Etimology
Etimology


#1 слайд
Тақырыбы
The Etymology of
English Words The earliest group of English
borrowings.
Celtic borrowings.
The period of Christianization.
The characteristic features of
Scandinavian borrowings.
Norman borrowings.
The Renaissance Period.
The etymological structure of
English vocabulary.
1 слайд
Тақырыбы The Etymology of English Words The earliest group of English borrowings. Celtic borrowings. The period of Christianization. The characteristic features of Scandinavian borrowings. Norman borrowings. The Renaissance Period. The etymological structure of English vocabulary.

#2 слайд
English vocabulary
contains an immense
number of words of
foreign origin.
Explanations for this
should be sought in the
history of the language
which is closely
connected with the
history of the nation
speaking the language.
2 слайд
English vocabulary contains an immense number of words of foreign origin. Explanations for this should be sought in the history of the language which is closely connected with the history of the nation speaking the language.

#3 слайд
The first century B.C. Most territory
now known to us as Europe is
occupied by the Roman Empire.
Among the inhabitants of the continent
are Germanic tribes, “barbarians” as
the arrogant Romans call them. Theirs
is really a rather primitive stage of
development, especially if compared
with the high civilization and
refinement of Rome.
3 слайд
The first century B.C. Most territory now known to us as Europe is occupied by the Roman Empire. Among the inhabitants of the continent are Germanic tribes, “barbarians” as the arrogant Romans call them. Theirs is really a rather primitive stage of development, especially if compared with the high civilization and refinement of Rome.
#4 слайд
Several of the Germanic
tribes (the most numerous
amongst them being the
Angles, the Saxons and the
Jutes) migrated across the sea
now known as the English
Channel to the British Isles.
There they were confronted
by the Celts, the original
inhabitants of the Isles. The
Celts desperately defended
their lands against the
invaders. Celtic words (Modern English bald,
down, glen (лощина), druid
(кельтский жрец), bard,
cradle(колыбель)Celtic borrowings.
4 слайд
Several of the Germanic tribes (the most numerous amongst them being the Angles, the Saxons and the Jutes) migrated across the sea now known as the English Channel to the British Isles. There they were confronted by the Celts, the original inhabitants of the Isles. The Celts desperately defended their lands against the invaders. Celtic words (Modern English bald, down, glen (лощина), druid (кельтский жрец), bard, cradle(колыбель)Celtic borrowings.

#5 слайд
This century was significant for the
hristianization of England. Latin
was the official language of the
Christian church, and consequently
the spread of Christianity was
accomplished by a new period of
Latin borrowings.
Additionally, there were educational
terms. It was quite natural that
these were also Latin borrowings,The period of Cristianization.
5 слайд
This century was significant for the hristianization of England. Latin was the official language of the Christian church, and consequently the spread of Christianity was accomplished by a new period of Latin borrowings. Additionally, there were educational terms. It was quite natural that these were also Latin borrowings,The period of Cristianization.

