Short term plan
|
Unit: 1 Our World lesson 1 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
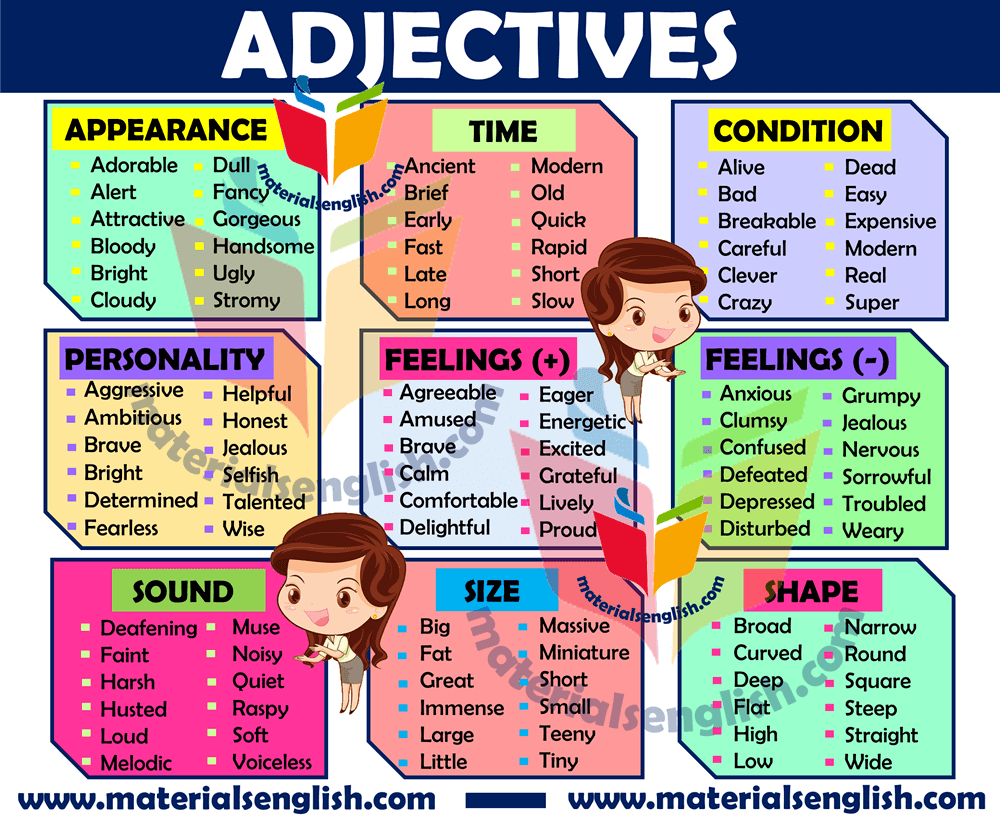
Welcome; Adjectives |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 8.2.7.1 recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level of a growing range of spoken genres 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Review adjectives. . • Do a quiz on The world around you. • Ask and answer questions using adjectives. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask individual students questions such as What’s your favourite TV programme / animal / food? Ask them to describe the item they have chosen. Write any adjectives they use on the board and elicit that they are adjectives. • Elicit and write up other adjectives that students know Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary to do with television.
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:4 • Read through the adjectives in the box with the class. In a weaker class, match the first two items as an example. In a stronger class, you could start this as a quick quiz. Call out an adjective from the box at random and ask students to put up their hands as soon as they know the answer. • Students complete the activity individually or in pairs. After confirming their answers with the recording, you could play the audio again to drill the pronunciation of any new adjectives Ex: 2 p:4 • Read the title of the quiz with the class and elicit a translation or definition. You may need to explain around: you could say that this quiz covers the things we see, hear and experience in the world. • In a weaker class, check that students have chosen the correct words before they move on to think of answers. • Students think of answers individually or in pairs. • Ask the class for ideas for each question, then confirm with the recording Ex: 1 p:5 • In a weaker class, allow students to find the comparative and superlative forms and write the rules in pairs. Ex: 2 p:5 • Go through the example with the class. Encourage students to think about the adjective exciting in relation to all three activities. Ex: 4 p:5 • Students complete the sentences in pairs. In a weaker class, write these answers on the board and highlight the third person singular changes to prompt the class. • In a stronger class, elicit the rule as a class activity |
Students match adjectives with their opposites in the box. ANSWERS : 1 cheap 2 rare 3 weak 4 quiet 5 dangerous 6 unhealthy 7 clean 8 near 9 easy 10 heavy 11 useless 12 exciting
Students work in pairs. Choose the correct words in World around you quiz. Then think of an answer for each description. ANSWERS : 1 near (Neptune) 2 noisy (Tokyo) 3 common (mosquito) 4 powerful (whale) 5 cheap (plastic) 6 expensive (platinum) Students complete the tables with adjectives. Then answer the question. ANSWERS: 1 rarer 2 expensive 3 further 4 nearest 5 hottest 6 common 7 furthest Students write a comparative and superlative sentence for each group of words. ANSWERS: Students own answer Students complete the sentences from the quiz. ANSWERS: 1 make 2 don’t speak 3 loves 4 doesn’t live |
Descriptor: - match adjectives with their opposites Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - Choose the correct words Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the tables with adjectives Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - complete the sentences from the quiz Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit: 1 Our World lesson 2 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Everyday objects |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.1.1understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.6.2.1 use a growing variety of quantifiers for countable and uncountable nouns including several, plenty, a large/small number/amount on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.3.1.1 use formal and informal registers in their talk on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary of household goods. • Learn how to say numbers. • Do a quiz about human consumers. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the words carbon footprint on the board and ask students what they understand by it. Ask if students think they have a big or small carbon footprint and why. • Ask what makes a person’s carbon footprint bigger, and elicit some ideas such as travelling by car, using energy in the home and buying lots of goods Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria - Practise comparing opinions.
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:8 • After students have matched the words and photos, check answers, and drill pronunciation of new words. Ex: 2 p:8 Discuss students’ ideas with the class. Ex: 3 p: 9 • Read through the key phrases with the class before students write the numbers. In a weaker class, do the first item on the board as an example, then allow them to complete the activity in pairs. In a stronger class, invite volunteers up to the board to write the numbers, and encourage the rest of the class to correct any mistakes. • Play the CD and pause for students to repeat the numbers. • Students work individually to answer the quiz by choosing the numbers they think complete each gap. Don’t check answers at this stage. Ex: 4 p: 9 • Ask students to compare their answers. If they have made different choices from their partner, ask them to explain their reasons for their answer, but don’t say who is correct. • Play the CD twice for them to check. |
Students match the words in the boxes with photos. The listen and check ANSWERS : 1 a can of fizzy drink 2 a bottle of shampoo 3 a roll of toilet paper 4 a box of washing powder 5 a packet of crisps 6 a bag of apples 7 a bar of chocolate 8 a jar of coffee 9 a tube of toothpaste 10 a carton of juice Students work in pairs. Think of more containers and contents ANSWERS: Students of answer Students study the key phrases and write the numbers. Listen and say the numbers. ANSWERS: Students of answer Students compare your answers to the quiz with a partner. Then listen and check ANSWERS: 1) 628; 1,700 2) 4.8; 9.8 3) 198; 656 4) 4.5, 21; 1,201 5) 10,354; 854 6)120,000; 8 7) 24,000; 720,000 8) 276; 4,239 9) 74,802; 49,717; 38,320 |
Descriptor: - match the words in the boxes with photos Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples
Descriptor: - work in pairs Total: 1 point Descriptor: - study the key phrases and write the numbers Total: 1 point Descriptor: - compare your answers to the quiz Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 24 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit: 1 Our World lesson 3 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Grammar: much, many, a lot of |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 8.3.3.1 give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.6.2.1 use a growing variety of quantifiers for countable and uncountable nouns including several, plenty, a large/small number/amount on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn expressions of quantity and practise using them. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the words carbon footprint on the board and ask students what they understand by it. Ask if students think they have a big or small carbon footprint and why. • Ask what makes a person’s carbon footprint bigger, and elicit some ideas such as travelling by car, using energy in the home and buying lots of goods Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary to do with television.
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 5 p:9 • Make sure that students understand the terms countable and uncountable. In a weaker class, give examples, such as Apples – can you count them? (Yes.) Water – can you count it? (No.) In a stronger class, ask students to give you examples. • Look at the sentences and ask students to identify the nouns. Ask students to work in pairs to decide whether the nouns are countable or uncountable and complete the table by putting the blue phrases in the correct columns. Ex: 6 p:9 • Students choose the correct words individually • In a stronger class, once you have checked answers, ask students to invent answers to the questions
Ex: 7 p:9 • Read through the task with the class, and make sure students understand what they have to do. • Recap the phrases in exercise 5, and remind students to refer to the completed version in their notebooks. • Go through the examples, then model the activity by asking one or two confident students the first few questions. • Students work in pairs to ask and answer the questions. • Ask some students to report back to the class on what they learnt about their partner |
Students read the sentences. Are the nouns countable or uncountable? Complete the table with the words in blue. ANSWERS : 1 uncountable 2 countable 3 countable 4 uncountable 5 uncountable 6uncountable, countable, uncountable . 7countable, uncountable 8countable, uncountable Uncountable nouns: 2 much 3 a lot of 4 some Countable nouns: 1 not many 5 not any Students choose the correct words ANSWERS : 1 much 2 many 3 some 4 much 5 any 6 any Students work in pairs. Ask and answer with your own ideas. Use the phrases in the table in ex.5 and numbers. ANSWERS: 1 Do you eat much pasta each week? How much? 2 Do you walk many kilometres every month? How many? 3 Are there many books in the school library? How many? 4 Do you use a lot of toothpaste each year? How much? 5 Do you drink much milk every week? How much? 6 Do you say many words every day? How many? Students’ own answers
|
Descriptor: - Complete the table with the words in blue Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - work in pairs Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit: Our World lesson 4 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The "no impact" family |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts and some extended texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.2.3.1 understand with little or no support most of the detail of an argument in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.3.1 give an opinion at discourse level on a range of general and curricular range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn how to predict before you read. • Read about a family that wants to reduce its impact on the environment. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Learn about compound nouns |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the words low impact and high impact on the board. • Explain that your impact on the environment is the effect that you have, through things you do such as travelling and using energy. • Ask students if they think they have a low impact or a high impact on the environment. Ask how they could reduce their impact. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria - Learn the negative and question forms of the past simple. |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:10 • Refer students to the pictures and the title of the text. Explain that trying to predict what the text is about before they read will help them to understand it better. • Students decide which of the sentences they think are true and false. They can discuss their ideas in pairs. , • Encourage students to read the text quickly to check their ideas. Tell them not to worry about the gaps at this stage. Ex: 2 p: 10 • Focus students on the sentences and explain that these complete the gaps in the text. • Explain that students should read each paragraph carefully. When they reach the gap, they should read through all the options to see which one contains information which is correct and relevant. • Students can work individually then compare their ideas in pairs Ex: 3 p:10 • Read through the information and examples with the class. Students find four more compound nouns in the text. Ask them to read silently then put up their hands when they find one, for you to write on the board. There are several more examples in the text, so you can stop at four or carry on with more examples • In a stronger class, ask students if they can think of any more examples that aren’t in the text. Ex: 4 p:10 • Explain that students are going to practise some more compound nouns. • Students complete the sentences individually, then compare with a partner. In a weaker class, do the first item as an example. |
Students look at the photos and the title of the text. Predict which of the sentences are true or false. Then read the text and check your answers. ANSWERS : 1 True. 2 False. 3 True. 4 True. 5 False. 6 True. Students complete the text with sentences. There is one sentence that you don’t need. Then listen and check your answer. ANSWERS: 1 b 2 e 3 c 4 a Students read the information and complete the examples. Then find four more compound nouns in the text. ANSWERS : 1 shopping 2 bed 3 washes More compound nouns in the text: toilet paper, dishwasher, light bulb, bathroom, shampoo bottles, toothpaste, secondhand things, plastic bags, takeaway food, plastic cup, plastic pots, lifestyle Students complete the sentences with the words in the box. ANSWERS : 1 strawberry 4 washing 2 Christmas 5 kitchen 3 shopping 6 chicken |
Descriptor: - read the text Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the text with sentences Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - read the information and complete the examples Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the words in the box Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 4 P: 25 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit: Our World lesson 5 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: S |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: Relative pronouns |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn about relative pronouns. • Practise using relative pronouns. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students back to exercise 3 on page 20 and ask: What’s a shopping bag? • Write the answer a bag which is for shopping on the board and underline the relative pronoun which. • Ask the questions What’s a teacher? and What’s a school? Elicit the answers, e.g. a person who teaches and a place where you learn and write these on the board. If students use the correct relative pronouns, underline them; if students use incorrect relative pronouns, leave these as gaps on the board Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for television programmes
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:11 • Ask students to work in pairs to complete the sentences and the rules. • Check answers with the class, then if the examples on the board are still gapped, ask students to complete them. Ex: 2 p:11 • Read the title of the text with the class. In a weaker class, translate the title then discuss students’ opinion of the concept of buying locally, in L1 if necessary. In a stronger class, elicit an explanation of the title then ask students if this is something they think about when shopping. • After students have completed the text with the correct relative pronouns, ask them to compare answers in pairs before you check answers with the class. Ex: 3 p:11 • Students write their sentences individually then compare with a partner. Encourage them to correct any mistakes in their partner’s sentences. • Ask individual students to read out some of their sentences to the class, and correct any errors. Ex: 4 p:11 • Read through the task with the class. Ask two students to read out the example, and check students understand how to use the table. Then ask a confident student to think of another sentence, or give one yourself. Encourage another class member to guess the person, place or thing, and if they are not correct, encourage someone else to guess. • Students continue the activity. Allow them time to write their sentences, and go round helping if necessary. In a weaker class, check students have formed the sentences correctly before they ask and answer. In a stronger class, you might find that students can think of items spontaneously without needing a long planning stage. |
Students complete the sentences from the text. Then complete the rules with places, people, reasons and things ANSWERS : 1 who 2 where 3 which
Rules ANSWERS 1 people 2 places 3 things
Students complete the text with who, why, where and which ANSWERS : 1 which 2 where 3 which 4 where 5 which 6 who Students complete the sentences with your own ideas. Use who, where or which. Compare with a partner. ANSWERS: 1 where … 2 which … 3 who … 4 which … 5 who … 6 which … Students write six sentences with who, where, why and which. ANSWERS: Students own answer |
Descriptor: - complete the sentences - complete the rules Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples
Descriptor: - complete the text with who, why, where and which Total: 1 point
-Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - write six sentences with who, where, why and which Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End |
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 6 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
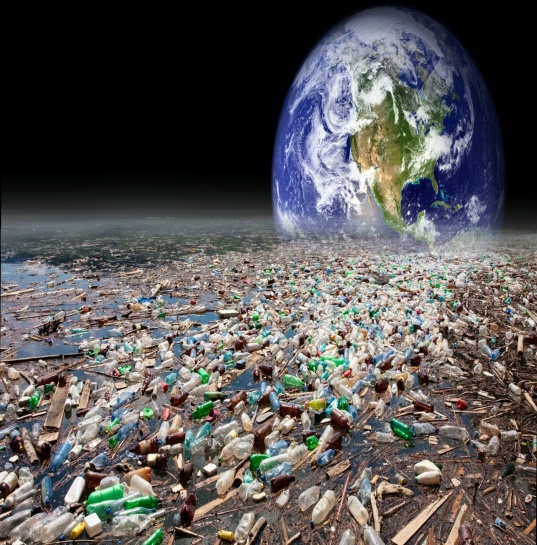
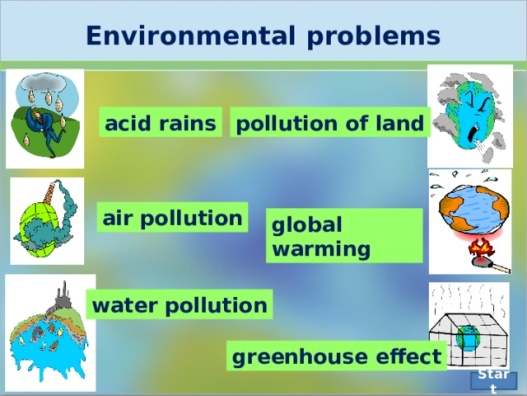
Pollution and the environment |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary relating to the environment. • Listen to an account of someone who decided to make a difference to the environment. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students what things they already do to help the environment. • Write students’ ideas on the board. Ask what other things people can do to help the environment. Ask if they think that an individual can make a big difference. Encourage students to express their own opinions Lead - In
How do we solve this problem? |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:11 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words and choose the correct words in the text. • Students listen to the complete text to check their answers. Encourage them to correct any mistakes. • Check answers and model and drill pronunciation Ex: 2 p:11 • Allow students time to read through the questions individually before they ask and answer in pairs. • Elicit some answers from the class. If students are interested in the subject, you could conduct a short class discussion on some of the issues raised. Ex: 3 p:11 • Focus on the pictures and ask students which problem they think Rebecca Hosking was concerned about. • Explain that the sentences summarize different parts of the text, but that they are in the wrong sequence. Ask students to read the sentences carefully, and check vocabulary with them. Encourage students to think about the key words carrying meaning in each sentence, as this will help them when they listen. • After students have put the information about Rebecca in order, allow them to listen to check their answers. • Find out how many guessed the sequence correctly. Ex: 4 p:11 • Allow students time to read the questions. Explain that in a true / false task, they should read the statements they are given very carefully. They may hear the opposite of these statements, so encourage them to think about relevant vocabulary first. • In a stronger class, ask if students can answer any of these before they listen again |
Students check the meaning of the words in blue. Choose the correct words. Then listen and check ANSWERS : 1 throw away 2 reuse 3 recycle 4 destroy 5 burn 6 poisons 7 bury
Students work in pairs. Ask and answer the question ANSWERS : Students’ own answers Students read the information about Rebecca Hosking Order sentences then listen and check ANSWERS: b, d, a, c Students listen again and write true or false. Correct the false sentences. ANSWERS: 1 False. The speaker is the presenter of SOS Environment. 2 True. 3 False. She was shocked when she saw how many creatures were dying because of all the plastic in the sea. 4 True. 5 False. None of the shops give plastic bags. 6 True.
