Short term lesson plan III term (the ninth grade)
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5. Reading for pleasure.Lesson plan 49 |
School: |
||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher's name: |
||||||||
|
CLASS: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|||||||
|
Lesson title |
Vocabulary and language Focus. Literary genres. p.56 – p.57 |
||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) |
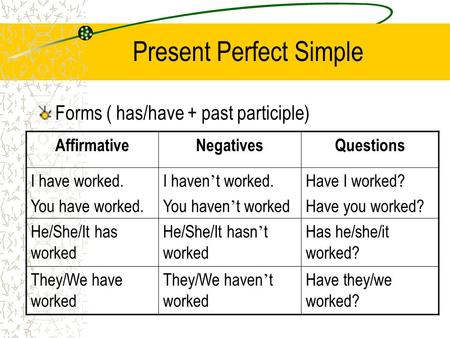
9.C9 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 9.L1 understand the main points in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics 9.S1 use formal and informal language registers in their talk on a range of general and curricular topics 9.S6 communicate meaning clearly at sentence level during, pair, group and whole class exchanges |
||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||
|
S |
The lesson greeting. Pre-learning (W) Teacher greets the class. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk about literature and books. Look at the portraits of some writers and name the books you read at the lessons. How many books do you read a year? When did paperbacks first appear? |
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions Students think critically, exploring, developing, evaluating and making choices about their own and others’ ideas |
Formative assessment is held through observation/monitoring. Emoticon |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT Whiteboard Writing Worksheet |
|||||
|
Main part 15 min |
Lead-in (W, I)
Revise the genres of books pupils know making a list by asking students to add more words to the list they already guessed. Brainstorm with the class and write words on the board as pupils call it out. Organise the class into four teams. Ask a student to come to the front of the class and give him/hersubject card. (E.g. Fiction). Say the whole class can ask a maximum of 10 questions to discover a subject. He/she can only give Yes or No answers. Demonstrate the question types and their short answer forms:
Name the genres of books. Ex. 2 – 3 p.56. Read the information about genres and describe them with complex nouns from the table. Ex.4 p.5
PRE - LISTENING TASK: Ex.4 p.57( Check the meaning of phrases and add your word - combinations from ex.3):
|
A learner
Ss listen |
Formative assessment is held through observation/monitoring. Comments |
Whiteboard Writing Worksheet Student Book p.56 Student Book p.56 Pictures" Test your knowledge" on genres of literature. CD 2.13 Writing Worksheet |
|||||
|
End 3 min. |
Home task. WB p.38 |
Feedback |
|||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5Reading for pleasure. Lesson plan 50 |
School: |
||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher's name: |
||||||
|
CLASS: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|||||
|
Lesson title |
Reading. Fiction. Discussing a text about the benefits of reading. |
||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) |
9.S1 use formal and informal language registers in their talk on a range of general and curricular topics 9.S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S3 explain and justify their own and others’ point of view on a range of general and curricular topics |
||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||
|
Start |
Class organisation The lesson greeting. Warm up. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Good afternoon, dear students and guests! Welcome to our English lesson Pre-learning (W)
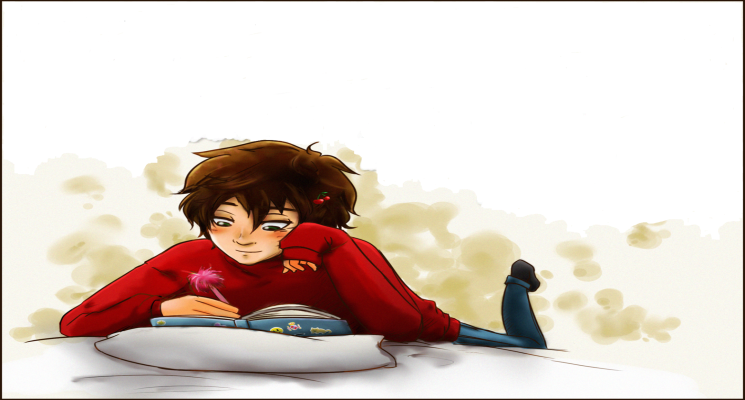
Look at the picture and say what is the boy doing and how is he doing it? In front of you there is a poem. I’d like you to read it and in groups discuss the meaning of it? Lead-in (W, I) Pre-reading stage. Listening and reading about the benefits of reading Ex.1 – 2 p.58 Each Sts. Tries to give a good title for the text. Do you enjoy losing yourself in a good book? (As for me…. As I think…. To my mind…). Ex.4 p.58 Build Your vocabulary: Find the active words from the text and explain by your own words. What is a
Book? A book is pages, pictures and
words Each group prepares its presentation. What does the boy prefer doing? Why? Make a list of books you read while you have free time? (revision of genres of books). |
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions Students think critically, exploring, developing, evaluating and making choices about their own and others’ ideas A learner:
|
Formative assessment is held through observation/monitoring. Emoticon Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT The picture of a boy reading a book Whiteboard Poem A Table Whiteboard Writing Worksheet (new words) CD 2.14 Student Book p.58 Teacher's Book p. |
|||
|
End |
Home task. Ex.5p.58 (w). The story “The Fun they had”(I. Asimov) |
Feedback |
|||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5Lesson plan 51 |
School: |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher's name: |
||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASS: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Past Simple or Past Continuous p.59 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) |
9.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9.C9 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about an increased range of general and curricular topics 9.S8 recount extended stories and events on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.UE5 use a wide variety of question types on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.W8 spell most high-frequency vocabulary accurately for a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||||||||||||
|
Start
Main part
|
Class organisation
To present a mind - map
Read the examples in the table aloud and then elicit the answers to complete their own diagram. Lead-in (W, I) To practise active vocabulary
To practise vocabulary through personalisation and pair group. The story of I. Asimov “The Fun They Had”.
Group 1: I. Asimov Group 2: A real book Group 3: An old school. What did the children use to do? Group 4: A school of future(a mechanical teacher) Using a mind – map, each group prepares a summary of the text. Speak about a future school and our school.
While speaking about past events, we can use: Past simple or Past Continuous.
Ex. 1 – 2 p.59 (Pair Work). In the text, find the examples of two grammar tenses. Ex.3 p.59 should be done individually as a competition task. The winner gets a title – The Best in Grammar.
Illustrate a viewpoint in a discussion Descriptor: Match problems 1-6 with solution Read the text. Choose the correct words. Complete the columns. Write true or false for sentences 1-4. Ask and answer the questions Complete the table. Use the words in blue in sentences 1-4. |
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answers around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
Ss complete the diagram
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 10 Oral Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 10 |
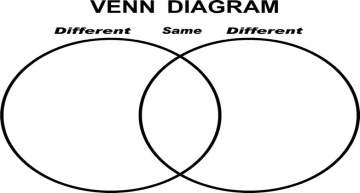
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT Writing Worksheet Writing Worksheet A mind – map Venn Diagram A Table Student’s Book p.59 Answers are in Teacher’s Book. |
|||||||||||||||
|
End |
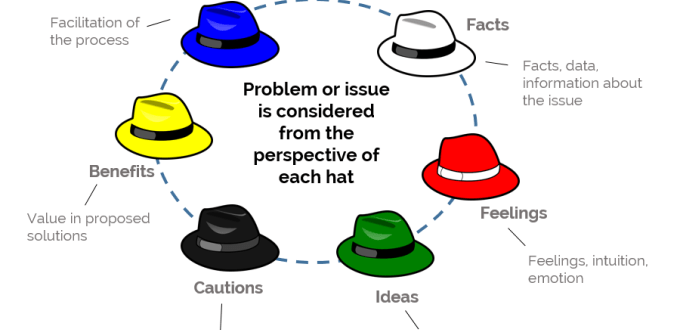
Home task: W.B. p.39 Feedback Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”: |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Differentiation: Can be achieved through content (Based on the theory of Multiple Intelligences different tasks are used with the same text). By support: Less able learners will be supported through step-be-step instructions, glossaries, thinking time. |
|||||||||||||||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Lesson plan 52 |
School: |
||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher's name: |
||||||
|
CLASS: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|||||
|
Lesson title |
Writing. Talking about writing a story. p. 60 |
||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) |
9.L6 deduce meaning from context in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about an increased range of general and curricular topics 9.S8 recount extended stories and events on a wide range of general and curricular topics |
||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||
|
Level of thinking |
Higher order thinking skills (according to the revised Bloom's taxonomy). |
||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||
|
Start Main part 15 min 10 min 5 min |
Class organisation
Pre-learning (W) The lesson greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. The teacher shows the picture and introduces the objectives of the lesson.
Warm up. Free talk. Have you ever tried to write your own stories, poems? If you have your poem, can you read it to us? What should people know to write a story? Make a cluster of this topic. Pre-reading stage. Predicting and guessing. Students move their eyes over the words and pictures on the whiteboard and predict the title of the text. Then they read the text in pairs, find out the meaning of the underlined words. After that students call out words, phrases they remember from the text, note them. Students work in pairs (1 minute) discuss what the text is about or (create a text using some of the previous written words). Students express their ideas (1 minute). While-reading stage. The teacher informs the class that they will be participating in the contest about the words and the process of writing successfully. Ex.1 – 3 p.60. Write down key – words from the text: Draw on your dream- become a writer - have a passion for writing – to test……. Make a list of recommendations for a beginning writer:
Ex.4.p. 60 (True – False sentences). If it’s false, prove the information. Answers: 1. False 2. True 3. False 4. False 5. True 6. True Who can be a writer or a journalist? What can you say about these professions? What would you like to be really good at? You are all in the ninth grade, some of you have already decided what he / she is going to be. Please in pairs speak about this problem.
Descriptor: A learner
Self-assessment. |
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
Ss complete the diagram
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 10 Oral Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 10 Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 10 |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT A cluster ” Writing a story” CD2.15 Dictionaries Student’s Book p.60 Whiteboard Student Book p.60 Ex.5 CD2.15 Writing Worksheet Teacher’s Book p.82 |
|||
|
End 3 min. |
Home task. W.B. p.40 Ex.5.p.60 orally Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
|
Slide (Homework) Slide "Six thinking hats" |
|||||
|
Differentiation: Can be achieved through content (Based on the theory of Multiple Intelligences different tasks are used with the same text). By support: Less able learners will be supported through step-be-step instructions, glossaries, thinking time. By task: For more able learners additional leveled tasks are offered. |
|||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Lesson plan 53 |
School: |
|
|
||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
|
|
||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|
|
|||||||
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Future Continuous.
many, a lot of. Talking about food and meals. |
|
|
||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9.C9 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 9.UE7 use perfect continuous forms and a variety of simple perfect active and passive forms including time adverbials … so far, lately, all my life , on a wide; use a variety of relative clauses including with which [whole previous clause reference] 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about an increased range of general and curricular topics 9.S8 recount extended stories and events on a wide range of general and curricular topics |
|
|
||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to: |
|
|
||||||||
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
Plan |
|
|
|||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|
|
|||||
|
Beginning the lesson |
The lesson greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk.
|
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT |
|
|
|||||
|
Main Activities |
Write the words in the list. The teacher points out that some words and explaining a new rule: Future Continuous. All Continuous tenses mean a process or duration and are happening in a certain time either in the present, past or future. Please, look at the sentences and make some sentences in the Future Continuous. What will you be eating at the party?
