Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 25 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Animals. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.2.1 ask more complex questions to get information about a growing range of general topics and some curricular topics 6.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of short, supported talk on a wide range of familiar topics 6.5.8.1 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Value links |
Family – Family values are moral and ethical principles of typical family life, including sacrificing for loved ones, putting your loved ones first, and keeping your loved ones at the centre of your thoughts and actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
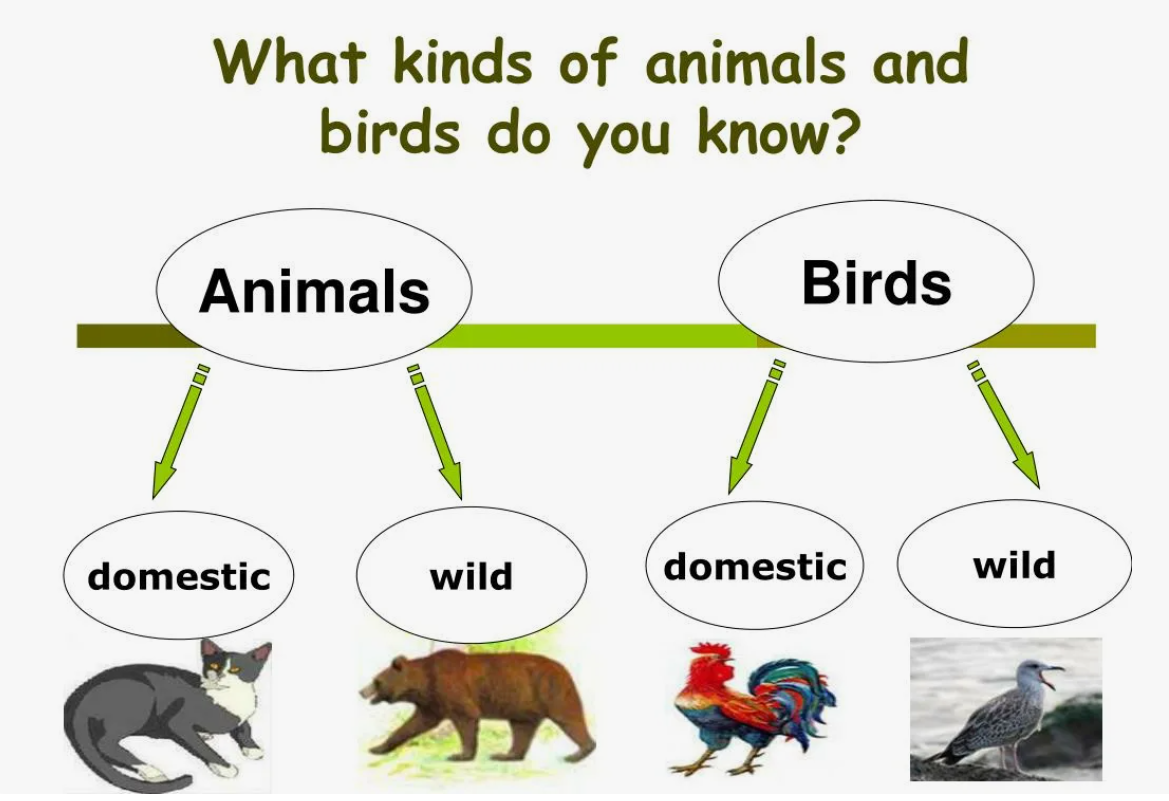
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre-listening: Warm-up • With books closed, ask students to work in pairs and write down as many animals as they can in English. • Elicit the names of a few animals from individual students and write them on the board Lead - In
How many animals do you see? Where do they live? What do they eat? |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 32 • In a weaker class, allow students to match the animals with the photos in pairs. • Elicit the answer to the question, but do not check answers to the matching task at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 32 Demonstrate how to use the key phrases in context. Ask students to look at the first picture in the quiz. Say an incorrect sentence, e.g. It looks like an elephant. Elicit that the animal is a whale, and see if students can form an answer with the key phrases, e.g. I’m sure it’s a whale. Ex: 4 P: 32 • Explain to students that they are going to hear some animal sounds and they must discuss what animals they think they are hearing, using the key phrases. • Play the CD, pausing after each animal sound Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students match the animals in the box with photos ANSWERS: Photo 14 is not an eye. It’s a butterfly wing. Students compare their answers in exercise 1 ANSWERS: 1 whale 2 spider 3 owl 4 shark 5 human 6 snake 7 fly 8 seal 9 falcon 10 parrot 11 frog 12 elephant 13 chameleon 14 butterfly 15 crocodile 16 bear Students listen and identify the animals. ANSWERS: 1 an owl 5 a seal 2 a fly 6 a whale 3 a frog 7 a bear 4 a falcon 8 a snake |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for animals. Descriptor: - match the animals in the box with photos pupils are evaluated by collecting fish Descriptor: compare their answers Descriptor: listen and identify the animals -Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 24 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 26 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading: The red list |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.C7 develop and sustain a consistent argument when speaking or writing 6.R2 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 6.S3 give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics( Ex.3 - 4 p.34) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Value links |
Loyalty – Loyalty might be a core personal value to you if you highly prize friends that are reliable and trustworthy. You might put your friends or chosen family first, always being there for them when they need you. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask: What’s your favourite animal? • Ask: Which animals do you dislike? Elicit answers from individual students, and ask why they dislike these animals Lead - In
The Red
Book of Kazakhstan - an annotated list of rare and endangered
animals in |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 34 • Refer students to the title of the article and the question. • Students discuss their answers in pairs. • In a stronger class, ask students to make a note of as many statistics as they can to support their answer complete the sentences with the correct form of the verbs in brackets Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 34 • Explain that students should now read the text again more carefully to find the specific information. In a weaker class, check key vocabulary, e.g. extinct, before students read. • Ask students to complete the answers individually, then compare their ideas with a partner Ex: 3 P: 34 • Students check the meaning of the blue words and identify which are verbs (attack and save). • Check understanding of the words and phrases, for example by asking students to use them in sentences Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students read and listen to the text ANSWERS: A person is more dangerous than a shark or a chair. Students read the text again and choose the correct answers ANSWERS: 1 a 2 c 3 c 4 c 5 a Students use the words to complete the sentences. ANSWERS: 1 attack 4 accidents 2 approximately 5 actions 3 save 6 pollution |
Assessment criteria Read about animals in danger Descriptor: - read and listen to the text
pupils are evaluated by collecting fish Descriptor: read the text again and choose the correct answers
-Make CCQ questions. Yes / No 1 Are crocodiles dangerous? Yes 2 Do people kill animals for fur? No 3 Do wolves live In Kazakhstan? Yes |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 24 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 27 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Present Continuous |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.C6 organise and present information clearly to others ( Ex.1 p.35) 6.W2 write with minimal support about real and imaginary present events, activities and experiences happening now on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics ( Ex.2,3,5 p.35) 6.S2 ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general topics ( Ex.6 |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Value links |
Fairness – If you value fairness, you might be highly sensitive to situations at school or in the workplace where a teacher or a peer has exhibited favoritism or allowed someone to get away with living by a different set of rules to everyone else. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
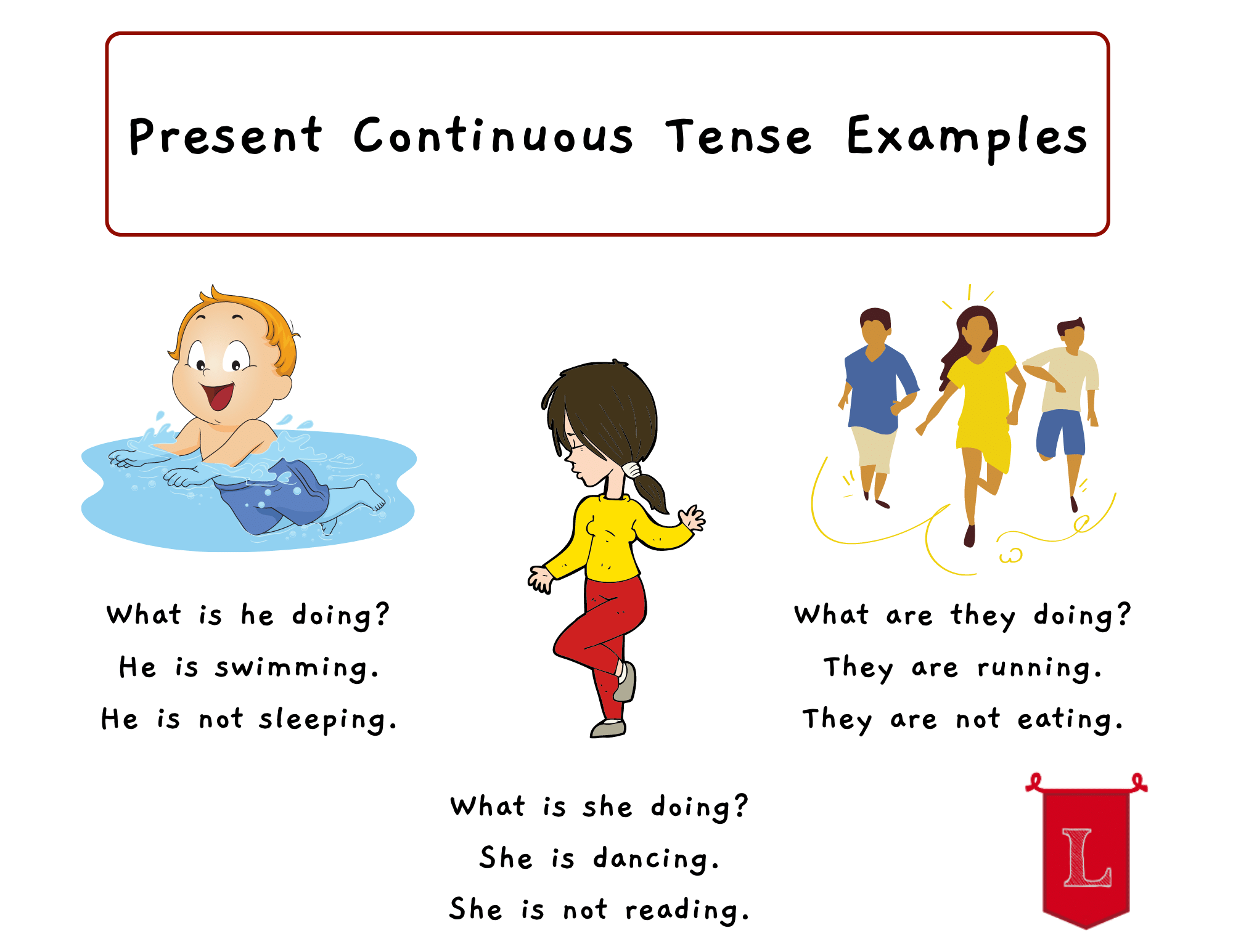
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Write four present continuous sentences on the board, two true and two false, e.g. I am teaching. The sun is shining. Elicit which ones are true and how students can tell. Elicit that the present continuous describes events happening now Lead - In
He is swimming. She is reading We are dancing They are running |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 35 When students have found the sentences, draw attention to the form Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. . Ex: 3 P: 35 • Tell students they are going to listen to seven recordings, and that they should identify what is happening. • Tell students to read the options in columns A and B before they listen, to give them an idea of the context and what they might hear Ex: 4 P: 35 • Allow students time to study the picture carefully and read the prompts. • Explain that they should write the negative sentence first, then an affirmative sentence using the word in brackets Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 are 2 aren’t 3 is Students match the things in A with the actions in B ANSWERS: 1 Two dogs are running in the park. 2 A parrot is speaking English. 3 A man is attacking a mosquito. 4 A whale is singing to its partner. 5 Children are making a cake. 6 A girl is practising the piano. 7 A lion is having a meal. Students work in pairs. Make affirmative and negative sentences using the present continuous ANSWERS: 1 A child isn’t feeding some bears. She is feeding some ducks. 2 A falcon isn’t sleeping. It is hunting. 3 Two people aren’t watching a chameleon. They are watching the falcon. 4 Three people aren’t swimming. They are running. |
Assessment criteria - Learn the affirmative and negative forms of the present continuous. Descriptor: - match the things in A with the actions in B
Descriptor: Make affirmative and negative sentences using the present continuous
pupils are evaluated by collecting pencils -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 24 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 28 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Animal behaviour |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups ( Ex.1,2 p.36) 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics ( Ex.3 p.36) 6.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics( Ex.4 p.36) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn verbs for animal behaviour. • Listen to an interview about animals. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. • Write about an animal and describe its behaviour |
||
|
Value links |
Honesty – You may highly value telling people the truth. This one gets tricky when being honest can be hurtful to others. So, a person who really puts honesty first might be the sort of person who will tell the truth even if it hurts to do so. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Write the word Behaviour on the board. • Elicit the meaning, then ask: What do animals do to survive? • Elicit ideas from the class, for example animals hunt for food, hide from other animals, find a safe place to sleep, keep warm in the winter. Lead - In
There are prides within 100 km of each other that display extremes in behavior, and in particular when it comes to feeding and drinking. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 36 • Refer students to the bold verbs. Tell them to use the Wordlist or their dictionaries to check the meaning of any verbs they do not know. • Refer students to the photos and ask them to choose the correct verbs. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. . Ex: 2 P: 36 • Look at the example answer and remind students that we do not use the definite article, the, when we are talking about things in general. • Students complete the sentences with the animals Ex: 3 P: 36 Explain that students are going to listen to an interview. While they listen for the first time they should look at the photos and identify the ones the speaker is talking about. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students check the meaning of the verbs in bold and choose the correct verbs ANSWERS: 1 feeding 3 catching 5 hunting 2 building 4 protecting 6 chasing Students complete the sentences with names of the animals ANSWERS: 1 Snakes 4 Sharks 2 Bears 5 Humans 3 Chameleons 6 Whales. Students listen to an interview with Mike. Which of the photos does Mike speak about? ANSWERS: He speaks about photos 1, 3, 4 and 6 |
Assessment criteria - identify verbs for animal behaviour. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the verbs in bold and choose the correct verbs
Descriptor: complete the sentences with names of the animals
pupils are evaluated by collecting colour pencils Descriptor: listen to an interview with Mike. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets CD 1.31 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 26 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 29 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Present Continuous. Questions |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others ( ex1 - 5 p.37) 6.5.2.1 write with minimal support about real and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics ( Ex.6,7 p.37) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the question forms of the present continuous. • Write questions and answers using the present continuous. • Identify the difference between the present continuous and the present simple |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students back to the photos on page 42. Ask students what questions they can ask about the animals Lead - In
