Назар аударыңыз. Бұл материалды сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзса, осында жазыңыз. Біз ең жылдам уақытта материалды сайттан өшіреміз
Жақын арада сайт әкімшілігі сізбен хабарласады

Бонусты жинап картаңызға (kaspi Gold, Halyk bank) шығарып аласыз


ҚМЖ жинағы English Plus 6 1-2-3-4 term.docx
Дипломдар мен сертификаттарды алып үлгеріңіз!


Материалдың толық нұсқасын
жүктеп алып көруге болады
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our class |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A classroom. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.1.1 understand a sequence of supported classroom instructions 6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics ( Ex.1 p 4,describe a classroom, revise a verb " to be") |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
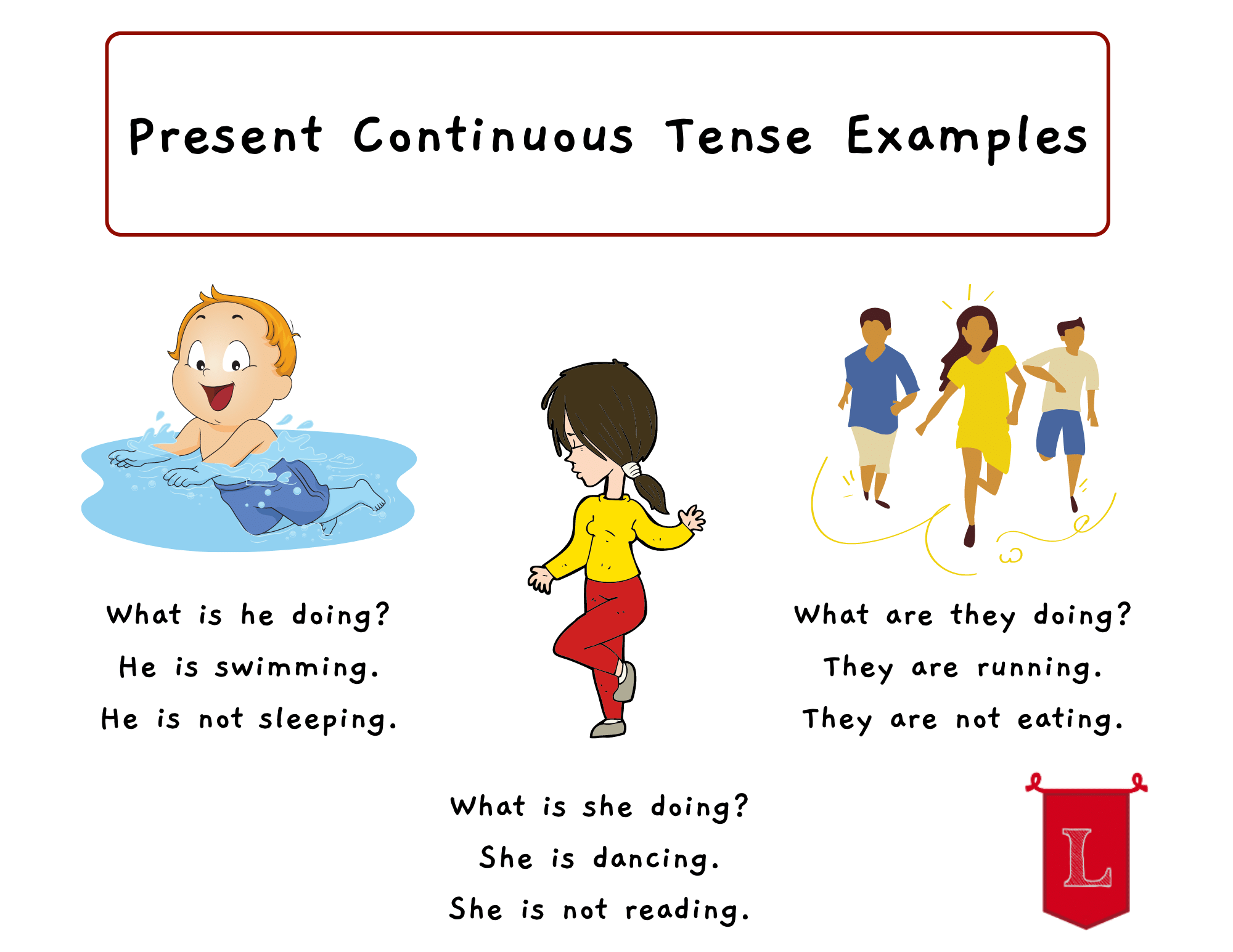
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre-listening: Warm-up With books closed, ask: Where are we at the moment? • Elicit the word classroom and write it on the board. • Ask: What can you find in a classroom? Elicit a few words from individual students. Lead - In Look at the picture and say what the theme of our lesson will be? You see different word in the picture. What can you see in this picture?
It is a board. It is a clock. There are six chairs in the classroom.
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
While-listening: To present/practise vocabulary related to class's hobbies and interests Play the next recording. Ss listen and repeat chorally or individually. Elicit the L1 equivalents from various Ss. Exercise 1 • Go through the words in the wordpool with students and check understanding. Then study the picture with the class and do the example. Students complete the activity. In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs. • Model and drill the pronunciation of any new words Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Exercise 2 Read out the example sentence. Ask students to find the poster and the door, and then to say whether the sentence is true or false. Confirm that the sentence is false, because the poster is not near the door in this picture Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
. Ss listen and repeat chorally or individually. Students write the name of objects 1-16 in the picture. Then listen and check. ANSWERS 1 window 2 laptop 3 CD player 4 shelf 5 DVD 6 door 7 board 8 clock 9 poster 10 chair 11 notebook 12 pen 13 desk 14 dictionary 15 ruler 16 bag
Students read the sentences and write true or false ANSWERS 1 true 2 false 3 false 4 true 5 false 6 false
|
Assessment criteria - identify some specific information from the text Descriptor: -Understand classroom instructions Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: -Use topic related vocabulary in group discussion -Make CCQ questions
|
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 1,2 P: 4 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our class |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Possessive’s and subject and object pronouns |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics ( Ex.1 - 2. p.10). 6.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a ( Ex.3.p. 10) 6.3.3.1 give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics ( Ex.5 p.10) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Ask an individual student to hold up their pen or notebook. • Ask: Is that my pen / notebook? • Elicit the answer (No, it’s Anna’s pen / notebook). • Repeat the process with a different student. Lead - In Ask questions about your friend’s family.
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say about their family.
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 2 Demonstrate on the board how to use the prompts to write phrases with the possessive ’s in the correct place. In a weaker class, explain that they do not need to write full sentences. In a stronger class, students could look at the picture on page 4 and write full sentences Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Exercise 4 • In a weaker class, you could ask students to do this exercise in pairs Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students write phrases for 1-6. Add an apostrophe (‘) or ‘s ANSWERS 1David’s laptop 4 Larissa’s dictionary 2 the teacher’s CD player 5 Liam’s notebook 3 the girl’s DVDs 6 the students’ pens Students choose the correct words ANSWERS 1 Her 2 She’s 3 We’re 4 Our 5 He’s 6 His 7 my 8 They’re
|
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise the use of ’s and s’ to talk about possession. Descriptor: Can tolk about possession Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: -Learn and use object pronouns. -Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Wrkshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 5 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our class |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Basic adjectives Diagnostic test |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.2.1 understand an increasing range of unsupported basic questions which ask for personal information 6.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects ( Category of hobbies - topic discussion) p.12 6.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in short, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topics ( Ex.4 p.12) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre-listening: Warm-up • With books closed, ask students about a current TV programme, e.g. Do you like Big Brother on TV? Why? • Elicit some answers from the class, and elicit adjectives such as funny, interesting and boring and write them on the board. • Elicit or tell students that these words are adjectives and we use them to describe things. Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Students find adjectives |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment Good job!
|
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
While-listening: Exercise 1 • Look at adjectives 1–7 with the class. Translate any they do not know In a weaker class, you could check understanding by asking students to translate all the adjectives into their own language. In a stronger class, ask if students can tell you any more adjectives and their opposites Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Exercise 2 Students order the days. In a stronger class, ask students to close their books and do this orally. In a weaker class, write each day on the board as it is said, and ask them to copy the list into their notebooks when it is complete. Use the CD to drill pronunciation Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students match adjectives and give their opposites. ANSWERS 1 bad 5 small 2 unpopular 6 expensive 3 boring 7 horrible 4 difficult Students write the name of objects 1-16 in the picture. Then listen and check. ANSWERS 1 window 2 laptop 3 CD player 4 shelf 5 DVD 6 door 7 board 8 clock 9 poster 10 chair 11 notebook 12 pen 13 desk 14 dictionary 15 ruler 16 bag
|
Assessment criteria - Learn the meaning of basic adjectives. Descriptor: -can give their opposites Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Use days and months in personalized sentences -Make CCQ questions
|
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 1,2 P: 4 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our class |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: be affirmative, negative and questions |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.1.1 understand a sequence of supported classroom instructions 6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics ( Ex.1 p 4,describe a classroom, revise a verb " to be") |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre-listening: Warm-up With books closed, ask: Where are we at the moment? • Elicit the word classroom and write it on the board. • Ask: What can you find in a classroom? Elicit a few words from individual students. Lead - In Look at the picture and say what the theme of our lesson will be? You see different word in the picture. What can you see in this picture?
It is a board. It is a clock. There are six chairs in the classroom.
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
While-listening: To present/practise vocabulary related to class's hobbies and interests Play the next recording. Ss listen and repeat chorally or individually. Elicit the L1 equivalents from various Ss. Exercise 1 • Go through the words in the wordpool with students and check understanding. Then study the picture with the class and do the example. Students complete the activity. In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs. • Model and drill the pronunciation of any new words Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Exercise 2 Read out the example sentence. Ask students to find the poster and the door, and then to say whether the sentence is true or false. Confirm that the sentence is false, because the poster is not near the door in this picture Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
. Ss listen and repeat chorally or individually. Students write the name of objects 1-16 in the picture. Then listen and check. ANSWERS 1 window 2 laptop 3 CD player 4 shelf 5 DVD 6 door 7 board 8 clock 9 poster 10 chair 11 notebook 12 pen 13 desk 14 dictionary 15 ruler 16 bag
Students read the sentences and write true or false ANSWERS 1 true 2 false 3 false 4 true 5 false 6 false
|
Assessment criteria - identify some specific information from the text Descriptor: -Understand classroom instructions Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: -Use topic related vocabulary in group discussion -Make CCQ questions
|
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 1,2 P: 4 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our class |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Free time |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.1.1 understand a sequence of supported classroom instructions 6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics ( Ex.1 p 4,describe a classroom, revise a verb " to be") |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre-listening: Warm-up With books closed, ask: Where are we at the moment? • Elicit the word classroom and write it on the board. • Ask: What can you find in a classroom? Elicit a few words from individual students. Lead - In Look at the picture and say what the theme of our lesson will be? You see different word in the picture. What can you see in this picture?
It is a board. It is a clock. There are six chairs in the classroom.
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
While-listening: To present/practise vocabulary related to class's hobbies and interests Play the next recording. Ss listen and repeat chorally or individually. Elicit the L1 equivalents from various Ss. Exercise 1 • Go through the words in the wordpool with students and check understanding. Then study the picture with the class and do the example. Students complete the activity. In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs. • Model and drill the pronunciation of any new words Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Exercise 2 Read out the example sentence. Ask students to find the poster and the door, and then to say whether the sentence is true or false. Confirm that the sentence is false, because the poster is not near the door in this picture Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
. Ss listen and repeat chorally or individually. Students write the name of objects 1-16 in the picture. Then listen and check. ANSWERS 1 window 2 laptop 3 CD player 4 shelf 5 DVD 6 door 7 board 8 clock 9 poster 10 chair 11 notebook 12 pen 13 desk 14 dictionary 15 ruler 16 bag
Students read the sentences and write true or false ANSWERS 1 true 2 false 3 false 4 true 5 false 6 false
|
Assessment criteria - identify some specific information from the text Descriptor: -Understand classroom instructions Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: -Use topic related vocabulary in group discussion -Make CCQ questions
|
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 1,2 P: 4 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our class |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading. What are you into? |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 6.3.2.1 ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general topics 6.6.3.1 use a growing variety of demonstrative pronouns: this/that, these/ those on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre-listening: Warm-up With books closed, revise the free-time activities from the previous lesson. Ask around the class to find out the most popular activity or activities. • In a stronger class, ask students to say sentences using the key phrases, e.g. I’m into martial arts. In a weaker class, write one or two sentences of this type on the board and ask students to read them out Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Pre teach: New vocabulary. Exercise 1 Ask students to look at the photos on page 10 and guess what the three people’s interests are. • Elicit some ideas and write them on the board, but do not confirm or deny at this stage. • Pre-teach the words belt and camera Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Exercise 2 • Students read the texts again more closely and answer the questions. In a weaker class, ask students to underline the part of the texts where they found the answer. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs, then check with the class. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students look at the photos and about their hobbies. Students read the texts again and choose the correct wnswer. ANSWERS 1 c 2 b 3 b 4 a 5 c 6 a
|
Assessment criteria - Descriptor: -read about people’s hobby Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: -write your interests and hobbies -Make CCQ questions
|
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 1,2 P: 4 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our class |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: have got. Prepositions |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context with little or no support in extended talk on a growing range of general and curricular topics ( p.15) 6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre-listening: Warm-up Ask individual students questions using have got, for example: Have you got a pet? Have you got a bicycle? • Write have got on the board and elicit that it refers to possession Lead - In Look at the picture and say what the theme of our lesson will be? You see different word in the picture. What can you see in this picture?
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 In a stronger class, ask students to complete the sentences from memory
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 11 P:Students work individually for 3–5 minutes to match the questions with the answers. Ex: 3 P: 11 • In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs, and do the example with them, demonstrating how the cross indicates a negative answer Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students complete the rule ANSWERS 1 has got 2 haven’t got 3 hasn’t got 4 haven’t got 5 ’ve got
Students match the questions with the answers. ANSWERS 1 has 2 haven’t 3 hasn Students use have got/ has got ANSWERS 1 We’ve got two dogs. 2 I haven’t got a poster of Johnny Depp. 3 My mum’s got two cars. 4 She hasn’t got a Ferrari. 5 I’ve got a camera. 6 My parents haven’t got a computer |
Assessment criteria - Learn the affirmative, negative and question forms of have got. Descriptor: Use the rule correctly Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: -Use topic related vocabulary in group discussion -Make CCQ questions
|
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 1,2 P: 4 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our class |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Hobbies and interests |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.6.9.1 use simple present and simple past regular and irregular forms to describe routines, habits and states on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of short, supported talk on a wide range of familiar topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre-listening: Warm-up • Revise the free-time words from lesson 1 of the unit. Write the heading Free time in the centre of the board, and ask students to say as many words as they can remember. • Write them on the board around the heading, linking each one to the heading with a line Lead - In To present interrogative pronouns
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 Students study the diagram with the class and separate the words in the bos of the mind map.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 11 Students read the clues and identify the correct word, then add the words to the mind map from exercise 1. Ex: 3 P: 11 Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students complete the mind map with the words in the box. ANSWERS Sport: team, player, swimming Music: hip hop, guitar, group, classical Computers email, website, mouse, laptop TV and cinema: programme, film, actor
Students read the clues and match. ANSWERS 1 drummer, singer (Music) 2 skiing (Sport) 3 director (TV and cinema) 4 webcam (Computers) 5 match (Sport Students use have got/ has got ANSWERS 1 We’ve got two dogs. 2
|
Assessment criteria - Use a mind map to group words according to meaning Descriptor: -Can classify yhe words Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: -Use topic related vocabulary in group discussion -Make CCQ questions
|
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 1,2 P: 4 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our class |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Interrogative pronouns. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.6.9.1 use simple present and simple past regular and irregular forms to describe routines, habits and states on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of short, supported talk on a wide range of familiar topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre-listening: Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they can remember any of the questions from the Find-a-friend questionnaire. • Elicit a few examples and write the interrogative pronouns on the board as students say them, e.g. How old …, Where …, etc. • Tell students these words are called interrogative pronouns, and we use them to form questions. • Ask students to look at the questionnaire again and find more examples of interrogative pronouns Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 Read the task with the class, and make sure students understand that they must complete the sentences before looking at the questionnaire. • In a weaker class, ask students to copy the sentences into their notebooks and write answers that are true for them. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 13 Read the task with the class and make sure students understand that they must read each answer to know what question is being asked. In a weaker class, demonstrate this by doing the first few items together. Students complete the questions with the correct interrogative pronouns. Ex: 4 P: 13 In pairs, students complete the quiz questions by adding the correct interrogative pronouns. Check answers with the class, then students do the quiz together. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students complete the questions ANSWERS 1 Who 2 Where 3 When 4 How old 5 How many
Students complete the questions to match the answer ANSWERS 1 How many 2 Who 3 What 4 Where 5 When 6 How old Students work in pairs
|
Assessment criteria - Learn interrogative pronouns Descriptor: - answers the questions properly; Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Write questions using interrogative pronouns. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: Do a quiz on interests. |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 1,2 P: 4 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our class |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Meeting people. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.2.1 ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general topics 6.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of short, supported talk on a wide range of familiar topics 6.6.3.1 use a growing variety of demonstrative pronouns: this/that, these/ those on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -Learn key phrases for greeting and introducing people. • Listen to a conversation in which people meet and greet each other. • Learn and use the demonstrative pronouns this, that, these and those. • Practise meeting and greeting people. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – listening Warm-up • Students look at the photo and say what they think the boy is interested in. Ask them to give reasons for their ideas, but do not confirm or deny their answers at this stage. • If students find this difficult, help them by suggesting that the image on his T-shirt could be waves in the sea Lead - In
This an apple. That is books. These are pencils. Those are toys. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
While – listening Exercise 1 • Students look at the photo and say what they think the boy is interested in. Ask them to give reasons for their ideas, but do not confirm or deny their answers at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Listening for details : Students listen for groups of words and phrases at sentence level. Ex: 2 P: 14 Refer students to the dialogue next to the photo. Model the pronunciation of the names before students listen. In a weaker class, identify each speaker in the photo: Jake is the boy, Laura is the girl in the blue T-shirt, and Tina is the girl in the grey T-shirt
Ex: 3 P: 14 . • Play the CD. Students listen and repeat the key phrases. • Students find the key phrases in the dialogue and identify the responses. Check answers with the class Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Post listening: students answer comprehension questions, analyze listening material and do follow-up activities |
Students look the photo and what hobby do you think the boy in interested.
Students listen to the dialogue and check their answer. ANSWERS Jake is into surfing. Students practise the language. ANSWERS 1 Not bad. 2 Hello, (Tina). 3 And you. 4 Yes, (but I’m not very good). 5 I’m from (Florida). 6 Yeah. See you later.
|
Assessment criteria - Learn key phrases for greeting and introducing people. Descriptor: - answers the questions properly; Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: Do a quiz on interests. |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 1,2 P: 4 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our class |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Writing: An email. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context with little or no support in extended talk on a growing range of general and curricular topics ( p.15) 6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model email. • Learn key phrases for an informal email. • Learn about and, or and but. • Write an email about your interests. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, ask students: Do you use the internet? Do you send emails? Who do you send emails to? Find out if any students use emails to write to penfriends, or in any other context where they might introduce themselves, such as a chat room or online group Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
While – listening Ex:1 P:15 Read the task and the questions with the class, and make sure students understand formal / informal. • Students read the text and answer the questions. Check answers with the class Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Listening for details : Students listen for groups of words and phrases at sentence level. Ex: 2 P: 15 -Students complete the key phrases from the email. • They check their answers in the text, and work out the meaning of the phrases Ex: 3 P: 15 Ask students to find examples of and, or, and but in the email in exercise 1 and work out the meaning. Encourage them to do this by looking at the context of the email. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students read the model text and answer the question ANSWERS: 1 b 2 To introduce Beth, describe her interests and ask about someone else’s interests. 3 Informal. 4 Paragraph 3. 5 Paragraph 2. 6 Paragraph 1.