Ex.1 -3 p.61. Complete the sentences. (In a weaker class this ex. can be done in pairs). The Consolidation of a structure: Past Simple and Past Continuous). A story in the Past Tenses. Make a group presentation about the rules and change a story in the past tenses into Future Simple and Future Continuous. Ex. 4 - 5 p. 61. Choose the correct words and read a dialogue. What have you learnt from these exercises? Ex.6 p.61. Creative exercise Speak in pairs about the activities next weekend at a certain time. OPTIONAL ACTIVITY: Writing and Speaking. Write about the group’s plan for the next holidays. What will a student be doing at this time during the holidays? Make a mind – map of the Future Continuous. Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
|
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answer around the class. Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 10 Oral |
Writing Worksheet A crossword Student Book p.61 Writing Worksheet Teacher’s Book p.83 Writing Worksheet A mind - map |
|||||||
|
Ending the lesson |
Giving the home task. W.B. p.41 Peer-assessment.Rubric |
|
|
||||||||
|
End 1min |
Feedback: Teacher asks students what task was difficult to them and which pair worked well. |
|
|
||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|
||||||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Lesson plan 54 |
School: |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Planning a project. Talking about how to plan an event.p. 62 A book blurb. p.63 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.S1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 9.C6 organise and present information clearly to others 9.R5 deduce meaning from context in extended texts on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics, and some unfamiliar topics 9.W1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics 9.W5 link without support sentences using basic coordinating connectors |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to: |
|||||||||||||||||
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Plan |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
||||||||||||||
|
Beginning the lesson |
The lesson greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk.
|
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT Student Book p.62 Writing Worksheet A picture |
||||||||||||||
|
Main Activities |
LISTENING TASK: Listen to the dialogue and answer the question: How will book club members decide which books to read? In groups of 3, write the work of a book club and choose the first book to read and discuss together. Look at the key phrases. Invitations. Ex.3 p.62. Sentence completion task. Role-play. The teacher offers the groups 5 books and asks them to read the book blurbs and speak about the books. Ex.1 p.63 Work with the blurb of “The Lost World”. Find compound adjectives and quantities in the text.
Ex. 2 – 3 p.63 (a pair – work). Writing Guide: A Blurb in English for any book. Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
|
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Emoticon
Formative assessment
Oral
8
10
Oral
|
Student Book p.62 CD2.16
CD2.07. Pair work. Teacher's Photocopiable Resources p.203 Student Book p.63
A Table
Student Book p.63
Writing Worksheet |
||||||||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task. Ex.4 p.63 (project), W.B. p.43 Ex. 1 -2 Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
Yellow: What did you like about today's lesson? Slide (Homework) Slide "Six thinking hats"
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Lesson plan 55 |
School: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
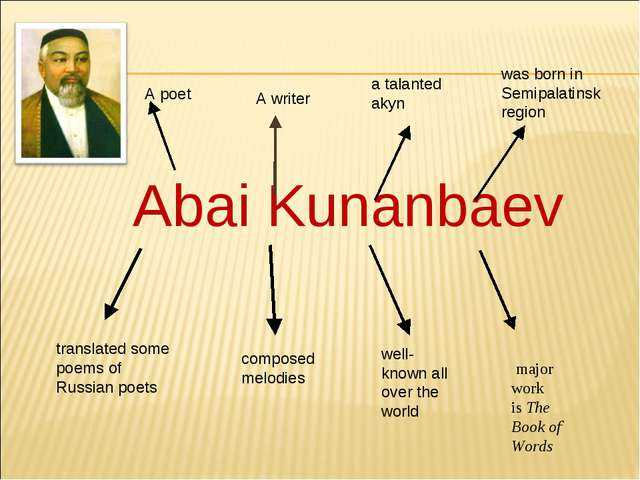
My Country.Abai Qunanbaiuli. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9.L7 recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level of a range of spoken genres 9.C8 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about an increased range of general and curricular topics 9.UE3 use a variety of compound adjectives, adjectives as participles, comparative structures indicating degree, and intensifying adjectives on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.R5 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Plan |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Beginning the lesson |
Org.moment The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk.
Group work of three.
|
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PP Poems of Abai Kunanbaiuli Cluster |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Main Activities |
LISTENING and READING TASKS: Listen and read the text quickly. What interesting facts about a great person have you learnt?
While-reading stage. Students move their eyes over the text quickly (3 minutes). Then they close the book. After that students call out words, phrases they remember from the text, note them. Students work in pairs (1 minute) discusses what the text is about. Discussion Director(Interpersonal Intelligence). Task 1 : Lead the discussion. Prepare 2 open-ended and thought-provoking questions about the story that your group might want to discuss. Help others talk about the main idea, help them share their thoughts and feelings. Descriptors: 1. Write 2 open-ended questions. 2. Write your responses to these questions. 3. Keep the discussion going
Passage Picker(Body-Kinesthetic Intelligence). Task 2: Choose a paragraph that you think your group would like to re-read. Descriptors: 1. Choose an interesting or important paragraph and write down its location. 2. Read passage aloud yourself (using body language), or ask someone else to read it, or ask the group to read it silently a Word Wizard (Verbal-linguistic Intelligence). Task: Find in the text 5 words or phrases that you had difficulty reading or understand in the story. Descriptors: 1. Write 3 unfamiliar or puzzling words in a full sentence. (You may also find familiar word repeated a lot).
Task 3 : Prepare a brief description of the key points in the story. Descriptors: 1. Write at least 4 sentences. 2. Write in your own words. 3. Present the important events in a logical order. Task 4: Find a part of the story that reminds you of something you have seen, heard, done or read about before. Descriptors: 1. Write at least 2 sentences. Make connections with your own experience, another text or the world. 2. Give evidence from the book to support your connection. Post-reading stage. Next, students complete peer-evaluation form. Ex.4 – 5 p.64
What other Kazakh writers and poets do you know?
Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation.
|
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Emoticon
Formative assessment
Oral
8
10
Oral
Oral
8
10
Oral
|
Student Book p.64 CD2.18.
Pair work. Student Book p.66
Writing Worksheet
Student Book p.64
Writing Worksheets
Writing Worksheets
Student Book p.64 Ex.1 – 3 p.64
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task. W.B.p.42, Kazakh writers( a report) Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Differentiation – Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Lesson plan 56 |
School: |
||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Language and literature: The realist novel. |
||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C8 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 9.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9.L4 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 9.R5 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||||||
|
Beginning the lesson |
Greeting.
The teacher shows a fragment from the film and asks the students to set the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson.
Warm up. Free talk.
A Realistic novel/ Adventure novel/Romantic novel/ Science fiction novel Literary realism is a branch of literature which set out to reflect society as it was, to get as close to the bone of real life as it could. It often depicts more humble or banal events than Romantic writers. So most of Jane Austen's novels are realist because they are fairly mundane; they depict fairly ordinary people, usually woman, doing fairly ordinary things. There are few locked room mysteries, no strange and mysterious happenings, or insane wives. The women do ordinary things like get married and the men are fairly ordinary men. If you compare Pride and Prejudice to a novel like Jane Eyre, the differences become clear: no secret insane wives imprisoned in the home, no misplaced identities and no Byronic heroes. |
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT A fragment from a film ”Pride and Prejudice”. Student Book p.65 Writing Worksheet Whiteboard |
|||||||||
|
Main Activities 15 min. 13 min. |
PRE -LISTENING TASK: Ex.1 p.65. (Name the period in history and give characteristic features of that time).
It is set in the nineteenth century. LISTENING TASK: Ex.2 - 3 p.65. Speak about: 1. Families with unmarried daughters 2. Love in the 19 – th century 3. Marriage in the 19 – thin century (Do this task in groups of 3). While reading the text, compare the men and women status in the 19 – th century. Do it in the form of a table.
Ex.4 p.65 Speak about a famous Kazakh novelist. Mukhtar Auezov Sabit Mukanov Gabit Musrepov Olzhas Suleimenov
Gabit Musrepov was born in 1902 in the Kostanay region. His work in the press began with an ordinary employee and up to the chief editor. He was a brilliant journalist. Working as a journalist, he received a school of life and stories for future works. The play "Amangeldy", like the film with the same name, was created from a newspaper essay. Literary works: "Kyz Zhibek", "Kozy Korpesh and Bayan Sulu", "Akhan-sere-Aktokty". Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner:
|
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Emoticon
Formative assessment
Oral
8
10
Oral
Oral
8
10
Oral
|
Student Book p.65
Whiteboard
CD1.31 CD2.19.
Student Book p.65
Writing Worksheet
Student Book p.65
Writing Worksheet
Writing Worksheet
Teacher’s Book p.87 Teacher’s Photocopiable Recourse p.p.216 - 217 |
|||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task. W.B. p.43. Ex.3 Ex.4.p.65 retell Rules of a game (w) Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
Peer-assessment |
||||||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Lesson plan 57 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher's name: |
||
|
CLASS: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review of Unit 5 |
||
|
Learning objectives(s) |
9.L2 understand most specific information in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S5interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics 9.W2 write independently about factual and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.UE8 use a variety of future active and passive and future continuous forms on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|
Start |
Organisation moments (WC): Teacher informs learners that the aims of this lesson are to revise the material that was taught in this unit. |
Sts warm greet teacher
|
stickers |
Slide (objectives) Slide (useful phrases) PPT |
|
Middle |
Revision. Consolidation. (GW) Rules for Jeopardy game There are 2 kinds of games. Teacher can feel free to choose any or play during the whole lesson. 1. Students play jeopardy in groups. 2. They have to choose a category and a point value. 3. Teacher clicks on the chosen box for the question. (The teacher may want to set a time limit for answering the question) 4. To see if a student or group is correct, click again for the answer. 5. Click the Back to Board button on the slide to return to the main board. 5. If the student or team is correct, they are awarded the point value of the question 6. Continue until all questions have been answered. The team with the most points wins. Ex. 1 - 3 p.66(Revision of vocabulary) Revision of Grammar. Past Simple" and «Past ContinuousTenses(- ? forms) Ex. 4 - 5 p.66 Listening Task You will listen to a text about the writer talking about her new book, try to understand it and make a graph organizer in any form you like: a table, cluster, diagram, etc. Keys: 1. developing a plot 4. getting feedback 7. looking for inspiration 8. creating interesting characters 9. drawing on her own experiences b. school c. languages at school d. free time activities Reading Task: Read the text and be able to do a short test. Everyone has heard of Sherlock Holmes. The author of all the Sherlock Holmes stories was Sir Arthur Conan Doyle. Once Sir Arthur was in Paris. He was going from the railroad station to the hotel where he decided to spend the night. He arrived at the hotel, got out of the taxi and paid the taxi-driver. 'Thank you very much, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle,' said the taxi-driver smiling. 'Oh, do you know who I am?' said Sir Arthur. He was very surprised. 'Well, sir, I read in the newspaper yesterday that you were coming to Paris from the south of France. The train on which you arrived came from the south of France. I also noticed that you hair was last cut by a barber in the south of France. 'Your clothes, and especially your hat, told me that you were English. I put all this together and realized at once that you were Sir Arthur Conan Doyle.' 'That is wonderful, ' said Sir Arthur. 'With so few facts you were really about to know me?' 'Of course,' said the taxi-driver, 'your name is on both your travelling bags. That also helped'. 1. Finish the sentences: The text is about A Sherlock Holmes in Paris. В the famous detective Sherlock Holmes. С the author of the Sherlock Holmes stories. D the railroad station hotel. 2. Choose the true sentence. A Sherlock Holmes spent the night at the hotel. В Conan Doyle decided to spend the night in Paris. С The taxi-driver did not recognize Conan Doyle. D Conan Doyle came to Paris from the north of France. 3. Choose the false sentence. A Conan Doyle was angry with the taxi-driver. В Conan Doyle came to the hotel in a taxi. С The taxi-driver thanked Conan Doyle smiling. D The newspapers wrote about Conan Doyle's visit to Paris. 4. Choose the right answer: Why was Conan Doyle surprised? A taxi-driver was rude to him. В The taxi-driver did not like his clothes. С The taxi-driver could not speak English. D The taxi-driver knew his name. Learners managed to understand the rules and do the tasks. |
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 10 Oral Oral 8 10 Oral |
Student's book p.66 PPT Jeopardy Student's book p.66 Mind - maps " Past Simple" and " Past Continuous" a graph organizer CD 2.20 Student's book Ex.6 p.66 Writing Worksheet |
|
End |
Home task. W.B. p.44, a sonnet of W. Shakespeare |
Slide |
||
|
Differentiation Learners can contribute at their own language level for this activity, as it is relatively open-ended. This gives each learner a chance to be successful. Reflection at the end of the lesson and teacher summary provides support for progress and achievement, and challenge to thinking and setting future objectives. |
||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Lesson plan 58 |
School: |
||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Project: A poem |
||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C8 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 9.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9.S1 use formal and informal language registers in their talk on a range of general and curricular topics 9.S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S3 explain and justify their own and others’ point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.R5 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||||||
|
Beginning the lesson |
Greeting.
