
Жамбыл облысы Байзақ ауданы
№1 мектеп-гимназиясы
Ізденуші : Нишанова Жұлдыз
7 «б» сынып оқушысы
ЖҮЗІМ ҰЛУЫНЫҢ ТҰРАҚТАНДЫРЫЛҒАН РЕФЛЕКСТІ
ДАМЫТУДЫҢ
ДИНАМИКАСЫ
Бағыты: Жаратылыстану
Секция: Биология
Ғылыми жетекшісі: Нурманова Айгуль Куйчибаевна
Биология пәнінің мұғалімі
Мазмұны
І.Кіріспе
Моллюскілердің экономикалық
маңызы
ІІ.Негізгі бөлім
2. 1. Жүзім ұлуының эколого-биологиялық ерекшеліктері
2.2. Шартты рефлекс және оның мағынасы
2.3 Шырындардың шартты қорғаныс рефлексін ұйымдастыру
2.4 Препараттардың жү,йке жүйесіне әсері ,
ІІІ. Зерттеу бөлімі
3.1.Құралдарды дайындау
3.2. Эксперименттердің нәтижелері
Қорытынды
Пайдаланылған әдебиеттер
Қосымша
Кіріспе
Өркениеттің дамуының қазіргі кезеңінде табиғатқа антропогендік әсері экожүйелердің нашарлауына және биосфераның гендік әртүрлілігінің төмендеуіне әкелетін қайтарымсыз процестерге әкеледі. Көптеген өсімдіктер мен жануарлардың түрлерін сақтау және биоценозды қорғау бойынша шаралар жүйесін әзірлеу қажеттілігі бұрыннан танылды.
Соған қарамастан, жануарлардың кейбір түрлері, негізінен омыртқасыздар, биологиялық әртүрлілікті сақтауға қатысты көптеген зерттеушілердің назарынан тыс қалған. Алайда, бұл ағзалардың экожүйелердің тұрақтылығын қамтамасыз етудегі рөлі, табиғат заттарының циклы процестері, топырақтың қалыптасуы және биодеградация өте жоғары және бұл биогеоценоздың бұл компоненттеріне әсер етеді, бұл қоғамдағы қайтымсыз өзгерістерге алып келеді.
Тазартулар Қазақстанның жерүсті экожүйесінің ажырамас бөлігі болып табылады. Органикалық заттардың ыдырауы мен минералдануына қатысады, олар табиғатта заттардың айналымында маңызды байланыс ретінде әрекет етеді [8]. Моллюскілердің экономикалық маңызы бар. Қазіргі уақытта биологиялық ғалымдардың, микробиологтардың, дәрігерлердің зерттеулерінің арқасында жүзім ұлуын қолдану ауқымы кеңейіп келеді, демек, бұл моллюсгумның коммерциялық маңыздылығы үнемі артып келеді. Бұл факт, жүзімдік ұлуларын адамның тарапынан ерекше назар аударатындығына әкелді. Ол ойластырылмаған көптеген жоюлардан қорғалуы керек, сондықтан ол туралы толық ақпарат қажет [5].
Жануарларды сыртқы ортада өмір сүрудің өзгеретін жағдайына бейімдеу жүйке жүйесінің қызметі арқылы қамтамасыз етіледі және рефлексиялық белсенділік арқылы жүзеге асырылады. Эволюция процесінде галеолярлы реакциялар (шартсыз рефлекстер) пайда болды, түрлі органдардың функцияларын біріктіреді және үйлестіреді, ағзаны бейімдеуді жүзеге асырады [2].
Helix тектес жүзім ұлуының жүйке жүйесін ұйымдастыру адамның жүйке жүйесіне қарағанда қарапайым, бірақ сигнал беру және құрылымның принципі бірдей. Бұл жүйрік жүйенің салыстырмалы қарапайымдылығы нейробиологиядағы зерттеулер үшін тартымды етеді. Зығырдың қол жетімділігі мен үлкен мөлшері оларды неміс ғалымдарының зерттеуге дейінгі объектісі болуға мүмкіндік берді, тіпті соңғы ғасырда да [3].
Мақсаты мен міндеттері
Біз гипотезаны жасадық: түрлі дәрі-дәрмектер және сыртқы жағдайлар жүзім ұлуындағы шартты рефлексті дамытуға және бекітуге әсер етуі мүмкін.
Осыған байланысты осы зерттеудің мақсаты жүзім ұлуының тастарындағы шартты рефлексті дамытуға әртүрлі дәрілік заттар мен түрлі температуралардың әсерін анықтау болды.
Мақсатқа сүйене отырып, келесі міндеттер қойылды:
- жүзім ұлуының тұтқында өмірін және мінез-құлқын зерттеу;
- эксперименталды 5 топтарда жүзім ұлуының шартты қорғаныс рефлексін дамыту;
- әртүрлі зерттеу топтарындағы жүзім ұлуының шартты рефлексті сақтау уақытын анықтау
2.1.Жүзім ұлуының эколого-биологиялық ерекшеліктері
Жүзім ұлуы(Helium pomatia) - біздің жануарлар әлемінің ең ірі былқылдақ денелі жануарлар. Жүйелік позиция [8] (А қосымшасы):
Патшалық - жануарлар;
Түрі - ұлулар;
Class - былқылдақ денелілер;
Отряд – өкпе ұлулары;
Отбасы - гелицид;
Отбасы - Helix;
Түрі - жүзім ұлуы;
Халықаралық ғылыми атауы - Helix pomatia
Жүзім ұлуының туған жері - Орталық және Оңтүстік-Шығыс Еуропа. Ұзақ уақыт бойы адамдар жүзім ұлуын азық ретінде пайдаланды, олар нәзіктікке ие болмады, ал кез-келген әлеуметтік мәртебелі адамдар оларды қолжетімді және пайдалы тамақ ретінде пайдаланды [8].
Жүзім ұлуы Еуропаның солтүстік бөліктерінен басқа Балтық теңізінің жағалауына қоныстанды. Ол бұталардың шабақтарында, жеңіл орман шетінде, бақшаларда, саябақтарда тұрады. Ұлулар көктемнен алғашқы суыққа дейін белсенді, содан кейін топыраққа 30 см тереңдікте еніп, анабиозға түседі. Анабиоз кезінде қабықтың ауызы қылшықпен жабылады – эпифрагма, қалыңдығы қыс мезгілінің ауырлығына байланысты. Табиғатта жүзім ұлуы орта есеппен 7-8 жыл өмір сүреді, бірақ оларды жыртқыштар жеп қоймаса, жиі 20 жылға дейін өмір сүре алады [12].
Сыртқы көрінісі
Денесі, топтың барлық өкілдері секілді сыртқы қабаттағы қабырға мен магистральға бөлінеді. Соңғысында аяқ және бас ерекшеленеді. Ішкі органдар мантиямен қоршалған, оның бір бөлігі сыртынан көрінеді.
Ересектердің қабығының диаметрі орта есеппен 3-4,5 см құрайды; оның көлемі бүкіл денені толығымен орналастыру үшін жеткілікті. Қабық спиральды қисық; Түрлі ұшақтарда (турбо-спираль деп аталатын) 4,5 төңкеріс бар; оңға бұралған; сағат тіліне қарсы. Мұндай қабықшалар дезоксотропты деп аталады.
Қабықтың түсі сары-қоңырдан қоңыр-ақ түсті болады. 2-3 революцияның бүкіл ұзындығы бойында 5 қара және 5 жеңіл жолақ бар. Кейбір ұлулардың қабығының түсі қара, ал басқаларында ашық рең. Түстің қанықтылығы тіршілік ету ортасына байланысты және жарықтың қарқындылығымен және қоршаған орта фонымен байланысты, яғни ол маскировка жасауға көмектеседі. Қабықтың түсі жеген тағам түріне байланысты өзгеруі мүмкін.
Қабық қабырғалы. Бұл жер бетінің аумағын көбейтеді, бұл сізге ылғалды көп жинақтауға мүмкіндік береді. Қабырғалар да қабықты күшейтеді, сонымен қатар, арқасында раковинаның салмағы аз [11].
Ересектердің аяқтың қалыпты ұзындығы 3,5-5 см, ал жануар 8-9 см дейін созылуы мүмкін.
Жузім ұлуын - жүзімдіктен, ал жалаңаш шырышты бау-бақшалар мен өзге заттар астынан кездестіре аламыз. Бұлардың көпшілігінің денесін бақалшақ қаптайды. Бақалшақтарының пішіні әр түрлі болады. Кейбіреулерінде, мысалы, жалаңаш шырыш денесінде бақалшақ қалдығы ғана сақталған. Денесі жұмсақ. Бақалшақты ұлулардың денесін жобалан бас, тұлға және аяққа жіктеуге болады. Аяғы дененің астыңғы бөлігі - бауырын толық қамтитындықтан, бұлар бауыраяқты ұлулар класына жатқызылады. Бауыраяқтылардың 80 мыңға жуық түрлері белгілі. Бау-бақшаға, жүзімдіктерге, баққа жалаңаш шырыш, жүзім ұлуы айтарлықтай зиян келтіреді. [10].
Тыныс алу
Жүзім ұлуы өкпенің көмегімен дем алады. Тыныс алу тесіктері - пневмостиль - мантияның қаптамалары арасында қабықтың революциясымен бірдей орналасқан.
Қозғалуы
Жүзім ұлуы оның бұлшық еттерінің көмегімен қозғалады. Бұлшықеттердің қысылуының көмегімен жануар сырғып кетіп, бетінен бет бұрады. Жылжытқанда, шырышты босатады, ол субстрат арқылы қозғалысты жеңілдететін үйкелісті жұмсартады. Былғары былғары безі дененің алдыңғы бөлігінде орналасқан. Қозғалыс орташа жылдамдығы шамамен секундына 1,5 мм.
Анабиоз
Жыртқыш ұлудың анабиозы 3 айға дейін созылады. Қазақстанның табиғи жағдайында - кем дегенде 5 ай, ал анабиоздық кезеңде тәулігіне 60 күннен кем моллюскалар, сондай-ақ, эксперименттік жағдайларда азайтылған құнарлылығымен ерекшеленді немесе жұмыртқаны мүлдем бермеді
Табиғи жаулар
Жүзім ұлуының табиғи жаулары – кірпілер, жер, жыландар және басқа жануарлар, сондай-ақ жүзім ұлуының ішіне тыныс алу жолдары арқылы өтетін саңырауқұлақ қоңыздарының түрлі түрлері [7].
Өсіру
Жүзім ұлулар ежелгі дәуірден бері өсіріледі. Қазір бірқатар елдерде «ұлу шаруашылықтары» деп аталады, олар экспорт үшін - жүзім ұлуын өсіріп, оларға қолайлы жағдай жасау арқылы көп мөлшерде дайындайды.
Жүзім ұлуларының еті 10% протеин, 30% май, 5% көмірсулар, сондай-ақ B6, B12 дәрумендері, темір, кальций, магний бар. Қазақстан Республикасының Ұлттық ғылым академиясының Балық шаруашылығы институтының мәліметі бойынша, -65% протеин, шамамен 5% май, қалғандары - төменгі молекулалық органикалық және минералды қосылыстар - күл. Бірқатар елдерде хош иісті заттар фармацевтика өнеркәсібінде мейрамханаларда сатуға арналған [1]
Медицинада
Бронхо-босаңсытқыштың қасиеттеріне байланысты жүзім ұлуларынан алынған глицитин сығындысы қолданылады. Түрлердің өкілдері бағалы заттарды - лириндерді оқшаулау үшін де қолданылады
Ауыл шаруашылығына зиян келтіреді
Жүзім ұлуы ауыл шаруашылығының жауы болып табылады, ең алдымен ол жас өсімдіктердің өнуі барысында, әсіресе жүзім ктерді жейді [6].
Жүзім ұлу - тұтқында ұстаудың керемет және қолжетімді нысаны. Олар мүлдем қарабайыр емес сияқты көрінеді. Жүйке жүйесі өте қарапайым болғанына қарамастан, ұлулар үйренуге қабілетті. Ұзақ уақытты есте сақтайды және оларға қамқорлықпен қарайтын болсаңыз, олар оңай және жылдам пайдаланылады және тыныштықта қолға оңай беріледі.
2.2. Шартты рефлекс және оның мағынасы
Шартты рефлекс - бұрынғы немқұрайлы емес ынталандыруды пайдалана отырып, сөзсіз рефлекстер негізінде әзірленген кешенді көп компонентті реакция. Ол сигнал сипатына ие, және ағза дайындалған шартсыз ынталандырудың әсеріне жауап береді [3].
Шартты рефлекстер осы жануарларға экологиялық жағынан ұқсас әсер ету үшін оңай шығарылады. Осыған байланысты шартты рефлекстер табиғи және жасанды рефлекстерге бөлінеді. Табиғи шартты рефлекстер ынталандырумен бірге табиғи түрде әрекет ететін агенттер үшін әзірленеді, бұл сөзсіз рефлексті, мысалы, тағамның түрі, оның иісі және т.б.). Барлық басқа шартты рефлекстер жасанды болып табылады; агенттер үшін әдетте жасалынбайды, олар әдетте шартсыз ынталандырудың әрекетімен байланысты [2].
1.Шартты рефлекстерді жасау үшін қажетті ең негізгі жағдай – индифренттік (өздігінше осы реакцияны тудыра алмайтын, кез келген бөтен) тітіркендіру мен шартсыз, сол реакцияны міндетті түрде тудыратын тітіркендірудің әсер ететін уақытының бір-біріне дәл келуі (ұштасуы).
2. Бөтен тітіркендіргіш шартсыз тітіркендіргіштердің әсеті басталар алдында әсер етуі керек. Екі тітіркендіргіш әсері бір уақытта берілсе шартты рефлекстің жасалуы едәуір қиындайды. Ал алдымен шартсыз, одан кейін индифренттік тітіркендіргіш әсет етсе, шартты рефлекс алынғанмен, ол өте тұрақсыз болады. (Алдымен шартсыз, кейін бөтен тітіркендірумен әсер еткенде шартты рефлекстің жасалуының қиын болатын себебі, теріс индукция заңымен және шартсыз тітіркендірудің күшінен бөтен тітіркендіргіш күшінің кемдігімен түсіндіріледі). Жасалған шартты рефлексті ұзақ уақыт сақтау үшін, оны мезгіл-мезгіл шартсыз тітіркендіргішпен бекітіп отыру қажет.
3. ми қыртысы клеткаларының жеткілікті жоғары қозғыштығы болуы керек. Ол үшін ми қыртысы түрліше басқа әсерлерден бос болу керек. Сонда ғана белгілі тітіркендіруге жүйке клеткалары жоғары қозумен жауап бере алады.
4. Шартты рефлекс жасалу қолданылатын тітіркендіргіштің қасиеті мен күшіне де байланысты. Бөтен тітіркендіргіштің күші қыртыста қозу ошағын тудыруға жететін болуы керек.
Ұлуларда бір комбинациядан кейін шартты рефлексті дамытуға болады. Егер тұздыққа саңырауқұлақтар берілсе, ол оны әрдайым ұнатады, оларды көміртегі қос тотығымен улану арқылы біріктірсе, онда жануар әрдайым тағамның басқа түрлерін таңдап, саңырауқұлақтардан үнемі бас тартады [3].
2.3. Шырындардың шартты қорғаныс рефлексін ұйымдастыру
Бұл жұмыста Helix тектес жүзім ұлуының қорғаныс рефлексі пайдаланылды, сондықтан біз оның нейрондық ұйымын (тұжырымдамалық рефлексиялық доғаның) қарастырамыз. Тітіркендіргіш (тері тесігі) рецепторлар тобында әрекет етеді және қозғалтқыш алаңдары бар мотоневрондар мен бірнеше командалық нейрондармен байланысты жергілікті детекторды қоздырады. Байланыс лейколярлық синапспен байланысты. Әрбір қозғалғышты бұлшық ет бөлігін құрайтын бұлшықет жасушаларының тобымен байланысты. Сонымен қатар, кейбір командалық нейрондар бұлшықет бірліктеріне тікелей байланыстырады, бұл командалық нейронның қозғалтқыш алаңының фокусын жасайды. Сондай-ақ, непластикалық синапстардың арқасында байланыс жасайтын жергілікті ғана емес, сонымен қатар нозицептивті детекторлар бар. Рефлексия доғаның маңызды бөлігі - нозицептивті детекторлар. Модуляциялы нейрондардың аксону командалық нейрондағы жергілікті детекторлардың прессинаптически аяғында аяқталады. Олар детекторлардың синтездерінің тиімділігін нейрон командалары бойынша арттырады [3].
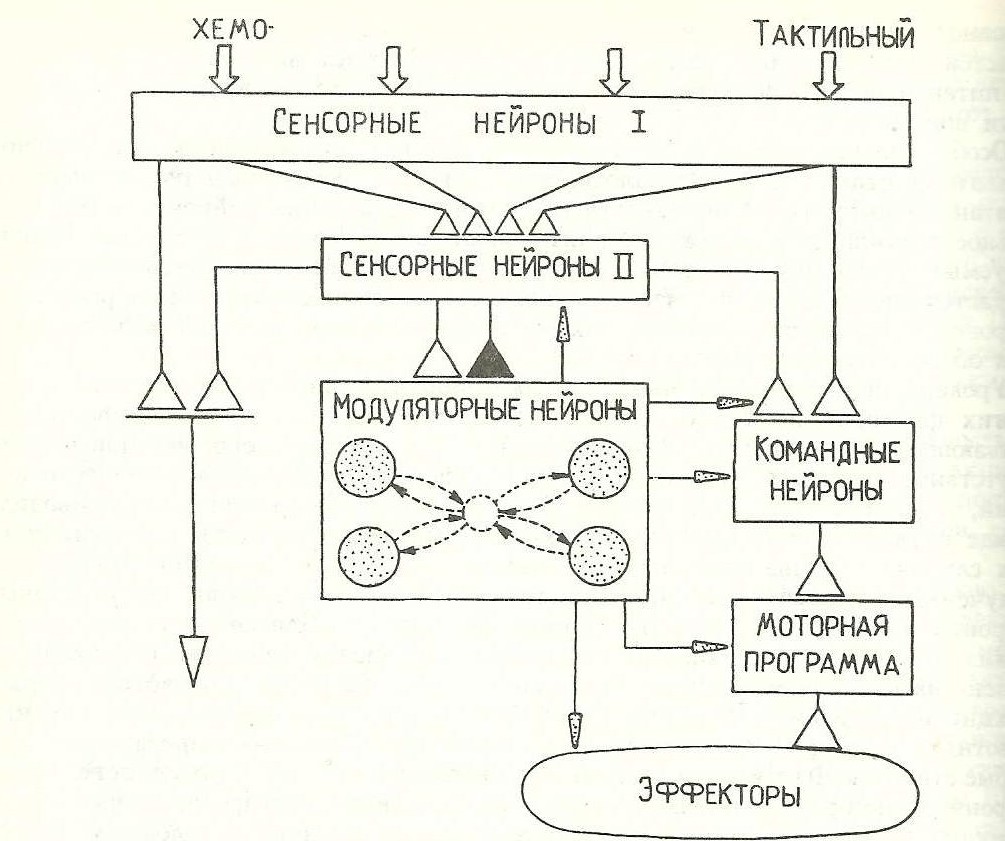
1-сурет. Жүзім ұлуының УОР рефлексі
1. Нейрондық командалық нейронның қозғалтқыштық алаңы оған қосылған мотоинурондардың құрамымен анықталады.
