Applied Biology with the basics of soil
Applied Biology with the basics of soil


#1 слайд
APPLIED BIOLOGY WITH THE
BASICS OF SOIL
1 слайд
APPLIED BIOLOGY WITH THE BASICS OF SOIL

#2 слайд
Soil is a special body of the
Earth
1. Soil formation and their diversity
2. Composition and properties of soil
3. Care of soil
4. Effect of plants on soil
5. Destruction of soils
6. Soil protection
2 слайд
Soil is a special body of the Earth 1. Soil formation and their diversity 2. Composition and properties of soil 3. Care of soil 4. Effect of plants on soil 5. Destruction of soils 6. Soil protection

#3 слайд
The soil is the upper thin layer of the earth's crust (from tens of
centimeters to two or three meters), mostly covered with
vegetation and fertile. It is able to provide plants with water, air,
heat and the necessary substances, so that plants develop.
Let's get acquainted with how the soil is formed.
Soil formation
The emergence and formation of soil is a very complex process.
Soil is the result of the impact on the rocks of climatic factors
and living organisms. Although the soil was formed from rock,
but it does not resemble it.
Sharp change of temperature, wind, water destroy rocks, they
lose strength, crumble.
Invisible by the simple eye microorganisms (bacteria,
microscopic fungi), secreting active substances, perform great
work on the transformation of rock into soil.
3 слайд
The soil is the upper thin layer of the earth's crust (from tens of centimeters to two or three meters), mostly covered with vegetation and fertile. It is able to provide plants with water, air, heat and the necessary substances, so that plants develop. Let's get acquainted with how the soil is formed. Soil formation The emergence and formation of soil is a very complex process. Soil is the result of the impact on the rocks of climatic factors and living organisms. Although the soil was formed from rock, but it does not resemble it. Sharp change of temperature, wind, water destroy rocks, they lose strength, crumble. Invisible by the simple eye microorganisms (bacteria, microscopic fungi), secreting active substances, perform great work on the transformation of rock into soil.

#4 слайд
In addition, they decompose the remains of plants and the
remains of animals, resulting in the formation of humus, which
makes the soil fertile.
In the soil live different animals: earthworms,
ants, various larvae, beetles and other insects.
In addition, there are often field mice, ground
squirrels, hamsters and other earthworms.
Some of them live in the soil permanently,
others only hibernate in it, others hide from the
heat, some lay eggs in the soil or use it as a
refuge (Figure 1 ). All of them affect the
condition of the soil: grind and recycle plant
remains, break and loosen the soil, and mix its
layers. So the soil with a certain structure and
properties is formed.
4 слайд
In addition, they decompose the remains of plants and the remains of animals, resulting in the formation of humus, which makes the soil fertile. In the soil live different animals: earthworms, ants, various larvae, beetles and other insects. In addition, there are often field mice, ground squirrels, hamsters and other earthworms. Some of them live in the soil permanently, others only hibernate in it, others hide from the heat, some lay eggs in the soil or use it as a refuge (Figure 1 ). All of them affect the condition of the soil: grind and recycle plant remains, break and loosen the soil, and mix its layers. So the soil with a certain structure and properties is formed.
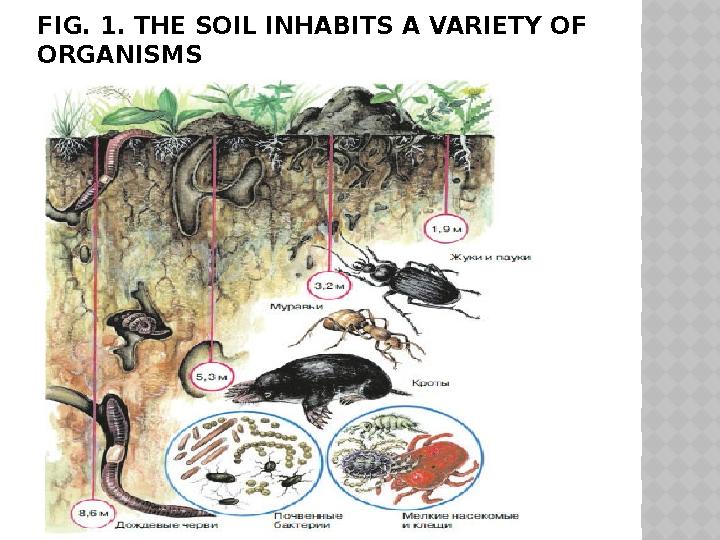
#5 слайд
FIG. 1. THE SOIL INHABITS A VARIETY OF
ORGANISMS
5 слайд
FIG. 1. THE SOIL INHABITS A VARIETY OF ORGANISMS

