РОКАХ БИОЛОГИИҒылымилылық және жүйелілік принциптері
РОКАХ БИОЛОГИИҒылымилылық және жүйелілік принциптері


#1 слайд
Тақырып:
Ғылымилылық және
жүйелілік
принциптері
Академик Е.А. Бөкетов атындағы Қарағанды университеті
Орындаған: Шымберген Мереке Қорғанбекқызы
Группа: М2-БО-23-1К
Қабылдаған: Елеупаева Шынар Каукербековна
1 слайд
Тақырып: Ғылымилылық және жүйелілік принциптері Академик Е.А. Бөкетов атындағы Қарағанды университеті Орындаған: Шымберген Мереке Қорғанбекқызы Группа: М2-БО-23-1К Қабылдаған: Елеупаева Шынар Каукербековна

#2 слайд
1.Жүйелілік принципі.
2.Cell concept
3.Composition of living organisms
4.Levels of organization of living things
5.Ways of obtaining energy by organisms
Жоспар:
2 слайд
1.Жүйелілік принципі. 2.Cell concept 3.Composition of living organisms 4.Levels of organization of living things 5.Ways of obtaining energy by organisms Жоспар:

#3 слайд
Жүйелілік принципі – оқытудың қатаң
логикалық реттілікте бекітіледі,
жүйелілікті меңгеруде оқушыларды нақты
білім шеңберінде, білік пен дағдыларды,
оқу материалынан ауытқымастан
қадағалаулардан туындайды. Жуйелілік оқу
материалын оқытуда, өткен материалдан
алдағы материал бастау алып, соған
сүйеніп және жаңа материалды қабылдау
сатысы болып табылады, бұл алынған
білімді практикалық тапсырмаларды
шешуге және қиын тапсырмаларда
көмектеседі. Тағы да, Я.А. Коменский
көрсеткен, табиғатта да біріне бірі
жүйеленіп жалғасады, сол сияқты оқуда да
бірін екіншісімен байланыстыра білу керек.
3 слайд
Жүйелілік принципі – оқытудың қатаң логикалық реттілікте бекітіледі, жүйелілікті меңгеруде оқушыларды нақты білім шеңберінде, білік пен дағдыларды, оқу материалынан ауытқымастан қадағалаулардан туындайды. Жуйелілік оқу материалын оқытуда, өткен материалдан алдағы материал бастау алып, соған сүйеніп және жаңа материалды қабылдау сатысы болып табылады, бұл алынған білімді практикалық тапсырмаларды шешуге және қиын тапсырмаларда көмектеседі. Тағы да, Я.А. Коменский көрсеткен, табиғатта да біріне бірі жүйеленіп жалғасады, сол сияқты оқуда да бірін екіншісімен байланыстыра білу керек.

#4 слайд
The main task of biology is to study the properties,
patterns of formation and development of the entire
organic world (animals, plants, fungi, bacteria).
4 слайд
The main task of biology is to study the properties, patterns of formation and development of the entire organic world (animals, plants, fungi, bacteria).