|
Descriptor: - Choose the correct words Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - work in pairs Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - read the information about Rebecca Hosking Order Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the information about Rebecca Hosking Order Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 24 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 7 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
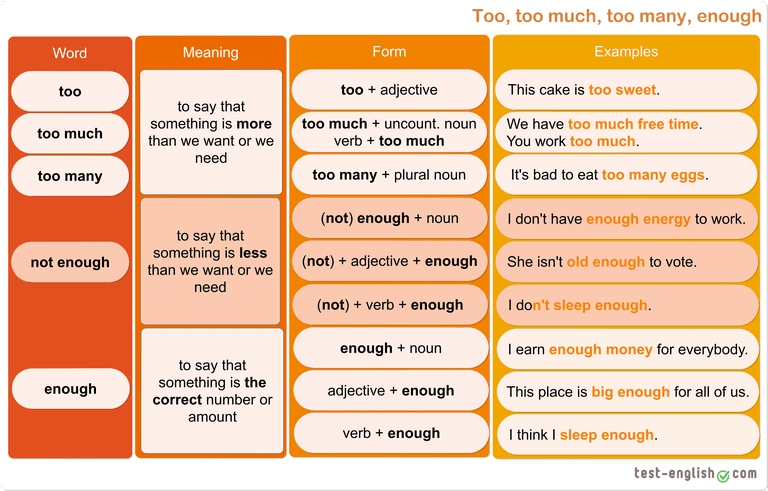
Language focus: too, too much, too many, enough, not enough |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn too, too much, too many, enough and not enough. • Practise using too, too much, too many, enough and not enough. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students if they can remember the missing words from the recording. If they can, fill in the gaps and ask why we say too much plastic but too many plastic bags (because much refers to the noun, plastic and many referes to the noun, bags). • If students cannot remember the missing words, elicit the words in their own language meaning ‘more than we need’, which would fill the gaps Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:13 • After studying the examples, students copy the rules and complete them. Encourage them to compare ideas in pairs before you check answers. Ex: 2 p:13 • Students complete the sentences individually. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes before you check answers with the class Ex: 3 p:13 • Read the example sentences and elicit the target word (enough). Look at the bold words and demonstrate that the relevant part of speech is shown in brackets. • In a weaker class, students can discuss the rules in pairs before you check answers. In a stronger class, do this as a class discussion and write the answers on the board. Ex: 4 p:13 • Students work individually to order the questions. Check these before students listen to the CD. • After listening to the CD, ask students to write the answers and to compare in pairs before you check with the class Ex: 5 p:13 • Look at the shopping list and the picture with the class. Go through the examples and ask students to point to the items shown. Ask: How much soap is there on the list? (One bar.) How much soap is there in the basket? (One bar.) Ask Is this enough, not enough or too much soap? (Enough.) Repeat with packets of crisps and show that there are too many packets of crisps. • In a weaker class, quickly revise which items are countable and which are uncountable. • Put students into pairs to write sentences. |
Students study these sentences from the listening. Then complete the rules with adjectives, countable nouns and uncountable nouns ANSWERS : 1 uncountable nouns 2 countable nouns 3 adjective
Students complete the sentences with too, too much or too many. ANSWERS : 1 too 2 too much 3 too many 4 too much 5 too many 6 too 7 too many, too much Students study these sentences from the listening. Then complete the rules with before or after ANSWERS: 1 after 2 after 3 before Student order the words to make questions. Then listen to a conversation and answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 Is this pizza big enough? Yes, it’s big enough. 2 Are there enough apples? There are too many apples. 3 Have we got enough drinks? No, we haven’t got enough drinks. 4 Is this soup hot enough? No, it’s cold. 5 Have we got enough sandwiches? Yes, we’ve got a lot. 6 Is this coffee strong enough? Yes, the coffee’s really strong |
Descriptor: - complete the rules with adjectives Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the sentences with too, too much or too many Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - make questions Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 8 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Offering and asking for help |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.4.1 understand with little or no support most of the implied meaning in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a growing range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a dialogue in which people offer and ask for help. • Learn key phrases for offering and asking for help. • Practise offering and asking for help. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they ever organize events with their friends. • Ask them to imagine that they want to organize a party or barbecue with some friends. Ask what things they need to plan, and elicit some ideas. • Ask if one person will do everything, and elicit that they will ask their friends for help. • Tell students they are going to practise offering and asking for help. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:14 • Look at the photo and elicit ideas. Tell students to look at clues in the photo such as the food and the outdoor setting. Ex: 2 p:14 • Read the task and clarify that the first time students listen, they should just identify what it is that Adam needs. They do not need to understand every word at this stage. Ex: 3 p:14 • Point out that covering the dialogue will help students to focus on the form of the key phrases. • In a weaker class, if students can’t remember the exact phrasing, ask them to identify the type of word that is missing in each case (a verb). Clarify that these phrases are all polite ways to offer to do something, or ask someone to do something to help. • Students listen and check or complete their answers. Ex: 4 p:14 • Read out the first sentence and emphasize how the words ending in consonants are linked in speech to those beginning with vowels (A bag of ice). Ex: 5 p:14 • In a weaker class, do an example with students. Look at the first sentence and identify the adjective dirty. Ask student to think of verbs that would offer help in this situation (clean / tidy). Help them transform this into a sentence (Shall I (help you) clean / tidy it?) |
Students look at the photo. What are Lucy and Adam preparing? ANSWERS : Lucy and Adam are preparing a barbecue.
Students listen to the dialogue. What does Adam need? ANSWERS : Adam needs some more drinks, a bag of ice and some bags for the rubbish. Students cover the dialogue and complete the key phrases. ANSWERS: 1 help you with anything? (offering help) 2 get a few cartons of juice or something? (offering help) 3 get a bag of ice, too. (offering help) 4 get some? (asking for help) 5 see what they’ve got. (offering help) Student listen and repeat the sentences practise linking the words ANSWERS: 1 clean it 2 help you 3 come with you 4 be quiet 5 buy some more 6 call him
|
Descriptor: - look at the photo. Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - cover the dialogue Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - listen and repeat the sentences Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 9 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
An environmental problem 1 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a growing range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study an email about an environmental problem. • Learn key phrases for writing about a problem. • Learn about so and because. • Write an email about an environmental problem. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students what environmental problems there are in their town or area. Elicit some ideas. • Ask students what they can do if they notice an environmental problem in their area. Elicit that they can write to people in the area, encouraging them to help solve the problem. If students do not come up with this idea, prompt them by asking what Rebecca Hosking did when she noticed the problem with plastic bags Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:15 • Focus students on the photo and ask for ideas about the topic of the text. Discuss these as a class, then read the title and confirm that it is about dirty beaches. • After reading the model text and answering the questions, students can compare answers in pairs before you check with the class. Ex: 2 p:15 • Read through the key phrases with the class and ask students to identify the phrases that are used in the text to start the paragraphs. • Check answers, then allow students to complete each phrase with their own ideas. • Ask students to find the key phrases in the model text. Ex: 3 p:15 • Read the examples with the class and elicit the continuation from the text: I’m writing because I was at the beach … . There aren’t enough bins … , so I think we need more. • If necessary, explain the difference between so and because by transforming the second example so that it contains because: We need more bins because there aren’t enough bins. Ask students to translate the two sentences into their own language. • Students match and link the sentence halves. Ex: 4 p:15 • Read the task with the class. • Students think and plan their emails individually. In a weaker class, brainstorm some ideas and vocabulary first with the class. • Students write their emails. This can be set for homework. • Tell students to check their work, and check they have used so and because correctly, and that they have used too, too much, too many, enough, not enough, and possibly, perhaps, maybe, definitely. In a stronger class, encourage students to swap their emails with a partner for correction |
Students read the model text and choose the correct answers ANSWERS : 1 b 2 b 3 b 4 c
Students study the key phrases. Complete the key phrases with your own ideas ANSWERS : I’m writing because … I think there are possibly (two) reasons for this. We must do something about … Students’ own answers. Students complete the examples from the text. Then match with a-e. Use so or because ANSWERS: 1 d; because 2 a; so 3 e; so 4 c; because 5 b; because Student follow the steps in the writing guide. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers.