#6 слайд
Soil structure
If you take a handful of the top layer of soil
rich in humus, squeeze it, then open your
fingers, then you will see that a lump of earth
scattered into a lot of dark little lumps. Such
a land is loose, it is available for air, water is
better preserved in it. This soil is structural;
on structural soils plants grow well, because
the roots receive enough moisture and air.
Unstructured soil is finely divided, silty.
Compared with structural soil, it is more
prone to flushing with water, blowing. It
practically does not retain water, and plants
develop very poorly.
6 слайд
Soil structure If you take a handful of the top layer of soil rich in humus, squeeze it, then open your fingers, then you will see that a lump of earth scattered into a lot of dark little lumps. Such a land is loose, it is available for air, water is better preserved in it. This soil is structural; on structural soils plants grow well, because the roots receive enough moisture and air. Unstructured soil is finely divided, silty. Compared with structural soil, it is more prone to flushing with water, blowing. It practically does not retain water, and plants develop very poorly.
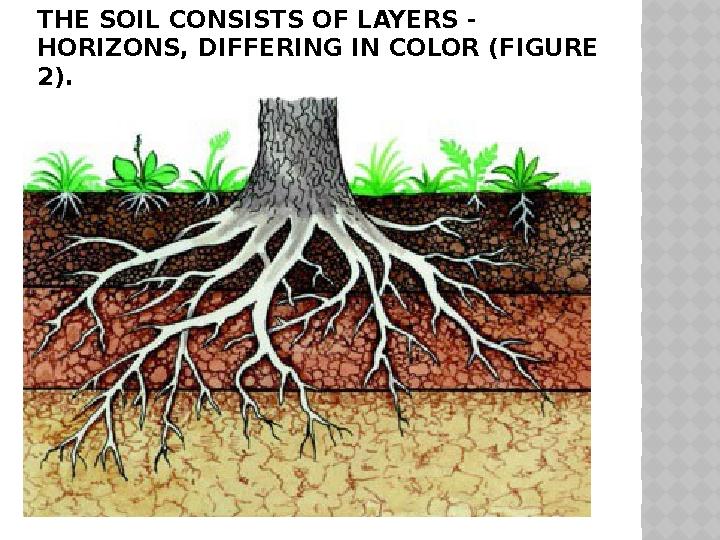
#7 слайд
THE SOIL CONSISTS OF LAYERS -
HORIZONS, DIFFERING IN COLOR (FIGURE
2).
7 слайд
THE SOIL CONSISTS OF LAYERS - HORIZONS, DIFFERING IN COLOR (FIGURE 2).

