Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic Waves


#1 слайд
UCSD Physics 10
ElectromagnetismElectromagnetism
Electromagnetic InductionElectromagnetic Induction
Electromagnetic WavesElectromagnetic WavesJames Clerk Maxwell Michael Faraday
1 слайд
UCSD Physics 10 ElectromagnetismElectromagnetism Electromagnetic InductionElectromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic WavesElectromagnetic WavesJames Clerk Maxwell Michael Faraday
#2 слайд
Spring 2008 2UCSD Physics 10
ElectromagnetismElectromagnetism
•
Electricity and magnetism are different facets of Electricity and magnetism are different facets of
electromagnetismelectromagnetism
–
a moving electric charge produces magnetic fields
–
changing magnetic fields move electric charges
•
This connection first elucidated by Faraday, MaxwellThis connection first elucidated by Faraday, Maxwell
•
Einstein saw electricity and magnetism as frame-Einstein saw electricity and magnetism as frame-
dependent facets of dependent facets of
unifiedunified
electromagneticelectromagnetic
force force
2 слайд
Spring 2008 2UCSD Physics 10 ElectromagnetismElectromagnetism • Electricity and magnetism are different facets of Electricity and magnetism are different facets of electromagnetismelectromagnetism – a moving electric charge produces magnetic fields – changing magnetic fields move electric charges • This connection first elucidated by Faraday, MaxwellThis connection first elucidated by Faraday, Maxwell • Einstein saw electricity and magnetism as frame-Einstein saw electricity and magnetism as frame- dependent facets of dependent facets of unifiedunified electromagneticelectromagnetic force force
#3 слайд
Spring 2008 3UCSD Physics 10
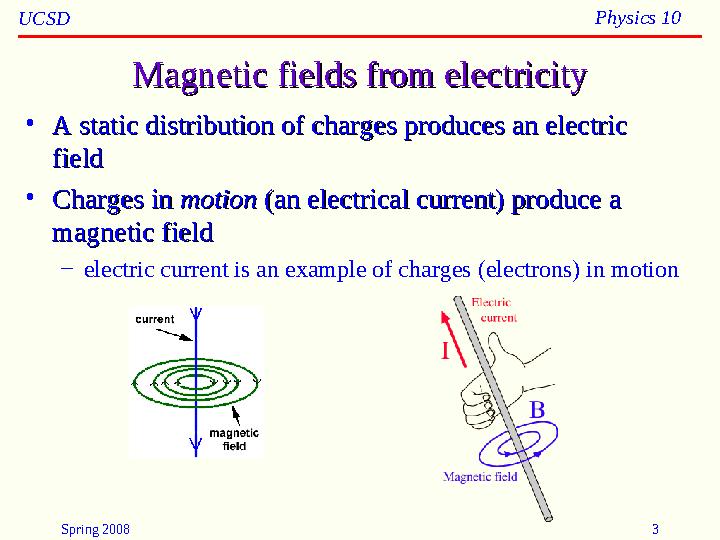
Magnetic fields from electricityMagnetic fields from electricity
•
A static distribution of charges produces an electric A static distribution of charges produces an electric
fieldfield
•
Charges in Charges in
motionmotion
(an electrical current) produce a (an electrical current) produce a
magnetic fieldmagnetic field
–
electric current is an example of charges (electrons) in motion
3 слайд
Spring 2008 3UCSD Physics 10 Magnetic fields from electricityMagnetic fields from electricity • A static distribution of charges produces an electric A static distribution of charges produces an electric fieldfield • Charges in Charges in motionmotion (an electrical current) produce a (an electrical current) produce a magnetic fieldmagnetic field – electric current is an example of charges (electrons) in motion
#4 слайд
Spring 2008 4UCSD Physics 10
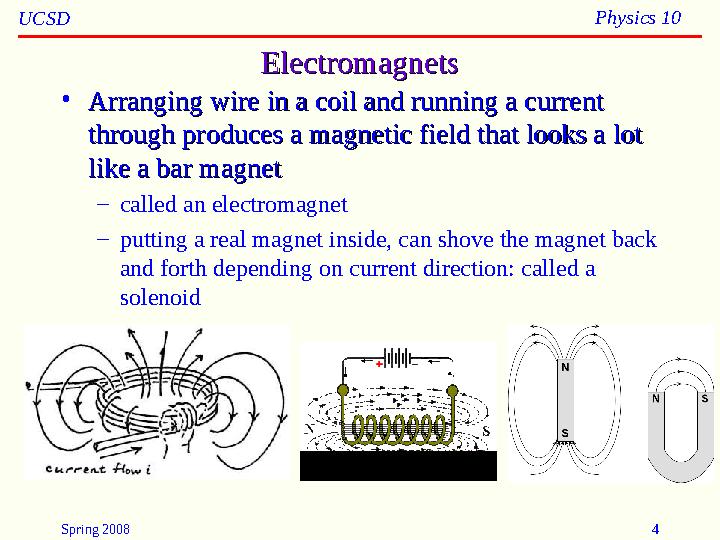
ElectromagnetsElectromagnets
•
Arranging wire in a coil and running a current Arranging wire in a coil and running a current
through produces a magnetic field that looks a lot through produces a magnetic field that looks a lot
like a bar magnetlike a bar magnet
–
called an electromagnet
–
putting a real magnet inside, can shove the magnet back
and forth depending on current direction: called a
solenoid
4 слайд