2. Детектор - кіріс сигналының параметрлерін таңдайтын нейрон.
3. Басқа моторлы нейрондармен байланысты нейрондық командирлеу - интерферон.
4. модуляторлық нейрондар қорғаныс рефлексі кальций иондық арналар қалыптастыру протеиндер phosphorylates серотонин босату, әкеледі электрохимиялық ынталандыру, олардың бассейн серотонинергической нейрондарды іске қосады adeninatsiklazu т.б. ұсынылған ..
5. Пластикалық синапс - шығарылған ацетилхолин концентрациясының өзгеруіне байланысты (реакция), жай сигнал беру (сезімталу)
2.4. Препараттардың жүйке жүйесіне әсері
Адреналин - жүйке жүйесіне ынталандырушы әсер етеді. Ол ояу деңгейін, ақыл-ой мен белсенділіктің деңгейін арттырады, ақыл-ойды жұмылдыруға, бағдарлау реакциясына және алаңдаушылыққа, алаңдаушылыққа немесе стресстікке әкеледі [9].
Денеге әсер ететін дифенгидрамин бұлшықетке босаңсытатын әсер береді, ауырсынуды жеңілдетеді, сондай-ақ ауырсынуды азайтатын белгілі жүйке түйіндерінің аяқтарын қалыпты түрде блоктайды [9].
ІІІ. Зерттеудің әдістері мен орны
1. Қолданылатын қысқартулардың тізімі: УОР - шартты қорғаныс рефлексі; УС - шартты ынталандыру; БС - сөзсіз ынталандыру; ГА - адреналинге ұшыраған ұлулардың тобы;
ГД- димедролға ұшыраған ұлулар тобы; ГХ- суық суға ұшыраған ұлулардың тобы; ГГ ыстық суға ұшыраған ұлулардың тобы; ГК - әсер етпейтін (бақылау) ұлулардың тобы.
2. 2018 жылдың мамыр айының аяғында Жамбыл облысының Байзақ ауданында жүзім құймалары қоршаған ортаны алып тастады. Барлық талаптарды ескере отырып, арнайы жасалынған құтыға қойыңыз. Екі айдың ішінде жаңа мекендейтін орындарға бейімделу және қолдарға әдеттену. Тәжірибе 2018 жылдың тамызында мектеп зертханасында өткізілді.
3. Эксперименттерде біркелкі массаның және өлшемдердің жүзімдік ұлуларының жетілген үлгілерін қолдандық. Моллюскалар жалпы термориумда бөлме температурасында, жоғары ылғалдылықта және азық-түліктің астығында сақталған. Эксперимент басталмас бұрын, ұлулар екі ай бойы бейімделді. Раковинадағы клиникалық УОР жасалды.
УС-та раковинаның үстінде қолданылғандықтан, нормада қорғаныстық реакция туындаған жоқ. БС қабық аймағында коклеяны тітіркендіреді, бұл гаммофордың (антеннаның) кері кетуінің сөзсіз қорғаныстық реакциясына әкелді [2]. Сигналдардың комбинациясы арасындағы интервал 3-5 минут, БС және УС презентациясы 1 секунд болды.
Бұл оқыту түрі бес тәжірибелік топта өткізілді. Ұлулардың алғашқы тобы адреналин (ГА) әсеріне ұшырады. Екінші топ - дифенгидрамин (ГД) әрекеті. Жүзім ұлуның жүйке жүйесі перифериялық жүйке сақинасында топтастырылған ганглияның концентрациясының өте жоғары деңгейімен ерекшеленеді, сондықтан осы аймақта дененің бетіне қолданылды. Дене тығыз теріге ие емес және препараттың сіңірілуі сыртта пайда болады.
Препараттың дозасы ұлулардың денесінің салмағын ескере отырып есептелді. Препарат инъекцияға арналған дистилденген сумен қажетті концентрацияға дейін сұйылтылған. Есірткі дозасын есептеу құйрықтардың массасын ескере отырып жүргізілді.
3.1.Құралдарды дайындау:
Тамырдан енгізу үшін адреналин және димедрол қабылданған шешімдер, адам денесінің 60 кг салмағына шаққанда 1 мл тәуліктік доза. Тиісінше, ұлулар салмағына теңейміз (ұлулар орташа салмағы - раковина бар 25,6 грамм, раковинасы болмаған жағдайда орташа салмағы 15 грамм) 0,0025 мл - коклеяның күнделікті нормасы. Тамшы мөлшері - ең кішкентай, онда көрсетілген көлемі көп немесе аз тұрақты, алайда қор шешім 13,2 есеге инъекцияға арналған тазартылған сумен таратылған болатын ұлулар үшін үлкен 13,2рет күнделікті 0,033 мл, болып табылады. Енді ұлулар үшін күнделікті деңгейі 0.033 мл, яғни 1 тамшы болып табылады.
Бауыр аяқтар мен мантияның теріге шашыраған жеке сезімтал жасушалар қабылдаған тактильді, химиялық, температура ынталандырғыштарын қолдануға жақсы жауап береді, сондықтан тәжірибелік шарттар кеңейтілді. Үшінші зерттеу тобы УОР өндірісіне дейін 15 минут бойы (ГХ) суық суда (40С) алдын-ала шартталған. Төртінші топ сондай-ақ ыстық суда 450 ° C (ГГ) температурада сақталды (2-сурет, B қосымшасы).
Ұлулардың бесінші тобы қандай да бір әсерге ұшырамай, бақылауға ие болды. Әрбір топ бес ұлаудан тұрды.
1. Адреналинді ерітіндімен емдеу.
2. Адреналиннің (УС) раковинаның үстінде басу.
3. Тактилдік тітіркену (БС).
Бірқалыпты ұлуларды іріктеу үшін, біз салмақтарын өлшеу жұмыстарын жүргіздік (1-сурет, 2-сурет, Қосымша B).

Қабықтың биіктігі мен енін білу, кейбір болжамдарға негізделген, қабықтың көлемін есептеді. Атап айтқанда, тікұшақ тәрізді қабықшалар үшін бұл жүзім құстың жүзім шелегі бар, көлемі мынадай формула бойынша есептеледі:
SB = SD2 * (SH / 2),
онда,
SB - қабықтың көлемі;
SD - қабықтың үлкен диаметрі; SH - қабықтың биіктігі.
4. Өзінің жеке гипотезасын растайтын немесе қабылдамайтын барлық деректерді алған соң, х2 әдісі қолданылды (Pearson келісімшартының өлшемі)
3.2. Эксперименттердің нәтижелері
Экспериментке дейін барлық өлшеулер жүргізілді: салмақ, биіктікті өлшеу, қабықтың ені, аяқтың ұзындығы және сынақ топтарындағы ұлуларды таңдау үшін қабықтың көлемі. Әр топтың деректері (орташа мән) 1-кестеде келтірілген. Әрбір эксперименталды топ үшін өлшеулердегі минималды ауытқуларға ие бес бөлік таңдалған.
1-кесте - топтар бойынша ұлулардың өлшемі
-
салмағы (г)
ені (см)
биіктігі(см)
көлемі (см3)
аяғының ұзындығы (см)
ГА
25
2,9
3,5
14,7
10,2
ГД
27
3,1
3,5
16,8
10,5
ГГ
25
3,0
3,4
15,3
9,8
ГХ
26
2,9
3,1
13,0
10,1
ГК
25
3,0
3,2
14,4
10,0
Топтардағы әрбір ұлу түрлі түске боялған. Snails ГА - қызыл түсті, ГД- бұрыштық түсі, ГГ - қызғылт түсті, ГХ - көк түс және ГК- сары түсті. Тәулік ішінде ұлуларға эксперименталды топтан кездейсоқ түсіп, УС және БС комбинацияларының 7 жиынтығын жасады. УС - раковинадағы ағаш балғамен 5 есе қысып, күшті болмауы керек, бірақ хош иісті сезінуі керек.БС - пластик түтікшесі бар таяқшасы күшті болмауы керек, бірақ тұмсық хемматофорларды (антеннаны) тартады. Эксперимент тұрақты УОР-нің дамуынан 5 күн бұрын жүргізілді. Барлығы 175 УС және БС комбинациясы болды.
УОР дамуының сандық деректері кестеде көрсетілген.
2-кесте - Эксперименттік топтарда УОР даму динамикасы (%)
-
Топтар
Саны УС және БС
Орташа саны
10
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
ГА
20
40
40
40
ГД
20
60
20
160
ГГ
40
40
20
120
ГХ
40
40
20
60
ГК
20
60
20
80
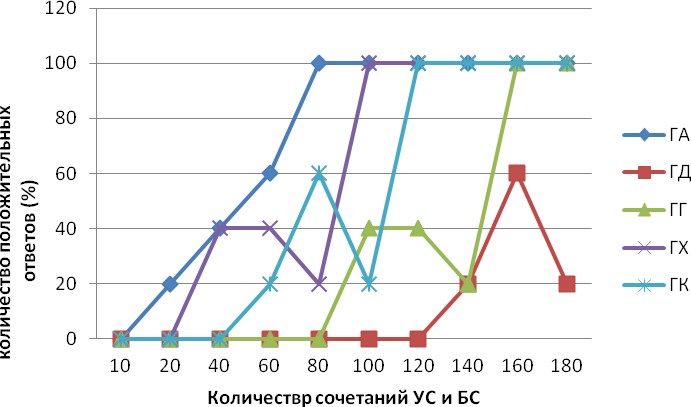 Нақтырақ айтсақ, деректер
уақыт айырмашылығын және УОР дамытуға арналған комбинациялар санын
көрсететін графиктер түрінде
берілген.
Нақтырақ айтсақ, деректер
уақыт айырмашылығын және УОР дамытуға арналған комбинациялар санын
көрсететін графиктер түрінде
берілген.
3-сурет - жүзім ұлуының тұрақтыУОР өндірісінің динамикасы
Эксперимент барысында топтарда серияның басы мен аяғымен байланысты УОР баллының айтарлықтай күшті ауытқуы болды. Яғни, сериялардың арасындағы жүзім ұлуы УОР деңгейін төмендетті, сондықтан жаңа сериялар бұрынғы сериялардың соңында жұзім ұлуы балымен емес , бірақ сәл кішірек балмен басталмады. Баллды анықтау үшін УОР үшін бес баллдық рейтингті жүйені енгіздім.
БС-де антенналарды алу дәрежесі: 5 ұпай - толқындар толығымен тартылады; 4 ұпай - біреуі толық, екінші жартысы; 3 ұпай - екеуі де екі есе азайған; 2 ұпай - тек біреуі ғана жинақталған; 1-ші нүкте - қышқылданып кетеді.
УОР шарларының ауытқуы 3-кестеде көрсетілген.
-
1 күн
2 күн
3 күн
4 күн
5
күн
ГА
5/100
5/100
5/40
5/20
4/20
4/60
4/80
3/80
ГД
5/100
5/40
5/20
5/20
3/20
4/60
4/20
3/40
1/80
3/60
2/40
ГГ
5/100
5/80
5/20
4/20
2/60
3/20
4/60
3/60
1/40
2/20
1/20
ГХ
5/100
4/80
5/40
5/20
4/40
3/20
4/40
4/20
3/20
2/20
2/60
1/40
ГК
5/100
5/100
5/80
5/40
5/20
3/20
4/20
3/40
3/40
2/40
Табиғи жүзім ұлуының шаршағанын кестеден көруге болады: сәнді ұлулар сәтті комбинациядан кейін антенналарын ұстап қалғысы келмеген сәтте [4].
Екі топтағы соңғы күнде сезімталдық сезімталдығы - кез-келген әсерге жауап беруден бас тартқан кезде шаршағандық сезімі анық байқалды. Сезімталдығы, әдетте, серияның соңында пайда болды, бәлкім, бұл әдеттердің механизмі.
Тұрақты УОР құрастырылғаннан кейін, рефлекторды сақтау уақыты тексерілді, яғни. Жүзім ұлуы УС-тың БС күшейтуінсіз әрекетіне ұшырады. Осылайша, қорғаныстық реакция (обмотофорды шеттету) болды.
Жақсартылған рефлектор 40 күн бойы сақталды (4-сурет). Сонда ұлулар УС-қа жауап бермеді. Диаграмма УС-қа оң жауаптардың төмендеуін көрсетеді.
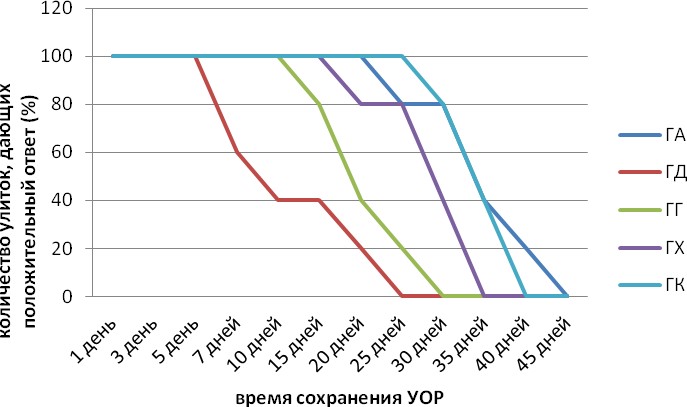
4-сурет - УОР сақтау динамикасы
Эксперимент барысында құйрықтардың қорғаныс реакцияларының көбеюі жаттығулар орын алған жағдайда ғана көрінді. Бұл тұзақты заттар шартты және шартсыз ынталандырулармен ұсынылған жағдайды бөліп бере алатындығын растайды.
Тәжірибенің әрбір күні хаттамаларда жазылған.
5. Алынған нәтижелерді талдау УОР әзірленгеннен кейін барлық деректер өңделді және талданды. Бес зерттеу топтарында УОР-ні дамытуға арналған уақыт пен айқастардың саны айтарлықтай таралады (6-сурет).

Диаграмманы талдай отырып, ГА-ның ұлуларының
ең жақсы нәтиже екендігі анықталды: 20% ертінділердің (1 ұлпа)
УС-қа 20 комбинациядан кейін бірінші күні оң әсерін көрсетті, ал
қалғаны келесі күні оң жауап берді, ал спрэд комбинациялар саны
бойынша ғана (2 сыбағасы серияның басында және серияның соңында 2).
Сонымен қатар біз ГК-дағы жыландарда тұрақты УОР байқап отырмыз,
бірақ тұтастай алғанда бүкіл топ үшін тұрақты рефлексті дамыту
уақыты ұлғайып отырады, сондықтан 20% жыландар 3-ші күнде серияның
басында УОР және 2-ші күн сериясының соңында 60%
көрсетеді.
Суық судың әсеріне ұшыраған ұлулар ГК хош иістерінен әлдеқайда жақсы нәтиже көрсетті. Көптеген хош иісті заттар (80%) екінші күні соңында оңға қарай жауап береді. Мүмкін суда болу, жасушалардың азаюына әкеледі және ақпараттың қысқартылуына әкеледі. Екінші нұсқа, бұл суда болған, ұлулардың денесінен шырындар жуылады, бұл БС-ден тактикалық тітіркенуді азайтады.
Ең баяу уақыт интервалы мен комбинациялардың ең көп саны ГД және ГГ хош иістері арқылы талап етілді. ГГ субъектісі үшінші күні (40%) тұрақты УОР көрсетті, қалғандары 4-ші күні оң жауап берді. Ыстық суда қалу хош иісті заттарға тән емес. Табиғи жағдайда мұндай жағдай болмайды. Жүзім ұлуы алынатын биотопта ауа температурасы ең ыстық күндерде 300 ° C-тан аспайды. Сондықтан жасанды түрде жасалған жағдайлар қоршаған әсерді барынша азайтуға және ұлулар осындай жағдайда раковинада жасырынады. Экспериментті бастау үшін раковинадан толығымен шыққанға дейін біз 3-4 минут күтіп тұрдық.
Дифенгидраминнің ерітіндісіне ұшырағанұлулар ұзақ уақыт бойы қолдануға тағайындалды Жоғарыда айтылғандай, дифенгидрамин бұлшықетпен босаңсу әсер етеді, сонымен қатар кейбір жүйке түйіндерінің аяқтарын қалыпты түрде блоктайды, бұл УОР өндірісінің уақытын едәуір арттырады: 1 сыбағасы (20%) БС-ге 4-ші күні оң жауап береді, ал қалған 5-ші соңында 160-170 комбинациясы бар күн.
Осы топтан шыққан ұлу еті жиі шаршау мен уайым сезімін көрсетті. Яғни, серияда БС-ге оң және теріс жауаптың ауысуы байқалды. ГА-дан гауһарлар шаршауды іс жүзінде көрсеткен жоқ, ал 5-ші күні ГК тобынан шаршаудың кішкене көрінісі байқалды.
Алынған нәтижелер дәрілік препараттар мен дене температурасының әсері туралы біз ұсынған гипотезаны УОР өндіру жылдамдығымен растайды. Гипотезаның дұрыстығын тексеру үшін х2 өлшемі (Пирсон шартының өлшемі) көмегімен шешілді.