Is he swimming? Is she reading? Are we dancing? Are they running? |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 37 • In a weaker class, you could play the CD (2.06) again Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 37 Check understanding by asking and answering some present continuous questions as a class. Ex: 3 P: 37 In a weaker class do another example with the whole class, and then ask and answer. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students complete the question form ANSWERS: 1 is 2 Is 3 Is Students match the questions in exercise 1 ANSWERS: 1 c 2 a 3 b Rules: 1 is 2 aren’t Students write questions for the answers using the words in brackets. ANSWERS: 1 Where are those seals swimming to? 2 Why are they doing that? 3 What is that seal doing? 4 Who is watching the seals in that small boat? 5 Why are they watching the seals? 6 Where is that scientist going? |
Assessment criteria - Learn the question forms of the present continuous. Descriptor: - match the questions in exercise 1 Descriptor: write questions for the answers using the words
Self assessment -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 30 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Phoning a friend |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics. 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics (Key phrases p.38) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for talking on the phone. • Listen to a conversation on the phone. • Practise a telephone conversation about what is happening now. • Learn how to improve pronunciation. |
||
|
Value links |
Generosity – This may be a core value of yours if you cherish people who will give their time and resources to people in need. You may consider yourself to be a generous person if you find joy and meaning in giving to others. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students if they often speak to their friends on the phone. • Ask when they use their mobile phones during the day. • Elicit a few answers, for example when they want to meet someone. • Ask them what they would say to answer the phone in English (Hello). Lead - In
Phone calls are the number one way I improve my mood. When I’m feeling down or confused or alone, I pick up the phone and call a friend. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 38 • Remind students that they should use any photos they are given to help them think about the context before they read or listen. • Ask students to identify Tina and say where she is, but do not check their answers at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 38 • Students can follow the dialogues in their books as they listen. • Remind them that the information they should listen for on this first hearing is where Tina is, and what she is doing Ex: 3 P: 38 • Explain that the blue words in the dialogue are responses to the key phrases. In a weaker class, match the first one together. • Students match the phrases in pairs. To check answers, ask one student to read out a numbered phrase, and another student to give the appropriate answer from the blue phrases Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students look at the photo. Where is Tina? ANSWERS: Students listen to the dialogue and check the answers ANSWERS: Tina is at the Brighton aquarium. She is looking at sharks. Students match the key phrases. ANSWERS: 1 Yeah, it’s really interesting. 2 Sure. 3 Hi, there. 4 OK, great! 5 I’m at the Brighton aquarium. 6 Fine, thanks |
Assessment criteria Learn key phrases for talking on the phone. Descriptor: - listen to the dialogue and check the answers
Descriptor: match the key phrases.
pupils are evaluated by collecting colour pencils -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 30 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Phoning a friend |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics. 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics (Key phrases p.38) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for talking on the phone. • Listen to a conversation on the phone. • Practise a telephone conversation about what is happening now. • Learn how to improve pronunciation. |
||
|
Value links |
Generosity – This may be a core value of yours if you cherish people who will give their time and resources to people in need. You may consider yourself to be a generous person if you find joy and meaning in giving to others. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students if they often speak to their friends on the phone. • Ask when they use their mobile phones during the day. • Elicit a few answers, for example when they want to meet someone. • Ask them what they would say to answer the phone in English (Hello). Lead - In
Phone calls are the number one way I improve my mood. When I’m feeling down or confused or alone, I pick up the phone and call a friend. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 38 • Remind students that they should use any photos they are given to help them think about the context before they read or listen. • Ask students to identify Tina and say where she is, but do not check their answers at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 38 • Students can follow the dialogues in their books as they listen. • Remind them that the information they should listen for on this first hearing is where Tina is, and what she is doing Ex: 3 P: 38 • Explain that the blue words in the dialogue are responses to the key phrases. In a weaker class, match the first one together. • Students match the phrases in pairs. To check answers, ask one student to read out a numbered phrase, and another student to give the appropriate answer from the blue phrases Differentiation: Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students look at the photo. Where is Tina? ANSWERS: Students listen to the dialogue and check the answers ANSWERS: Tina is at the Brighton aquarium. She is looking at sharks. Students match the key phrases. ANSWERS: 1 Yeah, it’s really interesting. 2 Sure. 3 Hi, there. 4 OK, great! 5 I’m at the Brighton aquarium. 6 Fine, thanks |
Assessment criteria Learn key phrases for talking on the phone. Descriptor: - listen to the dialogue and check the answers
Descriptor: match the key phrases.
pupils are evaluated by collecting colour pencils -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 31 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A description of a wildlife photo. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.5.6.1 link independently, sentences into coherent paragraphs using a variety of basic connectors on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model article about an animal. • Learn about because. • Write an article about an animal |
||
|
Value links |
Integrity – Integrity is the quality of having strong moral principles. So, a person with integrity will always act with honesty and adhere to their own moral code regardless of what others do. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students if they ever read about animals. Ask them where you can read about animals. • Elicit some answers, for example in an encyclopedia, on the internet or in a magazine. Lead – In
The snow leopard is a large cat native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia. It is listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures about wildlife animals PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 3ұ • Refer to the model text and make sure that students understand that it is divided into three paragraphs. • In a weaker class, ask them to find the answers in pairs Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 39 Elicit the first pair of sentences and how they can be joined using because. In a weaker class, discuss the function of because. What does the second sentence tell us? (The reason for the first statement.) Ex: 3 P: 39 • Check understanding of the key phrases, then ask students to match them to the paragraphs in the model text. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students read the model text and answer the questions. ANSWERS: 1 Paragraph 2 describes the life and habitat of the orca. Paragraph 3 describes a problem. 2 Yes, they do. 3 Fish, squid, seals and turtles. 4 Every two or three years. 5 They are becoming extinct because there is pollution in the sea, and they also die in fishing nets. Students match sentences with using because ANSWERS: 1 c Orcas are in danger because there is pollution in the sea. 2 e They’re hunting because they’re hungry. 3 a I don’t swim because I don’t like the water., 4 f She’s having a good time because she’s at the aquarium. 5 b He’s running because he’s late. 6 d They’re hiding because they’re scared. Students match the key phrases with paragraphs. ANSWERS: a paragraph 2 b paragraph 2 c paragraph 1 d paragraph 3 e paragraph 1 |
Assessment criteria Study a model article about an animal. Descriptor: - read the model text and answer the questions.
Assessment criteria: Learn about because. Descriptor: match sentences with using because -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: National parks. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.3.1 respect differing points of view 6.4.6.1 recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 6.6.14.1 use prepositions to talk about time and location; use prepositions like to describe things and about to denote topic; use prepositions of direction to, into, out of, from, towards on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn about the flora and fauna in one of Kazakhstan’s national parks • Identify numbers in a text • Learn and revise prepositions of place |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Ask students if they have visited any of Kazakhstan’s national parks. Ask them the name of the park and what they saw there. Ask students why countries have national parks (to preserve landscapes and the habitats they contain for plants (flora) and animals (fauna)), and if they can think of any benefits (helping maintain species, preserving beautiful areas and important habitats for future generations). Lead - In
What do you know about Karkaraly National Park? |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1/2 P: 40 Focus students’ attention on the text. If you have access to the internet, you can bring up a map of the Park’s location. Ask students what sort of landscape they think the park has (mountains, desert, steppe, etc.). Tell them to read the questions first, then read the text. Students answer the questions individually, before checking in pairs Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 4 P: 40 Go through the answers with the class. Make sure they say the answers correctly, especially 260 (two hundred and sixty). Point out that we only use and after hundreds not thousands, so 2650 is two thousand, six hundred and fifty NOT two thousand and six hundred and fifty. Ex: 3 P: 40 Students complete the exercise individually before checking their answer in pairs. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students look at the photo and describe what can they see? ANSWERS: 1 The name of the park is Altyn-Emel. 2 It is in the south-east of Kazakhstan, between the Aktau Mountains and the River Ili. 3 The landscape is dry, there are mountains and sand dunes. 4 You can find fish, 260 species of vertebrates, birds, including four types of eagle, Przewalski’s horses and eagle owls. 5 You can see singing sand dunes and rocks with very old paintings on them. 6 There are imperial eagles, eagle owls, Przewalski’s horse and 11 species on Kazakhstan’s red list and Turanga trees Students read the text again and find the numbers ANSWERS: 1) 4,600km 2) 4 500m 6) 26 2) 1,800 5) 3,000 7) 13 3) 11 Students complete the sentences with the correct prepositions ANSWERS: 1 in 5 above 2 between 6 under 3 on 7 behind 4 along, next to 8 in front of /opposite |
Assessment criteria Learn about the flora and fauna in one of Kazakhstan’s national parks Descriptor: - look at the photo and describe what can they see?