#8 слайд
The uppermost horizon is dark. It accumulates the
remains of dead living organisms that form humus. The
main property of the soil depends on the amount of
humus - its fertility. The more humus in the soil, the
better the plants are provided with the necessary
substances. Below is a layer containing a little humus,
so it has a gray, as in ash, color. The soil in which this
layer is well developed is called podzolic.
Podzolic soils are formed in the northern regions of our
country under the canopy of the forest and under the
grassy cover of meadows. Here, moisture accumulates
in the soil and favorable conditions for rotting are
created. Under the influence of microbes, fallen leaves
and branches turn into humus, in which soil acids form
during decomposition. That is why podzolic soils are
often acidic. The humus horizon in podzolic soils is
small, so they are poor in substances necessary for
plants.
8 слайд
The uppermost horizon is dark. It accumulates the remains of dead living organisms that form humus. The main property of the soil depends on the amount of humus - its fertility. The more humus in the soil, the better the plants are provided with the necessary substances. Below is a layer containing a little humus, so it has a gray, as in ash, color. The soil in which this layer is well developed is called podzolic. Podzolic soils are formed in the northern regions of our country under the canopy of the forest and under the grassy cover of meadows. Here, moisture accumulates in the soil and favorable conditions for rotting are created. Under the influence of microbes, fallen leaves and branches turn into humus, in which soil acids form during decomposition. That is why podzolic soils are often acidic. The humus horizon in podzolic soils is small, so they are poor in substances necessary for plants.

#9 слайд
In the south of our country, the soil was
formed with powerful humus deposits -
chernozems. In them, a black color layer of
soil reaches more than a meter in thickness.
Chernozem soils from podzolic differ
considerably in the number of substances
important for plants.
In different natural conditions, soils are
formed, which differ significantly in
composition, structure, and properties. In our
country, except podzolic and chernozem,
peat, solonchak, sandy, clayey types of soils
are encountered (Fig. 3 ).
9 слайд
In the south of our country, the soil was formed with powerful humus deposits - chernozems. In them, a black color layer of soil reaches more than a meter in thickness. Chernozem soils from podzolic differ considerably in the number of substances important for plants. In different natural conditions, soils are formed, which differ significantly in composition, structure, and properties. In our country, except podzolic and chernozem, peat, solonchak, sandy, clayey types of soils are encountered (Fig. 3 ).
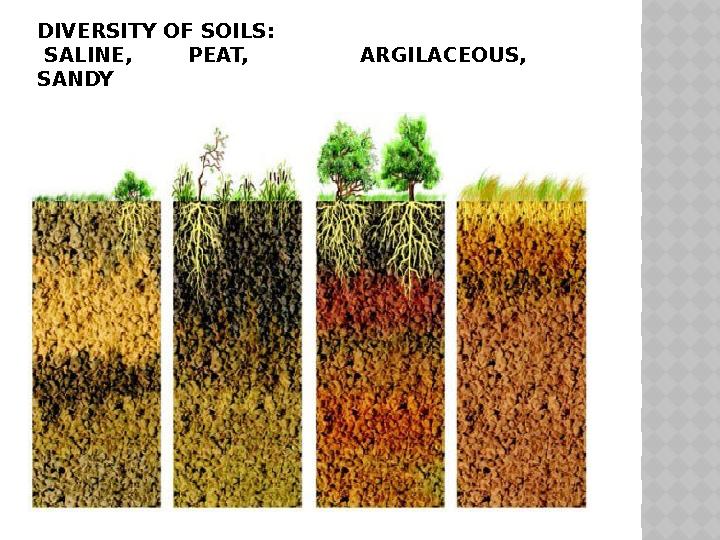

#10 слайд
DIVERSITY OF SOILS:
SALINE, PEAT, ARGILACEOUS,
SANDY
10 слайд
DIVERSITY OF SOILS: SALINE, PEAT, ARGILACEOUS, SANDY

#11 слайд
COMPOSITION AND PROPERTIES OF
SOIL
The soil consists of sand, clay and humus. It has
the necessary water and air for living
organisms. In addition, it contains soluble and
water-insoluble mineral salts. Sand, clay, water,
air, mineral salts are inorganic substances of
the soil. Humus is formed by organic
substances, which are the remains of plants
and animal remains, processed by
microorganisms.
Sandy soil, in which sand predominates, the
particles are loosely linked and the roots of
plants are difficult to harden. Sandy soil quickly
warms up and becomes dry. Since plants can
not live without water, sandy soils are
unsuitable for them.
11 слайд
COMPOSITION AND PROPERTIES OF SOIL The soil consists of sand, clay and humus. It has the necessary water and air for living organisms. In addition, it contains soluble and water-insoluble mineral salts. Sand, clay, water, air, mineral salts are inorganic substances of the soil. Humus is formed by organic substances, which are the remains of plants and animal remains, processed by microorganisms. Sandy soil, in which sand predominates, the particles are loosely linked and the roots of plants are difficult to harden. Sandy soil quickly warms up and becomes dry. Since plants can not live without water, sandy soils are unsuitable for them.