#5 слайд
Cell is the smallest unit of size of all
living organisms.
Cytology is the science that studies cells.
5 слайд
Cell is the smallest unit of size of all living organisms. Cytology is the science that studies cells.
#6 слайд
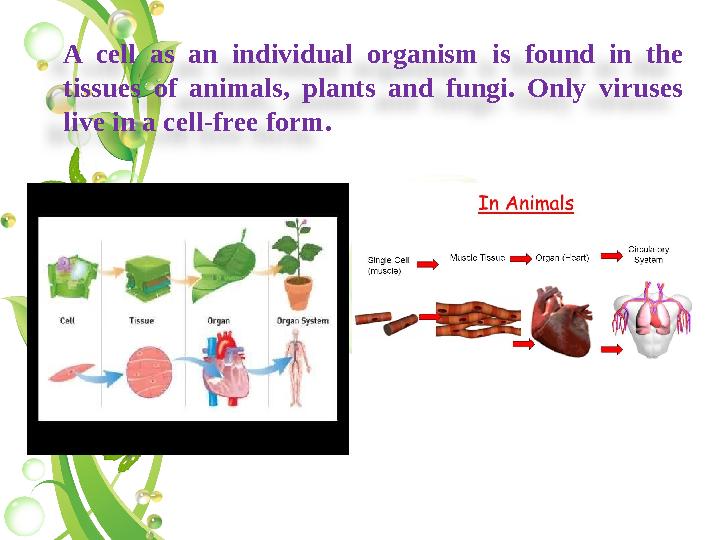
A cell as an individual organism is found in the
tissues of animals, plants and fungi. Only viruses
live in a cell-free form.
6 слайд
A cell as an individual organism is found in the tissues of animals, plants and fungi. Only viruses live in a cell-free form.
#7 слайд
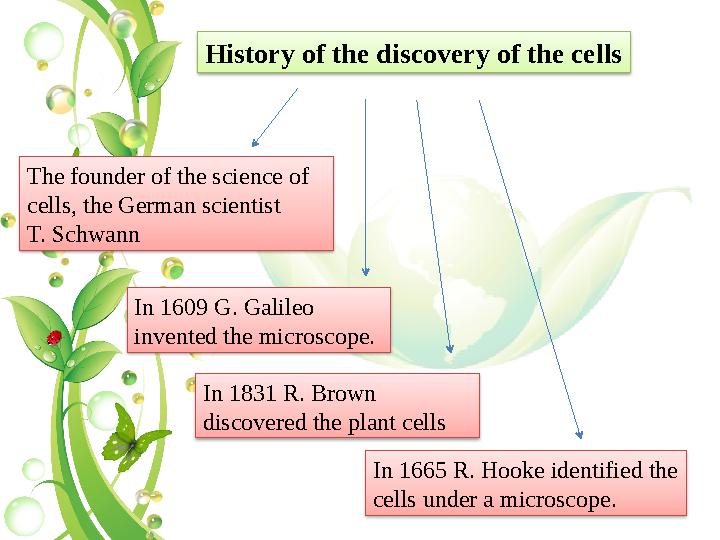
In 1609 G. Galileo
invented the microscope.
History of the discovery of the cells
In 1665 R. Hooke identified the
cells under a microscope.
In 1831 R. Brown
discovered the plant cells
The founder of the science of
cells, the German scientist
T. Schwann
7 слайд
In 1609 G. Galileo invented the microscope. History of the discovery of the cells In 1665 R. Hooke identified the cells under a microscope. In 1831 R. Brown discovered the plant cells The founder of the science of cells, the German scientist T. Schwann
#8 слайд
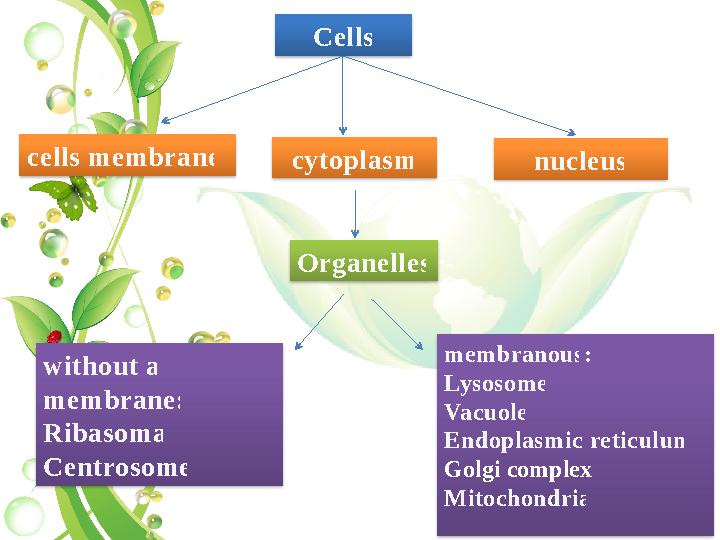