Assessment criteria: - Identify numbers in a text -Learn and revise prepositions of place Descriptor: -read the text again and find the numbers -complete the sentences with the correct prepositions -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Natural science: Animals / Summative Control work 3 for Unit 3 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world (Ex.1-3 p.41) 6.2.4.1 (6.L4) Understand with limited support the main points of extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.3.3.1 (6.S3) Give an opinion at sentence and discourse level on an increasing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about animals. Identify the main ideas in extended talk with some support Provide a point of view in conversations and discussions Retell extended stories and episodes on a given topic |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the names of several different types of animals on the board, for example: dog, pigeon, crocodile. • Ask students: What types of animals are these? What’s the difference between them? What do they have in common? Lead - In
Bats produce incredibly high frequency sound pulses, or squeaks. Research shows that some bats can produce a frequency of over 100,000 Hz. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 41 • Students check the meaning of the words in their dictionaries. Point out that some of the words, for example scales, have more than one meaning, and students should find the meaning to do with animals Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 41 • Read through the questions with the class and check understanding. Ask students to work individually and read the text again in more detail Summative Control work for the unit “Our countryside” Listening Task 1. Listen to the story and choose the correct option. Task 2. Listen to the second time and complete the sentences Speaking Task 3. Learners work in pairs. |
Students check the meaning of thewords. ANSWERS: 1 fins 4 legs 2 lungs 5 hair 3 feathers Students read and listen to the text then answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 Fish. 2 Fish and reptiles. 3 Mammals. 4 They haven’t got four legs. 5 Amphibians. 6 Mammals Students listen to the story and choose the correct option. ANSWERS: 1 farm friends 2 a bad animal 3 friendly 1 cat 2 dog 3 man / farmer Students work in pairs. ANSWERS: Students own answers. |
Assessment criteria Learn vocabulary for talking about animals. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words.
Assessment criteria: Identify the main ideas in extended talk with some support Descriptor: listen to the story and choose the correct option. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.5.1 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn verbs for animal behaviour. Write about an animal and describe its behaviour. |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Elicit ideas from the class, for example animals hunt for food, hide from other animals, find a safe place to sleep, keep warm in the winter. Lead - In The Great Barrier Reef. Scientists sometimes call Earth ‘the blue planet’ because about 75% of it is the sea! Many plants, fish and animals live in the sea, and it’s got a lot of important ecosystems. The Great Barrier Reef, near Australia, is a big ecosystem. The reef is long – 26,000 kilometres! The water is very clean, so seaweed, sea grass and coral have got a lot of solar energy. Fish and crabs eat these producers. Different species of turtles also eat the sea grass, and they leave their eggs on the local beaches. Other consumers eat the smaller animals. Sea birds catch fish and crabs |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 42 • Refer students to the bold verbs. Tell them to use the Wordlist or their dictionaries to check the meaning of any verbs they do not know. • Refer students to the photos and ask them to choose the correct verbs Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 42 Students complete the exercise individually before checking their answer in pairs. Ex: 3 P: 42 • Remind students that they should look for the present continuous forms, not the verbs as they appear here. • Read the verbs and check understanding, then allow students time to read the spelling rules carefully Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students choose the correct verbs in bold ANSWERS: Kill Eat Hide Dig Protect Catch Fly climb students complete the text with words in the box. ANSWERS: Extinct Pollution Climate Live Habitat Hunt swim Students complete the sentences with the present continuous ANSWERS: Students own answers |
Assessment criteria Writes correct verbs Descriptor: - choose the correct verbs in bold
Assessment criteria: - Identify numbers in a text Descriptor: -read the text again and find the numbers -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 28 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Skills Round - up. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.5.1 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 6.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in short, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topics 6.6.10.1 use present continuous forms with present meaning on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to an interview about animals. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. • Write about an animal and describe its behaviour. |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students if they ever read about animals. Ask them where you can read about animals. • Elicit some answers, for example in an encyclopedia, on the internet or in a magazine. Lead - In
Play a game to consolidate students’ understanding of the present continuous. Write on the board: What am I doing? Then mime an action, for example reading a book. Tell students they should ask you questions, and you will answer. For example: Are you reading a newspaper? No, I’m not reading a newspaper. Are you reading a book? Yes, I a |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 43 • Remind students of the importance of looking at photos before they listen to a text. Students identify the animals and say where they can be found. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 43 • Explain that students are going to listen to somebody talking about the photos. The first time they hear the CD, they should identify which ones are Jon’s., Ex: 3 P: 43 • Play the CD again for students to find the specific information to answer the questions. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Ex: 3 P: 43 • Read the task with the class and check everyone understands what to do. • Point out that at this stage they should use the questions to help them structure their ideas. They should work in pairs and make notes. |
Students look at the animals in the photos. Where can you see these animals? ANSWERS: From left to right, shark, dolphin, whale, crocodile, and they can all be found in water. Students listen to a dialogue. Which are Jone’s two photo? ANSWERS: The second and fourth photos. Students listen again and complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 photos 2 swimming 3 dolphins and whales 4 more dangerous 5 India, Bangladesh 6 extinct 7 French 8 mobile phone Students work in pairs and prepare a dialogue ANSWERS: Students own answers |
Assessment criteria Descriptor: - look at the photo and describe what can they see?
Assessment criteria: - Identify numbers in a text -Learn and revise prepositions of place Descriptor: -read the text again and find the numbers -complete the sentences with the correct prepositions -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.38 Workshets CD 1.38 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 30 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
,
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Films and theatre |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn irregular verbs about acting in the present and past simple. • Learn how to compare answers. • Learn and use collocations about acting. |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students: What games do you like playing? • Elicit some answers and write them on the board. Try to elicit some traditional games and some computer games. • Ask: What’s your favourite game? Elicit some answers. Lead - In
Kazakhstan, 1729: A ferocious Mongol tribe sweeps across the steppes, and Kazakh sultans leave their people to fend for themselves. Young Sartai and other survivors flee to the mountains but revenge drives Sartai and his friends back to the steppe, where he falls in |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture love with the beautiful Zere, daughter of a local khan who chose to protect his village by working with the hated Mongols |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 44 • Read through the list of verbs with the class and make sure students understand them all. • Students find the past forms in the game. In a weaker class or if you are short of time, allow them to work in pairs and find four each Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 44 • Explain that these key phrases can all be used to compare ideas. Allow students time to read through the phrases, and encourage them to guess the answers. Ex: 4 P: 44 • Read the rules with the class. • Put students into teams of three or four. • Allow students time to read the first question and discuss their answers. Play the CD, pausing after the first answer. Check whether any teams have lost a life. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students check the meaning of the verbs and match these verbs with their past form ANSWERS: 1 broke 2 scored 3 ran 4 took part 5 won 6 played 7 beat 8 lost Students complete the key phrases with the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 answer 2 sure 3 agree 4 don’t 5 right 6 think Students match the verbs ANSWERS: 1 b 2 c 3 a 4 c 5 a 6 a 7 b 8 b 9 b |
Assessment criteria -Learn irregular verbs about acting in the present and past simple. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the verbs and match these verbs with their past form
Assessment criteria: - Learn how to compare answers. Descriptor: - complete the key phrases with the words in the box. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 32 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The action game |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn how to compare answers. • Learn and use collocations about acting. |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students: What games do you like playing? • Elicit some answers and write them on the board. Try to elicit some traditional games and some computer games. • Ask: What’s your favourite game? Elicit some answers. Lead - In
The best acting games are those that your child loves, and that helps them to explore and grow in new ways. Finding the right theater activities for your child is an adventure. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 4 P: 45 • Demonstrate how certain words from each group go together to make collocations. • Point out that there are only seven phrases in group B, so the words here can match with more than one verb. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 5 P: 45 • Read through the sports and games in the box and check understanding by asking for names of famous people who do these sports Ex: 6 P: 45 • Students complete the sentences with personalized information. • Go round and listen as they discuss in pairs. • Ask some students to report back to the class. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students match the verbs. With the phrases to make collocation. ANSWERS: act in a play Students match the words in the box to the pictures. ANSWERS: Picture 1 ice-hockey Picture 2 cycling Picture 3 athletics Picture 4 football Picture 5 swimming Picture 6 chess Picture 7 American football Picture 8 skateboarding Picture 9 tennis Students complete the sentences about performing so they are true for you. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. |
Assessment criteria - Learn how to compare answers Descriptor: - match the verbs. With the phrases to make collocation.
Assessment criteria: - Learn and use collocations about acting. Descriptor: - match the words in the box to the pictures. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 32 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 07.12.22 |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading: Video Games on! |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.4.1 respond with limited flexibility at sentence level to unexpected comments on an increasing range of general and curricular topics 6.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about video games. • Read for specific information. • Ask and answer questions about games. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to look at the pictures on page 70 and the title of the text. Ask what they think the text is about. • Elicit or teach the word video game and write it on the board Lead - In
Android games are diversified into many categories; informational, educational, shooting games, puzzles, sports, racing, augmented reality games, location-based games and more. All these types are available for both high end and low-end Android phones. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 46 Students look at the pictures. If they recognize the games, ask them to describe some details about the games. Picture 1 is a SIMS game, picture 2 is a Mario game. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 46 When students have matched the correct sentences, ask them to identify the extra sentence. Ex: 3 P: 46 • Ask students to read the verbs and find the nouns in the text, and work out the meanings. • Ask questions like What does a designer do? to elicit sentences using the verbs (He / She designs things). • In a stronger class, elicit some sentences using the new words. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students discuss the video games in the photo ANSWERS: Students own answers Students read the text and complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 d 2 b 3 e 4 a C is the extra sentence. Students find the nouns for these verbs in the article. ANSWERS: 1 designers 2 creator 3 entertainment 4 choice 5 player 6 imagination 7 memory |
Assessment criteria - Read about video games. Descriptor: - discuss the video games in the photo
Assessment criteria: - Read for specific information. Descriptor: - find the nouns for these verbs in the article. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.41 Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 32 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Past Simple |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others plans on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.6.9.1 use simple past regular and irregular forms to describe past events on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the difference between regular and irregular verbs in the past simple. • Practise using the Irregular verbs list. • Use regular and irregular verbs to play a true and false game about activities in the past. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they can remember any of the irregular verbs they learnt at the beginning of the unit. • Ask students if they can remember any verbs that are regular • Elicit some examples and write these on the board. • Ask: How do you know if a verb is regular or irregular? Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
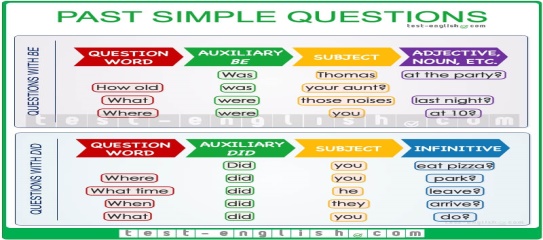
Ex: 1 P: 47 Refer students to the sentences and ask the question to the whole class Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 47 • Remind students to look at the sentences in exercise 2 as well as the main text.\ • Refer students to the Irregular verbs list in their Workbooks to check their answers Ex: 4 P: 47 Read the example with the class. Point out that students must write two sentences for each answer, one negative and one affirmative. • Students write their sentences individually, then compare with a partner Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students look at the forms of play and make in the sentences. ANSWERS: 1 Play is regular because the past simple affirmative form is made by adding -ed. Students find the past simple forms of these verbs. ANSWERS: Regular verbs: designed, preferred, created Irregular verbs: sold, bought, became, thought, built, took Students make affirmative and negative sentences. ANSWERS: 1 I didn’t have a sandwich for lunch. 2 I didn’t meet my friend in town. 3 We didn’t go to a café. 4 I didn’t read a book in bed. 5 We didn’t eat at home on Friday. 6 I didn’t write a letter to a friend. Affirmative sentences are students’ own answers. |
Assessment criteria - Learn the difference between regular and irregular verbs in the past simple. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the verbs and match these verbs with their past form
Assessment criteria: - Practise using the Irregular verbs list. Descriptor: -make affirmative and negative sentences. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 33 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Describing People |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 6.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn adjectives to describe people. • Practise describing people. • Listen to an interview about a crime and some suspects. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, tell students you are going to describe someone in the class and they must guess who it is. • Choose a student and, without saying their name, describe them to the class. For example: This student is quite short and she’s got long blonde hair Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 48 • Refer students to the illustrations and ask: What is an avatar? Elicit some ideas. In a weaker class, accept answers in their own language. Ask students if any of them use an avatar. • Refer students to the missing words. Ask students to work in pairs and complete the guide. • Check answers with the class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 48 • Refer students to the pictures and the descriptions. • Students complete the descriptions individually. Ex: 3 P: 48 Allow students time to read the introduction. Play the CD and ask: Who did the waitress see in the cafe? Differentiation: Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Ex: 4 P: 48 • Allow students time to read the questions, then play the CD again. • After checking, elicit ideas from the class about who the murderer was. |
Students complete in the character guide with the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 slim 2 dark 3 curly 4 blue 5 moustache Students complete the descriptions with words in exercise 1 in pairs ANSWERS: 1 blue, short 2 tall, long 3 short, glasses 4 fat, moustache Students read the text about TV programme ANSWERS: The waitress saw three different people in the café. Students listen the text again and answer the question. ANSWERS: 1 No, she didn’t. 2 She sat by the window. 3 No, she left at ten past eight. 4 He talked to Koji. 5 Yes, she was with the man with a beard. 6 She bought a coffee for Koji. 7 No, there wasn’t a man with long black hair. 8 No, he didn’t. |
Assessment criteria - Learn adjectives to describe people. Descriptor: - complete in the character guide with the words in the box.