#12 слайд
Clay soil, in which clay predominates, is also of
little use for plant life. When there is no rain
and the clay soil dries, it becomes hard as a
stone, and does not allow the roots of plants to
grow. In rainy times the clay becomes viscous,
swells and does not allow water to go deep.
From this, it stagnates, and the roots of plants
without air begin to rot.
The amount of mineral salts in the soil is not
the same. If there are a lot of salts in the soil, it
is harmful to plants and they grow poorly. Such
soil is called solonchak soil. The excess of acids
in the soil also adversely affects the
development of plants.
Sandy, clayey, solonchak, acidic soils are
unfavorable for the development of plants.
12 слайд
Clay soil, in which clay predominates, is also of little use for plant life. When there is no rain and the clay soil dries, it becomes hard as a stone, and does not allow the roots of plants to grow. In rainy times the clay becomes viscous, swells and does not allow water to go deep. From this, it stagnates, and the roots of plants without air begin to rot. The amount of mineral salts in the soil is not the same. If there are a lot of salts in the soil, it is harmful to plants and they grow poorly. Such soil is called solonchak soil. The excess of acids in the soil also adversely affects the development of plants. Sandy, clayey, solonchak, acidic soils are unfavorable for the development of plants.

#13 слайд
Soil properties
You know that the water in the soil can move from top to
bottom and to the sides. However, it can move in the soil
and from the bottom up. How does this happen? Between
the smallest particles of the soil are gaps, which are called
capillaries. Water sticks to the walls of the capillaries and
as if creeps upwards. The thinner the capillaries of the soil,
the higher the water rises over them.
The property of the soil to raise water from the bottom up
is of great importance in plant life. When there is no rain
for a long time, plants use water coming from deeper
layers of soil.
But through the capillaries water from the soil evaporates.
After heavy rain or watering, the earth is covered with a
crust that crackles. In the crust there are a lot of
capillaries, so the earth dries quickly. To keep moisture in
the soil, it should be loosened.
Soil is the environment in which agricultural plants are
grown.
The ability of the soil to meet the needs of plants in the
necessary substances, water, air is called fertility.
Soil fertility depends on the amount of humus in it: the
more it is, the more fertile soil.
13 слайд
Soil properties You know that the water in the soil can move from top to bottom and to the sides. However, it can move in the soil and from the bottom up. How does this happen? Between the smallest particles of the soil are gaps, which are called capillaries. Water sticks to the walls of the capillaries and as if creeps upwards. The thinner the capillaries of the soil, the higher the water rises over them. The property of the soil to raise water from the bottom up is of great importance in plant life. When there is no rain for a long time, plants use water coming from deeper layers of soil. But through the capillaries water from the soil evaporates. After heavy rain or watering, the earth is covered with a crust that crackles. In the crust there are a lot of capillaries, so the earth dries quickly. To keep moisture in the soil, it should be loosened. Soil is the environment in which agricultural plants are grown. The ability of the soil to meet the needs of plants in the necessary substances, water, air is called fertility. Soil fertility depends on the amount of humus in it: the more it is, the more fertile soil.

#14 слайд
CARE OF SOIL
For a long time people who work on the
earth treat it with love and respect,
because their life depends largely on
the land.
Soil cultivation
The soil of our country is far from being
everywhere fertile. To improve the
fertility of the soil, it must be properly
processed. Plants develop better on
loose soil, rich in water and air. Plowed
with a plow or spade-sprinkled soil
becomes loose (Figure 3 ).
14 слайд
CARE OF SOIL For a long time people who work on the earth treat it with love and respect, because their life depends largely on the land. Soil cultivation The soil of our country is far from being everywhere fertile. To improve the fertility of the soil, it must be properly processed. Plants develop better on loose soil, rich in water and air. Plowed with a plow or spade-sprinkled soil becomes loose (Figure 3 ).