Students complete the key phrases ANSWERS 1 student 2 really 3 about 4 one 5 now Students complete the sentences with and,or or but ANSWERS 1 and 2 but 3 or 4 but 5 or 6 and |
Assessment criteria - Study a model email. Descriptor: - read the model text and answer the question Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: Learn key phrases for an informal email. Descriptor: complete the key phrases -Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 13 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our class |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Daily routines. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics ( Ex.1 p.16) 6.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 6.6.16.1 use conjunctions so, if, when, where, before, after to link parts of sentences on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about routines. • Read a text about a Kazakh schoolgirl’s daily routine. • Learn when to use if / when as linkers. • Learn the difference between so and because and when to use them. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – teach Warm-up • Bring images, from magazines or the internet, to the class and put them on the board. • Put the students into two teams and ask them to write a list of the activities they know the names of. Allow them about three minutes. Lead – In
Do you get up early? Do you wash your face? Does she wash her teeth? |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:16 Focus students’ attention on the words in the box. Tell them to work individually and to put the activities in the order they do them on school days. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 16 • Read through the questions together and check understanding. • Ask a few students for their predictions to some of the questions. Ex: 5 P: 16 • Students do the exercise individually then check their answers in pairs. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Post listening: students answer comprehension questions, analyze listening material and do follow-up activities |
Students put the words in the box in the order you do every day
Students read the text about Omar’s daily routine and answer the questions ANSWERS 1 There are 1,500 students. 2 She usually gets up at 7 o’clock. 3 She goes to school on foot. 4 Her favourite lesson is Kazakh. 5 In the afternoons, she does her homework and gets ready for the next day. Three days a week she goes to music school. 6 In the evening, she goes for a walk with her brother and her friends. Students complete the sentences with if or when ANSWERS 1 if 4 If / When 2 If 5 when 3 when / if |
Assessment criteria -. Learn vocabulary for talking about routines. Descriptor: - put the words in the box in the order you do every day Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: • Read a text about a Kazakh schoolgirl’s daily routine. Descriptor: read the text about Omar’s daily routine and answer the questions -Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 14 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our class |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Visual arts: Colour. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks 6.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects ( Ex.3 - 4 p.17) 6.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in short, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Revise vocabulary for colours. • Learn vocabulary for talking about colour. • Practise talking about colour in a painting. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – teach Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they know any famous paintings. Ask them to describe the paintings. • Ask students what colours are in their favourite paintings. Elicit some colour words and write them on the board. Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
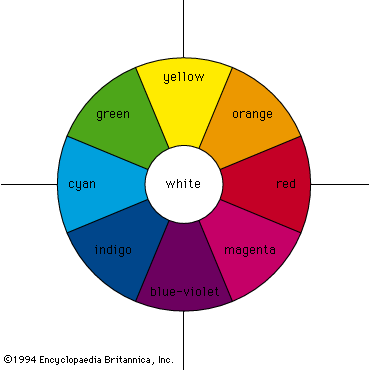
Ex: 1 P:17 Look at the colour wheel with the class. Students match the colour words with the colours. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Listening for details : Students listen for groups of words and phrases at sentence level. Ex: 2 P: 17 -Students check the meaning of the words using their dictionaries. Point out that some of the words, for example warm, have more than one meaning. Tell students to find the meaning that relates to colour Ex: 3 P: 14 Refer students to the pictures and ask if they recognize them Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Post listening: students answer comprehension questions, analyze listening material and do follow-up activities |
Students match the words with colours on the colour wheel ANSWERS: 1 orange 4 blue 2 red 5 green 3 purple 6 yellow
Students complete the words in the box ANSWERS 1 primary 4 cool 2 secondary 5 complementary 3 warm 6 contrast Students look at pictures. A and B complete the texts with words in the boxes ANSWERS : 1 cool 4 warm 2 green 5 blue 3 contrast 6 complementar |
Assessment criteria - Revise vocabulary for colours. Descriptor: - match the words with colours on the colour wheel Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: • Learn vocabulary for talking about colour. Descriptor: -find the meaning that relates to colour Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 15 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our class |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review. Unit 1 p.18 Summative assessment for the unit 1 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.4.1.1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: Learn vocabulary for classroom objects Learn the affirmative, negative and question forms of have got. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – teach Warm-up . Ask individual students questions using have got, for example: Have you got a pet? Have you got a bicycle? • Write have got on the board and elicit that it refers to possession Lead - In
Billy hasn’t got a car. Have they got bikes? Yes,they have got Has she got a CD player? No, she hasn’t |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 P:17 Complete the sentences and find the odd word Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Listening for details : Students listen for groups of words and phrases at sentence level. Ex: 2 P: 17 Students complete the words in the box , Summative assessment for the unit 1 Task 1. Reading. Read the text about Lera’s school and do the task. Task 2. Speaking Answer the questions. |
Students find the odd word ANSWERS: 1 skiing 2 science fiction 3 cycling 4 website 5 programme 6 email
Students complete the words in the box ANSWERS 1 mad 2 fan 3 good 4 especially 5 prefer 6 can’
|
Assessment criteria Learn vocabulary for classroom objects Descriptor: - find the odd word Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: • Identify particular facts and parts in reading passage Descriptor: -read the about Lera’s school Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 6 P: 18 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our class |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project: Poster about your class p.19 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 6.5.6.1 link, with some support, sentences into a coherent paragraph using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics 6.3.6.1 communicate meaning clearly at sentence level during, pair, group and whole class exchanges |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a poster and identify different topics. • Follow the steps in a project checklist. • Create a poster giving personal information. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – teach Warm-up Recap the vocabulary of the unit by writing words in mixed up letters on the board, for example: trosp (sport) csium (music) rpotcmuse (computers) Ask individual students up to the board to write the correct words. Check spelling, then ask students to identify what these words describe (hobbies and interests) Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 P:19 Look at the poster with the class. Explain that this introduces Class 6B and describes their hobbies and interests Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Listening for details : Students listen for groups of words and phrases at sentence level. Ex: 2 P: 19 • Tell students that they are now going to make a similar poster about their own class. Go through the points in the project checklist. Check students understand each of these. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Post listening: students answer comprehension questions, analyze listening material and do follow-up activities |
Students match the texts with a heading from the box ANSWERS: 1 Name and age 2 Pets 3 Sport 4 Music 5 Computers 6 Books and comics 7 TV and films
Students make a poster about your class
|
Assessment criteria - Read a poster and identify different topics Descriptor: - match the texts with a heading from the box Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: • Follow the steps in a project checklist Descriptor: - make a poster about your class Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 7 P: 15 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Helping and heroes |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Countries, nationalities and languages. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.1.1 understand a sequence of supported classroom instructions 6.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion p.21 6.3.6.1 communicate meaning clearly at sentence level during, pair, group and whole class exchanges |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for countries, nationalities and languages. • Do a quiz about different countries, nationalities and languages. • Learn key phrases for guessing answers. • Practise guessing answers. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – listening Warm-up • With books closed, ask students to work in pairs and write down as many countries as they can in English . • Elicit the names of a few nationalities and languages from the countries on the board. Lead - In
Where are you from? I am from Kazakhstan/ Where is he from? He is from China |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
While - listening Ex: 1 P: 20 Students complete the quiz. In a weaker class allow them to compare answers in pairs. In a stronger class, encourage them to work individually, then compare ideas with a partner Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Listening for details : Students listen for groups of words and phrases at sentence level. Ex: 2 P: 20 -• Point out that the names for the countries can all be found in the quiz. Students read the quiz again more carefully to find the correct information. Ex: 3 P: 20 Explain to students that they are going to hear people talking in different languages and that the aim for them is not to work out what they are saying, but to identify the language Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Post listening: students answer comprehension questions, analyze listening material and do follow-up activities |
Students listen and check their answers ANSWERS: 1 English 7 five 2 Washington, D.C. 8 false (seven) 3 football 9 pizza 4 the pound 10 Mandarin 5 the Rhine 11 Tokyo 6 false (over 65 million) 12 Italy
Students look at the quiz and write countries ANSWERS : 1 Canada 7 Spain 2 the USA 8 Poland 3 Brazil 9 Italy 4 the UK 10 China 5 Germany 11 Japan 6 France 12 Australia Students look at pictures. A and B complete the texts with words in the boxes Students listen to people from six different countries ANSWERS : 1 Mandarin 2 Spanish 3 English 4 Italian 5 German 6 French |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for countries, nationalities and languages. Descriptor: - complete the quiz Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: • Do a quiz about different countries, nationalities and languages. Descriptor: - listen to people from six different countries Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 16 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Helping and heroes |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading. A cosmopolitan city. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.3.1 give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics ( Ex.1 p.22) 6.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a ( Ex.3.p.22) 6.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in short, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about the different cultures that exist in Almaty. • Discuss multiculturalism at school and in the capital city. • Discuss other countries that students want to visit. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – listening Warm-up With books closed, ask the class to think about large cities in their country. Ask about the types of people who live in them, and whether they are multicultural places or not Lead - In
Almaty has perhaps one of the most striking and beautiful locations of any city in the world. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Located in the spectacular foothills of the Zilishkiy Alatau Mountains, Almaty is a pleasant city to live in, vibrant, green, and with thriving cosmopolitan culture. The impressive mountains are only half an hour’s drive from the city center. Almaty’s population is 1.5 million. |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
While-listening Ex: 1 P: 22 • If students find it difficult to say anything about Almaty, ask specific questions, for example: Do any famous people live in Almaty? What languages do people in Almaty speak? Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 22 • Ask students to listen closely for the different languages. • In a weaker class remind students that the words for languages are often the same as those for nationalities. Draw a table on the board, and label the first column Languages and the second column Nationalities Listening for details : Students listen for groups of words and phrases at sentence level. Ex: 3 P: 22 • Allow time for students to read the sentences and the options carefully, then check understanding. \ • Students work individually, then compare their answers in pairs. Check the answers with the class. Post listening: students answer comprehension questions, analyze listening material and do follow-up activities |
Students talk about Almaty and answer the question • Brainstorm ideas around the class and write useful information on the board
Students read and listen to the text. How many people in Almaty have family or ancestors from other countries ANSWERS : 6 – French, German, Spanish, Mandarin, English, Turkish Students read the text again then choose correct answers. ANSWERS : 1 b 2 c 3 a 4 c 5 c |
Assessment criteria - Read about the different cultures that exist in Almaty. Descriptor: - talk about Almaty and answer the question Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: Discuss multiculturalism at school and in the capital city. Descriptor: - listen closely for the different languages. Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 20 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Helping and heroes |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: Zh.Dzhumanova |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Present Simple: affirmative and negative. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics ( p.23 Mind map) 6.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects ( Facts and routine) p.23 6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups ( Ex.3,5 p.23) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the affirmative and negative forms of the present simple. • Learn spelling rules for the third person singular in the present simple. • Use the present simple to talk about habits and likes / dislikes. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – teach Warm-up With books closed, ask students what they can remember about the people from Almaty. Write the names Artur, and Sung on the board. Lead - In
I go to school every morning. She doesn’t speak French. Does he know about history of Turkestan? |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
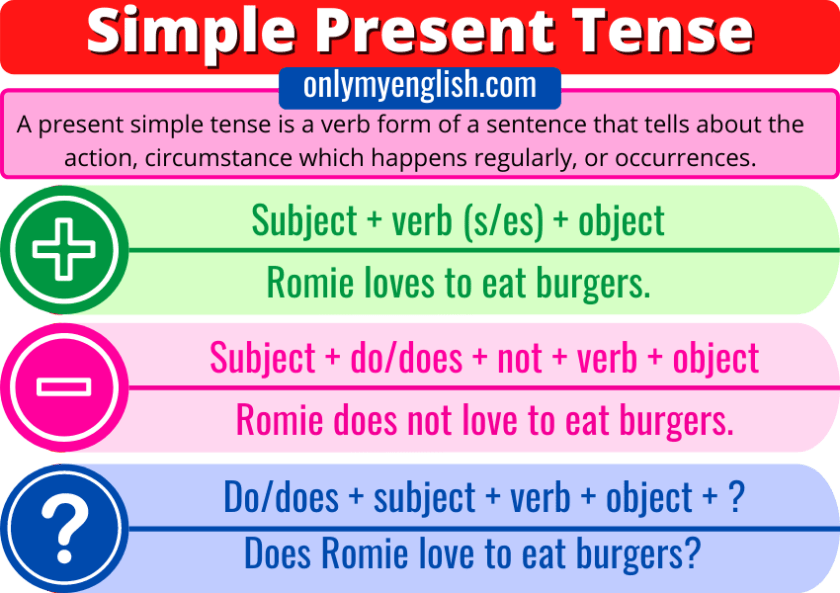
Ex: 1 P: 23 Students read quietly to find the examples. Ask individuals to read these out, and write the answers on the board. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Listening for details : Students listen for groups of words and phrases at sentence level. Ex: 2 P: 23 Allow students time to check the meanings, using a dictionary if necessary. Ask for translations to check understanding. Ex: 3 P: 23 Remind students to use the spelling rules to help them decide on the correct verb forms. Point out that they can make the verbs affirmative or negative so that the sentences are true for them Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Post listening: students answer comprehension questions, analyze listening material and do follow-up activities |
Students complete the examples using information from the text ANSWERS: 1 don’t speak 2 tells me 3 don’t see 4 speaks 5 also Rules 1 facts and routines 2 affirmative 3 doesn’t, don’t
Students check the meaning of the verbs ANSWERS : 1 uses, writes, listens, eats, knows, sleeps, buys, comes, makes, walks, thinks 2 goes, mixes, finishes, watches, teaches, does 3 tries, carries have doesn’t go in any group. Students use the verbs in brackets and write true sentences in the present tense ANSWERS : 1 goes / doesn’t go 5 try / don’t try 2 teaches / doesn’t teach 6 writes / doesn’t write 3 do / don’t do 7 like / don’t like 4 watch / don’t watch 8 play / don’t play |
Assessment criteria - Learn the affirmative and negative forms of the present simple. Descriptor: - complete the examples using information from the text Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: -Learn spelling rules for the third person singular in the present simple. Descriptor: - can make the verbs affirmative or negative so that the sentences are true for them Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 16 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Helping and heroes |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Daily lives Summative assessment for the unit 2 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics ( My Day p.24) 6.5.2.1 write with support a sequence of short sentences in a paragraph on a limited range of familiar general topics ( p.24) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a text about child labour. • Learn adverbs of frequency. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. • Write personal sentences about your daily lives. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – teach Warm-up • Write on the board: Daily lives. • Ask students: What do you do on weekdays? What do you do at the weekend? Lead - In
I get up at 6 o’clock every day I wash my face then I have breakfast. My school starts at half past eight. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 P: 24 Look at the photos with the students and ask for ideas about the different people who are shown in them. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Listening for details : Students listen for groups of words and phrases at sentence level. Ex: 2 P: 24 Students think about their own daily routines and make sentences individually, using exercise 1 as a model. Summative assessment for the unit 2
Reading Task 1. Read the text and complete the tasks below.
Writing Task 2. Write about your Sunday household chores. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students check the meaning of the words in blue ANSWERS: get up, go to school, do exercises, have a break, have lunch, go home, watch TV, have dinner, do homework, go to bed
Students rewrite the sentences use adverb if frequency ANSWERS : Students’ own answers. Students read the text and complete the tasks Students write about your Sunday household chores. |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a text about child labour. Descriptor: - use the words in blue Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Identify the author’s attitude and viewpoint in short texts -Write high-frequency topic related words accurately Descriptor: - writes about the importance to help people. Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 18 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Helping and heroes |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Present Simple: Questions. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.6.9.1 use simple present and simple past regular and irregular forms to describe routines, habits and states on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.6.12.1 use common regular and irregular adverbs, simple and comparative forms, adverbs of frequency on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -Apply simple present and simple past regular and irregular forms to describe routines, habits and states -Identify common regular and irregular adverbs, simple and comparative forms, adverbs of frequency -Write questions using wh- words and the present simple -Ask and answer questions using the present simple. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – teach Warm-up • With books closed, ask individual students questions using the present simple, for example: Do you go to school? • Allow students to answer with simply yes or no. Lead - In
What time do you get up? What do you do after getting up? What time does she go to school? When does she go to her grandparents? |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students talk about girl’s daily routine and answer the questions.
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 P: 25 Teacher explain that options a and c–e are short answers to the questions, and that students should look for subject pronouns that match the questions Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 25 Students work individually to write questions. Check these before they move on to the speaking. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Ex: 3 P:25 • Write the question words used in this exercise on the board. Ask if students can translate them, and provide any answers they do not know. • Look at answers a–h, and point out that they give more information than the short answers. |
Students match questions with answers ANSWERS: 1 e 2 d 3 c 4 a 5 b Rules 1 do / does 2 don’t add 3 beginning
Students write question and short answer ANSWERS : 1 Do your parents play tennis? 2 Does your mother speak French? 3 Do you watch TV every evening? 4 Does this book teach vocabulary? 5 Does your father work in a factory? 6 Do you and your friends go to school on Saturdays? 7 Do you and your family live in a modern building? 8 Does your friend come to your home after school? Students complete the questions ANSWERS 1 do you and your family go; h 5 do your friends like; b 2 does your best friend live; g 6 do you watch; c 3 do you do; f 7 do you do; e 4 do you travel; a |
Assessment criteria - Apply simple present and simple past regular and irregular forms to describe routines, habits and states Descriptor: - Use the question forms of the present simple. Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Identify common regular and irregular adverbs, simple and comparative forms, adverbs of frequency Descriptor: - write question and short answer Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 19 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Helping and heroes |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Helping with housework. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.1.1use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups. 6.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects 6.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in short, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -Apply speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups. -Write with support at text level which describe people, places and objects -Listen to a conversation about likes and dislikes -Prepare and practise a dialogue talking about likes and dislikes. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – listening Warm-up • Ask if any of the students play an instrument, and what kind of music students like. They can answer in their own language. Write their ideas on the board. • If they do not like music, ask them to name a few of their other hobbies Lead - In
Do you help your mother at home? Who does do the washing up in your house? Do you make your bed every day? |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Well done
|
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 P: 26 When students have answered the questions, refer back to the ideas from the warm-up. Does anyone in the class play the trumpet or like the samba? Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Listening for details : Students listen for groups of words and phrases at sentence level. Ex: 2 P: 26 • Ask students to read the dialogue quietly, then check any words they do not know. In a stronger class, ask other students to help each other rather than offering translations straight away. • Check students understand the phrases in the box. In a weaker class, they can complete the dialogue in pairs. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Ex:5 P:26 Explain to the class that they are now going to listen to a new conversation. Ask them to read through the dialogue before you play the CD, without worrying about the gaps or the words in blue. |
Students check the meaning of the verbs in the box. ANSWERS: Laura has got a trumpet. The samba is Brazilian music
Students complete the dialogue then listen ANSWERS : 1 c 2 d 3 b 4 a Students ask and answer questions with a partner using the activities in the box. ANSWERS: 1 watching DVDs 2 reading comics 3 listening to classical music 4 playing tennis
|
Assessment criteria - Apply speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups. Descriptor: - check the meaning verbs Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Write with support at text level which describe people, places and objects Descriptor: - writes about the importance to help people. Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 18 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Helping and heroes |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Country and language report. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 6.3.2.1 ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general topics 6.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -synthesis and present information clearly to others -Write with support at text level which describe people, places and objects -Write a report about nationalities and languages in your class |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – teach Warm-up • With books closed, ask students: Who writes reports? Do you write reports? When do you write reports? • Refer students to the title of the model report and ask students what they know about Canada. Lead - In
How many words do you find in these pictures? |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students find different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Well done
|
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 P: 27 Read the instructions and the words in the box first, and remind students that the first time they read, they should read for general meaning and not worry about words or phrases they do not understand. The aim of the first read is to work out the topic of each paragraph. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 27 • This time, students should read the text more carefully and find the specific information to answer the questions. • Ask them to work individually at first, then compare answers with a partner. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Ex:5 P:27 Explain to the class that they are now going to listen to a new conversation. Ask them to read through the dialogue before you play the CD, without worrying about the gaps or the words in blue. |
Students read the model text and match the paragraphs ANSWERS: Paragraph 1 Where it is Paragraph 2 Languages Paragraph 3 Population
Students complete the dialogue then listen ANSWERS : 1 c 2 d 3 b 4 a Students ask and answer questions with a partner using the activities in the box. ANSWERS: 1 watching DVDs 2 reading comics 3 listening to classical music 4 playing tennis
|
Assessment criteria - Apply speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups. Descriptor: - check the meaning verbs Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Write with support at text level which describe people, places and objects Descriptor: - writes about the importance to help people. Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 18 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Helping and heroes |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative assessment for the term 1 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.5.1 Understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.4.1.1 Understand the main points in a growing range of short, simple texts on general and curricular topics curricular topics 6.5.3.1 Write with some support about persona feelings and opinions on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.3.1.1 Provide basic information about themselves and others at discourse level on a range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -understand more complex supported questions on a growing range of general and curricular topics; -recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level in a range of written genres; -write with some support topics with some paragraphs to give basic personal information; |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Listening Task. Listen to the talk with Ben and Katy twice. CD3. Tapescript 1.And transcript for listening task can be found after the mark scheme. Choose the correct option to complete the sentences 1. Ben… [1] A) does not study B) studies and does well C) studies but does not do well D) does not go to school 2. Ben usually studies… [1] A) in the library B) at home C) in his friend’s house D) in the park 3. On Ben’s desk there are… [1] A) papers, books and pens B) pencils, books and pens C) a pencil case and pens D) copybooks and a laptop |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students listen to the talk with Ben and Katy twice ANSWERS: 1 C 2 B 3 A 4 study 5 break
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Well done
|
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Reading Task. Read the article about London police. Answer the questions. 1. Why did people stay in their homes as much as possible? [1] 2. How did “Bow Street Runners” get their name? [1]
Choose True or False. 3. In 1800, there were not enough policemen in London. [1] True False 4. All of the first 3000 London Police Force rode horses. [1] True False 5. Today, police officers who work with horses are paid more than their colleagues. [1] True False
Writing Task. Choose ONE of the topics below. Topic 1. Our class Think about your favourite class. Give some information about the subject and classmates. Topic 2. Helping and Heroes Think about heroes of modern life. Give some information about any hero. Speaking Task. Work in pairs. Choose one of the cards and make a dialogue with a partner. Give own opinion on topic, ask questions, explain your position and answer your partners’ questions. You have 1 minute to prepare and 2 minutes to talk. |
Students read the article about London police. ANSWERS: 1 There were many thieves 2 because they worked near Bow Street 3 false 4 false 5 true
Students Choose ONE of the topics below.
ANSWERS : Students’ own answers Students choose one of the cards and make a dialogue with a partner.
|
Assessment criteria - Apply speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups. Descriptor: - check the meaning verbs Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Write with support at text level which describe people, places and objects Descriptor: - writes about the importance to help people. Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 18 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Helping and heroes |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My Country. National heroes. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about jobs. • Read a text about Kazakh heroes. • Learn how to use question tags. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – teach Warm-up Books closed. Divide students into pairs and write Heroes on the board. Allow students about two minutes to tell each other who their Kazakh heroes are. Get feedback from the class by asking a few students to say who their pair thought were heroes and asking how many other students agree with them Lead - In
Kazakh people have always admired their daughters for their beauty, intelligence and courage. The women of the great steppe always held high status in the socio-political hierarchy of Kazakh governments.
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students talk about Kazakh heroe.
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Well done
|
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 P: 28 Tell students to cover the interview and focus their attention on the photos. Ask students if they know who the people are and what they are famous for. Encourage students to give as much information as they can Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 28 Check that students understand that they have to complete each sentence with a name of one of the three heroes. Students read the texts again in detail and complete the sentences before checking their answers with a partner Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Ex:4 P:28 Draw students’ attention to Mariya’s questions in the text and tell them to complete the questions in the exercise. Ask student how they are different from normal questions. Elicit that the question form is at the end of a statement |
Students look at the photos and answer the question ANSWERS: 1 They are Toktar Aubakirov, Roza Baglanova and Abilkhan Kasteev. 2 Toktar Aubakirov was the first Kazakh cosmonaut. Roza Baglanova was a famous opera singer. Abilkhan Kasteev was a famous painter. He painted over 2,000 pictures.
