
Secondary school №11
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Entertainment and media |
Lesson 57 |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: Kvach T.V. |
||
|
Grade: 7 G |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Comparative and Superlative adjectives |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics, and some curricular topics 7.6.3.1 use common participles as adjectives and order adjectives correctly in front of nouns on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.5.2.1 write with some support about real and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a limited range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn comparative and superlative forms of adjectives. • Make sentences using comparative and superlative adjectives. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 7 min |
Organization moment Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the words elephant and monkey on the board. • Write the adjectives big and intelligent on the board and ask students how they can compare the two animals using the adjectives on the board. • Refer students back to exercise 5 on page 52 and ask them to find examples of how we can compare things in English. |
Students fill in the daily calendar Students try to describe and compare animals using adjectives |
Descriptor: - can describe animals - can compare them 2 points |
Positive attitude quote
Grammar table Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 28 min |
Ex:1 P:69 • LANGUAGE NOTE We do not use more and most with short adjectives: An elephant is bigger than a monkey. NOT An elephant is more big than a monkey. Some adjectives are irregular, for example, bad, worse, worst. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 69 • Refer students back to the table in exercise 1 and to the example sentences. Allow students time to look at the forms, then ask them to complete the rules.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 69 • Explain to students that there are spelling rules for forming regular comparative and superlative adjectives, which are summarized in the table. • Ask students to apply what they have covered and to complete the rules. In a weaker class, ask them to do this in pairs.
Ex: 4 P: 69 • Explain to students the task. • Ask students to make sentences using information from the box
|
Students complete the table with comparative and superlative adjectives ANSWERS 1 faster 4 more artistic 2 bigger 5 the most intelligent 3 noisiest Students study the example sentences and complete the rules ANSWERS 1 than 2 the Students study the table in exercise 1 again. Complete the spelling rules and add examples. ANSWERS 1 fastest 2 rarer 3 bigger Students to make sentences using information from the box ANSWERS Students own answers |
Descriptor: - learn comparative and superlative forms of adjectives - complete the table 2 points Descriptor: - study the example sentences and the table - make sentences using comparative and superlative adjectives 2 points Descriptor: - study the example sentences and complete the rules 1 point Descriptor: - make sentences using information from the box - write and read the sentences -can make their own sentences 3 points |
Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Reflection. Ask students to answer the question: Which step have you reached today? Home task: Ex: 5 P: 69 |
|
|
|
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
Comparative and Superlative adjectives
Comparative and Superlative adjectives
Secondary school №11
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Entertainment and media |
Lesson 57 |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: Kvach T.V. |
||
|
Grade: 7 G |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Comparative and Superlative adjectives |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics, and some curricular topics 7.6.3.1 use common participles as adjectives and order adjectives correctly in front of nouns on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.5.2.1 write with some support about real and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a limited range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn comparative and superlative forms of adjectives. • Make sentences using comparative and superlative adjectives. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 7 min |
Organization moment Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the words elephant and monkey on the board. • Write the adjectives big and intelligent on the board and ask students how they can compare the two animals using the adjectives on the board. • Refer students back to exercise 5 on page 52 and ask them to find examples of how we can compare things in English. |
Students fill in the daily calendar Students try to describe and compare animals using adjectives |
Descriptor: - can describe animals - can compare them 2 points |
Positive attitude quote
Grammar table Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 28 min |
Ex:1 P:69 • LANGUAGE NOTE We do not use more and most with short adjectives: An elephant is bigger than a monkey. NOT An elephant is more big than a monkey. Some adjectives are irregular, for example, bad, worse, worst. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 69 • Refer students back to the table in exercise 1 and to the example sentences. Allow students time to look at the forms, then ask them to complete the rules.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 69 • Explain to students that there are spelling rules for forming regular comparative and superlative adjectives, which are summarized in the table. • Ask students to apply what they have covered and to complete the rules. In a weaker class, ask them to do this in pairs.
Ex: 4 P: 69 • Explain to students the task. • Ask students to make sentences using information from the box
|
Students complete the table with comparative and superlative adjectives ANSWERS 1 faster 4 more artistic 2 bigger 5 the most intelligent 3 noisiest Students study the example sentences and complete the rules ANSWERS 1 than 2 the Students study the table in exercise 1 again. Complete the spelling rules and add examples. ANSWERS 1 fastest 2 rarer 3 bigger Students to make sentences using information from the box ANSWERS Students own answers |
Descriptor: - learn comparative and superlative forms of adjectives - complete the table 2 points Descriptor: - study the example sentences and the table - make sentences using comparative and superlative adjectives 2 points Descriptor: - study the example sentences and complete the rules 1 point Descriptor: - make sentences using information from the box - write and read the sentences -can make their own sentences 3 points |
Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Reflection. Ask students to answer the question: Which step have you reached today? Home task: Ex: 5 P: 69 |
|
|
|

шағым қалдыра аласыз




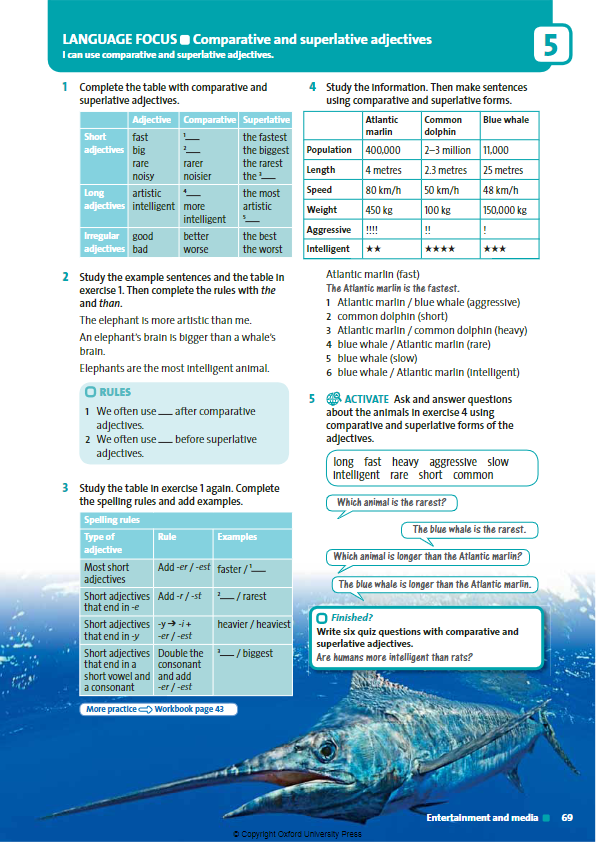 Students copy the table and complete the
missing forms. Point out that only regular forms are
gapped.
Students copy the table and complete the
missing forms. Point out that only regular forms are
gapped.