Жүзім ұлуының шырышында УОР өндіру туралы ғылыми деректердің 95-105 тіркесімінің шектерінде екендігін білу (орташа мәні 100 [4]), біз байқаған деректер біздің күтілетіндерден өте ерекшеленеді, өйткені дәрі-дәрмектер мен дене температурасы әлі де бар RBM дамуының жылдамдығына ықпал ету. Мұны тексереміз: χ2 = Σ (фо-fe) 2 / к, мұнда fo және fe - бұл ынталандырудың күтілген және күтілетін тіркесімі. Топтама кестенің барлық ұяшықтары бойынша орындалады. Бізде: χ2=(40-100)2/100+(160-100)2/100+(120-100)2/100+(60-100)2/100+(80- 100)2/100 = 16
Бізде еркіндік дәрежесі саны 4 (жолдардың саны - 1), сондықтан бақыланатын мән ықтималдығы кездейсоқ ауытқу 0,5% болуы мүмкін. Біз алған 16 шамасы сыни мәннен 14.86 асып түседі, бұл біз ұсынған гипотезаны дұрыс деп санауға құқылы.
Біз үшін әр түрлі препараттар мен температура әсерінен өндірілген УОР қанша уақыт бойы өмір сүруі қызықты болды. Жүзімнің тұзағындағы дамыған УОР оқытудың сыртқы жағдайларына еске салғанда 52 күн бойы [4] қалады. Біздің экспериментімізде УОР сақтаудың ең ұзақ уақыты 40 күн болды. Айналдыру уақытының өзгеруіне сыртқы ортадағы өзгерістер әсер етілді (ауа температурасының орташа 100 ° C-қа төмендеуі).
4-кестені талдай отырып, топтардың арасында УОРсақтау динамикасы ішкі топ көрсеткіштерінен айтарлықтай ерекшеленетінін байқауға болады.
4-кесте - жүзім ұлуының УОР сақтау динамикасы (%)
-
ГА
ГД
ГГ
ГХ
ГК
1 күн
100
100
100
100
100
3 күн
100
100
100
100
100
5 күн
100
100
100
100
100
7 күн
100
60
100
100
100
10 күн
100
40
100
100
100
15 күн
100
40
80
100
100
20 күн
100
20
40
80
100
25 күн
80
0
20
80
100
30 күн
80
0
0
40
80
35 күн
40
0
0
0
40
40 күн
20
0
0
0
0
45 күн
0
0
0
0
0
УС -ке оң жауап күн сайын тексерілді. Бұл топтардан ең ұзын реакция АГ тобынан жасалған ұлуларға оң реакция болатыны көрінеді. ГД тобының ұлулары барлығынан бұрын ұрып көруге жауап реакциясы болмажы, бұл рефлекстің сақталуы, сонымен бірге, оның әзірлену уақытына байланысты болды, өйткені осы топтағыұлулар 4 және 5 күндерде тұрақты оң рефлексті көрсетті, содан кейін УС пен БС-дің бұдан кейінгі комбинациясы тоқтатылды және басқа топтар, бірінші оң жауап алғаннан кейін ұзақ уақытқа созылды.
Сондықтан, УОР сақтау бойынша препараттың әсер және температура туралы айтуға дәл болады. Кез келген жағдайда, біз ұзақ уақыт бойы әр топта екенін көріп оң жауап санының азаюы болып табылады, және сайып келгенде, ол жерден 0. төмен келеді, біз бірінші оң жауап бастап және 5 созылды эксперимент, соңына дейін уақыт әсер туралы жорамал жасауға болады Ассамблея құрышы 1-2 күнге дейін оң жауап берді, және шоғырландыру үшін эксперимент және уақыт соңы астам 3 күн болды, бұрын олардың жаттығу жүргізілді болса, онда ДГ уақыт шоғырландырудан ұлулар өте аз болады.
Қорытындылар
Осылайша, біздің эксперименттеріміз көрсетті:
1. Адреналин және дифенгидрамин есірткі тұрақты УОР өндірісінің жылдамдығына әсер етеді. Осы топтардағы өндіріс уақытының айырмашылығы айтарлықтай. ГК-да УОР қалыптастыру жылдамдығы ГД-де жылдамдықтың 4 есе жоғары.
2. Ұлулардың денесінің температурасы УОР даму жылдамдығына әсер етеді. ГГ тобында УОР өндіру жылдамдығы ГК ұқсас рефлекстің даму жылдамдығынан 2 есе төмен.
3. Адреналин мен дифенгидрамин ерітіндісін және температураны УОР- ның өндіріс жылдамдығына әсері статистикалық маңызды.
4. Ұстағыштардың ұзақ мерзімді есте сақтау қабілеті бар, бірақ ол сыртқы жағдайларға байланысты, яғни Ұстағыш УС-қа оқу жағдайларына ұқсас жағдайларда оң жауап береді. УОР уақытын сақтау уақыты оқу уақытына байланысты
Зерттеудің практикалық маңыздылығы мен бағыттары
Жануарларға этикалық эксперименттер көптеген пікірсайыстардың тақырыбы болып табылады. Бүгінде ғылымдағы прогресс үшін эксперименттердің қажеттілігі - жануарлардың азаптауы (зертханалық жануарлар санының азаюы) жағдайында қазіргі басым көзқарас.
Біздің жағдайда әр топтағы эксперименталдық ұлулар саны азайып, препараттық инені тітіркендіретін пластикалық түтікпен тітіркенген тітіркенуді ауыстырды, бұл да көрінетін, бірақ әлдеқайда аз ауыр сезім береді.
Қорытынды
Біздің жұмысымыздың нәтижелерін қолдану бірнеше бағытта болуы мүмкін:
1. Оқу үдерісінде. Бұл зерттеулер биологиялық класстарда (8 жасуша) қолданылуы мүмкін шартты рефлексті дамытуды айқын көрсетеді. Эксперименттерді қайта қарап шығудың қажеті жоқ, жай ғана бейне көруге болады. Медицина сабақтарында (10-11 жасушалар), тақырыпты зерттегенде осы материалды қолдануға болады
«Дәрілік препараттар». Оқудан тыс іс-шараларда және кейінгі сағаттық іс-шараларда, бізбен бірге өмір сүретін жануарлар биотопта биоәртүрлілікті сақтаудың ажырамас бөлігі болып табылады.
2. Медицинада (фармакология). Дəрілік заттардың əйнектерге әсері адамдарға ұқсас, сондықтан жаңа ұлулар мен олардың компоненттерінің әсерін тексеру үшін жүзім ұлуын қолдануға болады, өйткені хош иісті заттар салыстырмалы қарапайым жүйке жүйесі мен өте күрделі мінез-құлық репертуарымен өте үлкен нейрондарға ие.
3.Мал шаруашылығында.
Мал шаруашылығы тәжірибеде шартты рефлекстердің кеңінен пайдалану жануарлардың өнімділігін арттыруға болады. оның жұмысына, ұлулар шартты рефлексті мүмкіндігін көрсететін, біз ұлулар дене салмағын тез арттыру үшін оң тамақ рефлексі дамыту ұсынамыз. Ал одан әрі дамыту және оны біріктіру үшін қосымша ынталандырушы факторларды қолдануға болады. Мұны істеу үшін аталатын жасаңыз
[7] сол уақытта қолайлы жағдайлар оларды қабылдау, үлкен сандар одан әрі дайындау немесе экспорт үшін ұлулар өсіру, ол «ұлу фермаларын енгізу».
4. Ұлулардың фитофаг ретінде қолданылуы. Тұздық үлкен жапырақты арамшөпті жейді - шалшық, сиыр-аққайың, шөп, олардың орнында шалғынды шөп өседі, себебі топырақ Калифорниялық құрттың сыртына қарағанда он есе тиімдірек жүзім құстағыларының қышқылымен байытылған. Мұны істеу үшін, ұлулар сиырда, әсіресе біздің аймағымыз үшін өте маңызды, тұрақты азық-түлік рефлексін дамытуы керек [11].
Келешекте жүзім ұлуларын зерттеуді жалғастыру жоспарланып отыр. Рефлекстің дәрі-дәрмектерге тұрақтылығына тәуелділігін тексеру, пирамидаларға арналған оң тағам рефлексін дамыту және іс жүзінде потенциалды ынталандыруды табу әдісі ретінде күресу әдісі ретінде оны сынау.
Introduction
At the present stage of the development of civilization, the increasing anthropogenic impact on nature causes irreversible processes leading to the degradation of ecosystems and a decrease in the diversity of the biosphere's gene pool. The need to preserve many species of plants and animals and to develop a system of measures for the protection of biocoenoses has been recognized long ago. Nevertheless, until recently, some species of animals, mostly invertebrates, were out of sight of most researchers concerned with the conservation of biological diversity. However, the role of these organisms in maintaining the stability of ecosystems, the processes of circulation of substances in nature, soil formation and biodegradation is extremely high, and it is the effects on these components of biogeocenoses that lead to irreversible changes in communities [10].
Mollusks are an integral component of Kazakhstan's terrestrial ecosystems. Participating in the decomposition and mineralization of organic substances, they act as an important link in the circulation of substances in nature [8]. Molluscs also have economic significance. Currently, the range of application of grape snails is increasingly expanding due to the research of biology scientists, microbiologists, physicians, and consequently, the commercial importance of this molluscum is constantly increasing. It is this fact that led to the fact that the grape snail has become the object of close attention on the part of man. It needs to be protected from thoughtless extermination, and for this, the most comprehensive knowledge about it is necessary [5].
The adaptation of animals to the changing conditions of existence in the external environment is provided by the activity of the nervous system and is realized through reflex activity. In the process of evolution, hereditarily fixed reactions (unconditioned reflexes) arose,which unite and coordinate the functions of various organs, carry out the adaptation of the organism [2].
The organization of the nervous system of the snails of the genus Helix is simpler than the human nervous system, but the very principle of signal transmission and structure are similar. And it is the relative simplicity of the nervous system of the snails that makes them attractive for research in neurobiology. The availability and large size of the snails allowed them to become an object of research by German scientists even in the century before last [3].
Purpose and objectives of work:
We hypothesized: various medications and external conditions can influence the development and fixation of a conditioned reflex in a grape snail.
In connection with this, the purpose of this study was to determine the effect of various medications and different temperatures on the development of a conditioned reflex in a snail of grape.
Based on the goal, the following tasks were set:
- to investigate the life and behavior of snails in captivity;
- develop a conditioned defense reflex in snails in five experimental groups;
- determine the time of preservation of the conditioned reflex in snails in different study groups.
2.1. Ecological and biological features of a snail of grape The grape snail (Helix pomatia) is the largest land mollusk of our fauna. Systematic position [8] (Appendix A): The kingdom is animals; Type - mollusks; Class - gastropods; Detachment - pulmonary snails; Family - helicides; Family - Helix; View - grape snail;
The international scientific name is Helix pomatia.
It is believed that the birthplace of the grape snail is Central and South-Eastern Europe. For a long time people used grape snails as food, with a delicacy they were not, and people of any social status used them as an affordable and healthy food [8].
The species settled in all but the northern parts of Europe and the coast of the Baltic Sea. It lives in thickets of bush, on light forest edges, in gardens, parks. The snail is active from spring to the first cold, then burrows into the soil to a depth of 30 cm and falls into anabiosis. As a rule, it hibernates in the same shelters. During anabiosis, the mouth of the shell is closed by a calcareous stopper - an epiphragm, the thickness of which depends on the severity of winter time.
In nature, a grape snail lives on average 7-8 years, but can often live up to 20 years, if it is not eaten by a predator [12].
Appearance
The body, like all representatives of the class, is externally divided into a shell and trunk. In the latter, the leg and head are distinguished. The internal organs are surrounded by a mantle, part of which is visible from the outside.
The diameter of the shell of an adult on average is 3-4.5 cm; its volume is enough to completely accommodate the whole body. The shell is spirally curved; has 4.5 revolutions, lying in different planes (so-called turbo-spiral); is twisted to the right; untwists clockwise. Such shells are called deixotropic.
The color of the shell varies from yellow-brown to brownish-white. Along the entire length of the 2-3 first revolutions there are 5 dark and 5 light strips. The color of the shell in some individuals is more dark, in others it is lighter. The color saturation depends on the habitat and is related to the intensity of illumination and the background of the environment, that is, it helps masking. The color of the shell can vary depending on what kind of food the individual uses.
The shell is ribbed. This increases the surface area, which allows you to accumulate more moisture. Ribs also give the shell more strength and, in addition, thanks to them, the sink weighs less [11].
The usual length of the adult's leg is 3.5-5 cm, but the animal can stretch out, up to 8-9 cm.
The body of the grape snail is very elastic. Its color varies in different individuals, as does the color of the shell. Usually the color of the body is beige with a brown tinge, less often dark gray. The body is completely covered with wrinkles, the areas between them have the form of quadrangles. Wrinkles increase the surface area of the foot, moisture is retained in them [10].
There are two pairs of tentacles above the oral opening of the cochlea. The length of the front tentacles - labial - varies from 2.5 to 4.5 mm. They have an olfactory function. The length of the posterior tentacles - the ocular tentacles - is from 1 to 2 cm. At the end of the latter are the eyes, all of whose receptors contain the same photopigment, which is the cause of the color blindness of the animal. However, the eyes are able not only to distinguish the intensity of illumination, but also to see objects at a distance of up to 1 cm.
Tentacles are very mobile. Both pairs are very sensitive: if you accidentally touch the object, the tentacles are instantly removed inside. Eye tentacles also react negatively to very bright light [11].
Like all representatives of the class, the digestive system of the grape snail is divided into the ectodermal anterior gut and the endodermal midgut. Breathing is pulmonary. The heart located above the hindgut consists of the left atrium and ventricle and is surrounded by the pericardium. The blood is colorless. The nervous system is sparse-nodular, consists of several ganglia. The excretory system consists of one kidney communicating with one end of the pericardium, and the other one opening into the mantle cavity next to the anus. The reproductive system is hermaphroditic, fertilization is transverse.
The grape snail is herbivorous: it feeds on both living vegetation and plant remains. Consume leaves of grapes and wild strawberries, cabbage, horse sorrel, nettle, burdock, medinitsu, dandelion, plantain, radish, horseradish. To build up the shell, the animal needs calcium salts. Cases of eating food of animal origin are also observed. The eggs that emerged from the eggs during the first time feed only on substances contained in the soil [12].
Breath
The grape snail breathes with the help of a lung. The breathing hole - a pneumostyle - is located between the folds of the mantle, on the same side as the shell's revolutions.
Movement
The grape snail moves with the help of its muscular leg. With the help of muscle contractions, the animal, slipping, repels from the surface. When moving, mucus is released, which softens friction, facilitating movement through the substrate. Glands that secrete mucus are located in the front of the body. The average speed of movement is about 1.5 mm per second.
Anabiosis
Anabiosis in a grape snail lasts up to 3 months. In the natural conditions of Belarus - at least 5 months, while mollusks with an anabiosis period of less than 60 days under the experimental conditions further differed in reduced fecundity or did not give eggs at all.
Natural enemies
The natural enemies of the grape snail are hedgehogs, shrews, lizards, moles and some other animals, as well as various species of crawling beetles that can crawl inside the grape snail through the respiratory opening [7].
Breeding
Grape snails have been bred since ancient times. Now in a number of countries there are so-called "street farms", in which in large quantities for subsequent preparation or export grape snails, creating favorable conditions for them.
The meat of grape snails contains 10% protein, 30% fat, 5% carbohydrates, as well as vitamins B6, B12, iron, calcium, magnesium .. In the air-dry matter of grape snails meat, according to the Institute of Fisheries of the National Academy of Sciences of Belarus, contains 60 -65% protein, about 5% fat, the rest - low-molecular organic and mineral compounds - ash. In a number of countries, snails are widely bred for sale in restaurants for the pharmaceutical industry [1].
In medicine
Extract made from grape snails - gelicidin - is used because of its properties of the broncho-relaxant. Representatives of the species are also used to isolate valuable substances - lectins.
Harm to agriculture
The grape snail is the enemy of agriculture, primarily because it feeds on young shoots of crops, in particular grapes [6].
Snails are a wonderful and accessible object of observation in captivity. They are not at all as primitive as it may seem. Despite the fact that their nervous system is quite simple, snails are capable of learning. They have a long-term memory and if you treat them with care, they get used easily and quickly and calmly are given in hand.
2.2. The conditioned reflex and its meaning
A conditioned reflex is a complex multicomponent reaction that is developed on the basis of unconditioned reflexes using the preceding indifferent stimulus. It has a signal character, and the organism meets the influence of the unconditioned stimulus prepared [3].
Conditional reflexes are easier to produce for ecologically similar effects to a given animal. In connection with this, conditioned reflexes are divided into natural and artificial reflexes. Natural conditioned reflexes are developed for agents that act naturally together with the stimulus, causing an unconditioned reflex, for example, the type of food, its odor, etc.). All other conditioned reflexes are artificial; are developed for agents that are not normally associated with the action of an unconditioned stimulus [2].
For the elaboration of a conditioned reflex it is necessary:
1.The presence of two stimuli, one of which is unconditioned (food, pain stimulus, etc.), which induces an unconditioned reflex reaction, and the other is a conditioned reflex, signaling the forthcoming unconditioned stimulation (light, sound, pain, etc.).
2. Multiple combination of conditioned and unconditioned stimuli (although the formation of a conditioned reflex is possible with their single combination).
3. The conditioned stimulus must precede the action of the unconditioned stimulus.
4. As a conditioned stimulus, any stimulus of the external or internal medium can be used, which should be as indifferent as possible, do not cause a defensive reaction, do not have excessive force, and is capable of attracting attention.
5. An unconditioned stimulus must be strong enough.
6. Excitation from the unconditioned stimulus should be stronger than from the conditioned stimulus.
7. It is necessary to eliminate extraneous stimuli, since they can cause inhibition of the conditioned reflex.
8. An animal that develops a conditioned reflex should be healthy.
9. In developing a conditioned reflex, motivation should be expressed [2].
In mollusks, it is possible to develop a conditioned reflex after one combination. If the snail is given mushrooms, which it always prefers, combining them with carbon dioxide poisoning, then the animal then always avoids the fungi, preferring other types of food [3].
2.3. Organization of the conditioned defense reflex of snails
In this work, the defensive reflex of the
snails of the genus Helix was used, so we will consider its neural
organization (the conceptual reflex arc). Irritant (skin prick)
acts on a group of receptors and excites a local detector
associated with motoneurons and several command neurons that have
overlapping motor fields. Communication is due to the lamellar
synapse. Each motoneuron is associated with a group of muscle cells
forming a muscle unit. In addition, some team neurons have direct
links to muscle units, which creates a focus of the motor field of
the command neuron.
Also there are not only local, but also
nociceptive detectors, which carry out communication due to
nonplastic synapses. An important part of the reflex arc is
nociceptive detectors. The axons of the modulating neurons
terminate at the presynaptic endings of the local detectors on the
command neuron. They increase the efficiency of synapses of
detectors on the command neuron
[3].