Students read the text again. Complete the sentences with the names of the people ANSWERS : 1 Roza Baglanova 2 Toktar Aubakirov 3 Abilkhan Kasteev 4 Toktar Aubakirov 5 Abilkhan Kasteev 6 Roza Baglanova Students look at the interview again. Complete the ANSWERS: 1 doesn’t he 2 is it 3 aren’t they
|
Assessment criteria - Apply speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups. Descriptor: - check the meaning verbs Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Write with support at text level which describe people, places and objects Descriptor: - writes about the importance to help people. Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 19 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
Тексерілді: _________________________
|
Unit of a long term plan: Helping and heroes |
School: By name _________ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _________ |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Language and literature: Non - verbal language. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks 6.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Revise vocabulary of emotions. • Read a text about non-verbal language. • Read for general meaning and specific detail. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – teach Warm-up • Give some examples of things they might need to communicate, and elicit ideas for how they would do this. For example: I’m cold. I’m hungry. Can I borrow your phone? Students will probably use a mixture of expressions and gestures to try to communicate the ideas. Elicit the words expression and gesture and write them on the board. • Tell students these are examples of non-verbal communication. Lead - In
I am happy I am suprise |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students find different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Well done
|
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 P: 29 • Students work in pairs to check the meaning of the words and match them with the faces. • Check answers, and check that students understand all the words. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 29 Students read and listen to the text and find the answer to the gist task. Remind them that they do not need to worry about understanding every word at this stage Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Ex:3 P:29 • Students read the text again more carefully. This time they should check any words they are not sure of. |
Students match the words with pictures ANSWERS: 1 happy 2 surprised 3 angry 4 tired 5 confused
Students read and listen to the text ANSWERS : Non-verbal language is communication with facial expressions and gesture, colours, pictures and symbols. It is important because it helps us to communicate when people don’t speak our language. Students read the text again and write true or false ANSWERS: 1 True. 2 False. Verbal language is words. 3 True. 4 False. If we don’t speak someone’s language we can understand their non-verbal language. 5 True. |
Assessment criteria - Apply speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups. Descriptor: - check the meaning verbs Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Write with support at text level which describe people, places and objects Descriptor: - writes about the importance to help people. Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 18 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 25 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Animals. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.2.1 ask more complex questions to get information about a growing range of general topics and some curricular topics 6.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of short, supported talk on a wide range of familiar topics 6.5.8.1 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Value links |
Family – Family values are moral and ethical principles of typical family life, including sacrificing for loved ones, putting your loved ones first, and keeping your loved ones at the centre of your thoughts and actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre-listening: Warm-up • With books closed, ask students to work in pairs and write down as many animals as they can in English. • Elicit the names of a few animals from individual students and write them on the board Lead - In
How many animals do you see? Where do they live? What do they eat? |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 32 • In a weaker class, allow students to match the animals with the photos in pairs. • Elicit the answer to the question, but do not check answers to the matching task at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 32 Demonstrate how to use the key phrases in context. Ask students to look at the first picture in the quiz. Say an incorrect sentence, e.g. It looks like an elephant. Elicit that the animal is a whale, and see if students can form an answer with the key phrases, e.g. I’m sure it’s a whale. Ex: 4 P: 32 • Explain to students that they are going to hear some animal sounds and they must discuss what animals they think they are hearing, using the key phrases. • Play the CD, pausing after each animal sound Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students match the animals in the box with photos ANSWERS: Photo 14 is not an eye. It’s a butterfly wing. Students compare their answers in exercise 1 ANSWERS: 1 whale 2 spider 3 owl 4 shark 5 human 6 snake 7 fly 8 seal 9 falcon 10 parrot 11 frog 12 elephant 13 chameleon 14 butterfly 15 crocodile 16 bear Students listen and identify the animals. ANSWERS: 1 an owl 5 a seal 2 a fly 6 a whale 3 a frog 7 a bear 4 a falcon 8 a snake
|
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for animals. Descriptor: - match the animals in the box with photos pupils are evaluated by collecting fish Descriptor: compare their answers Descriptor: listen and identify the animals -Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 24 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 26 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading: The red list |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.C7 develop and sustain a consistent argument when speaking or writing 6.R2 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 6.S3 give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics( Ex.3 - 4 p.34) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Value links |
Loyalty – Loyalty might be a core personal value to you if you highly prize friends that are reliable and trustworthy. You might put your friends or chosen family first, always being there for them when they need you. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask: What’s your favourite animal? • Ask: Which animals do you dislike? Elicit answers from individual students, and ask why they dislike these animals Lead - In
The Red Book of Kazakhstan - an annotated
list of rare and endangered animals
in |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 34 • Refer students to the title of the article and the question. • Students discuss their answers in pairs. • In a stronger class, ask students to make a note of as many statistics as they can to support their answer complete the sentences with the correct form of the verbs in brackets Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 34 • Explain that students should now read the text again more carefully to find the specific information. In a weaker class, check key vocabulary, e.g. extinct, before students read. • Ask students to complete the answers individually, then compare their ideas with a partner Ex: 3 P: 34 • Students check the meaning of the blue words and identify which are verbs (attack and save). • Check understanding of the words and phrases, for example by asking students to use them in sentences Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students read and listen to the text ANSWERS: A person is more dangerous than a shark or a chair. Students read the text again and choose the correct answers ANSWERS: 1 a 2 c 3 c 4 c 5 a Students use the words to complete the sentences. ANSWERS: 1 attack 4 accidents 2 approximately 5 actions 3 save 6 pollution |
Assessment criteria Read about animals in danger Descriptor: - read and listen to the text
pupils are evaluated by collecting fish Descriptor: read the text again and choose the correct answers
-Make CCQ questions. Yes / No 1 Are crocodiles dangerous? Yes 2 Do people kill animals for fur? No 3 Do wolves live In Kazakhstan? Yes |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 24 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 27 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Present Continuous |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.C6 organise and present information clearly to others ( Ex.1 p.35) 6.W2 write with minimal support about real and imaginary present events, activities and experiences happening now on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics ( Ex.2,3,5 p.35) 6.S2 ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general topics ( Ex.6 |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Value links |
Fairness – If you value fairness, you might be highly sensitive to situations at school or in the workplace where a teacher or a peer has exhibited favoritism or allowed someone to get away with living by a different set of rules to everyone else. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Write four present continuous sentences on the board, two true and two false, e.g. I am teaching. The sun is shining. Elicit which ones are true and how students can tell. Elicit that the present continuous describes events happening now Lead - In
He is swimming. She is reading We are dancing They are running |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 35 When students have found the sentences, draw attention to the form Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. . Ex: 3 P: 35 • Tell students they are going to listen to seven recordings, and that they should identify what is happening. • Tell students to read the options in columns A and B before they listen, to give them an idea of the context and what they might hear Ex: 4 P: 35 • Allow students time to study the picture carefully and read the prompts. • Explain that they should write the negative sentence first, then an affirmative sentence using the word in brackets Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 are 2 aren’t 3 is Students match the things in A with the actions in B ANSWERS: 1 Two dogs are running in the park. 2 A parrot is speaking English. 3 A man is attacking a mosquito. 4 A whale is singing to its partner. 5 Children are making a cake. 6 A girl is practising the piano. 7 A lion is having a meal. Students work in pairs. Make affirmative and negative sentences using the present continuous ANSWERS: 1 A child isn’t feeding some bears. She is feeding some ducks. 2 A falcon isn’t sleeping. It is hunting. 3 Two people aren’t watching a chameleon. They are watching the falcon. 4 Three people aren’t swimming. They are running. |
Assessment criteria - Learn the affirmative and negative forms of the present continuous. Descriptor: - match the things in A with the actions in B
Descriptor: Make affirmative and negative sentences using the present continuous
pupils are evaluated by collecting pencils -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 24 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 28 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Animal behaviour |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups ( Ex.1,2 p.36) 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics ( Ex.3 p.36) 6.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics( Ex.4 p.36) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn verbs for animal behaviour. • Listen to an interview about animals. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. • Write about an animal and describe its behaviour |
||
|
Value links |
Honesty – You may highly value telling people the truth. This one gets tricky when being honest can be hurtful to others. So, a person who really puts honesty first might be the sort of person who will tell the truth even if it hurts to do so. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Write the word Behaviour on the board. • Elicit the meaning, then ask: What do animals do to survive? • Elicit ideas from the class, for example animals hunt for food, hide from other animals, find a safe place to sleep, keep warm in the winter. Lead - In
There are prides within 100 km of each other that display extremes in behavior, and in particular when it comes to feeding and drinking. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 36 • Refer students to the bold verbs. Tell them to use the Wordlist or their dictionaries to check the meaning of any verbs they do not know. • Refer students to the photos and ask them to choose the correct verbs. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. . Ex: 2 P: 36 • Look at the example answer and remind students that we do not use the definite article, the, when we are talking about things in general. • Students complete the sentences with the animals Ex: 3 P: 36 Explain that students are going to listen to an interview. While they listen for the first time they should look at the photos and identify the ones the speaker is talking about. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students check the meaning of the verbs in bold and choose the correct verbs ANSWERS: 1 feeding 3 catching 5 hunting 2 building 4 protecting 6 chasing Students complete the sentences with names of the animals ANSWERS: 1 Snakes 4 Sharks 2 Bears 5 Humans 3 Chameleons 6 Whales. Students listen to an interview with Mike. Which of the photos does Mike speak about? ANSWERS: He speaks about photos 1, 3, 4 and 6 |
Assessment criteria - identify verbs for animal behaviour. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the verbs in bold and choose the correct verbs
Descriptor: complete the sentences with names of the animals
pupils are evaluated by collecting colour pencils Descriptor: listen to an interview with Mike. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets CD 1.31 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 26 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 29 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Present Continuous. Questions |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others ( ex1 - 5 p.37) 6.5.2.1 write with minimal support about real and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics ( Ex.6,7 p.37) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the question forms of the present continuous. • Write questions and answers using the present continuous. • Identify the difference between the present continuous and the present simple |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students back to the photos on page 42. Ask students what questions they can ask about the animals Lead - In
Is he swimming? Is she reading? Are we dancing? Are they running?
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 37 • In a weaker class, you could play the CD (2.06) again Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 37 Check understanding by asking and answering some present continuous questions as a class. Ex: 3 P: 37 In a weaker class do another example with the whole class, and then ask and answer.
Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students complete the question form ANSWERS: 1 is 2 Is 3 Is Students match the questions in exercise 1 ANSWERS: 1 c 2 a 3 b Rules: 1 is 2 aren’t Students write questions for the answers using the words in brackets. ANSWERS: 1 Where are those seals swimming to? 2 Why are they doing that? 3 What is that seal doing? 4 Who is watching the seals in that small boat? 5 Why are they watching the seals? 6 Where is that scientist going? |
Assessment criteria - Learn the question forms of the present continuous. Descriptor: - match the questions in exercise 1 Descriptor: write questions for the answers using the words
Self assessment -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 30 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Phoning a friend |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics. 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics (Key phrases p.38) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for talking on the phone. • Listen to a conversation on the phone. • Practise a telephone conversation about what is happening now. • Learn how to improve pronunciation. |
||
|
Value links |
Generosity – This may be a core value of yours if you cherish people who will give their time and resources to people in need. You may consider yourself to be a generous person if you find joy and meaning in giving to others. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students if they often speak to their friends on the phone. • Ask when they use their mobile phones during the day. • Elicit a few answers, for example when they want to meet someone. • Ask them what they would say to answer the phone in English (Hello). Lead - In
Phone calls are the number one way I improve my mood. When I’m feeling down or confused or alone, I pick up the phone and call a friend. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 38 • Remind students that they should use any photos they are given to help them think about the context before they read or listen. • Ask students to identify Tina and say where she is, but do not check their answers at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 38 • Students can follow the dialogues in their books as they listen. • Remind them that the information they should listen for on this first hearing is where Tina is, and what she is doing Ex: 3 P: 38 • Explain that the blue words in the dialogue are responses to the key phrases. In a weaker class, match the first one together. • Students match the phrases in pairs. To check answers, ask one student to read out a numbered phrase, and another student to give the appropriate answer from the blue phrases Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students look at the photo. Where is Tina? ANSWERS: Students listen to the dialogue and check the answers ANSWERS: Tina is at the Brighton aquarium. She is looking at sharks. Students match the key phrases. ANSWERS: 1 Yeah, it’s really interesting. 2 Sure. 3 Hi, there. 4 OK, great! 5 I’m at the Brighton aquarium. 6 Fine, thanks |
Assessment criteria Learn key phrases for talking on the phone. Descriptor: - listen to the dialogue and check the answers
Descriptor: match the key phrases.
pupils are evaluated by collecting colour pencils -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 30 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Phoning a friend |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics. 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics (Key phrases p.38) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for talking on the phone. • Listen to a conversation on the phone. • Practise a telephone conversation about what is happening now. • Learn how to improve pronunciation. |
||
|
Value links |
Generosity – This may be a core value of yours if you cherish people who will give their time and resources to people in need. You may consider yourself to be a generous person if you find joy and meaning in giving to others. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students if they often speak to their friends on the phone. • Ask when they use their mobile phones during the day. • Elicit a few answers, for example when they want to meet someone. • Ask them what they would say to answer the phone in English (Hello). Lead - In
Phone calls are the number one way I improve my mood. When I’m feeling down or confused or alone, I pick up the phone and call a friend. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 38 • Remind students that they should use any photos they are given to help them think about the context before they read or listen. • Ask students to identify Tina and say where she is, but do not check their answers at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 38 • Students can follow the dialogues in their books as they listen. • Remind them that the information they should listen for on this first hearing is where Tina is, and what she is doing Ex: 3 P: 38 • Explain that the blue words in the dialogue are responses to the key phrases. In a weaker class, match the first one together. • Students match the phrases in pairs. To check answers, ask one student to read out a numbered phrase, and another student to give the appropriate answer from the blue phrases Differentiation: Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students look at the photo. Where is Tina? ANSWERS: Students listen to the dialogue and check the answers ANSWERS: Tina is at the Brighton aquarium. She is looking at sharks. Students match the key phrases. ANSWERS: 1 Yeah, it’s really interesting. 2 Sure. 3 Hi, there. 4 OK, great! 5 I’m at the Brighton aquarium. 6 Fine, thanks |
Assessment criteria Learn key phrases for talking on the phone. Descriptor: - listen to the dialogue and check the answers
Descriptor: match the key phrases.
pupils are evaluated by collecting colour pencils -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 31 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A description of a wildlife photo. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.5.6.1 link independently, sentences into coherent paragraphs using a variety of basic connectors on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model article about an animal. • Learn about because. • Write an article about an animal |
||
|
Value links |
Integrity – Integrity is the quality of having strong moral principles. So, a person with integrity will always act with honesty and adhere to their own moral code regardless of what others do. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students if they ever read about animals. Ask them where you can read about animals. • Elicit some answers, for example in an encyclopedia, on the internet or in a magazine. Lead – In
The snow leopard is a large cat native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia. It is listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures about wildlife animals PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 3ұ • Refer to the model text and make sure that students understand that it is divided into three paragraphs. • In a weaker class, ask them to find the answers in pairs Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 39 Elicit the first pair of sentences and how they can be joined using because. In a weaker class, discuss the function of because. What does the second sentence tell us? (The reason for the first statement.) Ex: 3 P: 39 • Check understanding of the key phrases, then ask students to match them to the paragraphs in the model text. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students read the model text and answer the questions. ANSWERS: 1 Paragraph 2 describes the life and habitat of the orca. Paragraph 3 describes a problem. 2 Yes, they do. 3 Fish, squid, seals and turtles. 4 Every two or three years. 5 They are becoming extinct because there is pollution in the sea, and they also die in fishing nets. Students match sentences with using because ANSWERS: 1 c Orcas are in danger because there is pollution in the sea. 2 e They’re hunting because they’re hungry. 3 a I don’t swim because I don’t like the water., 4 f She’s having a good time because she’s at the aquarium. 5 b He’s running because he’s late. 6 d They’re hiding because they’re scared. Students match the key phrases with paragraphs. ANSWERS: a paragraph 2 b paragraph 2 c paragraph 1 d paragraph 3 e paragraph 1 |
Assessment criteria Study a model article about an animal. Descriptor: - read the model text and answer the questions.
Assessment criteria: Learn about because. Descriptor: match sentences with using because -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: National parks. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.3.1 respect differing points of view 6.4.6.1 recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 6.6.14.1 use prepositions to talk about time and location; use prepositions like to describe things and about to denote topic; use prepositions of direction to, into, out of, from, towards on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn about the flora and fauna in one of Kazakhstan’s national parks • Identify numbers in a text • Learn and revise prepositions of place |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Ask students if they have visited any of Kazakhstan’s national parks. Ask them the name of the park and what they saw there. Ask students why countries have national parks (to preserve landscapes and the habitats they contain for plants (flora) and animals (fauna)), and if they can think of any benefits (helping maintain species, preserving beautiful areas and important habitats for future generations). Lead - In
What do you know about Karkaraly National Park? |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1/2 P: 40 Focus students’ attention on the text. If you have access to the internet, you can bring up a map of the Park’s location. Ask students what sort of landscape they think the park has (mountains, desert, steppe, etc.). Tell them to read the questions first, then read the text. Students answer the questions individually, before checking in pairs Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 4 P: 40 Go through the answers with the class. Make sure they say the answers correctly, especially 260 (two hundred and sixty). Point out that we only use and after hundreds not thousands, so 2650 is two thousand, six hundred and fifty NOT two thousand and six hundred and fifty. Ex: 3 P: 40 Students complete the exercise individually before checking their answer in pairs. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students look at the photo and describe what can they see? ANSWERS: 1 The name of the park is Altyn-Emel. 2 It is in the south-east of Kazakhstan, between the Aktau Mountains and the River Ili. 3 The landscape is dry, there are mountains and sand dunes. 4 You can find fish, 260 species of vertebrates, birds, including four types of eagle, Przewalski’s horses and eagle owls. 5 You can see singing sand dunes and rocks with very old paintings on them. 6 There are imperial eagles, eagle owls, Przewalski’s horse and 11 species on Kazakhstan’s red list and Turanga trees Students read the text again and find the numbers ANSWERS: 1) 4,600km 2) 4 500m 6) 26 2) 1,800 5) 3,000 7) 13 3) 11 Students complete the sentences with the correct prepositions ANSWERS: 1 in 5 above 2 between 6 under 3 on 7 behind 4 along, next to 8 in front of /opposite |
Assessment criteria Learn about the flora and fauna in one of Kazakhstan’s national parks Descriptor: - look at the photo and describe what can they see?
Assessment criteria: - Identify numbers in a text -Learn and revise prepositions of place Descriptor: -read the text again and find the numbers -complete the sentences with the correct prepositions -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Natural science: Animals / Summative Control work 3 for Unit 3 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world (Ex.1-3 p.41) 6.2.4.1 (6.L4) Understand with limited support the main points of extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.3.3.1 (6.S3) Give an opinion at sentence and discourse level on an increasing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about animals. Identify the main ideas in extended talk with some support Provide a point of view in conversations and discussions Retell extended stories and episodes on a given topic |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the names of several different types of animals on the board, for example: dog, pigeon, crocodile. • Ask students: What types of animals are these? What’s the difference between them? What do they have in common? Lead - In
Bats produce incredibly high frequency sound pulses, or squeaks. Research shows that some bats can produce a frequency of over 100,000 Hz. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 41 • Students check the meaning of the words in their dictionaries. Point out that some of the words, for example scales, have more than one meaning, and students should find the meaning to do with animals Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 41 • Read through the questions with the class and check understanding. Ask students to work individually and read the text again in more detail Summative Control work for the unit “Our countryside” Listening Task 1. Listen to the story and choose the correct option.
Task 2. Listen to the second time and complete the sentences
Speaking
Task 3. Learners work in pairs. |
Students check the meaning of thewords. ANSWERS: 1 fins 4 legs 2 lungs 5 hair 3 feathers Students read and listen to the text then answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 Fish. 2 Fish and reptiles. 3 Mammals. 4 They haven’t got four legs. 5 Amphibians. 6 Mammals Students listen to the story and choose the correct option. ANSWERS: 1 farm friends 2 a bad animal 3 friendly 1 cat 2 dog 3 man / farmer Students work in pairs. ANSWERS: Students own answers. |
Assessment criteria Learn vocabulary for talking about animals. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words.
Assessment criteria: Identify the main ideas in extended talk with some support Descriptor: listen to the story and choose the correct option. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.5.1 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn verbs for animal behaviour. Write about an animal and describe its behaviour. |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Elicit ideas from the class, for example animals hunt for food, hide from other animals, find a safe place to sleep, keep warm in the winter. Lead - In The Great Barrier Reef. Scientists sometimes call Earth ‘the blue planet’ because about 75% of it is the sea! Many plants, fish and animals live in the sea, and it’s got a lot of important ecosystems. The Great Barrier Reef, near Australia, is a big ecosystem. The reef is long – 26,000 kilometres! The water is very clean, so seaweed, sea grass and coral have got a lot of solar energy. Fish and crabs eat these producers. Different species of turtles also eat the sea grass, and they leave their eggs on the local beaches. Other consumers eat the smaller animals. Sea birds catch fish and crabs |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 42 • Refer students to the bold verbs. Tell them to use the Wordlist or their dictionaries to check the meaning of any verbs they do not know. • Refer students to the photos and ask them to choose the correct verbs Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 42 Students complete the exercise individually before checking their answer in pairs. Ex: 3 P: 42 • Remind students that they should look for the present continuous forms, not the verbs as they appear here. • Read the verbs and check understanding, then allow students time to read the spelling rules carefully Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students choose the correct verbs in bold ANSWERS: Kill Eat Hide Dig Protect Catch Fly climb
students complete the text with words in the box. ANSWERS: Extinct Pollution Climate Live Habitat Hunt swim Students complete the sentences with the present continuous ANSWERS: Students own answers |
Assessment criteria Writes correct verbs Descriptor: - choose the correct verbs in bold
Assessment criteria: - Identify numbers in a text Descriptor: -read the text again and find the numbers -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 28 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Skills Round - up. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.5.1 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 6.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in short, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topics 6.6.10.1 use present continuous forms with present meaning on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to an interview about animals. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. • Write about an animal and describe its behaviour. |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students if they ever read about animals. Ask them where you can read about animals. • Elicit some answers, for example in an encyclopedia, on the internet or in a magazine. Lead - In
Play a game to consolidate students’ understanding of the present continuous. Write on the board: What am I doing? Then mime an action, for example reading a book. Tell students they should ask you questions, and you will answer. For example: Are you reading a newspaper? No, I’m not reading a newspaper. Are you reading a book? Yes, I a |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 43 • Remind students of the importance of looking at photos before they listen to a text. Students identify the animals and say where they can be found. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 43 • Explain that students are going to listen to somebody talking about the photos. The first time they hear the CD, they should identify which ones are Jon’s., Ex: 3 P: 43 • Play the CD again for students to find the specific information to answer the questions.
Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Ex: 3 P: 43 • Read the task with the class and check everyone understands what to do. • Point out that at this stage they should use the questions to help them structure their ideas. They should work in pairs and make notes. |
Students look at the animals in the photos. Where can you see these animals? ANSWERS: From left to right, shark, dolphin, whale, crocodile, and they can all be found in water.
Students listen to a dialogue. Which are Jone’s two photo? ANSWERS: The second and fourth photos. Students listen again and complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 photos 2 swimming 3 dolphins and whales 4 more dangerous 5 India, Bangladesh 6 extinct 7 French 8 mobile phone Students work in pairs and prepare a dialogue ANSWERS: Students own answers |
Assessment criteria Descriptor: - look at the photo and describe what can they see?
Assessment criteria: - Identify numbers in a text -Learn and revise prepositions of place Descriptor: -read the text again and find the numbers -complete the sentences with the correct prepositions -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.38 Workshets CD 1.38 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 30 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
,
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Films and theatre |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn irregular verbs about acting in the present and past simple. • Learn how to compare answers. • Learn and use collocations about acting. |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students: What games do you like playing? • Elicit some answers and write them on the board. Try to elicit some traditional games and some computer games. • Ask: What’s your favourite game? Elicit some answers. Lead - In
Kazakhstan, 1729: A ferocious Mongol tribe sweeps across the steppes, and Kazakh sultans leave their people to fend for themselves. Young Sartai and other survivors flee to the mountains but revenge drives Sartai and his friends back to the steppe, where he falls in |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture love with the beautiful Zere, daughter of a local khan who chose to protect his village by working with the hated Mongols |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 44 • Read through the list of verbs with the class and make sure students understand them all. • Students find the past forms in the game. In a weaker class or if you are short of time, allow them to work in pairs and find four each Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 44 • Explain that these key phrases can all be used to compare ideas. Allow students time to read through the phrases, and encourage them to guess the answers. Ex: 4 P: 44 • Read the rules with the class. • Put students into teams of three or four. • Allow students time to read the first question and discuss their answers. Play the CD, pausing after the first answer. Check whether any teams have lost a life. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students check the meaning of the verbs and match these verbs with their past form ANSWERS: 1 broke 2 scored 3 ran 4 took part 5 won 6 played 7 beat 8 lost Students complete the key phrases with the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 answer 2 sure 3 agree 4 don’t 5 right 6 think Students match the verbs ANSWERS: 1 b 2 c 3 a 4 c 5 a 6 a 7 b 8 b 9 b |
Assessment criteria -Learn irregular verbs about acting in the present and past simple. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the verbs and match these verbs with their past form
Assessment criteria: - Learn how to compare answers. Descriptor: - complete the key phrases with the words in the box. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 32 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The action game |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn how to compare answers. • Learn and use collocations about acting. |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students: What games do you like playing? • Elicit some answers and write them on the board. Try to elicit some traditional games and some computer games. • Ask: What’s your favourite game? Elicit some answers. Lead - In
The best acting games are those that your child loves, and that helps them to explore and grow in new ways. Finding the right theater activities for your child is an adventure. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 4 P: 45 • Demonstrate how certain words from each group go together to make collocations. • Point out that there are only seven phrases in group B, so the words here can match with more than one verb. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 5 P: 45 • Read through the sports and games in the box and check understanding by asking for names of famous people who do these sports Ex: 6 P: 45 • Students complete the sentences with personalized information. • Go round and listen as they discuss in pairs. • Ask some students to report back to the class. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students match the verbs. With the phrases to make collocation. ANSWERS: act in a play Students match the words in the box to the pictures. ANSWERS: Picture 1 ice-hockey Picture 2 cycling Picture 3 athletics Picture 4 football Picture 5 swimming Picture 6 chess Picture 7 American football Picture 8 skateboarding Picture 9 tennis Students complete the sentences about performing so they are true for you. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. |
Assessment criteria - Learn how to compare answers Descriptor: - match the verbs. With the phrases to make collocation.