Spring 2008 4UCSD Physics 10 ElectromagnetsElectromagnets • Arranging wire in a coil and running a current Arranging wire in a coil and running a current through produces a magnetic field that looks a lot through produces a magnetic field that looks a lot like a bar magnetlike a bar magnet – called an electromagnet – putting a real magnet inside, can shove the magnet back and forth depending on current direction: called a solenoid
#5 слайд
Spring 2008 5UCSD Physics 10
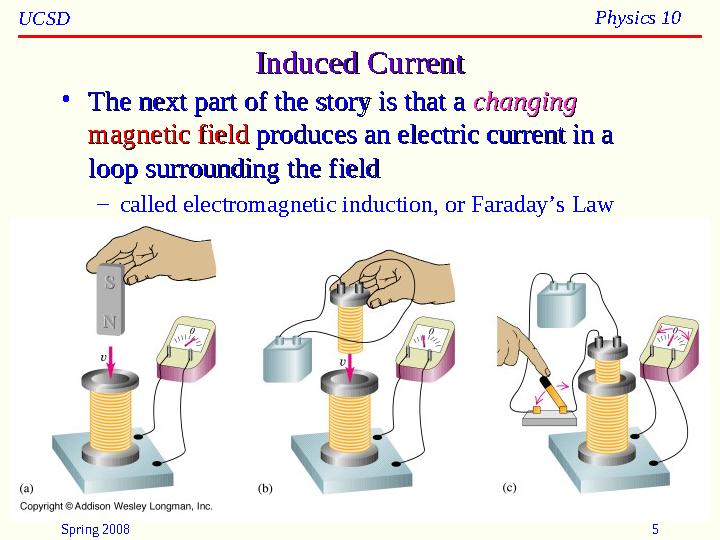
Induced CurrentInduced Current
•
The next part of the story is that a The next part of the story is that a
changingchanging
magnetic fieldmagnetic field
produces an electric current in a produces an electric current in a
loop surrounding the fieldloop surrounding the field
–
called electromagnetic induction, or Faraday’s Law
5 слайд
Spring 2008 5UCSD Physics 10 Induced CurrentInduced Current • The next part of the story is that a The next part of the story is that a changingchanging magnetic fieldmagnetic field produces an electric current in a produces an electric current in a loop surrounding the fieldloop surrounding the field – called electromagnetic induction, or Faraday’s Law
#6 слайд
Spring 2008 6UCSD Physics 10
The Electromagnetic ConnectionThe Electromagnetic Connection
•
A A
changingchanging
magnetic field produces an electric field, and a magnetic field produces an electric field, and a
changing electric field produces a magnetic field. changing electric field produces a magnetic field.
•
Electric and Magnetic fields can produce forces on chargesElectric and Magnetic fields can produce forces on charges
•
An An
acceleratingaccelerating
charge produces electromagnetic waves charge produces electromagnetic waves
(radiation)(radiation)
•
Both electric and magnetic fields can transport energyBoth electric and magnetic fields can transport energy
–
Electric field energy used in electrical circuits, e.g., released in
lightning
–
Magnetic field carries energy through transformer, for example
6 слайд
Spring 2008 6UCSD Physics 10 The Electromagnetic ConnectionThe Electromagnetic Connection • A A changingchanging magnetic field produces an electric field, and a magnetic field produces an electric field, and a changing electric field produces a magnetic field. changing electric field produces a magnetic field. • Electric and Magnetic fields can produce forces on chargesElectric and Magnetic fields can produce forces on charges • An An acceleratingaccelerating charge produces electromagnetic waves charge produces electromagnetic waves (radiation)(radiation) • Both electric and magnetic fields can transport energyBoth electric and magnetic fields can transport energy – Electric field energy used in electrical circuits, e.g., released in lightning – Magnetic field carries energy through transformer, for example

#7 слайд
Spring 2008 7UCSD Physics 10
Electromagnetic RadiationElectromagnetic Radiation
•
Interrelated electric and magnetic fields traveling through spaceInterrelated electric and magnetic fields traveling through space
•
All electromagnetic radiation travels at All electromagnetic radiation travels at
cc
= 3 = 3
1010 88
m/s m/s
in in
vacuum – vacuum –
thethe
cosmic speed limit! cosmic speed limit!
