
|
Topic: |
Cytology: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes |
03.10.2018 |
|||
|
Teaching aim: |
To learn about the two levels of cellular organization: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. |
||||
|
Lesson objec- tives: |
Know:
Be able to:
|
||||
|
Communication |
|
||||
|
Cognition |
|
||||
|
Culture |
- understanding that different organisms have different cell structure |
||||
|
Vocabulary: Grammar and functional lan- guage: |
Prokaryotes, eukaryotes, non-nuclear, nuclear, bacteria, cells, nucleus, membrane, mi- tochondria, ribosome, vacuole
I think it’s… I think they are… describing objects ‘will’ for prediction |
||||
|
Materials and equipment: |
pictures of animals, plants, bacteria; a ball, laptop, projector; worksheets |
||||
|
Lesson Procedure |
|||||
|
Stage/Aim |
Time 45 m |
|
|||
|
Procedure (Teacher) |
Procedure (Students) |
||||
|
Warm up |
3 min |
A greeting, creating an emotional mood. T: Good morning students. How are you? Let’s start our lesson.
Ss play a game with a ball, revising the organisms biology studies. T: Let’s form a circle. I will throw you the ball and you name one thing that biology studies (e.g. plants, fish, insects, etc) |
Students throw the ball to each other, calling the organisms Biology studies (e.g. animals, plants, fungi, bacteria, viruses, etc.) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lead-in (to set the context and activate prior knowledge) |
5 min |
T: Look at the board, please. You can see some pic- tures (App. 1) -What is shown in these pictures? -What do all living organisms consist of? - Do you think that cells have the same or different structure?
T: Today we will talk about the structure of prokar- yotic and eukaryotic organisms and find out wheth- er they have similarities and differences.
T writes the topic of the lesson on the board.
T: During the lesson you will get a star for the right answers |
Suggested answers:
|
|
Presentation (to present the structure of cells) |
25 min |
Ss read the text and label the structure of cells on the diagrams.
T: Now you will work in pairs, I'll give you cards which contain information about the structure and features of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Read the information and then label the structure of the cell. (App 2) You have 7 minutes.
T: Have you finished? Now turn to another pair and check your answers (2 min). T: Let’s check together. Look at the right answers on the board (2 min). T gives stars for the correct answers Ss are divided into two groups. They need to find their partners by matching words and their defini- tions,
T: The first group will get cards with the name of the cell organelles, the second group will get the functions that these organelles perform. Your task is to find your partner. (App. 3) Check answers as whole class (2 minutes) Answers are shown on the board.
Nucleus |
Ss work in pairs. Read the information, label the structure of the cell (recognize the structure of prokaryotic and eu- karyotic cells) (8 components: nucleus, cell membrane, cyto- plasm, vacuole, mito- chondria, lysosomes, ribosome, flagella) Students get cards, look for a partner, thus mak- ing up a definition. Key: The nucleus - surround- ed by a double mem- brane with pores, it con- tains the cell's DNA A cell membrane is a cell defense. Mitochondria is a cell power plant. The cytoplasm is the liquid part of the cell in which the components of the cell are located. |
|
|
|
Surrounded by a double membrane with pores, it contains the cell's DNA
T gives stars for the correct answers. T: Now you have learned about the functions that cell organelles perform. What is the main component of eukaryotic cell? What organelle is missing in prokaryotes? T gives stars for the correct answers |
Vacuole - space in the central part of the cell, filled with cell sap Lysosomes - contain digestive enzymes, break down organic substances. Ribosomes are orga- nelles on which protein synthesis occurs. Flagellum - allows the cell to move. |
|
T: Let's give the definitions of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. For this, we divide into two groups. I will give you cards with words. Put these words in the right order and to create the defini- tions. (App. 4) You have 5 minutes. T checks answers in open class. T gives stars for the correct answers |
Students are divided into two groups. Make up the definitions of the words on the board.
|
||
|
Practice (to consoli- date the ma- |
12 min |
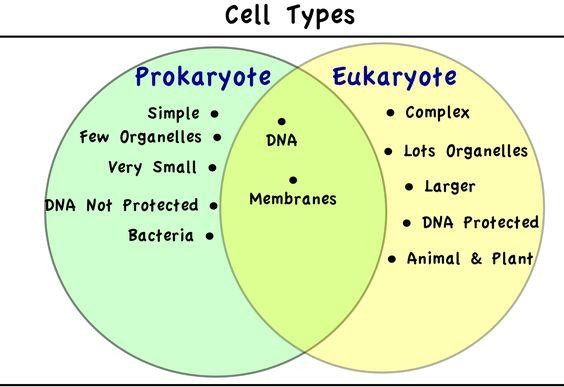
T: Knowing the characteristics of cells, let's com- pare the eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. On the board you can see a Venn’s diagram. Work in groups and complete the diagram. Write down the similarities and differences (App. 5) Differentiation: T can ask more able Ss to fill out the diagram on their own, and give cards with prompts to less able Ss (App. 5).
Teacher groups students T: You have 7 minutes. Check answers – groups present their projects. T gives stars for the correct answers T: Today we have learned a lot of new information about cells. You worked well in the lesson. Let's count your stars. The winner will get a prize. The teacher records the results in a table and awards the winner |
Students work in groups. They fill out the Venn diagram using stickers. (Key in App.5) |
|
terial, to |
|
|
|
|
check under- |
|
|
|
|
standing of |
|
|
|
|
the topic) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Students count the stars |
![]()
 App. 1.
App. 1.