The teacher begins the lesson with a sonnet of W. Shakespeare” Age and Youth”. The students see the portraits of well – known Kazakh, Russian, English, American and French poets. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk. Today we are having an unusual lesson – The lesson of Poetry.
|
Sts warm greet teacher |
stickers |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT The portraits of well – known Kazakh, Russian, English, American and French poets. Writing Worksheet |
|||||||||
|
Main Activities |
In groups make a poster about the meaning of a poem by R.L. Stevenson. Follow the structure of answers. Ex.1 – 3 p.67. Two students will speak about the biography of R.L. Stevenson.
Find rhyming words: Speak about the patterns od rhyming words: ABAB CDCD EFEF AABBCCDD Ex.3 – 4 p.67
A Contest of poems devoted to love Students prepared poems in different languages with a presentation of a poet. After the reciting of a poem, they ask the group the meaning of it.
Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
|
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Emoticon
Formative assessment
|
Student Book p.67 CD2.21
Writing Worksheet
Whiteboard
|
|||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task. W.B. p.45 A project: a poem Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
Peer-assessment |
||||||||||||
|
Differentiation – can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners.
|
|||||||||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6 Tradition and language Lesson plan 59 |
School: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Relationships. Talking about traditional stories. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9.C2 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 9.C3 respect differing points of view 9.C5 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 9.W8 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics of familiar general topic 9.S3 give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
Make a presentation about traditions of Kazakhstan. Respond to and discuss the reading passage using interpretive, evaluative and creative thinking skills. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Beginningof the lesson |
Greeting.
The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk.
Thanksgiving (fourth Thursday in November) Toy dastarkhan Betashar Maslenitsa
Britain is full of culture and traditions which have been around for hundreds of years. British customs and traditions are famous all over the world. When people think of Britain they often think of people drinking tea, eating fish and chips and wearing bowler hats, but there is more to Britain than just those things. Poppy Day or Remembrance Day
In groups speak about these traditions. |
Sts warm greet teacher Students answer the question |
stickers |
Slide (useful phrases). Pictures PPT Student Book p.68 Writing Worksheet Pictures PPT Writing Worksheet |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Main Activities |
READING TASK: Match the facts with people and countries. Don’t forget to underline new words and be able to say their meanings. Answer: free Ex.1 - 2 p.68 How do people keep the traditions alive? Do traditional stories travel from one country to another? While reading the text write down word – combinations:
Which of the traditional stories did you like best of all? Explain: “Remember the ant”.
THE INTRODUCTION OF GRAMMAR. Present Perfect. Ex.4 - 5 p.69 Sentence completion task with adverbs:
The teacher asks Sts. to listen to the song " Brighton in the rain" and put down the verbs and underline the position of adverbs in the Present Perfect. Brighton in the Rain Fill in the gaps and complete the song lyrics with the Present Perfect Tense of the verbs listed below. (verbs may be used more than once).Listen to the song and check your answer
Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
discusses questions and answers the questions |
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Emoticon
Formative assessment
Peer assessment
Oral
comments |
Student Book p.68
Student Book p.68
Writing Worksheet A Table
Student Book p.68
Student Book p.69
A Table
A song“Brighton in the Rain”.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Homework: W.B. p.46, Ex.5 – 6 p.69 St.B. Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
Peer-assessment |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6 Tradition and language Lesson plan 60 |
School: |
||||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||||||||||
|
Class: 911 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Reading: Marriage. p.70 |
||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.S3 give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics 9.R5 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.R6 recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer in short texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 9.R7 recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level in a limited range of written genres 9.W8 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics of familiar general topic 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics |
||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||||||||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
Greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson.
Speak about arranged
marriage
Warm up. Free talk. On the board you can see the word: Marriage What do you imagine when you hear this word? How will you choose your future husbands /wives? ARRANGED MARRIAGE What do you think about it? |
Sts warm greet teacher Students answer the question |
stickers |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT Student Book p.70 Writing Worksheet Pictures Student Book p.70 Ex.1 Teacher’s Book p.92 Background. |
|||||||||||
|
Main Activities |
LISTENING TASK: Read and listen to the text and express your opinions:
Discuss the text using the method of six hats: 1 group will speak about facts. 2 group - feelings. 3 group - creative ideas. 4 group -negative aspects. 5 group - benefit from the holidays in jungle. 6 group - conclusion. Ex.2 p.70 True - false sentences. Vocabulary work: find verbs with prepositions and make your sentences. Ex. 3 - 4 p.70.
Ex.5 p.70. Creative exercise Optional activity: Reading. Teacher's Book p.92. Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner:
discusses questions and answers the questions within th |
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Emoticon
Formative assessment
Peer assessment
Oral
comments |
Student Book p.70 CD2.22
Writing Worksheet
Six hats method Student Book p.70 A table
Teacher's Book p.92. |
|||||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task: W.B. p.50 Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
Peer-assessment |
||||||||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 61 |
School: |
||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus: Present Perfect + for and since |
||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C8 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 9.S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S3 explain and justify their own and others’ point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.UE9 use appropriately a wide variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.R8 use a wide range of familiar and unfamiliar paper and digital reference resources to check meaning and extend understanding |
||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
The lesson greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk. When you want to speak about activities which you have done recently and have a result, what structures and grammar tenses can you use? We can use Present Perfect with a definite word indicator. Look at the picture and give your sentences:
|
Sts warm greet teacher Students answer the question |
stickers |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT Student Book p.71 Writing Worksheet |
|||
|
Main Activities |
U2 SONG FOR TEACHING PRESENT PERFECT This song is great for teaching Present Perfect. There are around 10 present perfect sentences. Aside from the normal listening activities, get the students to complete blanks spaces. Ask them to identify the grammar mistake (I have spoke). For discussion the students can talk about all the things the singer "has done". After, students will write things they have done and things they still want to do. Think of something that you really want to do in your life, but you haven’t been able to do yet Ex.2 p.71 - since - if the starting point
is given (two o'clock, last Friday, 1998) Decide whether to use »since« or »for«.
Ex.3 p.71. Sentence completion task. Speak about the main character. Use ex.4 to make questions about you. Put the sentences into interrogative form: Ex.5 p.73. In groups of 4 write 4 sentences about the duration of the done activity using: How long A game" The best listener". The Sts. listen and try to pronounce correctly. Imagine a perfect holiday. Write about the activities you have done during it. Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
|
Sts answer around the class. Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment Peer assessment Oral comments |
Student Book p.71 A table U2 - I Still Haven't Found What I'm Looking for (Official Video)https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e3-5YC_oHjE Writing Worksheet Writing Worksheet Student Book p.71
|
|||
|
Ending the lesson |
Giving the home task. W.B. p.47 Ex.5 p.71 St. B. Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”: |
||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 62 |
School: |
|||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
|||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Extreme adjectives. |
|||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C9 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 9.C10 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 9.L1 understand the main points in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics 9.L2 understand specific information in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics |
|||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
|
|||||||||||||
|
Plan |
||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
||||||||||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
Greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk. Focus on the photos of great dates and elicit what the people are doing. What adjectives can you use to describe these things.(exciting, awful, stunning).
|
Sts answer around the class. Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment Peer assessment Oral comments |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT Student Book p.72 Writing Worksheet |
||||||||||
|
Main Activities |
LISTENING TASK: Vocabulary exercises. Ex.1 - 2 p.72 The teacher asks Sts. To give the meaning of extreme adjectives. Vocabulary work:
Ex.3 p.72. I have never done this because it’s….. Circle two adjectives to make a pair and describe great dates: 1. awful/ interesting/ hilarious/ bad 2. gorgeous/ furious/ angry/ memorable 3. exhausting/ unpleasant/ terrifying/ tiring 4. frightening/ terrifying/ hilarious/ unpleasant 5. funny/ interesting/ fascinating/ memorable 6. gorgeous/ revolting/ unpleasant/ terrifying.
LISTENING TASK. Ex. 4 -5 p.72. Complete the table. The class is divided into 7 groups and speaks about the experiences using extra adjectives.
Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner:
|
A learner
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Stickers
Emoticon
Formative assessment
Peer assessment
Oral
|
Student Book p.72 CD2.23
A table
Writing Worksheet
Teacher’s Book p.156
Writing Worksheet
CD2.24
Student Book p.72
Teacher's Book p.94.
|
||||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task. W.B. p.48 Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
|
|||||||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
||||||||||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 63 |
School: |
||||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus: Present Perfect and Past Simple. Present Perfect Simple and Continuous. p.73 |
||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S3 explain and justify their own and others’ point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.S6 link comments with flexibility to what others say at sentence and discourse level in pair, group and whole class exchanges 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about an increased range of general and curricular topics 9.C8 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 9.W3 write with grammatical accuracy on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||||||||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
The lesson greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk.
|
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT Writing Worksheet A book” Song – to study- English” |
|||||||||||
|
Main Activities 15 min. 13 min. |
LISTENING TASK: In the song, define grammar tenses and find time expressions.
1. Look at the photos. Match them with the words from the song. Then listen to the song. Arrange the sights in the way you hear. 2. Listen to in the song. Look at the lyrics. Put the words in the brackets into The Past Simple. Try to fill in the gaps with the words from the box. Listen and check. Ex.1 p.73 Complete the text, then listen and check. Ex. 2 p.73 Gist listening. Listen to the key phrases and reply. Practise the dialogue. Ex.3 p.73. Listen to 3 short conversations and choose the best answers to the questions. Make a short dialogue about your trip using time expressions. DESCRIPTION OF PICTURES:
The introduction of the Present Perfect Continuous. Ex 4 -5 p.73 Ex.6 p.73. Creative exercise. You look cold – I’ve been waiting for the bus. Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
|
Students respond to greeting
Ss answer the
questions
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
|
Emoticon
Formative assessment
Peer assessment
Oral
Comments
Peer assessment
Oral
comments |
Writing Worksheet A Table
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KoyNlVQbUPc
Writing Worksheet
CD2.25
Pictures
Student Book p.73
Workbook p.49
|
|||||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task: W.B. p.49. Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
|
||||||||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 64 |
School: |
||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||
|
Lesson title |
Invitations. An email to a friend. p.74 - p.75 |
||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C9 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 9.C10 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 9.L2 understand specific information in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics 9.L5 recognise the attitude or opinion of the speaker(s) in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics 9.S1 use formal and informal language registers in their talk on a range of general and curricular topics 9.W2 write independently about factual and imaginary past and future events, activities and experiences on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
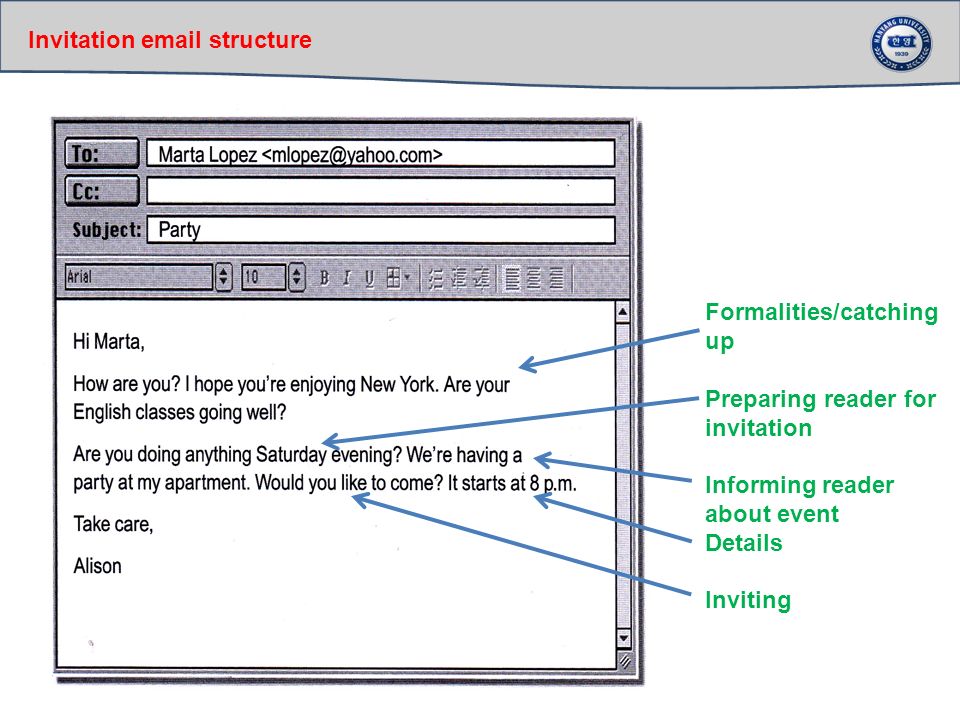
Greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk.