Assessment criteria: - Listen to an interview about a crime and some suspects. Descriptor: - read the text about TV programme -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Worksheet |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 34 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Past Simple: questions |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others plans on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.6.9.1 use simple past question forms to describe past events on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn question forms of the past simple. • Practise asking questions in the past simple. |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, remind students about Detective Lambert’s visit to the Corner Café, on page 72. • Ask: What did he do when he went to the café? Elicit that he interviewed the waitress and asked her questions. • Ask students if they can remember any of the questions he asked. Elicit some questions, but do not write them on the board, as students probably will not get the form correct at this stage Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 49 • Students refer back to exercise 4 on page 72 and complete the questions. • Check answers by asking students to read out the completed questions. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 49 • Read the task with the class. In a weaker class, model the example exchange. In a stronger class, ask students to read this out, then to think of another example using the prompts. • Allow students time to write the questions individually, then go round and listen as they ask and answer in pairs. Differentiation: Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Ex: 4 P: 49 • Look at the words in the box with the class. Elicit that they are question words, and that they are used in questions to find out specific information. • Explain that students will need to read the answer carefully to work out which question word is needed, and transform the verb in the question into the correct form to complete the answer |
Students complete the question from exercise 4 on page 48 ANSWERS: 1 speak 2 did 3 Did 4 have Students write questions in the past ANSWERS: 1 Did you read a book in bed? 2 Did you buy clothes last weekend? 3 Did you come to school on the bus this morning? 4 Did you go to bed early? 5 Did you have a lot of homework last night? 6 Did you eat chocolate yesterday? 7 Did you use a computer at school? 8 Did you phone a friend? Students complete the questions and answers in the dialogue. Use the question words in the box and the past tense of the verbs in brackets. ANSWERS: 1 What time 6 talked 2 came 7 What 3 Where 8 drank 4 sat 9 When 5 Who 10 died |
Assessment criteria - Learn question forms of the past simple. Descriptor: - write questions in the past
Assessment criteria: - Practise asking questions in the past simple. Descriptor: - complete the questions and answers in the dialogue. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Worksheet |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 35 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Speaking: Talking about past events / Summative assessment for the unit “Drama and comedy” |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 6.4.2.1 (6.R2) Understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 6.5.2.1 (6.W2) Write with some support about real and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a limited range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a conversation about past events. • Listen and identify intonation to show interest or boredom |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to name some activities they enjoy doing. Write ideas on the board. Then ask them to name some activities they do not like, and write these on the board. You will probably find that students have different opinions on the activities. Lead - In
Tom: Hi! Sara. Where did you go yesterday? Sara: I went to the shopping. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 2 P: 50 • Tell students to read the dialogue carefully and look at the sentences on both sides of the gap before choosing the answer Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 50 • Make sure that students understand what intonation is. If necessary, write a sentence on the board (for example: I watched TV last night.) and say it with different kinds of intonation, sounding interested or bored. • Play the CD. Students decide whether the speakers are interested or bored. Summative assessment for the unit “Drama and comedy” Reading Task 1. Read about a famous movie’ Life of Pi’ and do the task below Circle True or False for these sentences. 1. Pi moves to Canada in 16. True False 2. Pi is scared when he sees the animals in the lifeboat. True False 3. Pi fights with a big shark. True False 4. At the end they land in the USA. Writing Task 2. Look at the facts about a famous cartoon ‘Rio 2’. Write 2 paragraphs using the information below. |
Students complete the dialogue with sentences. ANSWERS: 1 d 2 b 3 a 4 c Students listen to the intonation.Is the speaker interested or bored. ANSWERS: 1 bored 2 interested 3 bored 4 interested 5 bored 6 interested Students read about a famous movie’ Life of Pi’ and do the task below Circle True or False for these sentences. ANSWERS: 1 true 2 true 3 false 4 false Students writes strong lead sentence using given structure; |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a conversation about past events Descriptor: - complete the dialogue with sentences
Assessment criteria: - Listen and identify intonation to show interest or boredom Descriptor: - listen to the intonation. Is the speaker interested or bored -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 35 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Writing: A profile. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model text. • Learn key phrases for writing about a famous person. • Learn about also. • Write a profile of a sportsperson. |
||
|
Value links |
Integrity – Integrity is the quality of having strong moral principles. So, a person with integrity will always act with honesty and adhere to their own moral code regardless of what others do. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Write a few names on the board, then ask: What do you know about this person? Elicit some sentences using the present tense (e.g. she’s a singer) and the past simple (e.g. she started singing when she was ten). Lead - In
The one who believed in himself when no one else did. The world famous people Indian actor Shahrukh Khan was so broke, he had to sleep on streets and sell tea in a cinema to make ends meet. Today he is one of the most Famous People on the planet! |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 51 • Read the questions with the students. Ask them how their answer to question 1 can help them answer the others. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 51 • In a weaker class, ask students to identify the paragraph topics by referring them to question 1 in exercise 1. Ex: 3 P: 51 Students read the rules and choose the correct answers. • Check answers with the class |
Students read the text and answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 Paragraph 2 is about his career in general, paragraph 3 is about the things he won and paragraph 3 is about personal details. 2 In Madeira, Portugal 3 1 metre 85 centimetres. 4 He played for Sporting in Portugal. 5 In 2007 Students study the key phrases. Match the phrases with the three paragraphs in the model texts. ANSWERS: 1 paragraph 1 5 paragraph 1 2 paragraph 2 6 paragraph 2 3 paragraph 3 7 paragraph 3 4 paragraph 1 Students read the rule and the examples. Then choose the correct position for also in sentences. ANSWERS: 1 also lost 2 He’s also 3 also went 4 was also Students writes strong lead sentence using given structure; |
Assessment criteria - Study a model text. Descriptor: - read the text and answer the questions
Assessment criteria: - Learn about also Descriptor: - choose the correct position for also in sentences -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 37 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Kazakh films |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.4.1 respond with limited flexibility at sentence level to unexpected comments on an increasing range of general and curricular topics 6.6.15.1 use common verbs followed by infinitive verb / verb + ing patterns on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • To read and understand a text about an important figure in films and theatre in Kazakhstan. • To learn and practise verb patterns verb + -ing and verb + to infinitive |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Books closed. Write ‘Kazakh actors’ on the board. Allow students about three minutes to work in pairs and to tell their partners who their favourite Kazakh actors are and why they like them. Get feedback from the class by asking a few students to say who their favourite actors are and why they like them. Lead - In
Doskhan Zholzhaksynov’s ‘Kunanbay’ was awarded with the State Prize in Literature and Art. The film was recognized the best one in Central Asia at the Eurasia International Festival. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 2 P: 52 Ask a few confident students if they like going to the cinema or theatre, and why. What the last film or play they saw was and who the actors were. Finally, ask them if they liked it or not. When you have modelled the conversation put students in pairs and ask them to ask and answer the questions themselves Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 52 Focus
students’ attention on the name in the title of the text. Ask them
what they know about Asanaly Ashimov. Students read and listen to
the text and answer the questions individually, before checking
them in pairs. Go through the answers with the
class. Ex: 2 P: 52 -Ask students if they like acting. Then ask if they like to go to the cinema. Elicit the verb patterns that you are using and write them on the board. Point out that there are two patterns for the one verb. -Draw students’ attention to the words in blue in the text and the sentences in exercise 3 |
Students work in pairs. Ask and answer the questions. ANSWERS: Students own answers Students read and listen to the text and write true or false. ANSWERS: 1 False. He grew up in a village. 2 False. He made his first film while he was still a student. 3 True 4 False. Kyz-Zhibek was extremely popular. 5 True 6 True Students look at the words in blue in the text. Choose the correct word to complete the sentences. ANSWERS: 1 acting / to act 2 to go 3 to watch 4 working / to work 5 waiting / to wait 6 acting 7 to buy 8 eating Students writes strong lead sentence using given structure; |
Assessment criteria - To read and understand a text about an important figure in films and theatre in Kazakhstan. Descriptor: - Ask and answer the questions.