Figure 1 - UOR reflex snail grape
1. The motor field of the command neuron is determined by the composition of motoneurons with which it is connected. 2. Detector - a neuron, selectively tuned to the parameters of the input signal.
3. Command neuron - interneuron associated with other motor neurons.
4. Modulatory neurons of the defensive reflex are represented by a pool of serotonergic neurons, the electrochemical irritation of which leads to the release of serotonin, which phosphorylates proteins forming ionic calcium channels, activates adenine cyclase and the like.
5. Plastic synapse - can slow down the reaction due to changes in the concentration of the released acetylcholine (addictive), simple signal transmission (sensitization)
2.4. The effect of drugs on the nervous system
Adrenaline - has a stimulating effect on the nervous system. It increases the level of wakefulness, mental energy and activity, causes mental mobilization, an orientation reaction and a sense of anxiety, anxiety, or stress [9].
Influencing the body, diphenhydramine has a relaxing effect on the musculature, relieves pain, and also moderately blocks the endings of certain nerve nodes, which greatly dulls the pain [9].
3. Methods and location of the study
1.The list of abbreviations used: UOR - conditional defense reflex; CSS is a conditional stimulus; BS - unconditional stimulus; GA is a group of snails exposed to adrenaline; - a group of snails exposed to dimedrol; GC - a group of snails exposed to cold water; GG is a group of snails exposed to hot water; GK is a group of snails that are not affected (control).
2.Grape snails were removed from the environment at the end of May 2018 in the vicinity of the Baizak region of the Zhambyl region. Put in a specially made snail, taking into account all the requirements. Within two months adaptation to new habitats and habituation to the hands took place. The experiment was conducted in August 2018 in the school laboratory.
3. In experiments we used mature specimens of grape snails of uniform mass and size. Molluscs were kept in a common terrarium at room temperature, high humidity and an excess of food. Before the experiment began, the snails were adapted and were active for two months. Developed a classic RBM for tapping on the sink.
As the US used tapping on the sink, which in the norm almost did not cause a defensive reaction. BS served as an irritation of the cochlea in the shell area, which led to an unconditional defensive reaction of retraction of the ommatophore (antennae) (Fig. 2). The RBM was developed according to the scheme proposed by OA Maksimova and PM Balaban (1983) [2].
The interval between combinations of stimuli was 3-5 minutes, the time of presentation of BS and US was 1 second.
This form of training was conducted in five experimental groups. The first group of snails was exposed to the action of adrenaline (HA). The second group is the action of diphenhydramine (DG). The nervous system of a grape snail is characterized by a very high degree of concentration of ganglia, grouped in the peripheral nerve ring, so the drugs were applied to the surface of the body in this area. The body does not have dense skin and the absorption of the drug occurs externally.
The dosage of the drug was calculated taking into account the weight of the body of the snails. The drug was diluted to the required concentration with distilled water for injection. Calculation of the dosage of drugs was carried out taking into account the mass of the snails.
Preparation of preparations: Adrenaline and diphenhydramine solutions are taken for intramuscular injection, the daily dose of which is 1 ml per 60 kg of human body weight. Correspondingly, we recalculate the cochlea (the average mass of the cochlea is 25.6 grams with a sink, without a shell, an average mass of 15 grams); 0,0025 ml is the daily norm for the cochlea. The volume of the drop, the smallest, whose volume is more or less constant, is 0.033 ml, which is 13.2 times more than the daily norm for snails, so dilute the original solutions with distilled water for injections in 13.2 times. Now the daily norm of solutions for snails is 0.033 ml, i.е. 1 drop.
The gastropods respond well to the application of tactile, chemical, temperature stimuli perceived by individual sensitive cells scattered in the skin of the legs and mantle, so the experimental conditions were extended. The third study group was pre-conditioned in cold water (40C) for 15 minutes (GC) before the production of RBM. The fourth group was similarly maintained in hot water at a temperature of 450 ° C (GG) (Figure 3, Appendix B).
The fifth group of snails was not subjected to any influence and was a control. Each group consisted of five snails.
Figure 2
1. Treatment with aralinine solution.
2. Tapping on the sink (US) of adrenaline.
3. Tactile irritation (BS).
For the selection of uniform snails, we measured and weighed snails (Figure 1, Figure 2, Appendix B).
Knowing the height and width of the shell, based on some assumptions, calculated the volume of the shell. In particular, for shells of a helicoidal shape, this grape snail has a grape snail, the volume is calculated according to the formula [6]:
SB = SD2 * (SH / 2),
Where,
SB - the volume of the shell;
SD - large diameter of the shell; SH is the height of the shell.
4. After receiving all the data to confirm or deny its own hypothesis, the χ2 method was used (Pearson's agreement criterion).
3.1. Results of experiments
Before the experiment, all the measurements were made: weighing, measurement of height, width of the shell, length of the leg and volume of the shell for the selection of individuals in the test groups. The data of each group (mean value) are given in Table 1. Five snails with minimal deviations in the measurements were selected for each experimental group.
Table 1 - Data of snail measurements by groups
|
|
The weight snails (g) |
Width sinks (cm) |
Height sinks (cm) |
Volume Shells (cm3) |
Length feet (cm) |
|
GA |
25 |
2,9 |
3,5 |
14,7 |
10,2 |
|
DG |
27 |
3,1 |
3,5 |
16,8 |
10,5 |
|
YY |
25 |
3,0 |
3,4 |
15,3 |
9,8 |
|
GC |
26 |
2,9 |
3,1 |
13,0 |
10,1 |
|
GK |
25 |
3,0 |
3,2 |
14,4 |
10,0 |
Each snail in the groups was marked with a different color. Snails GA - crimson color, DG - burgundy color, GG - pink color, GC - blue color and HA - yellow color.
During the day, snails were taken randomly from the experimental group and made 7 sets of combinations of CSS and BS. US - tapping on the sink with a wooden hammer 5 times, should not be strong, but the snail should feel it. BS - a prick with a plastic tube, should not be strong, but palpable, so that the snail draws ommatophores (antennae). The experiment was carried out for 5 days before the development of a stable RBM. In total, there were 175 combinations of CSS and BS.
Quantitative data on the development of RBM are reflected in Table 2.
Table 2 - Dynamics of development of RBM in the experimental groups (%)
-
Groups
Number of CM and BS combinations
Average number combinations10
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
GA
20
40
40
40
DG
20
60
20
160
YY
40
40
20
120
GC
40
40
20
60
GK
20
60
20
80
More clearly, the data are
presented in the form of graphs showing the time difference and the
number of combinations for the development of
RBM
Figure 3 - Dynamics of production of a stable RBM in a grape snail
In the groups during the experiment, there was a fairly strong fluctuation of the RBM score associated with the beginning and end of the series. That is, the time between series of snails reduced the level of RBM, so the new series did not start with a score that the snails had at the end of the previous series, but with a slightly smaller one. To determine the score, I introduced a five-point ranking system for RBM.
The degree of retraction of the antennae on the BS: 5 points - ommatophore pulls completely; 4 points - one ommatophore retracts fully, the second half; 3 points - both ommatophore are retracted in half; 2 points - only one ommatophore is drawn in; 1 point - the ommatophore is retracted. The fluctuations of the RBM ball are reflected in Table 3.
Table 3 - RBM score /% of snails
-
1 day
2 day
3 day
4 day
5 day
5 day
5/100
5/100
5/40
5/20
4/20
GA
4/60
4/80
3/80
DG
5/100
5/40
5/20
5/20
3/20
4/60
4/20
3/40
1/80
3/60
2/40
YY
5/100
5/80
5/20
4/20
2/60
3/20
4/60
3/60
1/40
2/20
1/20
GC
5/100
4/80
5/40
5/20
4/40
3/20
4/40
4/20
3/20
2/20
2/60
1/40
GK
5/100
5/100
5/80
5/40
5/20
3/20
4/20
3/40
3/40
2/40
It can be seen from the table that snails are fatigued - the moment when snails are very reluctant to stick out their antennae after a successful combination [4].
The last day in the two groups there was insensitivity - an extreme measure of fatigue, when the snail ceases to respond to any effects. Insensitivity, as a rule, appeared at the end of the series, perhaps this is due to the mechanism of habituation.
After the development of a stable RBM, the time of preservation of the reflex was checked, i.e. Snails were exposed to the action of the US without the reinforcement of the BS. And thus there was a defensive reaction (retraction of ommatophores). The elaborated reflex was maintained for 40 days (Fig. 5). Then the snails did not react to the US. The diagram shows a decrease in positive responses to the US in time.
Figure 5 - Dynamics of conservation of RBM
In the course of the experiment, it was found that the snails demonstrate an increase in defensive reaction only in the situation in which the training took place. This confirms the assumption that snails can differentiate the situation in which they were presented with conditional and unconditional stimuli.

Each day of the experiment was
recorded in the
protocols.
3.2. Analysis of the results obtained
After the development of the RBM, all data were processed and analyzed.
In the five study groups, there is a significant spread in the time and number of combinations for the development of RBM (Figure 6).
Analyzing the diagram, it is clear that snails from GA are the best results: 20% of snails (1 snail) showed a positive response to the US on the first day after 20 combinations, the rest showed a positive response the next day, the spread was only in the number of combinations (2 snails at the beginning of the series and 2 at the end of the series).
At the same time, we observe a stable RBM in snails in the GK, but the time for the development of a stable reflex for the entire group as a whole is increased, so 20% of snails show RBM at the beginning of the series on day 3, and 60% of snails at the end of the series of the 2nd day.
Snails exposed to cold water show slightly better results than snails of the HA. The majority of snails (80%) give a positive response to tapping at the end of the second day. Probably staying in water leads to a reduction in cells and a shortening of the way information is transmitted. And the second version, that having been in the water, slime is washed off from the body of the snails, which reduces the tactile irritation from the BS.
The slowest time interval and the largest number of combinations was required by snails from the DG and GG. Subject cohorts of the GH showed a stable RBM on the third day (40%), the rest gave a positive response on the 4th day. Staying in hot water is unnatural for snails. In natural conditions, this does not happen. In the biotope, from which the snails are seized, the temperature of the air does not exceed 300 ° C on the hottest days. Therefore, artificially created conditions cause the cochlea to minimize the surrounding effect and it hides in the sink. We had to wait 3-4 minutes until they completely emerge from the sink to start the experiment.
Snails exposed to a solution of diphenhydramine for the longest time could not be trained. As already mentioned above, diphenhydramine has a relaxing effect on the musculature, it also moderately blocks the endings of some nerve nodes, which significantly increases the time of RBM production: 1 snail (20%) gives a positive response to BS on the 4th day, the rest at the end of 5 day with 160-170 combinations.
Snails from this group often showed a manifestation of fatigue and numbness. That is, during the series there was an alternation of positive and negative response to the BS. Snails from GA practically did not show fatigue, and from group GK a small display of fatigue on the 5th day.
The obtained results confirm the hypothesis put forward by us on the effect of drugs and body temperature on the rate of production of RBM. To check the correctness of the hypothesis, it was decided with the help of the criterion χ2 (Pearson's agreement criterion).
Knowing that the scientific data on the production of RBM in a grape snail are within the limits of 95-105 combinations (mean value 100 [4]), we see that the data observed by us are very different from the expected ones, since medications and body temperature seem to still have influence on the rate of development of RBM. We check this: χ2 = Σ (fo-fe) 2 / k, where fo and fe are the observed and expected combinations of stimuli. The summation is performed over all cells of the table. We have: x2 = (40-100) 2/100 + (160-100) 2/100 + (120-100) 2/100 + (60-100) 2/100 + (80-100) 2/100 = 16
The number of degrees of freedom in us is 4 (the number of lines is 1), so the probability of the observed value can be a random deviation of 0.5%. The value of 16 obtained by us exceeds the critical value 14.86, which gives us the right to consider the hypothesis put forward by us to be correct.
For us, it was interesting how long the produced RBM would survive under the action of various drugs and temperature. It is well known that the developed RBM in a snail of grape remains for 52 days [4] when reminding the external conditions of training. In our experiment, the longest time of conservation of RBM was 40 days. It can be assumed that the change in the time of preservation of the reflex was influenced by a change in the external environment (a decrease in air temperature by an average of 100 ° C).
Analyzing Table 4, it can be seen that the dynamics of the preservation of RBM between groups is significantly different from the intra-group indicators.
Table 4 - Dynamics of conservation of RBM in a grape snail (%)
-
GA
DG
YY
GH
GC
1 day100
100
100
100
100
3 day
100
100
100
100
100
5 day
100
100
100
100
100
7 days
100
60
100
100
100
10 days
100
40
100
100
100
15 days
100
40
80
100
100
20 days
100
20
40
80
100
25 days
80
0
20
80
100
30 days
80
0
0
40
80
35 days
40
0
0
0
40
40 days
20
0
0
0
0
45 days
0
0
0
0
0
A positive response to the CSS was checked
daily. It can be seen from the groups that the longest response was
the positive response to the snail from the GA group. Snails from
the GD group stopped responding to tapping before everyone else,
apparently the preservation of the reflex also depends on the time
of its elaboration, since the cochlea from this group showed a
stable positive reflex on days 4 and 5, then the further
combination of US and BS was discontinued, and in other groups, it
lasted longer after receiving the first positive response.
Therefore, it is incorrect to talk about the effect of the drug and
the temperature on the preservation of
RBM.
In any case, we see that in
each group the number of positive answers decreases over time, and
eventually it reduces to 0. Here we can make an assumption about
the influence of the time passed from the moment of the first
positive response and to the end of the experiment that lasted 5
days, if the snails from the GA gave a positive response for 1-2
days, and their training was carried out until the end of the
experiment and the time for fastening was more than 3 days, then
there was very little time for fixing snails from the
DG.
Сonclusions
Thus, our experiments showed:
1. Drugs adrenaline and diphenhydramine affect the rate of production of stable RBM. The difference in production time in these groups is significant. The speed of generation of RBM in the GA is 4 times the speed in the DG.
2. The temperature of the cochlea's body affects the rate of development of RBM. The rate of production of RBM in the GG group is 2 times lower than the rate of development of a similar reflex in the GC.
3. The effect of the adrenaline and diphenhydramine solution and temperature on the production rate of RBM is statistically significant.
4. Snails have a long-term memory, but it depends on external conditions, i.e. The snail gives a positive response to the US in conditions similar to the training conditions. The time of preservation of RBM depends on the time of training.
Practical significance and direction of further research
Ethical experiments on animals are the subject of numerous debates. The dominant point of view today is the need for experiments for the sake of progress in science, under the condition that the suffering of animals will be minimized (as well as the number of laboratory animals) [9]. In our case, the minimum number of experimental snails in each group was taken, and irritation with the preparative needle was replaced by tactile irritation with a plastic tube, which is also palpable, but much less Delivers painful sensations.
The application of the results of our work can be in several directions:
1. In the educational process. These studies clearly demonstrate the development of a conditioned reflex, which can be used in biology classes (8 cells). There is no need to re-run the experiments, just watching the video. At the lessons of medicine (10-11 cells.), It is possible to use this material when studying the topic "Medications". In extracurricular activities and after-hours activities, since animals living with us in one biotope are an integral part of biodiversity conservation.
2. In medicine (pharmacology). The effect of drugs on snails is similar to that of humans, so it may be possible to use snails to test the effect of new neurostimulating drugs or their components, since snails have fairly large neurons with a relatively simple nervous system and a fairly complex behavioral repertoire.
3. In animal husbandry. The widespread use of conditioned reflexes in the practice of animal husbandry makes it possible to increase the productivity of animals. In our work, showing the possibility of elaborating a conditioned reflex in a cochlea, we propose to develop a positive food reflex for the fastest increase in the weight of the body of the cochlea. And for further development and its consolidation, additional stimulating factors can be used. To do this, create so-called "Street farms," in which in large quantities to breed snails for later cooking or export, while creating favorable conditions for them [7].
4. Use of a snail as a phytophagous. The snail eats large-leaved weeds - nettles, cow-bream, hay, in their place the meadow grass grows, as the soil is enriched with excrement of grape snails, which are ten times more effective than the excrement of the Californian worm. To do this, the snails need to develop a stable food reflex, in particular, on the cow, which is very important for our region [11].
In the future it is planned to continue studying the grape snail. To check the dependence of the stability of the reflex on medications, to develop a positive food reflex to cowbler and to test in practice as a method of fighting hogweed, for this, to find a positive stimulus.
Қосымшалар

Ұлуды өлшеу

Ыстық суда ұлулардың шыдамдылығын бақылау

Ұлулардың салмағын өлшеу
ҚОЛДАНЫЛҒАН ӘДЕБИЕТТЕР ТІЗІМІ
1.Қазақстан Республикасы Үкіметінің 2012 жылғы 23 тамыздағы № 1080 қаулысымен бекітілген Орта білім берудің (бастауыш, негізгі орта, жалпы орта білім беру) мемлекеттік жалпыға міндетті стандарты.
2.«Биология» пәнінен зертханалық және практикалық сабақтарды өткізу» Әдістемелік құрал Астана 2014.
3. Қазақстан Республикасының Білім және ғылым министрінің 2013 жылғы 3 сәуірде №115 бұйрығымен бекітілген «Жаратылыстану» білім саласы пәндерінің оқу бағдарламаcы.
4.Оразымбетова Б.Б.«Биологияны оқыту әдістемесі»Методикалық оқулық. Қостанай. –2010ж 93-96б.
5.Сидоров Е.Г., Белякова Ю.В., Куналиев Д. Ш., К оценке ситуации по описторхозу в зоне канала Иртыш-Караганда, Мед. паразитол /. 1991. 40 б -42 б.
6.Фролова Е.С. Малакофауна некоторых бессточных озер Северного Казахстана. Вопросы малакологии Сибири. – Томск, 1969. 52 б -54б.
7.Фролова Е.С. Пресноводные моллюскиСеверного Казахстана и их роль в биомассе бентоса в природных комплексах. Заметки по фауне и флоре Сибири. - Томск: Изд-во ТГУ, 1984 / . 42 б -50 б.
8.НаталиВ.Ф. «Зоология беспозвоночных»Учебник для студ. биолог. Фак. Пед. ин-овПод. Ред. О.Н.Сазановой.Изд. 3-е, перераб. и доп. М.«Просвещение», 1975., 487 стр. С илл.
9.АхметоваБ.А.«Омыртқасыздарзоологиясынанлабораториялықсабақтарөткізуге арналған методикалық нұсқаулар» А.1989.
