Political System
Political System


#1 слайд
Theme: Political System.
1 слайд
Theme: Political System.
#2 слайд
Plan:
1 •
The Constitution, and the Bill of Rights.
2 •
Branches of the Government
3 •
Political Parties and elections
2 слайд
Plan: 1 • The Constitution, and the Bill of Rights. 2 • Branches of the Government 3 • Political Parties and elections

#3 слайд
•
The United States is a
constitution-based federal
republic.
•
Each state has its own state
government and state law.
•
This country is made up of
50 states and the
independent District of
Columbia.
3 слайд
• The United States is a constitution-based federal republic. • Each state has its own state government and state law. • This country is made up of 50 states and the independent District of Columbia.

#4 слайд
THE CONSTITUTION
The Articles of Confederation failed as a governing document for the United States because the states did
not cooperate as expected. When it came time to pay wages to the national army or the war debt to France,
some states refused to contribute. To cure this weakness, the congress asked each state to send a delegate
to a convention. The so-called Constitutional Convention met in Philadelphia in May of 1787, with George
Washington presiding. The delegates struck a balance between those who wanted a strong central
government and those who did not. The resulting master plan, or Constitution, set up a system in which
some powers were given to the national, or federal, government, while others were reserved for the states.
The Constitution divided the national government into three parts, or branches: the legislative (the
Congress, which consists of a House of Representatives and a Senate), the executive (headed by the
president), and the judicial (the federal courts). Called "separation of powers," this division gives each
branch certain duties and substantial independence from the others. It also gives each branch some
authority over the others through a system of "checks and balances."
4 слайд
THE CONSTITUTION The Articles of Confederation failed as a governing document for the United States because the states did not cooperate as expected. When it came time to pay wages to the national army or the war debt to France, some states refused to contribute. To cure this weakness, the congress asked each state to send a delegate to a convention. The so-called Constitutional Convention met in Philadelphia in May of 1787, with George Washington presiding. The delegates struck a balance between those who wanted a strong central government and those who did not. The resulting master plan, or Constitution, set up a system in which some powers were given to the national, or federal, government, while others were reserved for the states. The Constitution divided the national government into three parts, or branches: the legislative (the Congress, which consists of a House of Representatives and a Senate), the executive (headed by the president), and the judicial (the federal courts). Called "separation of powers," this division gives each branch certain duties and substantial independence from the others. It also gives each branch some authority over the others through a system of "checks and balances."

#5 слайд
Here are a few examples of how checks and balances work in practice.
•
If Congress passes a proposed law, or "bill," that the president considers
unwise, he can veto it. That means that the bill is dead unless two-thirds of the
members of both the House and the Senate vote to enact it despite the
president's veto.
•
If Congress passes, and the president signs, a law that is challenged in the
federal courts as contrary to the Constitution, the courts can nullify that law.
(The federal courts cannot issue advisory or theoretical opinions, however;
their jurisdiction is limited to actual disputes.)
•
The president has the power to make treaties with other nations and to make
appointments to federal positions, including judgeships. The Senate, however,
must approve all treaties and confirm the appointments before they can go
into effect.
5 слайд
Here are a few examples of how checks and balances work in practice. • If Congress passes a proposed law, or "bill," that the president considers unwise, he can veto it. That means that the bill is dead unless two-thirds of the members of both the House and the Senate vote to enact it despite the president's veto. • If Congress passes, and the president signs, a law that is challenged in the federal courts as contrary to the Constitution, the courts can nullify that law. (The federal courts cannot issue advisory or theoretical opinions, however; their jurisdiction is limited to actual disputes.) • The president has the power to make treaties with other nations and to make appointments to federal positions, including judgeships. The Senate, however, must approve all treaties and confirm the appointments before they can go into effect.

#6 слайд
•
The Constitution written in Philadelphia in 1787 could not go into effect until it was ratified by a majority of
citizens in at least 9 of the then 13 U.S. states. During this ratification process, misgivings arose. Many
citizens felt uneasy because the document failed to explicitly guarantee the rights of individuals. The
desired language was added in 10 amendments to the Constitution, collectively known as the Bill of Rights.
•
The Bill of Rights guarantees a speedy trial to anyone accused of a crime. The trial must be by jury if
requested, and the accused person must be allowed representation by a lawyer and to call witnesses to
speak for him or her. Cruel and unusual punishment is forbidden. With the addition of the Bill of Rights,
the Constitution was ratified by all 13 states and went into effect in 1789. Since then 17 other amendments
have been added to the Constitution. Perhaps the most important of these are the Thirteenth and
Fourteenth, which outlaw slavery and guarantee all citizens equal protection of the laws, and the
Nineteenth, which gives women the right to vote. The Constitution can be amended in either of two ways.
Congress can propose an amendment, provided that two-thirds of the members of both the House and the
Senate vote in favor of it. Or the legislatures of two-thirds of the states can call a convention to propose
amendments. (This second method has never been used.) In either case a proposed amendment does not
go into effect until ratified by three-fourths of the states. BILL OF RIGHTS
6 слайд
• The Constitution written in Philadelphia in 1787 could not go into effect until it was ratified by a majority of citizens in at least 9 of the then 13 U.S. states. During this ratification process, misgivings arose. Many citizens felt uneasy because the document failed to explicitly guarantee the rights of individuals. The desired language was added in 10 amendments to the Constitution, collectively known as the Bill of Rights. • The Bill of Rights guarantees a speedy trial to anyone accused of a crime. The trial must be by jury if requested, and the accused person must be allowed representation by a lawyer and to call witnesses to speak for him or her. Cruel and unusual punishment is forbidden. With the addition of the Bill of Rights, the Constitution was ratified by all 13 states and went into effect in 1789. Since then 17 other amendments have been added to the Constitution. Perhaps the most important of these are the Thirteenth and Fourteenth, which outlaw slavery and guarantee all citizens equal protection of the laws, and the Nineteenth, which gives women the right to vote. The Constitution can be amended in either of two ways. Congress can propose an amendment, provided that two-thirds of the members of both the House and the Senate vote in favor of it. Or the legislatures of two-thirds of the states can call a convention to propose amendments. (This second method has never been used.) In either case a proposed amendment does not go into effect until ratified by three-fourths of the states. BILL OF RIGHTS