Assessment criteria: - To learn and practise verb patterns verb + -ing and verb + to infinitive Descriptor: - Choose the correct word to complete the sentences. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 38 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
summative assessment for the 2 term |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.L6 Deduce meaning from context in supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.R3 Understand the detail of an argument on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 6.W8 Spell most highfrequency vocabulary accurately for a limited range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics 6.S7 Use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -True/False tasks require learners to indicate whether the provided option right or wrong. -Gap filling tasks is a task in which words/numbers are removed from a text and replaced with spaces. Learners have to fill each space with the missing word/number or a suitable word. |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Lead - In summative assessment for the 2 term Listening Task.1 Listen to the conversation between Harry and Elizabeth twice. Transcript for listening task can be found after the mark scheme. Teacher reads the transcript. Mark sentences as True or False. 1 A horror movie is scary. True False 2 Harry likes movies about love. True False 3 Harry really hates action and adventure movies True False Fill in the gaps with ONE word. 4 Musicals do not sound too ___________________ for Harry. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students listen to the conversation and write true or false ANSWERS: 1 true 2 false 3 false 4 exciting 5 killer |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
5 I heard it's pretty exciting because nobody can guess who the ______________________ is. Reading Task. Read the text about Alex’s hometown. My town – Newquay Newquay is a small town on the Atlantic coast in the south of England. It has got great beaches and is the best place to surf in the United Kingdom. There are lots of surf schools where you can learn how to surf. I go surfing with my friends every weekend. Circle the 3 things Alex writes about. A Rainy weather in Newquay B Water activities in Newquay, C Interesting history of Newquay D Water attraction to visit in Newquay E Tasty meals in Newquay F Location of Newquay in England Complete the sentences below follow the sentence structure: 4 Alex likes Newquay because he can go … 5 While coasteering you should always take a special instructor with you because it involves… Writing Task. Choose ONE of the topics below. Follow the tips for writing Topic 1. Our countryside Think about your home place (home town or village) and write some information about it. Topic 2. Drama and comedy Think about your genre preferences and write some information about your experience. Speaking Task. Choose one of the cards and prepare an individual talk. Provide own experience on topics, using appropriate subject-specific vocabulary. You have 1 minute to prepare and 1-2 minutes to talk |
Students read the text about Alex’s hometown and circle the 3 things Alex writes about ANSWERS: B) Water activities in Newquay D) Water attraction to visit in Newquay F) Location of Newquay in England Students choose ONE of the topics below. Follow the tips for writing ANSWERS: Students own answers Students choose one of the cards and prepare an individual talk. ANSWERS: Students own answers |
Assessment criteria - True/False tasks require learners to indicate whether the provided option right or wrong. Descriptor: - listen to the conversation and write true or false
Assessment criteria: - Learners have to fill each space with the missing word/number or a suitable word. Descriptor: - read the text about Alex’s hometown and circle the 3 things Alex writes about -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 38 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL: Technology |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.4.1.1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about the internet. • Read a text about the internet. • Learn how to recognize which country website addresses come from. |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the word internet on the board. • Ask students if they use the internet, and how often. Ask if they think it is important in modern life. • Elicit some ideas, and write these on the board. • Tell students they are going to read a text about how people use the internet. Lead - In
Internet and Information technology concept. internet connection on a smart phone for sharing and doing anything |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 2 P: 53 • Refer students to the introduction only. Ask them to read it through, then discuss the activities in blue with the class Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 53 • Read the question with the class to check students understand what information they should listen for. • Play the CD once while students listen and read the text for general information. • Check the
answer with the class. If students find this difficult, explain
that the internet is a network of computers around the world that
share information, and the World Wide Web is all the information
that is stored on the internet, as
websites Ex: 3 P: 53 • Allow students time to read the questions first. • Students read the whole text again more carefully and answer the questions. |
Students read the introduction on the text. Which of the things in blue do you do on the internet? ANSWERS: Students own answers Students read and listen to the text. What invention was very important for the development of the internet. ANSWERS: The World Wide Web, invented by Tim Berners-Lee. Students read the text again and answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 It was called ARPANET. 2 Universities used it 3 He sent the first email message. 4 He worked in Geneva, and it represented Switzerland. 5 There were millions of websites and it wasn’t easy to find information. |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for talking about the internet. Descriptor: - read the introduction on the text Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Read a text about the internet Descriptor: - read the text again and answer the questions -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 38 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project: Trump card game. Review |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Play the trump card game and guess the identity of famous people. • Follow the steps in a project checklist. • Create a trump card with clues about famous people. |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, tell students you are going to give them clues about a famous person, and they must guess the identity of the person. • Give these clues for David Beckham in order, pausing after each one for students to guess the answer: He’s a sportsman. He’s a football player. He’s English. He’s got a famous wife Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 55 • Read the rules with the class and check understanding. Ask students to play the game with a partner. They should each choose one of the cards and ask the questions on it. At this stage, it does not matter if they see each other’s cards, the important thing is that they learn the process of the game. • Check answers with the class and ask a few students how many points they scored. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 55 Tell students that they are now going to make their own trump cards. • Go through the points in the project checklist. Check students understand each of these. Ex: 2 P: 55 When all the cards are completed, set aside time in class to do further work with them. Put students into groups of six to play the game. Ask them to exchange trump card clues and guess the famous person. Tell them to note down their score. • When students have finished, ask them to change partners and repeat the process four or five times, noting down their score each time. • Ask students to add up their scores. The student with the highest score is the winner. |
Students read the rules and the trump card game with a partner. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. The people are Tobey Maguire and Christopher Columbus Students make a trump card and follow the steps ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. Students play the trump card game with five people in class. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers |
Assessment criteria - Play the trump card game and guess the identity of famous people Descriptor: - read the rules and the trump card game with a partner.
Assessment criteria: - Follow the steps in a project checklist. Descriptor: - make a trump card and follow the steps -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 38 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
6-сынып бойынша 2-тоқсан ҚМЖ English plus кітабы бойынша
6-сынып бойынша 2-тоқсан ҚМЖ English plus кітабы бойынша
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 25 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Animals. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.2.1 ask more complex questions to get information about a growing range of general topics and some curricular topics 6.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of short, supported talk on a wide range of familiar topics 6.5.8.1 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Value links |
Family – Family values are moral and ethical principles of typical family life, including sacrificing for loved ones, putting your loved ones first, and keeping your loved ones at the centre of your thoughts and actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre-listening: Warm-up • With books closed, ask students to work in pairs and write down as many animals as they can in English. • Elicit the names of a few animals from individual students and write them on the board Lead - In
How many animals do you see? Where do they live? What do they eat? |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 32 • In a weaker class, allow students to match the animals with the photos in pairs. • Elicit the answer to the question, but do not check answers to the matching task at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 32 Demonstrate how to use the key phrases in context. Ask students to look at the first picture in the quiz. Say an incorrect sentence, e.g. It looks like an elephant. Elicit that the animal is a whale, and see if students can form an answer with the key phrases, e.g. I’m sure it’s a whale. Ex: 4 P: 32 • Explain to students that they are going to hear some animal sounds and they must discuss what animals they think they are hearing, using the key phrases. • Play the CD, pausing after each animal sound Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students match the animals in the box with photos ANSWERS: Photo 14 is not an eye. It’s a butterfly wing. Students compare their answers in exercise 1 ANSWERS: 1 whale 2 spider 3 owl 4 shark 5 human 6 snake 7 fly 8 seal 9 falcon 10 parrot 11 frog 12 elephant 13 chameleon 14 butterfly 15 crocodile 16 bear Students listen and identify the animals. ANSWERS: 1 an owl 5 a seal 2 a fly 6 a whale 3 a frog 7 a bear 4 a falcon 8 a snake |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for animals. Descriptor: - match the animals in the box with photos pupils are evaluated by collecting fish Descriptor: compare their answers Descriptor: listen and identify the animals -Make CCQ questions |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 24 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 26 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading: The red list |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.C7 develop and sustain a consistent argument when speaking or writing 6.R2 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 6.S3 give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics( Ex.3 - 4 p.34) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Value links |
Loyalty – Loyalty might be a core personal value to you if you highly prize friends that are reliable and trustworthy. You might put your friends or chosen family first, always being there for them when they need you. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask: What’s your favourite animal? • Ask: Which animals do you dislike? Elicit answers from individual students, and ask why they dislike these animals Lead - In
The Red
Book of Kazakhstan - an annotated list of rare and endangered
animals in |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 34 • Refer students to the title of the article and the question. • Students discuss their answers in pairs. • In a stronger class, ask students to make a note of as many statistics as they can to support their answer complete the sentences with the correct form of the verbs in brackets Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 34 • Explain that students should now read the text again more carefully to find the specific information. In a weaker class, check key vocabulary, e.g. extinct, before students read. • Ask students to complete the answers individually, then compare their ideas with a partner Ex: 3 P: 34 • Students check the meaning of the blue words and identify which are verbs (attack and save). • Check understanding of the words and phrases, for example by asking students to use them in sentences Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students read and listen to the text ANSWERS: A person is more dangerous than a shark or a chair. Students read the text again and choose the correct answers ANSWERS: 1 a 2 c 3 c 4 c 5 a Students use the words to complete the sentences. ANSWERS: 1 attack 4 accidents 2 approximately 5 actions 3 save 6 pollution |
Assessment criteria Read about animals in danger Descriptor: - read and listen to the text
pupils are evaluated by collecting fish Descriptor: read the text again and choose the correct answers
-Make CCQ questions. Yes / No 1 Are crocodiles dangerous? Yes 2 Do people kill animals for fur? No 3 Do wolves live In Kazakhstan? Yes |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 24 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 27 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Present Continuous |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.C6 organise and present information clearly to others ( Ex.1 p.35) 6.W2 write with minimal support about real and imaginary present events, activities and experiences happening now on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics ( Ex.2,3,5 p.35) 6.S2 ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general topics ( Ex.6 |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Value links |
Fairness – If you value fairness, you might be highly sensitive to situations at school or in the workplace where a teacher or a peer has exhibited favoritism or allowed someone to get away with living by a different set of rules to everyone else. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Write four present continuous sentences on the board, two true and two false, e.g. I am teaching. The sun is shining. Elicit which ones are true and how students can tell. Elicit that the present continuous describes events happening now Lead - In
He is swimming. She is reading We are dancing They are running |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 35 When students have found the sentences, draw attention to the form Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. . Ex: 3 P: 35 • Tell students they are going to listen to seven recordings, and that they should identify what is happening. • Tell students to read the options in columns A and B before they listen, to give them an idea of the context and what they might hear Ex: 4 P: 35 • Allow students time to study the picture carefully and read the prompts. • Explain that they should write the negative sentence first, then an affirmative sentence using the word in brackets Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 are 2 aren’t 3 is Students match the things in A with the actions in B ANSWERS: 1 Two dogs are running in the park. 2 A parrot is speaking English. 3 A man is attacking a mosquito. 4 A whale is singing to its partner. 5 Children are making a cake. 6 A girl is practising the piano. 7 A lion is having a meal. Students work in pairs. Make affirmative and negative sentences using the present continuous ANSWERS: 1 A child isn’t feeding some bears. She is feeding some ducks. 2 A falcon isn’t sleeping. It is hunting. 3 Two people aren’t watching a chameleon. They are watching the falcon. 4 Three people aren’t swimming. They are running. |
Assessment criteria - Learn the affirmative and negative forms of the present continuous. Descriptor: - match the things in A with the actions in B
Descriptor: Make affirmative and negative sentences using the present continuous
pupils are evaluated by collecting pencils -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 24 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 28 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Animal behaviour |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups ( Ex.1,2 p.36) 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics ( Ex.3 p.36) 6.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics( Ex.4 p.36) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn verbs for animal behaviour. • Listen to an interview about animals. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. • Write about an animal and describe its behaviour |
||
|
Value links |
Honesty – You may highly value telling people the truth. This one gets tricky when being honest can be hurtful to others. So, a person who really puts honesty first might be the sort of person who will tell the truth even if it hurts to do so. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Write the word Behaviour on the board. • Elicit the meaning, then ask: What do animals do to survive? • Elicit ideas from the class, for example animals hunt for food, hide from other animals, find a safe place to sleep, keep warm in the winter. Lead - In
There are prides within 100 km of each other that display extremes in behavior, and in particular when it comes to feeding and drinking. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 36 • Refer students to the bold verbs. Tell them to use the Wordlist or their dictionaries to check the meaning of any verbs they do not know. • Refer students to the photos and ask them to choose the correct verbs. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. . Ex: 2 P: 36 • Look at the example answer and remind students that we do not use the definite article, the, when we are talking about things in general. • Students complete the sentences with the animals Ex: 3 P: 36 Explain that students are going to listen to an interview. While they listen for the first time they should look at the photos and identify the ones the speaker is talking about. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students check the meaning of the verbs in bold and choose the correct verbs ANSWERS: 1 feeding 3 catching 5 hunting 2 building 4 protecting 6 chasing Students complete the sentences with names of the animals ANSWERS: 1 Snakes 4 Sharks 2 Bears 5 Humans 3 Chameleons 6 Whales. Students listen to an interview with Mike. Which of the photos does Mike speak about? ANSWERS: He speaks about photos 1, 3, 4 and 6 |
Assessment criteria - identify verbs for animal behaviour. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the verbs in bold and choose the correct verbs
Descriptor: complete the sentences with names of the animals
pupils are evaluated by collecting colour pencils Descriptor: listen to an interview with Mike. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets CD 1.31 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 26 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 29 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Present Continuous. Questions |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others ( ex1 - 5 p.37) 6.5.2.1 write with minimal support about real and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics ( Ex.6,7 p.37) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the question forms of the present continuous. • Write questions and answers using the present continuous. • Identify the difference between the present continuous and the present simple |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students back to the photos on page 42. Ask students what questions they can ask about the animals Lead - In
Is he swimming? Is she reading? Are we dancing? Are they running? |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 37 • In a weaker class, you could play the CD (2.06) again Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 37 Check understanding by asking and answering some present continuous questions as a class. Ex: 3 P: 37 In a weaker class do another example with the whole class, and then ask and answer. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students complete the question form ANSWERS: 1 is 2 Is 3 Is Students match the questions in exercise 1 ANSWERS: 1 c 2 a 3 b Rules: 1 is 2 aren’t Students write questions for the answers using the words in brackets. ANSWERS: 1 Where are those seals swimming to? 2 Why are they doing that? 3 What is that seal doing? 4 Who is watching the seals in that small boat? 5 Why are they watching the seals? 6 Where is that scientist going? |
Assessment criteria - Learn the question forms of the present continuous. Descriptor: - match the questions in exercise 1 Descriptor: write questions for the answers using the words
Self assessment -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 30 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Phoning a friend |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics. 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics (Key phrases p.38) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for talking on the phone. • Listen to a conversation on the phone. • Practise a telephone conversation about what is happening now. • Learn how to improve pronunciation. |
||
|
Value links |
Generosity – This may be a core value of yours if you cherish people who will give their time and resources to people in need. You may consider yourself to be a generous person if you find joy and meaning in giving to others. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students if they often speak to their friends on the phone. • Ask when they use their mobile phones during the day. • Elicit a few answers, for example when they want to meet someone. • Ask them what they would say to answer the phone in English (Hello). Lead - In
Phone calls are the number one way I improve my mood. When I’m feeling down or confused or alone, I pick up the phone and call a friend. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 38 • Remind students that they should use any photos they are given to help them think about the context before they read or listen. • Ask students to identify Tina and say where she is, but do not check their answers at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 38 • Students can follow the dialogues in their books as they listen. • Remind them that the information they should listen for on this first hearing is where Tina is, and what she is doing Ex: 3 P: 38 • Explain that the blue words in the dialogue are responses to the key phrases. In a weaker class, match the first one together. • Students match the phrases in pairs. To check answers, ask one student to read out a numbered phrase, and another student to give the appropriate answer from the blue phrases Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students look at the photo. Where is Tina? ANSWERS: Students listen to the dialogue and check the answers ANSWERS: Tina is at the Brighton aquarium. She is looking at sharks. Students match the key phrases. ANSWERS: 1 Yeah, it’s really interesting. 2 Sure. 3 Hi, there. 4 OK, great! 5 I’m at the Brighton aquarium. 6 Fine, thanks |
Assessment criteria Learn key phrases for talking on the phone. Descriptor: - listen to the dialogue and check the answers
Descriptor: match the key phrases.
