Specific heat of capacity
Specific heat of capacity


#1 слайд
Specific Heat
Capacity
Меншікті
жылу
сыйымдылы
қ
Or the amount of energy needed to heat
substances up
1 слайд
Specific Heat Capacity Меншікті жылу сыйымдылы қ Or the amount of energy needed to heat substances up

#2 слайд
Terminology
To store- сақтау
Substance- зат
Relationship- байланыс
Engine- қозғалтқыш
Specific- меншікті
2 слайд
Terminology To store- сақтау Substance- зат Relationship- байланыс Engine- қозғалтқыш Specific- меншікті
#3 слайд
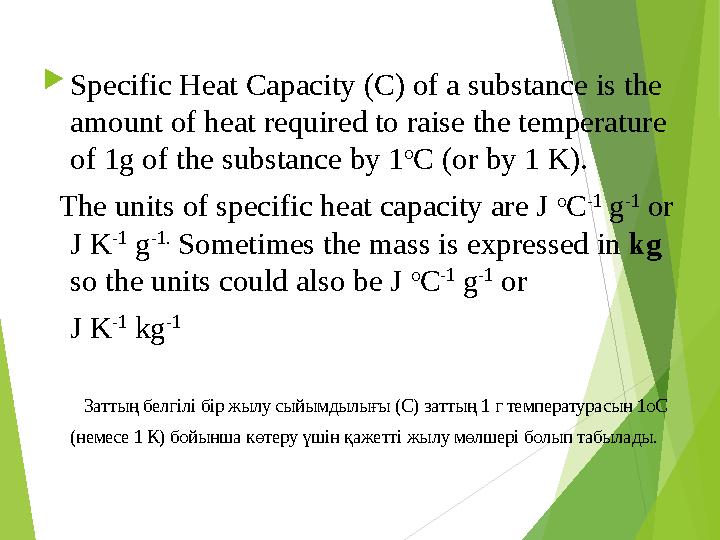
Specific Heat Capacity (C) of a substance is the
amount of heat required to raise the temperature
of 1g of the substance by 1 o
C (or by 1 K).
The units of specific heat capacity are J o
C -1
g -1
or
J K -1
g -1.
Sometimes the mass is expressed in kg
so the units could also be J o
C -1
g -1
or
J K -1
kg -1
Заттың белгілі бір жылу сыйымдылығы ( C) заттың 1 г температурасын 1 oC
( немесе 1 К) бойынша көтеру үшін қажетті жылу мөлшері болып табылады.
3 слайд
Specific Heat Capacity (C) of a substance is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1g of the substance by 1 o C (or by 1 K). The units of specific heat capacity are J o C -1 g -1 or J K -1 g -1. Sometimes the mass is expressed in kg so the units could also be J o C -1 g -1 or J K -1 kg -1 Заттың белгілі бір жылу сыйымдылығы ( C) заттың 1 г температурасын 1 oC ( немесе 1 К) бойынша көтеру үшін қажетті жылу мөлшері болып табылады.