|
Descriptor: - read the model text Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - Complete the key phrases Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - listen and repeat the sentences Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 10 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My county: Our world |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.7.1 recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level of a growing range of spoken genres 8.6.2.1 use a growing variety of quantifiers for countable and uncountable nouns including several, plenty, a large/small number/amount on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a text about an environmental problem in Kazakhstan. • Review phrases to talk about quantity with countable and uncountable nouns. • Learn verbs connected with the environment. • Participate in a discussion about local environmental problems. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Draw students’ attention to the photo of the stranded ships and ask them where they think it is and what has happened. • Ask students to think of any other environmental problems and their causes Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:16 • Ask students to use a dictionary to check the meanings of the words in the box • Check the meaning of the words, either in translation or as definitions. Get students to think of synonyms, for example, litter / rubbish / trash, or similar phrases, for example, irrigate – move water to a place which has a small amount of water. • Tell students to read the text and complete the gaps. Note that there are eight verbs in the box but only six are needed. • Play the CD so that students can hear the complete text and check their answers. Ex: 2 p:16 • Play the CD again so that students can answer the true / false questions. • In a weaker class, play the CD twice so that students can correct the false sentences. • In a stronger class, ask students to correct the false sentences as they listen the first time. Ex: 3 p:16 • Ask students what the words in blue in the text have in common (they all refer to quantity). • Get students to complete the rules and definitions using the examples in the text. • Go through the rules and definitions with the class. Ask students to think of examples for each phrase, for example, a small amount of sugar / energy / water, plenty of milk / people information. Ex: 4 p:16 • Tell students to use the rules to choose the correct words in the sentences. • Give them a few minutes to complete the sentences. Go round the class and monitor, helping where necessary. • Check answers as a class. |
Students check the meaning of these verbs in a dictionary. Complete the text with six of the verbs. Then listen and check your answers ANSWERS : 1 irrigate 2 shrink 3 split 4 restore 5 flow 6 increase Students read and listen to the text. Write true or false. Correct the false sentences ANSWERS : 1 F - It was one of the largest lakes in the world. 2 F – It’s in Kazakhstan. 3 T 4 F – A small number of freshwater fish species have returned. 5 T Student study the words in blue in the text. Then choose the correct words to complete the rules and definitions ANSWERS: 1 uncountable 2 two 3 two 4 countable 5 100 percent 6 more than enough Students choose the correct words ANSWERS: 1 amount 2 plenty 3 both 4 several 5 all
|
Descriptor: - complete the text with six of the verbs Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - Write true or false. Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - choose the correct words to complete the rules and definitions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 11 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
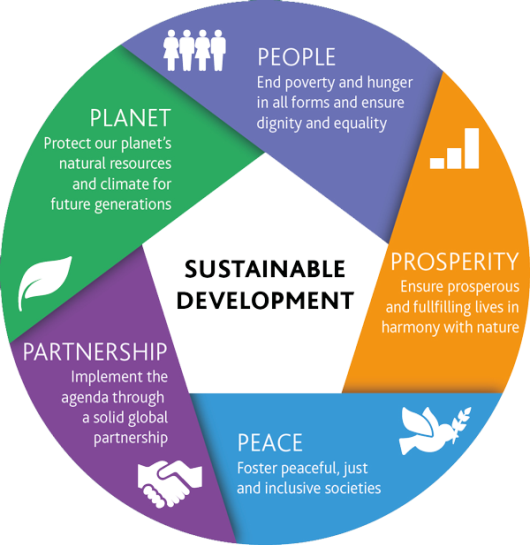
CLIL Geography: Sustainable development |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.5.1 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 8.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a growing range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics 8.2.7.1 recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level of a growing range of spoken genres |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary to do with sustainable development. • Read a text about sustainable development. • Talk about environmental problems and solutions. • Write a letter about an environmental problem. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, write the phrase sustainable development on the board. • Elicit or explain the meaning, and ask students to give examples of development that is sustainable. • Encourage students to contribute ideas, but do not confirm or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:17 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words, then use them to complete the text. • Do not check answers at this stage. Ex: 2 p:17 • After students have checked their answers to exercise 1, ask round the class to find out how many students answered correctly. Ex: 3 p:17 • Students read the text again more carefully and decide if the sentences are true or false. Remind them to correct the false sentence Ex: 4 p:17 • In pairs, students think of problems and sustainable solutions. If students are struggling, prompt them with suggestions, such as use of lights and heating, paper use, food packaging in packed lunches and in the canteen. • In a weaker class, allow students to discuss ideas in L1. In a stronger class, encourage them to use English as much as they can. |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box. Then complete the text. ANSWERS : Students’ own answer
Students read and listen to the text. Check yours answers’ in exercise 1 ANSWERS : 1 environment 2 solutions 3 recycles 4 community 5 facilities 6 save Student read the text again and write true or false. Correct the false sentences ANSWERS: 1 False. The leaders of more than 100 countries met at the Earth Summit. 2 True. 3 True. 4 False. It is easy for individuals to do something small every day to contribute to Local Agenda 21. 5 True. 6 False. People need their local councils to provide good facilities, such as recycling and public transport Students think about things at your school which have a negative impact on the environment. Make a list of problems and solutions ANSWERS: Students’ own answer
|
Descriptor: - complete the text. Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - read and listen to the text Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - write true or false. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - make a list of problems and solutions Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 12 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Unit Review 1 SAU 1 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.1.1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Practise vocabulary of household goods • Use vocabulary relating to the environment. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, write the phrase sustainable development on the board. • Elicit or explain the meaning, and ask students to give examples of development that is sustainable. • Encourage students to contribute ideas, but do not confirm or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:18 • After students have matched the words and photos, check answers, and drill pronunciation of new words. Ex: 2 p:18 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words and choose the correct words in the text. • Students listen to the complete text to check their answers. Encourage them to correct any mistakes. • Check answers and model and drill pronunciation. Ex: 3 p:18 • Students complete the sentences individually. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes before you check answers with the class. Summative Assessment for the unit 1 Speaking Task 1. Choose one card. Discuss statements with your partner saying whether you agree or disagree with him/her. Provide explanation to your answer. Answer the questions while speaking. You should speak at least 2 minutes. Listening Task 2. Listen to the speakers twice and choose the best answer A, B, C or D. CD2. Tapescript 1. And transcript for listening task can be found after the rubrics. |
Students complete the phrases with the words in the box ANSWERS : 1 a bottle 2 a roll 3 a tube 4 a bar 5 a tin / a can 6 a jar 7 a packet 8 a can Students complete the sentences with the verbs in the box ANSWERS : 1 throw away, recycle 2 save 3 pollute 4 poisons 5 burn 6 bury 7 waste Student choose the correct words ANSWERS: 1 many 2 too many 3 many 4 a lot of 5 any 6 enough 7 many 8 too many 9 fast enough 10 enough Students choose one card. Discuss statements with your partner saying whether you agree or disagree with him/her ANSWERS: Students’ own answer Students listen to the speakers twice and choose the best answer
|
Descriptor: - complete the phrases. Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 13 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review Unit 1 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.1.1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Practise vocabulary of household goods • Use vocabulary relating to the environment. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, write the phrase sustainable development on the board. • Elicit or explain the meaning, and ask students to give examples of development that is sustainable. • Encourage students to contribute ideas, but do not confirm or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 4 p:18 • Students write their sentences individually then compare with a partner. Encourage them to correct any mistakes in their partner’s sentences. • Ask individual students to read out some of their sentences to the class, and correct any errors. Ex: 5 p:18 • Point out that covering the dialogue will help students to focus on the form of the key phrases. • In a weaker class, if students can’t remember the exact phrasing, ask them to identify the type of word that is missing in each case (a verb). Clarify that these phrases are all polite ways to offer to do something, or ask someone to do something to help. • Students listen and check or complete their answers Ex: 6 p:18 • Allow students time to read the questions. Explain that in a true / false task, they should read the statements they are given very carefully. They may hear the opposite of these statements, so encourage them to think about relevant vocabulary first. • In a stronger class, ask if students can answer any of these before they listen again |
Students match the two parts of the sentences. Then complete the sentences with who, which, why and where. ANSWERS : 1 who e 2 which c 3 where a 4 where f 5 who d 6 which b
Students complete the dialogue with the phrases in the box ANSWERS : 1 How much 2 a lot 3 If you wan 4 that’s fine 5 some Student listen to a conversation about a ‘no impact’ lifestyle. Write true or false. ANSWERS: 1 False. She is interviewing Joe, who read Colin Beavan’s book. 2 True. 3 False. He buys bananas. 4 False. He buys fruit and vegetables from farmers’ markets. He still gets some things from the supermarket. 5 True. 6 False. He walks and travels by bus |
Descriptor: - complete the phrases. Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 14 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The internet |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.7.1 recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level of a growing range of spoken genres 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.2.1 write with minimal support about real and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topic |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn nouns and verbs to do with the internet. • Do a questionnaire about internet usage. • Learn the affirmative and negative forms of the present perfect. • Write sentences using the present perfect. • Write about your own experiences using the present perfect. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the word internet on the board. • Ask students how often they use the internet and what they use it for. Encourage students to contribute ideas. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:20 • In a stronger class, see if students can complete the table before referring to the text. In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs to complete the table. • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. • Check that students understand the new vocabulary. Draw attention to the way many verbs are created from nouns in modern English. Model and drill the pronunciation of any words that are new to students. Ex: 2 p:21 • Students do the questionnaire individually and check the key, then compare their answers in pairs. If students find any words in the key difficult, encourage them to discuss them with a partner to try to work out the meaning from the context. Ex: 3 p:21 • Look at the example with the class and check students understand how to use the verbs and nouns correctly. • In a weaker class, allow students time to prepare some questions individually, then ask and answer their questions in pairs. • In a stronger class, encourage students to ask and answer spontaneously. Ex: 4 p:21 • To introduce this language point, refer students back to the statements in the internet questionnaire on page 28. • Focus on the verbs and ask students if they know what tense they are in. Accept suggestions, but do not confirm or reject any ideas at this stage. Ex: 5 p:21 • Students work individually to write affirmative and negative sentences using the present perfect. • In a weaker class, do item 1 as an example as well, to model the affirmative form. • In a stronger class, you could ask students to write both the affirmative and negative form for each item. |
Students complete the table with words or phrases from the Are you well-connected questionnaire. Then listen and check ANSWERS : 1 download 2 share 3 message 4 blog 5 create 6 chat 7 play 8 search 9 use 10 attachment Students do the questionnaire. Answer yes or no. then check the key. ANSWERS : Students’ own answers. Student work in pairs. Ask and answer questions using the nouns and verbsю ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. Students study the examples. What are the long forms of ‘ve, ‘s, hasn’t and haven’t? Then choose the correct words in the rule ANSWERS: ’ve = have, ’s = has, hasn’t = has not, haven’t = have not 1 have 2 -ed 3 experiences Students write sentences using the present perfect affirmative and negative. ANSWERS: 1 We’ve created a webpage for our school. 2 I haven’t posted any messages this week. 3 She hasn’t looked at my blog. 4 My friend has changed his email address. 5 I haven’t chatted a lot today. 6 We haven’t downloaded that programme. 7 The internet has changed the way we communicate. 8 I’ve visited a lot of music websites. |
Descriptor: - complete the phrases. Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 15 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Internet addiction |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.5.1 Interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks 8.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.6.1 link, independently, sentences into coherent paragraphs using a variety of basic connectors on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about a virtual world and online computer games. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Learn about verb and noun collocations. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they play any games on their computers. • Elicit some answers, then ask if anyone plays Habbo or World of Warcraft. Ask students to describe what they do in the game and why they enjoy it. Ask how many hours a week they spend playing Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:22 • Refer students to the title of the article and elicit their answers. Encourage their suggestions, but do not confirm or deny their answers at this stage. Ex: 2 p:22 • Allow students time to read the list of ideas, then explain that they should scan the text and look for information that matches four of the headings. • In a weaker class, ask students to tell you which words they have underlined before they do the matching part of the exercise. In a stronger class, they can do both parts of the exercise before you check answers. • When students have listened to the CD, ask how many matched the sentences correctly. In a stronger class, ask students to explain which words helped them match the headings to the text. Ex: 3 p:22 • Students complete the summary of the text. In a weaker class, encourage them to work in pairs for support. Ex: 4 p:22 • Students match the verb and noun collocations by finding them in the text Ex: 5 p:22 • In a stronger class, you could ask the class what other collocations they can make with the verbs. |
Students read the title of the article. What do you think it means to be trapped in the net? ANSWERS : Students’ own answers. Students read the text and underline words and ideas that go with headings. Then match the headings with paragraphs. There is one heading that you don’t need. ANSWERS : 1 d 2 a 3 e 4 b Student complete the summary of the text with six of the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 internet 2 virtual 3 plays games 4 chat rooms 5 real 6 psychologists Students find the nouns in the text that go with this verbs ANSWERS: fight – battles recognize – a problem make – a sandwich feel – tired / depressed / isolated play – games spend – time Students complete the sentences with the correct form of the verbs. What are the new collocations? ANSWERS: 1 recognize 2 feel 3 spend 4 plays 5 make 6 fight New collocations: turn on, feel angry, spend money, play the piano, make noise, recognize a person, fight enemies |
Descriptor: - read the title of the article Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the summary of the text Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the correct form Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 16 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: Present perfect: regular and irregular verbs |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 8.6.7.1 use a variety of simple perfect forms to express recent, indefinite and unfinished past on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.2.3.1 understand with little or no support most of the detail of an argument in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn regular and irregular past participles. • Identify use of the present perfect in a conversation. • Practise using the present perfect in a discussion. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
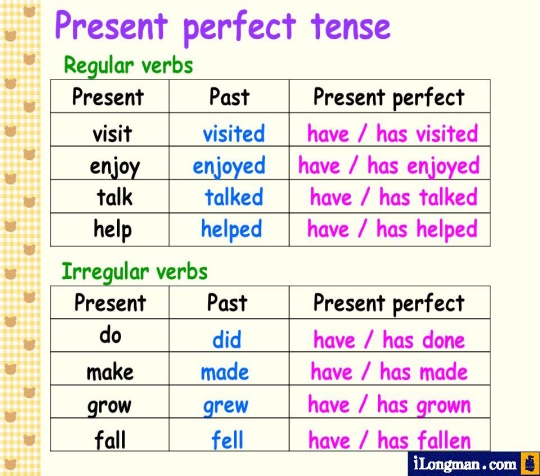
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students back to the language focus section on page 29 and ask how we form the past participle of most verbs. • Elicit that for regular verbs such as the ones on page 29, the past participle is the same as the past simple form: we add -ed to the verb. • Elicit examples of some irregular verbs. Explain that some verbs also have irregular past participles. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:23 • Once students have completed the table individually, ask them to check their answers in pairs. If students are not sure whether a verb is regular or irregular, tell them to check in their Irregular Verb list or a dictionary. • After students have checked their answers in the text, ask individual students to read out their answers Ex: 2 p:23 • Students add the verbs to the table from exercise 1. Again, refer them to Irregular Verb list or a dictionary if they need help with the irregular forms. In a weaker class, you could write the irregular verbs on the board in alphabetical order, to help them find the correct past participles. Ex: 3 p:23 • Tell students they are going to listen to a conversation about three people’s internet usage. • Play the CD twice. The first time, students should listen and see how much they can understand. The second time they listen, they can complete the table • Check answers by copying the table on the board and asking students to come up and complete the rows. Ex: 4 p:23 • Go through the examples with the class. • Refer students to the table for ideas. Students write their sentences in pairs. • Elicit some answers from the class. Ask the class to say whether the sentences are correct and to correct any mistakes. • Play the CD again for the pairs to check their answers. Ex: 5 p:23 • In a weaker class, allow students time to prepare some sentences individually, then ask them to compare their answers in pairs. • In a stronger class, encourage students to work with their books closed, if they can. They can refer to the vocabulary on page 28 to prompt them. |
Students complete the table with the past participle form of the verbs in the box. ANSWERS : Regular: join – joined, ruin – ruined Irregular: buy – bought, sleep – slept, eat – eaten, be – been, spend – spent Students add the verbs in the box to the table ANSWERS : Regular: stay – stayed, design – designed, play – played, visit – visited Irregular: have – had, find – found, sell – sold, write – written, speak – spoken, put – put, go – been/gone, make – made Student listen to a conversation. Tick things that the speakers have done and put a cross for things they haven’t done ANSWERS:
Students work in pairs and write sentences about Mark, Mary and Paul using verbs from ex. 1 and 2. Then listen again and check ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. Students compare your internet shopping activities With a partner. Then tell the class about your partner’s internet shopping ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. |
Descriptor: - complete the table Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - add the verbs in the box Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - work in pairs and write sentences Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 17 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Cybercrime |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary relating to cybercrime. • Listen to a radio programme about cybercrime. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. • Discuss problems with internet use. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write cybercrime on the board and elicit the meaning (crime which is committed using the internet or computers). • Ask students whether they can think of any types of crime that can be committed online and whether they know anyone who has had anything bad happen to them online. • Elicit ideas, and encourage students to participate and talk about their own experiences. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:24 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words in the box. • Check that students understand the new vocabulary. Model and drill the pronunciation of any words that are new to students. In a stronger class, check understanding by asking students to put the words into sentences. Ex: 2 p:24 • Read the texts with the class and explain that one of them is the correct introduction to a radio programme. They are going to listen to the complete radio programme and should then select which text is the correct presentation. • In a weaker class, help students by reminding them to look at the key words in each of the texts, then play the first paragraph of the recording twice for them to identify the best match Ex: 3 p:24 • Encourage students to read the options and look at the pictures. Tell them to think about what they remember from hearing the programme the first time and try to complete some of the answers if they can. • After checking answers, in a stronger class, encourage students to explain the reasons for their choices, and to say why the other options were not suitable. In a weaker class, you could provide a transcript of the text as a follow-up activity. Students identify the parts of the text with the information needed for the exercise. Ex: 4 p:24 • Students prepare their answers individually, then compare with a partner. In a weaker class, encourage students to make notes about their answers, to use as support while they are working. • Go round and listen as students are working and help as necessary. • Ask some students to report back to the class on their discussions.