Look at the model text and say what the email is about? |
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases). Pictures PPT Student Book p.74 Writing Worksheet Slide (useful phrases). |
|||
|
Main Activities |
Speaking (Pre-listening) (P) In pairs, learners discuss the following questions of Ex.1 p.74. Vocabulary (W) Teacher asks learners to match 10 pictures with the words and check as a whole class. A game" The best interpreter". One pupil reads the sentences, the partner translates it into Russian. Then the second St. gives Russian sentences and asks to give English translation. The third paragraph should be translated into Kazakh or other language. Key – words for making and responding to invitations. Ex 3 – 6 p. 74. THE INTRODUCTION OF a structure of email invitations. Look at the email and be ready to speak about it.
WRITING TASK: Ex.4 p.75. Write an email to a friend. You are going to celebrate a birthday. (Do this task in groups). Ex.2 – 3 p.75. Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner:
discusses questions and answers the questions within |
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions
Sts answer around the class. Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end Ss to tell the class. Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end
|
Emoticon Formative assessment Peer assessment Oral Comments Peer assessment Oral comments |
Student Book p.74 CD2.26 Student Book p.74 Writing Worksheet Student Book p.75 Cambridge Dictionary. Student Book p.75 |
|||
|
Ending the lesson |
Giving the home task. W.B. p.51, An invitation (w). Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”: |
||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 65 |
School: |
|||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
|||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
||||||
|
Lesson title |
My Country. Traditions and language. Talking about wedding traditions in Kazakhstan. p.76 |
|||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C8 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 9.C9 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 9.L1 understand the main points in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics 9.L6 deduce meaning from context in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics |
|||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
|||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
||||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
Greeting. Pre-learning (W) Teacher greets the class and suggests playing the game to the learners. Teacher explains the rules for this game.
One person stands back to the picture of a holiday adventure; Classmates should not name the holiday adventure; Classmates can give some associations with the holiday adventure; Classmates can mime the holiday adventure; Classmates can sing some lines from the songs.
The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson looking a short film about wedding traditions in Kazakhstan. Warm up. Free talk about the wedding. W-E-D-D-I-N-G
Give one word with this letter connected with the theme |
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases). Pictures PPT Student Book p.76 Writing Worksheet Pictures PPT Slide (useful phrases). |
||||
|
Main Activities |
Reading about the wedding traditions in Kazakhstan (W I)
(P) Learners work with new vocabulary first. They get a list of words, read the words with the teacher and write them down into their vocabularies. Learners create 3-4 sentences with new words to show the meaning of them. Differentiation Learners that are more able help the others to read the words correctly. Ex.1 p.76. Working with active words. POST -READING ACTIVITY: Ex.2 p.76. Check answers as a class. Ex.3 p.76 Revision of grammar. A teacher draws Sts. attention to the grammar tenses used in the texts.Ex - 4 .p.76. Ex.5 p.76 Creative Exercise. Speak about other Kazakh traditions in groups. Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner:
discusses questions and answers the questions within |
Sts answer around the class. Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end Ss to tell the class. Ss and elicit their comments at the end
|
Emoticon Formative assessment Peer assessment Oral Comments Peer assessment Oral comments |
Student Book p.76 Teacher’s Book p.98 CD. 2.28 Student Book p.76 Pictures PPT |
||||
|
Ending the lesson |
Giving the home task. W.B. p.52 Ex.1 "Wedding traditions in Kazakhstan"(topic or a presentation). Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”: |
|||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners |
||||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 66 |
School: |
|||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
|||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
||||||
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Language and literature: Word building: adjectives.p.77 |
|||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C3 respect differing points of view 9.C5 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 9.L6 deduce meaning from context in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics 9.W1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics 9.S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.UE3 use a variety of compound adjectives, adjectives as participles, comparative structures indicating degree, and intensifying adjectives on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics |
|||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
|
|||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
||||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
Greeting.
The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk. Look at the cover of the book; tell your partner if he/ she knows what the book is about and who the main character is. In pairs, name words associated with it and make a cluster.
|
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases). Pictures PPT Student Book p.77 Gulliver's Travels Trailer Cluster "Gulliver's Travels". Pictures PPT |
||||
|
Main Activities |
LISTENING TASK: Read the text and choose the correct words. Listen and check your answers. Ex.1 p.77 . Pay attention to the new words: Proudly, army, dishonesty, neighbours, customs, murder, judges, laws. Ex.2 p.77. Match the words from Ex.1 Look at the text again and do Ex.3 p.77. Sts. can work in pairs. Answers: 1. customs 2. proudly 3. laws 4. judges 5. army 6. neighbours 7. murder 8. dishonestyScore - 8 Ex.3 Answers: 1. True 2. True 3. False 4. True 5. False 6. False Score - 6 To the false sentences give the right answers. Each student counts the scores for the tasks. In group of 4, fill in a story map. Ex.4. Form an adjective with the help of suffixes. Ex.5 p.77 (Activate). In groups, make a short play of the conversation between a king and Gulliver. Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner:
|
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end Ss to tell the class. Ss and elicit their comments at the end
|
Emoticon Formative assessment Peer assessment Oral Comments Peer assessment Oral comments |
Student Book p.77 CD2.29. Writing Worksheet Student Book p.77 Pictures A story map graphic organiser Teacher's Book A Table p.77 Optional Activity. Teacher’s Book p.99 |
||||
|
Ending the lesson |
Giving the home task. W.B. p.52 Ex.3 -5. Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”: |
|||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
||||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 67. |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher's name: |
||
|
CLASS: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative assessment for the 6th unit. Review |
||
TERM 3.
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TASKS
Summative assessment for the 6th unit "Tradition and language."
|
Learning objectives |
9.L2 understand most specific information in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S3 explain and justify their own point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about an increased range of general and curricular topics 9.UE3 use a variety of compound adjectives and adjectives as participles and a variety of comparative structures to indicate degree on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
|
Assessment criteria |
Identify the position of speakers in an extended talk with some support Express thoughts about the given topic in the conversations Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences |
|
Level of thinking skills |
Application Knowledge and comprehension Higher order thinking skills |
|
Duration |
20 minutes |
Listening. Task 1.
Speaking. Task 2. An individual interview on the suggested topic for approximately 2 minutes for each student.
Review. Unit6
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 68 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher's name: |
||
|
CLASS: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Skills Round - up. p.79 |
||
|
Learning objectives(s) |
9.S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S3 explain and justify their own and others’ point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.S6 link comments with flexibility to what others say at sentence and discourse level in pair, group and whole class exchanges 9.S8 recount extended stories and events on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.W3 write with grammatical accuracy on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.W6 write coherently at text level using a variety of connectors on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson |
Organisation moments (WC): Teacher informs learners that the aims of this lesson are to revise the material that was taught in this unit. |
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions
|
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (objectives) Slide (useful phrases) PPT |
|
Main activities |
Revision. Consolidation. (GW) Rules for Jeopardy game There are 2 kinds of games. Teacher can feel free to choose any or play during the whole lesson. 1. Students play jeopardy in groups. 2. They have to choose a category and a point value. 3. Teacher clicks on the chosen box for the question. (The teacher may want to set a time limit for answering the question) 4. To see if a student or group is correct, click again for the answer. 5. Click the Back to Board button on the slide to return to the main board. 5. If the student or team is correct, they are awarded the point value of the question 6. Continue until all questions have been answered. The team with the most points wins. Ex. 1 - 2 p. 78 (Revision of vocabulary) Revision of Grammar. Present Perfect/ Present Perfect Continuous/ Past Simple ( +, -, ? forms ) Ex. 3 - 4 ( do ex. individually) LISTENING TASK: You will listen to a text and complete the sentences: COMMUNICATION. Choose the correct responses to the sentences: Ex. 6 p.78 SKILLS ROUND - UP. LISTENING. Ex. 1 - 3 p.79. Speaking: Ex.4 - 5 p.79. Situations in a big city. Writing: Ex.6. p.79 A letter to a friend about a situation of losing or finding something. (Fast finishes can swap emails with another fast finisher. If a teacher has time, she/ he can ask students to do Optional activity: Consolidation. Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner:
|
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end Ss to tell the class.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
|
Emoticon Formative assessment Peer assessment Oral Comments Peer assessment Oral comments |
Student's book p.78 p.79 PPT Jeopardy Student's book p.78 A mind - map "Past Simple" a graph organizer CD 2.31. Student's book p.79 Teacher’s Book p.101 |
|
End |
Home task. W.B. p.53, St.B. p.78 Ex. 4. FEEDBACK: Your impression! Sts write their impression of the whole unit and share ideas with their classmates. 3 – new words you have taught at the lesson; 2 – adjectives to describe the lesson 1 – one activity you like |
Slide |
||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 7Music and film Lesson plan 69 |
School: |
||||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Music and film images. p.80 - p.81 |
||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9.C6 organise and present information clearly to others 9.S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S3 explain and justify their own and others’ point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about an increased range of general and curricular topics 9.UE6 use a wide variety of relative, demonstrative, indefinite, quantitative]of pronouns and reflexive pronoun structures on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||||||||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
The lesson greeting. Pre-learning (W) Teacher greets the class and suggests watching a video. Before the short film Sts. Name form of art they know. Watch a video about music and film images. A - R - T - Give one word with this letter connected with the theme. Do you like to read or listen? What do you watch on T.V.? |
Sts answer around the class.
|
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases). Pictures PPT film-english.com/2012/02/05/the-joy-of-books/. Films. Writing Worksheet |
|||||||||||
|
Main Activities |
Start Thinking. Group Work. Music and film Quiz. p.80 Ex.1 p.80. Vocabulary Work: match the words with the definitions and put in a correct column in the table. What can people do to change the personal appearance? Why? Differentiation In a weaker class: drill the pronunciation of the difficult words (beard, moustache, dreadlocks, tattoo, and braids). In a stronger class, ask students to make up sentences. St. support or critique a strong change in appearance. Ex.3.p.81 THE INTRODUCTION OF GRAMMAR: Reflective pronouns.
Sts. give their examples with pronouns. Ex. 4 - 6p.81. Choose the correct pronoun. ACTIVATE: Language focus. Write answers to the questions. What is the difference between reflective pronouns and each other? Workbook p.p.40 – 41(more practice). Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
|
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end Ss to tell the class.
Ss and elicit their comments at the e |
Peer assessment
Oral
Comments
Peer assessment
|
Student Book p.80 English - Russian Oxford Dictionary
Student Book p.81
Writing Worksheet
Teacher's Book p.103. |
|||||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task. W.B. p.54
Topic» Body Decoration" or presentation Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
|
||||||||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||||||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 7 Music and film Lesson plan 70 |
School: |
||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||
|
Lesson title |
Reading. Galymzhan Moldanazar. p.82 |
||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.R5 deduce meaning from context in extended texts on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics, and some unfamiliar topics 9.R6 recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer in extended texts on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.L8 understand supported narratives, including some extended talk, on an increasing range of general and curricular topics 9.W4 use style and register to achieve appropriate degree of formality in a growing variety of written genres on a range of general and curricular topics 9.W5 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a wide range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics 9.S1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics |
||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
The lesson greeting. Pre-learning (W) Teacher greets the class and suggests playing the game to the learners. Teacher explains the rules for this game.
One person stands back to the picture of a popular Kazakh singer ; Classmates should not call the name of the singer ; Classmates can give some lines from the song of this singer ; Classmates can sing some lines from the songs.
The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson.
