differentiation: A less motivated learner to choose the correct words with support by helpers |
Students write the nouns for these words. ANSWERS 1 loneliness 2 infection 3 medication 4 depression 5 illness 6 reduction 7 commitment 8 intelligence |
T’s ffedback
Descriptor: - work in pairs - write the nouns Total: 2 point |
Worksheets Student’s book |
|
|
Task. III (Task for understanding) Ex: 3 P: 30 Ask students to work in pairs. Ask students to complete the sentences individually, but allow them to check their answers in pairs Complete the sentences with correct tense of the words in the box. |
Learners complete the sentences with the words in the box. ANSWERS 1 down 4 up 2 without 5 off 3 up 6 on |
Pair assessment
- complete the sentences - use the words in the box Total: 2 point |
|
|
|
Task. IV Ex: 4 P: 30 Ask students to complete the sentences with the affirmative or negative form of could, can and will be able to. |
Learners complete the sentences with the affirmative or negative form of could, can and will be able to. ANSWERS 1will be able to 2 couldn’t, can 3 can’t 4 couldn’t 5 could 6 won’t be able to |
Descriptor: - choose the correct words - complete the task Total: 2 point |
|
|
End 5 min |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. T asks Ss to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. Green- I understood Yellow-I have some questions Red-I need a help. Ex: P: Home task |
Ss use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson
|
Poster Success Ladder |
|

шағым қалдыра аласыз





 ell done! Brilliant!
Good job! I like it!
ell done! Brilliant!
Good job! I like it!