|
LESSON: General biological understanding Unit: Making connections in biology |
|
|||||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: Ceylan S.B. |
|||||
|
Group: |
Number present: |
absent: |
||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
Read a wide range of extended fiction and non-fiction texts on topic. |
|||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All students: By the end of the lesson all students will learn some definitions and new vocabulary. Most students: Most students will realize the meaning of the Mendel’s theory and will know how to apply it in the real life. Some students: Some students will use high-order thinking skills and create questions according to the topic. |
|||||
|
Plan |
||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s action |
Pupil’s actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
||
|
|
The lesson greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Teacher asks questions:
(I look like…. I’m as tall as my … I have eyes like my….)
|
Warm up
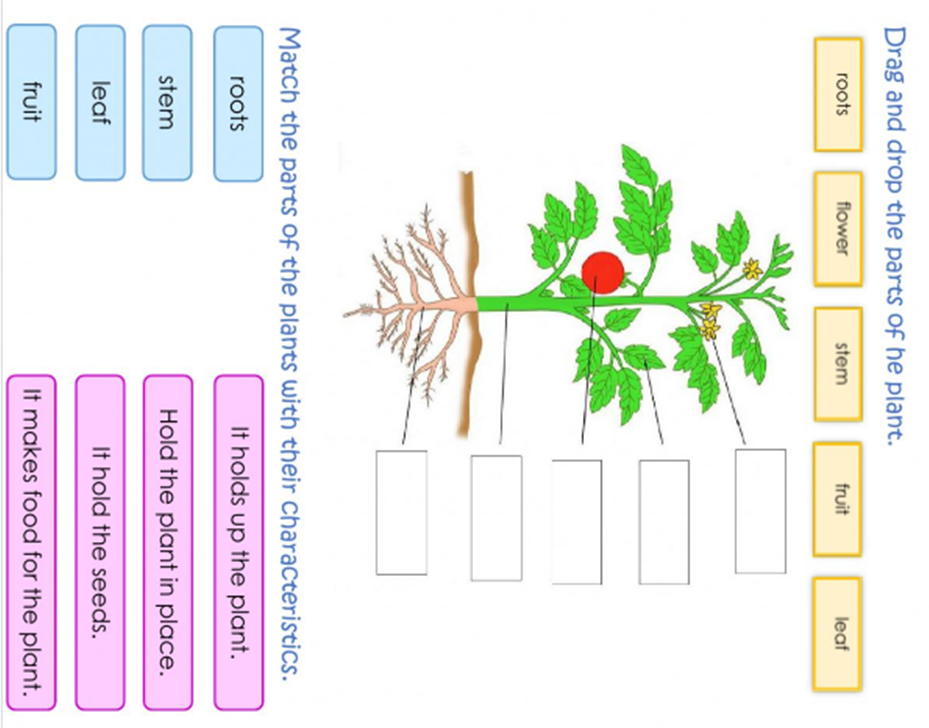
Ss are talking who are they look like. Ss name the plant’s body parts and explain the meaning of each part.