Assessment criteria: - Learn and use collocations about acting. Descriptor: - match the words in the box to the pictures. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 32 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 07.12.22 |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading: Video Games on! |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.4.1 respond with limited flexibility at sentence level to unexpected comments on an increasing range of general and curricular topics 6.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about video games. • Read for specific information. • Ask and answer questions about games. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to look at the pictures on page 70 and the title of the text. Ask what they think the text is about. • Elicit or teach the word video game and write it on the board Lead - In
Android games are diversified into many categories; informational, educational, shooting games, puzzles, sports, racing, augmented reality games, location-based games and more. All these types are available for both high end and low-end Android phones. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 46 Students look at the pictures. If they recognize the games, ask them to describe some details about the games. Picture 1 is a SIMS game, picture 2 is a Mario game. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 46 When students have matched the correct sentences, ask them to identify the extra sentence. Ex: 3 P: 46 • Ask students to read the verbs and find the nouns in the text, and work out the meanings. • Ask questions like What does a designer do? to elicit sentences using the verbs (He / She designs things). • In a stronger class, elicit some sentences using the new words. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students discuss the video games in the photo ANSWERS: Students own answers Students read the text and complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 d 2 b 3 e 4 a C is the extra sentence. Students find the nouns for these verbs in the article. ANSWERS: 1 designers 2 creator 3 entertainment 4 choice 5 player 6 imagination 7 memory |
Assessment criteria - Read about video games. Descriptor: - discuss the video games in the photo
Assessment criteria: - Read for specific information. Descriptor: - find the nouns for these verbs in the article. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.41 Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 32 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Past Simple |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others plans on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.6.9.1 use simple past regular and irregular forms to describe past events on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the difference between regular and irregular verbs in the past simple. • Practise using the Irregular verbs list. • Use regular and irregular verbs to play a true and false game about activities in the past. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they can remember any of the irregular verbs they learnt at the beginning of the unit. • Ask students if they can remember any verbs that are regular • Elicit some examples and write these on the board. • Ask: How do you know if a verb is regular or irregular? Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 47 Refer students to the sentences and ask the question to the whole class Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 47 • Remind students to look at the sentences in exercise 2 as well as the main text.\ • Refer students to the Irregular verbs list in their Workbooks to check their answers Ex: 4 P: 47 Read the example with the class. Point out that students must write two sentences for each answer, one negative and one affirmative. • Students write their sentences individually, then compare with a partner Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students look at the forms of play and make in the sentences. ANSWERS: 1 Play is regular because the past simple affirmative form is made by adding -ed. Students find the past simple forms of these verbs. ANSWERS: Regular verbs: designed, preferred, created Irregular verbs: sold, bought, became, thought, built, took Students make affirmative and negative sentences. ANSWERS: 1 I didn’t have a sandwich for lunch. 2 I didn’t meet my friend in town. 3 We didn’t go to a café. 4 I didn’t read a book in bed. 5 We didn’t eat at home on Friday. 6 I didn’t write a letter to a friend. Affirmative sentences are students’ own answers. |
Assessment criteria - Learn the difference between regular and irregular verbs in the past simple. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the verbs and match these verbs with their past form
Assessment criteria: - Practise using the Irregular verbs list. Descriptor: -make affirmative and negative sentences. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 33 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Describing People |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 6.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn adjectives to describe people. • Practise describing people. • Listen to an interview about a crime and some suspects. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, tell students you are going to describe someone in the class and they must guess who it is. • Choose a student and, without saying their name, describe them to the class. For example: This student is quite short and she’s got long blonde hair Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 48 • Refer students to the illustrations and ask: What is an avatar? Elicit some ideas. In a weaker class, accept answers in their own language. Ask students if any of them use an avatar. • Refer students to the missing words. Ask students to work in pairs and complete the guide. • Check answers with the class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 48 • Refer students to the pictures and the descriptions. • Students complete the descriptions individually. Ex: 3 P: 48 Allow students time to read the introduction. Play the CD and ask: Who did the waitress see in the cafe? Differentiation: Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Ex: 4 P: 48 • Allow students time to read the questions, then play the CD again. • After checking, elicit ideas from the class about who the murderer was. |
Students complete in the character guide with the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 slim 2 dark 3 curly 4 blue 5 moustache Students complete the descriptions with words in exercise 1 in pairs ANSWERS: 1 blue, short 2 tall, long 3 short, glasses 4 fat, moustache Students read the text about TV programme ANSWERS: The waitress saw three different people in the café. Students listen the text again and answer the question. ANSWERS: 1 No, she didn’t. 2 She sat by the window. 3 No, she left at ten past eight. 4 He talked to Koji. 5 Yes, she was with the man with a beard. 6 She bought a coffee for Koji. 7 No, there wasn’t a man with long black hair. 8 No, he didn’t. |
Assessment criteria - Learn adjectives to describe people. Descriptor: - complete in the character guide with the words in the box.
Assessment criteria: - Listen to an interview about a crime and some suspects. Descriptor: - read the text about TV programme -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Worksheet
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 34 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Past Simple: questions |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others plans on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.6.9.1 use simple past question forms to describe past events on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn question forms of the past simple. • Practise asking questions in the past simple. |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, remind students about Detective Lambert’s visit to the Corner Café, on page 72. • Ask: What did he do when he went to the café? Elicit that he interviewed the waitress and asked her questions. • Ask students if they can remember any of the questions he asked. Elicit some questions, but do not write them on the board, as students probably will not get the form correct at this stage Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 49 • Students refer back to exercise 4 on page 72 and complete the questions. • Check answers by asking students to read out the completed questions. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 49 • Read the task with the class. In a weaker class, model the example exchange. In a stronger class, ask students to read this out, then to think of another example using the prompts. • Allow students time to write the questions individually, then go round and listen as they ask and answer in pairs. Differentiation: Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Ex: 4 P: 49 • Look at the words in the box with the class. Elicit that they are question words, and that they are used in questions to find out specific information. • Explain that students will need to read the answer carefully to work out which question word is needed, and transform the verb in the question into the correct form to complete the answer |
Students complete the question from exercise 4 on page 48 ANSWERS: 1 speak 2 did 3 Did 4 have Students write questions in the past ANSWERS: 1 Did you read a book in bed? 2 Did you buy clothes last weekend? 3 Did you come to school on the bus this morning? 4 Did you go to bed early? 5 Did you have a lot of homework last night? 6 Did you eat chocolate yesterday? 7 Did you use a computer at school? 8 Did you phone a friend? Students complete the questions and answers in the dialogue. Use the question words in the box and the past tense of the verbs in brackets. ANSWERS: 1 What time 6 talked 2 came 7 What 3 Where 8 drank 4 sat 9 When 5 Who 10 died |
Assessment criteria - Learn question forms of the past simple. Descriptor: - write questions in the past
Assessment criteria: - Practise asking questions in the past simple. Descriptor: - complete the questions and answers in the dialogue. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Worksheet
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 35 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Speaking: Talking about past events / Summative assessment for the unit “Drama and comedy” |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 6.4.2.1 (6.R2) Understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 6.5.2.1 (6.W2) Write with some support about real and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a limited range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a conversation about past events. • Listen and identify intonation to show interest or boredom |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to name some activities they enjoy doing. Write ideas on the board. Then ask them to name some activities they do not like, and write these on the board. You will probably find that students have different opinions on the activities. Lead - In
Tom: Hi! Sara. Where did you go yesterday? Sara: I went to the shopping.
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 2 P: 50 • Tell students to read the dialogue carefully and look at the sentences on both sides of the gap before choosing the answer Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 50 • Make sure that students understand what intonation is. If necessary, write a sentence on the board (for example: I watched TV last night.) and say it with different kinds of intonation, sounding interested or bored. • Play the CD. Students decide whether the speakers are interested or bored. Summative assessment for the unit “Drama and comedy” Reading Task 1. Read about a famous movie’ Life of Pi’ and do the task below Circle True or False for these sentences. 1. Pi moves to Canada in 16. True False 2. Pi is scared when he sees the animals in the lifeboat. True False 3. Pi fights with a big shark. True False 4. At the end they land in the USA. Writing Task 2. Look at the facts about a famous cartoon ‘Rio 2’. Write 2 paragraphs using the information below. |
Students complete the dialogue with sentences. ANSWERS: 1 d 2 b 3 a 4 c Students listen to the intonation.Is the speaker interested or bored. ANSWERS: 1 bored 2 interested 3 bored 4 interested 5 bored 6 interested Students read about a famous movie’ Life of Pi’ and do the task below Circle True or False for these sentences. ANSWERS: 1 true 2 true 3 false 4 false Students writes strong lead sentence using given structure; |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a conversation about past events Descriptor: - complete the dialogue with sentences
Assessment criteria: - Listen and identify intonation to show interest or boredom Descriptor: - listen to the intonation. Is the speaker interested or bored -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 35 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Writing: A profile. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model text. • Learn key phrases for writing about a famous person. • Learn about also. • Write a profile of a sportsperson. |
||
|
Value links |
Integrity – Integrity is the quality of having strong moral principles. So, a person with integrity will always act with honesty and adhere to their own moral code regardless of what others do. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Write a few names on the board, then ask: What do you know about this person? Elicit some sentences using the present tense (e.g. she’s a singer) and the past simple (e.g. she started singing when she was ten). Lead - In
The one who believed in himself when no one else did. The world famous people Indian actor Shahrukh Khan was so broke, he had to sleep on streets and sell tea in a cinema to make ends meet. Today he is one of the most Famous People on the planet! |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 51 • Read the questions with the students. Ask them how their answer to question 1 can help them answer the others. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 51 • In a weaker class, ask students to identify the paragraph topics by referring them to question 1 in exercise 1. Ex: 3 P: 51 Students read the rules and choose the correct answers. • Check answers with the class |
Students read the text and answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 Paragraph 2 is about his career in general, paragraph 3 is about the things he won and paragraph 3 is about personal details. 2 In Madeira, Portugal 3 1 metre 85 centimetres. 4 He played for Sporting in Portugal. 5 In 2007 Students study the key phrases. Match the phrases with the three paragraphs in the model texts. ANSWERS: 1 paragraph 1 5 paragraph 1 2 paragraph 2 6 paragraph 2 3 paragraph 3 7 paragraph 3 4 paragraph 1 Students read the rule and the examples. Then choose the correct position for also in sentences. ANSWERS: 1 also lost 2 He’s also 3 also went 4 was also Students writes strong lead sentence using given structure; |
Assessment criteria - Study a model text. Descriptor: - read the text and answer the questions
Assessment criteria: - Learn about also Descriptor: - choose the correct position for also in sentences -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 37 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Kazakh films |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.4.1 respond with limited flexibility at sentence level to unexpected comments on an increasing range of general and curricular topics 6.6.15.1 use common verbs followed by infinitive verb / verb + ing patterns on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • To read and understand a text about an important figure in films and theatre in Kazakhstan. • To learn and practise verb patterns verb + -ing and verb + to infinitive |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Books closed. Write ‘Kazakh actors’ on the board. Allow students about three minutes to work in pairs and to tell their partners who their favourite Kazakh actors are and why they like them. Get feedback from the class by asking a few students to say who their favourite actors are and why they like them. Lead - In
Doskhan Zholzhaksynov’s ‘Kunanbay’ was awarded with the State Prize in Literature and Art. The film was recognized the best one in Central Asia at the Eurasia International Festival. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 2 P: 52 Ask a few confident students if they like going to the cinema or theatre, and why. What the last film or play they saw was and who the actors were. Finally, ask them if they liked it or not. When you have modelled the conversation put students in pairs and ask them to ask and answer the questions themselves Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 52
Focus students’ attention on the name in
the title of the text. Ask them what they know about Asanaly
Ashimov. Students read and listen to the text and answer the
questions individually, before checking them in pairs. Go through
the answers with the class. Ex: 2 P: 52 -Ask students if they like acting. Then ask if they like to go to the cinema. Elicit the verb patterns that you are using and write them on the board. Point out that there are two patterns for the one verb. -Draw students’ attention to the words in blue in the text and the sentences in exercise 3 |
Students work in pairs. Ask and answer the questions. ANSWERS: Students own answers Students read and listen to the text and write true or false. ANSWERS: 1 False. He grew up in a village. 2 False. He made his first film while he was still a student. 3 True 4 False. Kyz-Zhibek was extremely popular. 5 True 6 True Students look at the words in blue in the text. Choose the correct word to complete the sentences. ANSWERS: 1 acting / to act 2 to go 3 to watch 4 working / to work 5 waiting / to wait 6 acting 7 to buy 8 eating Students writes strong lead sentence using given structure; |
Assessment criteria - To read and understand a text about an important figure in films and theatre in Kazakhstan. Descriptor: - Ask and answer the questions.
Assessment criteria: - To learn and practise verb patterns verb + -ing and verb + to infinitive Descriptor: - Choose the correct word to complete the sentences. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 38 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
summative assessment for the 2 term |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.L6 Deduce meaning from context in supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.R3 Understand the detail of an argument on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 6.W8 Spell most highfrequency vocabulary accurately for a limited range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics 6.S7 Use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -True/False tasks require learners to indicate whether the provided option right or wrong. -Gap filling tasks is a task in which words/numbers are removed from a text and replaced with spaces. Learners have to fill each space with the missing word/number or a suitable word. |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Lead - In summative assessment for the 2 term Listening Task.1 Listen to the conversation between Harry and Elizabeth twice. Transcript for listening task can be found after the mark scheme. Teacher reads the transcript. Mark sentences as True or False. 1 A horror movie is scary. True False 2 Harry likes movies about love. True False 3 Harry really hates action and adventure movies True False Fill in the gaps with ONE word. 4 Musicals do not sound too ___________________ for Harry. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students listen to the conversation and write true or false ANSWERS: 1 true 2 false 3 false 4 exciting 5 killer |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
5 I heard it's pretty exciting because nobody can guess who the ______________________ is.
Reading Task. Read the text about Alex’s hometown. My town – Newquay Newquay is a small town on the Atlantic coast in the south of England. It has got great beaches and is the best place to surf in the United Kingdom. There are lots of surf schools where you can learn how to surf. I go surfing with my friends every weekend.
Circle the 3 things Alex writes about. A Rainy weather in Newquay B Water activities in Newquay, C Interesting history of Newquay D Water attraction to visit in Newquay E Tasty meals in Newquay F Location of Newquay in England
Complete the sentences below follow the sentence structure: 4 Alex likes Newquay because he can go … 5 While coasteering you should always take a special instructor with you because it involves…
Writing Task. Choose ONE of the topics below. Follow the tips for writing Topic 1. Our countryside Think about your home place (home town or village) and write some information about it. Topic 2. Drama and comedy Think about your genre preferences and write some information about your experience. Speaking Task. Choose one of the cards and prepare an individual talk. Provide own experience on topics, using appropriate subject-specific vocabulary. You have 1 minute to prepare and 1-2 minutes to talk |
Students read the text about Alex’s hometown and circle the 3 things Alex writes about ANSWERS: B) Water activities in Newquay D) Water attraction to visit in Newquay F) Location of Newquay in England Students choose ONE of the topics below. Follow the tips for writing ANSWERS: Students own answers Students choose one of the cards and prepare an individual talk. ANSWERS: Students own answers
|
Assessment criteria - True/False tasks require learners to indicate whether the provided option right or wrong. Descriptor: - listen to the conversation and write true or false
Assessment criteria: - Learners have to fill each space with the missing word/number or a suitable word. Descriptor: - read the text about Alex’s hometown and circle the 3 things Alex writes about -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 38 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL: Technology |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.4.1.1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about the internet. • Read a text about the internet. • Learn how to recognize which country website addresses come from. |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the word internet on the board. • Ask students if they use the internet, and how often. Ask if they think it is important in modern life. • Elicit some ideas, and write these on the board. • Tell students they are going to read a text about how people use the internet. Lead - In
Internet and Information technology concept. internet connection on a smart phone for sharing and doing anything |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 2 P: 53 • Refer students to the introduction only. Ask them to read it through, then discuss the activities in blue with the class Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 53 • Read the question with the class to check students understand what information they should listen for. • Play the CD once while students listen and read the text for general information. •
Check the answer with the class. If
students find this difficult, explain that the internet is a
network of computers around the world that share information, and
the World Wide Web is all the information that is stored on the
internet, as websites Ex: 3 P: 53 • Allow students time to read the questions first. • Students read the whole text again more carefully and answer the questions. |
Students read the introduction on the text. Which of the things in blue do you do on the internet? ANSWERS: Students own answers Students read and listen to the text. What invention was very important for the development of the internet. ANSWERS: The World Wide Web, invented by Tim Berners-Lee. Students read the text again and answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 It was called ARPANET. 2 Universities used it 3 He sent the first email message. 4 He worked in Geneva, and it represented Switzerland. 5 There were millions of websites and it wasn’t easy to find information. |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for talking about the internet. Descriptor: - read the introduction on the text Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Read a text about the internet Descriptor: - read the text again and answer the questions -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 38 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project: Trump card game. Review |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Play the trump card game and guess the identity of famous people. • Follow the steps in a project checklist. • Create a trump card with clues about famous people. |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, tell students you are going to give them clues about a famous person, and they must guess the identity of the person. • Give these clues for David Beckham in order, pausing after each one for students to guess the answer: He’s a sportsman. He’s a football player. He’s English. He’s got a famous wife Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 55 • Read the rules with the class and check understanding. Ask students to play the game with a partner. They should each choose one of the cards and ask the questions on it. At this stage, it does not matter if they see each other’s cards, the important thing is that they learn the process of the game. • Check answers with the class and ask a few students how many points they scored. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 55 Tell students that they are now going to make their own trump cards. • Go through the points in the project checklist. Check students understand each of these.
Ex: 2 P: 55 When all the cards are completed, set aside time in class to do further work with them. Put students into groups of six to play the game. Ask them to exchange trump card clues and guess the famous person. Tell them to note down their score. • When students have finished, ask them to change partners and repeat the process four or five times, noting down their score each time. • Ask students to add up their scores. The student with the highest score is the winner. |
Students read the rules and the trump card game with a partner. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. The people are Tobey Maguire and Christopher Columbus Students make a trump card and follow the steps ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. Students play the trump card game with five people in class. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers |
Assessment criteria - Play the trump card game and guess the identity of famous people Descriptor: - read the rules and the trump card game with a partner.
Assessment criteria: - Follow the steps in a project checklist. Descriptor: - make a trump card and follow the steps -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 38 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our health |
Lesson 49 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Activities in and out of school |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 6.2.1.1 understand a sequence of supported classroom instructions 6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for school and free-time activities. • Do a general knowledge quiz. • Learn how to talk about school routines. • Write sentences about your routines. |
||
|
Value links |
Family – Family values are moral and ethical principles of typical family life, including sacrificing for loved ones, putting your loved ones first, and keeping your loved ones at the centre of your thoughts and actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students: What do you usually do at the weekend? Elicit ideas and write them on the board. • Ask: What activities do you do at school? Elicit some ideas and write them on the board. Lead - In
The School’s Out team is made up of a blend of different backgrounds and specialities to ensure we deliver the best camp experience to all children. From qualified Primary School Teachers to experienced Sports Coaches, our team is driven to providing premium holiday activities. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 56 Point out the full forms of PE and ICT. • Ask students to match the words individually, then compare their answers in pairs. • Check answers, and check understanding of the remaining words in the box. Drill the pronunciation of any unfamiliar words Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 56 • In a weaker class, allow students to do the quiz in pairs. • If you have time to extend this activity, you can let them look up answers they do not know. • Check answers with the class. Find out who got the most correct answers. Ex: 23 P: 56 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meanings. • Point out that several combinations are possible. Students must think carefully about meaning and make logical combinations. |
Students with photos. ANSWERS: 1 football 2 ICT 3 maths 4 chess 5 art 6 science 7 geography 8 drama Students do the Test your knowledge ANSWERS: 1 a 2 c 3 a 4 c 5 b 6 b 7 c 8 b Students check the meaning of phrases with the words in blue ANSWERS: 1 dance/basketball/music/chess/football practice 2 maths/science/history/geography/French/music/ICT test 3 maths/science/history/geography/French/music/ICT/art homework 4 ICT/PE/drama/maths/science/history/geography/French/ dance/art/music class. 5 maths/science/history/geography/French/art/music/ ICT exam 6 football/basketball match |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for school and free-time activities. Descriptor: - match eight of words in the box Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Do a general knowledge quiz. Descriptor: - do the Test your knowledge -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 40 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our health |
Lesson 50 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading: School life |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about life at a boarding school. • Read for specific information. • Talk about your school and give your opinion about boarding schools. |
||
|
Value links |
Loyalty – Loyalty might be a core personal value to you if you highly prize friends that are reliable and trustworthy. You might put your friends or chosen family first, always being there for them when they need you. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Write the word boarding school on the board and elicit or explain that it is a school where children also live during term time. • Ask students if they would like to go to a boarding school. Lead - In
The school life is the best life. Most children enjoy going to school in the early years of schooling. A man, who has been the student, knows what school life is. During their early primary years, children will learn the basics of reading, writing, and arithmetic while getting to know new friends |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 58 • Discuss the questions with the class and write their ideas on the board. Background There are hundreds of boarding schools in Britain. Most are private, for which parents pay fees, but there are also a few state boarding schools. Boarding schools were declining in popularity, but have enjoyed a revival following the success of the Harry Potter books and films Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 58 • Ask students to read the text quickly and count the number of paragraphs (seven). • Then ask them to read through the questions. Explain that seven of these will match the paragraphs. Check students understand the questions. You may need to pre-teach homesick and typical. • Play the CD. Students listen and read Ex: 23 P: 58 • In a weaker class, tell students to underline the parts of the text where they find the answers. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs, then check with the class |
Students read the text and discuss about Bilim Innovation Lyceums ANSWERS: Students’ own answers Students read about Bibit’s school and match questions ANSWERS: a 2 b 6 c 1 d not used e 3 f 7 g 4 h 5 Students read the text again and answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 8.30 2 Three times a week. 3 In a break before they do their homework. 4 To the swimming pool. 5 His two best friends. 6 Three times a year in the holidays. |
Assessment criteria - Read about life at a boarding school. Descriptor: - read the text and discuss about Bilim Innovation Lyceums Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Read for specific information. Descriptor: - read about Bibit’s school and match questions -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 40 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our health |
Lesson 51 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Can for ability and permission. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.6.13.1 use might may could to express possibility on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics 6.5.8.1 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the form and use of can for ability and permission. • Write sentences about your abilities using can. • Learn how to request, give and refuse permission. • Practise a dialogue in which you ask for permission. |
||
|
Value links |
Fairness – If you value fairness, you might be highly sensitive to situations at school or in the workplace where a teacher or a peer has exhibited favoritism or allowed someone to get away with living by a different set of rules to everyone else. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask individual students questions using can, for example: Can you swim? Can you play the guitar? • Ask students to find examples of can in the text on page 50. • Discuss the examples with the class and elicit that we use can to talk about abilities or permission Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 59 • Ask students to read the sentences carefully, then answer the questions. • Make sure that students understand the meaning, for example by asking them to translate the sentences into their own language Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 59 • Students identify the use of can in the sentences individually. In a weaker class, check understanding by doing the first item together as an example. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs before you check with the class Ex: 23 P: 59 • Read the example with the class and elicit one or two more examples of sentences using can for ability. • Go through the ideas in the box and check understanding. In a stronger class ask students to write more sentences, using their own ideas. • Students write their sentences individually. In a weaker class, check students’ answers at this point before they go on to ask and answer. |
Students look at the sentence and answer the question ANSWERS: 1 a and d 3 can’t 2 b, c and e 4 No, we don’t. Students look at the sentences and write P (permission) or A (ability) ANSWERS: 1 A 2 P 3 A 4 P 5 P 6 A Students write sentences about your ability ANSWERS: Students’ own answers I can play chess. I can speak three languages I can run one killometre |
Assessment criteria - Learn the form and use of can for ability and permission. Descriptor: - look at the sentence and answer the question Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Write sentences about your abilities using can. Descriptor: -write sentences about your ability -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 41 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our health |
Lesson 52 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Food and drink. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.5.5.1 link without support sentences using basic coordinating connectors |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for food and drink. • Listen to a report about healthy eating in schools. • Practise extending vocabulary. |
||
|
Value links |
Honesty – You may highly value telling people the truth. This one gets tricky when being honest can be hurtful to others. So, a person who really puts honesty first might be the sort of person who will tell the truth even if it hurts to do so. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask individual students what they have for lunch when they are at school. • If there is a school canteen, ask if the meals are healthy. • Ask students if they make an effort to eat healthy food. Lead - In