Cells cells membrane cytoplasm nucleus Organelles without a membrane: Ribasoma Centrosome membranous : Lysosome Vacuole Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi complex Mitochondria
8 слайд
Cells cells membrane cytoplasm nucleus Organelles without a membrane: Ribasoma Centrosome membranous : Lysosome Vacuole Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi complex Mitochondria
#9 слайд
9 слайд
#10 слайд
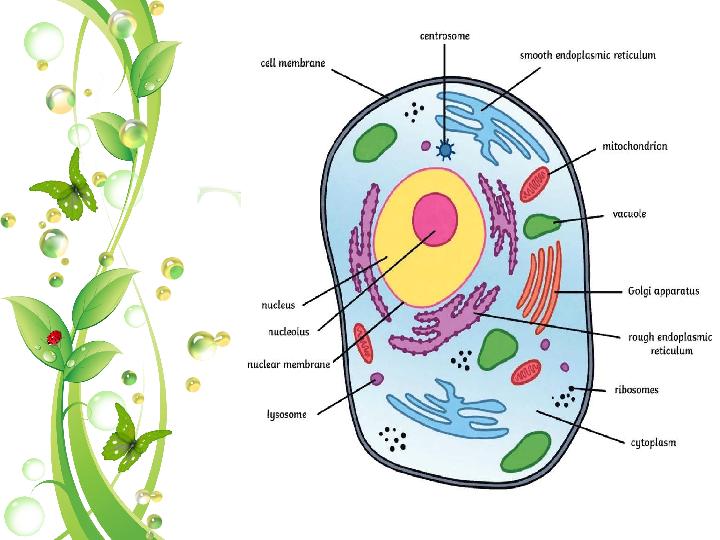
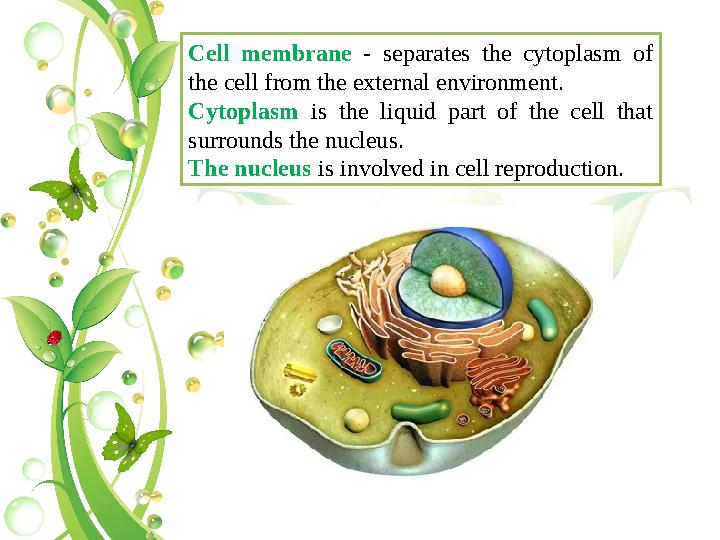
Cell membrane - separates the cytoplasm of
the cell from the external environment.
Cytoplasm is the liquid part of the cell that
surrounds the nucleus.
The nucleus is involved in cell reproduction.
10 слайд
Cell membrane - separates the cytoplasm of the cell from the external environment. Cytoplasm is the liquid part of the cell that surrounds the nucleus. The nucleus is involved in cell reproduction.
#11 слайд
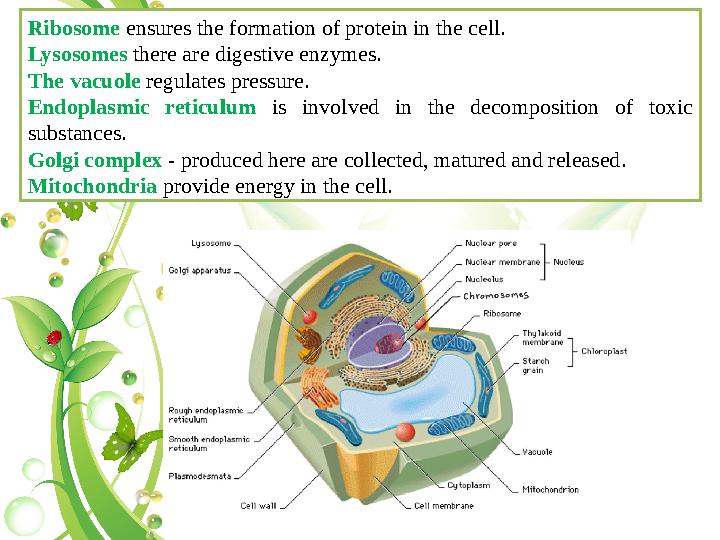
Ribosome ensures the formation of protein in the cell.
Lysosomes there are digestive enzymes.
The vacuole regulates pressure.
Endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the decomposition of toxic
substances.
Golgi complex - produced here are collected, matured and released.
Mitochondria provide energy in the cell.
11 слайд
