Kazakh medical system
Kazakh medical system


#1 слайд
Kazakh medical
system
1 слайд
Kazakh medical system

#2 слайд
Medicine in Kazakhstan, like in any
other country, is called upon to
protect the health and well-being of
citizens of Kazakhstan.
The health status of the population is
an integral indicator of the social
orientation of society and social
guarantees that characterize the
degree of state responsibility to its
citizens
2 слайд
Medicine in Kazakhstan, like in any other country, is called upon to protect the health and well-being of citizens of Kazakhstan. The health status of the population is an integral indicator of the social orientation of society and social guarantees that characterize the degree of state responsibility to its citizens

#3 слайд
In Kazakhstan the responsibility for public health and health
promotion activities is shared by the following major actors: the
sanitary-epidemiological services, the HIVAAIDS centres, the
National Centre for Healthy Lifestyles, primary health care
providers, NGOs and international agencies.
The most important challenge of the country's health sector in
the domain of public health lies in clarifying, coordinating and
streamlining the roles and responsibilities of these different
agencies and actors.Public health
3 слайд
In Kazakhstan the responsibility for public health and health promotion activities is shared by the following major actors: the sanitary-epidemiological services, the HIVAAIDS centres, the National Centre for Healthy Lifestyles, primary health care providers, NGOs and international agencies. The most important challenge of the country's health sector in the domain of public health lies in clarifying, coordinating and streamlining the roles and responsibilities of these different agencies and actors.Public health