#15 слайд
FIG. 3 . PLOWING - ONE OF THE WAYS TO
CARE FOR THE SOIL
15 слайд
FIG. 3 . PLOWING - ONE OF THE WAYS TO CARE FOR THE SOIL

#16 слайд
Large lumps should be crushed, but do not turn
them into dust.
Plants grow, take away certain substances from
the soil and drain it, make it less fertile. That's why
the soil needs to be fertilized. The best fertilizer is
manure. This organic fertilizer contains all the
substances necessary for plants. After application
of manure to the soil, it becomes more loose,
better passes water and air to the roots of plants.
Mineral fertilizers, containing the mineral salts
necessary for the plant, also contribute to the soil.
To increase the fertility of acidic soils, lime is
introduced into them (it must first be finely
ground). It reduces the acidity of the soil, reacts
chemically with soil acids, forming substances that
are harmless to living organisms. In addition to
lime, ash and finely ground limestone can be used.
To increase the fertility of saline soils, they need to
bring in grinded gypsum.
16 слайд
Large lumps should be crushed, but do not turn them into dust. Plants grow, take away certain substances from the soil and drain it, make it less fertile. That's why the soil needs to be fertilized. The best fertilizer is manure. This organic fertilizer contains all the substances necessary for plants. After application of manure to the soil, it becomes more loose, better passes water and air to the roots of plants. Mineral fertilizers, containing the mineral salts necessary for the plant, also contribute to the soil. To increase the fertility of acidic soils, lime is introduced into them (it must first be finely ground). It reduces the acidity of the soil, reacts chemically with soil acids, forming substances that are harmless to living organisms. In addition to lime, ash and finely ground limestone can be used. To increase the fertility of saline soils, they need to bring in grinded gypsum.

#17 слайд
EFFECT OF PLANTS ON SOIL
You already know that plants from the
soil receive water, dissolved in it mineral
salts, air for breathing roots. Conversely,
plants affect the soil. The vegetation
cover of the Earth is constantly
changing. For example, where there was
a forest, a shrub grew, and a birch tree
appeared on the place of the field
(Figure 4 ). The reasons for such changes
are different: climate impact, fires,
human activities (logging, grazing) and
much more. Soil also does not remain
unchanged.
17 слайд
EFFECT OF PLANTS ON SOIL You already know that plants from the soil receive water, dissolved in it mineral salts, air for breathing roots. Conversely, plants affect the soil. The vegetation cover of the Earth is constantly changing. For example, where there was a forest, a shrub grew, and a birch tree appeared on the place of the field (Figure 4 ). The reasons for such changes are different: climate impact, fires, human activities (logging, grazing) and much more. Soil also does not remain unchanged.

#18 слайд
FIG. 4 . IN PLACE OF THE FIELD
APPEARED BIRCH
18 слайд
FIG. 4 . IN PLACE OF THE FIELD APPEARED BIRCH

#19 слайд
Let's mentally go into the thick spruce forest.
It is gloomy, cool. On the surface of the soil
there is almost no grass: it can not survive
without light and heat. But a lot of fallen pine
needles, which contain various substances
that are harmful to the life of bacteria. That's
why the needles do not rot. Here settle very
small, invisible mushrooms. They, in turn,
secrete substances that dissolve the mineral
salts of the soil.
When precipitation occurs, mineral salts are
washed from the upper horizons of the soil
downward. Many organic substances
disappear, the soil structure is destroyed,
and it becomes podzolic, infertile.
19 слайд
Let's mentally go into the thick spruce forest. It is gloomy, cool. On the surface of the soil there is almost no grass: it can not survive without light and heat. But a lot of fallen pine needles, which contain various substances that are harmful to the life of bacteria. That's why the needles do not rot. Here settle very small, invisible mushrooms. They, in turn, secrete substances that dissolve the mineral salts of the soil. When precipitation occurs, mineral salts are washed from the upper horizons of the soil downward. Many organic substances disappear, the soil structure is destroyed, and it becomes podzolic, infertile.