Warm up. Free talk about popular Kazakh singers. Look at the portraits of some singers, what can you say about them?Can you name any Kazakh musicians? |
Sts answer around the class.
|
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases). Pictures PPT Writing Worksheet Pictures PPT Student Book p.82 Slide (useful phrases). |
|||
|
Main Activities |
Ex.1 p.82 Look at the portraits of young people? What do you know about them? Students give their own answers.
The students in groups will read information about a musician and make a story map. Then a leader is going to present Galymzhan Moldanazar. Reading and listen to the text about a Kazakh musician. (W I). Teacher suggests the list of new vocabulary with their synonyms or opposites for learners. Ex.1,3 p.82 (P) Learners work with new vocabulary first. They get a list of words, read the words with the teacher and write them down into their vocabularies. Learners create 3-4 sentences with new words. Differentiation Learners that are more able help the others to read the words correctly. Ex.3 p.82. Working with active words. POST -READING ACTIVITY: Ex.4 p.82. Give the definition of the underlined words. The teacher divide the class into 2 groups: boys and girls. One group will speak about a popular singer of 80s and the second group will retell the text about a modern musician. They should do it in the form of presentation. Ex.5 p.82. Creative task. Speak about a life of a musician. Make a conclusion: Have you ever wanted to sing in public? Describe another musician in pairs. Try to make a story map. Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
|
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end Ss to tell the class. Ss and elicit their comments at the e |
Peer assessment Oral Comments Peer assessment |
Student Book p.82 Pictures PPT Cluster or a table. Student Book p.82 CD. 3.01 Pictures PPT Cluster or a table. Student Book p.82 |
|||
|
Ending the lesson |
Giving the home task. W.B. p.56 Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”: |
||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||
|
Short term lesson plan
Short term lesson plan
TERM 3. SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TASKS
Summative assessment for the seventh unit "Music and films"
Short term lesson plan
Short term lesson plan
TERM 3 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TASKS Summative assessment 7 for the unit “Reading for pleasure” Learning objective: 6.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 6.C5 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 6.W6 link, with some support, sentences into a coherent paragraph using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics • Identify the position of speakers in an extended talk with some support • Write a text keeping the layout and format of a given genre with a little support Level of thinking skills: Knowledge and comprehension Application Duration 20 minutes Listening Task 1. Listen to the conversation twice and answer the questions:
Short term lesson plan
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
English plus 9 сынып 3-тоқсан ҚМЖ жинағы
English plus 9 сынып 3-тоқсан ҚМЖ жинағы
Short term lesson plan III term (the ninth grade)
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5. Reading for pleasure.Lesson plan 49 |
School: |
||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher's name: |
||||||||
|
CLASS: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|||||||
|
Lesson title |
Vocabulary and language Focus. Literary genres. p.56 – p.57 |
||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) |
9.C9 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 9.L1 understand the main points in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics 9.S1 use formal and informal language registers in their talk on a range of general and curricular topics 9.S6 communicate meaning clearly at sentence level during, pair, group and whole class exchanges |
||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||
|
S |
The lesson greeting. Pre-learning (W) Teacher greets the class. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk about literature and books. Look at the portraits of some writers and name the books you read at the lessons. How many books do you read a year? When did paperbacks first appear? |
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions Students think critically, exploring, developing, evaluating and making choices about their own and others’ ideas |
Formative assessment is held through observation/monitoring. Emoticon |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT Whiteboard Writing Worksheet |
|||||
|
Main part 15 min |
Lead-in (W, I)
Revise the genres of books pupils know making a list by asking students to add more words to the list they already guessed. Brainstorm with the class and write words on the board as pupils call it out. Organise the class into four teams. Ask a student to come to the front of the class and give him/hersubject card. (E.g. Fiction). Say the whole class can ask a maximum of 10 questions to discover a subject. He/she can only give Yes or No answers. Demonstrate the question types and their short answer forms:
Name the genres of books. Ex. 2 – 3 p.56. Read the information about genres and describe them with complex nouns from the table. Ex.4 p.5
PRE - LISTENING TASK: Ex.4 p.57( Check the meaning of phrases and add your word - combinations from ex.3):
|
A learner
Ss listen |
Formative assessment is held through observation/monitoring. Comments |
Whiteboard Writing Worksheet Student Book p.56 Student Book p.56 Pictures" Test your knowledge" on genres of literature. CD 2.13 Writing Worksheet |
|||||
|
End 3 min. |
Home task. WB p.38 |
Feedback |
|||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5Reading for pleasure. Lesson plan 50 |
School: |
||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher's name: |
||||||
|
CLASS: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|||||
|
Lesson title |
Reading. Fiction. Discussing a text about the benefits of reading. |
||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) |
9.S1 use formal and informal language registers in their talk on a range of general and curricular topics 9.S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S3 explain and justify their own and others’ point of view on a range of general and curricular topics |
||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||
|
Start |
Class organisation The lesson greeting. Warm up. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Good afternoon, dear students and guests! Welcome to our English lesson Pre-learning (W)
Look at the picture and say what is the boy doing and how is he doing it? In front of you there is a poem. I’d like you to read it and in groups discuss the meaning of it? Lead-in (W, I) Pre-reading stage. Listening and reading about the benefits of reading Ex.1 – 2 p.58 Each Sts. Tries to give a good title for the text. Do you enjoy losing yourself in a good book? (As for me…. As I think…. To my mind…). Ex.4 p.58 Build Your vocabulary: Find the active words from the text and explain by your own words. What is a
Book? A book is pages, pictures and
words Each group prepares its presentation. What does the boy prefer doing? Why? Make a list of books you read while you have free time? (revision of genres of books). |
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions Students think critically, exploring, developing, evaluating and making choices about their own and others’ ideas A learner:
|
Formative assessment is held through observation/monitoring. Emoticon Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT The picture of a boy reading a book Whiteboard Poem A Table Whiteboard Writing Worksheet (new words) CD 2.14 Student Book p.58 Teacher's Book p. |
|||
|
End |
Home task. Ex.5p.58 (w). The story “The Fun they had”(I. Asimov) |
Feedback |
|||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5Lesson plan 51 |
School: |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher's name: |
||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASS: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Past Simple or Past Continuous p.59 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) |
9.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9.C9 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about an increased range of general and curricular topics 9.S8 recount extended stories and events on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.UE5 use a wide variety of question types on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.W8 spell most high-frequency vocabulary accurately for a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||||||||||||
|
Start
Main part
|
Class organisation
To present a mind - map
Read the examples in the table aloud and then elicit the answers to complete their own diagram. Lead-in (W, I) To practise active vocabulary
To practise vocabulary through personalisation and pair group. The story of I. Asimov “The Fun They Had”.
Group 1: I. Asimov Group 2: A real book Group 3: An old school. What did the children use to do? Group 4: A school of future(a mechanical teacher) Using a mind – map, each group prepares a summary of the text. Speak about a future school and our school.
While speaking about past events, we can use: Past simple or Past Continuous.
Ex. 1 – 2 p.59 (Pair Work). In the text, find the examples of two grammar tenses. Ex.3 p.59 should be done individually as a competition task. The winner gets a title – The Best in Grammar.
Illustrate a viewpoint in a discussion Descriptor: Match problems 1-6 with solution Read the text. Choose the correct words. Complete the columns. Write true or false for sentences 1-4. Ask and answer the questions Complete the table. Use the words in blue in sentences 1-4. |
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answers around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
Ss complete the diagram
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 10 Oral Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 10 |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT Writing Worksheet Writing Worksheet A mind – map Venn Diagram A Table Student’s Book p.59 Answers are in Teacher’s Book. |
|||||||||||||||
|
End |
Home task: W.B. p.39 Feedback Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”: |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Differentiation: Can be achieved through content (Based on the theory of Multiple Intelligences different tasks are used with the same text). By support: Less able learners will be supported through step-be-step instructions, glossaries, thinking time. |
|||||||||||||||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Lesson plan 52 |
School: |
||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher's name: |
||||||
|
CLASS: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|||||
|
Lesson title |
Writing. Talking about writing a story. p. 60 |
||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) |
9.L6 deduce meaning from context in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about an increased range of general and curricular topics 9.S8 recount extended stories and events on a wide range of general and curricular topics |
||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||
|
Level of thinking |
Higher order thinking skills (according to the revised Bloom's taxonomy). |
||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||
|
Start Main part 15 min 10 min 5 min |
Class organisation
Pre-learning (W) The lesson greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. The teacher shows the picture and introduces the objectives of the lesson.
Warm up. Free talk. Have you ever tried to write your own stories, poems? If you have your poem, can you read it to us? What should people know to write a story? Make a cluster of this topic. Pre-reading stage. Predicting and guessing. Students move their eyes over the words and pictures on the whiteboard and predict the title of the text. Then they read the text in pairs, find out the meaning of the underlined words. After that students call out words, phrases they remember from the text, note them. Students work in pairs (1 minute) discuss what the text is about or (create a text using some of the previous written words). Students express their ideas (1 minute). While-reading stage. The teacher informs the class that they will be participating in the contest about the words and the process of writing successfully. Ex.1 – 3 p.60. Write down key – words from the text: Draw on your dream- become a writer - have a passion for writing – to test……. Make a list of recommendations for a beginning writer:
Ex.4.p. 60 (True – False sentences). If it’s false, prove the information. Answers: 1. False 2. True 3. False 4. False 5. True 6. True Who can be a writer or a journalist? What can you say about these professions? What would you like to be really good at? You are all in the ninth grade, some of you have already decided what he / she is going to be. Please in pairs speak about this problem.
Descriptor: A learner
Self-assessment. |
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
Ss complete the diagram
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 10 Oral Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 10 Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 10 |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT A cluster ” Writing a story” CD2.15 Dictionaries Student’s Book p.60 Whiteboard Student Book p.60 Ex.5 CD2.15 Writing Worksheet Teacher’s Book p.82 |
|||
|
End 3 min. |
Home task. W.B. p.40 Ex.5.p.60 orally Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
|
Slide (Homework) Slide "Six thinking hats" |
|||||
|
Differentiation: Can be achieved through content (Based on the theory of Multiple Intelligences different tasks are used with the same text). By support: Less able learners will be supported through step-be-step instructions, glossaries, thinking time. By task: For more able learners additional leveled tasks are offered. |
|||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Lesson plan 53 |
School: |
|
|
||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
|
|
||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|
|
|||||||
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus. Future Continuous.
many, a lot of. Talking about food and meals. |
|
|
||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9.C9 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 9.UE7 use perfect continuous forms and a variety of simple perfect active and passive forms including time adverbials … so far, lately, all my life , on a wide; use a variety of relative clauses including with which [whole previous clause reference] 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about an increased range of general and curricular topics 9.S8 recount extended stories and events on a wide range of general and curricular topics |
|
|
||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to: |
|
|
||||||||
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
Plan |
|
|
|||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|
|
|||||
|
Beginning the lesson |
The lesson greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk.
|
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT |
|
|
|||||
|
Main Activities |
Write the words in the list. The teacher points out that some words and explaining a new rule: Future Continuous. All Continuous tenses mean a process or duration and are happening in a certain time either in the present, past or future. Please, look at the sentences and make some sentences in the Future Continuous. What will you be eating at the party?
Ex.1 -3 p.61. Complete the sentences. (In a weaker class this ex. can be done in pairs). The Consolidation of a structure: Past Simple and Past Continuous). A story in the Past Tenses. Make a group presentation about the rules and change a story in the past tenses into Future Simple and Future Continuous. Ex. 4 - 5 p. 61. Choose the correct words and read a dialogue. What have you learnt from these exercises? Ex.6 p.61. Creative exercise Speak in pairs about the activities next weekend at a certain time. OPTIONAL ACTIVITY: Writing and Speaking. Write about the group’s plan for the next holidays. What will a student be doing at this time during the holidays? Make a mind – map of the Future Continuous. Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
|
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answer around the class. Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 10 Oral |
Writing Worksheet A crossword Student Book p.61 Writing Worksheet Teacher’s Book p.83 Writing Worksheet A mind - map |
|||||||
|
Ending the lesson |
Giving the home task. W.B. p.41 Peer-assessment.Rubric |
|
|
||||||||
|
End 1min |
Feedback: Teacher asks students what task was difficult to them and which pair worked well. |
|
|
||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|
||||||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Lesson plan 54 |
School: |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Planning a project. Talking about how to plan an event.p. 62 A book blurb. p.63 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.S1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics 9.C6 organise and present information clearly to others 9.R5 deduce meaning from context in extended texts on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics, and some unfamiliar topics 9.W1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics 9.W5 link without support sentences using basic coordinating connectors |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to: |
|||||||||||||||||
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Plan |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
||||||||||||||
|
Beginning the lesson |
The lesson greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk.
|
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT Student Book p.62 Writing Worksheet A picture |
||||||||||||||
|
Main Activities |
LISTENING TASK: Listen to the dialogue and answer the question: How will book club members decide which books to read? In groups of 3, write the work of a book club and choose the first book to read and discuss together. Look at the key phrases. Invitations. Ex.3 p.62. Sentence completion task. Role-play. The teacher offers the groups 5 books and asks them to read the book blurbs and speak about the books. Ex.1 p.63 Work with the blurb of “The Lost World”. Find compound adjectives and quantities in the text.