#4 слайд
The Ministry of Health is in charge of the following functions with regard
to public health (President of Kazakhstan, 2009):
regulating the
registration of
baby food
products, food
and biologically
active
supplements,
genetically
modified
sources,
disinfection
materials,
repellents, and
products and
substances
harmful to
health; ensuring
intersectoral
coordination in
implementatio
n of national
and sectoral
programmes
on health
protection and
the promotion
of healthy
lifestyles. regulating the
registration of
infectious,
parasitic,
occupational
and other
diseases and
poisoning; developing
national
policies, plans
and
programmes
on public
health; establishing the
rules for sanitary-
epidemiological
monitoring;
4 слайд
The Ministry of Health is in charge of the following functions with regard to public health (President of Kazakhstan, 2009): regulating the registration of baby food products, food and biologically active supplements, genetically modified sources, disinfection materials, repellents, and products and substances harmful to health; ensuring intersectoral coordination in implementatio n of national and sectoral programmes on health protection and the promotion of healthy lifestyles. regulating the registration of infectious, parasitic, occupational and other diseases and poisoning; developing national policies, plans and programmes on public health; establishing the rules for sanitary- epidemiological monitoring;
#5 слайд
Trends in life expectancy in Kazakhstan are broadly similar to those observed in the CIS overall, although the
decline in life expectancy after 1991 was steeper and life expectancy in Kazakhstan has remained below the
CIS average.
Life expectancy dropped from 68.81 in 1990 to 64.4 in 1996, and has since increased again to 68.67 in 2009.
However, this still fell over a year short of its 1990 level and was 12.2 years lower than average life
expectancy in the EUIS, which was recorded at 80.8 years in 2009, Kazakhstan has a large gender gap in life
expectancy.
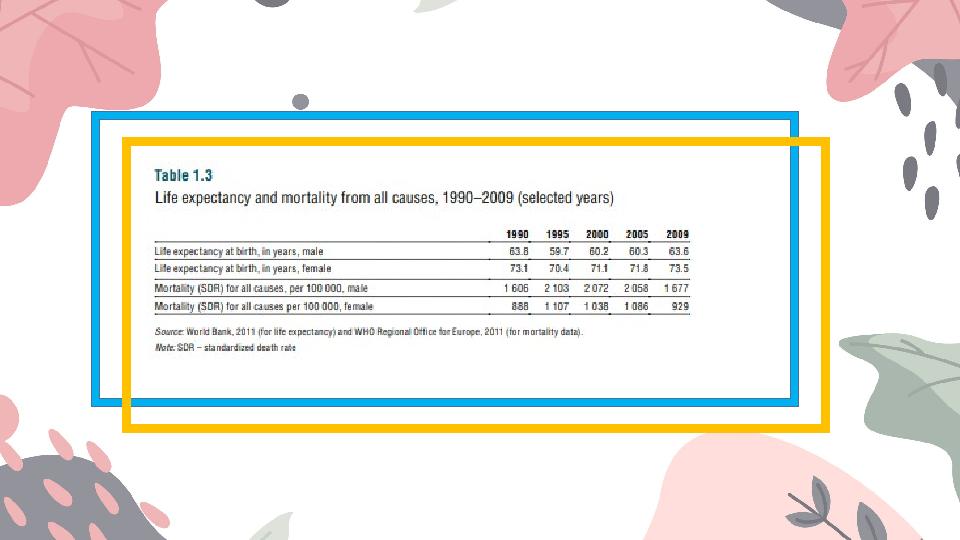
In 2009, males could expect to live 63.6 years, while female life expectancy was 73.5 years (able 1.3). Male
life expectancy also fell much more steeply than female life expectancy in the first half of the 1990s, from
63.9 years in 1990 to 58.93 years in 1996, while neither of the genders has yet regained life expectancy levels
seen in 1990, There are also substantial regional variations in life expectancy.
The most prosperous areas (Almaty city and the capital Astana) have a substantial advantage in terms of life
expectancy over other, more deprived areas of the country. Age-standardized all-cause mortality in
Kazakhstan in 2009 was 1677 per 100 000 population for males and 929 for females, which are among the
highest rates in the WHO European Region (Table 1.3).Health status
5 слайд