#20 слайд
Fig. 5 . Spruce forest. In conditions of excessive moisture,
trees grow poorly, some die; the forest is thinning
20 слайд
Fig. 5 . Spruce forest. In conditions of excessive moisture, trees grow poorly, some die; the forest is thinning

#21 слайд
When the soil is drained or excessively moistened, it
reflects on the trees. They grow poorly, some die
(Figure 74), so the forest thinens, becomes light, it
begins to grow more grass. Under the grass podzolic
soils vary greatly. Grasses, dying off, enrich the soil
with humus, the soil sticks together into clumps,
becomes structural. And now there is a new fertile
soil with a large supply of necessary substances for
plants.
Thus, with the change of vegetation, the soil also
changes.
Why do plants change the soil so much? Scientists
have found out that between the soil and plants
there is a constant exchange of various substances.
Plants absorb substances from the soil, use them
and form new substances in their body. After the
plants die in the soil, humus is partially returned to
the soil in the form of humus and new substances
are formed, which are formed in the plants. It is
through this exchange that plants can change the
soil (Figure 75). It is also important because the soil
is not depleted due to it.
21 слайд
When the soil is drained or excessively moistened, it reflects on the trees. They grow poorly, some die (Figure 74), so the forest thinens, becomes light, it begins to grow more grass. Under the grass podzolic soils vary greatly. Grasses, dying off, enrich the soil with humus, the soil sticks together into clumps, becomes structural. And now there is a new fertile soil with a large supply of necessary substances for plants. Thus, with the change of vegetation, the soil also changes. Why do plants change the soil so much? Scientists have found out that between the soil and plants there is a constant exchange of various substances. Plants absorb substances from the soil, use them and form new substances in their body. After the plants die in the soil, humus is partially returned to the soil in the form of humus and new substances are formed, which are formed in the plants. It is through this exchange that plants can change the soil (Figure 75). It is also important because the soil is not depleted due to it.
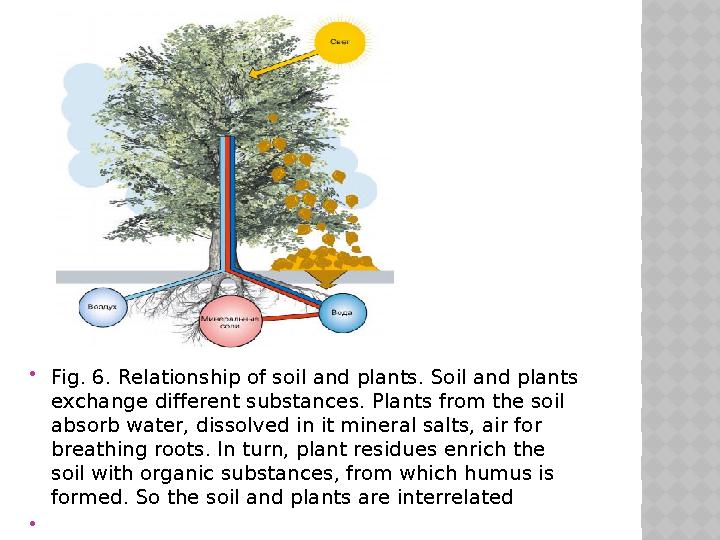
#22 слайд
Fig. 6 . Relationship of soil and plants. Soil and plants
exchange different substances. Plants from the soil
absorb water, dissolved in it mineral salts, air for
breathing roots. In turn, plant residues enrich the
soil with organic substances, from which humus is
formed. So the soil and plants are interrelated
22 слайд
Fig. 6 . Relationship of soil and plants. Soil and plants exchange different substances. Plants from the soil absorb water, dissolved in it mineral salts, air for breathing roots. In turn, plant residues enrich the soil with organic substances, from which humus is formed. So the soil and plants are interrelated