Ex. 2 – 3 p.63 (a pair – work). Writing Guide: A Blurb in English for any book. Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
|
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Emoticon
Formative assessment
Oral
8
10
Oral
|
Student Book p.62 CD2.16
CD2.07. Pair work. Teacher's Photocopiable Resources p.203 Student Book p.63
A Table
Student Book p.63
Writing Worksheet |
||||||||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task. Ex.4 p.63 (project), W.B. p.43 Ex. 1 -2 Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
Yellow: What did you like about today's lesson? Slide (Homework) Slide "Six thinking hats"
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Lesson plan 55 |
School: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
My Country.Abai Qunanbaiuli. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9.L7 recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level of a range of spoken genres 9.C8 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about an increased range of general and curricular topics 9.UE3 use a variety of compound adjectives, adjectives as participles, comparative structures indicating degree, and intensifying adjectives on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.R5 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Plan |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Beginning the lesson |
Org.moment The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk.
Group work of three.
|
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PP Poems of Abai Kunanbaiuli Cluster |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Main Activities |
LISTENING and READING TASKS: Listen and read the text quickly. What interesting facts about a great person have you learnt?
While-reading stage. Students move their eyes over the text quickly (3 minutes). Then they close the book. After that students call out words, phrases they remember from the text, note them. Students work in pairs (1 minute) discusses what the text is about. Discussion Director(Interpersonal Intelligence). Task 1 : Lead the discussion. Prepare 2 open-ended and thought-provoking questions about the story that your group might want to discuss. Help others talk about the main idea, help them share their thoughts and feelings. Descriptors: 1. Write 2 open-ended questions. 2. Write your responses to these questions. 3. Keep the discussion going
Passage Picker(Body-Kinesthetic Intelligence). Task 2: Choose a paragraph that you think your group would like to re-read. Descriptors: 1. Choose an interesting or important paragraph and write down its location. 2. Read passage aloud yourself (using body language), or ask someone else to read it, or ask the group to read it silently a Word Wizard (Verbal-linguistic Intelligence). Task: Find in the text 5 words or phrases that you had difficulty reading or understand in the story. Descriptors: 1. Write 3 unfamiliar or puzzling words in a full sentence. (You may also find familiar word repeated a lot).
Task 3 : Prepare a brief description of the key points in the story. Descriptors: 1. Write at least 4 sentences. 2. Write in your own words. 3. Present the important events in a logical order. Task 4: Find a part of the story that reminds you of something you have seen, heard, done or read about before. Descriptors: 1. Write at least 2 sentences. Make connections with your own experience, another text or the world. 2. Give evidence from the book to support your connection. Post-reading stage. Next, students complete peer-evaluation form. Ex.4 – 5 p.64
What other Kazakh writers and poets do you know?
Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation.
|
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Emoticon
Formative assessment
Oral
8
10
Oral
Oral
8
10
Oral
|
Student Book p.64 CD2.18.
Pair work. Student Book p.66
Writing Worksheet
Student Book p.64
Writing Worksheets
Writing Worksheets
Student Book p.64 Ex.1 – 3 p.64
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task. W.B.p.42, Kazakh writers( a report) Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Differentiation – Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Lesson plan 56 |
School: |
||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Language and literature: The realist novel. |
||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C8 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 9.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9.L4 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 9.R5 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||||||
|
Beginning the lesson |
Greeting.
The teacher shows a fragment from the film and asks the students to set the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson.
Warm up. Free talk.
A Realistic novel/ Adventure novel/Romantic novel/ Science fiction novel Literary realism is a branch of literature which set out to reflect society as it was, to get as close to the bone of real life as it could. It often depicts more humble or banal events than Romantic writers. So most of Jane Austen's novels are realist because they are fairly mundane; they depict fairly ordinary people, usually woman, doing fairly ordinary things. There are few locked room mysteries, no strange and mysterious happenings, or insane wives. The women do ordinary things like get married and the men are fairly ordinary men. If you compare Pride and Prejudice to a novel like Jane Eyre, the differences become clear: no secret insane wives imprisoned in the home, no misplaced identities and no Byronic heroes. |
Sts warm greet the teacher
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT A fragment from a film ”Pride and Prejudice”. Student Book p.65 Writing Worksheet Whiteboard |
|||||||||
|
Main Activities 15 min. 13 min. |
PRE -LISTENING TASK: Ex.1 p.65. (Name the period in history and give characteristic features of that time).
It is set in the nineteenth century. LISTENING TASK: Ex.2 - 3 p.65. Speak about: 1. Families with unmarried daughters 2. Love in the 19 – th century 3. Marriage in the 19 – thin century (Do this task in groups of 3). While reading the text, compare the men and women status in the 19 – th century. Do it in the form of a table.
Ex.4 p.65 Speak about a famous Kazakh novelist. Mukhtar Auezov Sabit Mukanov Gabit Musrepov Olzhas Suleimenov
Gabit Musrepov was born in 1902 in the Kostanay region. His work in the press began with an ordinary employee and up to the chief editor. He was a brilliant journalist. Working as a journalist, he received a school of life and stories for future works. The play "Amangeldy", like the film with the same name, was created from a newspaper essay. Literary works: "Kyz Zhibek", "Kozy Korpesh and Bayan Sulu", "Akhan-sere-Aktokty". Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner:
|
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Emoticon
Formative assessment
Oral
8
10
Oral
Oral
8
10
Oral
|
Student Book p.65
Whiteboard
CD1.31 CD2.19.
Student Book p.65
Writing Worksheet
Student Book p.65
Writing Worksheet
Writing Worksheet
Teacher’s Book p.87 Teacher’s Photocopiable Recourse p.p.216 - 217 |
|||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task. W.B. p.43. Ex.3 Ex.4.p.65 retell Rules of a game (w) Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
Peer-assessment |
||||||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Lesson plan 57 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher's name: |
||
|
CLASS: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review of Unit 5 |
||
|
Learning objectives(s) |
9.L2 understand most specific information in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S5interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics 9.W2 write independently about factual and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.UE8 use a variety of future active and passive and future continuous forms on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|
Start |
Organisation moments (WC): Teacher informs learners that the aims of this lesson are to revise the material that was taught in this unit. |
Sts warm greet teacher
|
stickers |
Slide (objectives) Slide (useful phrases) PPT |
|
Middle |
Revision. Consolidation. (GW) Rules for Jeopardy game There are 2 kinds of games. Teacher can feel free to choose any or play during the whole lesson. 1. Students play jeopardy in groups. 2. They have to choose a category and a point value. 3. Teacher clicks on the chosen box for the question. (The teacher may want to set a time limit for answering the question) 4. To see if a student or group is correct, click again for the answer. 5. Click the Back to Board button on the slide to return to the main board. 5. If the student or team is correct, they are awarded the point value of the question 6. Continue until all questions have been answered. The team with the most points wins. Ex. 1 - 3 p.66(Revision of vocabulary) Revision of Grammar. Past Simple" and «Past ContinuousTenses(- ? forms) Ex. 4 - 5 p.66 Listening Task You will listen to a text about the writer talking about her new book, try to understand it and make a graph organizer in any form you like: a table, cluster, diagram, etc. Keys: 1. developing a plot 4. getting feedback 7. looking for inspiration 8. creating interesting characters 9. drawing on her own experiences b. school c. languages at school d. free time activities Reading Task: Read the text and be able to do a short test. Everyone has heard of Sherlock Holmes. The author of all the Sherlock Holmes stories was Sir Arthur Conan Doyle. Once Sir Arthur was in Paris. He was going from the railroad station to the hotel where he decided to spend the night. He arrived at the hotel, got out of the taxi and paid the taxi-driver. 'Thank you very much, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle,' said the taxi-driver smiling. 'Oh, do you know who I am?' said Sir Arthur. He was very surprised. 'Well, sir, I read in the newspaper yesterday that you were coming to Paris from the south of France. The train on which you arrived came from the south of France. I also noticed that you hair was last cut by a barber in the south of France. 'Your clothes, and especially your hat, told me that you were English. I put all this together and realized at once that you were Sir Arthur Conan Doyle.' 'That is wonderful, ' said Sir Arthur. 'With so few facts you were really about to know me?' 'Of course,' said the taxi-driver, 'your name is on both your travelling bags. That also helped'. 1. Finish the sentences: The text is about A Sherlock Holmes in Paris. В the famous detective Sherlock Holmes. С the author of the Sherlock Holmes stories. D the railroad station hotel. 2. Choose the true sentence. A Sherlock Holmes spent the night at the hotel. В Conan Doyle decided to spend the night in Paris. С The taxi-driver did not recognize Conan Doyle. D Conan Doyle came to Paris from the north of France. 3. Choose the false sentence. A Conan Doyle was angry with the taxi-driver. В Conan Doyle came to the hotel in a taxi. С The taxi-driver thanked Conan Doyle smiling. D The newspapers wrote about Conan Doyle's visit to Paris. 4. Choose the right answer: Why was Conan Doyle surprised? A taxi-driver was rude to him. В The taxi-driver did not like his clothes. С The taxi-driver could not speak English. D The taxi-driver knew his name. Learners managed to understand the rules and do the tasks. |
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment Oral 8 10 Oral Oral 8 10 Oral |
Student's book p.66 PPT Jeopardy Student's book p.66 Mind - maps " Past Simple" and " Past Continuous" a graph organizer CD 2.20 Student's book Ex.6 p.66 Writing Worksheet |
|
End |
Home task. W.B. p.44, a sonnet of W. Shakespeare |
Slide |
||
|
Differentiation Learners can contribute at their own language level for this activity, as it is relatively open-ended. This gives each learner a chance to be successful. Reflection at the end of the lesson and teacher summary provides support for progress and achievement, and challenge to thinking and setting future objectives. |
||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Lesson plan 58 |
School: |
||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Project: A poem |
||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C8 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 9.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9.S1 use formal and informal language registers in their talk on a range of general and curricular topics 9.S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S3 explain and justify their own and others’ point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.R5 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||||||
|
Beginning the lesson |
Greeting.
The teacher begins the lesson with a sonnet of W. Shakespeare” Age and Youth”. The students see the portraits of well – known Kazakh, Russian, English, American and French poets. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk. Today we are having an unusual lesson – The lesson of Poetry.
|
Sts warm greet teacher |
stickers |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT The portraits of well – known Kazakh, Russian, English, American and French poets. Writing Worksheet |
|||||||||
|
Main Activities |
In groups make a poster about the meaning of a poem by R.L. Stevenson. Follow the structure of answers. Ex.1 – 3 p.67. Two students will speak about the biography of R.L. Stevenson.
Find rhyming words: Speak about the patterns od rhyming words: ABAB CDCD EFEF AABBCCDD Ex.3 – 4 p.67
A Contest of poems devoted to love Students prepared poems in different languages with a presentation of a poet. After the reciting of a poem, they ask the group the meaning of it.
Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
|
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Emoticon
Formative assessment
|
Student Book p.67 CD2.21
Writing Worksheet
Whiteboard
|
|||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task. W.B. p.45 A project: a poem Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
Peer-assessment |
||||||||||||
|
Differentiation – can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners.
|
|||||||||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6 Tradition and language Lesson plan 59 |
School: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Relationships. Talking about traditional stories. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9.C2 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 9.C3 respect differing points of view 9.C5 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 9.W8 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics of familiar general topic 9.S3 give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
Make a presentation about traditions of Kazakhstan. Respond to and discuss the reading passage using interpretive, evaluative and creative thinking skills. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Beginningof the lesson |
Greeting.