Lemonade and summer go hand-in-hand. This quintessential refreshment is also the perfect companion for a fresh and fruity appetizer like this strawberry fields salad. For an added burst of strawberry flavor, try making a strawberry-lemonade variation (recipe below)! |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 60 • Students work in pairs to match the words with the pictures. Point out that not all the words in the box are needed. • Play the CD for students to check their answers. • Check that students understand the meaning of all the words. Play the CD again and get students to repeat. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 60 • Remind students that a useful way to learn vocabulary is to put new words in groups and list them in their vocabulary notebooks. • Check students understand the first word in each group. • Students copy the word groups and add two more words to each group. They can use dictionaries for this. In a stronger class, tell them to find four more words. Ex: 3 P: 60 • When students have done the questionnaire, discuss their responses and ask if they agree with the key Ex: 5 P: 60 • Explain that students are going to listen again for specific information. Allow them time to read the sentences and the multiple choice options. • Play the CD twice. Students answer the questions while they listen. |
Students match in the photos with words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 soup 9 ice cream 2 water 10 fizzy drink 3 fish 11 chips 4 rice 12 burger 5 salad 13 sweets 6 cheese 14 juice 7 meat 15 sandwiches 8 beans 16 crisps . Students think of two more words to add to each group ANSWERS: Students’ own answers Students ask and answer the questions with a partner ANSWERS: Students’ own answers Students listen to the programme again and choose the correct answers ANSWERS: 1 Some 2 many 3 There are a lot of 4 eat 5 isn’t much |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for food and drink. Descriptor: - match in the photos with words in the box. Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Listen to a report about healthy eating in schools. Descriptor: - listen to the programme again and choose the correct answers -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our health |
Lesson 53 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Countable and uncountable nouns. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 6.6.2.1 use quantifiers many, much, a lot of ,a few on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.3.2.1 ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn about countable and uncountable nouns. • Learn the difference between a / an, the, some, any, much, many and a lot of. • Write about what you usually eat and drink. |
||
|
Value links |
Generosity – This may be a core value of yours if you cherish people who will give their time and resources to people in need. You may consider yourself to be a generous person if you find joy and meaning in giving to others. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students what kinds of foods they like. Elicit some words and write them on the board, for example: bread, chips, vegetables, fish, meat. • Point out that some words are in the singular and some are plural. Elicit that some are countable nouns and some are uncountable Lead - In
It's important to distinguish between countable and uncountable nouns in English because their usage is different in regards to both determiners and verbs. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 61 • Read the rules with the class, and allow students time to read through the text quietly. • Students work individually to match the words from the text to the rules, then compare their answers in pairs. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 61 • Students now put the rules into practice by completing the text. • In a weaker class, allow students to do this in pairs. • Check answers with the class. Encourage students to explain their choices, making reference to the rules. Ex: 3 P: 61 • Refer students to the pictures and elicit that they are made of different foods. Identify some of the foods as a class before they start. • Students complete the table. In a stronger class, ask if students can think of more food for each category |
Students study the rules and match the words in blue. ANSWERS: a shop rule 1 a sandwich rule 2 the school cafeteria rule 3 the shop rule 4 Students complete the text with a / an and the ANSWERS: 1 a 2 the 3 a 4 a 5 a 6 a 7 the 8 the Students look at the pictures and complete the table with the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 rice 2 cheese 3 water 4 vegetables 5 pears 6 crisps |
Assessment criteria - Learn about countable and uncountable nouns. Descriptor: - study the rules and match the words in blue. Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Write about what you usually eat and drink. Descriptor: - look at the pictures and complete the table with the words in the box. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 43 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our health |
Lesson 54 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Speaking: Making, accepting and refusing invitations |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a conversation about making, accepting and refusing invitations. • Learn key phrases for making, accepting and refusing invitations. • Listen to three dialogues about invitations. • Practise a dialogue about making, accepting and refusing invitations. |
||
|
Value links |
Integrity – Integrity is the quality of having strong moral principles. So, a person with integrity will always act with honesty and adhere to their own moral code regardless of what others do. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students to the photograph and ask: What do you think Jake and Tina are talking about? . • Suggest that they might be arranging to meet, and then ask: What do you think they are saying? Elicit some phrases they might be using to invite each other to do something. Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 62 • In a weaker class, read through the questions with the class and check understanding before they ask and answer. • Allow students a few minutes to talk, then ask a few individuals for their ideas. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 62 • Read the task with the class and explain that they should listen to answer the general question. • When students have listened to the CD, ask the question for the class to answer. Ex: 23 P: 62 • Read through the key phrases and check understanding. • Students can use the main dialogue as a guide to help them complete the gapped dialogue. • After they have listened to the CD to confirm the answers, students can practise the dialogue in pairs |
Students answer the question with a partner ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. Students listen to the dialogue. Can Tina go to the shopping centre on Saturday? ANSWERS: Yes, she can. Students complete the dialogue with the key phrases. ANSWERS: 1 Are you busy 2 Do you want 3 No, sorry; I can’t. 4 That’s a pity. 5 Sounds good |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a conversation about making, accepting and refusing invitations Descriptor: - answer the question with a partner Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for making, accepting and refusing invitations Descriptor: - complete the dialogue with the key phrases. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 5 P: 43 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our health |
Lesson 55 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Writing:An email about school |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model email. • Learn key phrases for writing emails. • Learn about giving examples. • Write an email about your school. |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students: Do you send emails? Who do you send them to? Elicit some ideas. • Ask: What kind of language do you use in emails? Elicit that we use informal language. Lead - In
How to write an email to your teacher.Tip #1: Be respectful Tip #2: Always include your name Tip #3: Drop the text lingo Tip #4: Know when to talk to your teacher in person Tip #5: Check your inbox for a response |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 63 • Refer students to the email and ask: Who is the email from? What greeting does the writer use? (Hi!) What ending does the writer use? (Bye for now.) • In a weaker class, students can answer the questions in pairs. Ex: 2 P: 63 • Read through the key phrases with the class. • Ask students to find the phrases in the email and complete them. • Ask students to translate the phrases into their own language. • Model pronunciation, and ask students to repeat the phrases Ex: 3 P: 63 • Elicit examples from the model text. • Students complete the sentences with their own ideas. • Ask some students to read out their sentences to the class. • Point out that we use a comma before such as and for example, but not before like
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. |
Students read the model text and answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 To give her exchange student some information about her school. 2 The email is informal 3 Paragraph 3 4 Paragraph 4 5 Five: English, maths, science, geography, and French. Students complete the key phrases for giving information. ANSWERS: 1 some; about 2 starts; there are 3 classes; long 4 All; can 5 after Students use like, for example and such as to give examples. Find examples of these in the text. ANSWERS: ... subjects like geography and French. There are clubs after school, for example,drama ... ... snack food, such as sandwiches and pizza ... |
Assessment criteria - Study a model email. Descriptor: - read the model text and answer the questions Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for writing emails. Descriptor: - complete the key phrases for giving information. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 45 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our health |
Lesson 56 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My Country. Almaty Marathon |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 6.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.6.2.1 use quantifiers many, much, a lot of ,a few on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a text about the Almaty Marathon • Revise and learn nationality words • Learn how to use something, anything, nothing, ever and every • Make a video about fitness training |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Books closed. Put students into small groups. Ask them to discuss what sports they do and whether they do any extra fitness training. Ask the groups to feedback what they found out about each other and who does the most exercise / training. Lead - In
The seventh Almaty Marathon has come to an end, but emotions and impressions are still being discussed by the participants. Some of them remembered new tracks, or added a new medal and start number to their collection, some are preparing for new starts. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 64 Students quickly read the text and find the country words. Tell them to write a list in their notebooks with the nationality word next to it in English. Students may need to use their dictionaries for any new nationalities such as Norwegian. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 64 Focus students’ attention on the questions. Give them a minute to read them before playing the recording for students to listen to while they read. Students check their answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. Ex: 3 P: 64 -Draw students’ attention to the blue words in the text. Ask them to read out the sentences they are in and write them on the board. Tell students to look at the sentences and in pairs look at the rules 1–4. -Go through the answers with the class. Make sure they understand that anything is used in questions and negative - not affirmative - sentences. Also point out that in English a double negative = a positive. For example, I don’t have nothing means I have something. |
Students listen and read the text quickly. Which nationalities run in the Almaty Marathon ANSWERS: Russia – Russian Kyrgystan – Kyrgyzstani The UK – British Italy – Italian Spain – Spanish Denmark –Danish Norway – Norwegian Kazakhstan – Kazakh Students read the text again and choose the correct answers. ANSWERS: 1 a 2 b 3 c 4 a 5 b Students look at the words in blue in the text. Complete the rules ANSWERS: 1 something I need something to eat. 2 anything, nothing I didn’t do anything. I’ve got nothing to do. 3 every Every Monday evening I go to music school. 4 each We give food to each of the |
Assessment criteria - Read a text about the Almaty Marathon Descriptor: - listen and read the text quickly. Which nationalities run in the Almaty Marathon Assessment criteria: - Learn how to use something, anything, nothing, ever and every Descriptor: - look at the words in blue in the text. Complete the rules -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 45 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our health |
Lesson 57 |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Physical Education: Rules of a game |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about the rules of a game. • Read a text about basketball. • Practise talking about the rules of a game. |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students: What’s your favourite game? Elicit a few ideas and write them on the board. • Point to one of the games and ask: How do you play this game? Elicit some ideas. Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 65 • Students work in pairs to match the verbs with the actions in the pictures. If students find this difficult, remind them to look closely at the arrows for clues if necessary. • Check answers by calling out the picture numbers at random and asking students to say the verbs Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 65 • Refer students to the photo and the title of the text, and elicit that it is about basketball. • Read the question with the class, then play the CD and ask students to read and listen for the information to answer this gist task. • Elicit the answer to the question. Ex: 23 P: 65 • Students work individually to read the text again more closely and answer the questions. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs, and check any answers they disagree on. • Check that students understand the use of can / can’t for permission when talking about rules. |
Students match the verbs in the box with actions ANSWERS: 1 kick 2 catch 3 pass 4 bounce 5 shoot 6 score 7 throw Students read and listen to the text. how many players are there on the court in a basketball game? ANSWERS: There are ten players on the court. Students read the text again and answer the questions. ANSWERS: 1 It’s from North America. 2 Substitutes change with others during the match. 3 Forty-eight minutes long. 4 You can use one hand to bounce the ball. 5 No, you can’t kick the ball. 6 The other team gets the ball. |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for talking about the rules of a game. Descriptor: - match the verbs in the box with actions Assessment criteria: - Read a text about basketball. Descriptor: - read and listen to the text. how many players are there on the court in a basketball game? -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 46 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our health |
Lesson 58 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review 5 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.5.1 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 6.5.6.1 link, with some support, sentences into a coherent paragraph using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: Use vocabulary for school and free-time activities Write sentences using can or can’t |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students: What do you usually do at the weekend? Elicit ideas and write them on the board • Ask: What activities do you do at school? Elicit some ideas and write them on the board • Ask individual students questions using can, for example: Can you swim? Can you play the guitar? Pre-teaching
Go camping- Go fishing- Go for a bike ride- Go for a walk- Go out for a drink- Go out for dinner- Go shopping- Go to a concert- Go to a party-
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 66 • Ask students to match the words individually, then compare their answers in pairs. • Check answers, and check understanding of the remaining words in the box. Drill the pronunciation of any unfamiliar words Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 66 Students do the exercise individually and check their answers in pairs. Ex: 3 P: 66 In a stronger class ask students to write true sentences, using can or can’t • Students write their sentences individually. In a weaker class, check students’ answers at this point before they go on to ask and answer. |
Students match the words in the box with sentences ANSWERS: 1 chess 2 history 3 ICT 4 PE 5 break 6 maths 7 exam 8 music Students complete the list with the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 basketball 2 French 3 class 4 juice 5 chips 6 pears Students write true sentences with can or can’t ANSWERS: I can play tennis I can’t swim one kilometre I can’t speak Mandarin I can’t stand on my hands I can cook Pizza |
Assessment criteria - Use vocabulary for school and free-time activities Descriptor: - match the words in the box with sentences Assessment criteria: - Write sentences using can or can’t Descriptor: - write true sentences with can or can’t -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 46 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our health |
Lesson 59 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project: My Dream school. Summative assessment for the unit “Our health” |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.2.7.1 (6.L7) Recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) in supported extended talk on a limited range of general and curricular topics 6.3.5.1 (6.S5) Keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Create a poster about a dream school. • Follow the steps in a project checklist. • Identify the position of speakers in an extended talk with support |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students to list three positive points about their school. Discuss these as a class, then ask for students’ ideas about any ways they could change their school. Do not go into too much detail at this stage, but write their ideas on the board Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 67 • Put students into groups of four or five. Read through the questions with them and check understanding. • Remind students to use the questions to help them focus their discussion. • It will be helpful if they make notes at this stage. You might like to nominate one person in each group to make notes. • Go round and listen as students talk. Check that they are focusing on the specific questions, and encourage them to give reasons for their ideas. Ex: 2 P: 67 • Students read through the text individually, then discuss the question in their groups. You could ask for feedback at this stage to find out how many of the ideas in the text had been covered in the students’ discussions. • In a weaker class, help with any vocabulary in the text that students find hard, or refer them to a dictionary Summative assessment for the unit “Our health” Listening Task 1. Listen to the talk twice and circle the correct answer. Go to this link to listen: https://listenaminute.com/h/health.html. Transcript can be found after the rubrics.
Speaking Task 2. The learners are arranged in pairs. It is a two-way conversation. You have 1 minute to prepare and 2 minutes to talk on the topic. |
Students work in groups and answer the question. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. Students read the text. How many of the ideas are the same as yours. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. Students listen to the talk twice and circle the correct answer ANSWERS: 1 A 2 C 3 B 4 A 5 B Students the learners are arranged in pairs |
Assessment criteria - Create a poster about a dream school. Descriptor: - work in groups and answer the question Assessment criteria: - Identify the position of speakers in an extended talk with support Descriptor: - listen to the talk twice and circle the correct answer -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 46 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Travel and holidays |
Lesson 60 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Travel equipment |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.5.8.1 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics of familiar general topic 6.3.3.1 give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for travel equipment. • Do a Rainforest Survival quiz. • Learn about imperatives. |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the word rainforest on the board and elicit the meaning. • Teach the words expedition, survival and survive. • Ask students what they think it is like on an expedition in a rainforest. Ask what they think the dangers are, and if it is difficult to survive. Ask: What do you need to take with you when you go to the rainforest? Elicit some ideas and write them on the board. Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 68 • Encourage students to read all the words carefully. Point out that four of them are not shown in the photo. • After listening, check that students understand all the vocabulary, and drill pronunciation of any words that are new to students. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 68 • Students do the quiz individually. In a weaker class, they can work in pairs. • Ask them to work in pairs to add up their scores and read the key. Ask them to discuss whether or not they agree with the key. Ex: 3 P: 68 • Students complete the table individually, then answer the question.
LANGUAGE NOTE The full form for negative imperatives is do not, but in spoken language we usually use the contraction don’t: Do not disturb (a notice on a door). Don’t worry. We use imperatives to ask or tell someone to do something: Turn left by the supermarket. Be careful! Don’t watch that film – it’s terrible! Have a nice holiday! We can say please after imperatives to make them more polite: Hurry up, please. |
Students match the equipment with photos. Which four things are not in the photos? ANSWERS: 1 tent 2 sleeping bag 3 rucksack 4 stove 5 waterproof clothes 6 torch 7 first aid kit 8 satellite phone 9 compass 10 map 11 sunscreen 12 insect repellent Not in the photos: rope, sunglasses, gloves, helmet Students do the Rainforest Survival quiz ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. Students complete the table with imperatives from the quiz. ANSWERS: Affirmative: go back, look, watch, stay, wear, be quiet, shine, light, get in, eat, use, call, give, go Negative: don’t worry, don’t eat We use imperatives for instructions. |
Assessment criteria - • Learn vocabulary for travel equipment Descriptor: - match the equipment with photos. Which four things are not in the photos? Assessment criteria: • Do a Rainforest Survival quiz Descriptor: - do the Rainforest Survival quiz -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 48 WB
|
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 Travel and holidays |
Lesson 61 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading: An adventure story |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.3.1 give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics 6.4.7.1 recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level in a limited range of written genres 6.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of short, supported talk on a wide range of familiar topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about a jungle wildlife holiday. • Read for general meaning and specific detail. • Talk about your holiday experiences |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, ask students who they think travels to the jungle and why. • Elicit that scientists go there to study the animals and plants, and many students or other people go there for adventure holidays. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Background Jungles are rainy, humid areas with dense vegetation. They contain many species of wildlife, such as tigers, monkeys, parrots, snakes, and alligators, as well as lots of insects. A jungle is different to a rainforest, because the vegetation in a jungle is thicker and harder to travel through. Ex: 1 P: 70 • Discuss as a class where the people in the photos are and what they are doing. Discuss all the photos around the text, and elicit as much detail as possible. • In a weaker class, accept answers in students’ own language if necessary. • Elicit some ideas from the class but do not accept or reject any at this stage. Ex: 2 P:70 • Pre-teach stupid if necessary. Read the three titles and point out that students should choose the best title, and identify what it was that Carol and Peter did that was stupid. • Play the CD. Students read and listen to the text, and answer the questions. • Discuss the answers with the class. Encourage them to give reasons for their answers. Ex: 3 P:70 • Remind students to read the sentences very carefully and compare them with the relevant parts of the text. Tell them to correct the false sentences. • In a weaker class do the first sentence with the class as an example. |
Students look at the photos. Where are the people? What are they doing? ANSWERS: Students’ own answers.. Students read and listen to Carol’s story and choose the best title. What stupid thing did Carol and Peter do? ANSWERS: The best title is b, because it includes the word ‘lost’. Carol and Peter went walking without a map and without telling anyone where they were going
Students read the text again and write true or false. Correct the false sentences. ANSWERS: 1 False. Carol was with eight people: her brother, the guide Juan, and six others. 2 True. 3 False. They wanted to take photos of monkeys. 4 True. 5 False. They weren’t far from the campsite when they got lost. 6 True. |
Assessment criteria - Read about a jungle wildlife holiday. Descriptor: - look at the photos. Where are the people? What are they doing? Assessment criteria: - Read for general meaning and specific detail.
Descriptor: - read and listen to Carol’s story and choose the best title
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 48 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 Travel and holidays |
Lesson 62 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus to be going to will / won't |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.3.1 give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics 6.6.8.1 use future forms will for predictions and be going to to talk about already decided plans on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topic |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the affirmative, negative and questions forms of be going to. • Use be going to to talk about plans. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Refer students back to the text on page 80. Ask students to look at the second paragraph and find the sentence: I’m not going to walk further. • Ask students whether this sentence refers to the past, the present, or the future (the future). • Ask students to find other examples of be going to in the text. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 71 • Read all the examples and elicit what parts of the sentences are missing. • Look at the words in the box and point out that these are needed to complete the sentences. • Check the answers to the first stage of the exercise before students complete the rules LANGUAGE NOTE We use the
appropriate part of the verb be + going to + infinitive: I am going
to leave. He is going to leave. We usually use contracted forms:
I’m going to leave. He’s going to leave. The full form of the
negative is made with not: I am not going to leave. He is not going
to leave. These forms are usually contracted: I’m not going to
leave. He isn’t going to leave. Students often forget the to before
the infinitive: We are going to travel by boat. NOT
Ex: 2 P:71 • In a weaker class, tell students to circle the subject to help them choose the correct option. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs, then check answers with the class Ex: 3 P:71 • Ask students to read through the text quickly. To check comprehension, ask the class: Where is Ray going to travel to? (The USA.) • In a weaker class, do the first item as an example, and remind students to use the affirmative or negative forms as specified in the wordpool. Students can work in pairs. • In a stronger class, students should complete the text individually. Ask students to swap with a partner and see if they can find any mistakes in their partner’s sentences. |
Students complete the sentences with the words in the box. Then complete the rules ANSWERS: 1 to take 2 ’s 3 aren’t 4 going Rules 1 future 2 be, pronoun Students choose the correct words. ANSWERS: 1 is 2 aren’t 3 aren’t 4 have 5 ’m not 6 wear
Students complete the text with the verbs in the box and the correct form of be going to. ANSWERS: 1 isn’t going to travel \ 2 isn’t going to see 3 ’s going to phone 4 ’m going to learn 5 ’m going to see 6 ’m going to meet 7 is going to eat 8 isn’t going to take 9 are going to read 10 ’s going to write |
Assessment criteria - Learn the affirmative, negative and questions forms of be going to.
Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the words in the box. Then complete the rules Assessment criteria: - Use be going to to talk about plans.
Descriptor: - complete the text with the verbs in the box and the correct form of be going to.
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 49 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 Travel and holidays |
Lesson 63 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Weather conditions |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 6.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of short, supported talk on a wide range of familiar topics 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn adjectives to describe the weather. • Practise talking about the weather. • Learn how to change nouns to adjectives. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, write the word weather on the board. • Ask the class: What’s the weather like today? Elicit some ideas. Ask: What’s the weather like in summer / winter? Elicit some ideas. Ask: What weather do you like / dislike? |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 72 • Students match the words to the pictures in pairs. • Play the CD and ask students to check their answers. • Check that students understand all the adjectives in the box, and drill pronunciation of any new words. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:72 • Read the task with the class and do an example. In a weaker class, this can be done as a whole class activity. Encourage students to use a variety of actions and expressions. • Monitor while students are speaking, and ask individuals to mime to the class at the end Ex: 3 P:72 • Students match the adjectives from exercise 1 with the nouns, and answer the question. LANGUAGE NOTE We can form adjectives from some nouns by adding -y to the noun. Sometimes there are other spelling changes, e.g. sometimes the final consonant doubles: sun-sunny, fogfoggy and if the noun ends in -e, it is deleted when -y is added: ice-icy. Not all nouns use this ending, some form adjectives in different ways, for example: heat-hot, cold-cold |
Students match six of the words in the box with the photos. Then listen and check. ANSWERS: 1 snowy 2 sunny 3 rainy 4 stormy 5 foggy 6 icy Students work in pairs. Mime and guess weather words in exercise 1 ANSWERS: Students’ own answers.
Students match the nouns with adjectives in exercise 1. Which word doesn’t change ANSWERS: sunny – sun, cold – cold, foggy – fog, windy – wind, icy – ice, . snowy – snow, hot – heat, rainy – rain, cloudy – cloud, stormy – storm ‘cold’ doesn’t change |
Assessment criteria - Learn adjectives to describe the weather.
Descriptor: - match six of the words in the box with the photos. Assessment criteria: - Learn how to change nouns to adjectives
Descriptor: - match the nouns with adjectives in exercise 1. Which word doesn’t change
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 50 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 Travel and holidays |
Lesson 64 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus will / won't |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.2.1 ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general topics 6.6.8.1 use future forms will for predictions and be going to to talk about already decided plans on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topic |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the affirmative, negative and question forms of will. • Ask and answer questions using will. • Write predictions about the future. |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, ask students what they want to do when they are older. They should just say the activity, do not encourage them to use the form be going to. • Write their ideas on the board. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say differentwords from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 73 • Refer students back to page 82 to complete the sentences. • Check answers with the class, then ask students to answer the questions. In a weaker class, check understanding of predictions. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:73 • Tell students to study the pronouns and the verb forms carefully when matching. • Check answers by asking individual students to read out the question and the matching answer. • Students complete the rules. In a weaker class, do this together as a group. In a stronger class, ask individual students to read out the completed rules. If they make any mistakes, ask another student for the correct answer. Ex: 3 P:73 • Read the task and the example with the class and check understanding. • Students write the sentences individually • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes. |
Students complete the sentences and answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 is going to 2 won’t 3 will 4 will 5 ’s going to 1 Sentences 1 and 5 are plans. 2 Sentences 2, 3 and 4 are predictions. 3 won’t Students match the questions with the answers. Complete the rules. ANSWERS: 1 b 2 c 3 a Rules 1 will 2 No 3 won’t
Students write sentences with will and won’t and the verbs in brackets. ANSWERS: 1 won’t use 4 won’t get 2 will be 5 ’ll see 3 ’ll phone 6 won’t rain |
Assessment criteria - Learn the affirmative, negative and question forms of will.
Descriptor: - complete the sentences and answer the questions Assessment criteria: - Ask and answer questions using will.
Descriptor: -write sentences with will and won’t and the verbs in brackets.
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 51 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 Travel and holidays |
Lesson 65 |
||
|
|
|
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Speaking: How was your weekend? |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a conversation about a trip. • Learn key phrases for talking about the weekend. • Practise talking about a recent past event. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Tell students about a trip you went on recently. For example: I visited Paris last year. It was wonderful. • Invite some students to use the same verbs and tell the class about a trip that they went on: I went to Rome last month. It was exciting. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 74 • Remind students that they can use photos to help them establish certain information before they read or listen to a text. • Students identify who has been on a trip, and give reasons. Do not confirm or deny their ideas at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:74 • In a weaker class, allow students to complete the dialogue in pairs. • After students have listened to the CD to check their answers, find out how many students answered exercise 1 correctly. Ex: 3 P:74 • Read through the key phrases and the responses with the class. • Encourage students to try to match these from memory before listening to the CD again. • Play the CD. Students listen and reply as a class.\ • Check answers before students move on to practise the dialogue in pairs. |
Students look at the photo. Who is returning from a trip? ANSWERS: Student’s own answers Students complete the dialogue. Then listen and check. ANSWERS: 1 visited 2 travelled 3 were 4 there 5 was 6 wasn’t Tina has been on a trip, because she’s got a suitcase.