pupils are evaluated by collecting colour pencils -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 30 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Phoning a friend |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics. 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics (Key phrases p.38) |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for talking on the phone. • Listen to a conversation on the phone. • Practise a telephone conversation about what is happening now. • Learn how to improve pronunciation. |
||
|
Value links |
Generosity – This may be a core value of yours if you cherish people who will give their time and resources to people in need. You may consider yourself to be a generous person if you find joy and meaning in giving to others. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students if they often speak to their friends on the phone. • Ask when they use their mobile phones during the day. • Elicit a few answers, for example when they want to meet someone. • Ask them what they would say to answer the phone in English (Hello). Lead - In
Phone calls are the number one way I improve my mood. When I’m feeling down or confused or alone, I pick up the phone and call a friend. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 38 • Remind students that they should use any photos they are given to help them think about the context before they read or listen. • Ask students to identify Tina and say where she is, but do not check their answers at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 38 • Students can follow the dialogues in their books as they listen. • Remind them that the information they should listen for on this first hearing is where Tina is, and what she is doing Ex: 3 P: 38 • Explain that the blue words in the dialogue are responses to the key phrases. In a weaker class, match the first one together. • Students match the phrases in pairs. To check answers, ask one student to read out a numbered phrase, and another student to give the appropriate answer from the blue phrases Differentiation: Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students look at the photo. Where is Tina? ANSWERS: Students listen to the dialogue and check the answers ANSWERS: Tina is at the Brighton aquarium. She is looking at sharks. Students match the key phrases. ANSWERS: 1 Yeah, it’s really interesting. 2 Sure. 3 Hi, there. 4 OK, great! 5 I’m at the Brighton aquarium. 6 Fine, thanks |
Assessment criteria Learn key phrases for talking on the phone. Descriptor: - listen to the dialogue and check the answers
Descriptor: match the key phrases.
pupils are evaluated by collecting colour pencils -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
Lesson 31 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A description of a wildlife photo. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.5.6.1 link independently, sentences into coherent paragraphs using a variety of basic connectors on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model article about an animal. • Learn about because. • Write an article about an animal |
||
|
Value links |
Integrity – Integrity is the quality of having strong moral principles. So, a person with integrity will always act with honesty and adhere to their own moral code regardless of what others do. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students if they ever read about animals. Ask them where you can read about animals. • Elicit some answers, for example in an encyclopedia, on the internet or in a magazine. Lead – In
The snow leopard is a large cat native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia. It is listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures about wildlife animals PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 3ұ • Refer to the model text and make sure that students understand that it is divided into three paragraphs. • In a weaker class, ask them to find the answers in pairs Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 39 Elicit the first pair of sentences and how they can be joined using because. In a weaker class, discuss the function of because. What does the second sentence tell us? (The reason for the first statement.) Ex: 3 P: 39 • Check understanding of the key phrases, then ask students to match them to the paragraphs in the model text. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students read the model text and answer the questions. ANSWERS: 1 Paragraph 2 describes the life and habitat of the orca. Paragraph 3 describes a problem. 2 Yes, they do. 3 Fish, squid, seals and turtles. 4 Every two or three years. 5 They are becoming extinct because there is pollution in the sea, and they also die in fishing nets. Students match sentences with using because ANSWERS: 1 c Orcas are in danger because there is pollution in the sea. 2 e They’re hunting because they’re hungry. 3 a I don’t swim because I don’t like the water., 4 f She’s having a good time because she’s at the aquarium. 5 b He’s running because he’s late. 6 d They’re hiding because they’re scared. Students match the key phrases with paragraphs. ANSWERS: a paragraph 2 b paragraph 2 c paragraph 1 d paragraph 3 e paragraph 1 |
Assessment criteria Study a model article about an animal. Descriptor: - read the model text and answer the questions.
Assessment criteria: Learn about because. Descriptor: match sentences with using because -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: National parks. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.3.1 respect differing points of view 6.4.6.1 recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 6.6.14.1 use prepositions to talk about time and location; use prepositions like to describe things and about to denote topic; use prepositions of direction to, into, out of, from, towards on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn about the flora and fauna in one of Kazakhstan’s national parks • Identify numbers in a text • Learn and revise prepositions of place |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Ask students if they have visited any of Kazakhstan’s national parks. Ask them the name of the park and what they saw there. Ask students why countries have national parks (to preserve landscapes and the habitats they contain for plants (flora) and animals (fauna)), and if they can think of any benefits (helping maintain species, preserving beautiful areas and important habitats for future generations). Lead - In
What do you know about Karkaraly National Park? |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1/2 P: 40 Focus students’ attention on the text. If you have access to the internet, you can bring up a map of the Park’s location. Ask students what sort of landscape they think the park has (mountains, desert, steppe, etc.). Tell them to read the questions first, then read the text. Students answer the questions individually, before checking in pairs Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 4 P: 40 Go through the answers with the class. Make sure they say the answers correctly, especially 260 (two hundred and sixty). Point out that we only use and after hundreds not thousands, so 2650 is two thousand, six hundred and fifty NOT two thousand and six hundred and fifty. Ex: 3 P: 40 Students complete the exercise individually before checking their answer in pairs. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students look at the photo and describe what can they see? ANSWERS: 1 The name of the park is Altyn-Emel. 2 It is in the south-east of Kazakhstan, between the Aktau Mountains and the River Ili. 3 The landscape is dry, there are mountains and sand dunes. 4 You can find fish, 260 species of vertebrates, birds, including four types of eagle, Przewalski’s horses and eagle owls. 5 You can see singing sand dunes and rocks with very old paintings on them. 6 There are imperial eagles, eagle owls, Przewalski’s horse and 11 species on Kazakhstan’s red list and Turanga trees Students read the text again and find the numbers ANSWERS: 1) 4,600km 2) 4 500m 6) 26 2) 1,800 5) 3,000 7) 13 3) 11 Students complete the sentences with the correct prepositions ANSWERS: 1 in 5 above 2 between 6 under 3 on 7 behind 4 along, next to 8 in front of /opposite |
Assessment criteria Learn about the flora and fauna in one of Kazakhstan’s national parks Descriptor: - look at the photo and describe what can they see?
Assessment criteria: - Identify numbers in a text -Learn and revise prepositions of place Descriptor: -read the text again and find the numbers -complete the sentences with the correct prepositions -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Natural science: Animals / Summative Control work 3 for Unit 3 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world (Ex.1-3 p.41) 6.2.4.1 (6.L4) Understand with limited support the main points of extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.3.3.1 (6.S3) Give an opinion at sentence and discourse level on an increasing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about animals. Identify the main ideas in extended talk with some support Provide a point of view in conversations and discussions Retell extended stories and episodes on a given topic |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the names of several different types of animals on the board, for example: dog, pigeon, crocodile. • Ask students: What types of animals are these? What’s the difference between them? What do they have in common? Lead - In
Bats produce incredibly high frequency sound pulses, or squeaks. Research shows that some bats can produce a frequency of over 100,000 Hz. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 41 • Students check the meaning of the words in their dictionaries. Point out that some of the words, for example scales, have more than one meaning, and students should find the meaning to do with animals Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 41 • Read through the questions with the class and check understanding. Ask students to work individually and read the text again in more detail Summative Control work for the unit “Our countryside” Listening Task 1. Listen to the story and choose the correct option. Task 2. Listen to the second time and complete the sentences Speaking Task 3. Learners work in pairs. |
Students check the meaning of thewords. ANSWERS: 1 fins 4 legs 2 lungs 5 hair 3 feathers Students read and listen to the text then answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 Fish. 2 Fish and reptiles. 3 Mammals. 4 They haven’t got four legs. 5 Amphibians. 6 Mammals Students listen to the story and choose the correct option. ANSWERS: 1 farm friends 2 a bad animal 3 friendly 1 cat 2 dog 3 man / farmer Students work in pairs. ANSWERS: Students own answers. |
Assessment criteria Learn vocabulary for talking about animals. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words.
Assessment criteria: Identify the main ideas in extended talk with some support Descriptor: listen to the story and choose the correct option. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 27 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.5.1 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn verbs for animal behaviour. Write about an animal and describe its behaviour. |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Elicit ideas from the class, for example animals hunt for food, hide from other animals, find a safe place to sleep, keep warm in the winter. Lead - In The Great Barrier Reef. Scientists sometimes call Earth ‘the blue planet’ because about 75% of it is the sea! Many plants, fish and animals live in the sea, and it’s got a lot of important ecosystems. The Great Barrier Reef, near Australia, is a big ecosystem. The reef is long – 26,000 kilometres! The water is very clean, so seaweed, sea grass and coral have got a lot of solar energy. Fish and crabs eat these producers. Different species of turtles also eat the sea grass, and they leave their eggs on the local beaches. Other consumers eat the smaller animals. Sea birds catch fish and crabs |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 42 • Refer students to the bold verbs. Tell them to use the Wordlist or their dictionaries to check the meaning of any verbs they do not know. • Refer students to the photos and ask them to choose the correct verbs Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 42 Students complete the exercise individually before checking their answer in pairs. Ex: 3 P: 42 • Remind students that they should look for the present continuous forms, not the verbs as they appear here. • Read the verbs and check understanding, then allow students time to read the spelling rules carefully Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students choose the correct verbs in bold ANSWERS: Kill Eat Hide Dig Protect Catch Fly climb students complete the text with words in the box. ANSWERS: Extinct Pollution Climate Live Habitat Hunt swim Students complete the sentences with the present continuous ANSWERS: Students own answers |
Assessment criteria Writes correct verbs Descriptor: - choose the correct verbs in bold
Assessment criteria: - Identify numbers in a text Descriptor: -read the text again and find the numbers -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 28 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Our countryside |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Skills Round - up. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.5.1 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 6.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in short, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topics 6.6.10.1 use present continuous forms with present meaning on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to an interview about animals. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. • Write about an animal and describe its behaviour. |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students if they ever read about animals. Ask them where you can read about animals. • Elicit some answers, for example in an encyclopedia, on the internet or in a magazine. Lead - In
Play a game to consolidate students’ understanding of the present continuous. Write on the board: What am I doing? Then mime an action, for example reading a book. Tell students they should ask you questions, and you will answer. For example: Are you reading a newspaper? No, I’m not reading a newspaper. Are you reading a book? Yes, I a |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 43 • Remind students of the importance of looking at photos before they listen to a text. Students identify the animals and say where they can be found. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 43 • Explain that students are going to listen to somebody talking about the photos. The first time they hear the CD, they should identify which ones are Jon’s., Ex: 3 P: 43 • Play the CD again for students to find the specific information to answer the questions. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Ex: 3 P: 43 • Read the task with the class and check everyone understands what to do. • Point out that at this stage they should use the questions to help them structure their ideas. They should work in pairs and make notes. |
Students look at the animals in the photos. Where can you see these animals? ANSWERS: From left to right, shark, dolphin, whale, crocodile, and they can all be found in water. Students listen to a dialogue. Which are Jone’s two photo? ANSWERS: The second and fourth photos. Students listen again and complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 photos 2 swimming 3 dolphins and whales 4 more dangerous 5 India, Bangladesh 6 extinct 7 French 8 mobile phone Students work in pairs and prepare a dialogue ANSWERS: Students own answers |
Assessment criteria Descriptor: - look at the photo and describe what can they see?