The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk.
Thanksgiving (fourth Thursday in November) Toy dastarkhan Betashar Maslenitsa
Britain is full of culture and traditions which have been around for hundreds of years. British customs and traditions are famous all over the world. When people think of Britain they often think of people drinking tea, eating fish and chips and wearing bowler hats, but there is more to Britain than just those things. Poppy Day or Remembrance Day
In groups speak about these traditions. |
Sts warm greet teacher Students answer the question |
stickers |
Slide (useful phrases). Pictures PPT Student Book p.68 Writing Worksheet Pictures PPT Writing Worksheet |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Main Activities |
READING TASK: Match the facts with people and countries. Don’t forget to underline new words and be able to say their meanings. Answer: free Ex.1 - 2 p.68 How do people keep the traditions alive? Do traditional stories travel from one country to another? While reading the text write down word – combinations:
Which of the traditional stories did you like best of all? Explain: “Remember the ant”.
THE INTRODUCTION OF GRAMMAR. Present Perfect. Ex.4 - 5 p.69 Sentence completion task with adverbs:
The teacher asks Sts. to listen to the song " Brighton in the rain" and put down the verbs and underline the position of adverbs in the Present Perfect. Brighton in the Rain Fill in the gaps and complete the song lyrics with the Present Perfect Tense of the verbs listed below. (verbs may be used more than once).Listen to the song and check your answer
Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
discusses questions and answers the questions |
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Emoticon
Formative assessment
Peer assessment
Oral
comments |
Student Book p.68
Student Book p.68
Writing Worksheet A Table
Student Book p.68
Student Book p.69
A Table
A song“Brighton in the Rain”.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Homework: W.B. p.46, Ex.5 – 6 p.69 St.B. Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
Peer-assessment |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6 Tradition and language Lesson plan 60 |
School: |
||||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||||||||||
|
Class: 911 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Reading: Marriage. p.70 |
||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.S3 give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics 9.R5 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.R6 recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer in short texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 9.R7 recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level in a limited range of written genres 9.W8 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics of familiar general topic 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics |
||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||||||||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
Greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson.
Speak about arranged
marriage
Warm up. Free talk. On the board you can see the word: Marriage What do you imagine when you hear this word? How will you choose your future husbands /wives? ARRANGED MARRIAGE What do you think about it? |
Sts warm greet teacher Students answer the question |
stickers |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT Student Book p.70 Writing Worksheet Pictures Student Book p.70 Ex.1 Teacher’s Book p.92 Background. |
|||||||||||
|
Main Activities |
LISTENING TASK: Read and listen to the text and express your opinions:
Discuss the text using the method of six hats: 1 group will speak about facts. 2 group - feelings. 3 group - creative ideas. 4 group -negative aspects. 5 group - benefit from the holidays in jungle. 6 group - conclusion. Ex.2 p.70 True - false sentences. Vocabulary work: find verbs with prepositions and make your sentences. Ex. 3 - 4 p.70.
Ex.5 p.70. Creative exercise Optional activity: Reading. Teacher's Book p.92. Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner:
discusses questions and answers the questions within th |
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Emoticon
Formative assessment
Peer assessment
Oral
comments |
Student Book p.70 CD2.22
Writing Worksheet
Six hats method Student Book p.70 A table
Teacher's Book p.92. |
|||||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task: W.B. p.50 Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
Peer-assessment |
||||||||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 61 |
School: |
||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus: Present Perfect + for and since |
||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C8 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 9.S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S3 explain and justify their own and others’ point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.UE9 use appropriately a wide variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.R8 use a wide range of familiar and unfamiliar paper and digital reference resources to check meaning and extend understanding |
||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Student’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
The lesson greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk. When you want to speak about activities which you have done recently and have a result, what structures and grammar tenses can you use? We can use Present Perfect with a definite word indicator. Look at the picture and give your sentences:
|
Sts warm greet teacher Students answer the question |
stickers |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT Student Book p.71 Writing Worksheet |
|||
|
Main Activities |
U2 SONG FOR TEACHING PRESENT PERFECT This song is great for teaching Present Perfect. There are around 10 present perfect sentences. Aside from the normal listening activities, get the students to complete blanks spaces. Ask them to identify the grammar mistake (I have spoke). For discussion the students can talk about all the things the singer "has done". After, students will write things they have done and things they still want to do. Think of something that you really want to do in your life, but you haven’t been able to do yet Ex.2 p.71 - since - if the starting point
is given (two o'clock, last Friday, 1998) Decide whether to use »since« or »for«.
Ex.3 p.71. Sentence completion task. Speak about the main character. Use ex.4 to make questions about you. Put the sentences into interrogative form: Ex.5 p.73. In groups of 4 write 4 sentences about the duration of the done activity using: How long A game" The best listener". The Sts. listen and try to pronounce correctly. Imagine a perfect holiday. Write about the activities you have done during it. Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
|
Sts answer around the class. Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment Peer assessment Oral comments |
Student Book p.71 A table U2 - I Still Haven't Found What I'm Looking for (Official Video)https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e3-5YC_oHjE Writing Worksheet Writing Worksheet Student Book p.71
|
|||
|
Ending the lesson |
Giving the home task. W.B. p.47 Ex.5 p.71 St. B. Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”: |
||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 62 |
School: |
|||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
|||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Extreme adjectives. |
|||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C9 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 9.C10 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 9.L1 understand the main points in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics 9.L2 understand specific information in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics |
|||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
|
|||||||||||||
|
Plan |
||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
||||||||||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
Greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk. Focus on the photos of great dates and elicit what the people are doing. What adjectives can you use to describe these things.(exciting, awful, stunning).
|
Sts answer around the class. Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment Peer assessment Oral comments |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT Student Book p.72 Writing Worksheet |
||||||||||
|
Main Activities |
LISTENING TASK: Vocabulary exercises. Ex.1 - 2 p.72 The teacher asks Sts. To give the meaning of extreme adjectives. Vocabulary work:
Ex.3 p.72. I have never done this because it’s….. Circle two adjectives to make a pair and describe great dates: 1. awful/ interesting/ hilarious/ bad 2. gorgeous/ furious/ angry/ memorable 3. exhausting/ unpleasant/ terrifying/ tiring 4. frightening/ terrifying/ hilarious/ unpleasant 5. funny/ interesting/ fascinating/ memorable 6. gorgeous/ revolting/ unpleasant/ terrifying.
LISTENING TASK. Ex. 4 -5 p.72. Complete the table. The class is divided into 7 groups and speaks about the experiences using extra adjectives.
Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner:
|
A learner
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
|
Stickers
Emoticon
Formative assessment
Peer assessment
Oral
|
Student Book p.72 CD2.23
A table
Writing Worksheet
Teacher’s Book p.156
Writing Worksheet
CD2.24
Student Book p.72
Teacher's Book p.94.
|
||||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task. W.B. p.48 Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
|
|||||||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
||||||||||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 63 |
School: |
||||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus: Present Perfect and Past Simple. Present Perfect Simple and Continuous. p.73 |
||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S3 explain and justify their own and others’ point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.S6 link comments with flexibility to what others say at sentence and discourse level in pair, group and whole class exchanges 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about an increased range of general and curricular topics 9.C8 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 9.W3 write with grammatical accuracy on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||||||||
|
Plan |
|||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||||||||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
The lesson greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk.
|
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases) Pictures PPT Writing Worksheet A book” Song – to study- English” |
|||||||||||
|
Main Activities 15 min. 13 min. |
LISTENING TASK: In the song, define grammar tenses and find time expressions.
1. Look at the photos. Match them with the words from the song. Then listen to the song. Arrange the sights in the way you hear. 2. Listen to in the song. Look at the lyrics. Put the words in the brackets into The Past Simple. Try to fill in the gaps with the words from the box. Listen and check. Ex.1 p.73 Complete the text, then listen and check. Ex. 2 p.73 Gist listening. Listen to the key phrases and reply. Practise the dialogue. Ex.3 p.73. Listen to 3 short conversations and choose the best answers to the questions. Make a short dialogue about your trip using time expressions. DESCRIPTION OF PICTURES:
The introduction of the Present Perfect Continuous. Ex 4 -5 p.73 Ex.6 p.73. Creative exercise. You look cold – I’ve been waiting for the bus. Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
|
Students respond to greeting
Ss answer the
questions
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
Ss to tell the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
|
Emoticon
Formative assessment
Peer assessment
Oral
Comments
Peer assessment
Oral
comments |
Writing Worksheet A Table
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KoyNlVQbUPc
Writing Worksheet
CD2.25
Pictures
Student Book p.73
Workbook p.49
|
|||||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task: W.B. p.49. Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
|
||||||||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 64 |
School: |
||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||
|
Lesson title |
Invitations. An email to a friend. p.74 - p.75 |
||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C9 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 9.C10 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 9.L2 understand specific information in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics 9.L5 recognise the attitude or opinion of the speaker(s) in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics 9.S1 use formal and informal language registers in their talk on a range of general and curricular topics 9.W2 write independently about factual and imaginary past and future events, activities and experiences on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
Greeting. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk.
Look at the model text and say what the email is about? |
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases). Pictures PPT Student Book p.74 Writing Worksheet Slide (useful phrases). |
|||
|
Main Activities |
Speaking (Pre-listening) (P) In pairs, learners discuss the following questions of Ex.1 p.74. Vocabulary (W) Teacher asks learners to match 10 pictures with the words and check as a whole class. A game" The best interpreter". One pupil reads the sentences, the partner translates it into Russian. Then the second St. gives Russian sentences and asks to give English translation. The third paragraph should be translated into Kazakh or other language. Key – words for making and responding to invitations. Ex 3 – 6 p. 74. THE INTRODUCTION OF a structure of email invitations. Look at the email and be ready to speak about it.
WRITING TASK: Ex.4 p.75. Write an email to a friend. You are going to celebrate a birthday. (Do this task in groups). Ex.2 – 3 p.75. Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner:
discusses questions and answers the questions within |
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions
Sts answer around the class. Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end Ss to tell the class. Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end
|
Emoticon Formative assessment Peer assessment Oral Comments Peer assessment Oral comments |
Student Book p.74 CD2.26 Student Book p.74 Writing Worksheet Student Book p.75 Cambridge Dictionary. Student Book p.75 |
|||
|
Ending the lesson |
Giving the home task. W.B. p.51, An invitation (w). Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”: |
||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 65 |
School: |
|||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
|||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
||||||
|
Lesson title |
My Country. Traditions and language. Talking about wedding traditions in Kazakhstan. p.76 |
|||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C8 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 9.C9 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 9.L1 understand the main points in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics 9.L6 deduce meaning from context in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics |
|||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
|||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
||||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
Greeting. Pre-learning (W) Teacher greets the class and suggests playing the game to the learners. Teacher explains the rules for this game.
One person stands back to the picture of a holiday adventure; Classmates should not name the holiday adventure; Classmates can give some associations with the holiday adventure; Classmates can mime the holiday adventure; Classmates can sing some lines from the songs.