|
Students check the meaning of the words in the box. Then complete the dialogue with six of the words ANSWERS : 1 inbox 2 spam filter 3 virus 4 firewall 5 phishing 6 password Students read presentation texts. Listen to the radio programme and choose the correct text. ANSWERS : 3 Student listen again and choose the correct answers ANSWERS: 1 a 2 c 3 b 4 a 5 a 6 c Students ask and answer the questions ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. |
Descriptor: - complete the dialogue with six of the words Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - choose the correct text. Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - ask and answer the questions Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 18 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: Present perfect: questions |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.2.1 ask more complex questions to get information about a growing range of general topics and some curricular topics 8.6.7.1 use a variety of simple perfect forms to express recent, indefinite and unfinished past on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the question form of the present perfect. • Learn how to talk about experiences. • Practise asking and answering questions about experiences using the present perfect. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students back to text 2 in exercise 2 on page 32. • Ask students to find verbs in the present perfect (Has … ever had, Have … received). • Elicit that the verbs use the question form of the present perfect. Ask students what they notice about the word order in the present perfect questions (the auxiliary verb have usually comes before the subject). Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:25 • Remind students of the radio programme they heard in the previous lesson. They do not need to remember every word, but explain that the gapped sentences come from there. • Ask students how they say ever in their language, and elicit the opposite of ever (never). • Read out the questions and elicit short answers. Ex: 2 p:25 • Students order the words individually, then compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes. Ex: 3 p:25 • In a weaker class, do the first question as an example with the class. In a stronger class, ask a volunteer to do the first item, and encourage other students to say whether it is correct or not. • After students have written the questions, check answers before students ask and answer. • Go round and listen as students ask and answer. Check they are using short answers correctly. If they answer yes to the questions, encourage them to give more details. Ex: 4 p:25 • Read the task with the students. Point out that there is one gap for each word that is missing from the dialogue, so they should remember this when they check their answers. • In a weaker class, remind students to read the responses in order to help them choose which verb to use. • Students work individually to complete the dialogue with the questions, then compare their answers in pairs. Students should correct any mistakes before you check with the class |
Students complete the sentences from the listening with the words in the box. ANSWERS : 1 attacked 2 Has 3 have 4 ’s Students order the words to make questions. Then write answers for the questions ANSWERS : 1 What websites have you visited recently? 2 Have your friends downloaded any music recently? 3 Why have you put that photo on the internet? 4 Have you ever lost a computer file? 5 Has she ever visited a chat room? 6 What have they written on the message board? Students complete the questions using the present perfect. Then ask and answer with a partner. ANSWERS: 1 Have you read 2 Has a virus attacked 3 Has your friend made 4 Have your grandparents used 5 Have you emailed 6 Has your teacher used Students complete the dialogue with questions in the present perfect ANSWERS: 1 Have you made 2 have you won 3 Have you created 4 have visited 5 Have you met 6 Have you stolen |
Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - order the words to make questions Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - complete the dialogue with questions in the present perfect Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 19 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Online shopping |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.13.1 use a growing variety of modal forms for different functions: obligation, necessity, possibility, permission, requests, suggestions, prohibition on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary relating to online shopping • Listen for general meaning and specific details. • Discuss problems with internet use. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students back to text 2 in exercise 2 on page 32. • Ask students to find verbs in the present perfect (Has … ever had, Have … received). • Elicit that the verbs use the question form of the present perfect. Ask students what they notice about the word order in the present perfect questions (the auxiliary verb have usually comes before the subject). Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:26 • Ask students how they say ever in their language, and elicit the opposite of ever (never). Explain the students look at the photo and answer the question • Read out the questions and elicit short answers. Ex: 2 p:26 • Listen the task with the students. Listen to the dialogue what does Lucy want to buy. • Students work individually to complete the dialogue with the questions, then compare their answers in pairs. Students should correct any mistakes before you check with the class Ex: 3 p:25 • Listen the task with the students. Complete the key phrases from the dialogue, so they should remember this when they check their answers. • Students work individually to complete the dialogue with the questions, then compare their answers in pairs. Students should correct any mistakes before you check with the class Ex: 4 p:25 • Read the task with the students. Read the rule and the examples to find three more examples in the dialogue. • Students work individually to complete the dialogue with the questions, then compare their answers in pairs. Students should correct any mistakes before you check with the class
|
Students look at the photo and answer the question ANSWERS : Lucy says she hasn't been on the computer for a long time Students listen to the dialogue what does Lucy want to buy. ANSWERS : Lucy want to buy an e-reader Students complete the key phrases from the dialogue ANSWERS: 1) blowing 2) bargain 3) sold 4) reviews 5) include 6) payment Students read the rule and the examples to find three more examples in the dialogue ANSWERS: Could you ask me next time? (request) May I order it? (request) Can you order it today? (permission) |
Descriptor: - answer the question Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the key phrases from the dialogue Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - find three more examples in the dialogue Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 20 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A comment on a website |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.6,1 recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended text 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model comment on an internet forum. • Learn key phrases for expressing opinions on an internet forum. • Learn how to add or contrast ideas. • Write a comment for an internet forum. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the word internet forum on the board and elicit the meaning. • Ask students what subjects people discuss on internet forums. Ask if students ever post comments on internet forums, and ask what they have posted comments about. • Elicit ideas and encourage students to participate and exchange ideas. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:27 • Look at the model text with the class and elicit ideas about where it is from (a website). Read the introductory question out to the class and check students understand what the rest of the article is (an opinion posted by somebody who has read the question). • In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs. • When you check answers, ask students to indicate the part of the text which gives the answers. Ex: 2 p:27 • Students complete the key phrases individually, then check their answers in the text. • Ask students to find the key phrases in the model text and translate them into their own language Ex: 3 p:27 • Once you have drawn attention to the blue words, students complete the table by identifying whether they add or contrast ideas. In a weaker class, ask students to translate the words. In a stronger class, encourage students to use them in their own sentences to show understanding Ex: 4 p:27 • Before students complete the sentences, remind them to read the sentences carefully to check they understand how the two ideas are linked.
|
Students read the model text and answer the question ANSWERS : 1 The writer is a 15-year-old boy called Sean. 2 The readers are other young people who use the internet. 3 The writer goes online every day. 4 Some of his friends are internet addicts. 5 The real problem is with the person, not with the activity they are addicted to. Students complete the key phrases. Then read the model text again and check ANSWERS : 1 my 2 seen 3 problem 4 reason Students study the words in blue in the model text. Then put these words into two groups ANSWERS: Adding ideas: also, too Contrast: but, Although, However Students complete the sentences with the words ANSWERS: 1 but 2 too 3 also 4 However 5 Although 6 but |
Descriptor: - read the model text Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the key phrases Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 21 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Daily life and shopping |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.6.1 use a variety of pronouns including indefinite pronouns anybody, anyone, anything and quantitative pronouns everyone, everything, none, more, less, a few on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a text about different types of shops. • Review how to use indefinite pronouns. • Develop vocabulary related to shopping. • Practise talking about shopping experiences. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Give students one minute to think of as many types of shop as they can and make a list. • Go through the students’ ideas as a class and write their suggestions on the board. You could do this as a competition – the winner is the student with the longest list. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:28 • Ask students to use a dictionary to check the meanings of the words in the box. • Check the meaning of the words, either in translation or as definitions. • Draw students’ attention to the word diagrams (sometimes called word spiders) and check they understand the idea by asking them where to put shop assistant (in the People category). • Give students enough time to add all the words to the diagram. Walk round and monitor Ex: 2 p:28 • Play the CD so that students can follow as they read. Students should just focus on the advantages of shopping rather than understanding the whole text. • Go through the answers with the whole class Ex: 3 p:28 • Draw students’ attention to the highlighted words in the text and ask them to complete the table. • In weaker classes, get students to discuss the question about some and any in pairs. In stronger classes, students can work individually. Ex: 4 p:28 • Tell students to use the indefinite pronouns from the table to complete the sentences with the correct words, focusing on whether the sentence is a statement, question or negative. • Give them a few minutes to complete the sentences. Go round the class and monitor, helping where necessary |
Students check the meaning words from the text in a dictionary. Then add the words to the correct category. ANSWERS : people: seller, customer places: bazaar, flea market, mall, stall, bakery things: sample, product activities: buy, haggle, pay, offer, order Students read and listen to the text, What advantages of shopping malls does the author mention? ANSWERS : The shops in malls are open until late. You can often get discounts in the sales. There are a lot of cafés, bakeries and restaurants where you can order both local and international food. There are entertainment facilities. Students read the rule and complete the table with indefinite pronouns from the text. ANSWERS: 1 everything 2 something 3 anywhere 4 no one Students choose the correct indefinite pronouns. ANSWERS: 1 No one 2 anything 3 everywhere 4 anyone 5 somewhere |
Descriptor: - read the model text Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - Students read and listen to the text Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - read the rule and complete the table with indefinite pronouns Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 22 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL Technology: The internet - wikis |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.1.1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary to do with newspapers. • Read a text about different types of newspaper. • Discuss different types of newspaper in your country. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they read any newspapers. If so, elicit the names of the newspapers. If not, elicit the names of different newspapers they have heard of. • Ask students what the differences are between the newspapers they have mentioned. Ask what types of information you would find in each. Elicit some ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:29 • After students have checked the meaning of the words, focus on the photos and ask students what they think is in each newspaper. Elicit a few ideas. • In pairs, students match the words to the photos. • Do not check answers at this stage. Ex: 2 p:29 • Students read and listen, and check their answers to exercise 1. Ex: 3 p:29 • Students read the text again and decide if the sentences are true or false. Tell them they should write a question mark if the point is not mentioned. • Ask students to compare answers in pairs, then check answers with the class. Ex: 4 p:29 • Allow students time to prepare their answers individually, then put them in pairs to ask and answer the questions. Monitor and help round the class. • Ask one or two students to read one of their answers to the class |
Students check the meaning words in the box. Then complete the text below ANSWERS : Students’ own answer Students read and listen to the text. Check your answer. Then match the headings with paragraphs. There is one heading that you don’t need. ANSWERS : Photo A: 2, 5, 6, 7, 9 Photo B: 1, 3, 4, 8, 9, 10 9 appears in both types of newspaper. Students read the text again and answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 False. A lot of people still prefer to get the news in a more traditional way, by reading a newspaper. 2 Don’t know. 3 True. 4 False. Quality newspapers use a formal style of language with longer sentences and technical vocabulary. Sensationalist newspapers use shorter words and sentences, with colloquial words and expressions. 5 True. 6 False. Both types of newspaper contain articles about sport. Students follow the instructions and create your own wiki ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. |
Descriptor: - read the model text Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - read the text again and answer the questions Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - follow the instructions and create your own wiki Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 23 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review unit 2 SAU 2 for unit |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.6.1 use a variety of pronouns including indefinite pronouns anybody, anyone, anything and quantitative pronouns everyone, everything, none, more, less, a few on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use nouns and verbs to do with the internet. • Use the word about a virtual world and online computer games. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they read any newspapers. If so, elicit the names of the newspapers. If not, elicit the names of different newspapers they have heard of. • Ask students what the differences are between the newspapers they have mentioned. Ask what types of information you would find in each. Elicit some ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:30 • In a stronger class, see if students can complete the table before referring to the text. In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs to complete the table. • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. • Check that students understand the new vocabulary. Draw attention to the way many verbs are created from nouns in modern English. Model and drill the pronunciation of any words that are new to students. Ex: 2 p:30 • Students complete the summary of the text. In a weaker class, encourage them to work in pairs for support. Ex: 3 p:29 • Students add the verbs to the table from exercise 1. Again, refer them to Irregular Verb list or a dictionary if they need help with the irregular forms. In a weaker class, you could write the irregular verbs on the board in alphabetical order, to help them find the correct past participles. Summative assessment for the unit 2 Reading Task 1. Read the text carefully. Select if the statements are TRUE or FALSE, put a tick in an appropriate column and EXPLAIN your choice. Writing Task 2. Write an essay about daily routine. You should write your essay according to the plan and structure and it has to be in the present simple. Look at the example of the essay that is given below |
Students complete the sentences with the words in the box ANSWERS : 1 email 2 download 3 message 4 blog 5 online games 6 posted 7 engines 8 website Students choose the correct words ANSWERS : 1 hacker 2 anti-virus software 3 spam 4 password 5 virus 6 a firewall Students write affirmative or negative sentences using the present perfect ANSWERS: 1 My mum has created a blog. 2 My friend has sent me a lot of emails. 3 We haven’t downloaded videos. 4 I’ve played an online game once. 5 My grandparents haven’t used the internet. 6 My friends have made money on the internet a few time |
Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - choose the correct Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - write affirmative or negative sentences Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 24 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review unit 2 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.6.1 use a variety of pronouns including indefinite pronouns anybody, anyone, anything and quantitative pronouns everyone, everything, none, more, less, a few on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use nouns and verbs to do with the internet. • Use the word about a virtual world and online computer games. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they read any newspapers. If so, elicit the names of the newspapers. If not, elicit the names of different newspapers they have heard of. • Ask students what the differences are between the newspapers they have mentioned. Ask what types of information you would find in each. Elicit some ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 4 p:30 • In a stronger class, see if students can complete the table before referring to the text. In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs to complete the table. • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. • Check that students understand the new vocabulary. Draw attention to the way many verbs are created from nouns in modern English. Model and drill the pronunciation of any words that are new to students. Ex: 5 p:30 • Students complete the summary of the text. In a weaker class, encourage them to work in pairs for support. Ex: 6 p:29 • Students add the verbs to the table from exercise 1. Again, refer them to Irregular Verb list or a dictionary if they need help with the irregular forms. In a weaker class, you could write the irregular verbs on the board in alphabetical order, to help them find the correct past participles.