Students listen to the key phrases and reply with the correct responses ANSWERS: 1 c 2 a 3 d 4 b |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a Conversation about a trip.
Descriptor: - look at the photo. Who is returning from a trip? Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for talking about the weekend. Descriptor: - listen to the key phrases and reply with the correct responses Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 51 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 Travel and holidays |
Lesson 66 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Writing: A blog. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 6.5.6.1 link, with some support, sentences into a coherent paragraph using basic connectors on a limited range 6.3.3.1 give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a conversation about a trip. • Learn key phrases for talking about the weekend. • Practise talking about a recent past event. |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Tell students about a trip you went on recently. For example: I visited Paris last year. It was wonderful. • Invite some students to use the same verbs and tell the class about a trip that they went on: I went to Rome last month. It was exciting. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 75 • Remind students that they can use photos to help them establish certain information before they read or listen to a text. • Students identify who has been on a trip, and give reasons. Do not confirm or deny their ideas at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:75 • In a weaker class, allow students to complete the dialogue in pairs. • After students have listened to the CD to check their answers, find out how many students answered exercise 1 correctly. Ex: 3 P:75 • Read through the key phrases and the responses with the class. • Encourage students to try to match these from memory before listening to the CD again. • Play the CD. Students listen and reply as a class. • Check answers before students move on to practise the dialogue in pairs Ex: 3 P:75 • Refer the class to the tables, and allow time for students to read them. In a weaker class, elicit or demonstrate a few examples. • Play the CD. Students listen and note down the questions and answers that they hear. |
Students read the model text and answer the questions ANSWERS: Student’s own answers. Students study the key phrases ANSWERS: 1 visited 2 travelled 3 were 4 there 5 was 6 wasn’t Tina has been on a trip, because she’s got a suitcase
Students match 1-6 with a-f and write sentences using so. ANSWERS: 1 c 2 a 3 d 4 b Students follow the steps in the writing guide. ANSWERS: 1 How was the trip? 2 The weather was really bad. 3 How was the party? 4 The people were very nice. 5 How was the match? 6 Manchester United were rubbish |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a conversation about a trip.
Descriptor: - read the model text and answer the questions Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for talking about the weekend.
Descriptor: - study the key phrases
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 4 P: 51 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 Travel and holidays |
Lesson 67 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My Country. An adventure holiday |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 6.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a text about white-water rafting in Kazakhstan • Talk about different types of holiday • Learn how to talk about the future using could, may and might • Write about a holiday |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In Books closed. Put students into groups and write Holidays on the board. Give students two minutes to tell each other where they went on their last holiday and what they did. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 76 • Focus students’ attention on the words in the box. • Ask them to remember what people said about their holiday and to match the words to people in their group. • Elicit from the class what you do on each type of holiday, or explain if they don’t know. • Then students go back into their groups and discuss questions 2–4. • Monitor and give help where needed. • Get feedback by asking a few different students to tell you what their group discussed. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:76 •Tell students to read the questions before you play the recording for them to listen to while they read the text. • Check students understand all the vocabulary in the questions. • Students check their answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class. For question 4, ask students what clothes you should wear when you go white-water rafting and check they understand the meaning of the words in the text Ex: 3 P:76 • Draw students’ attention to the speech bubbles. Elicit what the verbs are (could fall, might like, may want). Ask them how this form is different in meaning to will fall, will like, will want (they suggest the speakers aren’t certain) • Point out that could has more of a sense of suggestion or possibility based on facts than the other two modals. Students fill in the rules and check their answers with their partners |
Students look at the types of holiday in the box and answer the questions. ANSWERS: Student’s own answers. Students study the key phrases ANSWERS: 1 visited 2 travelled 3 were 4 there 5 was 6 wasn’t Tina has been on a trip, because she’s got a suitcase
Students read and listen to the text and write true or false. Correct the false sentences. ANSWERS: 1 False. Children can try it if they are with an adult. 2 True 3 False. You will get wet. 4 False. You should wear a swimming costume under your clothes, such as shorts or tracksuit bottoms and a sweatshirt. 5 True, 6 False. It is a more difficult river. Students look at the speech bubbles. Complete the rules ANSWERS: 1 might, may 2 could, may 3 could, may |
Assessment criteria - Talk about different types of holiday
Descriptor: - look at the types of holiday in the box and answer the questions. Assessment criteria: - Learn how to talk about the future using could, may and might Descriptor: - Complete the rules
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 52 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 Travel and holidays |
Lesson 68 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Natural science: Weather ad climate |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.3.1 respect differing points of view 6.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of short, supported talk on a wide range of familiar topics 6.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about the weather. • Read a text about the water cycle. • Read about climate, and study two weather charts. • Practise drawing weather charts. |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, write the word weather on the board. • Put students in pairs and give them two minutes to think of as many words as possible to do with the weather. • Elicit answers, and write the vocabulary on the board. • Write the phrase the water cycle on the board. Ask students what they understand by this phrase, and elicit some ideas. Do not accept or reject students’ ideas at this stage |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 77 • Refer students to the illustration and allow time for them to look at it. Elicit that it shows how water from the sea goes up into the atmosphere and falls again as rain. • Students read the text and choose the correct answers. • Play the CD for students to check their answers and allow them time to correct any mistakes. • Check answers with the class, and make sure that students understand all the weather vocabulary. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:77 • Students read the text again and match the words with the labels. In a weaker class, allow them to work in pairs. Ex: 3 P:77 • Ask students to read the text and study the weather charts carefully. Help them to interpret the data in the tables. • Make sure that students understand that the letters at the bottom of each chart refer to the months of the year. • Clarify that there are three mistakes in the text where the information does not match the weather chart. In a stronger class, ask students to write the correct information. • In a weaker class, students can complete this in pairs. Ask them to find the information that is wrong, then correct it as a class. |
Students read the text and choose the correct words. Then listen and check your answers. ANSWERS: 1 sunny 2 water vapour 3 air 4 colder 5 clouds 6 Wind
Students read the text again and match the words in the box with lables in the picture ANSWERS: 1 evaporation 2 transpiration 3 precipitation 4 condensation Students look at the weather charts for the average precipitation and temperature in Almaty and read the text. Find three mistakes in the text. ANSWERS: 1 False: It’s very cold and snowy in summer. (It’s very cold and snowy in winter.) 2 False: There’s more precipitation in winter than in summer (There’s more precipitation in summer than in winter.) 3 False: It’s colder in December than in any other month of the year. (It’s colder in January than in any other month of the year.) |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a conversation about a trip.
Descriptor: - read the model text and answer the questions Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for talking about the weekend.
Descriptor: - study the key phrases
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 53 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 Travel and holidays |
Lesson 69 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review unit 6 Summative Assessment for the unit “Travel and holidays” |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.5.6.1 link, with some support, sentences into a coherent paragraph using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics 6.4.5.1 (6.R5) Deduce meaning from context on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 6.5.7.1 (6.W7) Use with some support appropriate layout at text level for a growing range of written genres on familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use vocabulary for travel equipment. • Write adjectives to describe the weather • Identify the meaning and details of the reading texts • Write a text adhering to the layout and format of a given genre with some support |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, write the word weather on the board. • Put students in pairs and give them two minutes to think of as many words as possible to do with the weather. • Elicit answers, and write the vocabulary on the board. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 78 • Encourage students to read all the words carefully. Point out that four of them are not shown in the photo. • Сheck that students understand all the vocabulary, and drill pronunciation of any words that are new to students. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:78 • Students match the adjectives with the nouns Summative Assessment for the unit “Travel and holidays” Reading Task 1.Read the text below and complete the task. Mark the sentences True or False. Example: Sam finds summer an enjoyable season. True
Writing Task 2. Write a postcard to a friend. Include Greeting and closing sentence. Use Present Continuous tense.
The following questions will help you to organize your writing: What are you doing at the moment? Where are you staying? What’s the weather like? What are you going to do this evening/ tomorrow?
Example: My friends and I are leaving for Canada soon. |
Students match the words in the box with the definitions. ANSWERS: 1 rucksack 2 torch 3 sunscreen 4 gloves 5 sunglasses 6 insect repellent 7 stove Students write the adjective form of these nouns ANSWERS: 1 windy 2 sunny 3 foggy 4 snowy 5 cloudy 6 stormy 7 icy 8 rainy 9 hot 10 cold Students read the text below and complete the task. 1 true 2 true 3 false 4 false 5 true 6 false Students write a postcard to a friend. Greeting and closing sentence. Use Present Continuous tense. |
Assessment criteria - Use vocabulary for travel equipment.
Descriptor: - match the words in the box with the definitions. Assessment criteria: - Identify the meaning and details of the reading texts -Write a text adhering to the layout and format of a given genre with some support Descriptor: - read the text below and complete the task. -write a postcard to a friend. -follows the structure of a postcard; -writes greetings and closing sentence; Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 53 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 Travel and holidays |
Lesson 70 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Skills Round - up. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - Listen to a conversation about friends camp - Learn vocabulary for talking about camping. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 79 • Look at the photos with the class and elicit ideas about what the people are doing, and where they are. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:79 • Explain that students are going to listen to a conversation between two friends about a camping trip. • Play the CD. Students listen and identify the location. Ex: 3 P:79 Explain that students should listen again and complete the sentences
Ex: 4 P:79 • Put students into groups of three. Tell them to use the questions to help them prepare their conversations. They should ensure they answer all of them. • Encourage them to add as much information as they can, using their own ideas. |
Students look at the photos. Where are the people? What are they going? ANSWERS: The people in each photo are camping, and the photos show the countryside/a river, a beach and the mountains. Students listen to a conversation. Where are the friends going to camp? ANSWERS: By the sea.
Students listen again and complete the sentences. ANSWERS: 1 sunny 2 year 3 swimming 4 food 5 stove 6 pasta 7 bus 8 rucksack, sleeping bag, torch Students work
in groups of three and prepare a conversation. Imagine you are
planning a camping weekend. Answer these questions. Students’ own answers |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a Conversation about friends camp
Descriptor: - look at the photos. Where are the people? What are they going? Assessment criteria: - Learn vocabulary for talking about camping.
Descriptor: - listen again and complete the sentences.
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 6 P: 55 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 71 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talking about books. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics 6.4.1.1 understand the main points in a limited range of short simple texts on general and curricular topics 6.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about books • Identify what people are talking about in a listening • Ask and answer questions about books • Write about favourite books |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, ask around the class: How often do you read a book?
|
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 80 • Draw students’ attention to the Book Quiz on p81. Students read the quiz carefully to identify the blue words and their meaning then match them to the descriptions in 1–8. You may wish to ask students to check their answers in pairs. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:80 • Explain to students that they are now going to do the quiz and that if they don’t know any answers they should guess. Allow them to check their answers with a partner and then ask individual students what their answers are for each question. Accept all answers. • Play the audio for students to listen and check. • Ask: Who got all the questions right? Who get one wrong? Etc. to find out who got the most answers right. Ex: 3 P:80 • Books closed write in and on on the board. Ask students if they can give you sentences about times and places using in and on. Right a few correct ones on the board. • Draw students’ attention to the grammar box and go through it, to make sure you have covered all the points. • Students do the exercise individually then check in pairs. • In a stronger class, ask students to write six sentences with in and on (three with in and three with on) |
Students check the meaning of the words in blue in the Book Quiz. Match the words with the definitions ANSWERS: 1 plot 2 comic book 3 paperback book 4 hardback book 5 novel 6 sequel 7 the blurb 8 fiction 9 non-fiction Students work in pairs. Do the Book Quiz. Listen and check your answers. ANSWERS: 1 b 130 million 2 c 1900s 3 c all three 4 a Jurassic World 5 c 823 words 6 c $30,802,500 7 1876 8 b they are both sequels to other books
Students look at the information about in and on. Then choose correct prepositions in the sentences from the quiz. ANSWERS: 1 in 2 in 3 in 4 in 5 on |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for talking about books Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words in blue in the Book Quiz. Match the words with the definitions Assessment criteria: - Ask and answer questions about books
Descriptor: - look at the information about in and on. Then choose correct prepositions in the sentences from the quiz. Make CCQ questions Yes / No 1 Are there 130million in the world? Yes 2 Did the first paperback books appear 1800s? No
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 72 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Young writers |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 6.2.8.1 understand supported narratives, including some extended talk, on an increasing range of general and curricular topics 6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a text about two young writers • Learn more vocabulary connected to books • Talk about books and video games |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, revise the book vocabulary students learned last lesson. Ask questions including each of the words they have learned. You could use some of the quiz questions to see if the students remembered the answers. e.g. How many hardbacks do you read a year? When did paperbacks first appear? |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 82 • Ask students to look at the photographs of the authors and ask them what kind of books they write and why. Accept all answers. Add supplementary questions, such as How old are the writers in the photos? and How old were they when they started writing? Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:82 • Play the recording for students to listen to while they read the text. Stop the recording after the first text and ask the questions again for students to give the correct ones. Then do the same for the text on Christopher. • Play the recording again for students who struggled, to see if they can hear the answers now they know what they are. Ex: 3 P:82 • Students read the text again and do the exercise individually, before checking the answers with a partner. • When you have been through the answers, ask students if they have heard of the authors or their books. If they have, ask students if they have read any of the books and whether they liked them. Ex: 4 P:82 • Draw students’ attention to the words in blue in the text. Tell students to read the definitions carefully and match them to the blue words. Ask them to compare their answers with a partner when they have finished. |
Students look at the photos of two young authors. What kind of books do you think they write? ANSWERS: Students’ own answers Students read and listen to the text. Check your answers to exercise 1 ANSWERS: The both write fantasy novels.
Students read the text again. Decide if each sentence is true for Helena (H), Christopher (C) or both (B) ANSWERS: 1 B 2 B 3 B 4 H 5 C 6 H Students find the words in blue in the text. Match them with the definitions. ANSWERS: 1 bestseller 2 publisher 3 setting 4 series 5 character |
Assessment criteria - Read a text about two young writers
Descriptor: - look at the photos of two young authors. What kind of books do you think they write? Assessment criteria: - Learn more Vocabulary connected to books
Descriptor: - find the words in blue in the text. Match them with the definitions. Make CCQ questions Yes / No 1 Do the both write fantasy novels? Yes 2 Are their books very popular in the USA? Yes 3 Did she start her first novel, when she was 23? No
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 73 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Present Perfect |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.4.1 evaluate and respond constructively to feedback from others 6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topic 6.6.7.1 use simple perfect forms of common verbs to express what has happened [indefinite time] on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the affirmative and negative forms of the present perfect. • Learn when we use the present perfect. • Learn some irregular past participles. |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Put students in pairs and ask them what exciting activities they have done in the past year. Tell them to work in pairs to make a list of their favourite activities. For feedback invite a few students to read their list to the class. Don’t expect full, accurate sentences, but correct the names of any activities |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets.
|
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 83 • In a stronger class, ask students to complete the sentences from memory. Rules • Ask students to think about the sentences they have just completed and to choose the correct words in the rules, before going through the answers as a class. • Explain that the present perfect links the past to the future, without talking about when exactly events happened Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:83 • Show students where they can find the irregular verbs list in their Workbooks and focus their attention on the Study Strategy. Tell them that they need to learn the irregular verbs because there aren’t any rules governing the way they are spelled. Some past participles are the same as the simple past and others are different. Students use the verb list in the Workbook to complete the table. Ex: 3 P:83 • Students complete the exercise individually then check their answers in pairs
|
Students complete the sentences about the text. Then choose the correct words in rules. ANSWERS: 1 has 2 hasn’t 3 have
ANSWERS A past b don’t say c have d the same as Students look at the irregular verbs list on workbook. Complete the table with the irregular verbs past participles. ANSWERS: 1 been 2 become 3 bought 4 had 5 made 6 read 7 seen 8 written
Students complete the sentences with affirmative and negative forms of the present perfect ANSWERS: 1 have read 2 has written 3 hasn’t become 4 have made 5 haven’t seen 6 haven’t played |
• In a weaker class, encourage a student to follow the text • In a weaker class, work in pair. Complete the table with the irregular verbs past participles by support teacher. |
Assessment criteria - Learn the affirmative and negative forms of the present perfect.
Descriptor: - complete the sentences about the text. Then choose the correct words in rules. Assessment criteria: - Learn some irregular past participles.
Descriptor: - Complete the table with the irregular verbs past participles. Make CCQ questions Yes / No
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketHome task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 74 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Books and writers |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.4.1 evaluate and respond constructively to feedback from others 6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and. curricular topics 6.4.8.1 use with some support familiar paper and digital reference resources to check meaning 6.5.8.1 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics of familiar general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read two book reviews and understand the reviewers’ views. • Learn adjectives to describe the details of plots and stories. • Listen to an interview about a famous author. • Write about a writer. |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • In pairs, students tell each other about the last book they read: what it was about, what was good about it and what not so good (if anything). • Get feedback by asking a few students to tell the class about their discussion. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets.
|
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 84 • You may want selected students to read the texts aloud to the class, to give them practice in pronunciation and intonation. Alternatively, students read the reviews by themselves and check the meaning of the blue words in their dictionaries, or in the back of their Workbooks. • Go through the words with the class and ask students which book they would like to read and why. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:84 • Students work individually before checking their answers in pairs. • Go through the answers a class. After you have finished ask a few questions using the adjectives to reinforce the vocabulary, for example: Have you ever read a dull book? Which authors do you think are imaginative? Ex: 3 P:84 • Books closed. Ask students if they have read My name is Kozha, or any other books by Berdibek Sokpakbaev. Did they enjoy it / them? Ask them what they would like to know about Berdibek Sokpakbaev and ask them to write three questions each in pairs. Focus their attention on the questions in exercise 3. Are any of their questions there? • Students listen and tick the questions they hear the interviewer asking, before conferring in pairs. • Go through the answers as a class |
Students read the two book reviews and check the meaning of the words in blue. ANSWERS: Students choose the correct words to complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 fascinating 2 scary 3 appealing 4 funny 5 dull 6 moving 7 imaginative 8 exciting
Students listen to an interview about Berdibek Sokpakbaev. Which questions does the interviewer ask? ANSWERS: 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8 |
• In a weaker class, read the text, but only more of them answer the questions, less able students work with teacher’s little support. • In a weaker class, work in pair. Complete the table with the irregular verbs past participles by support teacher. |
Assessment criteria - Read two book reviews and understand the reviewers’ views.
Descriptor: - read the two book reviews and check the meaning of the words in blue. Assessment criteria: - Learn adjectives to describe the details of plots and stories
Descriptor: - choose the correct words to complete the sentences
Make CCQ questions Yes / No
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 75 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 10.03.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Present Perfect: Questions. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.4.1 evaluate and respond constructively to feedback from others 6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics 6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn how to form the present perfect: question form. • Learn and practise how to use the present perfect. • Talk about experiences |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Put students in pairs, and ask them what they can remember about the Berdibek Sokpakbaev from the interview. • Get feedback from the class by asking a few students to give a sentence each about the interview. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets.
|
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 85 • Students work individually to match the sentences to the answers and then work out the rules
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:85 • Students work individually and choose the correct answers, before checking in pairs Ex: 3 P:85 Focus students’ attention on the note about J.K. Rowling. Go through the first item on the list and elicit what the question would be. Write it on the board. Then elicit the answer. • Students then work in pairs and write questions and answers.
|
Students match the questions with the answers. Then choose the correct answers in the rules. ANSWERS: 1 No, I haven’t. 2 Yes, it has. Rules 1 past participle 2 have, has 3 don’t repeat Students choose correct words in the questions and short answers. ANSWERS: 1 Have, have 2 Has, hasn’t 3 Have, haven’t 4 Has, has 5 Have, have
Students look at the information about J.K. Rowling, the author of the Harry Potter books. Write questions and answers about her. ANSWERS: 1 Has she written lots of books? Yes, she has. 2 Has she become very rich? Yes, she has. 3 Have her books become films? Yes, they have. 4 Has she acted in one of her films? No, she hasn’t. 5 Has she had (any) children? Yes, she has. 6 Have her children become famous? No, they haven’t |
• In a weaker class, work in pair and choose the correct answers in the rules. • In a weaker class, work in pair. Choose correct words in the questions and short answers with teacher’s support. |
Assessment criteria - • Learn how to form the present perfect: question form
Descriptor: - match the questions with the answers. Then choose the correct answers in the rules. Assessment criteria: - Learn and practice how to use the present perfect.
Descriptor: - choose correct words in the questions and short answers.