|
|
https://www.toppr.com/guides/biology/principles-of-inheritance-and-variations/laws-of-inheritance/ |
||
|
|
Grammar topic: (TD) Teacher demonstration
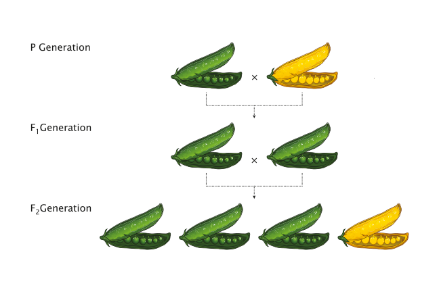
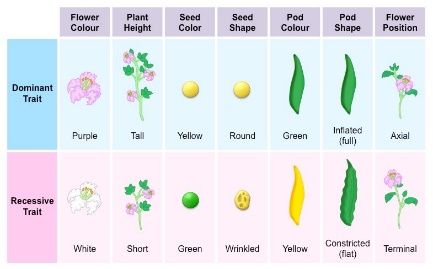
Gregor Johann Mendel was a scientist who is recognized as the Father and Founder of genetics was born in in 1822. Mendel conducted many experiments on the pea plant. He had chosen pea plant because The pea plants were easy to grow and it breeds in short time. Peas are naturally self-pollinating but can also be cross-pollinated. He studies some characteristics: (S)
Grammar: Adjective complement
An adjective complement is defined as a functional part of a sentence that completes the meaning of, or complements, an adjective or adjective phrase. A noun clause is simply two or more words that function as a noun. It should have a subject and a verb, and, since it takes the place of a noun, it’s a dependent clause and cannot stand alone. A noun clause starts with the words “that," “how,” “if,” and the wh- words “what,” “when,” “why,” "who," and "where." A prepositional phrase starts with a preposition — such as “with,” “about,” “on,” or “in” — and is followed by a noun, pronoun, noun phrase, pronoun phrase, or noun clause. We were shocked by the news. (prepositional phrase) I am curious what color you picked. (noun clause) |
Vocabulary work: Inheritance – мұрагерлік To apply – қолдану Seed – тұқым ұрық Stem – сабақ Allele – қасиет Generation –ұрпақ Breeding – көбею Offspring – ұрпақ
P 8 – 9 read the text and make up some questions: Suggested questions: 1. Why J Mendel was recognized as a the Father of genetics? 2. Why Mendel had chosen pea plant? 3. Is the theory applicable for animals?
Look at these table. Describe the meaning of the Mendel’s theory. Look at the pictures. Describe these pictures applying Mendel’s theory.
|
Fill the gaps: Characters dwarf dominant recessive generation The results of Mendel’s experiments on crossing a pure tall pea plant with a pure short pea plant: In the first generation, Mendel observed that all plants were tall. there were no dwarf plants. In the second _____, Mendel observed that 3 of the offsprings were tall whereas 1 was _____. Similar results were found when Mendel studied other ______. Mendel observed that in the first generation, the characters of only one parent appeared whereas, in the second generation, the characters of the other parent also appeared. The characters that appear in the first generation are called _______ traits and those that appear for the first time in the second generation are called ______ traits.
(answers: generation dwarf characters dominant recessive )
Descriptor: 1. S Explains the meaning of the theory and describes the picture. 2. S gives his own examples.
|
Worksheets
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||


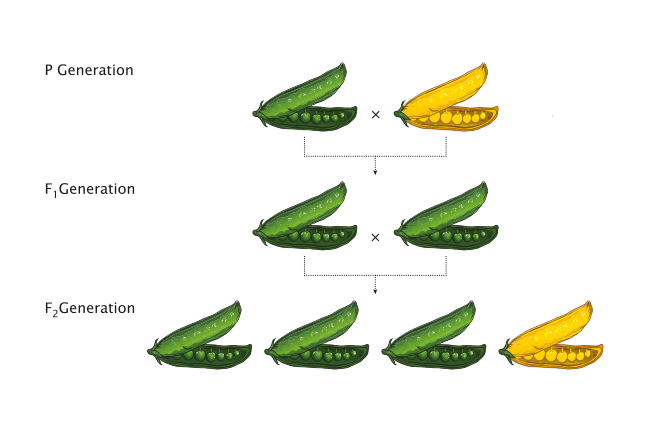
Fill the gaps:
Characters dwarf dominant recessive generation
The results of Mendel’s experiments on crossing a pure tall pea plant with a pure short pea plant:
In the first generation, Mendel observed that all plants were tall. there were no dwarf plants.
In the second _____, Mendel observed that 3 of the offsprings were tall whereas 1 was _____.
Similar results were found when Mendel studied other ______.
Mendel observed that in the first generation, the characters of only one parent appeared whereas, in the second generation, the characters of the other parent also appeared.
The characters that appear in the first generation are called _______ traits and those that appear for the first time in the second generation are called ______ traits.



жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
Action 11 Module 1 Mendel's Peas lesson plan
Action 11 Module 1 Mendel's Peas lesson plan
|
LESSON: General biological understanding Unit: Making connections in biology |
|
|||||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: Ceylan S.B. |
|||||
|
Group: |
Number present: |
absent: |
||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
Read a wide range of extended fiction and non-fiction texts on topic. |
|||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All students: By the end of the lesson all students will learn some definitions and new vocabulary. Most students: Most students will realize the meaning of the Mendel’s theory and will know how to apply it in the real life. Some students: Some students will use high-order thinking skills and create questions according to the topic. |
|||||
|
Plan |
||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s action |
Pupil’s actions |
Assessment |
Resources |
||
|
|
The lesson greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Teacher asks questions:
(I look like…. I’m as tall as my … I have eyes like my….)
|
Warm up
Ss are talking who are they look like. Ss name the plant’s body parts and explain the meaning of each part.
|
|
https://www.toppr.com/guides/biology/principles-of-inheritance-and-variations/laws-of-inheritance/ |
||
|
|
Grammar topic: (TD) Teacher demonstration
Gregor Johann Mendel was a scientist who is recognized as the Father and Founder of genetics was born in in 1822. Mendel conducted many experiments on the pea plant. He had chosen pea plant because The pea plants were easy to grow and it breeds in short time. Peas are naturally self-pollinating but can also be cross-pollinated. He studies some characteristics: (S)
Grammar: Adjective complement
An adjective complement is defined as a functional part of a sentence that completes the meaning of, or complements, an adjective or adjective phrase. A noun clause is simply two or more words that function as a noun. It should have a subject and a verb, and, since it takes the place of a noun, it’s a dependent clause and cannot stand alone. A noun clause starts with the words “that," “how,” “if,” and the wh- words “what,” “when,” “why,” "who," and "where." A prepositional phrase starts with a preposition — such as “with,” “about,” “on,” or “in” — and is followed by a noun, pronoun, noun phrase, pronoun phrase, or noun clause. We were shocked by the news. (prepositional phrase) I am curious what color you picked. (noun clause) |
Vocabulary work: Inheritance – мұрагерлік To apply – қолдану Seed – тұқым ұрық Stem – сабақ Allele – қасиет Generation –ұрпақ Breeding – көбею Offspring – ұрпақ
P 8 – 9 read the text and make up some questions: Suggested questions: 1. Why J Mendel was recognized as a the Father of genetics? 2. Why Mendel had chosen pea plant? 3. Is the theory applicable for animals?
Look at these table. Describe the meaning of the Mendel’s theory. Look at the pictures. Describe these pictures applying Mendel’s theory.
|
Fill the gaps: Characters dwarf dominant recessive generation The results of Mendel’s experiments on crossing a pure tall pea plant with a pure short pea plant: In the first generation, Mendel observed that all plants were tall. there were no dwarf plants. In the second _____, Mendel observed that 3 of the offsprings were tall whereas 1 was _____. Similar results were found when Mendel studied other ______. Mendel observed that in the first generation, the characters of only one parent appeared whereas, in the second generation, the characters of the other parent also appeared. The characters that appear in the first generation are called _______ traits and those that appear for the first time in the second generation are called ______ traits.
(answers: generation dwarf characters dominant recessive )
Descriptor: 1. S Explains the meaning of the theory and describes the picture. 2. S gives his own examples.
|
Worksheets
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||



Fill the gaps:
Characters dwarf dominant recessive generation
The results of Mendel’s experiments on crossing a pure tall pea plant with a pure short pea plant:
In the first generation, Mendel observed that all plants were tall. there were no dwarf plants.
In the second _____, Mendel observed that 3 of the offsprings were tall whereas 1 was _____.
Similar results were found when Mendel studied other ______.
Mendel observed that in the first generation, the characters of only one parent appeared whereas, in the second generation, the characters of the other parent also appeared.
The characters that appear in the first generation are called _______ traits and those that appear for the first time in the second generation are called ______ traits.





шағым қалдыра аласыз