–
real number is 299792458.0 m/s exactly
7 слайд
Spring 2008 7UCSD Physics 10 Electromagnetic RadiationElectromagnetic Radiation • Interrelated electric and magnetic fields traveling through spaceInterrelated electric and magnetic fields traveling through space • All electromagnetic radiation travels at All electromagnetic radiation travels at cc = 3 = 3 1010 88 m/s m/s in in vacuum – vacuum – thethe cosmic speed limit! cosmic speed limit! – real number is 299792458.0 m/s exactly

#8 слайд
Spring 2008 8UCSD Physics 10
What’s “Waving” in EM waves?What’s “Waving” in EM waves?
•
What medium transports sound waves?What medium transports sound waves?
–
Can there be sound waves in the vacuum of outer space?
•
What medium transports water waves?What medium transports water waves?
•
What medium transports radio waves?What medium transports radio waves?
•
A topic of considerable debate in the late 1800’s and early A topic of considerable debate in the late 1800’s and early
1900’s1900’s
•
Led to the concept of the “luminiferous ether” – an invisible Led to the concept of the “luminiferous ether” – an invisible
“jello” that was thought to vibrate electromagnetically “jello” that was thought to vibrate electromagnetically
•
Experiments that sought this ether didn’t find it! Experiments that sought this ether didn’t find it!
•
This was quite a surpriseThis was quite a surprise
Electromagnetic waves travel through empty space!
8 слайд
Spring 2008 8UCSD Physics 10 What’s “Waving” in EM waves?What’s “Waving” in EM waves? • What medium transports sound waves?What medium transports sound waves? – Can there be sound waves in the vacuum of outer space? • What medium transports water waves?What medium transports water waves? • What medium transports radio waves?What medium transports radio waves? • A topic of considerable debate in the late 1800’s and early A topic of considerable debate in the late 1800’s and early 1900’s1900’s • Led to the concept of the “luminiferous ether” – an invisible Led to the concept of the “luminiferous ether” – an invisible “jello” that was thought to vibrate electromagnetically “jello” that was thought to vibrate electromagnetically • Experiments that sought this ether didn’t find it! Experiments that sought this ether didn’t find it! • This was quite a surpriseThis was quite a surprise Electromagnetic waves travel through empty space!

#9 слайд
Spring 2008 9UCSD Physics 10
Examples of Electromagnetic RadiationExamples of Electromagnetic Radiation
•
AM and FM radio waves (including TV signals)AM and FM radio waves (including TV signals)
•
Cell phone communication linksCell phone communication links
•
MicrowavesMicrowaves
•
Infrared radiationInfrared radiation
•
Light Light
•
X-raysX-rays
•
Gamma raysGamma rays
•
What distinguishes these from one another?What distinguishes these from one another?
9 слайд
Spring 2008 9UCSD Physics 10 Examples of Electromagnetic RadiationExamples of Electromagnetic Radiation • AM and FM radio waves (including TV signals)AM and FM radio waves (including TV signals) • Cell phone communication linksCell phone communication links • MicrowavesMicrowaves • Infrared radiationInfrared radiation • Light Light • X-raysX-rays • Gamma raysGamma rays • What distinguishes these from one another?What distinguishes these from one another?