|
Students write questions and short answers for the sentences ANSWERS : 1 Has your mum ever created a blog? Yes, she has. 2 Has your friend ever sent you a lot of emails? Yes, he / she has. 3 Have you ever downloaded videos? No, we haven’t. 4 Have you ever played an online game? Yes, I have. 5 Have your grandparents ever used the internet? No, they haven’t. 6 Have your friends ever made money on the internet? Yes, they have. Students match sentences with responses ANSWERS : 1 f 2 g 3 c 4 d 5 h 6 e 7 b 8 a Students listen to an interview with a mystery shopper and complete the notes ANSWERS: 1 Canadian 2 seventeen 3 hacker 4 eleven 5 programs 6 fun 7 easy 8 information 9 a few times 10 once or twice |
Descriptor: - write questions and short answers Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - match sentences with responses Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - listen to an interview with a mystery shopper Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 25 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Tasks for the Summative Assessment for the term 1 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.3.1 Understand with little or no support most of the detail of an argument in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.4.3.1 Understand the detail of an argument on a range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.5.3.1 Write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics. 8.3.3.1 Give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use nouns and verbs to do with the internet. • Use the word about a virtual world and online computer games. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they read any newspapers. If so, elicit the names of the newspapers. If not, elicit the names of different newspapers they have heard of. • Ask students what the differences are between the newspapers they have mentioned. Ask what types of information you would find in each. Elicit some ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Tasks for the Summative Assessment for the term 1 Listening Task 1. Listen to Trent Simons twice. Mark the following sentences TRUE or FALSE. CD3. Tapescript 1. And transcript for listening task can be found after the mark scheme. Reading Task 1. Read the text and circle the most suitable answer. Writing Task. Choose ONE of the topics to write. Topic 1. You received a letter from your friend in which he says that he is having a problem in communication with his older sister. Write a reply giving your friend advice on how to make better relations with his family member. Pay attention to the grammar. Spell words correctly. Use the following plan: Topic 2. Write a letter to your friend inviting him to your country/city and describe how you would spend one day. Pay attention to the grammar. Spell words correctly. Use the following plan: Speaking Task. Choose one of the cards and answer the questions. You have 1 minute to prepare and 1-2 minutes to speak. |
Students listen to Trent Simons twice. Mark the following sentences TRUE or FALSE ANSWERS : Students read the text and circle the most suitable answer. ANSWERS : Students choose ONE of the topics to write. ANSWERS: Students choose one of the cards and answer the questions ANSWERS: |
Descriptor: - listen to Trent Simons twice Total: 6 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - read the text and circle the most suitable answer Total: 6 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - choose ONE of the topics to write Total: 6 point Descriptor: - choose one of the cards and answer the questions Total: 6 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 26 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Skills round-up 2. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 8.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a growing range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use nouns and verbs to do with the internet. • Use the word about a virtual world and online computer games. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they read any newspapers. If so, elicit the names of the newspapers. If not, elicit the names of different newspapers they have heard of. • Ask students what the differences are between the newspapers they have mentioned. Ask what types of information you would find in each. Elicit some ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:31 Using pictures related to the text for discussion. Ex: 2 p:31 Listening for global information Ex: 3 p:31 Listening for specific information. Sentence completion.
|
Students look at the photo and answer the question ANSWERS : A music festival Students listen to a conversation. ANSWERS : Dilnaz went to the FourE festival last year Students listen again and complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1) Almaty 2) art 3) online 4) tent 5) expensive 6) bread 7) bus 8) white
|
Descriptor: - answer the question Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - listen to a conversation. Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - listen again and complete the sentences |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
English plus, grade 8, term 1
English plus, grade 8, term 1
Short term plan
|
Unit: 1 Our World lesson 1 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Welcome; Adjectives |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 8.2.7.1 recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level of a growing range of spoken genres 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Review adjectives. . • Do a quiz on The world around you. • Ask and answer questions using adjectives. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask individual students questions such as What’s your favourite TV programme / animal / food? Ask them to describe the item they have chosen. Write any adjectives they use on the board and elicit that they are adjectives. • Elicit and write up other adjectives that students know Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary to do with television.
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:4 • Read through the adjectives in the box with the class. In a weaker class, match the first two items as an example. In a stronger class, you could start this as a quick quiz. Call out an adjective from the box at random and ask students to put up their hands as soon as they know the answer. • Students complete the activity individually or in pairs. After confirming their answers with the recording, you could play the audio again to drill the pronunciation of any new adjectives Ex: 2 p:4 • Read the title of the quiz with the class and elicit a translation or definition. You may need to explain around: you could say that this quiz covers the things we see, hear and experience in the world. • In a weaker class, check that students have chosen the correct words before they move on to think of answers. • Students think of answers individually or in pairs. • Ask the class for ideas for each question, then confirm with the recording Ex: 1 p:5 • In a weaker class, allow students to find the comparative and superlative forms and write the rules in pairs. Ex: 2 p:5 • Go through the example with the class. Encourage students to think about the adjective exciting in relation to all three activities. Ex: 4 p:5 • Students complete the sentences in pairs. In a weaker class, write these answers on the board and highlight the third person singular changes to prompt the class. • In a stronger class, elicit the rule as a class activity |
Students match adjectives with their opposites in the box. ANSWERS : 1 cheap 2 rare 3 weak 4 quiet 5 dangerous 6 unhealthy 7 clean 8 near 9 easy 10 heavy 11 useless 12 exciting
Students work in pairs. Choose the correct words in World around you quiz. Then think of an answer for each description. ANSWERS : 1 near (Neptune) 2 noisy (Tokyo) 3 common (mosquito) 4 powerful (whale) 5 cheap (plastic) 6 expensive (platinum) Students complete the tables with adjectives. Then answer the question. ANSWERS: 1 rarer 2 expensive 3 further 4 nearest 5 hottest 6 common 7 furthest Students write a comparative and superlative sentence for each group of words. ANSWERS: Students own answer Students complete the sentences from the quiz. ANSWERS: 1 make 2 don’t speak 3 loves 4 doesn’t live |
Descriptor: - match adjectives with their opposites Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - Choose the correct words Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the tables with adjectives Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - complete the sentences from the quiz Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit: 1 Our World lesson 2 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Everyday objects |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.1.1understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.6.2.1 use a growing variety of quantifiers for countable and uncountable nouns including several, plenty, a large/small number/amount on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.3.1.1 use formal and informal registers in their talk on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary of household goods. • Learn how to say numbers. • Do a quiz about human consumers. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the words carbon footprint on the board and ask students what they understand by it. Ask if students think they have a big or small carbon footprint and why. • Ask what makes a person’s carbon footprint bigger, and elicit some ideas such as travelling by car, using energy in the home and buying lots of goods Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria - Practise comparing opinions.
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:8 • After students have matched the words and photos, check answers, and drill pronunciation of new words. Ex: 2 p:8 Discuss students’ ideas with the class. Ex: 3 p: 9 • Read through the key phrases with the class before students write the numbers. In a weaker class, do the first item on the board as an example, then allow them to complete the activity in pairs. In a stronger class, invite volunteers up to the board to write the numbers, and encourage the rest of the class to correct any mistakes. • Play the CD and pause for students to repeat the numbers. • Students work individually to answer the quiz by choosing the numbers they think complete each gap. Don’t check answers at this stage. Ex: 4 p: 9 • Ask students to compare their answers. If they have made different choices from their partner, ask them to explain their reasons for their answer, but don’t say who is correct. • Play the CD twice for them to check. |
Students match the words in the boxes with photos. The listen and check ANSWERS : 1 a can of fizzy drink 2 a bottle of shampoo 3 a roll of toilet paper 4 a box of washing powder 5 a packet of crisps 6 a bag of apples 7 a bar of chocolate 8 a jar of coffee 9 a tube of toothpaste 10 a carton of juice Students work in pairs. Think of more containers and contents ANSWERS: Students of answer Students study the key phrases and write the numbers. Listen and say the numbers. ANSWERS: Students of answer Students compare your answers to the quiz with a partner. Then listen and check ANSWERS: 1) 628; 1,700 2) 4.8; 9.8 3) 198; 656 4) 4.5, 21; 1,201 5) 10,354; 854 6)120,000; 8 7) 24,000; 720,000 8) 276; 4,239 9) 74,802; 49,717; 38,320 |
Descriptor: - match the words in the boxes with photos Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples
Descriptor: - work in pairs Total: 1 point Descriptor: - study the key phrases and write the numbers Total: 1 point Descriptor: - compare your answers to the quiz Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 24 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit: 1 Our World lesson 3 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Grammar: much, many, a lot of |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 8.3.3.1 give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.6.2.1 use a growing variety of quantifiers for countable and uncountable nouns including several, plenty, a large/small number/amount on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn expressions of quantity and practise using them. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the words carbon footprint on the board and ask students what they understand by it. Ask if students think they have a big or small carbon footprint and why. • Ask what makes a person’s carbon footprint bigger, and elicit some ideas such as travelling by car, using energy in the home and buying lots of goods Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary to do with television.
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 5 p:9 • Make sure that students understand the terms countable and uncountable. In a weaker class, give examples, such as Apples – can you count them? (Yes.) Water – can you count it? (No.) In a stronger class, ask students to give you examples. • Look at the sentences and ask students to identify the nouns. Ask students to work in pairs to decide whether the nouns are countable or uncountable and complete the table by putting the blue phrases in the correct columns. Ex: 6 p:9 • Students choose the correct words individually • In a stronger class, once you have checked answers, ask students to invent answers to the questions
Ex: 7 p:9 • Read through the task with the class, and make sure students understand what they have to do. • Recap the phrases in exercise 5, and remind students to refer to the completed version in their notebooks. • Go through the examples, then model the activity by asking one or two confident students the first few questions. • Students work in pairs to ask and answer the questions. • Ask some students to report back to the class on what they learnt about their partner |
Students read the sentences. Are the nouns countable or uncountable? Complete the table with the words in blue. ANSWERS : 1 uncountable 2 countable 3 countable 4 uncountable 5 uncountable 6uncountable, countable, uncountable . 7countable, uncountable 8countable, uncountable Uncountable nouns: 2 much 3 a lot of 4 some Countable nouns: 1 not many 5 not any Students choose the correct words ANSWERS : 1 much 2 many 3 some 4 much 5 any 6 any Students work in pairs. Ask and answer with your own ideas. Use the phrases in the table in ex.5 and numbers. ANSWERS: 1 Do you eat much pasta each week? How much? 2 Do you walk many kilometres every month? How many? 3 Are there many books in the school library? How many? 4 Do you use a lot of toothpaste each year? How much? 5 Do you drink much milk every week? How much? 6 Do you say many words every day? How many? Students’ own answers
|
Descriptor: - Complete the table with the words in blue Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - work in pairs Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit: Our World lesson 4 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The "no impact" family |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts and some extended texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.2.3.1 understand with little or no support most of the detail of an argument in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.3.1 give an opinion at discourse level on a range of general and curricular range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn how to predict before you read. • Read about a family that wants to reduce its impact on the environment. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Learn about compound nouns |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the words low impact and high impact on the board. • Explain that your impact on the environment is the effect that you have, through things you do such as travelling and using energy. • Ask students if they think they have a low impact or a high impact on the environment. Ask how they could reduce their impact. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria - Learn the negative and question forms of the past simple. |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:10 • Refer students to the pictures and the title of the text. Explain that trying to predict what the text is about before they read will help them to understand it better. • Students decide which of the sentences they think are true and false. They can discuss their ideas in pairs. , • Encourage students to read the text quickly to check their ideas. Tell them not to worry about the gaps at this stage. Ex: 2 p: 10 • Focus students on the sentences and explain that these complete the gaps in the text. • Explain that students should read each paragraph carefully. When they reach the gap, they should read through all the options to see which one contains information which is correct and relevant. • Students can work individually then compare their ideas in pairs Ex: 3 p:10 • Read through the information and examples with the class. Students find four more compound nouns in the text. Ask them to read silently then put up their hands when they find one, for you to write on the board. There are several more examples in the text, so you can stop at four or carry on with more examples • In a stronger class, ask students if they can think of any more examples that aren’t in the text. Ex: 4 p:10 • Explain that students are going to practise some more compound nouns. • Students complete the sentences individually, then compare with a partner. In a weaker class, do the first item as an example. |
Students look at the photos and the title of the text. Predict which of the sentences are true or false. Then read the text and check your answers. ANSWERS : 1 True. 2 False. 3 True. 4 True. 5 False. 6 True. Students complete the text with sentences. There is one sentence that you don’t need. Then listen and check your answer. ANSWERS: 1 b 2 e 3 c 4 a Students read the information and complete the examples. Then find four more compound nouns in the text. ANSWERS : 1 shopping 2 bed 3 washes More compound nouns in the text: toilet paper, dishwasher, light bulb, bathroom, shampoo bottles, toothpaste, secondhand things, plastic bags, takeaway food, plastic cup, plastic pots, lifestyle Students complete the sentences with the words in the box. ANSWERS : 1 strawberry 4 washing 2 Christmas 5 kitchen 3 shopping 6 chicken |
Descriptor: - read the text Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the text with sentences Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - read the information and complete the examples Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the words in the box Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 4 P: 25 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit: Our World lesson 5 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: S |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: Relative pronouns |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn about relative pronouns. • Practise using relative pronouns. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students back to exercise 3 on page 20 and ask: What’s a shopping bag? • Write the answer a bag which is for shopping on the board and underline the relative pronoun which. • Ask the questions What’s a teacher? and What’s a school? Elicit the answers, e.g. a person who teaches and a place where you learn and write these on the board. If students use the correct relative pronouns, underline them; if students use incorrect relative pronouns, leave these as gaps on the board Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for television programmes
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:11 • Ask students to work in pairs to complete the sentences and the rules. • Check answers with the class, then if the examples on the board are still gapped, ask students to complete them. Ex: 2 p:11 • Read the title of the text with the class. In a weaker class, translate the title then discuss students’ opinion of the concept of buying locally, in L1 if necessary. In a stronger class, elicit an explanation of the title then ask students if this is something they think about when shopping. • After students have completed the text with the correct relative pronouns, ask them to compare answers in pairs before you check answers with the class. Ex: 3 p:11 • Students write their sentences individually then compare with a partner. Encourage them to correct any mistakes in their partner’s sentences. • Ask individual students to read out some of their sentences to the class, and correct any errors. Ex: 4 p:11 • Read through the task with the class. Ask two students to read out the example, and check students understand how to use the table. Then ask a confident student to think of another sentence, or give one yourself. Encourage another class member to guess the person, place or thing, and if they are not correct, encourage someone else to guess. • Students continue the activity. Allow them time to write their sentences, and go round helping if necessary. In a weaker class, check students have formed the sentences correctly before they ask and answer. In a stronger class, you might find that students can think of items spontaneously without needing a long planning stage. |
Students complete the sentences from the text. Then complete the rules with places, people, reasons and things ANSWERS : 1 who 2 where 3 which
Rules ANSWERS 1 people 2 places 3 things
Students complete the text with who, why, where and which ANSWERS : 1 which 2 where 3 which 4 where 5 which 6 who Students complete the sentences with your own ideas. Use who, where or which. Compare with a partner. ANSWERS: 1 where … 2 which … 3 who … 4 which … 5 who … 6 which … Students write six sentences with who, where, why and which. ANSWERS: Students own answer |
Descriptor: - complete the sentences - complete the rules Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples
Descriptor: - complete the text with who, why, where and which Total: 1 point
-Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - write six sentences with who, where, why and which Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End |
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 6 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Pollution and the environment |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary relating to the environment. • Listen to an account of someone who decided to make a difference to the environment. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students what things they already do to help the environment. • Write students’ ideas on the board. Ask what other things people can do to help the environment. Ask if they think that an individual can make a big difference. Encourage students to express their own opinions Lead - In
How do we solve this problem? |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:11 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words and choose the correct words in the text. • Students listen to the complete text to check their answers. Encourage them to correct any mistakes. • Check answers and model and drill pronunciation Ex: 2 p:11 • Allow students time to read through the questions individually before they ask and answer in pairs. • Elicit some answers from the class. If students are interested in the subject, you could conduct a short class discussion on some of the issues raised. Ex: 3 p:11 • Focus on the pictures and ask students which problem they think Rebecca Hosking was concerned about. • Explain that the sentences summarize different parts of the text, but that they are in the wrong sequence. Ask students to read the sentences carefully, and check vocabulary with them. Encourage students to think about the key words carrying meaning in each sentence, as this will help them when they listen. • After students have put the information about Rebecca in order, allow them to listen to check their answers. • Find out how many guessed the sequence correctly. Ex: 4 p:11 • Allow students time to read the questions. Explain that in a true / false task, they should read the statements they are given very carefully. They may hear the opposite of these statements, so encourage them to think about relevant vocabulary first. • In a stronger class, ask if students can answer any of these before they listen again |
Students check the meaning of the words in blue. Choose the correct words. Then listen and check ANSWERS : 1 throw away 2 reuse 3 recycle 4 destroy 5 burn 6 poisons 7 bury
Students work in pairs. Ask and answer the question ANSWERS : Students’ own answers Students read the information about Rebecca Hosking Order sentences then listen and check ANSWERS: b, d, a, c Students listen again and write true or false. Correct the false sentences. ANSWERS: 1 False. The speaker is the presenter of SOS Environment. 2 True. 3 False. She was shocked when she saw how many creatures were dying because of all the plastic in the sea. 4 True. 5 False. None of the shops give plastic bags. 6 True.