#4 слайд
The next table shows how much energy it takes to heat up
some different substances.
The small values show that not a lot of energy is needed to
produce a temperature change, whereas the large values
indicate a lot more energy is needed.
Келесі кестеде түрлі заттарды қыздыру үшін қанша
энергия қажет екендігі көрсетілген.
Шағын мәндер температураның өзгеруіне көп энергия
қажет емес екенін көрсетті, ал үлкен мәндер көп энергия
қажет екенін көрсетеді .
4 слайд
The next table shows how much energy it takes to heat up some different substances. The small values show that not a lot of energy is needed to produce a temperature change, whereas the large values indicate a lot more energy is needed. Келесі кестеде түрлі заттарды қыздыру үшін қанша энергия қажет екендігі көрсетілген. Шағын мәндер температураның өзгеруіне көп энергия қажет емес екенін көрсетті, ал үлкен мәндер көп энергия қажет екенін көрсетеді .
#5 слайд
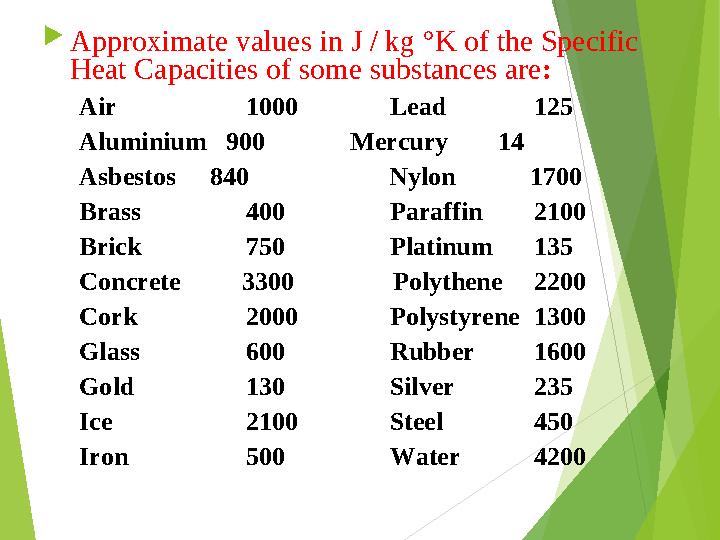
Approximate values in J / kg °K of the Specific
Heat Capacities of some substances are :
Air 1000 Lead 125
Aluminium 900 Mercury 14
Asbestos 840 Nylon 1700
Brass 400 Paraffin 2100
Brick 750 Platinum 135
Concrete 3300 Polythene 2200
Cork 2000 Polystyrene 1300
Glass 600 Rubber 1600
Gold 130 Silver 235
Ice 2100 Steel 450
Iron 500 Water 4200
5 слайд
Approximate values in J / kg °K of the Specific Heat Capacities of some substances are : Air 1000 Lead 125 Aluminium 900 Mercury 14 Asbestos 840 Nylon 1700 Brass 400 Paraffin 2100 Brick 750 Platinum 135 Concrete 3300 Polythene 2200 Cork 2000 Polystyrene 1300 Glass 600 Rubber 1600 Gold 130 Silver 235 Ice 2100 Steel 450 Iron 500 Water 4200

#6 слайд
The amount of heat energy (q)
gained or lost by a substance =
mass of substance (m) X specific
heat capacity (C) X change in
temperature (ΔT) or initial and final
temperatures (T1 and T2)
Q = m x C x ΔT The equation:
6 слайд
The amount of heat energy (q) gained or lost by a substance = mass of substance (m) X specific heat capacity (C) X change in temperature (ΔT) or initial and final temperatures (T1 and T2) Q = m x C x ΔT The equation:
#7 слайд
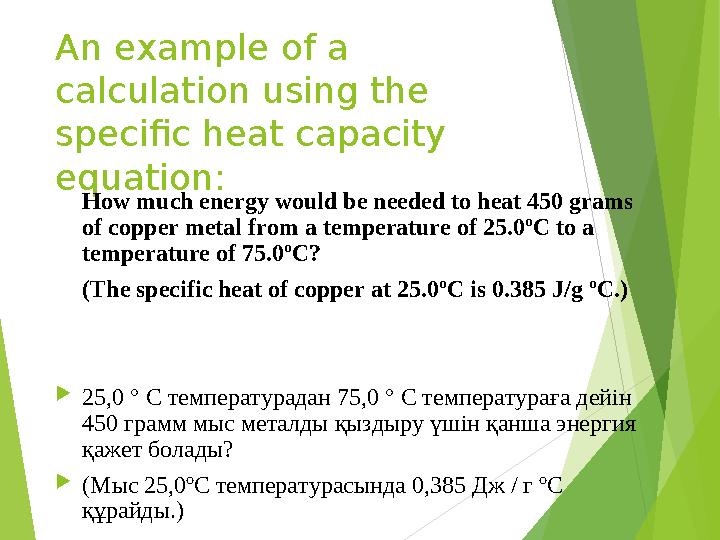
An example of a
calculation using the
specific heat capacity
equation:
How much energy would be needed to heat 450 grams
of copper metal from a temperature of 25.0ºC to a
temperature of 75.0ºC?
(The specific heat of copper at 25.0ºC is 0.385 J/g ºC.)
25,0 ° C температурадан 75,0 ° C температураға дейін
450 грамм мыс металды қыздыру үшін қанша энергия
қажет болады?
(Мыс 25,0ºC температурасында 0,385 Дж / г ºC
құрайды.)
7 слайд
An example of a calculation using the specific heat capacity equation: How much energy would be needed to heat 450 grams of copper metal from a temperature of 25.0ºC to a temperature of 75.0ºC? (The specific heat of copper at 25.0ºC is 0.385 J/g ºC.) 25,0 ° C температурадан 75,0 ° C температураға дейін 450 грамм мыс металды қыздыру үшін қанша энергия қажет болады? (Мыс 25,0ºC температурасында 0,385 Дж / г ºC құрайды.)