10.ТүсіповаК.С. «Омыртқасыздарзоологиясы» 2-ібөлімдікОқулық К.С.Түсіпова - Алматы: 1-бөлім.-1998. -336 б.
11.ЗеликманА.Л. «Практикум по зоологии беспозвоночных»Учеб. Пособие для ун-ов и пед. ин-ов. М. «Высшая школа»,1965., ЗЗІстр. с илл.
12.Сайт зоологического института Российской академии наук http://www.zin.ru/animalia/coleoptera/rus/index.htm
13.Энтомолог.narod.ru http://entomolog.narod.ru/metodiki.html *
14.Зоологические экскурсии по Байкалу Фауна в картинках http://zooex.baikal.ru/beetles/coleoptera.htm
15."Жужелицы мира (Carabidae of the World)" - таксономия, географическое распространение и прекрасные изображения жужелиц http://www.carabidae.ru/>
16.Зооклуб мегаэнциклопедия о животных http://www.zooclub. ru/chlen/nasek/zhuk.shtml
17.Coleoptera (Beetles, Kaefer, Brouci) - HomePage (крупнейший англоязычный колеоптерологический сайт) http://www.coleoptera.org/
18. Энтомологический кружок Алексея Куприянова (разнообразные сведения для начинающих энтомологовhttp://tinea.narod.ru/
19.Энциклопедия насекомых - большой сайт с разнообразной информацией (классификация, краткие описания видов, фотографии, определители) http://www.coleop123.narod.ru/
20. ДәуітбаеваК.Ә.«Омыртқасыздар зоологиясы» // Алматы. 1-кітап. -2004. – 374 б
21. Оразымбетова Б.Б., Көбеев М.С. «Жануартану пәнінде көрнекілікті қолдану» // Методикалық оқулық. Қостанай. - 2003.
22. Проценко А.И.К изучению энтомофауны Кустанайской области.Лесные экосистемы Тургайской впадины (тезисы докладов). Кустанай 1993 С. 56-59.
23.ТілменбаевӘ.Т.,ЖармұхамедоваГ.Э.Энтомология.Алматы,Кайнар, 19947 -336б.
24.Осмоловский Г.Е., Бондаренко Н.В. Энтомология. - Л.,«Колос», 1980. -360с.
25.Матпаева Б.Б., Тілменбаев Ә.Т.Ауыл шаруашылығына пайдалы жәндіктер.-Алматы:Қайнар,1973.20.Методы сбора и учетов численности насекомых. Е.А.Дунаев, А.С.Боголюбов.- М: Экосистема, 1996. - 25 с.
26.Методы исследований зообентоса и оценки экологического состояния водоемов (сост. А.С.Боголюбов). - М.: Экосистема, 1997 - 17 с.
27. Методы сбора и учетов численности насекомых. Е.А.Дунаев, А.С.Боголюбов.- М: Экосистема, 1996. - 25 с.
28.Методы исследований зообентоса и оценки экологического состояния водоемов (сост. А.С.Боголюбов). - М.: Экосистема, 1997 - 17 с.
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
ЖҮЗІМ ҰЛУЫНЫҢ ТҰРАҚТАНДЫРЫЛҒАН РЕФЛЕКСТІ ДАМЫТУДЫҢ ДИНАМИКАСЫ
ЖҮЗІМ ҰЛУЫНЫҢ ТҰРАҚТАНДЫРЫЛҒАН РЕФЛЕКСТІ ДАМЫТУДЫҢ ДИНАМИКАСЫ
Жамбыл облысы Байзақ ауданы
№1 мектеп-гимназиясы
Ізденуші : Нишанова Жұлдыз
7 «б» сынып оқушысы
ЖҮЗІМ ҰЛУЫНЫҢ ТҰРАҚТАНДЫРЫЛҒАН РЕФЛЕКСТІ
ДАМЫТУДЫҢ
ДИНАМИКАСЫ
Бағыты: Жаратылыстану
Секция: Биология
Ғылыми жетекшісі: Нурманова Айгуль Куйчибаевна
Биология пәнінің мұғалімі
Мазмұны
І.Кіріспе
Моллюскілердің экономикалық
маңызы
ІІ.Негізгі бөлім
2. 1. Жүзім ұлуының эколого-биологиялық ерекшеліктері
2.2. Шартты рефлекс және оның мағынасы
2.3 Шырындардың шартты қорғаныс рефлексін ұйымдастыру
2.4 Препараттардың жү,йке жүйесіне әсері ,
ІІІ. Зерттеу бөлімі
3.1.Құралдарды дайындау
3.2. Эксперименттердің нәтижелері
Қорытынды
Пайдаланылған әдебиеттер
Қосымша
Кіріспе
Өркениеттің дамуының қазіргі кезеңінде табиғатқа антропогендік әсері экожүйелердің нашарлауына және биосфераның гендік әртүрлілігінің төмендеуіне әкелетін қайтарымсыз процестерге әкеледі. Көптеген өсімдіктер мен жануарлардың түрлерін сақтау және биоценозды қорғау бойынша шаралар жүйесін әзірлеу қажеттілігі бұрыннан танылды.
Соған қарамастан, жануарлардың кейбір түрлері, негізінен омыртқасыздар, биологиялық әртүрлілікті сақтауға қатысты көптеген зерттеушілердің назарынан тыс қалған. Алайда, бұл ағзалардың экожүйелердің тұрақтылығын қамтамасыз етудегі рөлі, табиғат заттарының циклы процестері, топырақтың қалыптасуы және биодеградация өте жоғары және бұл биогеоценоздың бұл компоненттеріне әсер етеді, бұл қоғамдағы қайтымсыз өзгерістерге алып келеді.
Тазартулар Қазақстанның жерүсті экожүйесінің ажырамас бөлігі болып табылады. Органикалық заттардың ыдырауы мен минералдануына қатысады, олар табиғатта заттардың айналымында маңызды байланыс ретінде әрекет етеді [8]. Моллюскілердің экономикалық маңызы бар. Қазіргі уақытта биологиялық ғалымдардың, микробиологтардың, дәрігерлердің зерттеулерінің арқасында жүзім ұлуын қолдану ауқымы кеңейіп келеді, демек, бұл моллюсгумның коммерциялық маңыздылығы үнемі артып келеді. Бұл факт, жүзімдік ұлуларын адамның тарапынан ерекше назар аударатындығына әкелді. Ол ойластырылмаған көптеген жоюлардан қорғалуы керек, сондықтан ол туралы толық ақпарат қажет [5].
Жануарларды сыртқы ортада өмір сүрудің өзгеретін жағдайына бейімдеу жүйке жүйесінің қызметі арқылы қамтамасыз етіледі және рефлексиялық белсенділік арқылы жүзеге асырылады. Эволюция процесінде галеолярлы реакциялар (шартсыз рефлекстер) пайда болды, түрлі органдардың функцияларын біріктіреді және үйлестіреді, ағзаны бейімдеуді жүзеге асырады [2].
Helix тектес жүзім ұлуының жүйке жүйесін ұйымдастыру адамның жүйке жүйесіне қарағанда қарапайым, бірақ сигнал беру және құрылымның принципі бірдей. Бұл жүйрік жүйенің салыстырмалы қарапайымдылығы нейробиологиядағы зерттеулер үшін тартымды етеді. Зығырдың қол жетімділігі мен үлкен мөлшері оларды неміс ғалымдарының зерттеуге дейінгі объектісі болуға мүмкіндік берді, тіпті соңғы ғасырда да [3].
Мақсаты мен міндеттері
Біз гипотезаны жасадық: түрлі дәрі-дәрмектер және сыртқы жағдайлар жүзім ұлуындағы шартты рефлексті дамытуға және бекітуге әсер етуі мүмкін.
Осыған байланысты осы зерттеудің мақсаты жүзім ұлуының тастарындағы шартты рефлексті дамытуға әртүрлі дәрілік заттар мен түрлі температуралардың әсерін анықтау болды.
Мақсатқа сүйене отырып, келесі міндеттер қойылды:
- жүзім ұлуының тұтқында өмірін және мінез-құлқын зерттеу;
- эксперименталды 5 топтарда жүзім ұлуының шартты қорғаныс рефлексін дамыту;
- әртүрлі зерттеу топтарындағы жүзім ұлуының шартты рефлексті сақтау уақытын анықтау
2.1.Жүзім ұлуының эколого-биологиялық ерекшеліктері
Жүзім ұлуы(Helium pomatia) - біздің жануарлар әлемінің ең ірі былқылдақ денелі жануарлар. Жүйелік позиция [8] (А қосымшасы):
Патшалық - жануарлар;
Түрі - ұлулар;
Class - былқылдақ денелілер;
Отряд – өкпе ұлулары;
Отбасы - гелицид;
Отбасы - Helix;
Түрі - жүзім ұлуы;
Халықаралық ғылыми атауы - Helix pomatia
Жүзім ұлуының туған жері - Орталық және Оңтүстік-Шығыс Еуропа. Ұзақ уақыт бойы адамдар жүзім ұлуын азық ретінде пайдаланды, олар нәзіктікке ие болмады, ал кез-келген әлеуметтік мәртебелі адамдар оларды қолжетімді және пайдалы тамақ ретінде пайдаланды [8].
Жүзім ұлуы Еуропаның солтүстік бөліктерінен басқа Балтық теңізінің жағалауына қоныстанды. Ол бұталардың шабақтарында, жеңіл орман шетінде, бақшаларда, саябақтарда тұрады. Ұлулар көктемнен алғашқы суыққа дейін белсенді, содан кейін топыраққа 30 см тереңдікте еніп, анабиозға түседі. Анабиоз кезінде қабықтың ауызы қылшықпен жабылады – эпифрагма, қалыңдығы қыс мезгілінің ауырлығына байланысты. Табиғатта жүзім ұлуы орта есеппен 7-8 жыл өмір сүреді, бірақ оларды жыртқыштар жеп қоймаса, жиі 20 жылға дейін өмір сүре алады [12].
Сыртқы көрінісі
Денесі, топтың барлық өкілдері секілді сыртқы қабаттағы қабырға мен магистральға бөлінеді. Соңғысында аяқ және бас ерекшеленеді. Ішкі органдар мантиямен қоршалған, оның бір бөлігі сыртынан көрінеді.
Ересектердің қабығының диаметрі орта есеппен 3-4,5 см құрайды; оның көлемі бүкіл денені толығымен орналастыру үшін жеткілікті. Қабық спиральды қисық; Түрлі ұшақтарда (турбо-спираль деп аталатын) 4,5 төңкеріс бар; оңға бұралған; сағат тіліне қарсы. Мұндай қабықшалар дезоксотропты деп аталады.
Қабықтың түсі сары-қоңырдан қоңыр-ақ түсті болады. 2-3 революцияның бүкіл ұзындығы бойында 5 қара және 5 жеңіл жолақ бар. Кейбір ұлулардың қабығының түсі қара, ал басқаларында ашық рең. Түстің қанықтылығы тіршілік ету ортасына байланысты және жарықтың қарқындылығымен және қоршаған орта фонымен байланысты, яғни ол маскировка жасауға көмектеседі. Қабықтың түсі жеген тағам түріне байланысты өзгеруі мүмкін.
Қабық қабырғалы. Бұл жер бетінің аумағын көбейтеді, бұл сізге ылғалды көп жинақтауға мүмкіндік береді. Қабырғалар да қабықты күшейтеді, сонымен қатар, арқасында раковинаның салмағы аз [11].
Ересектердің аяқтың қалыпты ұзындығы 3,5-5 см, ал жануар 8-9 см дейін созылуы мүмкін.
Жузім ұлуын - жүзімдіктен, ал жалаңаш шырышты бау-бақшалар мен өзге заттар астынан кездестіре аламыз. Бұлардың көпшілігінің денесін бақалшақ қаптайды. Бақалшақтарының пішіні әр түрлі болады. Кейбіреулерінде, мысалы, жалаңаш шырыш денесінде бақалшақ қалдығы ғана сақталған. Денесі жұмсақ. Бақалшақты ұлулардың денесін жобалан бас, тұлға және аяққа жіктеуге болады. Аяғы дененің астыңғы бөлігі - бауырын толық қамтитындықтан, бұлар бауыраяқты ұлулар класына жатқызылады. Бауыраяқтылардың 80 мыңға жуық түрлері белгілі. Бау-бақшаға, жүзімдіктерге, баққа жалаңаш шырыш, жүзім ұлуы айтарлықтай зиян келтіреді. [10].
Тыныс алу
Жүзім ұлуы өкпенің көмегімен дем алады. Тыныс алу тесіктері - пневмостиль - мантияның қаптамалары арасында қабықтың революциясымен бірдей орналасқан.
Қозғалуы
Жүзім ұлуы оның бұлшық еттерінің көмегімен қозғалады. Бұлшықеттердің қысылуының көмегімен жануар сырғып кетіп, бетінен бет бұрады. Жылжытқанда, шырышты босатады, ол субстрат арқылы қозғалысты жеңілдететін үйкелісті жұмсартады. Былғары былғары безі дененің алдыңғы бөлігінде орналасқан. Қозғалыс орташа жылдамдығы шамамен секундына 1,5 мм.
Анабиоз
Жыртқыш ұлудың анабиозы 3 айға дейін созылады. Қазақстанның табиғи жағдайында - кем дегенде 5 ай, ал анабиоздық кезеңде тәулігіне 60 күннен кем моллюскалар, сондай-ақ, эксперименттік жағдайларда азайтылған құнарлылығымен ерекшеленді немесе жұмыртқаны мүлдем бермеді
Табиғи жаулар
Жүзім ұлуының табиғи жаулары – кірпілер, жер, жыландар және басқа жануарлар, сондай-ақ жүзім ұлуының ішіне тыныс алу жолдары арқылы өтетін саңырауқұлақ қоңыздарының түрлі түрлері [7].
Өсіру
Жүзім ұлулар ежелгі дәуірден бері өсіріледі. Қазір бірқатар елдерде «ұлу шаруашылықтары» деп аталады, олар экспорт үшін - жүзім ұлуын өсіріп, оларға қолайлы жағдай жасау арқылы көп мөлшерде дайындайды.
Жүзім ұлуларының еті 10% протеин, 30% май, 5% көмірсулар, сондай-ақ B6, B12 дәрумендері, темір, кальций, магний бар. Қазақстан Республикасының Ұлттық ғылым академиясының Балық шаруашылығы институтының мәліметі бойынша, -65% протеин, шамамен 5% май, қалғандары - төменгі молекулалық органикалық және минералды қосылыстар - күл. Бірқатар елдерде хош иісті заттар фармацевтика өнеркәсібінде мейрамханаларда сатуға арналған [1]
Медицинада
Бронхо-босаңсытқыштың қасиеттеріне байланысты жүзім ұлуларынан алынған глицитин сығындысы қолданылады. Түрлердің өкілдері бағалы заттарды - лириндерді оқшаулау үшін де қолданылады
Ауыл шаруашылығына зиян келтіреді
Жүзім ұлуы ауыл шаруашылығының жауы болып табылады, ең алдымен ол жас өсімдіктердің өнуі барысында, әсіресе жүзім ктерді жейді [6].
Жүзім ұлу - тұтқында ұстаудың керемет және қолжетімді нысаны. Олар мүлдем қарабайыр емес сияқты көрінеді. Жүйке жүйесі өте қарапайым болғанына қарамастан, ұлулар үйренуге қабілетті. Ұзақ уақытты есте сақтайды және оларға қамқорлықпен қарайтын болсаңыз, олар оңай және жылдам пайдаланылады және тыныштықта қолға оңай беріледі.
2.2. Шартты рефлекс және оның мағынасы
Шартты рефлекс - бұрынғы немқұрайлы емес ынталандыруды пайдалана отырып, сөзсіз рефлекстер негізінде әзірленген кешенді көп компонентті реакция. Ол сигнал сипатына ие, және ағза дайындалған шартсыз ынталандырудың әсеріне жауап береді [3].
Шартты рефлекстер осы жануарларға экологиялық жағынан ұқсас әсер ету үшін оңай шығарылады. Осыған байланысты шартты рефлекстер табиғи және жасанды рефлекстерге бөлінеді. Табиғи шартты рефлекстер ынталандырумен бірге табиғи түрде әрекет ететін агенттер үшін әзірленеді, бұл сөзсіз рефлексті, мысалы, тағамның түрі, оның иісі және т.б.). Барлық басқа шартты рефлекстер жасанды болып табылады; агенттер үшін әдетте жасалынбайды, олар әдетте шартсыз ынталандырудың әрекетімен байланысты [2].
1.Шартты рефлекстерді жасау үшін қажетті ең негізгі жағдай – индифренттік (өздігінше осы реакцияны тудыра алмайтын, кез келген бөтен) тітіркендіру мен шартсыз, сол реакцияны міндетті түрде тудыратын тітіркендірудің әсер ететін уақытының бір-біріне дәл келуі (ұштасуы).
2. Бөтен тітіркендіргіш шартсыз тітіркендіргіштердің әсеті басталар алдында әсер етуі керек. Екі тітіркендіргіш әсері бір уақытта берілсе шартты рефлекстің жасалуы едәуір қиындайды. Ал алдымен шартсыз, одан кейін индифренттік тітіркендіргіш әсет етсе, шартты рефлекс алынғанмен, ол өте тұрақсыз болады. (Алдымен шартсыз, кейін бөтен тітіркендірумен әсер еткенде шартты рефлекстің жасалуының қиын болатын себебі, теріс индукция заңымен және шартсыз тітіркендірудің күшінен бөтен тітіркендіргіш күшінің кемдігімен түсіндіріледі). Жасалған шартты рефлексті ұзақ уақыт сақтау үшін, оны мезгіл-мезгіл шартсыз тітіркендіргішпен бекітіп отыру қажет.
3. ми қыртысы клеткаларының жеткілікті жоғары қозғыштығы болуы керек. Ол үшін ми қыртысы түрліше басқа әсерлерден бос болу керек. Сонда ғана белгілі тітіркендіруге жүйке клеткалары жоғары қозумен жауап бере алады.
4. Шартты рефлекс жасалу қолданылатын тітіркендіргіштің қасиеті мен күшіне де байланысты. Бөтен тітіркендіргіштің күші қыртыста қозу ошағын тудыруға жететін болуы керек.
Ұлуларда бір комбинациядан кейін шартты рефлексті дамытуға болады. Егер тұздыққа саңырауқұлақтар берілсе, ол оны әрдайым ұнатады, оларды көміртегі қос тотығымен улану арқылы біріктірсе, онда жануар әрдайым тағамның басқа түрлерін таңдап, саңырауқұлақтардан үнемі бас тартады [3].