#10 слайд
Spring 2008 10UCSD Physics 10
Uses of Electromagnetic WavesUses of Electromagnetic Waves
•
Communication systems Communication systems
–
One-way and two-way
•
Radar Radar
•
Cooking (with microwaves)Cooking (with microwaves)
•
Medical Imaging (X rays)Medical Imaging (X rays)
•
““
Night Vision” (infrared)Night Vision” (infrared)
•
Astronomy (radio, Astronomy (radio,
wave, IR, visible, UV, gamma)wave, IR, visible, UV, gamma)
All that we experience through our eyes is conveyed by
electromagnetic radiation…
10 слайд
Spring 2008 10UCSD Physics 10 Uses of Electromagnetic WavesUses of Electromagnetic Waves • Communication systems Communication systems – One-way and two-way • Radar Radar • Cooking (with microwaves)Cooking (with microwaves) • Medical Imaging (X rays)Medical Imaging (X rays) • ““ Night Vision” (infrared)Night Vision” (infrared) • Astronomy (radio, Astronomy (radio, wave, IR, visible, UV, gamma)wave, IR, visible, UV, gamma) All that we experience through our eyes is conveyed by electromagnetic radiation…

#11 слайд
Spring 2008 11UCSD Physics 10
The Electromagnetic SpectrumThe Electromagnetic Spectrum
•
Relationship between frequency, speed and Relationship between frequency, speed and
wavelengthwavelength
f f
··
= c = c
ff
is frequency, is frequency,
is wavelength, is wavelength,
cc
is speed of light is speed of light
•
Different frequencies of electromagnetic radiation Different frequencies of electromagnetic radiation
are better suited to different purposesare better suited to different purposes
•
The frequency of a radio wave determines its The frequency of a radio wave determines its
propagation characteristics through various mediapropagation characteristics through various media
11 слайд
Spring 2008 11UCSD Physics 10 The Electromagnetic SpectrumThe Electromagnetic Spectrum • Relationship between frequency, speed and Relationship between frequency, speed and wavelengthwavelength f f ·· = c = c ff is frequency, is frequency, is wavelength, is wavelength, cc is speed of light is speed of light • Different frequencies of electromagnetic radiation Different frequencies of electromagnetic radiation are better suited to different purposesare better suited to different purposes • The frequency of a radio wave determines its The frequency of a radio wave determines its propagation characteristics through various mediapropagation characteristics through various media
#12 слайд
Spring 2008 12UCSD Physics 10
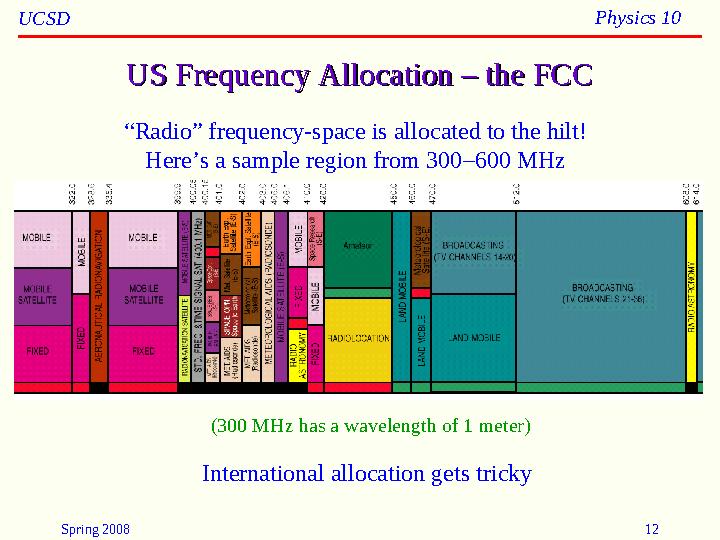
US Frequency Allocation – the FCCUS Frequency Allocation – the FCC
(300 MHz has a wavelength of 1 meter)“ Radio” frequency-space is allocated to the hilt!