 App.
2
App.
2
All living organisms can be distributed into one of two groups (prokaryotes or eukaryotes) de- pending on the structure of their cells. Prokaryotes - living organisms, consisting of cells that do not have a cell nucleus and membrane organelles. Eukaryotes are living organisms, the cells of which con- tain a nucleus, as well as membrane organelles.
-
Structure of the prokaryotic cell
Prokaryotes are organisms consisting of cells that do not have a cell nucleus or any membrane organelles. This means that the genetic material of DNA in the prokaryotes is not bound in the nucleus. Most prokaryotes consist of only one cell (unicellular), but there are several and multicellular.
Bacterial cell includes: The cytoplasmic membrane regulates the intake of substances into the cell and removes the products of metabolism. The cell wall gives the cell rigidity, shape, protects from damage. (Performs a defensive and support function). Permeable for water and ions, but impermeable to large molecules. The capsule is an additional protection of the cell, it participates in the formation of colonies. Nucleoid (DNA) provides storage of hereditary information. Ribosomes - synthesize pro- teins. Drank - cytoplasmic outgrowths for communication with other bacteria. Flagellates provide movement of bacterial cells.
-
Structure of the eukaryotic cell
Eukaryotic organisms can be unicellular and multicellular. All animals are eukaryotes. Also eukaryotes include plants, fungi and protozoa. The nucleus is the main part of the cell, containing ge- netic material: DNA molecules. Cell membrane - provides protection of the cell and gives it a definite shape. The cytoplasm is the liquid part of the cell in which the components of the cell are located. Mi- tochondria is a cell power plant that provides the cell with energy. Vacuol - space in the central part of the cell, filled with cell sap. Lysosomes - contain digestive enzymes, break down organic substances. Ribosomes are organelles on which protein synthesis occurs.
App. 3
-
Nucleus
Surrounded by a double mem- brane with pores, it contains the cell's DNA
Cell Membrane
A phospholipid bilayer that surrounds the cell
Mitochondria
The site of Aerobic respiration - the production of ATP
Cytoplasm
Fluid within the plasma membrane where organelles occur.
Vacuole
Vacuole space in the central part of the cell filled with cell sap
Lysosomes
Contain digestive enzymes, and can fuse
with vesicles containing damaged organelles.
Ribosomes
synthesis of proteins for use in the cell.
Flagella
Allows cell motility in unicellular prokaryotes
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() App.
4
App.
4
Cells
which
contain
the nucleus
are called
eukaryotic