|
Descriptor: - Choose the correct words Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - work in pairs Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - read the information about Rebecca Hosking Order Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the information about Rebecca Hosking Order Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 24 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 7 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: too, too much, too many, enough, not enough |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn too, too much, too many, enough and not enough. • Practise using too, too much, too many, enough and not enough. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students if they can remember the missing words from the recording. If they can, fill in the gaps and ask why we say too much plastic but too many plastic bags (because much refers to the noun, plastic and many referes to the noun, bags). • If students cannot remember the missing words, elicit the words in their own language meaning ‘more than we need’, which would fill the gaps Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:13 • After studying the examples, students copy the rules and complete them. Encourage them to compare ideas in pairs before you check answers. Ex: 2 p:13 • Students complete the sentences individually. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes before you check answers with the class Ex: 3 p:13 • Read the example sentences and elicit the target word (enough). Look at the bold words and demonstrate that the relevant part of speech is shown in brackets. • In a weaker class, students can discuss the rules in pairs before you check answers. In a stronger class, do this as a class discussion and write the answers on the board. Ex: 4 p:13 • Students work individually to order the questions. Check these before students listen to the CD. • After listening to the CD, ask students to write the answers and to compare in pairs before you check with the class Ex: 5 p:13 • Look at the shopping list and the picture with the class. Go through the examples and ask students to point to the items shown. Ask: How much soap is there on the list? (One bar.) How much soap is there in the basket? (One bar.) Ask Is this enough, not enough or too much soap? (Enough.) Repeat with packets of crisps and show that there are too many packets of crisps. • In a weaker class, quickly revise which items are countable and which are uncountable. • Put students into pairs to write sentences. |
Students study these sentences from the listening. Then complete the rules with adjectives, countable nouns and uncountable nouns ANSWERS : 1 uncountable nouns 2 countable nouns 3 adjective
Students complete the sentences with too, too much or too many. ANSWERS : 1 too 2 too much 3 too many 4 too much 5 too many 6 too 7 too many, too much Students study these sentences from the listening. Then complete the rules with before or after ANSWERS: 1 after 2 after 3 before Student order the words to make questions. Then listen to a conversation and answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 Is this pizza big enough? Yes, it’s big enough. 2 Are there enough apples? There are too many apples. 3 Have we got enough drinks? No, we haven’t got enough drinks. 4 Is this soup hot enough? No, it’s cold. 5 Have we got enough sandwiches? Yes, we’ve got a lot. 6 Is this coffee strong enough? Yes, the coffee’s really strong |
Descriptor: - complete the rules with adjectives Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the sentences with too, too much or too many Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - make questions Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 8 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Offering and asking for help |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.4.1 understand with little or no support most of the implied meaning in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a growing range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a dialogue in which people offer and ask for help. • Learn key phrases for offering and asking for help. • Practise offering and asking for help. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they ever organize events with their friends. • Ask them to imagine that they want to organize a party or barbecue with some friends. Ask what things they need to plan, and elicit some ideas. • Ask if one person will do everything, and elicit that they will ask their friends for help. • Tell students they are going to practise offering and asking for help. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:14 • Look at the photo and elicit ideas. Tell students to look at clues in the photo such as the food and the outdoor setting. Ex: 2 p:14 • Read the task and clarify that the first time students listen, they should just identify what it is that Adam needs. They do not need to understand every word at this stage. Ex: 3 p:14 • Point out that covering the dialogue will help students to focus on the form of the key phrases. • In a weaker class, if students can’t remember the exact phrasing, ask them to identify the type of word that is missing in each case (a verb). Clarify that these phrases are all polite ways to offer to do something, or ask someone to do something to help. • Students listen and check or complete their answers. Ex: 4 p:14 • Read out the first sentence and emphasize how the words ending in consonants are linked in speech to those beginning with vowels (A bag of ice). Ex: 5 p:14 • In a weaker class, do an example with students. Look at the first sentence and identify the adjective dirty. Ask student to think of verbs that would offer help in this situation (clean / tidy). Help them transform this into a sentence (Shall I (help you) clean / tidy it?) |
Students look at the photo. What are Lucy and Adam preparing? ANSWERS : Lucy and Adam are preparing a barbecue.
Students listen to the dialogue. What does Adam need? ANSWERS : Adam needs some more drinks, a bag of ice and some bags for the rubbish. Students cover the dialogue and complete the key phrases. ANSWERS: 1 help you with anything? (offering help) 2 get a few cartons of juice or something? (offering help) 3 get a bag of ice, too. (offering help) 4 get some? (asking for help) 5 see what they’ve got. (offering help) Student listen and repeat the sentences practise linking the words ANSWERS: 1 clean it 2 help you 3 come with you 4 be quiet 5 buy some more 6 call him
|
Descriptor: - look at the photo. Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - cover the dialogue Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - listen and repeat the sentences Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 9 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
An environmental problem 1 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a growing range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study an email about an environmental problem. • Learn key phrases for writing about a problem. • Learn about so and because. • Write an email about an environmental problem. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students what environmental problems there are in their town or area. Elicit some ideas. • Ask students what they can do if they notice an environmental problem in their area. Elicit that they can write to people in the area, encouraging them to help solve the problem. If students do not come up with this idea, prompt them by asking what Rebecca Hosking did when she noticed the problem with plastic bags Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:15 • Focus students on the photo and ask for ideas about the topic of the text. Discuss these as a class, then read the title and confirm that it is about dirty beaches. • After reading the model text and answering the questions, students can compare answers in pairs before you check with the class. Ex: 2 p:15 • Read through the key phrases with the class and ask students to identify the phrases that are used in the text to start the paragraphs. • Check answers, then allow students to complete each phrase with their own ideas. • Ask students to find the key phrases in the model text. Ex: 3 p:15 • Read the examples with the class and elicit the continuation from the text: I’m writing because I was at the beach … . There aren’t enough bins … , so I think we need more. • If necessary, explain the difference between so and because by transforming the second example so that it contains because: We need more bins because there aren’t enough bins. Ask students to translate the two sentences into their own language. • Students match and link the sentence halves. Ex: 4 p:15 • Read the task with the class. • Students think and plan their emails individually. In a weaker class, brainstorm some ideas and vocabulary first with the class. • Students write their emails. This can be set for homework. • Tell students to check their work, and check they have used so and because correctly, and that they have used too, too much, too many, enough, not enough, and possibly, perhaps, maybe, definitely. In a stronger class, encourage students to swap their emails with a partner for correction |
Students read the model text and choose the correct answers ANSWERS : 1 b 2 b 3 b 4 c
Students study the key phrases. Complete the key phrases with your own ideas ANSWERS : I’m writing because … I think there are possibly (two) reasons for this. We must do something about … Students’ own answers. Students complete the examples from the text. Then match with a-e. Use so or because ANSWERS: 1 d; because 2 a; so 3 e; so 4 c; because 5 b; because Student follow the steps in the writing guide. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers.
|
Descriptor: - read the model text Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - Complete the key phrases Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - listen and repeat the sentences Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 10 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My county: Our world |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.7.1 recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level of a growing range of spoken genres 8.6.2.1 use a growing variety of quantifiers for countable and uncountable nouns including several, plenty, a large/small number/amount on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a text about an environmental problem in Kazakhstan. • Review phrases to talk about quantity with countable and uncountable nouns. • Learn verbs connected with the environment. • Participate in a discussion about local environmental problems. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Draw students’ attention to the photo of the stranded ships and ask them where they think it is and what has happened. • Ask students to think of any other environmental problems and their causes Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:16 • Ask students to use a dictionary to check the meanings of the words in the box • Check the meaning of the words, either in translation or as definitions. Get students to think of synonyms, for example, litter / rubbish / trash, or similar phrases, for example, irrigate – move water to a place which has a small amount of water. • Tell students to read the text and complete the gaps. Note that there are eight verbs in the box but only six are needed. • Play the CD so that students can hear the complete text and check their answers. Ex: 2 p:16 • Play the CD again so that students can answer the true / false questions. • In a weaker class, play the CD twice so that students can correct the false sentences. • In a stronger class, ask students to correct the false sentences as they listen the first time. Ex: 3 p:16 • Ask students what the words in blue in the text have in common (they all refer to quantity). • Get students to complete the rules and definitions using the examples in the text. • Go through the rules and definitions with the class. Ask students to think of examples for each phrase, for example, a small amount of sugar / energy / water, plenty of milk / people information. Ex: 4 p:16 • Tell students to use the rules to choose the correct words in the sentences. • Give them a few minutes to complete the sentences. Go round the class and monitor, helping where necessary. • Check answers as a class. |
Students check the meaning of these verbs in a dictionary. Complete the text with six of the verbs. Then listen and check your answers ANSWERS : 1 irrigate 2 shrink 3 split 4 restore 5 flow 6 increase Students read and listen to the text. Write true or false. Correct the false sentences ANSWERS : 1 F - It was one of the largest lakes in the world. 2 F – It’s in Kazakhstan. 3 T 4 F – A small number of freshwater fish species have returned. 5 T Student study the words in blue in the text. Then choose the correct words to complete the rules and definitions ANSWERS: 1 uncountable 2 two 3 two 4 countable 5 100 percent 6 more than enough Students choose the correct words ANSWERS: 1 amount 2 plenty 3 both 4 several 5 all
|
Descriptor: - complete the text with six of the verbs Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - Write true or false. Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - choose the correct words to complete the rules and definitions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 11 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL Geography: Sustainable development |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.5.1 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 8.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a growing range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics 8.2.7.1 recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level of a growing range of spoken genres |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary to do with sustainable development. • Read a text about sustainable development. • Talk about environmental problems and solutions. • Write a letter about an environmental problem. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, write the phrase sustainable development on the board. • Elicit or explain the meaning, and ask students to give examples of development that is sustainable. • Encourage students to contribute ideas, but do not confirm or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:17 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words, then use them to complete the text. • Do not check answers at this stage. Ex: 2 p:17 • After students have checked their answers to exercise 1, ask round the class to find out how many students answered correctly. Ex: 3 p:17 • Students read the text again more carefully and decide if the sentences are true or false. Remind them to correct the false sentence Ex: 4 p:17 • In pairs, students think of problems and sustainable solutions. If students are struggling, prompt them with suggestions, such as use of lights and heating, paper use, food packaging in packed lunches and in the canteen. • In a weaker class, allow students to discuss ideas in L1. In a stronger class, encourage them to use English as much as they can. |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box. Then complete the text. ANSWERS : Students’ own answer
Students read and listen to the text. Check yours answers’ in exercise 1 ANSWERS : 1 environment 2 solutions 3 recycles 4 community 5 facilities 6 save Student read the text again and write true or false. Correct the false sentences ANSWERS: 1 False. The leaders of more than 100 countries met at the Earth Summit. 2 True. 3 True. 4 False. It is easy for individuals to do something small every day to contribute to Local Agenda 21. 5 True. 6 False. People need their local councils to provide good facilities, such as recycling and public transport Students think about things at your school which have a negative impact on the environment. Make a list of problems and solutions ANSWERS: Students’ own answer
|
Descriptor: - complete the text. Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - read and listen to the text Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - write true or false. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - make a list of problems and solutions Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 12 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Unit Review 1 SAU 1 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.1.1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Practise vocabulary of household goods • Use vocabulary relating to the environment. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, write the phrase sustainable development on the board. • Elicit or explain the meaning, and ask students to give examples of development that is sustainable. • Encourage students to contribute ideas, but do not confirm or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:18 • After students have matched the words and photos, check answers, and drill pronunciation of new words. Ex: 2 p:18 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words and choose the correct words in the text. • Students listen to the complete text to check their answers. Encourage them to correct any mistakes. • Check answers and model and drill pronunciation. Ex: 3 p:18 • Students complete the sentences individually. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes before you check answers with the class. Summative Assessment for the unit 1 Speaking Task 1. Choose one card. Discuss statements with your partner saying whether you agree or disagree with him/her. Provide explanation to your answer. Answer the questions while speaking. You should speak at least 2 minutes. Listening Task 2. Listen to the speakers twice and choose the best answer A, B, C or D. CD2. Tapescript 1. And transcript for listening task can be found after the rubrics. |