Here’s a sample region from 300 –600 MHz
International allocation gets tricky
12 слайд
Spring 2008 12UCSD Physics 10 US Frequency Allocation – the FCCUS Frequency Allocation – the FCC (300 MHz has a wavelength of 1 meter)“ Radio” frequency-space is allocated to the hilt! Here’s a sample region from 300 –600 MHz International allocation gets tricky
#13 слайд
Spring 2008 13UCSD Physics 10
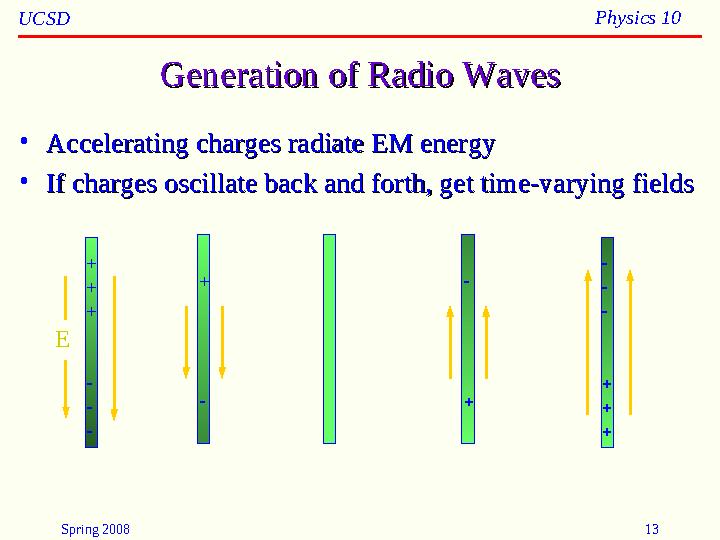
Generation of Radio WavesGeneration of Radio Waves
•
Accelerating charges radiate EM energyAccelerating charges radiate EM energy
•
If charges oscillate back and forth, get time-varying fieldsIf charges oscillate back and forth, get time-varying fields
E +
+
+
+
13 слайд
Spring 2008 13UCSD Physics 10 Generation of Radio WavesGeneration of Radio Waves • Accelerating charges radiate EM energyAccelerating charges radiate EM energy • If charges oscillate back and forth, get time-varying fieldsIf charges oscillate back and forth, get time-varying fields E + + + +
#14 слайд
Spring 2008 14UCSD Physics 10
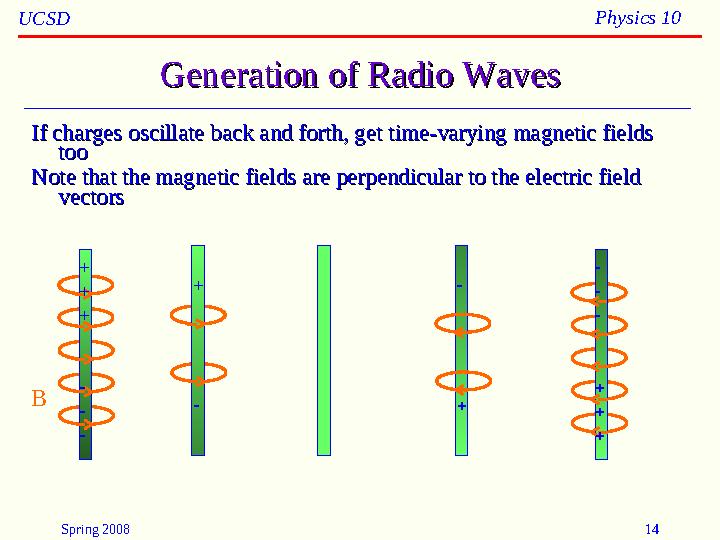
Generation of Radio WavesGeneration of Radio Waves
If charges oscillate back and forth, get time-varying magnetic fields If charges oscillate back and forth, get time-varying magnetic fields
tootoo
Note that the magnetic fields are perpendicular to the electric field Note that the magnetic fields are perpendicular to the electric field
vectorsvectors
B +
+
+
+
14 слайд
Spring 2008 14UCSD Physics 10 Generation of Radio WavesGeneration of Radio Waves If charges oscillate back and forth, get time-varying magnetic fields If charges oscillate back and forth, get time-varying magnetic fields tootoo Note that the magnetic fields are perpendicular to the electric field Note that the magnetic fields are perpendicular to the electric field vectorsvectors B + + + +
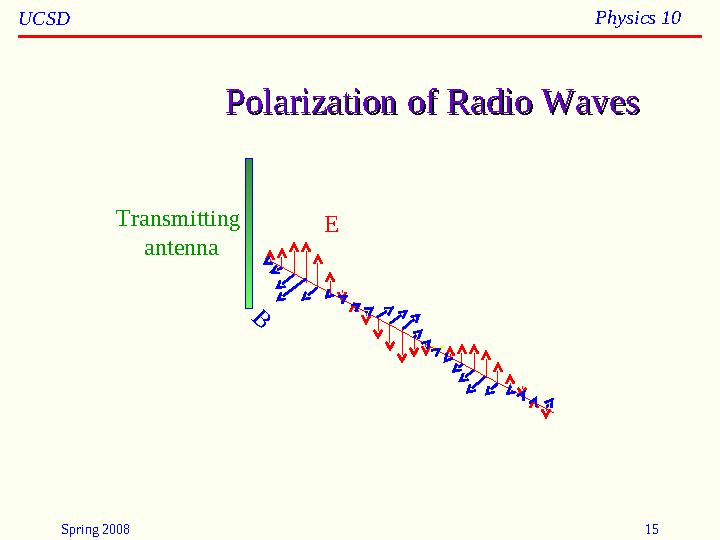
#15 слайд
Spring 2008 15UCSD Physics 10
Polarization of Radio WavesPolarization of Radio WavesB
ETransmitting
antenna
15 слайд
Spring 2008 15UCSD Physics 10 Polarization of Radio WavesPolarization of Radio WavesB ETransmitting antenna