Assessment criteria: - Identify numbers in a text -Learn and revise prepositions of place Descriptor: -read the text again and find the numbers -complete the sentences with the correct prepositions -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.38 Workshets CD 1.38 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 30 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
,
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Films and theatre |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn irregular verbs about acting in the present and past simple. • Learn how to compare answers. • Learn and use collocations about acting. |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students: What games do you like playing? • Elicit some answers and write them on the board. Try to elicit some traditional games and some computer games. • Ask: What’s your favourite game? Elicit some answers. Lead - In
Kazakhstan, 1729: A ferocious Mongol tribe sweeps across the steppes, and Kazakh sultans leave their people to fend for themselves. Young Sartai and other survivors flee to the mountains but revenge drives Sartai and his friends back to the steppe, where he falls in |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture love with the beautiful Zere, daughter of a local khan who chose to protect his village by working with the hated Mongols |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 44 • Read through the list of verbs with the class and make sure students understand them all. • Students find the past forms in the game. In a weaker class or if you are short of time, allow them to work in pairs and find four each Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 44 • Explain that these key phrases can all be used to compare ideas. Allow students time to read through the phrases, and encourage them to guess the answers. Ex: 4 P: 44 • Read the rules with the class. • Put students into teams of three or four. • Allow students time to read the first question and discuss their answers. Play the CD, pausing after the first answer. Check whether any teams have lost a life. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students check the meaning of the verbs and match these verbs with their past form ANSWERS: 1 broke 2 scored 3 ran 4 took part 5 won 6 played 7 beat 8 lost Students complete the key phrases with the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 answer 2 sure 3 agree 4 don’t 5 right 6 think Students match the verbs ANSWERS: 1 b 2 c 3 a 4 c 5 a 6 a 7 b 8 b 9 b |
Assessment criteria -Learn irregular verbs about acting in the present and past simple. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the verbs and match these verbs with their past form
Assessment criteria: - Learn how to compare answers. Descriptor: - complete the key phrases with the words in the box. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.32 Workshets CD 1.33 |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 32 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The action game |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn how to compare answers. • Learn and use collocations about acting. |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students: What games do you like playing? • Elicit some answers and write them on the board. Try to elicit some traditional games and some computer games. • Ask: What’s your favourite game? Elicit some answers. Lead - In
The best acting games are those that your child loves, and that helps them to explore and grow in new ways. Finding the right theater activities for your child is an adventure. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 4 P: 45 • Demonstrate how certain words from each group go together to make collocations. • Point out that there are only seven phrases in group B, so the words here can match with more than one verb. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 5 P: 45 • Read through the sports and games in the box and check understanding by asking for names of famous people who do these sports Ex: 6 P: 45 • Students complete the sentences with personalized information. • Go round and listen as they discuss in pairs. • Ask some students to report back to the class. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students match the verbs. With the phrases to make collocation. ANSWERS: act in a play Students match the words in the box to the pictures. ANSWERS: Picture 1 ice-hockey Picture 2 cycling Picture 3 athletics Picture 4 football Picture 5 swimming Picture 6 chess Picture 7 American football Picture 8 skateboarding Picture 9 tennis Students complete the sentences about performing so they are true for you. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. |
Assessment criteria - Learn how to compare answers Descriptor: - match the verbs. With the phrases to make collocation.
Assessment criteria: - Learn and use collocations about acting. Descriptor: - match the words in the box to the pictures. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 32 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 07.12.22 |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading: Video Games on! |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.4.1 respond with limited flexibility at sentence level to unexpected comments on an increasing range of general and curricular topics 6.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about video games. • Read for specific information. • Ask and answer questions about games. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to look at the pictures on page 70 and the title of the text. Ask what they think the text is about. • Elicit or teach the word video game and write it on the board Lead - In
Android games are diversified into many categories; informational, educational, shooting games, puzzles, sports, racing, augmented reality games, location-based games and more. All these types are available for both high end and low-end Android phones. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 46 Students look at the pictures. If they recognize the games, ask them to describe some details about the games. Picture 1 is a SIMS game, picture 2 is a Mario game. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 46 When students have matched the correct sentences, ask them to identify the extra sentence. Ex: 3 P: 46 • Ask students to read the verbs and find the nouns in the text, and work out the meanings. • Ask questions like What does a designer do? to elicit sentences using the verbs (He / She designs things). • In a stronger class, elicit some sentences using the new words. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students discuss the video games in the photo ANSWERS: Students own answers Students read the text and complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 d 2 b 3 e 4 a C is the extra sentence. Students find the nouns for these verbs in the article. ANSWERS: 1 designers 2 creator 3 entertainment 4 choice 5 player 6 imagination 7 memory |
Assessment criteria - Read about video games. Descriptor: - discuss the video games in the photo
Assessment criteria: - Read for specific information. Descriptor: - find the nouns for these verbs in the article. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book CD 1.41 Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 32 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Past Simple |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others plans on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.6.9.1 use simple past regular and irregular forms to describe past events on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the difference between regular and irregular verbs in the past simple. • Practise using the Irregular verbs list. • Use regular and irregular verbs to play a true and false game about activities in the past. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they can remember any of the irregular verbs they learnt at the beginning of the unit. • Ask students if they can remember any verbs that are regular • Elicit some examples and write these on the board. • Ask: How do you know if a verb is regular or irregular? Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 47 Refer students to the sentences and ask the question to the whole class Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 47 • Remind students to look at the sentences in exercise 2 as well as the main text.\ • Refer students to the Irregular verbs list in their Workbooks to check their answers Ex: 4 P: 47 Read the example with the class. Point out that students must write two sentences for each answer, one negative and one affirmative. • Students write their sentences individually, then compare with a partner Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students look at the forms of play and make in the sentences. ANSWERS: 1 Play is regular because the past simple affirmative form is made by adding -ed. Students find the past simple forms of these verbs. ANSWERS: Regular verbs: designed, preferred, created Irregular verbs: sold, bought, became, thought, built, took Students make affirmative and negative sentences. ANSWERS: 1 I didn’t have a sandwich for lunch. 2 I didn’t meet my friend in town. 3 We didn’t go to a café. 4 I didn’t read a book in bed. 5 We didn’t eat at home on Friday. 6 I didn’t write a letter to a friend. Affirmative sentences are students’ own answers. |
Assessment criteria - Learn the difference between regular and irregular verbs in the past simple. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the verbs and match these verbs with their past form
Assessment criteria: - Practise using the Irregular verbs list. Descriptor: -make affirmative and negative sentences. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 33 WB |
|
Poster Success |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Describing People |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 6.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn adjectives to describe people. • Practise describing people. • Listen to an interview about a crime and some suspects. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, tell students you are going to describe someone in the class and they must guess who it is. • Choose a student and, without saying their name, describe them to the class. For example: This student is quite short and she’s got long blonde hair Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 48 • Refer students to the illustrations and ask: What is an avatar? Elicit some ideas. In a weaker class, accept answers in their own language. Ask students if any of them use an avatar. • Refer students to the missing words. Ask students to work in pairs and complete the guide. • Check answers with the class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 48 • Refer students to the pictures and the descriptions. • Students complete the descriptions individually. Ex: 3 P: 48 Allow students time to read the introduction. Play the CD and ask: Who did the waitress see in the cafe? Differentiation: Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Ex: 4 P: 48 • Allow students time to read the questions, then play the CD again. • After checking, elicit ideas from the class about who the murderer was. |
Students complete in the character guide with the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 slim 2 dark 3 curly 4 blue 5 moustache Students complete the descriptions with words in exercise 1 in pairs ANSWERS: 1 blue, short 2 tall, long 3 short, glasses 4 fat, moustache Students read the text about TV programme ANSWERS: The waitress saw three different people in the café. Students listen the text again and answer the question. ANSWERS: 1 No, she didn’t. 2 She sat by the window. 3 No, she left at ten past eight. 4 He talked to Koji. 5 Yes, she was with the man with a beard. 6 She bought a coffee for Koji. 7 No, there wasn’t a man with long black hair. 8 No, he didn’t. |
Assessment criteria - Learn adjectives to describe people. Descriptor: - complete in the character guide with the words in the box.