Students complete the phrases with the words in the box ANSWERS : 1 a bottle 2 a roll 3 a tube 4 a bar 5 a tin / a can 6 a jar 7 a packet 8 a can Students complete the sentences with the verbs in the box ANSWERS : 1 throw away, recycle 2 save 3 pollute 4 poisons 5 burn 6 bury 7 waste Student choose the correct words ANSWERS: 1 many 2 too many 3 many 4 a lot of 5 any 6 enough 7 many 8 too many 9 fast enough 10 enough Students choose one card. Discuss statements with your partner saying whether you agree or disagree with him/her ANSWERS: Students’ own answer Students listen to the speakers twice and choose the best answer
|
Descriptor: - complete the phrases. Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Our World lesson 13 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review Unit 1 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.1.1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Practise vocabulary of household goods • Use vocabulary relating to the environment. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, write the phrase sustainable development on the board. • Elicit or explain the meaning, and ask students to give examples of development that is sustainable. • Encourage students to contribute ideas, but do not confirm or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution
|
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 4 p:18 • Students write their sentences individually then compare with a partner. Encourage them to correct any mistakes in their partner’s sentences. • Ask individual students to read out some of their sentences to the class, and correct any errors. Ex: 5 p:18 • Point out that covering the dialogue will help students to focus on the form of the key phrases. • In a weaker class, if students can’t remember the exact phrasing, ask them to identify the type of word that is missing in each case (a verb). Clarify that these phrases are all polite ways to offer to do something, or ask someone to do something to help. • Students listen and check or complete their answers Ex: 6 p:18 • Allow students time to read the questions. Explain that in a true / false task, they should read the statements they are given very carefully. They may hear the opposite of these statements, so encourage them to think about relevant vocabulary first. • In a stronger class, ask if students can answer any of these before they listen again |
Students match the two parts of the sentences. Then complete the sentences with who, which, why and where. ANSWERS : 1 who e 2 which c 3 where a 4 where f 5 who d 6 which b
Students complete the dialogue with the phrases in the box ANSWERS : 1 How much 2 a lot 3 If you wan 4 that’s fine 5 some Student listen to a conversation about a ‘no impact’ lifestyle. Write true or false. ANSWERS: 1 False. She is interviewing Joe, who read Colin Beavan’s book. 2 True. 3 False. He buys bananas. 4 False. He buys fruit and vegetables from farmers’ markets. He still gets some things from the supermarket. 5 True. 6 False. He walks and travels by bus |
Descriptor: - complete the phrases. Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 14 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The internet |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.7.1 recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level of a growing range of spoken genres 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.2.1 write with minimal support about real and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topic |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn nouns and verbs to do with the internet. • Do a questionnaire about internet usage. • Learn the affirmative and negative forms of the present perfect. • Write sentences using the present perfect. • Write about your own experiences using the present perfect. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the word internet on the board. • Ask students how often they use the internet and what they use it for. Encourage students to contribute ideas. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:20 • In a stronger class, see if students can complete the table before referring to the text. In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs to complete the table. • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. • Check that students understand the new vocabulary. Draw attention to the way many verbs are created from nouns in modern English. Model and drill the pronunciation of any words that are new to students. Ex: 2 p:21 • Students do the questionnaire individually and check the key, then compare their answers in pairs. If students find any words in the key difficult, encourage them to discuss them with a partner to try to work out the meaning from the context. Ex: 3 p:21 • Look at the example with the class and check students understand how to use the verbs and nouns correctly. • In a weaker class, allow students time to prepare some questions individually, then ask and answer their questions in pairs. • In a stronger class, encourage students to ask and answer spontaneously. Ex: 4 p:21 • To introduce this language point, refer students back to the statements in the internet questionnaire on page 28. • Focus on the verbs and ask students if they know what tense they are in. Accept suggestions, but do not confirm or reject any ideas at this stage. Ex: 5 p:21 • Students work individually to write affirmative and negative sentences using the present perfect. • In a weaker class, do item 1 as an example as well, to model the affirmative form. • In a stronger class, you could ask students to write both the affirmative and negative form for each item. |
Students complete the table with words or phrases from the Are you well-connected questionnaire. Then listen and check ANSWERS : 1 download 2 share 3 message 4 blog 5 create 6 chat 7 play 8 search 9 use 10 attachment Students do the questionnaire. Answer yes or no. then check the key. ANSWERS : Students’ own answers. Student work in pairs. Ask and answer questions using the nouns and verbsю ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. Students study the examples. What are the long forms of ‘ve, ‘s, hasn’t and haven’t? Then choose the correct words in the rule ANSWERS: ’ve = have, ’s = has, hasn’t = has not, haven’t = have not 1 have 2 -ed 3 experiences Students write sentences using the present perfect affirmative and negative. ANSWERS: 1 We’ve created a webpage for our school. 2 I haven’t posted any messages this week. 3 She hasn’t looked at my blog. 4 My friend has changed his email address. 5 I haven’t chatted a lot today. 6 We haven’t downloaded that programme. 7 The internet has changed the way we communicate. 8 I’ve visited a lot of music websites. |
Descriptor: - complete the phrases. Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 15 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Internet addiction |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.5.1 Interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks 8.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.6.1 link, independently, sentences into coherent paragraphs using a variety of basic connectors on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about a virtual world and online computer games. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Learn about verb and noun collocations. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they play any games on their computers. • Elicit some answers, then ask if anyone plays Habbo or World of Warcraft. Ask students to describe what they do in the game and why they enjoy it. Ask how many hours a week they spend playing Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:22 • Refer students to the title of the article and elicit their answers. Encourage their suggestions, but do not confirm or deny their answers at this stage. Ex: 2 p:22 • Allow students time to read the list of ideas, then explain that they should scan the text and look for information that matches four of the headings. • In a weaker class, ask students to tell you which words they have underlined before they do the matching part of the exercise. In a stronger class, they can do both parts of the exercise before you check answers. • When students have listened to the CD, ask how many matched the sentences correctly. In a stronger class, ask students to explain which words helped them match the headings to the text. Ex: 3 p:22 • Students complete the summary of the text. In a weaker class, encourage them to work in pairs for support. Ex: 4 p:22 • Students match the verb and noun collocations by finding them in the text Ex: 5 p:22 • In a stronger class, you could ask the class what other collocations they can make with the verbs. |
Students read the title of the article. What do you think it means to be trapped in the net? ANSWERS : Students’ own answers. Students read the text and underline words and ideas that go with headings. Then match the headings with paragraphs. There is one heading that you don’t need. ANSWERS : 1 d 2 a 3 e 4 b Student complete the summary of the text with six of the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 internet 2 virtual 3 plays games 4 chat rooms 5 real 6 psychologists Students find the nouns in the text that go with this verbs ANSWERS: fight – battles recognize – a problem make – a sandwich feel – tired / depressed / isolated play – games spend – time Students complete the sentences with the correct form of the verbs. What are the new collocations? ANSWERS: 1 recognize 2 feel 3 spend 4 plays 5 make 6 fight New collocations: turn on, feel angry, spend money, play the piano, make noise, recognize a person, fight enemies |
Descriptor: - read the title of the article Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the summary of the text Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the correct form Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 16 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: Present perfect: regular and irregular verbs |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 8.6.7.1 use a variety of simple perfect forms to express recent, indefinite and unfinished past on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.2.3.1 understand with little or no support most of the detail of an argument in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn regular and irregular past participles. • Identify use of the present perfect in a conversation. • Practise using the present perfect in a discussion. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students back to the language focus section on page 29 and ask how we form the past participle of most verbs. • Elicit that for regular verbs such as the ones on page 29, the past participle is the same as the past simple form: we add -ed to the verb. • Elicit examples of some irregular verbs. Explain that some verbs also have irregular past participles. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:23 • Once students have completed the table individually, ask them to check their answers in pairs. If students are not sure whether a verb is regular or irregular, tell them to check in their Irregular Verb list or a dictionary. • After students have checked their answers in the text, ask individual students to read out their answers Ex: 2 p:23 • Students add the verbs to the table from exercise 1. Again, refer them to Irregular Verb list or a dictionary if they need help with the irregular forms. In a weaker class, you could write the irregular verbs on the board in alphabetical order, to help them find the correct past participles. Ex: 3 p:23 • Tell students they are going to listen to a conversation about three people’s internet usage. • Play the CD twice. The first time, students should listen and see how much they can understand. The second time they listen, they can complete the table • Check answers by copying the table on the board and asking students to come up and complete the rows. Ex: 4 p:23 • Go through the examples with the class. • Refer students to the table for ideas. Students write their sentences in pairs. • Elicit some answers from the class. Ask the class to say whether the sentences are correct and to correct any mistakes. • Play the CD again for the pairs to check their answers. Ex: 5 p:23 • In a weaker class, allow students time to prepare some sentences individually, then ask them to compare their answers in pairs. • In a stronger class, encourage students to work with their books closed, if they can. They can refer to the vocabulary on page 28 to prompt them. |
Students complete the table with the past participle form of the verbs in the box. ANSWERS : Regular: join – joined, ruin – ruined Irregular: buy – bought, sleep – slept, eat – eaten, be – been, spend – spent Students add the verbs in the box to the table ANSWERS : Regular: stay – stayed, design – designed, play – played, visit – visited Irregular: have – had, find – found, sell – sold, write – written, speak – spoken, put – put, go – been/gone, make – made Student listen to a conversation. Tick things that the speakers have done and put a cross for things they haven’t done ANSWERS:
Students work in pairs and write sentences about Mark, Mary and Paul using verbs from ex. 1 and 2. Then listen again and check ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. Students compare your internet shopping activities With a partner. Then tell the class about your partner’s internet shopping ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. |
Descriptor: - complete the table Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - add the verbs in the box Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - work in pairs and write sentences Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 17 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Cybercrime |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary relating to cybercrime. • Listen to a radio programme about cybercrime. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. • Discuss problems with internet use. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write cybercrime on the board and elicit the meaning (crime which is committed using the internet or computers). • Ask students whether they can think of any types of crime that can be committed online and whether they know anyone who has had anything bad happen to them online. • Elicit ideas, and encourage students to participate and talk about their own experiences. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:24 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words in the box. • Check that students understand the new vocabulary. Model and drill the pronunciation of any words that are new to students. In a stronger class, check understanding by asking students to put the words into sentences. Ex: 2 p:24 • Read the texts with the class and explain that one of them is the correct introduction to a radio programme. They are going to listen to the complete radio programme and should then select which text is the correct presentation. • In a weaker class, help students by reminding them to look at the key words in each of the texts, then play the first paragraph of the recording twice for them to identify the best match Ex: 3 p:24 • Encourage students to read the options and look at the pictures. Tell them to think about what they remember from hearing the programme the first time and try to complete some of the answers if they can. • After checking answers, in a stronger class, encourage students to explain the reasons for their choices, and to say why the other options were not suitable. In a weaker class, you could provide a transcript of the text as a follow-up activity. Students identify the parts of the text with the information needed for the exercise. Ex: 4 p:24 • Students prepare their answers individually, then compare with a partner. In a weaker class, encourage students to make notes about their answers, to use as support while they are working. • Go round and listen as students are working and help as necessary. • Ask some students to report back to the class on their discussions.