App. 5

-
Membranes
DNA
Simple
Larger
Many organelles
Very small
Few organelles
DNA protected by the nucleus
DNA not protected by the nucleus
Animals, plants
Bacteria
Key
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
Cytology: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Cytology: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
|
Topic: |
Cytology: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes |
03.10.2018 |
|||
|
Teaching aim: |
To learn about the two levels of cellular organization: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. |
||||
|
Lesson objec- tives: |
Know:
Be able to:
|
||||
|
Communication |
|
||||
|
Cognition |
|
||||
|
Culture |
- understanding that different organisms have different cell structure |
||||
|
Vocabulary: Grammar and functional lan- guage: |
Prokaryotes, eukaryotes, non-nuclear, nuclear, bacteria, cells, nucleus, membrane, mi- tochondria, ribosome, vacuole
I think it’s… I think they are… describing objects ‘will’ for prediction |
||||
|
Materials and equipment: |
pictures of animals, plants, bacteria; a ball, laptop, projector; worksheets |
||||
|
Lesson Procedure |
|||||
|
Stage/Aim |
Time 45 m |
|
|||
|
Procedure (Teacher) |
Procedure (Students) |
||||
|
Warm up |
3 min |
A greeting, creating an emotional mood. T: Good morning students. How are you? Let’s start our lesson.
Ss play a game with a ball, revising the organisms biology studies. T: Let’s form a circle. I will throw you the ball and you name one thing that biology studies (e.g. plants, fish, insects, etc) |
Students throw the ball to each other, calling the organisms Biology studies (e.g. animals, plants, fungi, bacteria, viruses, etc.) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lead-in (to set the context and activate prior knowledge) |
5 min |
T: Look at the board, please. You can see some pic- tures (App. 1) -What is shown in these pictures? -What do all living organisms consist of? - Do you think that cells have the same or different structure?
T: Today we will talk about the structure of prokar- yotic and eukaryotic organisms and find out wheth- er they have similarities and differences.
T writes the topic of the lesson on the board.
T: During the lesson you will get a star for the right answers |
Suggested answers:
|
|
Presentation (to present the structure of cells) |
25 min |
Ss read the text and label the structure of cells on the diagrams.
T: Now you will work in pairs, I'll give you cards which contain information about the structure and features of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Read the information and then label the structure of the cell. (App 2) You have 7 minutes.
T: Have you finished? Now turn to another pair and check your answers (2 min). T: Let’s check together. Look at the right answers on the board (2 min). T gives stars for the correct answers Ss are divided into two groups. They need to find their partners by matching words and their defini- tions,
T: The first group will get cards with the name of the cell organelles, the second group will get the functions that these organelles perform. Your task is to find your partner. (App. 3) Check answers as whole class (2 minutes) Answers are shown on the board.
Nucleus |
Ss work in pairs. Read the information, label the structure of the cell (recognize the structure of prokaryotic and eu- karyotic cells) (8 components: nucleus, cell membrane, cyto- plasm, vacuole, mito- chondria, lysosomes, ribosome, flagella) Students get cards, look for a partner, thus mak- ing up a definition. Key: The nucleus - surround- ed by a double mem- brane with pores, it con- tains the cell's DNA A cell membrane is a cell defense. Mitochondria is a cell power plant. The cytoplasm is the liquid part of the cell in which the components of the cell are located. |
|
|
|
Surrounded by a double membrane with pores, it contains the cell's DNA
T gives stars for the correct answers. T: Now you have learned about the functions that cell organelles perform. What is the main component of eukaryotic cell? What organelle is missing in prokaryotes? T gives stars for the correct answers |
Vacuole - space in the central part of the cell, filled with cell sap Lysosomes - contain digestive enzymes, break down organic substances. Ribosomes are orga- nelles on which protein synthesis occurs. Flagellum - allows the cell to move. |
|
T: Let's give the definitions of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. For this, we divide into two groups. I will give you cards with words. Put these words in the right order and to create the defini- tions. (App. 4) You have 5 minutes. T checks answers in open class. T gives stars for the correct answers |
Students are divided into two groups. Make up the definitions of the words on the board.
|
||
|
Practice (to consoli- date the ma- |
12 min |
T: Knowing the characteristics of cells, let's com- pare the eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. On the board you can see a Venn’s diagram. Work in groups and complete the diagram. Write down the similarities and differences (App. 5) Differentiation: T can ask more able Ss to fill out the diagram on their own, and give cards with prompts to less able Ss (App. 5).
Teacher groups students T: You have 7 minutes. Check answers – groups present their projects. T gives stars for the correct answers T: Today we have learned a lot of new information about cells. You worked well in the lesson. Let's count your stars. The winner will get a prize. The teacher records the results in a table and awards the winner |
Students work in groups. They fill out the Venn diagram using stickers. (Key in App.5) |
|
terial, to |
|
|
|
|
check under- |
|
|
|
|
standing of |
|
|
|
|
the topic) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Students count the stars |
![]()
 App. 1.
App. 1.