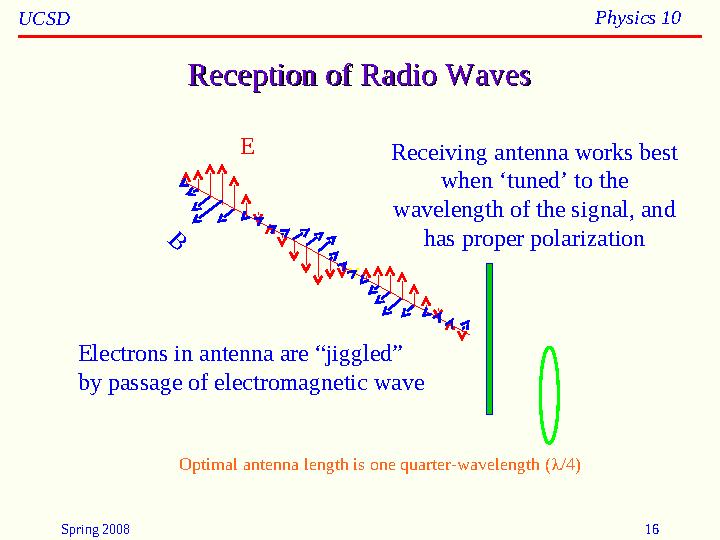
#16 слайд
Spring 2008 16UCSD Physics 10
Reception of Radio WavesReception of Radio Waves
Receiving antenna works best
when ‘tuned’ to the
wavelength of the signal, and
has proper polarization
Electrons in antenna are “jiggled”
by passage of electromagnetic waveB E
Optimal antenna length is one quarter-wavelength ( /4)
16 слайд
Spring 2008 16UCSD Physics 10 Reception of Radio WavesReception of Radio Waves Receiving antenna works best when ‘tuned’ to the wavelength of the signal, and has proper polarization Electrons in antenna are “jiggled” by passage of electromagnetic waveB E Optimal antenna length is one quarter-wavelength ( /4)

#17 слайд
Spring 2008 17UCSD Physics 10
QuestionsQuestions
Why are car radio antennas vertical?Why are car radio antennas vertical?
Why are cell phone antennas so short?Why are cell phone antennas so short?
How do polarizing sunglasses work?How do polarizing sunglasses work?
17 слайд
Spring 2008 17UCSD Physics 10 QuestionsQuestions Why are car radio antennas vertical?Why are car radio antennas vertical? Why are cell phone antennas so short?Why are cell phone antennas so short? How do polarizing sunglasses work?How do polarizing sunglasses work?

#18 слайд
Spring 2008 18UCSD Physics 10
AssignmentsAssignments
•
Read Chapter 31 for FridayRead Chapter 31 for Friday
•
Q/O #4 due 5/23 by midnightQ/O #4 due 5/23 by midnight
•
HW 6 due 5/23: 22.E.1, 22.E.5, 22.E.11, 22.E.16, HW 6 due 5/23: 22.E.1, 22.E.5, 22.E.11, 22.E.16,
22.E.20, 22.E.30, 22.E.33, 22.P.1, 23.E.3, 26.E.7, 22.E.20, 22.E.30, 22.E.33, 22.P.1, 23.E.3, 26.E.7,
26.E.9, 26.E.1126.E.9, 26.E.11
18 слайд
Spring 2008 18UCSD Physics 10 AssignmentsAssignments • Read Chapter 31 for FridayRead Chapter 31 for Friday • Q/O #4 due 5/23 by midnightQ/O #4 due 5/23 by midnight • HW 6 due 5/23: 22.E.1, 22.E.5, 22.E.11, 22.E.16, HW 6 due 5/23: 22.E.1, 22.E.5, 22.E.11, 22.E.16, 22.E.20, 22.E.30, 22.E.33, 22.P.1, 23.E.3, 26.E.7, 22.E.20, 22.E.30, 22.E.33, 22.P.1, 23.E.3, 26.E.7, 26.E.9, 26.E.1126.E.9, 26.E.11

шағым қалдыра аласыз
