Make CCQ questions Yes / No
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 76 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Speaking: Asking for and giving opinions. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.4.1 evaluate and respond constructively to feedback from others 6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics 6.5.8.1 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics of familiar general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for asking and giving opinions. • Listen to a conversation in which people as for and give opinions. • Discuss films and books using the key phrases. |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In
|
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:86 • Draw students’ attention to the photo and ask where the conversation is taking place, and what the people might be discussing. Ask students how they buy books, online or in a bookshop and how they choose a book. Do they ever choose one because someone has recommended it Ex: 2 P:86 • Refer students to the dialogue next to the photo. Check their understanding of real-life stories. The speakers mean stories set in the real world, rather than a fantasy world. They are still talking about fiction. Answers: (In a bookshop. Jess does but Ali hasn’t read it yet.) Ex: 3 P:86 • Play the CD. Students listen and repeat the key phrases. • Students find the key phrases in the dialogue and identify the responses. In pairs, they decide which are for asking someone’s opinion and which are for giving an opinion. , • Go through the answers as a class. Then play the recording again for students to listen to the intonation of the phrases, before they practise the dialogue in groups of three Answers: Asking for opinions: 1 What do you think of this (book)? 4 What / How about you? 5 Do you agree? Giving opinions: 2 I think (it’s brilliant). 3 I’d say (it’s quite funny). 6 I agree with you. 7 I’m not sure I agree. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the photo. Where are Ben, Jess and Ali Descriptor: - identify where the conversation is taking place Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to the dialogue and check their answers. Do Jess and Ali like this book? Descriptor: -listen the dialogue -answer the question Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students listen to the key phrases. Which are for asking for someone’s opinion and which are for given an opinion. Descriptor: - listen to the key phrases -make a dialogue using key phrases Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
-can talk about places - can identify the main idea Total: 1 point -can understand the dialogue -can answer the question Total: 1 point -can understand key phrases -can make a dialogue using key phrases Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 77 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative control work for the 3rd term |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.8.1 Understand supported narratives including some extended talk, on a range of general and curricular topics 6.4.4.1 Read independently a limited range of short simple fiction and non-fiction texts 6.5.5.1 Develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a limited range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics 6.3.4.1 Respond with limited flexibility at both sentence and discourse level to unexpected comments on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - summarize the main idea with the limited support of details they hear or write down -identify the details of a text - use simple transitional phrases (firstly, secondly…, in conclusion, then, but) -convey ideas and basic information (age, hobbies, interests, family and educational background) |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Books closed. Write the following words on the board in random order: country, village, city, town. Tell students to work in pairs to put these places in order of size, starting with the largest. Ask them to think of an example of each place from their own country. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Tasks for the Summative Assessment for the term 3 Listening Task. Listen to the conversation between the travel tour guide and the tourists twice. CD3. Tapescript 2. And transcript for listening task can be found after the mark scheme. Put in order three places that the tour guide will visit first. Task. Read the text about fast food. Mark sentences as True or False Write answers. 4. Who took the hamburger to the United States of America? 5. Why do people go to MacDonald’s? Writing Task. Choose ONE of the topics below. Write answers in full sentences. Give arguments supported by examples. Link these sentences into a well-structured paragraph with some basic connectors. Use future form ‘will’. What is it a healthy lifestyle? What should you personally do to stay healthy? How will you describe a healthy diet? What will you do to stay healthy? Speaking Task. Work in pairs. Choose one of the cards and make a dialogue with a partner. Give own points of view on topics, ask questions to clarify the answers and get the needed information, explain and justify your positions and answer your partner’s questions. You have 1 minute to prepare and 2 minutes to talk. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students listen to the recording and write the name of each room Descriptor: - write the names of each room. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students Read the text and complete the sentences using the words from the box Descriptor: -read the text -complete the sentences Students describe the places and write using the following questions. Descriptor: - describe the places Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students choose one card to speak about the topic Descriptor: - speak using questions Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
- can write the names of each room. Total: 5 point -can read the text Total: 5 point -can describe the places Total: 5 point -can speak using questions Total: 5 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 78 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My Country. A folktale |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.4.1 evaluate and respond constructively to feedback from others 6.1.7.1 develop and sustain a consistent argument when speaking or writing 6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a traditional story • Learn how to use the expression feel / sound / smell / taste + adjective • Learn how to use the expression feel / sound / smell / taste + like + noun • Write a folktale |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Focus students’ attention on the picture. Ask them what sort of story they think the text is. (A folk tale) • Ask them what sort of things usually happen in such stories. (There’s often romance, a search for something that involves a long journey, or a problem to be overcome. There is also often a sense of good versus bad.) |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:88 • • In pairs, students think about the stories they know and who the characters are. They tell each other which story is their favourite and who their favourite character is. • Get feedback from the class by asking a few students to say which story and character their partner likes best and why. Answers: Students’ own answers Ex: 2 P:88 Ask students if they know the story of Kyz-Zhibek and what they know about it. • Focus students’ attention on the questions and give them a minute to read them before you play the recording for them to listen to while they read. • Students work through the answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class. Ask students what they think about the story and whether they prefer stories with happy or sad endings. Answers: (1 It was first told in the 16th century. 2 Bararbai and his wife had 11 children. 3 Tulgen went on a long journey because he wanted to meet and marry Kyz-Zhibek. 4 When Tulgen met Kyz-Zhibek they fell in love. 5 He wanted to marry Kyz-Zhibek and challenged Tulgen to a fight. 6 She killed herself..) Ex: 3 P:88 • Focus students on the blue words in the text. Ask a couple of students to read them out. • Students complete the sentences in the exercise. • Draw students’ attention to the rules and make sure they are clear of the difference between following feel, look, etc with an adjective and with like + noun. Answers: 1 north 2 war 3 son 4 thunder 5 goddess Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students work in pairs. Make a list of the folktale names and the main characters. Which folktales do you know? Descriptor: - work in pairs - make a list of the folktale names Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read and listen to the story. Answer the question Descriptor: -listen the dialogue -answer the question Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students find the phrases in blue the story and complete the sentences. Then complete the rules. Descriptor: - find the phrases in blue - complete the sentences. Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
-can make a list of the folktale names Total: 1 point -can read and listen the story Total: 1 point -can find phrases in blue the story Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Our neighbourhood |
Lesson 81 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Places in a town |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of short, supported talk on a wide range of familiar topics curricular topics. 6.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 6.6.14.1 use prepositions to talk about time and location use prepositions like to describe things and about to denote topic use prepositions of direction to, into, out of, from, towards on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for places in a town. • Learn there is … , there are … with a, an, some and any to talk about a town. • Write sentences about a town. |
||
|
Value links |
Hospitality: Traditionally a nomadic culture, hospitality has always been an important part of Kazakh culture. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students: Do you live in a town or in the country? • Ask: What can you find in a town? Try to elicit some words for places in a town, e.g. shops, cinema |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:92 • Refer students to the picture on page 19. They match the words individually, then compare their answers in pairs. • Students listen and check their answers. • Drill the pronunciation of the words. • In a weaker class, check understanding of the words in the box and advise students to write translations of each word in their notebooks
Ex: 2 P:92 • Remind students to listen carefully for clues about where each speaker might be. • Ask students to check their answers in pairs. • If students disagree about their answers, play the CD again so that they can check. Ex: 3 P:92 • Point out the labels A–D on the map of the city. Refer students to the texts below the picture, and explain that each text describes the relevant area on the map. • Allow students time to read the texts and the options carefully, and choose option a or b
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students match twelve of the words in the box with places. Answers: 1 train station 2 factory 3 flats 4 park 5 shopping centre 6 offices 7 shops 8 school 9 sports centre 10 restaurant 11 river 12 car park Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen and answer the question. Where are the people in situations? Answers: 1 park 2 library 3 train station 4 restaurant 5 sports centre 6 factory 7 school 8 cinema Students work in pairs. Read the information. Answers: A a: This is a good place for the bus station. B a: This is a good place for the cinema. C a: This is a good place for the library. D b: This is a good place for the hospital. |
Descriptor: - match twelve of the words - work in pairs Total: 1 point Descriptor: -listen the task -answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - gives information about himself/herself; Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Our neighbourhood |
Lesson 82 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading: A description of a modern city |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 6.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of short, supported talk on a wide range of familiar topics 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about some interesting buildings. • Find spelling rules for plural nouns. • Talk about your town. |
||
|
Value links |
Tradition: Kazakh traditions and culture have been passed on from one generation to another through oral histories told by traditional Kazakh tribal leaders and elders. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Ask students to look at the photo on page 20 and the title of the text. Ask students to try to guess where this city is, but do not tell them whether they are right or not. • Elicit some ideas and write them on the board. • Pre-teach the words floor (a building with three floors), gym and lake. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:94 • Before students read the text, ask them to look at the photos and read the words in the box. Remind them that photos can help them interpret a text, and give them useful clues about the content. • Check understanding of the words in the box. In a stronger class, ask one or two students to say which words they chose and why. • When students have listened, discuss the words again and check their answer from the warm-up activity Ex: 2 P:94 • Allow students time to read the sentences carefully before they answer true or false. In a weaker class, they can complete this activity in pairs. • Check answers with the class. Ask students to identify the area of the text where they found the answer Ex: 3 P:94 • Refer students to the text, and explain that the plural forms of the nouns in the box can all be found in the text. In a stronger class, ask students to close their books while you check the answers. • Ask students when the -ies form is used. Elicit answers from individual students.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the photos and choose six words that you can use to describe the building. Then read, listen and check your answers. Answers: Not mentioned: museum, mountains Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the text again and write true or false. Correct the false sentences. Answers: 1 False. You can see the Burj Khalifa from 100 kilometres away. 2 False. The skyscraper is a modern building. 3 False. There are 900 flats in the skyscraper. 4 True. 5 False. The lifts in the tower are very fast Students find the plural forms of these words in the text. When do we form a plural with -ies Answers: offices, cities, flats, parks, shops, libraries We usually form a plural with -ies when the noun ends in consonant + -y. We change the -y to -i and add -es. |
Descriptor: - read the text - choose six words to describe the building Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the text - write true or false Total: 1 point Descriptor: - find the plural forms Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Our neighbourhood |
Lesson 83 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Is there/ Are there |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics general and curricular topics 6.6.14.1 use prepositions to talk about time and location use prepositions like to describe things and about to denote topic use prepositions of direction to, into, out of, from, towards and there is / there are on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and use the question forms Is there …? and Are there …? with the appropriate short answers. • Use key phrases to express quantity. • Describe an ideal place to live. |
||
|
Value links |
Freedom: Freedom is the major value of the civil society being formed in Kazakhstan. This must provide everyone with the possibility of creative self-realization. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Tell students to imagine they are visiting a new town or city. • Tell them that they need to find out whether there is a cinema in the town. Elicit the question they would ask, and write it on the board: Is there a cinema in this town? |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:95 • Refer students back to page 20. Point out that they should study the question forms in exercise 5 to complete the first part of the activity, then read the text again if necessary to answer each question. In a stronger class, encourage them to do this from memory. Ex: 2 P:95 • In a weaker class, allow students to complete the rules in pairs. Refer students back to exercise 1 for support. You may need to highlight the singular and plural nouns in the questions LANGUAGE NOTE To form
questions from there is / there are we put the verb first: Is there
…? / Are there …?: Is there a swimming pool? NOT
Ex: 3 P:95 • In a weaker class, tell students to circle the nouns to help them form the questions correctly. • Go round and listen as they are talking. Check that they are using short answers correctly
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the questions. Then match the questions with answers Answers: 1 any, b 2 are, a 3 Is, c Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students choose the correct answers Answers: 1 any 2 singular nouns 3 plural nouns Students complete the questions with is there / are there. Then ask and answer with a partner. Give short answer. Answers: 1 Is there 2 Are there 3 Are there 4 Is there 5 Are there 6 Are there 7 are there 8 are there Students’ own answers |
Descriptor: - read the text - match the questions with answers Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the rules - choose the correct answers Descriptor: - complete the questions - give short answer Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Our neighbourhood |
Lesson 84 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 03.04.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Describing places. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 6.2.1.1 understand a sequence of supported classroom instructions 6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn adjectives to describe places. • Use adjectives to complete sentences describing your town. • Listen to a conversation about different places. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. |
||
|
Value links |
Hospitality: Traditionally a nomadic culture, hospitality has always been an important part of Kazakh culture. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Write the heading My town on the board. • Ask students to describe their town. • Elicit some adjectives, for example big, small, nice, and write them on the board. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:96 • Students look at the pictures. Explain that the adjective below each picture describes that image, and that the words in the box are the opposites of these. • When students have checked their answers, use the recording to drill the pronunciation of any words that are new to students. Ex: 2 P:96 • Look at the example with the class. Check understanding of quite: it is used to modify the adjective and make it less strong. Then look at the word really in items 2 and 3. Elicit that this makes an adjective stronger. • Students complete the sentences using information that is true about their own town. • Ask students to compare their sentences in pairs. • Ask some students to read their sentences to the class, and ask the class if they agree Ex: 3 P:96 • Refer students to the photos and ask students what they think the two cities are like. • Play the CD. Students listen and answer the question. Ex: 4 P:96 • Allow students time to read the sentences. • Play the CD again. Students decide if the sentences are true or false. • Check that students are able to form the correct sentence where the sentence is false
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students match adjectives with their opposites. Then listen and check. Answers: 1 safe 2 unfriendly 3 quiet 4 dirty 5 pretty 6 modern Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students complete the sentences about where you live. Use the adjectives. Answers: Students’ own answers. Students Tina is from Miami and Tom is Brighton. Listen to their conversation. Which city does Tina prefer? Answers: Tina prefers Miami because her friends and family are there. Students listen again and write true or false Answers: 1 True 2 False 3 True 4 False 5 False 6 False |
Descriptor: - match adjectives with their opposites. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences using information - Use the adjectives Total: 1 point Descriptor: - discuss about photos Total: 1 point Descriptor: - write true or false Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Our neighbourhood |
Lesson 85 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 05.04.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Comparative adjectives |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics general and curricular topics 6.6.2.1 use quantifiers many, much , a lot of ,a few on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn comparative adjectives. • Complete a quiz comparing places around the world. • Use comparative adjectives to compare two places. • Express your opinions about different places. |
||
|
Value links |
Tradition: Kazakh traditions and culture have been passed on from one generation to another through oral histories told by traditional Kazakh tribal leaders and elders. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, write on the board the names of two cities, for example Brighton and Tokyo. • Ask students what they think the differences are between the two cites. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:97 • Refer students back to the adjectives presented on page 22, and explain that they have different comparative forms. Explain that these forms are used in exercise 4 on page 22, and they can be categorized in this table. • Students copy the comparative forms into the correct rows. • Check answers with the class. Then ask students to think about how comparative adjectives are formed in their language. Can they be categorized in the same way? Ex: 2 P:97 • Students complete the sentences individually. Check they have done this correctly before they start the pairwork. • In pairs, students ask and answer the questions. In a stronger class, you can allow extra time to look up any answers they do not know in an atlas or on the internet. • Play the CD to check the answers. Ex: 3 P:97 • Refer students to the prompts under the speech bubbles. Explain that they can use these ideas, or any of their own, and that they should write a mixture of true and false sentences. Point out that there is a choice of adjectives in the prompts, so they can choose how to compare the places. • Students write their sentences. • Go through the example exchange in the speech bubbles. Model it with a stronger student. • In pairs, students ask and answer the new questions.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the table with adjectives. How do you make comparatives in you language. Answers: 1 safer 2 bigger 3 prettier 4 friendlier 5 more exciting 6 better Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students complete the sentences. Do the quiz with a partner. Answers: 1 more expensive – True 2 newer – True 3 wider – False 4 higher – True 5 longer – False 6 more dangerous – True 7 older – False 8 further – False Students write six more sentences for the quiz using these words or your own ideas. Then test your partner Answers: Students’ own answers |
Descriptor: - complete the table with adjectives Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences - Use the adjectives Total: 1 point Descriptor: - write six more sentences Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Our neighbourhood |
Lesson 86 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 07.04.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Speaking: Asking for travel information |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for asking for travel information. • Learn travel uses of the prepositions by and on. • Listen to a conversation in which someone asks for travel information. • Practise asking for travel information |
||
|
Value links |
Freedom: Freedom is the major value of the civil society being formed in Kazakhstan. This must provide everyone with the possibility of creative self-realization. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Ask students how often they use trains, and how often they use coaches. Ask when they last travelled by one of these methods. Was it cheap or expensive? Did they travel a long way? |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:97 • Refer students to the photo and ask them to look for clues about where the people are. • If students find this difficult, point out clues in the photo, for example, the man is holding a train timetable, and Tina is carrying a bag. • You could remind students that they first met Tina in Unit 1, with her cousin Laura. Ex: 2 P:97 • Refer students to the dialogue and read the instructions with the class. • Explain that they have to listen for several pieces of specific information, in order to complete the gaps and answer the questions. Suggest that they listen the first time without writing anything. The second time you play the CD, they should complete the dialogue with the correct words. The third time, they should use the information they have written to say how far London is and which form of transport is more expensive. • Remind students not to worry about the blue words at this stage. Ex: 3 P:97 • Students can cover the dialogue for this exercise, and then refer back to it to check their answers and correct any mistakes. In a weaker class, ask them to do this in pairs. • Check answers with the class before students practise the dialogue with a partner.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the photo. Where are the people? What information does Tina want? Answers: They are at the train station. Tina wants information about how far London is, and how much it costs to get there Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen and complete the dialogue Answers: 1 50 2 ten 3 bus station London’s about fifty minutes from here. The train is more expensive than the coach Students cover the dialogue and complete these key phrases. Answers: 1 want 2 far 3 from 4 much |
Descriptor: - discuss about the photo Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen the dialogue - complete the dialogue Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete these key phrases. Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Our neighbourhood |
Lesson 87 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 10.04.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Speaking: Asking for travel information |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for asking for travel information. • Learn travel uses of the prepositions by and on. • Listen to a conversation in which someone asks for travel information. • Practise asking for travel information |
||
|
Value links |
Freedom: Freedom is the major value of the civil society being formed in Kazakhstan. This must provide everyone with the possibility of creative self-realization. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Ask students how often they use trains, and how often they use coaches. Ask when they last travelled by one of these methods. Was it cheap or expensive? Did they travel a long way? |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:98 • Refer students to the photo and ask them to look for clues about where the people are. • If students find this difficult, point out clues in the photo, for example, the man is holding a train timetable, and Tina is carrying a bag. • You could remind students that they first met Tina in Unit 1, with her cousin Laura Ex: 2 P:98 • Refer students to the dialogue and read the instructions with the class. • Explain that they have to listen for several pieces of specific information, in order to complete the gaps and answer the questions. Suggest that they listen the first time without writing anything. The second time you play the CD, they should complete the dialogue with the correct words. The third time, they should use the information they have written to say how far London is and which form of transport is more expensive. • Remind students not to worry about the blue words at this stage. Ex: 3 P:98 • Students can cover the dialogue for this exercise, and then refer back to it to check their answers and correct any mistakes. In a weaker class, ask them to do this in pairs. • Check answers with the class before students practise the dialogue with a partner.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the photo where are the people. What information does Tina want? Answers: They are at the train station. Tina wants information about how far London is, and how much it costs to get there. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen and complete the dialogue. How far is London? Which is more expensive the train or the coach? Answers: 1 50 2 ten 3 bus station London’s about fifty minutes from here. The train is more expensive than the coach. Students cover the dialogue and complete these key phrases. Pactise the dialogue. Answers: 1 want 2 far 3 from 4 much |
Descriptor: - discuss about the photo Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen the dialogue - compare the transport. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete these key phrases. Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Our neighbourhood |
Lesson 88 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 12.04.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Writing: A description of a town. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 6.2.1.1 understand a sequence of supported classroom instructions 6.3.2.1 ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model text. • Learn key phrases for describing a town or city. • Learn about the position of adjectives. • Write about a town you like |
||
|
Value links |
Respect: Respect of elders and of the spiritual freedom of other nations are principal values. It is important to develop a productive dialogue between confessions and to acknowledge religion as an element of civil society. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students: Do you like your town? Why? What’s your favourite place in the town? Why? • Elicit some ideas from students and then ask: What’s your favourite town? Why? |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with suppor |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:99 • Check answers with the class and make sure students understand the rule that adjectives usually come before, not after, nouns in English Ex: 2 P:99 • Go through the words in the box and check understanding. Clarify that these are pieces of information which complete the key phrases. • In a weaker class check understanding by asking students to translate the phrases into their own language. Ex: 4 P:99 • Focus students on the blue words in the text about Brighton. In a weaker class, recap that friendly, pretty, etc. are adjectives. Ask students to study where these words are placed in the sentences. • Check answers by asking individual students to read out the completed rules.
Ex: 5 P:99 • Students use the rules they have identified to order the words correctly. Allow them time to complete this individually, then check answers in
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students read the model text and answer the questions. Answers: 1 Yes. 2 Paragraph 3. 3 Paragraph 2. 4 Paragraph 1. 5 Students’ own answers Students complete the key phrases with the words in the box. Answers: 1 England 2 160,000 3 friendly 4 the beach and the aquarium 5 85, London Students look at the words in blue in the model text. Then choose the correct words in the rules. Answers: 1 before 2 before Students order the words to make sentences. Answers: 1 Manchester is a big city. 2 I like exciting places. 3 The streets are very safe. 4 The library is a very quiet building. 5 There are some really interesting shops. 6 The town has got a big park |
Descriptor: - read the model text Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the key phrases Total: 1 point Descriptor: - choose the correct words in the rules Total: 1 point Descriptor: - make sentences. Total: 1 point . |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Our neighbourhood |
Lesson 89 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 14.04.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My Country. A city park |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.4.7.1 recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level in a limited range of written genres 6.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about parks • Read a text about the First President’s Park • Revise comparative adjectives |
||
|
Value links |
Respect - treating people with respect, value and courtesy. Especially apologising to them where the situation calls for it. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In Books closed. In pairs, students think of a park they like and write a list of the things they like about it, for example beautiful trees, café, flowers, etc. Get feedback from the class by asking a few pairs to read their lists. Go through any words students use that other members of the class might have difficulty with. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:100 • Draw students’ attention to the words on the box. Put students in pairs and give out dictionaries if you have them, or ask students to use their own. Tell them to draw a table like the example in their notebooks. Then work through the words putting them into the correct column. • Point out that some can go in both. Check answers as a class, checking that students understand what all the words mean Ex: 2 P:100 • Draw students’ attention to the photo with the text. Ask them what they can see in the photo. Ask students if they know where the park is (Almaty) and if any of them have visited it. • Focus students on the questions and give them a minute to read through them before playing the recording while they read the text. • Check they understand the meaning of formal v informal and colonnade. Students write the answers individually, before checking them in pairs Ex: 3 P:100 • Focus students’ attention on the box and on the adjectives in the first column. • Ask students the different ways you can form comparative adjectives (adding -er, doubling the consonant and adding -er removing the y and adding -ier and adding more in front of the adjective) Ex: 4 P:100 Students work individually and complete the sentences with comparative and superlative adjectives. Check the answers as a class
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the words. Draw a table in your notebooks and write the words in the correct column. Use a dictionary to help you. Some words can do in both. Total: 1 point Answers: Countryside: trees, paths plants, animals, grass Parks: trees, seats, paths, band stands, flower beds, fountains, statues, plants, animals, grass, lawn Students read and listen to the text. Write true or false. Answers: 1 True 2 True south of the park . 3 False. 4 False. 5 False. They are to the It’s at the north end 6 True of the park. 7 True There are formal and informal area Students look at the words in blue in the text and complete the table. Answers: 1 the biggest 2 newer 3 the newest 4 the liveliest 5 more beautiful 6 the most beautiful 7 better 8 the best Students complete the sentences with the comparative or superlative of the words in brackets. Answers: 1 the highest 2 the best 3 more popular 4 further 5 more interesting
|
Descriptor: - draw a table Descriptor: - Write true or false. Total: 1 point -Descriptor: - Descriptor: Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the comparative or superlative. Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Our neighbourhood |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: 17.04.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Geography: Reading a map |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary and key phrases for reading a map. • Practise reading a map. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Write the word map on the board and elicit the meaning. • Ask students what information we can find on maps, and elicit some ideas. • Ask students when they use maps. • Tell students they are going to practise reading maps in English |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:101 • Students work in pairs to check the meaning of the words and match them with the symbols. • When students have listened and checked their answers, find out how many they got correct. • Check answers with the class and make sure that students understand the meaning of the words. • Model and drill the pronunciation if necessary. Ex: 2 P:101 • Ask students to read the text again carefully and answer the question. • In a stronger class, you could photocopy the legend of a map and allow students to use dictionaries to translate more words for the symbols on the key. Ex: 3 P:101 • Focus students on the two maps at the bottom of the page. Students work in pairs to look at map A and choose the correct options. • Check answers by asking individual students to read out the correct sentences
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students check the meaning of the words and match them with symbols. Read and listen to the text and check your answer. Answers: 1 river 4 railway 2 road 5 forest 3 hill 6 path Students read the text again. What other symbols are on a map. Answers: A black circle on a railway is a train station, and a red area is a city or town park. 7 True There are formal and informal areas Students look at map A and choose the correct words. Answers: 1 1:50,000 4 156 2 paths 5 road 3 hill 6 train station
|
Descriptor: - match the words with the symbols. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the text again. - read the text again. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the table. Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Our neighbourhood |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading: A description of a place WB / Summative assessment for the unit “Our Neighbourhood”. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.5.1 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 6.5.6.1 link, with some support, sentences into a coherent paragraph using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: Recognise detailed information in extended conversation with support Give basic information about themselves and others in a talk Make up simple interrogative sentences to get information about the topic and ask questions |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Write the word map on the board and elicit the meaning. • Ask students what information we can find on maps, and elicit some ideas. • Ask students when they use maps. • Tell students they are going to practise reading maps in English |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:68 • Before students read the text, ask them to look at the photos and read the words in the box. Remind them that photos can help them interpret a text, and give them useful clues about the content. • Check understanding of the words in the box. In a stronger class, ask one or two students to say which words they chose and why. • When students have listened, discuss the words again and check their answer from the warm-up activity Ex: 2 P:68 • Ask students to read the text again and match topics with paragraphs. In a weaker class, they can complete this activity in pairs. • Check answers with the class. Ask students to identify the area of the text where they found the answer Summative assessment for the unit “Our Neighbourhood”.
Listening Task 1.Listen to the conversation and fill in the gaps. Use NO MORE THAN ONE WORD and a NUMBER.
Speaking Task 2. Work with your partner and tell him/her about the neighbourhood you live in. You have 1 minute to prepare and 2-3 minutes to talk. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students read the text. Choose the correct box. Answers: C Sark Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the text again and match topics with paragraphs. Answers: 1E 2D 3 A 4 B Students Listen to the conversation and fill in the gaps Answers: 1 life 2 family 3 18 or eighteen 4 spent 5 relaxed 6 country
|
Descriptor: - read the text Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the text again. - match topics with paragraphs. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - fill in the gaps Total: 6 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Our neighbourhood |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review 8 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 6.5.6.1 link, with some support, sentences into a coherent paragraph using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use vocabulary for places in a town. • Use adjectives to describe places. • Write and use the question forms Is there …? and Are there …? |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Write the word map on the board and elicit the meaning. • Ask students what information we can find on maps, and elicit some ideas. • Ask students when they use maps. • Tell students they are going to practise reading maps in English |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:102 • Read the words in the box and check students understand them all. • Check students understand the task, and encourage them to be as imaginative as possible in order to create their ideal place to live. • Remind students to make sure they use there’s and there are correctly. • Students write their sentences individually. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs, then ask some students to read their sentences to the class. Ex: 2 P:102 • Explain that the adjective that the words in the box are the opposites of these. • When students have checked their answers, use the recording to drill the pronunciation of any words that are new to students.