Ribosome ensures the formation of protein in the cell. Lysosomes there are digestive enzymes. The vacuole regulates pressure. Endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the decomposition of toxic substances. Golgi complex - produced here are collected, matured and released. Mitochondria provide energy in the cell.
#12 слайд
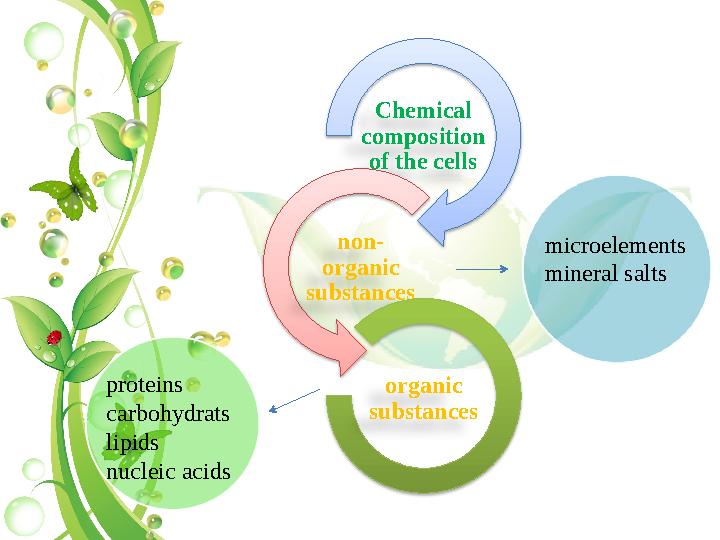
Chemical
composition
of the cells
non-
organic
substances
organic
substances
microelements
mineral salts
proteins
carbohydrats
lipids
nucleic acids
12 слайд
Chemical composition of the cells non- organic substances organic substances microelements mineral salts proteins carbohydrats lipids nucleic acids
#13 слайд
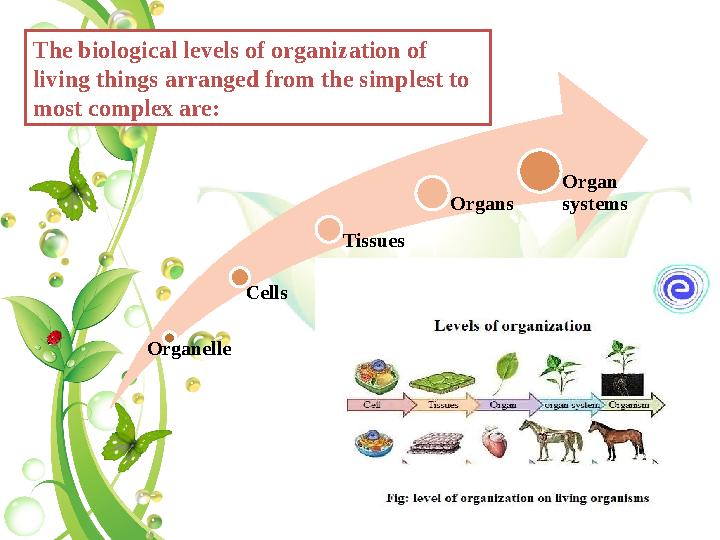
Organelle
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ
systems
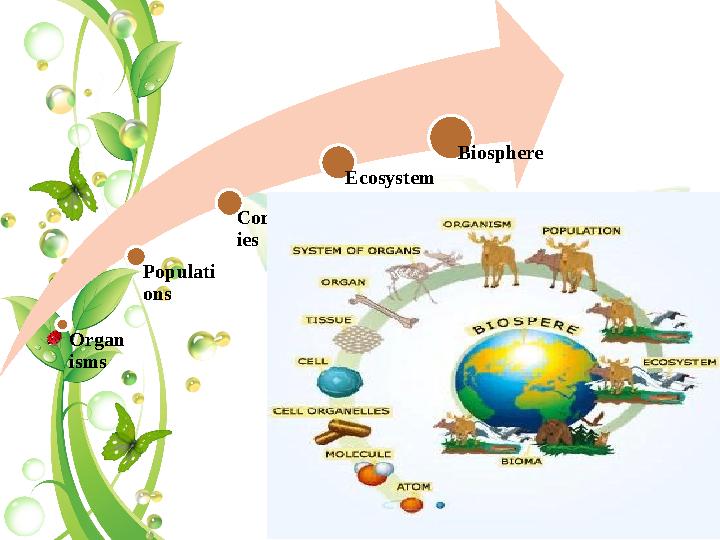
The biological levels of organization of
living things arranged from the simplest to
most complex are:
13 слайд
Organelle Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems The biological levels of organization of living things arranged from the simplest to most complex are:
#14 слайд
Organ
isms
Populati
ons
Communit
ies
Ecosystem
Biosphere
14 слайд
Organ isms Populati ons Communit ies Ecosystem Biosphere