#8 слайд
Explanation:
The change in temperature ( ΔT) is:
75 ºC - 25ºC = 50ºC
Given mass, two temperatures, and a specific heat capacity, you
have enough values to plug into the specific heat equation
q = m x C x ΔT .
and plugging in your values you get
Q= (450 g) x (0.385 J/g ºC) x (50.0ºC)
= 8700 J
Түсіндіру:
Температураның өзгеруі ( Δ T):75ºC - 25ºC = 50ºC
Белгіленген массаны, екі температураны және нақты жылу сыйымдылығын ескере
отырып, сіз нақты жылу теңдеуін қосу үшін жеткілікті мәндеріңіз бар
Q = m x C x Δ T.
және формулаға саламыз:
Q = (450 г) x (0,385 J / г ºC) x (50,0ºC)
= 8700 Дж
8 слайд
Explanation: The change in temperature ( ΔT) is: 75 ºC - 25ºC = 50ºC Given mass, two temperatures, and a specific heat capacity, you have enough values to plug into the specific heat equation q = m x C x ΔT . and plugging in your values you get Q= (450 g) x (0.385 J/g ºC) x (50.0ºC) = 8700 J Түсіндіру: Температураның өзгеруі ( Δ T):75ºC - 25ºC = 50ºC Белгіленген массаны, екі температураны және нақты жылу сыйымдылығын ескере отырып, сіз нақты жылу теңдеуін қосу үшін жеткілікті мәндеріңіз бар Q = m x C x Δ T. және формулаға саламыз: Q = (450 г) x (0,385 J / г ºC) x (50,0ºC) = 8700 Дж

#9 слайд
№ 1
250 г суды 5°С-қа қыздыру
үшін қанша жылу мөлшері
жұмсалады?
№ 2
0,2 кг жезден жасалған бөлшектің
температурасы 365°С. Ол 15°С-қа
дейін суытылғанда қоршаған
ортаға қанша жылу мөлшерін
береді?
9 слайд
№ 1 250 г суды 5°С-қа қыздыру үшін қанша жылу мөлшері жұмсалады? № 2 0,2 кг жезден жасалған бөлшектің температурасы 365°С. Ол 15°С-қа дейін суытылғанда қоршаған ортаға қанша жылу мөлшерін береді?

#10 слайд
Some good websites
http://www.s-cool.co.uk/gcse/physics/energy-
transfers/types-of-energy-transfers.html#types-of-
energy
10 слайд
Some good websites http://www.s-cool.co.uk/gcse/physics/energy- transfers/types-of-energy-transfers.html#types-of- energy

шағым қалдыра аласыз
