Ex: 3 P:102 • In a weaker class, tell students to circle the nouns to help them form the questions correctly. • Go round and listen as they are talking. Check that they are using short answers correctly. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students match the words in the box with sentences Answers: 1 train station 2 library 3 cinema 4 sports centre 5 restaurant 6 hospital 7 park 8 shop Students write the opposite. There are two adjectives that you don’t need. Answers: 1 ugly 2 dangerous 3 quiet 4 enormous 5 unfriendly 6 old 7 dirty 8 far Students write affirmative and negative sentences Answers: 1 There are some factories. 2 There aren’t any offices. 3 There are one or two cheap shops. 4 There isn’t a sports centre. 5 There aren’t any good restaurants. 6 There’s a train station. 7 There’s a nice library. 8 There are two cinemas |
Descriptor: -match the words in the box Total: 1 point Descriptor: - write the opposite. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - use there is and there are Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Our neighbourhood |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project. City profile |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.3.1 respect differing points of view 6.2.1.1 understand a sequence of supported classroom instructions 6.3.2.1 ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a city profile and find out key information from it. • Follow the steps in a project checklist. • Produce a profile about a famous city. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to think of some famous cities. Write these on the board, and ask them to say which country each city is in |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:103 • Allow students to look at the map quickly before they hide the text about Sydney. Point out that you want to find out how much they know about the city before they read the text. • Students write the answers to each question. They should complete this task individually if possible. • Discuss their ideas, but do not correct any wrong answers at this stage. Ex: 2 P:103 • Allow students time to read the text. Remind them that they should read it through quickly first, to get a general understanding of the meaning. Then they should read it again more carefully and find the information they need to check their answers from exercise 1. • Ask around the class to check answers, and to find out how many students answered correctly in exercise 1 Ex: 3 P:103 • Tell students that they are now going to make a similar poster about a famous city of their choice. • Put students into groups to prepare their posters. Allow them time to find out the information they need, using the internet or other resources. • Students will need to spend time on this outside the lesson, in order to gather photos and maps. Set a time limit for this, and encourage them to bring the material to the next lesson if possible. Alternatively, in a stronger class, you could ask them to plan their ideas in class and produce the whole project in their groups for homework. • If the project is being done in class, provide the materials each student will need for their poster: large pieces of paper and glue. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students cover the text and answer the question. What do you know about Sidney? Answers: Students own answers Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the text and check their answers. Answers: 1 Australia 2 On the east coast. 3 No, it isn’t. 4 4.4 million 5 English 6 Sydney Harbour Bridge, Sydney Opera House, Bondi Beach Students make a poster about a famous city. Follow the steps Answers: Students own answers
|
Descriptor: - read the text. - complete the task individually Total: 1 point . Descriptor: - read the text. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - make a poster -group work Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 Transport. |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Jobs |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for different jobs. • Do a quiz about famous people. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students what famous people they know. • Students will probably give the names of current celebrities. Accept a few names, then ask students if they know any famous people from the past. • Elicit a few names and write them on the board. Tell students they are going to do a quiz about famous people from the past. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:104 • In a weaker class, remind students what vowels are. • Students complete the quiz individually or in pairs. • If necessary, allow students to use the Wordlist or dictionaries to look up the words in the box. • Do not check answers at this stage. Ex: 2 P:104 •. Students listen and check their answers. In a weaker class, ask students if they need to listen again. • Make sure students understand the meaning of all the words from exercise 1, and model and drill the pronunciation of any words that are new to students. • Ask the question about the use of a and an and elicit the answer (we do). Ask students if this is the same or different in their own language. • Write on the board: My dad is a teacher. My parents are teachers. Elicit that we do not use a / an in plural sentences Ex: 3 P:104 • Go through the adjectives and check understanding. Ask for translations if necessary. • In a stronger class, you could categorize these into positive and negative adjectives in relation to work. Write positive and negative on the board as headings, and ask individual students to come up and write each word in the correct category. Not all of these will be clear cut, for instance some students might think that an easy job would be a positive thing, while others might want more challenge. In this case, encourage them to explain their ideas. • Students describe the jobs in pairs. Again, they will have different opinions about the jobs, so encourage them to give reasons for their choices. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the descriptions of the people with words in the box. Do the People and Transport Quiz. Answers: Students own answers Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen and check their answers. Do they use a and an with words for people in English. Answers: 2 businessman, Levi jeans 3 musician, saxophone 4 explorer, America 5 scientist, curium 6 queen, pizza 7 doctor, Doc Martens boots. Yes, we do use a and an with jobs in English.
Students look at the adjectives in the box. Which words can you use to describe the jobs and activities. Answers: Students own answers
|
Descriptor: - complete the quiz individually or in pairs. - do the quiz. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen and check their answers -use a and an article Total: 1 point Descriptor: - categorize the adjectives into positive and negative. Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 Transport. |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: 28.04.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Jobs2 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for talking about jobs. • Ask and answer about jobs you would like to do |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students what famous people they know. • Students will probably give the names of current celebrities. Accept a few names, then ask students if they know any famous people from the past. • Elicit a few names and write them on the board. Tell students they are going to do a quiz about famous people from the past. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 4 P:104 • Ask students to think about the kind of words that will complete each sentence – this is a useful skill in gapfill activities. • Check answers with the class, then play the CD to confirm. Ex: 5 P:104 • Students work individually to guess the jobs. • When they have listened to the CD to confirm their answers, ask how many students agree with the descriptions. Ask them to give reasons for their answers. • In a stronger class, ask students to write similar sentences describing different jobs. Ex: 6 P:104 • Students now put the key phrases into practice by discussing jobs. They should talk about jobs they would like to do and give reasons, as well as talk about the jobs that family members do. • Go round and listen as students are talking. Check they are using the adjectives appropriately to support their ideas.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the key phrases. Which phrases can you complete with a job. Answers: 1 job (mechanic) 2 job (actor) 3 job (teacher); adjective (stressful) 4 adjective (boring) 5 job (waiter)
Students read the descriptions and guess the jobs. Answers: 1 nurse 2 mechanic 3 businesswoman 4 waitress 5 teacher 6 fire fighter
Students work in pairs. Ask and answer the questions about jobs. Use the key phrases and the words in ex 3 discussing jobs Answers: Students own answers |
Descriptor: -complete the key phrases - listen and check Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work individually to guess the jobs. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - put the key phrases into practice by Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 Transport. |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading: The history of the steam engine |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 6.2.3.1 understand an increasing range of unsupported basic questions on general and curricular topics 6.3.2.1 ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general and curricular topics 6.4.4.1 read and understand with some support a limited range of short fiction and non-fiction texts understanding of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about English surnames and first names. • Read for general and specific information. • Talk about names. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Do a name survey in the class. Does anyone share a name? Do most people like their names, or would they like to change them? |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:106 • Ask students what the most popular first names are in their country. Ask if these names have always been popular, or if they have changed over time. Elicit that some first names remain popular, but others change according to fashions. Ask for examples of unusual names Background The top ten family names in England are: Smith, Jones, Williams, Taylor, Brown, Davies, Evans, Wilson, Thomas, and Johnson. In 2010 the most popular names for new babies in England were: (for boys) Jack, Harry, Alfie, Thomas and Oliver; (for girls) Olivia, Ruby, Emily, Grace and Lily Ex: 2 P:106 • Remind students that it is a good idea to read through all the headings first, before they read and listen to the text. Ex: 6 P:106 • In a stronger class, ask students to see how many they can answer before they read again and check. In a weaker class, ask students to say where they found the answers. • Students compare answers in pairs, before you check with the class. Check they have corrected the false sentences Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students answer the question. How often do use the train? Where do you go on it? of unusual names Answers: Students own answers Students read the text and match headings with paragraphs. Answers: 1 c 2 a 3 f 4 b 5 e Students read the text again and write true or false. Answers: 1 True. 2 True. 3 False. Surnames weren’t necessary in England because the population was small and most people lived in villages. 4 True. 5 False. Many parents named their daughters after the Queen of England in the 19th century.
|
Descriptor: -Ask for examples Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the text - match headings with paragraphs Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the text again - write true or false Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 Transport. |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: 05.05.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus: was/ were, there was/ there were |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.1.1 understand a sequence of supported classroom instructions 6.6.9.1 use simple present and simple past regular and irregular forms to describe routines, habits and states on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the affirmative, negative, and question forms of was and were. • Use was and were to ask and answer questions. • Learn the affirmative and negative forms of there was and there were. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Write was, wasn’t, were and weren’t on the board and elicit which are affirmative and which are negative. • Elicit that was and were are the past forms of is and are. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:107 • Refer students back to the first two paragraphs of the text on page 60, and ask them to complete the sentences. • Check answers with the class. • Allow students time to read the rules, and check they understand them. LANGUAGE NOTE We use was
with a singular subject and were with a plural subject: He was
happy. They were happy. NOT Ex: 2 P:107 • Students now apply the rules to the question and answer forms. Check they have completed items 1–6 correctly before they answer the questions. Ex: 3 P:107 • Read the example with the class and point out that students must write two sentences for each prompt, one negative and one affirmative. • Students write their sentences individually. • In a weaker class, check answers by asking students to read their sentences out, before students move on to ask and answer in pairs. • Go round and listen as students ask and answer. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the sentences from the text. Answers: 1 were 2 was 3 weren’t 4 wasn’t Students complete the questions and answers with was, were / wasn’t, weren’t Answers: 1 were 2 Was 3 wasn’t 4 Were 5 was 6 weren’t 1 Before 2 After Students write affirmative and negative sentence Answers: 1 William Boeing wasn’t a plane. He was an engineer. 2 The Beatles weren’t insects. They were musicians. 3 Henry Ford wasn’t a car. He was an inventor. 4 Marie and Pierre Curie weren’t explorers. They were scientists. 5 Bach and Mozart weren’t writers. They were musicians. 6 Queen Margherita wasn’t a pizza. She was a person. 7 Titanic wasn’t a village. It was a ship. 8 Picasso and Van Gogh weren’t actors. They were artists |
Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point
can complete the questions and answers with was, were / wasn’t, weren’t Total: 1 point Descriptor: - Read the example - write affirmative and negative sentence Total: 1 point |
Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 Transport. |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Strange Town USA |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the affirmative past simple form of regular verbs. • Practise the skills needed in multiple-choice listening tasks. • Listen to a radio programme about the origins of town names in America. • Listen for general meaning and specific details |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Write on the board: Christopher Columbus America. • Ask students what verb should go in the gap (discover) and elicit that the verb must be in the past tense because this happened in the past. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:108 • In a weaker class, check students understand the meaning of the verbs in the box, and allow them to complete the activity in pairs Ex: 2 P:108 • Read through the spelling rules with the class. • Students copy the table into their notebooks and add the past forms of the verbs from exercise 1. • Check answers with the class. Point out the double l in travelled and tell students that some verbs double their final consonant in their past tense form. Ex: 3 P:108 • Explain that if students read the questions and the options carefully, they may be able to eliminate some options that they know are false. • Do not check answers at this stage.
Ex: 4 P:108 • Refer students to the photos and the information about Strange Town USA. Allow students time to read it. • Play the CD. Students listen and choose the correct answers. Play it again for them to confirm their choices. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the sentences with the verbs in the box. Do the sentence refer to the past or the present? Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students study the spelling rules. Then complete the table with the verbs. Students read the information about Strange Town and listen to the programme.
|
- Descriptor: -complete the sentences Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the table with the verbs. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the information - listen to the programme Total: 1 point |
Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Transport. |
School: |
||
|
Date: 12.05.23 |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Past Simple of regular verbs |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.1.1 understand a sequence of supported classroom instructions 6.6.9.1 use simple present and simple past regular and irregular forms to describe routines, habits and states on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topic 6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the affirmative and negative past simple forms of regular verbs. • Write affirmative and negative sentences using the past simple. • Learn the use of different time expressionsto talk about time in the past. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Write on the board: Lions eat grass. • Elicit that the sentence is not true, and elicit the negative form: Lions don’t eat grass. • Write on the board: Columbus discovered Australia. • Elicit that the sentence is not true, and ask students how they would make this verb negative. • Elicit some ideas, but do not give students the answer. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:109 • Students study the sentences. Elicit that the blue words are time expressions, and that they refer to the present or the past. Ex: 2 P:109 • Allow students time to complete the rules individually, then check answers with the class. In a weaker class, do it as a whole class activity. LANGUAGE NOTE In negative
sentences in the past simple we use the base form of the verb, not
the past tense form: He didn’t play football. NOT
Ex: 3 P:109 • Read the example with the class. Point out that some of the affirmative sentences will be factually incorrect, so they should write correct sentences for these ones. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs. They may need to refer to other sources to find the answers to these. If possible, allow them time to do this in class
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students study the sentences and the words in blue. Which sentences refer to the present and which refer to the past? How do you know? Answers: 1 present 2 past 3 present 4 past ‘Now’ and ‘every Friday’ refer to the present. ‘In 2009’ and ‘last week’ refer to the past. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read and complete the rules. Answers: 1 Europeans explored Africa in the 18th century. False. Europeans explored Africa in the 19th century. 2 Tutankhamen lived in Egypt a long time ago. True. 3 The first astronauts visited space in 1981. False. The first astronauts visited space in 1961 4 Columbus arrived in South America about 500 years ago. False. Columbus arrived in Central America about 500 years ago. 5 People stopped using horses for transport in the 19th century. False. People stopped using horses for transport in the 20th century. Students write affirmative sentences using the past simple. Are they true or false?
|
Descriptor: - refer to the present or the past. -identify the tenses Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the rules individually Total: 1 point Answers: |
Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Transport. |
School: |
||
|
Date: 15.05.23 |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Speaking: Making and responding to suggestions. Summative Assessment for the unit “Transport”. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.5.5.1 link without support sentences using basic coordinating connectors |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to two conversations in which people make suggestions. • Learn key phrases for making and responding to suggestions |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Ask students about the last time they visited a new town / city. Ask what they took with them, and how they prepared before they left. • Write some ideas on the board. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:110 • Students look at the photo and answer the question. • Elicit that Tina and Jake are lost. Ask: What do you think they are saying? Elicit some ideas, then check students’ ideas about what they are looking at. Ex: 2 P:110 • Remind students to read the sentences on either side of the gap before choosing the correct option. • Students complete the dialogues, then confirm their ideas with the CD. In a weaker class, play it twice and allow them time to correct any mistakes Summative Assessment for the unit “Transport”. Reading Task 1.Read the text and definitions below. Find the proper word in the text and insert it into the table. Look up the words in the dictionary and check the answers.
Writing Task 2. Write a factual or fictitious story about your way to school. You can use the picture below or you can write about your own route to school.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the photo. What are Tina and Jake looking at? Answers: They are looking at a map because they are lost Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students complete the dialogue with sentences. Answers: 1 e 2 b 3 d 4 c 5 a Students read the text and definitions below Answers: 1 network 2 distance 3 railway 4 passenger 5 engine Students write a factual or fictitious story about your way to school Answers: Students’ own answers |
Descriptor: - look at the photo -answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the sentences - complete the dialogue with sentences. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the text Total: 5 point -can write about your own route to school. Total: 4 point |
Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 Transport. |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
An article about a town. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.6.9.1 use simple present and simple past regular and irregular forms to describe routines, habits and states on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model text. . • Learn about time expressions. • Learn key phrases for talking about a place. • Write an article about the history of London. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Refer students to the photo and ask: Where is Liverpool? (In the north of England.) • Ask students what they know about Liverpool. They will probably know about the football team, and may know that The Beatles came from there. Ask if they know anything about its history.. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:111 • Students read the model text and match the paragraphs Ex: 2 P:111 • Students read the text more closely to find more detailed information. In a weaker class, students can work in pairs.
Ex: 3 P:111 • Read through the key phrases with the class. To check understanding, ask students to translate the key phrases.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students read the model text. Match paragraphs with topics. Answers: 1 d 2 c 3a 4 b Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the model text again and answer the questions Answers: 1 The Mersey River. 2 Livpul. 3 About 500. 4 He was Queen Victoria’s husband Students study the key phrases. Match the key phrases with paragraphs.
|
Descriptor: - read the model text - match paragraphs with topics Total: 1 point
-can answer the questions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - study the key phrases. - match the key phrases with paragraphs Total: 1 point |
Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 Transport. |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My Country. Public transport. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 6.4.7.1 recognize typical features at word, sentence and text level in a limited range of written genres 6.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a text about getting around Almaty • Revise and learn transport words • Learn how to use the zero conditional • Write a questionnaire and write the results |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Books closed. Divide students into pairs and write Transport on the board. • Allow students two minutes to brainstorm how many forms of transport they can think of. Tell them to use the English words if they know them and to use Kazakh words if they don’t. • Ask students to give you the words. If they are in English, write them straight onto the board. If they are in Kazakh first ask other students if they know what the words are in English, before giving them the English translation and writing it on the board. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:112 • Students look at the words in the box. If there are any new words not mentioned in the warm-up ask if any of the students know the meaning before giving it to them. • Students circle the types of transport they can use locally before comparing their answers with a partner. • Check answers as a class Ex: 2 P:112 • Ask students if they have been to Almaty and, if so, what form of transport they used there. • Focus students’ attention on the questions and give them a minute to read them through before playing the audio for them to listen to while they read the texts. • Students complete the questions individually before checking in pairs. • Go through the answers as a class.
Ex: 3 P:112 • Focus students’ attention on the sentences in blue. Ask them what function is performed by these sentences (they are giving information/advice). • Ask them what tense is used after if in the sentence. And ask students to complete the first gap in the rules. • Then ask them whether the sentences refer to something that is always true or only sometimes true, and get students to circle the correct word in the sentence.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the words in the box and circle the types of transport you can use in your town. Answers: Students’ own answers Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read and listen to the text. Match the information to the type of transport. Total: 1 point Answers: 1 Trolley buses 2 Bikes 3 Bikes 4 Metro 5 Buses 6 Metro Students look at the sentences in blue and complete the rules for the zero conditionals. Answers: 1 present simple 2 always |
Descriptor: -look at the words in the box - circle the types of transport Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read and listen to the text - match the information to the type of transport Descriptor: - focus students’ attention on the sentences in blue - complete the rules for the zero conditionals Total: 1 point |
Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 Transport. |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. History: Famous explorers |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.6.9.1 use simple present and simple past regular and irregular forms to describe routines, habits and states on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn about Mount Everest and the first people who climbed it. • Discuss explorers from your country. • Think about and plan an expedition to an extreme place. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to name any big or important mountains in their country. Ask if they have visited or climbed any of them. • Ask if anyone enjoys mountain climbing as a hobby, or whether they would like to try it |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:113 • Look at the photos with the students. Before they read, they can guess the name of the mountain and who the people might be, but do not confirm or deny any answers at this stage. • Allow students time to read the text, but tell them not to worry about any words they do not understand. • When students have listened and checked their answers, find out how many answered correctly. Ex: 2 P:113 • Students read the text again more carefully and answer the questions. This time, they can look up any unfamiliar words in a dictionary. In a weaker class, you could explain the word summit to the class first. • Check answers with the class by asking individual students to read out their ideas.
Ex: 3 P:113 • Read through the questions with the class. Explain that they should think about each of the topics and make notes in order to plan their responses. • If students find it difficult to think of explorers, have a brainstorming session with the class before students start working in pairs. Write ideas on the board. • You could also allow students to do further research using the internet or reference books if either are available. • Students can discuss their answers with a partner. In a stronger class, you could ask one or two pairs of students to report their answers to questions 4 and 5 to the class
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the photos and answer the questions. Then read and listen to the text and check your answers. Answers: 1 Mount Everest. 2 Edmond Hillary and Tenzing Norgay Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the text again and answer the questions. Answers: 1 It is often very windy and cold. 2 To climb Everest. 3 Because there isn’t a lot of oxygen. 4 Heavy oxygen bottles. 5 Because the weather was good. Students answer the questions - answer the questions. Answers: Students’ own answers. |
Descriptor: - look at the photos - answer the questions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the text again - answer the questions. Total: 1 point -can answer the questions Total: 1 point |
Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
і
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 Transport. |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative Control work for the 4th term. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.4.1 Understand with limited support the main points of extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.4.2.1 Understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 6.5.3.1 Write with some support about personal feelings and opinions on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.3.7.1 Use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -follow the direction of the talk by tracking the key words - pronounce words and phrases correctly - identify specific information |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Listening Task. Listen to the talk twice. CD3. Tapescript 3. And transcript for listening task can be found after the mark scheme
Mark sentences as True or False.
Fill in the gaps. Write no more than ONE WORD OR A NUMBER for each answer.
Reading Task. Read the dialogue about transportation
Choose the right option. Answer the questions. Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS OR A NUMBER for each answer
Answer the questions. Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS OR A NUMBER for each answer
Writing Task. Choose ONE of the topics below.
Speaking Task. Choose one of the cards and make up an individual talk. Use subject related vocabulary while talking on a given topic. You have 1 minute to prepare and 1-2 minutes to talk Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students listen to the talk twice Answers: Student’s own answer Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the dialogue about transportation Answers: Students choose ONE of the topics below. Answers: Students choose one of the cards and make up an individual talk
|
Descriptor: - listen to the talk twice - Mark sentences as True or False. Total: 5 point Descriptor: -can read the dialogue about transportation Total: 5 point Descriptor: - answer the questions. -can choose ONE of the topics below. Total: 6 point Descriptor: - choose one of the cards - make up an individual talk Total: 6 point Answers: |
Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 Transport. |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review 9 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 6.5.6.1 link, with some support, sentences into a coherent paragraph using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions with diverse partners -write a coherent paragraph /short text stating and explaining an idea, or describing a place, object |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students what famous people they know. • Students will probably give the names of current celebrities. Accept a few names, then ask students if they know any famous people from the past. • Elicit a few names and write them on the board. Tell students they are going to do a quiz about famous people |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:114 • Ask students to reorder the letters and write the jobs • Check answers with the class.
Ex: 2 P:114 Ask students to choose the correct words.
Ex: 3 P:114 Explain the students complete the dialogue with the affirmative or negative form of was and were
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students reorder the letters and write the jobs. Answers: 1 waitress 2 farmer 3 builder 4 chef 5 actor 6 nurse 7 doctor 8 firefighter 9 mechanic 10 scientist Students choose the correct words. Answers: 1 discovered 2 surname 3 ago 4 chef 5 King 6 dangerous 7 century 8 brand name Students complete the dialogue with the affirmative or negative form of was and were Answers: 1 was 8 were 2 Were 9 was 3 was 10 Were 4 weren’t 11 weren’t 5 Was 12 were 6 wasn’t 13 were 7 wasn’t |
Descriptor: - reorder the letters - write the jobs Total: 1 point Descriptor: - choose the correct words. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the dialogue - use the affirmative or negative form of was and were Total: 1 point |
Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 Transport. |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Skill Round - up. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.6.3.1 use a growing variety of adjectives and regular and irregular comparative and superlative adjectives on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - conduct research, evaluate and communicate findings to answer questions or solve problems - pronounce words and phrases correctly |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students what famous people they know. • Students will probably give the names of current celebrities. Accept a few names, then ask students if they know any famous people from the past. • Elicit a few names and write them on the board. Tell students they are going to do a quiz about famous people |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:115 • Focus students on the four photos. Ask what they think the listening activity is going to be about (towns / cities). • Then go through the words in the box. In a weaker class, recap the meanings by asking for translations. • Students identify the places which aren’t shown in the photos.
Ex: 2 P:115 • Read the instructions with the class. Elicit that this means three of the pictures are in Cambridge, and one isn’t. • Play the CD. Students listen for this information.
Ex: 3 P:115 • Tell students that they are now going to listen again for more detailed information. • Allow them time to read the sentences carefully before they listen. Tell them to complete as much information as they can from memory. • Play the CD twice. Encourage students to make notes the first time they listen, and to complete the answers when they have heard the recording the second time
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the photos. Which of the places in the box are not in the photos. Answers: town centre, supermarket, school Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to a conversation. Which place in the photos is not in Cambridge. Answers: The Regency Café Students listen again and complete the sentences. Answers: 1 800 2 scientist 3 7 million 4 history 5 science; ICT 6 basketball 7 maths 8 salads; sandwiches
|
Descriptor: - Focus students on the four photos - identify the places which aren’t shown in the photos Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen to a conversation. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point |
Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! |
Poster
|