#6 слайд
N orm an F rench
borrow ingsFrom the end of the 8 th
c. to the
middle of the 11 th
c. England
underwent several Scandinavian
invasions which left their trace on
English vocabulary. Here are
some examples of early
Scandinavian borrowings: call v,
take v, die v, law n, husband,
window, ill.
Some of the words of this group
are easily recognizable as
Scandinavian borrowings by the
initial sk- combination. E.g. sky,
skill, skin, ski, skirt. The characteristic features of
Scandinavian borrowings.
With the famous Battle of Hastings, when
the English were defeated by the Normans
under William the Conqueror, we come to
the eventful epoch of the Norman Conquest.
6 слайд
N orm an F rench borrow ingsFrom the end of the 8 th c. to the middle of the 11 th c. England underwent several Scandinavian invasions which left their trace on English vocabulary. Here are some examples of early Scandinavian borrowings: call v, take v, die v, law n, husband, window, ill. Some of the words of this group are easily recognizable as Scandinavian borrowings by the initial sk- combination. E.g. sky, skill, skin, ski, skirt. The characteristic features of Scandinavian borrowings. With the famous Battle of Hastings, when the English were defeated by the Normans under William the Conqueror, we come to the eventful epoch of the Norman Conquest.
#7 слайд
Administrative words: state,
government, parliament.
Legal terms: court, judge, justice,
crime, prison.
Military terms: army, war, soldier,
officer, enemy.
Educational terms: pupil, lesson,
library, science, pen, pencil.
Numerous terms of everyday life
were also borrowed from French in
this period: e.g. table, plate, saucer,
dinner, supper, autumn, uncle, etc. 6. The Renaissance Period.
In England, as in all European
countries, this period was marked by
significant developments in science,
art and culture and, also, by a revival
of interest in the ancient civilizations
of Greece and Rome and their
languages.
Italian also contributed a
considerable number of words to
English, e.g. piano, violin, opera,
alarm.
7 слайд
Administrative words: state, government, parliament. Legal terms: court, judge, justice, crime, prison. Military terms: army, war, soldier, officer, enemy. Educational terms: pupil, lesson, library, science, pen, pencil. Numerous terms of everyday life were also borrowed from French in this period: e.g. table, plate, saucer, dinner, supper, autumn, uncle, etc. 6. The Renaissance Period. In England, as in all European countries, this period was marked by significant developments in science, art and culture and, also, by a revival of interest in the ancient civilizations of Greece and Rome and their languages. Italian also contributed a considerable number of words to English, e.g. piano, violin, opera, alarm.
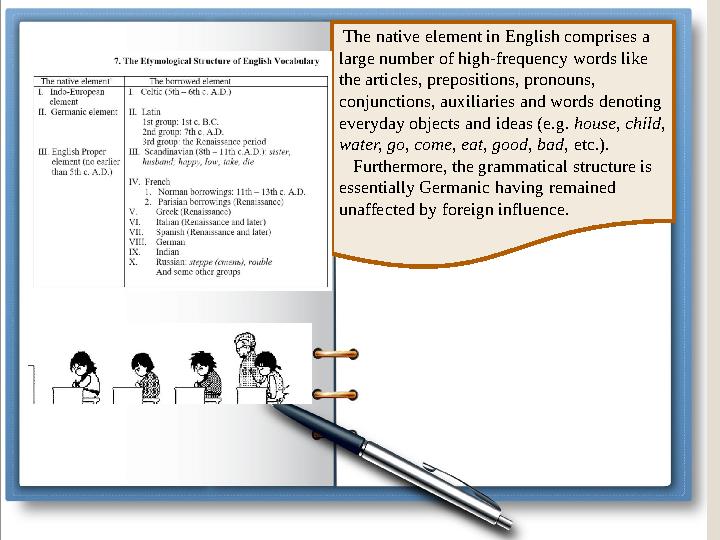
#8 слайд
The native element in English comprises a
large number of high-frequency words like
the articles, prepositions, pronouns,
conjunctions, auxiliaries and words denoting
everyday objects and ideas (e.g. house, child,
water, go, come, eat, good, bad, etc.).
Furthermore, the grammatical structure is
essentially Germanic having remained
unaffected by foreign influence.
8 слайд
The native element in English comprises a large number of high-frequency words like the articles, prepositions, pronouns, conjunctions, auxiliaries and words denoting everyday objects and ideas (e.g. house, child, water, go, come, eat, good, bad, etc.). Furthermore, the grammatical structure is essentially Germanic having remained unaffected by foreign influence.
#9 слайд
By the Indo-European element are
meant words of roots common to all or
most languages of the Indo-European
group.
I. Family relations: father, mother, brother, son, daughter.
II. Parts of the human body: foot, nose, lip, heart.
III. Animals: cow, swine, goose.
IV. Plants: tree, birch (ср. р. берёза), corn.
V. Time of day: day, night.
VI. Heavenly bodies (небесные тела): sun, moon, star.
VII. Numerous adjectives: red, new, glad, sad.
VIII. The numerals from one to a hundred.
IX. Pronouns – personal (except they which is a Scandinavian
borrowing); demonstrative.
X. Numerous verbs: be (ср. р усск . быть), stand (стоять), sit
(сидеть), eat (есть), know.
9 слайд
By the Indo-European element are meant words of roots common to all or most languages of the Indo-European group. I. Family relations: father, mother, brother, son, daughter. II. Parts of the human body: foot, nose, lip, heart. III. Animals: cow, swine, goose. IV. Plants: tree, birch (ср. р. берёза), corn. V. Time of day: day, night. VI. Heavenly bodies (небесные тела): sun, moon, star. VII. Numerous adjectives: red, new, glad, sad. VIII. The numerals from one to a hundred. IX. Pronouns – personal (except they which is a Scandinavian borrowing); demonstrative. X. Numerous verbs: be (ср. р усск . быть), stand (стоять), sit (сидеть), eat (есть), know.

#10 слайд
The Germanic element represents
words of roots common to all or most
Germanic languages. Some of the main
groups of Germanic words are the same
as in the Indo-European element.
I. Parts of the human body: head, hand, arm, finger, bone.
II. Animals: bear, fox, calf.
III. Plants: oak, fir, grass.
IV. Natural phenomena: rain, frost.
V. Seasons of the year: winter, spring, summer ( autumn is a French
borrowing).
VI. Landscape features: sea, land.
VII. Human dwellings and furniture: house, room, bench.
VIII. Sea-going vessels: boat, ship.
IX. Adjectives: green, blue, grey, white, small, high, old, good.
X. Verbs: see, hear, speak, tell, say, answer, make, drink.
10 слайд
The Germanic element represents words of roots common to all or most Germanic languages. Some of the main groups of Germanic words are the same as in the Indo-European element. I. Parts of the human body: head, hand, arm, finger, bone. II. Animals: bear, fox, calf. III. Plants: oak, fir, grass. IV. Natural phenomena: rain, frost. V. Seasons of the year: winter, spring, summer ( autumn is a French borrowing). VI. Landscape features: sea, land. VII. Human dwellings and furniture: house, room, bench. VIII. Sea-going vessels: boat, ship. IX. Adjectives: green, blue, grey, white, small, high, old, good. X. Verbs: see, hear, speak, tell, say, answer, make, drink.

#11 слайд
It has been mentioned that the
English proper element is opposed
to the first two groups. These words
are specifically English having no
cognates in other languages whereas
for Indo-European and Germanic
words such cognates can always be
found
Here are some examples of English
proper words. These words stand
quite alone in the vocabulary system
of Indo-European languages: bird,
boy, girl, lord, lady, woman, daisy,
always.
11 слайд
It has been mentioned that the English proper element is opposed to the first two groups. These words are specifically English having no cognates in other languages whereas for Indo-European and Germanic words such cognates can always be found Here are some examples of English proper words. These words stand quite alone in the vocabulary system of Indo-European languages: bird, boy, girl, lord, lady, woman, daisy, always.

шағым қалдыра аласыз
