#23 слайд
DESTRUCTION OF SOILS
Soil erosion
The wind, water and man by their activities can destroy the soil. In
areas where the wind reaches a great strength, it blows out the soil
and carries it in the form of dust for long distances. Dust storms are
formed. Especially strongly the wind blows freshly plowed, loosened
and unstructured soils. This leads to the fact that the fertile layer
becomes thinner. There were cases when he carried off the entire
arable layer from the field.
Destruction of the fertile layer of the soil by water and wind is called
erosion (in Latin, the word "erosion" means corroding).
Destruction of the soil under the influence of wind - wind erosion -
leads to the formation of deserts.
The soil can also be destroyed by water. After heavy rain,
muddy streams flow along the earth. The mud is nothing but
particles of soil washed away with water. Deep "wounds" it
inflicts on the ground: for several years it has washed huge
ravines, carried many tons of land to low places and rivers.
Wherever there is even a slight bias, the water is washed
away from it almost all the soil. There is water erosion (Figure
7 ).
23 слайд
DESTRUCTION OF SOILS Soil erosion The wind, water and man by their activities can destroy the soil. In areas where the wind reaches a great strength, it blows out the soil and carries it in the form of dust for long distances. Dust storms are formed. Especially strongly the wind blows freshly plowed, loosened and unstructured soils. This leads to the fact that the fertile layer becomes thinner. There were cases when he carried off the entire arable layer from the field. Destruction of the fertile layer of the soil by water and wind is called erosion (in Latin, the word "erosion" means corroding). Destruction of the soil under the influence of wind - wind erosion - leads to the formation of deserts. The soil can also be destroyed by water. After heavy rain, muddy streams flow along the earth. The mud is nothing but particles of soil washed away with water. Deep "wounds" it inflicts on the ground: for several years it has washed huge ravines, carried many tons of land to low places and rivers. Wherever there is even a slight bias, the water is washed away from it almost all the soil. There is water erosion (Figure 7 ).

#24 слайд
Fig. 7. Water erosion. Stormy streams of water wash away
the soil. The stages of erosion and growth of the ravine are
shown here
Erosion can also occur with improper soil cultivation. So, the
tractor, treating the field, leaves furrows on it. If they are laid
along the slope of the hill, then under the rain down streams
of water rush and rapidly expand the furrows, forming rills.
The latter often give rise to the formation of a ravine.
24 слайд
Fig. 7. Water erosion. Stormy streams of water wash away the soil. The stages of erosion and growth of the ravine are shown here Erosion can also occur with improper soil cultivation. So, the tractor, treating the field, leaves furrows on it. If they are laid along the slope of the hill, then under the rain down streams of water rush and rapidly expand the furrows, forming rills. The latter often give rise to the formation of a ravine.

#25 слайд
Soil protection
Plants are the best defenders of the soil. Herbs bind
it with roots and prevent erosion. They protect the
khoronyu soil and from blowing. Herbs contribute to
the formation of a structure (lumps) of soil, which is
more difficult to destroy.
Trees stop the growth of ravines, foliage cover the
soil from the wind and protect it from water erosion.
Under the trees, the soil absorbs water better than
in the fields. If several rows of trees are planted on
the slope, then, draining, the water will be rapidly
absorbed under them and go deep (Fig. 8).
25 слайд
Soil protection Plants are the best defenders of the soil. Herbs bind it with roots and prevent erosion. They protect the khoronyu soil and from blowing. Herbs contribute to the formation of a structure (lumps) of soil, which is more difficult to destroy. Trees stop the growth of ravines, foliage cover the soil from the wind and protect it from water erosion. Under the trees, the soil absorbs water better than in the fields. If several rows of trees are planted on the slope, then, draining, the water will be rapidly absorbed under them and go deep (Fig. 8).

#26 слайд
26 слайд

шағым қалдыра аласыз
