|
Students check the meaning of the words in the box. Then complete the dialogue with six of the words ANSWERS : 1 inbox 2 spam filter 3 virus 4 firewall 5 phishing 6 password Students read presentation texts. Listen to the radio programme and choose the correct text. ANSWERS : 3 Student listen again and choose the correct answers ANSWERS: 1 a 2 c 3 b 4 a 5 a 6 c Students ask and answer the questions ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. |
Descriptor: - complete the dialogue with six of the words Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - choose the correct text. Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - ask and answer the questions Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 18 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: Present perfect: questions |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.2.1 ask more complex questions to get information about a growing range of general topics and some curricular topics 8.6.7.1 use a variety of simple perfect forms to express recent, indefinite and unfinished past on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the question form of the present perfect. • Learn how to talk about experiences. • Practise asking and answering questions about experiences using the present perfect. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students back to text 2 in exercise 2 on page 32. • Ask students to find verbs in the present perfect (Has … ever had, Have … received). • Elicit that the verbs use the question form of the present perfect. Ask students what they notice about the word order in the present perfect questions (the auxiliary verb have usually comes before the subject). Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:25 • Remind students of the radio programme they heard in the previous lesson. They do not need to remember every word, but explain that the gapped sentences come from there. • Ask students how they say ever in their language, and elicit the opposite of ever (never). • Read out the questions and elicit short answers. Ex: 2 p:25 • Students order the words individually, then compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes. Ex: 3 p:25 • In a weaker class, do the first question as an example with the class. In a stronger class, ask a volunteer to do the first item, and encourage other students to say whether it is correct or not. • After students have written the questions, check answers before students ask and answer. • Go round and listen as students ask and answer. Check they are using short answers correctly. If they answer yes to the questions, encourage them to give more details. Ex: 4 p:25 • Read the task with the students. Point out that there is one gap for each word that is missing from the dialogue, so they should remember this when they check their answers. • In a weaker class, remind students to read the responses in order to help them choose which verb to use. • Students work individually to complete the dialogue with the questions, then compare their answers in pairs. Students should correct any mistakes before you check with the class |
Students complete the sentences from the listening with the words in the box. ANSWERS : 1 attacked 2 Has 3 have 4 ’s Students order the words to make questions. Then write answers for the questions ANSWERS : 1 What websites have you visited recently? 2 Have your friends downloaded any music recently? 3 Why have you put that photo on the internet? 4 Have you ever lost a computer file? 5 Has she ever visited a chat room? 6 What have they written on the message board? Students complete the questions using the present perfect. Then ask and answer with a partner. ANSWERS: 1 Have you read 2 Has a virus attacked 3 Has your friend made 4 Have your grandparents used 5 Have you emailed 6 Has your teacher used Students complete the dialogue with questions in the present perfect ANSWERS: 1 Have you made 2 have you won 3 Have you created 4 have visited 5 Have you met 6 Have you stolen |
Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - order the words to make questions Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - complete the dialogue with questions in the present perfect Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 19 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Online shopping |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.13.1 use a growing variety of modal forms for different functions: obligation, necessity, possibility, permission, requests, suggestions, prohibition on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary relating to online shopping • Listen for general meaning and specific details. • Discuss problems with internet use. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students back to text 2 in exercise 2 on page 32. • Ask students to find verbs in the present perfect (Has … ever had, Have … received). • Elicit that the verbs use the question form of the present perfect. Ask students what they notice about the word order in the present perfect questions (the auxiliary verb have usually comes before the subject). Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:26 • Ask students how they say ever in their language, and elicit the opposite of ever (never). Explain the students look at the photo and answer the question • Read out the questions and elicit short answers. Ex: 2 p:26 • Listen the task with the students. Listen to the dialogue what does Lucy want to buy. • Students work individually to complete the dialogue with the questions, then compare their answers in pairs. Students should correct any mistakes before you check with the class Ex: 3 p:25 • Listen the task with the students. Complete the key phrases from the dialogue, so they should remember this when they check their answers. • Students work individually to complete the dialogue with the questions, then compare their answers in pairs. Students should correct any mistakes before you check with the class Ex: 4 p:25 • Read the task with the students. Read the rule and the examples to find three more examples in the dialogue. • Students work individually to complete the dialogue with the questions, then compare their answers in pairs. Students should correct any mistakes before you check with the class
|
Students look at the photo and answer the question ANSWERS : Lucy says she hasn't been on the computer for a long time Students listen to the dialogue what does Lucy want to buy. ANSWERS : Lucy want to buy an e-reader Students complete the key phrases from the dialogue ANSWERS: 1) blowing 2) bargain 3) sold 4) reviews 5) include 6) payment Students read the rule and the examples to find three more examples in the dialogue ANSWERS: Could you ask me next time? (request) May I order it? (request) Can you order it today? (permission) |
Descriptor: - answer the question Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the key phrases from the dialogue Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - find three more examples in the dialogue Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 20 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A comment on a website |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.6,1 recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended text 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model comment on an internet forum. • Learn key phrases for expressing opinions on an internet forum. • Learn how to add or contrast ideas. • Write a comment for an internet forum. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the word internet forum on the board and elicit the meaning. • Ask students what subjects people discuss on internet forums. Ask if students ever post comments on internet forums, and ask what they have posted comments about. • Elicit ideas and encourage students to participate and exchange ideas. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:27 • Look at the model text with the class and elicit ideas about where it is from (a website). Read the introductory question out to the class and check students understand what the rest of the article is (an opinion posted by somebody who has read the question). • In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs. • When you check answers, ask students to indicate the part of the text which gives the answers. Ex: 2 p:27 • Students complete the key phrases individually, then check their answers in the text. • Ask students to find the key phrases in the model text and translate them into their own language Ex: 3 p:27 • Once you have drawn attention to the blue words, students complete the table by identifying whether they add or contrast ideas. In a weaker class, ask students to translate the words. In a stronger class, encourage students to use them in their own sentences to show understanding Ex: 4 p:27 • Before students complete the sentences, remind them to read the sentences carefully to check they understand how the two ideas are linked.
|
Students read the model text and answer the question ANSWERS : 1 The writer is a 15-year-old boy called Sean. 2 The readers are other young people who use the internet. 3 The writer goes online every day. 4 Some of his friends are internet addicts. 5 The real problem is with the person, not with the activity they are addicted to. Students complete the key phrases. Then read the model text again and check ANSWERS : 1 my 2 seen 3 problem 4 reason Students study the words in blue in the model text. Then put these words into two groups ANSWERS: Adding ideas: also, too Contrast: but, Although, However Students complete the sentences with the words ANSWERS: 1 but 2 too 3 also 4 However 5 Although 6 but |
Descriptor: - read the model text Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - complete the key phrases Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 21 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Daily life and shopping |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.6.1 use a variety of pronouns including indefinite pronouns anybody, anyone, anything and quantitative pronouns everyone, everything, none, more, less, a few on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a text about different types of shops. • Review how to use indefinite pronouns. • Develop vocabulary related to shopping. • Practise talking about shopping experiences. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Give students one minute to think of as many types of shop as they can and make a list. • Go through the students’ ideas as a class and write their suggestions on the board. You could do this as a competition – the winner is the student with the longest list. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:28 • Ask students to use a dictionary to check the meanings of the words in the box. • Check the meaning of the words, either in translation or as definitions. • Draw students’ attention to the word diagrams (sometimes called word spiders) and check they understand the idea by asking them where to put shop assistant (in the People category). • Give students enough time to add all the words to the diagram. Walk round and monitor Ex: 2 p:28 • Play the CD so that students can follow as they read. Students should just focus on the advantages of shopping rather than understanding the whole text. • Go through the answers with the whole class Ex: 3 p:28 • Draw students’ attention to the highlighted words in the text and ask them to complete the table. • In weaker classes, get students to discuss the question about some and any in pairs. In stronger classes, students can work individually. Ex: 4 p:28 • Tell students to use the indefinite pronouns from the table to complete the sentences with the correct words, focusing on whether the sentence is a statement, question or negative. • Give them a few minutes to complete the sentences. Go round the class and monitor, helping where necessary |
Students check the meaning words from the text in a dictionary. Then add the words to the correct category. ANSWERS : people: seller, customer places: bazaar, flea market, mall, stall, bakery things: sample, product activities: buy, haggle, pay, offer, order Students read and listen to the text, What advantages of shopping malls does the author mention? ANSWERS : The shops in malls are open until late. You can often get discounts in the sales. There are a lot of cafés, bakeries and restaurants where you can order both local and international food. There are entertainment facilities. Students read the rule and complete the table with indefinite pronouns from the text. ANSWERS: 1 everything 2 something 3 anywhere 4 no one Students choose the correct indefinite pronouns. ANSWERS: 1 No one 2 anything 3 everywhere 4 anyone 5 somewhere |
Descriptor: - read the model text Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - Students read and listen to the text Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - read the rule and complete the table with indefinite pronouns Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 22 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL Technology: The internet - wikis |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.1.1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary to do with newspapers. • Read a text about different types of newspaper. • Discuss different types of newspaper in your country. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they read any newspapers. If so, elicit the names of the newspapers. If not, elicit the names of different newspapers they have heard of. • Ask students what the differences are between the newspapers they have mentioned. Ask what types of information you would find in each. Elicit some ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:29 • After students have checked the meaning of the words, focus on the photos and ask students what they think is in each newspaper. Elicit a few ideas. • In pairs, students match the words to the photos. • Do not check answers at this stage. Ex: 2 p:29 • Students read and listen, and check their answers to exercise 1. Ex: 3 p:29 • Students read the text again and decide if the sentences are true or false. Tell them they should write a question mark if the point is not mentioned. • Ask students to compare answers in pairs, then check answers with the class. Ex: 4 p:29 • Allow students time to prepare their answers individually, then put them in pairs to ask and answer the questions. Monitor and help round the class. • Ask one or two students to read one of their answers to the class |
Students check the meaning words in the box. Then complete the text below ANSWERS : Students’ own answer Students read and listen to the text. Check your answer. Then match the headings with paragraphs. There is one heading that you don’t need. ANSWERS : Photo A: 2, 5, 6, 7, 9 Photo B: 1, 3, 4, 8, 9, 10 9 appears in both types of newspaper. Students read the text again and answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 False. A lot of people still prefer to get the news in a more traditional way, by reading a newspaper. 2 Don’t know. 3 True. 4 False. Quality newspapers use a formal style of language with longer sentences and technical vocabulary. Sensationalist newspapers use shorter words and sentences, with colloquial words and expressions. 5 True. 6 False. Both types of newspaper contain articles about sport. Students follow the instructions and create your own wiki ANSWERS: Students’ own answers. |
Descriptor: - read the model text Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - read the text again and answer the questions Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - follow the instructions and create your own wiki Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 23 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review unit 2 SAU 2 for unit |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.6.1 use a variety of pronouns including indefinite pronouns anybody, anyone, anything and quantitative pronouns everyone, everything, none, more, less, a few on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use nouns and verbs to do with the internet. • Use the word about a virtual world and online computer games. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they read any newspapers. If so, elicit the names of the newspapers. If not, elicit the names of different newspapers they have heard of. • Ask students what the differences are between the newspapers they have mentioned. Ask what types of information you would find in each. Elicit some ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:30 • In a stronger class, see if students can complete the table before referring to the text. In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs to complete the table. • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. • Check that students understand the new vocabulary. Draw attention to the way many verbs are created from nouns in modern English. Model and drill the pronunciation of any words that are new to students. Ex: 2 p:30 • Students complete the summary of the text. In a weaker class, encourage them to work in pairs for support. Ex: 3 p:29 • Students add the verbs to the table from exercise 1. Again, refer them to Irregular Verb list or a dictionary if they need help with the irregular forms. In a weaker class, you could write the irregular verbs on the board in alphabetical order, to help them find the correct past participles. Summative assessment for the unit 2 Reading Task 1. Read the text carefully. Select if the statements are TRUE or FALSE, put a tick in an appropriate column and EXPLAIN your choice. Writing Task 2. Write an essay about daily routine. You should write your essay according to the plan and structure and it has to be in the present simple. Look at the example of the essay that is given below |
Students complete the sentences with the words in the box ANSWERS : 1 email 2 download 3 message 4 blog 5 online games 6 posted 7 engines 8 website Students choose the correct words ANSWERS : 1 hacker 2 anti-virus software 3 spam 4 password 5 virus 6 a firewall Students write affirmative or negative sentences using the present perfect ANSWERS: 1 My mum has created a blog. 2 My friend has sent me a lot of emails. 3 We haven’t downloaded videos. 4 I’ve played an online game once. 5 My grandparents haven’t used the internet. 6 My friends have made money on the internet a few time |
Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - choose the correct Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - write affirmative or negative sentences Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 24 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review unit 2 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.6.1 use a variety of pronouns including indefinite pronouns anybody, anyone, anything and quantitative pronouns everyone, everything, none, more, less, a few on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use nouns and verbs to do with the internet. • Use the word about a virtual world and online computer games. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they read any newspapers. If so, elicit the names of the newspapers. If not, elicit the names of different newspapers they have heard of. • Ask students what the differences are between the newspapers they have mentioned. Ask what types of information you would find in each. Elicit some ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 4 p:30 • In a stronger class, see if students can complete the table before referring to the text. In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs to complete the table. • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. • Check that students understand the new vocabulary. Draw attention to the way many verbs are created from nouns in modern English. Model and drill the pronunciation of any words that are new to students. Ex: 5 p:30 • Students complete the summary of the text. In a weaker class, encourage them to work in pairs for support. Ex: 6 p:29 • Students add the verbs to the table from exercise 1. Again, refer them to Irregular Verb list or a dictionary if they need help with the irregular forms. In a weaker class, you could write the irregular verbs on the board in alphabetical order, to help them find the correct past participles.
|
Students write questions and short answers for the sentences ANSWERS : 1 Has your mum ever created a blog? Yes, she has. 2 Has your friend ever sent you a lot of emails? Yes, he / she has. 3 Have you ever downloaded videos? No, we haven’t. 4 Have you ever played an online game? Yes, I have. 5 Have your grandparents ever used the internet? No, they haven’t. 6 Have your friends ever made money on the internet? Yes, they have. Students match sentences with responses ANSWERS : 1 f 2 g 3 c 4 d 5 h 6 e 7 b 8 a Students listen to an interview with a mystery shopper and complete the notes ANSWERS: 1 Canadian 2 seventeen 3 hacker 4 eleven 5 programs 6 fun 7 easy 8 information 9 a few times 10 once or twice |
Descriptor: - write questions and short answers Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - match sentences with responses Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - listen to an interview with a mystery shopper Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 25 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Tasks for the Summative Assessment for the term 1 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.3.1 Understand with little or no support most of the detail of an argument in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.4.3.1 Understand the detail of an argument on a range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.5.3.1 Write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics. 8.3.3.1 Give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use nouns and verbs to do with the internet. • Use the word about a virtual world and online computer games. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they read any newspapers. If so, elicit the names of the newspapers. If not, elicit the names of different newspapers they have heard of. • Ask students what the differences are between the newspapers they have mentioned. Ask what types of information you would find in each. Elicit some ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Tasks for the Summative Assessment for the term 1 Listening Task 1. Listen to Trent Simons twice. Mark the following sentences TRUE or FALSE. CD3. Tapescript 1. And transcript for listening task can be found after the mark scheme. Reading Task 1. Read the text and circle the most suitable answer. Writing Task. Choose ONE of the topics to write. Topic 1. You received a letter from your friend in which he says that he is having a problem in communication with his older sister. Write a reply giving your friend advice on how to make better relations with his family member. Pay attention to the grammar. Spell words correctly. Use the following plan: Topic 2. Write a letter to your friend inviting him to your country/city and describe how you would spend one day. Pay attention to the grammar. Spell words correctly. Use the following plan: Speaking Task. Choose one of the cards and answer the questions. You have 1 minute to prepare and 1-2 minutes to speak. |
Students listen to Trent Simons twice. Mark the following sentences TRUE or FALSE ANSWERS : Students read the text and circle the most suitable answer. ANSWERS : Students choose ONE of the topics to write. ANSWERS: Students choose one of the cards and answer the questions ANSWERS: |
Descriptor: - listen to Trent Simons twice Total: 6 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - read the text and circle the most suitable answer Total: 6 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - choose ONE of the topics to write Total: 6 point Descriptor: - choose one of the cards and answer the questions Total: 6 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan
|
Unit 1: Daily life and shopping lesson 26 |
School |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Skills round-up 2. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 8.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a growing range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use nouns and verbs to do with the internet. • Use the word about a virtual world and online computer games. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they read any newspapers. If so, elicit the names of the newspapers. If not, elicit the names of different newspapers they have heard of. • Ask students what the differences are between the newspapers they have mentioned. Ask what types of information you would find in each. Elicit some ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others. Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Learn vocabulary about pollution |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 p:31 Using pictures related to the text for discussion. Ex: 2 p:31 Listening for global information Ex: 3 p:31 Listening for specific information. Sentence completion.
|
Students look at the photo and answer the question ANSWERS : A music festival Students listen to a conversation. ANSWERS : Dilnaz went to the FourE festival last year Students listen again and complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1) Almaty 2) art 3) online 4) tent 5) expensive 6) bread 7) bus 8) white
|
Descriptor: - answer the question Total: 1 point Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Descriptor: - listen to a conversation. Total: 1 point -Make CCQ questions Yes / No Descriptor: - listen again and complete the sentences |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: P: |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|

шағым қалдыра аласыз