2.3. Шырындардың шартты қорғаныс рефлексін ұйымдастыру
Бұл жұмыста Helix тектес жүзім ұлуының қорғаныс рефлексі пайдаланылды, сондықтан біз оның нейрондық ұйымын (тұжырымдамалық рефлексиялық доғаның) қарастырамыз. Тітіркендіргіш (тері тесігі) рецепторлар тобында әрекет етеді және қозғалтқыш алаңдары бар мотоневрондар мен бірнеше командалық нейрондармен байланысты жергілікті детекторды қоздырады. Байланыс лейколярлық синапспен байланысты. Әрбір қозғалғышты бұлшық ет бөлігін құрайтын бұлшықет жасушаларының тобымен байланысты. Сонымен қатар, кейбір командалық нейрондар бұлшықет бірліктеріне тікелей байланыстырады, бұл командалық нейронның қозғалтқыш алаңының фокусын жасайды. Сондай-ақ, непластикалық синапстардың арқасында байланыс жасайтын жергілікті ғана емес, сонымен қатар нозицептивті детекторлар бар. Рефлексия доғаның маңызды бөлігі - нозицептивті детекторлар. Модуляциялы нейрондардың аксону командалық нейрондағы жергілікті детекторлардың прессинаптически аяғында аяқталады. Олар детекторлардың синтездерінің тиімділігін нейрон командалары бойынша арттырады [3].

1-сурет. Жүзім ұлуының УОР рефлексі
1. Нейрондық командалық нейронның қозғалтқыштық алаңы оған қосылған мотоинурондардың құрамымен анықталады.
2. Детектор - кіріс сигналының параметрлерін таңдайтын нейрон.
3. Басқа моторлы нейрондармен байланысты нейрондық командирлеу - интерферон.
4. модуляторлық нейрондар қорғаныс рефлексі кальций иондық арналар қалыптастыру протеиндер phosphorylates серотонин босату, әкеледі электрохимиялық ынталандыру, олардың бассейн серотонинергической нейрондарды іске қосады adeninatsiklazu т.б. ұсынылған ..
5. Пластикалық синапс - шығарылған ацетилхолин концентрациясының өзгеруіне байланысты (реакция), жай сигнал беру (сезімталу)
2.4. Препараттардың жүйке жүйесіне әсері
Адреналин - жүйке жүйесіне ынталандырушы әсер етеді. Ол ояу деңгейін, ақыл-ой мен белсенділіктің деңгейін арттырады, ақыл-ойды жұмылдыруға, бағдарлау реакциясына және алаңдаушылыққа, алаңдаушылыққа немесе стресстікке әкеледі [9].
Денеге әсер ететін дифенгидрамин бұлшықетке босаңсытатын әсер береді, ауырсынуды жеңілдетеді, сондай-ақ ауырсынуды азайтатын белгілі жүйке түйіндерінің аяқтарын қалыпты түрде блоктайды [9].
ІІІ. Зерттеудің әдістері мен орны
1. Қолданылатын қысқартулардың тізімі: УОР - шартты қорғаныс рефлексі; УС - шартты ынталандыру; БС - сөзсіз ынталандыру; ГА - адреналинге ұшыраған ұлулардың тобы;
ГД- димедролға ұшыраған ұлулар тобы; ГХ- суық суға ұшыраған ұлулардың тобы; ГГ ыстық суға ұшыраған ұлулардың тобы; ГК - әсер етпейтін (бақылау) ұлулардың тобы.
2. 2018 жылдың мамыр айының аяғында Жамбыл облысының Байзақ ауданында жүзім құймалары қоршаған ортаны алып тастады. Барлық талаптарды ескере отырып, арнайы жасалынған құтыға қойыңыз. Екі айдың ішінде жаңа мекендейтін орындарға бейімделу және қолдарға әдеттену. Тәжірибе 2018 жылдың тамызында мектеп зертханасында өткізілді.
3. Эксперименттерде біркелкі массаның және өлшемдердің жүзімдік ұлуларының жетілген үлгілерін қолдандық. Моллюскалар жалпы термориумда бөлме температурасында, жоғары ылғалдылықта және азық-түліктің астығында сақталған. Эксперимент басталмас бұрын, ұлулар екі ай бойы бейімделді. Раковинадағы клиникалық УОР жасалды.
УС-та раковинаның үстінде қолданылғандықтан, нормада қорғаныстық реакция туындаған жоқ. БС қабық аймағында коклеяны тітіркендіреді, бұл гаммофордың (антеннаның) кері кетуінің сөзсіз қорғаныстық реакциясына әкелді [2]. Сигналдардың комбинациясы арасындағы интервал 3-5 минут, БС және УС презентациясы 1 секунд болды.
Бұл оқыту түрі бес тәжірибелік топта өткізілді. Ұлулардың алғашқы тобы адреналин (ГА) әсеріне ұшырады. Екінші топ - дифенгидрамин (ГД) әрекеті. Жүзім ұлуның жүйке жүйесі перифериялық жүйке сақинасында топтастырылған ганглияның концентрациясының өте жоғары деңгейімен ерекшеленеді, сондықтан осы аймақта дененің бетіне қолданылды. Дене тығыз теріге ие емес және препараттың сіңірілуі сыртта пайда болады.
Препараттың дозасы ұлулардың денесінің салмағын ескере отырып есептелді. Препарат инъекцияға арналған дистилденген сумен қажетті концентрацияға дейін сұйылтылған. Есірткі дозасын есептеу құйрықтардың массасын ескере отырып жүргізілді.
3.1.Құралдарды дайындау:
Тамырдан енгізу үшін адреналин және димедрол қабылданған шешімдер, адам денесінің 60 кг салмағына шаққанда 1 мл тәуліктік доза. Тиісінше, ұлулар салмағына теңейміз (ұлулар орташа салмағы - раковина бар 25,6 грамм, раковинасы болмаған жағдайда орташа салмағы 15 грамм) 0,0025 мл - коклеяның күнделікті нормасы. Тамшы мөлшері - ең кішкентай, онда көрсетілген көлемі көп немесе аз тұрақты, алайда қор шешім 13,2 есеге инъекцияға арналған тазартылған сумен таратылған болатын ұлулар үшін үлкен 13,2рет күнделікті 0,033 мл, болып табылады. Енді ұлулар үшін күнделікті деңгейі 0.033 мл, яғни 1 тамшы болып табылады.
Бауыр аяқтар мен мантияның теріге шашыраған жеке сезімтал жасушалар қабылдаған тактильді, химиялық, температура ынталандырғыштарын қолдануға жақсы жауап береді, сондықтан тәжірибелік шарттар кеңейтілді. Үшінші зерттеу тобы УОР өндірісіне дейін 15 минут бойы (ГХ) суық суда (40С) алдын-ала шартталған. Төртінші топ сондай-ақ ыстық суда 450 ° C (ГГ) температурада сақталды (2-сурет, B қосымшасы).
Ұлулардың бесінші тобы қандай да бір әсерге ұшырамай, бақылауға ие болды. Әрбір топ бес ұлаудан тұрды.
1. Адреналинді ерітіндімен емдеу.
2. Адреналиннің (УС) раковинаның үстінде басу.
3. Тактилдік тітіркену (БС).
Бірқалыпты ұлуларды іріктеу үшін, біз салмақтарын өлшеу жұмыстарын жүргіздік (1-сурет, 2-сурет, Қосымша B).

Қабықтың биіктігі мен енін білу, кейбір болжамдарға негізделген, қабықтың көлемін есептеді. Атап айтқанда, тікұшақ тәрізді қабықшалар үшін бұл жүзім құстың жүзім шелегі бар, көлемі мынадай формула бойынша есептеледі:
SB = SD2 * (SH / 2),
онда,
SB - қабықтың көлемі;
SD - қабықтың үлкен диаметрі; SH - қабықтың биіктігі.
4. Өзінің жеке гипотезасын растайтын немесе қабылдамайтын барлық деректерді алған соң, х2 әдісі қолданылды (Pearson келісімшартының өлшемі)
3.2. Эксперименттердің нәтижелері
Экспериментке дейін барлық өлшеулер жүргізілді: салмақ, биіктікті өлшеу, қабықтың ені, аяқтың ұзындығы және сынақ топтарындағы ұлуларды таңдау үшін қабықтың көлемі. Әр топтың деректері (орташа мән) 1-кестеде келтірілген. Әрбір эксперименталды топ үшін өлшеулердегі минималды ауытқуларға ие бес бөлік таңдалған.
1-кесте - топтар бойынша ұлулардың өлшемі
-
салмағы (г)
ені (см)
биіктігі(см)
көлемі (см3)
аяғының ұзындығы (см)
ГА
25
2,9
3,5
14,7
10,2
ГД
27
3,1
3,5
16,8
10,5
ГГ
25
3,0
3,4
15,3
9,8
ГХ
26
2,9
3,1
13,0
10,1
ГК
25
3,0
3,2
14,4
10,0
Топтардағы әрбір ұлу түрлі түске боялған. Snails ГА - қызыл түсті, ГД- бұрыштық түсі, ГГ - қызғылт түсті, ГХ - көк түс және ГК- сары түсті. Тәулік ішінде ұлуларға эксперименталды топтан кездейсоқ түсіп, УС және БС комбинацияларының 7 жиынтығын жасады. УС - раковинадағы ағаш балғамен 5 есе қысып, күшті болмауы керек, бірақ хош иісті сезінуі керек.БС - пластик түтікшесі бар таяқшасы күшті болмауы керек, бірақ тұмсық хемматофорларды (антеннаны) тартады. Эксперимент тұрақты УОР-нің дамуынан 5 күн бұрын жүргізілді. Барлығы 175 УС және БС комбинациясы болды.
УОР дамуының сандық деректері кестеде көрсетілген.
2-кесте - Эксперименттік топтарда УОР даму динамикасы (%)
-
Топтар
Саны УС және БС
Орташа саны
10
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
ГА
20
40
40
40
ГД
20
60
20
160
ГГ
40
40
20
120
ГХ
40
40
20
60
ГК
20
60
20
80
 Нақтырақ айтсақ, деректер
уақыт айырмашылығын және УОР дамытуға арналған комбинациялар санын
көрсететін графиктер түрінде
берілген.
Нақтырақ айтсақ, деректер
уақыт айырмашылығын және УОР дамытуға арналған комбинациялар санын
көрсететін графиктер түрінде
берілген.
3-сурет - жүзім ұлуының тұрақтыУОР өндірісінің динамикасы
Эксперимент барысында топтарда серияның басы мен аяғымен байланысты УОР баллының айтарлықтай күшті ауытқуы болды. Яғни, сериялардың арасындағы жүзім ұлуы УОР деңгейін төмендетті, сондықтан жаңа сериялар бұрынғы сериялардың соңында жұзім ұлуы балымен емес , бірақ сәл кішірек балмен басталмады. Баллды анықтау үшін УОР үшін бес баллдық рейтингті жүйені енгіздім.
БС-де антенналарды алу дәрежесі: 5 ұпай - толқындар толығымен тартылады; 4 ұпай - біреуі толық, екінші жартысы; 3 ұпай - екеуі де екі есе азайған; 2 ұпай - тек біреуі ғана жинақталған; 1-ші нүкте - қышқылданып кетеді.
УОР шарларының ауытқуы 3-кестеде көрсетілген.
-
1 күн
2 күн
3 күн
4 күн
5
күн
ГА
5/100
5/100
5/40
5/20
4/20
4/60
4/80
3/80
ГД
5/100
5/40
5/20
5/20
3/20
4/60
4/20
3/40
1/80
3/60
2/40
ГГ
5/100
5/80
5/20
4/20
2/60
3/20
4/60
3/60
1/40
2/20
1/20
ГХ
5/100
4/80
5/40
5/20
4/40
3/20
4/40
4/20
3/20
2/20
2/60
1/40
ГК
5/100
5/100
5/80
5/40
5/20
3/20
4/20
3/40
3/40
2/40
Табиғи жүзім ұлуының шаршағанын кестеден көруге болады: сәнді ұлулар сәтті комбинациядан кейін антенналарын ұстап қалғысы келмеген сәтте [4].
Екі топтағы соңғы күнде сезімталдық сезімталдығы - кез-келген әсерге жауап беруден бас тартқан кезде шаршағандық сезімі анық байқалды. Сезімталдығы, әдетте, серияның соңында пайда болды, бәлкім, бұл әдеттердің механизмі.
Тұрақты УОР құрастырылғаннан кейін, рефлекторды сақтау уақыты тексерілді, яғни. Жүзім ұлуы УС-тың БС күшейтуінсіз әрекетіне ұшырады. Осылайша, қорғаныстық реакция (обмотофорды шеттету) болды.
Жақсартылған рефлектор 40 күн бойы сақталды (4-сурет). Сонда ұлулар УС-қа жауап бермеді. Диаграмма УС-қа оң жауаптардың төмендеуін көрсетеді.

4-сурет - УОР сақтау динамикасы
Эксперимент барысында құйрықтардың қорғаныс реакцияларының көбеюі жаттығулар орын алған жағдайда ғана көрінді. Бұл тұзақты заттар шартты және шартсыз ынталандырулармен ұсынылған жағдайды бөліп бере алатындығын растайды.
Тәжірибенің әрбір күні хаттамаларда жазылған.
5. Алынған нәтижелерді талдау УОР әзірленгеннен кейін барлық деректер өңделді және талданды. Бес зерттеу топтарында УОР-ні дамытуға арналған уақыт пен айқастардың саны айтарлықтай таралады (6-сурет).

Диаграмманы талдай отырып, ГА-ның ұлуларының
ең жақсы нәтиже екендігі анықталды: 20% ертінділердің (1 ұлпа)
УС-қа 20 комбинациядан кейін бірінші күні оң әсерін көрсетті, ал
қалғаны келесі күні оң жауап берді, ал спрэд комбинациялар саны
бойынша ғана (2 сыбағасы серияның басында және серияның соңында 2).
Сонымен қатар біз ГК-дағы жыландарда тұрақты УОР байқап отырмыз,
бірақ тұтастай алғанда бүкіл топ үшін тұрақты рефлексті дамыту
уақыты ұлғайып отырады, сондықтан 20% жыландар 3-ші күнде серияның
басында УОР және 2-ші күн сериясының соңында 60%
көрсетеді.
Суық судың әсеріне ұшыраған ұлулар ГК хош иістерінен әлдеқайда жақсы нәтиже көрсетті. Көптеген хош иісті заттар (80%) екінші күні соңында оңға қарай жауап береді. Мүмкін суда болу, жасушалардың азаюына әкеледі және ақпараттың қысқартылуына әкеледі. Екінші нұсқа, бұл суда болған, ұлулардың денесінен шырындар жуылады, бұл БС-ден тактикалық тітіркенуді азайтады.
Ең баяу уақыт интервалы мен комбинациялардың ең көп саны ГД және ГГ хош иістері арқылы талап етілді. ГГ субъектісі үшінші күні (40%) тұрақты УОР көрсетті, қалғандары 4-ші күні оң жауап берді. Ыстық суда қалу хош иісті заттарға тән емес. Табиғи жағдайда мұндай жағдай болмайды. Жүзім ұлуы алынатын биотопта ауа температурасы ең ыстық күндерде 300 ° C-тан аспайды. Сондықтан жасанды түрде жасалған жағдайлар қоршаған әсерді барынша азайтуға және ұлулар осындай жағдайда раковинада жасырынады. Экспериментті бастау үшін раковинадан толығымен шыққанға дейін біз 3-4 минут күтіп тұрдық.
Дифенгидраминнің ерітіндісіне ұшырағанұлулар ұзақ уақыт бойы қолдануға тағайындалды Жоғарыда айтылғандай, дифенгидрамин бұлшықетпен босаңсу әсер етеді, сонымен қатар кейбір жүйке түйіндерінің аяқтарын қалыпты түрде блоктайды, бұл УОР өндірісінің уақытын едәуір арттырады: 1 сыбағасы (20%) БС-ге 4-ші күні оң жауап береді, ал қалған 5-ші соңында 160-170 комбинациясы бар күн.
Осы топтан шыққан ұлу еті жиі шаршау мен уайым сезімін көрсетті. Яғни, серияда БС-ге оң және теріс жауаптың ауысуы байқалды. ГА-дан гауһарлар шаршауды іс жүзінде көрсеткен жоқ, ал 5-ші күні ГК тобынан шаршаудың кішкене көрінісі байқалды.
Алынған нәтижелер дәрілік препараттар мен дене температурасының әсері туралы біз ұсынған гипотезаны УОР өндіру жылдамдығымен растайды. Гипотезаның дұрыстығын тексеру үшін х2 өлшемі (Пирсон шартының өлшемі) көмегімен шешілді.
Жүзім ұлуының шырышында УОР өндіру туралы ғылыми деректердің 95-105 тіркесімінің шектерінде екендігін білу (орташа мәні 100 [4]), біз байқаған деректер біздің күтілетіндерден өте ерекшеленеді, өйткені дәрі-дәрмектер мен дене температурасы әлі де бар RBM дамуының жылдамдығына ықпал ету. Мұны тексереміз: χ2 = Σ (фо-fe) 2 / к, мұнда fo және fe - бұл ынталандырудың күтілген және күтілетін тіркесімі. Топтама кестенің барлық ұяшықтары бойынша орындалады. Бізде: χ2=(40-100)2/100+(160-100)2/100+(120-100)2/100+(60-100)2/100+(80- 100)2/100 = 16
Бізде еркіндік дәрежесі саны 4 (жолдардың саны - 1), сондықтан бақыланатын мән ықтималдығы кездейсоқ ауытқу 0,5% болуы мүмкін. Біз алған 16 шамасы сыни мәннен 14.86 асып түседі, бұл біз ұсынған гипотезаны дұрыс деп санауға құқылы.
Біз үшін әр түрлі препараттар мен температура әсерінен өндірілген УОР қанша уақыт бойы өмір сүруі қызықты болды. Жүзімнің тұзағындағы дамыған УОР оқытудың сыртқы жағдайларына еске салғанда 52 күн бойы [4] қалады. Біздің экспериментімізде УОР сақтаудың ең ұзақ уақыты 40 күн болды. Айналдыру уақытының өзгеруіне сыртқы ортадағы өзгерістер әсер етілді (ауа температурасының орташа 100 ° C-қа төмендеуі).