 App.
2
App.
2
All living organisms can be distributed into one of two groups (prokaryotes or eukaryotes) de- pending on the structure of their cells. Prokaryotes - living organisms, consisting of cells that do not have a cell nucleus and membrane organelles. Eukaryotes are living organisms, the cells of which con- tain a nucleus, as well as membrane organelles.
-
Structure of the prokaryotic cell
Prokaryotes are organisms consisting of cells that do not have a cell nucleus or any membrane organelles. This means that the genetic material of DNA in the prokaryotes is not bound in the nucleus. Most prokaryotes consist of only one cell (unicellular), but there are several and multicellular.
Bacterial cell includes: The cytoplasmic membrane regulates the intake of substances into the cell and removes the products of metabolism. The cell wall gives the cell rigidity, shape, protects from damage. (Performs a defensive and support function). Permeable for water and ions, but impermeable to large molecules. The capsule is an additional protection of the cell, it participates in the formation of colonies. Nucleoid (DNA) provides storage of hereditary information. Ribosomes - synthesize pro- teins. Drank - cytoplasmic outgrowths for communication with other bacteria. Flagellates provide movement of bacterial cells.
-
Structure of the eukaryotic cell
Eukaryotic organisms can be unicellular and multicellular. All animals are eukaryotes. Also eukaryotes include plants, fungi and protozoa. The nucleus is the main part of the cell, containing ge- netic material: DNA molecules. Cell membrane - provides protection of the cell and gives it a definite shape. The cytoplasm is the liquid part of the cell in which the components of the cell are located. Mi- tochondria is a cell power plant that provides the cell with energy. Vacuol - space in the central part of the cell, filled with cell sap. Lysosomes - contain digestive enzymes, break down organic substances. Ribosomes are organelles on which protein synthesis occurs.
App. 3
-
Nucleus
Surrounded by a double mem- brane with pores, it contains the cell's DNA
Cell Membrane
A phospholipid bilayer that surrounds the cell
Mitochondria
The site of Aerobic respiration - the production of ATP
Cytoplasm
Fluid within the plasma membrane where organelles occur.
Vacuole
Vacuole space in the central part of the cell filled with cell sap
Lysosomes
Contain digestive enzymes, and can fuse
with vesicles containing damaged organelles.
Ribosomes
synthesis of proteins for use in the cell.
Flagella
Allows cell motility in unicellular prokaryotes
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() App.
4
App.
4
Cells
which
contain
the nucleus
are called
eukaryotic


App. 5

-
Membranes
DNA
Simple
Larger
Many organelles
Very small
Few organelles
DNA protected by the nucleus
DNA not protected by the nucleus
Animals, plants
Bacteria
Key


шағым қалдыра аласыз