#15 слайд
Living organisms obtain energy in three ways: photosynthesis,
chemosynthesis and nutrition of heterotrophs.
1. Photosynthesis is the
process of converting sunlight
energy into chemical bond
energy through green leaf
organoids, chloroplast. As a
result of photosynthesis, plants
on Earth produce more than
100 billion tons of organic
matter every year.
15 слайд
Living organisms obtain energy in three ways: photosynthesis, chemosynthesis and nutrition of heterotrophs. 1. Photosynthesis is the process of converting sunlight energy into chemical bond energy through green leaf organoids, chloroplast. As a result of photosynthesis, plants on Earth produce more than 100 billion tons of organic matter every year.

#16 слайд
2. Chemosynthesis is a type of
nutrition of bacteria by
oxidizing inorganic
compounds and absorbing
carbon dioxide (CO2).
Chemosynthesis does not need
light.
16 слайд
2. Chemosynthesis is a type of nutrition of bacteria by oxidizing inorganic compounds and absorbing carbon dioxide (CO2). Chemosynthesis does not need light.
#17 слайд
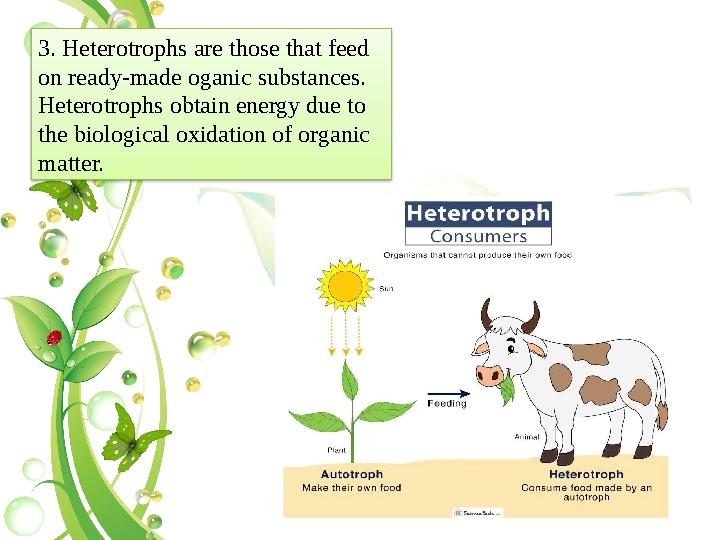
3. Heterotrophs are those that feed
on ready-made oganic substances.
Heterotrophs obtain energy due to
the biological oxidation of organic
matter.
17 слайд
3. Heterotrophs are those that feed on ready-made oganic substances. Heterotrophs obtain energy due to the biological oxidation of organic matter.

#18 слайд
Thank you for your attention!
18 слайд
Thank you for your attention!

шағым қалдыра аласыз
