4-кестені талдай отырып, топтардың арасында УОРсақтау динамикасы ішкі топ көрсеткіштерінен айтарлықтай ерекшеленетінін байқауға болады.
4-кесте - жүзім ұлуының УОР сақтау динамикасы (%)
-
ГА
ГД
ГГ
ГХ
ГК
1 күн
100
100
100
100
100
3 күн
100
100
100
100
100
5 күн
100
100
100
100
100
7 күн
100
60
100
100
100
10 күн
100
40
100
100
100
15 күн
100
40
80
100
100
20 күн
100
20
40
80
100
25 күн
80
0
20
80
100
30 күн
80
0
0
40
80
35 күн
40
0
0
0
40
40 күн
20
0
0
0
0
45 күн
0
0
0
0
0
УС -ке оң жауап күн сайын тексерілді. Бұл топтардан ең ұзын реакция АГ тобынан жасалған ұлуларға оң реакция болатыны көрінеді. ГД тобының ұлулары барлығынан бұрын ұрып көруге жауап реакциясы болмажы, бұл рефлекстің сақталуы, сонымен бірге, оның әзірлену уақытына байланысты болды, өйткені осы топтағыұлулар 4 және 5 күндерде тұрақты оң рефлексті көрсетті, содан кейін УС пен БС-дің бұдан кейінгі комбинациясы тоқтатылды және басқа топтар, бірінші оң жауап алғаннан кейін ұзақ уақытқа созылды.
Сондықтан, УОР сақтау бойынша препараттың әсер және температура туралы айтуға дәл болады. Кез келген жағдайда, біз ұзақ уақыт бойы әр топта екенін көріп оң жауап санының азаюы болып табылады, және сайып келгенде, ол жерден 0. төмен келеді, біз бірінші оң жауап бастап және 5 созылды эксперимент, соңына дейін уақыт әсер туралы жорамал жасауға болады Ассамблея құрышы 1-2 күнге дейін оң жауап берді, және шоғырландыру үшін эксперимент және уақыт соңы астам 3 күн болды, бұрын олардың жаттығу жүргізілді болса, онда ДГ уақыт шоғырландырудан ұлулар өте аз болады.
Қорытындылар
Осылайша, біздің эксперименттеріміз көрсетті:
1. Адреналин және дифенгидрамин есірткі тұрақты УОР өндірісінің жылдамдығына әсер етеді. Осы топтардағы өндіріс уақытының айырмашылығы айтарлықтай. ГК-да УОР қалыптастыру жылдамдығы ГД-де жылдамдықтың 4 есе жоғары.
2. Ұлулардың денесінің температурасы УОР даму жылдамдығына әсер етеді. ГГ тобында УОР өндіру жылдамдығы ГК ұқсас рефлекстің даму жылдамдығынан 2 есе төмен.
3. Адреналин мен дифенгидрамин ерітіндісін және температураны УОР- ның өндіріс жылдамдығына әсері статистикалық маңызды.
4. Ұстағыштардың ұзақ мерзімді есте сақтау қабілеті бар, бірақ ол сыртқы жағдайларға байланысты, яғни Ұстағыш УС-қа оқу жағдайларына ұқсас жағдайларда оң жауап береді. УОР уақытын сақтау уақыты оқу уақытына байланысты
Зерттеудің практикалық маңыздылығы мен бағыттары
Жануарларға этикалық эксперименттер көптеген пікірсайыстардың тақырыбы болып табылады. Бүгінде ғылымдағы прогресс үшін эксперименттердің қажеттілігі - жануарлардың азаптауы (зертханалық жануарлар санының азаюы) жағдайында қазіргі басым көзқарас.
Біздің жағдайда әр топтағы эксперименталдық ұлулар саны азайып, препараттық инені тітіркендіретін пластикалық түтікпен тітіркенген тітіркенуді ауыстырды, бұл да көрінетін, бірақ әлдеқайда аз ауыр сезім береді.
Қорытынды
Біздің жұмысымыздың нәтижелерін қолдану бірнеше бағытта болуы мүмкін:
1. Оқу үдерісінде. Бұл зерттеулер биологиялық класстарда (8 жасуша) қолданылуы мүмкін шартты рефлексті дамытуды айқын көрсетеді. Эксперименттерді қайта қарап шығудың қажеті жоқ, жай ғана бейне көруге болады. Медицина сабақтарында (10-11 жасушалар), тақырыпты зерттегенде осы материалды қолдануға болады
«Дәрілік препараттар». Оқудан тыс іс-шараларда және кейінгі сағаттық іс-шараларда, бізбен бірге өмір сүретін жануарлар биотопта биоәртүрлілікті сақтаудың ажырамас бөлігі болып табылады.
2. Медицинада (фармакология). Дəрілік заттардың əйнектерге әсері адамдарға ұқсас, сондықтан жаңа ұлулар мен олардың компоненттерінің әсерін тексеру үшін жүзім ұлуын қолдануға болады, өйткені хош иісті заттар салыстырмалы қарапайым жүйке жүйесі мен өте күрделі мінез-құлық репертуарымен өте үлкен нейрондарға ие.
3.Мал шаруашылығында.
Мал шаруашылығы тәжірибеде шартты рефлекстердің кеңінен пайдалану жануарлардың өнімділігін арттыруға болады. оның жұмысына, ұлулар шартты рефлексті мүмкіндігін көрсететін, біз ұлулар дене салмағын тез арттыру үшін оң тамақ рефлексі дамыту ұсынамыз. Ал одан әрі дамыту және оны біріктіру үшін қосымша ынталандырушы факторларды қолдануға болады. Мұны істеу үшін аталатын жасаңыз
[7] сол уақытта қолайлы жағдайлар оларды қабылдау, үлкен сандар одан әрі дайындау немесе экспорт үшін ұлулар өсіру, ол «ұлу фермаларын енгізу».
4. Ұлулардың фитофаг ретінде қолданылуы. Тұздық үлкен жапырақты арамшөпті жейді - шалшық, сиыр-аққайың, шөп, олардың орнында шалғынды шөп өседі, себебі топырақ Калифорниялық құрттың сыртына қарағанда он есе тиімдірек жүзім құстағыларының қышқылымен байытылған. Мұны істеу үшін, ұлулар сиырда, әсіресе біздің аймағымыз үшін өте маңызды, тұрақты азық-түлік рефлексін дамытуы керек [11].
Келешекте жүзім ұлуларын зерттеуді жалғастыру жоспарланып отыр. Рефлекстің дәрі-дәрмектерге тұрақтылығына тәуелділігін тексеру, пирамидаларға арналған оң тағам рефлексін дамыту және іс жүзінде потенциалды ынталандыруды табу әдісі ретінде күресу әдісі ретінде оны сынау.
Introduction
At the present stage of the development of civilization, the increasing anthropogenic impact on nature causes irreversible processes leading to the degradation of ecosystems and a decrease in the diversity of the biosphere's gene pool. The need to preserve many species of plants and animals and to develop a system of measures for the protection of biocoenoses has been recognized long ago. Nevertheless, until recently, some species of animals, mostly invertebrates, were out of sight of most researchers concerned with the conservation of biological diversity. However, the role of these organisms in maintaining the stability of ecosystems, the processes of circulation of substances in nature, soil formation and biodegradation is extremely high, and it is the effects on these components of biogeocenoses that lead to irreversible changes in communities [10].
Mollusks are an integral component of Kazakhstan's terrestrial ecosystems. Participating in the decomposition and mineralization of organic substances, they act as an important link in the circulation of substances in nature [8]. Molluscs also have economic significance. Currently, the range of application of grape snails is increasingly expanding due to the research of biology scientists, microbiologists, physicians, and consequently, the commercial importance of this molluscum is constantly increasing. It is this fact that led to the fact that the grape snail has become the object of close attention on the part of man. It needs to be protected from thoughtless extermination, and for this, the most comprehensive knowledge about it is necessary [5].
The adaptation of animals to the changing conditions of existence in the external environment is provided by the activity of the nervous system and is realized through reflex activity. In the process of evolution, hereditarily fixed reactions (unconditioned reflexes) arose,which unite and coordinate the functions of various organs, carry out the adaptation of the organism [2].
The organization of the nervous system of the snails of the genus Helix is simpler than the human nervous system, but the very principle of signal transmission and structure are similar. And it is the relative simplicity of the nervous system of the snails that makes them attractive for research in neurobiology. The availability and large size of the snails allowed them to become an object of research by German scientists even in the century before last [3].
Purpose and objectives of work:
We hypothesized: various medications and external conditions can influence the development and fixation of a conditioned reflex in a grape snail.
In connection with this, the purpose of this study was to determine the effect of various medications and different temperatures on the development of a conditioned reflex in a snail of grape.
Based on the goal, the following tasks were set:
- to investigate the life and behavior of snails in captivity;
- develop a conditioned defense reflex in snails in five experimental groups;
- determine the time of preservation of the conditioned reflex in snails in different study groups.
2.1. Ecological and biological features of a snail of grape The grape snail (Helix pomatia) is the largest land mollusk of our fauna. Systematic position [8] (Appendix A): The kingdom is animals; Type - mollusks; Class - gastropods; Detachment - pulmonary snails; Family - helicides; Family - Helix; View - grape snail;
The international scientific name is Helix pomatia.
It is believed that the birthplace of the grape snail is Central and South-Eastern Europe. For a long time people used grape snails as food, with a delicacy they were not, and people of any social status used them as an affordable and healthy food [8].
The species settled in all but the northern parts of Europe and the coast of the Baltic Sea. It lives in thickets of bush, on light forest edges, in gardens, parks. The snail is active from spring to the first cold, then burrows into the soil to a depth of 30 cm and falls into anabiosis. As a rule, it hibernates in the same shelters. During anabiosis, the mouth of the shell is closed by a calcareous stopper - an epiphragm, the thickness of which depends on the severity of winter time.
In nature, a grape snail lives on average 7-8 years, but can often live up to 20 years, if it is not eaten by a predator [12].
Appearance
The body, like all representatives of the class, is externally divided into a shell and trunk. In the latter, the leg and head are distinguished. The internal organs are surrounded by a mantle, part of which is visible from the outside.
The diameter of the shell of an adult on average is 3-4.5 cm; its volume is enough to completely accommodate the whole body. The shell is spirally curved; has 4.5 revolutions, lying in different planes (so-called turbo-spiral); is twisted to the right; untwists clockwise. Such shells are called deixotropic.
The color of the shell varies from yellow-brown to brownish-white. Along the entire length of the 2-3 first revolutions there are 5 dark and 5 light strips. The color of the shell in some individuals is more dark, in others it is lighter. The color saturation depends on the habitat and is related to the intensity of illumination and the background of the environment, that is, it helps masking. The color of the shell can vary depending on what kind of food the individual uses.
The shell is ribbed. This increases the surface area, which allows you to accumulate more moisture. Ribs also give the shell more strength and, in addition, thanks to them, the sink weighs less [11].
The usual length of the adult's leg is 3.5-5 cm, but the animal can stretch out, up to 8-9 cm.
The body of the grape snail is very elastic. Its color varies in different individuals, as does the color of the shell. Usually the color of the body is beige with a brown tinge, less often dark gray. The body is completely covered with wrinkles, the areas between them have the form of quadrangles. Wrinkles increase the surface area of the foot, moisture is retained in them [10].
There are two pairs of tentacles above the oral opening of the cochlea. The length of the front tentacles - labial - varies from 2.5 to 4.5 mm. They have an olfactory function. The length of the posterior tentacles - the ocular tentacles - is from 1 to 2 cm. At the end of the latter are the eyes, all of whose receptors contain the same photopigment, which is the cause of the color blindness of the animal. However, the eyes are able not only to distinguish the intensity of illumination, but also to see objects at a distance of up to 1 cm.
Tentacles are very mobile. Both pairs are very sensitive: if you accidentally touch the object, the tentacles are instantly removed inside. Eye tentacles also react negatively to very bright light [11].
Like all representatives of the class, the digestive system of the grape snail is divided into the ectodermal anterior gut and the endodermal midgut. Breathing is pulmonary. The heart located above the hindgut consists of the left atrium and ventricle and is surrounded by the pericardium. The blood is colorless. The nervous system is sparse-nodular, consists of several ganglia. The excretory system consists of one kidney communicating with one end of the pericardium, and the other one opening into the mantle cavity next to the anus. The reproductive system is hermaphroditic, fertilization is transverse.
The grape snail is herbivorous: it feeds on both living vegetation and plant remains. Consume leaves of grapes and wild strawberries, cabbage, horse sorrel, nettle, burdock, medinitsu, dandelion, plantain, radish, horseradish. To build up the shell, the animal needs calcium salts. Cases of eating food of animal origin are also observed. The eggs that emerged from the eggs during the first time feed only on substances contained in the soil [12].
Breath
The grape snail breathes with the help of a lung. The breathing hole - a pneumostyle - is located between the folds of the mantle, on the same side as the shell's revolutions.
Movement
The grape snail moves with the help of its muscular leg. With the help of muscle contractions, the animal, slipping, repels from the surface. When moving, mucus is released, which softens friction, facilitating movement through the substrate. Glands that secrete mucus are located in the front of the body. The average speed of movement is about 1.5 mm per second.
Anabiosis
Anabiosis in a grape snail lasts up to 3 months. In the natural conditions of Belarus - at least 5 months, while mollusks with an anabiosis period of less than 60 days under the experimental conditions further differed in reduced fecundity or did not give eggs at all.
Natural enemies
The natural enemies of the grape snail are hedgehogs, shrews, lizards, moles and some other animals, as well as various species of crawling beetles that can crawl inside the grape snail through the respiratory opening [7].
Breeding
Grape snails have been bred since ancient times. Now in a number of countries there are so-called "street farms", in which in large quantities for subsequent preparation or export grape snails, creating favorable conditions for them.
The meat of grape snails contains 10% protein, 30% fat, 5% carbohydrates, as well as vitamins B6, B12, iron, calcium, magnesium .. In the air-dry matter of grape snails meat, according to the Institute of Fisheries of the National Academy of Sciences of Belarus, contains 60 -65% protein, about 5% fat, the rest - low-molecular organic and mineral compounds - ash. In a number of countries, snails are widely bred for sale in restaurants for the pharmaceutical industry [1].
In medicine
Extract made from grape snails - gelicidin - is used because of its properties of the broncho-relaxant. Representatives of the species are also used to isolate valuable substances - lectins.
Harm to agriculture
The grape snail is the enemy of agriculture, primarily because it feeds on young shoots of crops, in particular grapes [6].
Snails are a wonderful and accessible object of observation in captivity. They are not at all as primitive as it may seem. Despite the fact that their nervous system is quite simple, snails are capable of learning. They have a long-term memory and if you treat them with care, they get used easily and quickly and calmly are given in hand.
2.2. The conditioned reflex and its meaning
A conditioned reflex is a complex multicomponent reaction that is developed on the basis of unconditioned reflexes using the preceding indifferent stimulus. It has a signal character, and the organism meets the influence of the unconditioned stimulus prepared [3].
Conditional reflexes are easier to produce for ecologically similar effects to a given animal. In connection with this, conditioned reflexes are divided into natural and artificial reflexes. Natural conditioned reflexes are developed for agents that act naturally together with the stimulus, causing an unconditioned reflex, for example, the type of food, its odor, etc.). All other conditioned reflexes are artificial; are developed for agents that are not normally associated with the action of an unconditioned stimulus [2].
For the elaboration of a conditioned reflex it is necessary:
1.The presence of two stimuli, one of which is unconditioned (food, pain stimulus, etc.), which induces an unconditioned reflex reaction, and the other is a conditioned reflex, signaling the forthcoming unconditioned stimulation (light, sound, pain, etc.).
2. Multiple combination of conditioned and unconditioned stimuli (although the formation of a conditioned reflex is possible with their single combination).
3. The conditioned stimulus must precede the action of the unconditioned stimulus.
4. As a conditioned stimulus, any stimulus of the external or internal medium can be used, which should be as indifferent as possible, do not cause a defensive reaction, do not have excessive force, and is capable of attracting attention.
5. An unconditioned stimulus must be strong enough.
6. Excitation from the unconditioned stimulus should be stronger than from the conditioned stimulus.
7. It is necessary to eliminate extraneous stimuli, since they can cause inhibition of the conditioned reflex.
8. An animal that develops a conditioned reflex should be healthy.
9. In developing a conditioned reflex, motivation should be expressed [2].
In mollusks, it is possible to develop a conditioned reflex after one combination. If the snail is given mushrooms, which it always prefers, combining them with carbon dioxide poisoning, then the animal then always avoids the fungi, preferring other types of food [3].
2.3. Organization of the conditioned defense reflex of snails
In this work, the defensive reflex of the
snails of the genus Helix was used, so we will consider its neural
organization (the conceptual reflex arc). Irritant (skin prick)
acts on a group of receptors and excites a local detector
associated with motoneurons and several command neurons that have
overlapping motor fields. Communication is due to the lamellar
synapse. Each motoneuron is associated with a group of muscle cells
forming a muscle unit. In addition, some team neurons have direct
links to muscle units, which creates a focus of the motor field of
the command neuron.
Also there are not only local, but also
nociceptive detectors, which carry out communication due to
nonplastic synapses. An important part of the reflex arc is
nociceptive detectors. The axons of the modulating neurons
terminate at the presynaptic endings of the local detectors on the
command neuron. They increase the efficiency of synapses of
detectors on the command neuron
[3].
Figure 1 - UOR reflex snail grape
1. The motor field of the command neuron is determined by the composition of motoneurons with which it is connected. 2. Detector - a neuron, selectively tuned to the parameters of the input signal.
3. Command neuron - interneuron associated with other motor neurons.
4. Modulatory neurons of the defensive reflex are represented by a pool of serotonergic neurons, the electrochemical irritation of which leads to the release of serotonin, which phosphorylates proteins forming ionic calcium channels, activates adenine cyclase and the like.
5. Plastic synapse - can slow down the reaction due to changes in the concentration of the released acetylcholine (addictive), simple signal transmission (sensitization)
2.4. The effect of drugs on the nervous system
Adrenaline - has a stimulating effect on the nervous system. It increases the level of wakefulness, mental energy and activity, causes mental mobilization, an orientation reaction and a sense of anxiety, anxiety, or stress [9].
Influencing the body, diphenhydramine has a relaxing effect on the musculature, relieves pain, and also moderately blocks the endings of certain nerve nodes, which greatly dulls the pain [9].