Assessment criteria: - Listen to an interview about a crime and some suspects. Descriptor: - read the text about TV programme -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Worksheet |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 34 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Past Simple: questions |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others plans on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.6.9.1 use simple past question forms to describe past events on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn question forms of the past simple. • Practise asking questions in the past simple. |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, remind students about Detective Lambert’s visit to the Corner Café, on page 72. • Ask: What did he do when he went to the café? Elicit that he interviewed the waitress and asked her questions. • Ask students if they can remember any of the questions he asked. Elicit some questions, but do not write them on the board, as students probably will not get the form correct at this stage Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 49 • Students refer back to exercise 4 on page 72 and complete the questions. • Check answers by asking students to read out the completed questions. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 49 • Read the task with the class. In a weaker class, model the example exchange. In a stronger class, ask students to read this out, then to think of another example using the prompts. • Allow students time to write the questions individually, then go round and listen as they ask and answer in pairs. Differentiation: Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Ex: 4 P: 49 • Look at the words in the box with the class. Elicit that they are question words, and that they are used in questions to find out specific information. • Explain that students will need to read the answer carefully to work out which question word is needed, and transform the verb in the question into the correct form to complete the answer |
Students complete the question from exercise 4 on page 48 ANSWERS: 1 speak 2 did 3 Did 4 have Students write questions in the past ANSWERS: 1 Did you read a book in bed? 2 Did you buy clothes last weekend? 3 Did you come to school on the bus this morning? 4 Did you go to bed early? 5 Did you have a lot of homework last night? 6 Did you eat chocolate yesterday? 7 Did you use a computer at school? 8 Did you phone a friend? Students complete the questions and answers in the dialogue. Use the question words in the box and the past tense of the verbs in brackets. ANSWERS: 1 What time 6 talked 2 came 7 What 3 Where 8 drank 4 sat 9 When 5 Who 10 died |
Assessment criteria - Learn question forms of the past simple. Descriptor: - write questions in the past
Assessment criteria: - Practise asking questions in the past simple. Descriptor: - complete the questions and answers in the dialogue. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Worksheet |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 35 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Speaking: Talking about past events / Summative assessment for the unit “Drama and comedy” |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 6.4.2.1 (6.R2) Understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 6.5.2.1 (6.W2) Write with some support about real and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a limited range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a conversation about past events. • Listen and identify intonation to show interest or boredom |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to name some activities they enjoy doing. Write ideas on the board. Then ask them to name some activities they do not like, and write these on the board. You will probably find that students have different opinions on the activities. Lead - In
Tom: Hi! Sara. Where did you go yesterday? Sara: I went to the shopping. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 2 P: 50 • Tell students to read the dialogue carefully and look at the sentences on both sides of the gap before choosing the answer Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 50 • Make sure that students understand what intonation is. If necessary, write a sentence on the board (for example: I watched TV last night.) and say it with different kinds of intonation, sounding interested or bored. • Play the CD. Students decide whether the speakers are interested or bored. Summative assessment for the unit “Drama and comedy” Reading Task 1. Read about a famous movie’ Life of Pi’ and do the task below Circle True or False for these sentences. 1. Pi moves to Canada in 16. True False 2. Pi is scared when he sees the animals in the lifeboat. True False 3. Pi fights with a big shark. True False 4. At the end they land in the USA. Writing Task 2. Look at the facts about a famous cartoon ‘Rio 2’. Write 2 paragraphs using the information below. |
Students complete the dialogue with sentences. ANSWERS: 1 d 2 b 3 a 4 c Students listen to the intonation.Is the speaker interested or bored. ANSWERS: 1 bored 2 interested 3 bored 4 interested 5 bored 6 interested Students read about a famous movie’ Life of Pi’ and do the task below Circle True or False for these sentences. ANSWERS: 1 true 2 true 3 false 4 false Students writes strong lead sentence using given structure; |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a conversation about past events Descriptor: - complete the dialogue with sentences
Assessment criteria: - Listen and identify intonation to show interest or boredom Descriptor: - listen to the intonation. Is the speaker interested or bored -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 35 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Writing: A profile. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model text. • Learn key phrases for writing about a famous person. • Learn about also. • Write a profile of a sportsperson. |
||
|
Value links |
Integrity – Integrity is the quality of having strong moral principles. So, a person with integrity will always act with honesty and adhere to their own moral code regardless of what others do. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Write a few names on the board, then ask: What do you know about this person? Elicit some sentences using the present tense (e.g. she’s a singer) and the past simple (e.g. she started singing when she was ten). Lead - In
The one who believed in himself when no one else did. The world famous people Indian actor Shahrukh Khan was so broke, he had to sleep on streets and sell tea in a cinema to make ends meet. Today he is one of the most Famous People on the planet! |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 51 • Read the questions with the students. Ask them how their answer to question 1 can help them answer the others. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 51 • In a weaker class, ask students to identify the paragraph topics by referring them to question 1 in exercise 1. Ex: 3 P: 51 Students read the rules and choose the correct answers. • Check answers with the class |
Students read the text and answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 Paragraph 2 is about his career in general, paragraph 3 is about the things he won and paragraph 3 is about personal details. 2 In Madeira, Portugal 3 1 metre 85 centimetres. 4 He played for Sporting in Portugal. 5 In 2007 Students study the key phrases. Match the phrases with the three paragraphs in the model texts. ANSWERS: 1 paragraph 1 5 paragraph 1 2 paragraph 2 6 paragraph 2 3 paragraph 3 7 paragraph 3 4 paragraph 1 Students read the rule and the examples. Then choose the correct position for also in sentences. ANSWERS: 1 also lost 2 He’s also 3 also went 4 was also Students writes strong lead sentence using given structure; |
Assessment criteria - Study a model text. Descriptor: - read the text and answer the questions
Assessment criteria: - Learn about also Descriptor: - choose the correct position for also in sentences -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 37 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Kazakh films |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.4.1 respond with limited flexibility at sentence level to unexpected comments on an increasing range of general and curricular topics 6.6.15.1 use common verbs followed by infinitive verb / verb + ing patterns on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • To read and understand a text about an important figure in films and theatre in Kazakhstan. • To learn and practise verb patterns verb + -ing and verb + to infinitive |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Books closed. Write ‘Kazakh actors’ on the board. Allow students about three minutes to work in pairs and to tell their partners who their favourite Kazakh actors are and why they like them. Get feedback from the class by asking a few students to say who their favourite actors are and why they like them. Lead - In
Doskhan Zholzhaksynov’s ‘Kunanbay’ was awarded with the State Prize in Literature and Art. The film was recognized the best one in Central Asia at the Eurasia International Festival. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 2 P: 52 Ask a few confident students if they like going to the cinema or theatre, and why. What the last film or play they saw was and who the actors were. Finally, ask them if they liked it or not. When you have modelled the conversation put students in pairs and ask them to ask and answer the questions themselves Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 52 Focus
students’ attention on the name in the title of the text. Ask them
what they know about Asanaly Ashimov. Students read and listen to
the text and answer the questions individually, before checking
them in pairs. Go through the answers with the
class. Ex: 2 P: 52 -Ask students if they like acting. Then ask if they like to go to the cinema. Elicit the verb patterns that you are using and write them on the board. Point out that there are two patterns for the one verb. -Draw students’ attention to the words in blue in the text and the sentences in exercise 3 |
Students work in pairs. Ask and answer the questions. ANSWERS: Students own answers Students read and listen to the text and write true or false. ANSWERS: 1 False. He grew up in a village. 2 False. He made his first film while he was still a student. 3 True 4 False. Kyz-Zhibek was extremely popular. 5 True 6 True Students look at the words in blue in the text. Choose the correct word to complete the sentences. ANSWERS: 1 acting / to act 2 to go 3 to watch 4 working / to work 5 waiting / to wait 6 acting 7 to buy 8 eating Students writes strong lead sentence using given structure; |
Assessment criteria - To read and understand a text about an important figure in films and theatre in Kazakhstan. Descriptor: - Ask and answer the questions.
Assessment criteria: - To learn and practise verb patterns verb + -ing and verb + to infinitive Descriptor: - Choose the correct word to complete the sentences. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 38 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
summative assessment for the 2 term |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.L6 Deduce meaning from context in supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 6.R3 Understand the detail of an argument on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 6.W8 Spell most highfrequency vocabulary accurately for a limited range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics 6.S7 Use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -True/False tasks require learners to indicate whether the provided option right or wrong. -Gap filling tasks is a task in which words/numbers are removed from a text and replaced with spaces. Learners have to fill each space with the missing word/number or a suitable word. |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Lead - In summative assessment for the 2 term Listening Task.1 Listen to the conversation between Harry and Elizabeth twice. Transcript for listening task can be found after the mark scheme. Teacher reads the transcript. Mark sentences as True or False. 1 A horror movie is scary. True False 2 Harry likes movies about love. True False 3 Harry really hates action and adventure movies True False Fill in the gaps with ONE word. 4 Musicals do not sound too ___________________ for Harry. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students listen to the conversation and write true or false ANSWERS: 1 true 2 false 3 false 4 exciting 5 killer |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
5 I heard it's pretty exciting because nobody can guess who the ______________________ is. Reading Task. Read the text about Alex’s hometown. My town – Newquay Newquay is a small town on the Atlantic coast in the south of England. It has got great beaches and is the best place to surf in the United Kingdom. There are lots of surf schools where you can learn how to surf. I go surfing with my friends every weekend. Circle the 3 things Alex writes about. A Rainy weather in Newquay B Water activities in Newquay, C Interesting history of Newquay D Water attraction to visit in Newquay E Tasty meals in Newquay F Location of Newquay in England Complete the sentences below follow the sentence structure: 4 Alex likes Newquay because he can go … 5 While coasteering you should always take a special instructor with you because it involves… Writing Task. Choose ONE of the topics below. Follow the tips for writing Topic 1. Our countryside Think about your home place (home town or village) and write some information about it. Topic 2. Drama and comedy Think about your genre preferences and write some information about your experience. Speaking Task. Choose one of the cards and prepare an individual talk. Provide own experience on topics, using appropriate subject-specific vocabulary. You have 1 minute to prepare and 1-2 minutes to talk |
Students read the text about Alex’s hometown and circle the 3 things Alex writes about ANSWERS: B) Water activities in Newquay D) Water attraction to visit in Newquay F) Location of Newquay in England Students choose ONE of the topics below. Follow the tips for writing ANSWERS: Students own answers Students choose one of the cards and prepare an individual talk. ANSWERS: Students own answers |
Assessment criteria - True/False tasks require learners to indicate whether the provided option right or wrong. Descriptor: - listen to the conversation and write true or false
Assessment criteria: - Learners have to fill each space with the missing word/number or a suitable word. Descriptor: - read the text about Alex’s hometown and circle the 3 things Alex writes about -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 38 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL: Technology |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.4.1.1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about the internet. • Read a text about the internet. • Learn how to recognize which country website addresses come from. |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the word internet on the board. • Ask students if they use the internet, and how often. Ask if they think it is important in modern life. • Elicit some ideas, and write these on the board. • Tell students they are going to read a text about how people use the internet. Lead - In
Internet and Information technology concept. internet connection on a smart phone for sharing and doing anything |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 2 P: 53 • Refer students to the introduction only. Ask them to read it through, then discuss the activities in blue with the class Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 53 • Read the question with the class to check students understand what information they should listen for. • Play the CD once while students listen and read the text for general information. • Check the
answer with the class. If students find this difficult, explain
that the internet is a network of computers around the world that
share information, and the World Wide Web is all the information
that is stored on the internet, as
websites Ex: 3 P: 53 • Allow students time to read the questions first. • Students read the whole text again more carefully and answer the questions. |
Students read the introduction on the text. Which of the things in blue do you do on the internet? ANSWERS: Students own answers Students read and listen to the text. What invention was very important for the development of the internet. ANSWERS: The World Wide Web, invented by Tim Berners-Lee. Students read the text again and answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 It was called ARPANET. 2 Universities used it 3 He sent the first email message. 4 He worked in Geneva, and it represented Switzerland. 5 There were millions of websites and it wasn’t easy to find information. |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for talking about the internet. Descriptor: - read the introduction on the text Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Read a text about the internet Descriptor: - read the text again and answer the questions -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 38 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|
Short term plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Drama and comedy |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project: Trump card game. Review |
||
|
Learning objectives |
6.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 6.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Play the trump card game and guess the identity of famous people. • Follow the steps in a project checklist. • Create a trump card with clues about famous people. |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, tell students you are going to give them clues about a famous person, and they must guess the identity of the person. • Give these clues for David Beckham in order, pausing after each one for students to guess the answer: He’s a sportsman. He’s a football player. He’s English. He’s got a famous wife Lead - In
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Describe and imagine the pictures Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
CD 1 Pictures PPT |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 37 min |
Ex: 1 P: 55 • Read the rules with the class and check understanding. Ask students to play the game with a partner. They should each choose one of the cards and ask the questions on it. At this stage, it does not matter if they see each other’s cards, the important thing is that they learn the process of the game. • Check answers with the class and ask a few students how many points they scored. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 55 Tell students that they are now going to make their own trump cards. • Go through the points in the project checklist. Check students understand each of these. Ex: 2 P: 55 When all the cards are completed, set aside time in class to do further work with them. Put students into groups of six to play the game. Ask them to exchange trump card clues and guess the famous person. Tell them to note down their score. • When students have finished, ask them to change partners and repeat the process four or five times, noting down their score each time. • Ask students to add up their scores. The student with the highest score is the winner. |
Students read the rules and the trump card game with a partner. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. The people are Tobey Maguire and Christopher Columbus Students make a trump card and follow the steps ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. Students play the trump card game with five people in class. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers |
Assessment criteria - Play the trump card game and guess the identity of famous people Descriptor: - read the rules and the trump card game with a partner.
Assessment criteria: - Follow the steps in a project checklist. Descriptor: - make a trump card and follow the steps -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Student’s book Workshets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 38 WB |
|
Poster Success
|
|

шағым қалдыра аласыз