Trends in life expectancy in Kazakhstan are broadly similar to those observed in the CIS overall, although the decline in life expectancy after 1991 was steeper and life expectancy in Kazakhstan has remained below the CIS average. Life expectancy dropped from 68.81 in 1990 to 64.4 in 1996, and has since increased again to 68.67 in 2009. However, this still fell over a year short of its 1990 level and was 12.2 years lower than average life expectancy in the EUIS, which was recorded at 80.8 years in 2009, Kazakhstan has a large gender gap in life expectancy. In 2009, males could expect to live 63.6 years, while female life expectancy was 73.5 years (able 1.3). Male life expectancy also fell much more steeply than female life expectancy in the first half of the 1990s, from 63.9 years in 1990 to 58.93 years in 1996, while neither of the genders has yet regained life expectancy levels seen in 1990, There are also substantial regional variations in life expectancy. The most prosperous areas (Almaty city and the capital Astana) have a substantial advantage in terms of life expectancy over other, more deprived areas of the country. Age-standardized all-cause mortality in Kazakhstan in 2009 was 1677 per 100 000 population for males and 929 for females, which are among the highest rates in the WHO European Region (Table 1.3).Health status
#6 слайд
6 слайд
#7 слайд
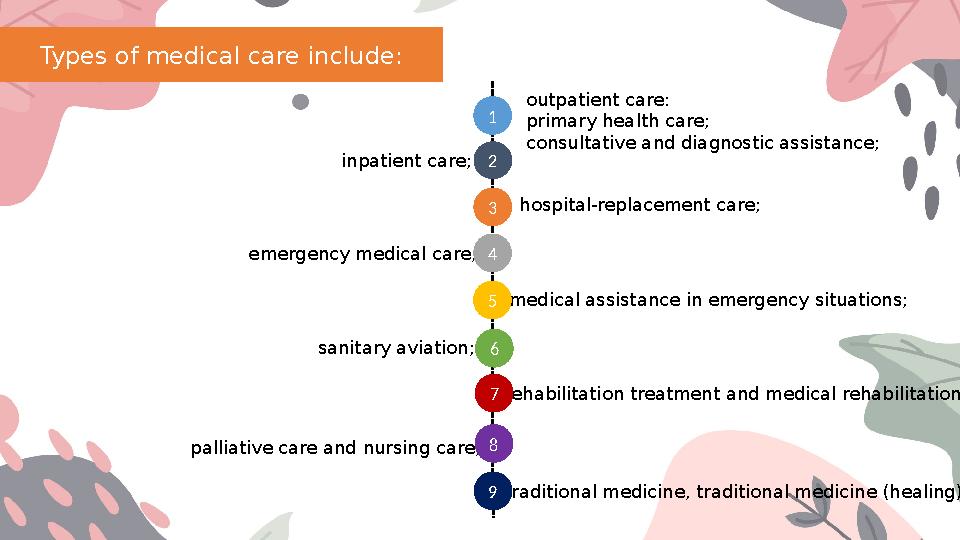
Types of medical care include:
outpatient care:
primary health care;
consultative and diagnostic assistance;
inpatient care;
hospital-replacement care;
emergency medical care;
sanitary aviation; medical assistance in emergency situations;
rehabilitation treatment and medical rehabilitation;
palliative care and nursing care;
traditional medicine, traditional medicine (healing).1
8 7 65 4 3 2
9
7 слайд
Types of medical care include: outpatient care: primary health care; consultative and diagnostic assistance; inpatient care; hospital-replacement care; emergency medical care; sanitary aviation; medical assistance in emergency situations; rehabilitation treatment and medical rehabilitation; palliative care and nursing care; traditional medicine, traditional medicine (healing).1 8 7 65 4 3 2 9
#8 слайд
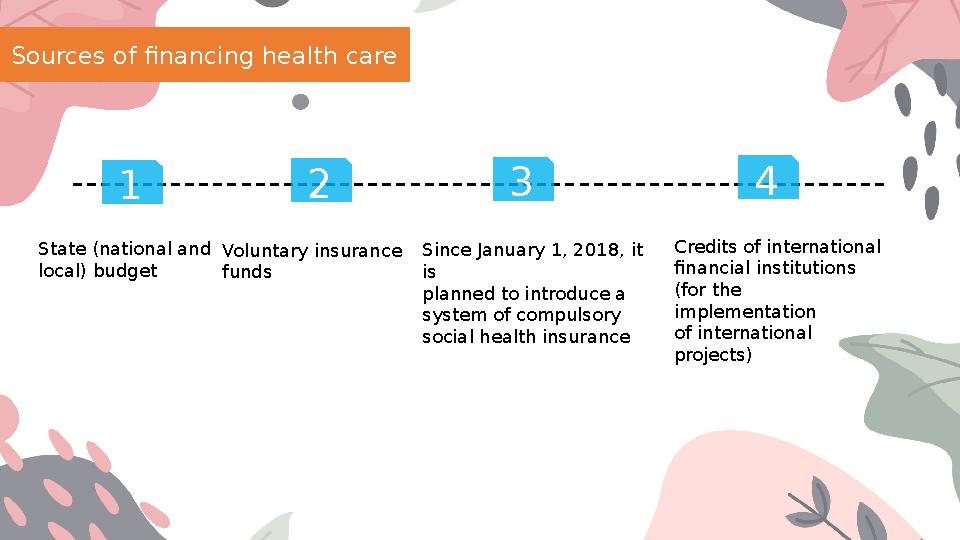
Sources of financing health care
State (national and
local) budget Voluntary insurance
funds Since January 1, 2018, it
is
planned to introduce a
system of compulsory
social health insurance Credits of international
financial institutions
(for the
implementation
of international
projects)1 4
3
2
8 слайд
Sources of financing health care State (national and local) budget Voluntary insurance funds Since January 1, 2018, it is planned to introduce a system of compulsory social health insurance Credits of international financial institutions (for the implementation of international projects)1 4 3 2

шағым қалдыра аласыз
