The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson looking a short film about wedding traditions in Kazakhstan. Warm up. Free talk about the wedding. W-E-D-D-I-N-G
Give one word with this letter connected with the theme |
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases). Pictures PPT Student Book p.76 Writing Worksheet Pictures PPT Slide (useful phrases). |
||||
|
Main Activities |
Reading about the wedding traditions in Kazakhstan (W I)
(P) Learners work with new vocabulary first. They get a list of words, read the words with the teacher and write them down into their vocabularies. Learners create 3-4 sentences with new words to show the meaning of them. Differentiation Learners that are more able help the others to read the words correctly. Ex.1 p.76. Working with active words. POST -READING ACTIVITY: Ex.2 p.76. Check answers as a class. Ex.3 p.76 Revision of grammar. A teacher draws Sts. attention to the grammar tenses used in the texts.Ex - 4 .p.76. Ex.5 p.76 Creative Exercise. Speak about other Kazakh traditions in groups. Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner:
discusses questions and answers the questions within |
Sts answer around the class. Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end Ss to tell the class. Ss and elicit their comments at the end
|
Emoticon Formative assessment Peer assessment Oral Comments Peer assessment Oral comments |
Student Book p.76 Teacher’s Book p.98 CD. 2.28 Student Book p.76 Pictures PPT |
||||
|
Ending the lesson |
Giving the home task. W.B. p.52 Ex.1 "Wedding traditions in Kazakhstan"(topic or a presentation). Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”: |
|||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners |
||||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 66 |
School: |
|||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
|||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
||||||
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Language and literature: Word building: adjectives.p.77 |
|||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C3 respect differing points of view 9.C5 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 9.L6 deduce meaning from context in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics, including talk on a limited range of unfamiliar topics 9.W1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics 9.S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.UE3 use a variety of compound adjectives, adjectives as participles, comparative structures indicating degree, and intensifying adjectives on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics |
|||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
|
|||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
||||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
Greeting.
The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm up. Free talk. Look at the cover of the book; tell your partner if he/ she knows what the book is about and who the main character is. In pairs, name words associated with it and make a cluster.
|
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions
Sts answer around the class. |
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases). Pictures PPT Student Book p.77 Gulliver's Travels Trailer Cluster "Gulliver's Travels". Pictures PPT |
||||
|
Main Activities |
LISTENING TASK: Read the text and choose the correct words. Listen and check your answers. Ex.1 p.77 . Pay attention to the new words: Proudly, army, dishonesty, neighbours, customs, murder, judges, laws. Ex.2 p.77. Match the words from Ex.1 Look at the text again and do Ex.3 p.77. Sts. can work in pairs. Answers: 1. customs 2. proudly 3. laws 4. judges 5. army 6. neighbours 7. murder 8. dishonestyScore - 8 Ex.3 Answers: 1. True 2. True 3. False 4. True 5. False 6. False Score - 6 To the false sentences give the right answers. Each student counts the scores for the tasks. In group of 4, fill in a story map. Ex.4. Form an adjective with the help of suffixes. Ex.5 p.77 (Activate). In groups, make a short play of the conversation between a king and Gulliver. Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner:
|
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end Ss to tell the class. Ss and elicit their comments at the end
|
Emoticon Formative assessment Peer assessment Oral Comments Peer assessment Oral comments |
Student Book p.77 CD2.29. Writing Worksheet Student Book p.77 Pictures A story map graphic organiser Teacher's Book A Table p.77 Optional Activity. Teacher’s Book p.99 |
||||
|
Ending the lesson |
Giving the home task. W.B. p.52 Ex.3 -5. Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”: |
|||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
||||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 67. |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher's name: |
||
|
CLASS: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative assessment for the 6th unit. Review |
||
TERM 3.
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TASKS
Summative assessment for the 6th unit "Tradition and language."
|
Learning objectives |
9.L2 understand most specific information in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S3 explain and justify their own point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about an increased range of general and curricular topics 9.UE3 use a variety of compound adjectives and adjectives as participles and a variety of comparative structures to indicate degree on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
|
Assessment criteria |
Identify the position of speakers in an extended talk with some support Express thoughts about the given topic in the conversations Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences |
|
Level of thinking skills |
Application Knowledge and comprehension Higher order thinking skills |
|
Duration |
20 minutes |
Listening. Task 1.
Speaking. Task 2. An individual interview on the suggested topic for approximately 2 minutes for each student.
Review. Unit6
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6. Tradition and language Lesson plan 68 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher's name: |
||
|
CLASS: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Skills Round - up. p.79 |
||
|
Learning objectives(s) |
9.S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S3 explain and justify their own and others’ point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.S6 link comments with flexibility to what others say at sentence and discourse level in pair, group and whole class exchanges 9.S8 recount extended stories and events on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.W3 write with grammatical accuracy on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.W6 write coherently at text level using a variety of connectors on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson |
Organisation moments (WC): Teacher informs learners that the aims of this lesson are to revise the material that was taught in this unit. |
Students respond to greeting Ss answer the questions
|
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (objectives) Slide (useful phrases) PPT |
|
Main activities |
Revision. Consolidation. (GW) Rules for Jeopardy game There are 2 kinds of games. Teacher can feel free to choose any or play during the whole lesson. 1. Students play jeopardy in groups. 2. They have to choose a category and a point value. 3. Teacher clicks on the chosen box for the question. (The teacher may want to set a time limit for answering the question) 4. To see if a student or group is correct, click again for the answer. 5. Click the Back to Board button on the slide to return to the main board. 5. If the student or team is correct, they are awarded the point value of the question 6. Continue until all questions have been answered. The team with the most points wins. Ex. 1 - 2 p. 78 (Revision of vocabulary) Revision of Grammar. Present Perfect/ Present Perfect Continuous/ Past Simple ( +, -, ? forms ) Ex. 3 - 4 ( do ex. individually) LISTENING TASK: You will listen to a text and complete the sentences: COMMUNICATION. Choose the correct responses to the sentences: Ex. 6 p.78 SKILLS ROUND - UP. LISTENING. Ex. 1 - 3 p.79. Speaking: Ex.4 - 5 p.79. Situations in a big city. Writing: Ex.6. p.79 A letter to a friend about a situation of losing or finding something. (Fast finishes can swap emails with another fast finisher. If a teacher has time, she/ he can ask students to do Optional activity: Consolidation. Assessment criteria: Identify the main idea in extended talks with little support. Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. Descriptor: A learner:
|
Sts answer around the class.
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end Ss to tell the class.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end
|
Emoticon Formative assessment Peer assessment Oral Comments Peer assessment Oral comments |
Student's book p.78 p.79 PPT Jeopardy Student's book p.78 A mind - map "Past Simple" a graph organizer CD 2.31. Student's book p.79 Teacher’s Book p.101 |
|
End |
Home task. W.B. p.53, St.B. p.78 Ex. 4. FEEDBACK: Your impression! Sts write their impression of the whole unit and share ideas with their classmates. 3 – new words you have taught at the lesson; 2 – adjectives to describe the lesson 1 – one activity you like |
Slide |
||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
||||
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 7Music and film Lesson plan 69 |
School: |
||||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||||||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Music and film images. p.80 - p.81 |
||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 9.C6 organise and present information clearly to others 9.S2 ask complex questions to get information about a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.S3 explain and justify their own and others’ point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about an increased range of general and curricular topics 9.UE6 use a wide variety of relative, demonstrative, indefinite, quantitative]of pronouns and reflexive pronoun structures on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||||||||||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
The lesson greeting. Pre-learning (W) Teacher greets the class and suggests watching a video. Before the short film Sts. Name form of art they know. Watch a video about music and film images. A - R - T - Give one word with this letter connected with the theme. Do you like to read or listen? What do you watch on T.V.? |
Sts answer around the class.
|
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases). Pictures PPT film-english.com/2012/02/05/the-joy-of-books/. Films. Writing Worksheet |
|||||||||||
|
Main Activities |
Start Thinking. Group Work. Music and film Quiz. p.80 Ex.1 p.80. Vocabulary Work: match the words with the definitions and put in a correct column in the table. What can people do to change the personal appearance? Why? Differentiation In a weaker class: drill the pronunciation of the difficult words (beard, moustache, dreadlocks, tattoo, and braids). In a stronger class, ask students to make up sentences. St. support or critique a strong change in appearance. Ex.3.p.81 THE INTRODUCTION OF GRAMMAR: Reflective pronouns.
Sts. give their examples with pronouns. Ex. 4 - 6p.81. Choose the correct pronoun. ACTIVATE: Language focus. Write answers to the questions. What is the difference between reflective pronouns and each other? Workbook p.p.40 – 41(more practice). Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
|
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs.
Ss and elicit their comments at the end Ss to tell the class.
Ss and elicit their comments at the e |
Peer assessment
Oral
Comments
Peer assessment
|
Student Book p.80 English - Russian Oxford Dictionary
Student Book p.81
Writing Worksheet
Teacher's Book p.103. |
|||||||||||
|
Ending the lesson
|
Giving the home task. W.B. p.54
Topic» Body Decoration" or presentation Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”:
|
||||||||||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||||||||||
Short term lesson plan
|
Unit of a long term plan Unit 7 Music and film Lesson plan 70 |
School: |
||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher’s name: |
||||||
|
Class: 9 |
Number present: |
Number absent: |
|||||
|
Lesson title |
Reading. Galymzhan Moldanazar. p.82 |
||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to |
9.R5 deduce meaning from context in extended texts on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics, and some unfamiliar topics 9.R6 recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer in extended texts on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.L8 understand supported narratives, including some extended talk, on an increasing range of general and curricular topics 9.W4 use style and register to achieve appropriate degree of formality in a growing variety of written genres on a range of general and curricular topics 9.W5 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a wide range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics 9.S1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics |
||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to:
Most learners will be able to:
Some learners will be able to:
|
||||||
|
Planned timings |
Teacher’s activities |
Pupil’s activities |
Marks |
Resources |
|||
|
Beginning of the lesson |
The lesson greeting. Pre-learning (W) Teacher greets the class and suggests playing the game to the learners. Teacher explains the rules for this game.
One person stands back to the picture of a popular Kazakh singer ; Classmates should not call the name of the singer ; Classmates can give some lines from the song of this singer ; Classmates can sing some lines from the songs.
The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson.
Warm up. Free talk about popular Kazakh singers. Look at the portraits of some singers, what can you say about them?Can you name any Kazakh musicians? |
Sts answer around the class.
|
Emoticon Formative assessment |
Slide (useful phrases). Pictures PPT Writing Worksheet Pictures PPT Student Book p.82 Slide (useful phrases). |
|||
|
Main Activities |
Ex.1 p.82 Look at the portraits of young people? What do you know about them? Students give their own answers.
The students in groups will read information about a musician and make a story map. Then a leader is going to present Galymzhan Moldanazar. Reading and listen to the text about a Kazakh musician. (W I). Teacher suggests the list of new vocabulary with their synonyms or opposites for learners. Ex.1,3 p.82 (P) Learners work with new vocabulary first. They get a list of words, read the words with the teacher and write them down into their vocabularies. Learners create 3-4 sentences with new words. Differentiation Learners that are more able help the others to read the words correctly. Ex.3 p.82. Working with active words. POST -READING ACTIVITY: Ex.4 p.82. Give the definition of the underlined words. The teacher divide the class into 2 groups: boys and girls. One group will speak about a popular singer of 80s and the second group will retell the text about a modern musician. They should do it in the form of presentation. Ex.5 p.82. Creative task. Speak about a life of a musician. Make a conclusion: Have you ever wanted to sing in public? Describe another musician in pairs. Try to make a story map. Assessment criteria:
Descriptor: A learner:
|
Students give their own examples using the correct forms of the verbs. Ss and elicit their comments at the end Ss to tell the class. Ss and elicit their comments at the e |
Peer assessment Oral Comments Peer assessment |
Student Book p.82 Pictures PPT Cluster or a table. Student Book p.82 CD. 3.01 Pictures PPT Cluster or a table. Student Book p.82 |
|||
|
Ending the lesson |
Giving the home task. W.B. p.56 Students express their attitude to the lesson and give self-assessment using the method: “Six thinking hats”: |
||||||
|
Differentiation can be achieved through the selection of activities, identification of learning outcomes for a certain student, provision of individual support to learners, selection of learning materials and resources based on the individual abilities of learners. |
|||||||
|
Short term lesson plan
Short term lesson plan
TERM 3. SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TASKS
Summative assessment for the seventh unit "Music and films"
Short term lesson plan
Short term lesson plan
TERM 3 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TASKS Summative assessment 7 for the unit “Reading for pleasure” Learning objective: 6.C1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 6.C5 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 6.W6 link, with some support, sentences into a coherent paragraph using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics • Identify the position of speakers in an extended talk with some support • Write a text keeping the layout and format of a given genre with a little support Level of thinking skills: Knowledge and comprehension Application Duration 20 minutes Listening Task 1. Listen to the conversation twice and answer the questions:
Short term lesson plan
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

шағым қалдыра аласыз