#7 слайд
THE SYSTEM
OF
GOVERMENT
OF THE
UNITED
STATES
7 слайд
THE SYSTEM OF GOVERMENT OF THE UNITED STATES
#8 слайд
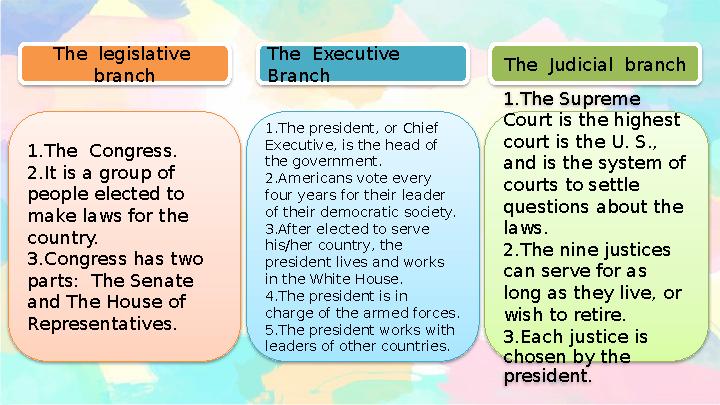
1.The Congress.
2.It is a group of
people elected to
make laws for the
country.
3.Congress has two
parts: The Senate
and The House of
Representatives. 1.The Supreme
Court is the highest
court is the U. S.,
and is the system of
courts to settle
questions about the
laws.
2.The nine justices
can serve for as
long as they live, or
wish to retire.
3.Each justice is
chosen by the
president.1.The president, or Chief
Executive, is the head of
the government.
2.Americans vote every
four years for their leader
of their democratic society.
3.After elected to serve
his/her country, the
president lives and works
in the White House.
4.The president is in
charge of the armed forces.
5.The president works with
leaders of other countries.The legislative
branch The Judicial branchThe Executive
Branch
8 слайд
1.The Congress. 2.It is a group of people elected to make laws for the country. 3.Congress has two parts: The Senate and The House of Representatives. 1.The Supreme Court is the highest court is the U. S., and is the system of courts to settle questions about the laws. 2.The nine justices can serve for as long as they live, or wish to retire. 3.Each justice is chosen by the president.1.The president, or Chief Executive, is the head of the government. 2.Americans vote every four years for their leader of their democratic society. 3.After elected to serve his/her country, the president lives and works in the White House. 4.The president is in charge of the armed forces. 5.The president works with leaders of other countries.The legislative branch The Judicial branchThe Executive Branch

#9 слайд
1.There are 100
senators.
2.Each state has two
senators.
3.A Senator is in office
for 6 years. This is
called a “term.”
4.Senators meet in the
U.S. Capitol building 1.There are 435
representatives.
2.The more people that
live in a state, the more
representatives it has.
3.Representatives serve
for a term of two years.
4.They can be elected
for more than one term.The senate The house of
representatives
9 слайд
1.There are 100 senators. 2.Each state has two senators. 3.A Senator is in office for 6 years. This is called a “term.” 4.Senators meet in the U.S. Capitol building 1.There are 435 representatives. 2.The more people that live in a state, the more representatives it has. 3.Representatives serve for a term of two years. 4.They can be elected for more than one term.The senate The house of representatives

#10 слайд
•
Today, there are two major political parties in the United States, the Democratic and the Republican. The
Democratic Party evolved from the party of Thomas Jefferson, formed before 1800. The Republican Party
was established in the 1850s by Abraham Lincoln and others who opposed the expansion of slavery into
new states then being admitted to the Union.
•
The Democratic Party is considered to be the more liberal party, and the Republican, the more
conservative. Democrats generally believe that government has an obligation to provide social and
economic programs for those who need them. Republicans are not necessarily opposed to such programs
but believe they are too costly to taxpayers.
•
Republicans put more emphasis on encouraging private enterprise in the belief that a strong private sector
makes citizens less dependent on government. Both major parties have supporters among a wide variety
of Americans and embrace a wide range of political views. Members, and even elected officials, of one
party do not necessarily agree with each other on every issue. Americans do not have to join a political
party to vote or to be a candidate for public office, but running for office without the money and campaign
workers a party can provide is difficult.POLITICAL PARTIES AND
ELECTIONS
10 слайд
• Today, there are two major political parties in the United States, the Democratic and the Republican. The Democratic Party evolved from the party of Thomas Jefferson, formed before 1800. The Republican Party was established in the 1850s by Abraham Lincoln and others who opposed the expansion of slavery into new states then being admitted to the Union. • The Democratic Party is considered to be the more liberal party, and the Republican, the more conservative. Democrats generally believe that government has an obligation to provide social and economic programs for those who need them. Republicans are not necessarily opposed to such programs but believe they are too costly to taxpayers. • Republicans put more emphasis on encouraging private enterprise in the belief that a strong private sector makes citizens less dependent on government. Both major parties have supporters among a wide variety of Americans and embrace a wide range of political views. Members, and even elected officials, of one party do not necessarily agree with each other on every issue. Americans do not have to join a political party to vote or to be a candidate for public office, but running for office without the money and campaign workers a party can provide is difficult.POLITICAL PARTIES AND ELECTIONS

шағым қалдыра аласыз
