3. Methods and location of the study
1.The list of abbreviations used: UOR - conditional defense reflex; CSS is a conditional stimulus; BS - unconditional stimulus; GA is a group of snails exposed to adrenaline; - a group of snails exposed to dimedrol; GC - a group of snails exposed to cold water; GG is a group of snails exposed to hot water; GK is a group of snails that are not affected (control).
2.Grape snails were removed from the environment at the end of May 2018 in the vicinity of the Baizak region of the Zhambyl region. Put in a specially made snail, taking into account all the requirements. Within two months adaptation to new habitats and habituation to the hands took place. The experiment was conducted in August 2018 in the school laboratory.
3. In experiments we used mature specimens of grape snails of uniform mass and size. Molluscs were kept in a common terrarium at room temperature, high humidity and an excess of food. Before the experiment began, the snails were adapted and were active for two months. Developed a classic RBM for tapping on the sink.
As the US used tapping on the sink, which in the norm almost did not cause a defensive reaction. BS served as an irritation of the cochlea in the shell area, which led to an unconditional defensive reaction of retraction of the ommatophore (antennae) (Fig. 2). The RBM was developed according to the scheme proposed by OA Maksimova and PM Balaban (1983) [2].
The interval between combinations of stimuli was 3-5 minutes, the time of presentation of BS and US was 1 second.
This form of training was conducted in five experimental groups. The first group of snails was exposed to the action of adrenaline (HA). The second group is the action of diphenhydramine (DG). The nervous system of a grape snail is characterized by a very high degree of concentration of ganglia, grouped in the peripheral nerve ring, so the drugs were applied to the surface of the body in this area. The body does not have dense skin and the absorption of the drug occurs externally.
The dosage of the drug was calculated taking into account the weight of the body of the snails. The drug was diluted to the required concentration with distilled water for injection. Calculation of the dosage of drugs was carried out taking into account the mass of the snails.
Preparation of preparations: Adrenaline and diphenhydramine solutions are taken for intramuscular injection, the daily dose of which is 1 ml per 60 kg of human body weight. Correspondingly, we recalculate the cochlea (the average mass of the cochlea is 25.6 grams with a sink, without a shell, an average mass of 15 grams); 0,0025 ml is the daily norm for the cochlea. The volume of the drop, the smallest, whose volume is more or less constant, is 0.033 ml, which is 13.2 times more than the daily norm for snails, so dilute the original solutions with distilled water for injections in 13.2 times. Now the daily norm of solutions for snails is 0.033 ml, i.е. 1 drop.
The gastropods respond well to the application of tactile, chemical, temperature stimuli perceived by individual sensitive cells scattered in the skin of the legs and mantle, so the experimental conditions were extended. The third study group was pre-conditioned in cold water (40C) for 15 minutes (GC) before the production of RBM. The fourth group was similarly maintained in hot water at a temperature of 450 ° C (GG) (Figure 3, Appendix B).
The fifth group of snails was not subjected to any influence and was a control. Each group consisted of five snails.
Figure 2
1. Treatment with aralinine solution.
2. Tapping on the sink (US) of adrenaline.
3. Tactile irritation (BS).
For the selection of uniform snails, we measured and weighed snails (Figure 1, Figure 2, Appendix B).
Knowing the height and width of the shell, based on some assumptions, calculated the volume of the shell. In particular, for shells of a helicoidal shape, this grape snail has a grape snail, the volume is calculated according to the formula [6]:
SB = SD2 * (SH / 2),
Where,
SB - the volume of the shell;
SD - large diameter of the shell; SH is the height of the shell.
4. After receiving all the data to confirm or deny its own hypothesis, the χ2 method was used (Pearson's agreement criterion).
3.1. Results of experiments
Before the experiment, all the measurements were made: weighing, measurement of height, width of the shell, length of the leg and volume of the shell for the selection of individuals in the test groups. The data of each group (mean value) are given in Table 1. Five snails with minimal deviations in the measurements were selected for each experimental group.
Table 1 - Data of snail measurements by groups
|
|
The weight snails (g) |
Width sinks (cm) |
Height sinks (cm) |
Volume Shells (cm3) |
Length feet (cm) |
|
GA |
25 |
2,9 |
3,5 |
14,7 |
10,2 |
|
DG |
27 |
3,1 |
3,5 |
16,8 |
10,5 |
|
YY |
25 |
3,0 |
3,4 |
15,3 |
9,8 |
|
GC |
26 |
2,9 |
3,1 |
13,0 |
10,1 |
|
GK |
25 |
3,0 |
3,2 |
14,4 |
10,0 |
Each snail in the groups was marked with a different color. Snails GA - crimson color, DG - burgundy color, GG - pink color, GC - blue color and HA - yellow color.
During the day, snails were taken randomly from the experimental group and made 7 sets of combinations of CSS and BS. US - tapping on the sink with a wooden hammer 5 times, should not be strong, but the snail should feel it. BS - a prick with a plastic tube, should not be strong, but palpable, so that the snail draws ommatophores (antennae). The experiment was carried out for 5 days before the development of a stable RBM. In total, there were 175 combinations of CSS and BS.
Quantitative data on the development of RBM are reflected in Table 2.
Table 2 - Dynamics of development of RBM in the experimental groups (%)
-
Groups
Number of CM and BS combinations
Average number combinations10
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
GA
20
40
40
40
DG
20
60
20
160
YY
40
40
20
120
GC
40
40
20
60
GK
20
60
20
80
More clearly, the data are
presented in the form of graphs showing the time difference and the
number of combinations for the development of
RBM
Figure 3 - Dynamics of production of a stable RBM in a grape snail
In the groups during the experiment, there was a fairly strong fluctuation of the RBM score associated with the beginning and end of the series. That is, the time between series of snails reduced the level of RBM, so the new series did not start with a score that the snails had at the end of the previous series, but with a slightly smaller one. To determine the score, I introduced a five-point ranking system for RBM.
The degree of retraction of the antennae on the BS: 5 points - ommatophore pulls completely; 4 points - one ommatophore retracts fully, the second half; 3 points - both ommatophore are retracted in half; 2 points - only one ommatophore is drawn in; 1 point - the ommatophore is retracted. The fluctuations of the RBM ball are reflected in Table 3.
Table 3 - RBM score /% of snails
-
1 day
2 day
3 day
4 day
5 day
5 day
5/100
5/100
5/40
5/20
4/20
GA
4/60
4/80
3/80
DG
5/100
5/40
5/20
5/20
3/20
4/60
4/20
3/40
1/80
3/60
2/40
YY
5/100
5/80
5/20
4/20
2/60
3/20
4/60
3/60
1/40
2/20
1/20
GC
5/100
4/80
5/40
5/20
4/40
3/20
4/40
4/20
3/20
2/20
2/60
1/40
GK
5/100
5/100
5/80
5/40
5/20
3/20
4/20
3/40
3/40
2/40
It can be seen from the table that snails are fatigued - the moment when snails are very reluctant to stick out their antennae after a successful combination [4].
The last day in the two groups there was insensitivity - an extreme measure of fatigue, when the snail ceases to respond to any effects. Insensitivity, as a rule, appeared at the end of the series, perhaps this is due to the mechanism of habituation.
After the development of a stable RBM, the time of preservation of the reflex was checked, i.e. Snails were exposed to the action of the US without the reinforcement of the BS. And thus there was a defensive reaction (retraction of ommatophores). The elaborated reflex was maintained for 40 days (Fig. 5). Then the snails did not react to the US. The diagram shows a decrease in positive responses to the US in time.
Figure 5 - Dynamics of conservation of RBM
In the course of the experiment, it was found that the snails demonstrate an increase in defensive reaction only in the situation in which the training took place. This confirms the assumption that snails can differentiate the situation in which they were presented with conditional and unconditional stimuli.

Each day of the experiment was
recorded in the
protocols.
3.2. Analysis of the results obtained
After the development of the RBM, all data were processed and analyzed.
In the five study groups, there is a significant spread in the time and number of combinations for the development of RBM (Figure 6).
Analyzing the diagram, it is clear that snails from GA are the best results: 20% of snails (1 snail) showed a positive response to the US on the first day after 20 combinations, the rest showed a positive response the next day, the spread was only in the number of combinations (2 snails at the beginning of the series and 2 at the end of the series).
At the same time, we observe a stable RBM in snails in the GK, but the time for the development of a stable reflex for the entire group as a whole is increased, so 20% of snails show RBM at the beginning of the series on day 3, and 60% of snails at the end of the series of the 2nd day.
Snails exposed to cold water show slightly better results than snails of the HA. The majority of snails (80%) give a positive response to tapping at the end of the second day. Probably staying in water leads to a reduction in cells and a shortening of the way information is transmitted. And the second version, that having been in the water, slime is washed off from the body of the snails, which reduces the tactile irritation from the BS.
The slowest time interval and the largest number of combinations was required by snails from the DG and GG. Subject cohorts of the GH showed a stable RBM on the third day (40%), the rest gave a positive response on the 4th day. Staying in hot water is unnatural for snails. In natural conditions, this does not happen. In the biotope, from which the snails are seized, the temperature of the air does not exceed 300 ° C on the hottest days. Therefore, artificially created conditions cause the cochlea to minimize the surrounding effect and it hides in the sink. We had to wait 3-4 minutes until they completely emerge from the sink to start the experiment.
Snails exposed to a solution of diphenhydramine for the longest time could not be trained. As already mentioned above, diphenhydramine has a relaxing effect on the musculature, it also moderately blocks the endings of some nerve nodes, which significantly increases the time of RBM production: 1 snail (20%) gives a positive response to BS on the 4th day, the rest at the end of 5 day with 160-170 combinations.
Snails from this group often showed a manifestation of fatigue and numbness. That is, during the series there was an alternation of positive and negative response to the BS. Snails from GA practically did not show fatigue, and from group GK a small display of fatigue on the 5th day.
The obtained results confirm the hypothesis put forward by us on the effect of drugs and body temperature on the rate of production of RBM. To check the correctness of the hypothesis, it was decided with the help of the criterion χ2 (Pearson's agreement criterion).
Knowing that the scientific data on the production of RBM in a grape snail are within the limits of 95-105 combinations (mean value 100 [4]), we see that the data observed by us are very different from the expected ones, since medications and body temperature seem to still have influence on the rate of development of RBM. We check this: χ2 = Σ (fo-fe) 2 / k, where fo and fe are the observed and expected combinations of stimuli. The summation is performed over all cells of the table. We have: x2 = (40-100) 2/100 + (160-100) 2/100 + (120-100) 2/100 + (60-100) 2/100 + (80-100) 2/100 = 16
The number of degrees of freedom in us is 4 (the number of lines is 1), so the probability of the observed value can be a random deviation of 0.5%. The value of 16 obtained by us exceeds the critical value 14.86, which gives us the right to consider the hypothesis put forward by us to be correct.
For us, it was interesting how long the produced RBM would survive under the action of various drugs and temperature. It is well known that the developed RBM in a snail of grape remains for 52 days [4] when reminding the external conditions of training. In our experiment, the longest time of conservation of RBM was 40 days. It can be assumed that the change in the time of preservation of the reflex was influenced by a change in the external environment (a decrease in air temperature by an average of 100 ° C).
Analyzing Table 4, it can be seen that the dynamics of the preservation of RBM between groups is significantly different from the intra-group indicators.
Table 4 - Dynamics of conservation of RBM in a grape snail (%)
-
GA
DG
YY
GH
GC
1 day100
100
100
100
100
3 day
100
100
100
100
100
5 day
100
100
100
100
100
7 days
100
60
100
100
100
10 days
100
40
100
100
100
15 days
100
40
80
100
100
20 days
100
20
40
80
100
25 days
80
0
20
80
100
30 days
80
0
0
40
80
35 days
40
0
0
0
40
40 days
20
0
0
0
0
45 days
0
0
0
0
0
A positive response to the CSS was checked
daily. It can be seen from the groups that the longest response was
the positive response to the snail from the GA group. Snails from
the GD group stopped responding to tapping before everyone else,
apparently the preservation of the reflex also depends on the time
of its elaboration, since the cochlea from this group showed a
stable positive reflex on days 4 and 5, then the further
combination of US and BS was discontinued, and in other groups, it
lasted longer after receiving the first positive response.
Therefore, it is incorrect to talk about the effect of the drug and
the temperature on the preservation of
RBM.
In any case, we see that in
each group the number of positive answers decreases over time, and
eventually it reduces to 0. Here we can make an assumption about
the influence of the time passed from the moment of the first
positive response and to the end of the experiment that lasted 5
days, if the snails from the GA gave a positive response for 1-2
days, and their training was carried out until the end of the
experiment and the time for fastening was more than 3 days, then
there was very little time for fixing snails from the
DG.
Сonclusions
Thus, our experiments showed:
1. Drugs adrenaline and diphenhydramine affect the rate of production of stable RBM. The difference in production time in these groups is significant. The speed of generation of RBM in the GA is 4 times the speed in the DG.
2. The temperature of the cochlea's body affects the rate of development of RBM. The rate of production of RBM in the GG group is 2 times lower than the rate of development of a similar reflex in the GC.
3. The effect of the adrenaline and diphenhydramine solution and temperature on the production rate of RBM is statistically significant.
4. Snails have a long-term memory, but it depends on external conditions, i.e. The snail gives a positive response to the US in conditions similar to the training conditions. The time of preservation of RBM depends on the time of training.
Practical significance and direction of further research
Ethical experiments on animals are the subject of numerous debates. The dominant point of view today is the need for experiments for the sake of progress in science, under the condition that the suffering of animals will be minimized (as well as the number of laboratory animals) [9]. In our case, the minimum number of experimental snails in each group was taken, and irritation with the preparative needle was replaced by tactile irritation with a plastic tube, which is also palpable, but much less Delivers painful sensations.
The application of the results of our work can be in several directions:
1. In the educational process. These studies clearly demonstrate the development of a conditioned reflex, which can be used in biology classes (8 cells). There is no need to re-run the experiments, just watching the video. At the lessons of medicine (10-11 cells.), It is possible to use this material when studying the topic "Medications". In extracurricular activities and after-hours activities, since animals living with us in one biotope are an integral part of biodiversity conservation.
2. In medicine (pharmacology). The effect of drugs on snails is similar to that of humans, so it may be possible to use snails to test the effect of new neurostimulating drugs or their components, since snails have fairly large neurons with a relatively simple nervous system and a fairly complex behavioral repertoire.
3. In animal husbandry. The widespread use of conditioned reflexes in the practice of animal husbandry makes it possible to increase the productivity of animals. In our work, showing the possibility of elaborating a conditioned reflex in a cochlea, we propose to develop a positive food reflex for the fastest increase in the weight of the body of the cochlea. And for further development and its consolidation, additional stimulating factors can be used. To do this, create so-called "Street farms," in which in large quantities to breed snails for later cooking or export, while creating favorable conditions for them [7].
4. Use of a snail as a phytophagous. The snail eats large-leaved weeds - nettles, cow-bream, hay, in their place the meadow grass grows, as the soil is enriched with excrement of grape snails, which are ten times more effective than the excrement of the Californian worm. To do this, the snails need to develop a stable food reflex, in particular, on the cow, which is very important for our region [11].
In the future it is planned to continue studying the grape snail. To check the dependence of the stability of the reflex on medications, to develop a positive food reflex to cowbler and to test in practice as a method of fighting hogweed, for this, to find a positive stimulus.
Қосымшалар

Ұлуды өлшеу

Ыстық суда ұлулардың шыдамдылығын бақылау

Ұлулардың салмағын өлшеу
ҚОЛДАНЫЛҒАН ӘДЕБИЕТТЕР ТІЗІМІ
1.Қазақстан Республикасы Үкіметінің 2012 жылғы 23 тамыздағы № 1080 қаулысымен бекітілген Орта білім берудің (бастауыш, негізгі орта, жалпы орта білім беру) мемлекеттік жалпыға міндетті стандарты.
2.«Биология» пәнінен зертханалық және практикалық сабақтарды өткізу» Әдістемелік құрал Астана 2014.
3. Қазақстан Республикасының Білім және ғылым министрінің 2013 жылғы 3 сәуірде №115 бұйрығымен бекітілген «Жаратылыстану» білім саласы пәндерінің оқу бағдарламаcы.
4.Оразымбетова Б.Б.«Биологияны оқыту әдістемесі»Методикалық оқулық. Қостанай. –2010ж 93-96б.
5.Сидоров Е.Г., Белякова Ю.В., Куналиев Д. Ш., К оценке ситуации по описторхозу в зоне канала Иртыш-Караганда, Мед. паразитол /. 1991. 40 б -42 б.
6.Фролова Е.С. Малакофауна некоторых бессточных озер Северного Казахстана. Вопросы малакологии Сибири. – Томск, 1969. 52 б -54б.
7.Фролова Е.С. Пресноводные моллюскиСеверного Казахстана и их роль в биомассе бентоса в природных комплексах. Заметки по фауне и флоре Сибири. - Томск: Изд-во ТГУ, 1984 / . 42 б -50 б.
8.НаталиВ.Ф. «Зоология беспозвоночных»Учебник для студ. биолог. Фак. Пед. ин-овПод. Ред. О.Н.Сазановой.Изд. 3-е, перераб. и доп. М.«Просвещение», 1975., 487 стр. С илл.
9.АхметоваБ.А.«Омыртқасыздарзоологиясынанлабораториялықсабақтарөткізуге арналған методикалық нұсқаулар» А.1989.
10.ТүсіповаК.С. «Омыртқасыздарзоологиясы» 2-ібөлімдікОқулық К.С.Түсіпова - Алматы: 1-бөлім.-1998. -336 б.
11.ЗеликманА.Л. «Практикум по зоологии беспозвоночных»Учеб. Пособие для ун-ов и пед. ин-ов. М. «Высшая школа»,1965., ЗЗІстр. с илл.
12.Сайт зоологического института Российской академии наук http://www.zin.ru/animalia/coleoptera/rus/index.htm
13.Энтомолог.narod.ru http://entomolog.narod.ru/metodiki.html *
14.Зоологические экскурсии по Байкалу Фауна в картинках http://zooex.baikal.ru/beetles/coleoptera.htm
15."Жужелицы мира (Carabidae of the World)" - таксономия, географическое распространение и прекрасные изображения жужелиц http://www.carabidae.ru/>
16.Зооклуб мегаэнциклопедия о животных http://www.zooclub. ru/chlen/nasek/zhuk.shtml
17.Coleoptera (Beetles, Kaefer, Brouci) - HomePage (крупнейший англоязычный колеоптерологический сайт) http://www.coleoptera.org/
18. Энтомологический кружок Алексея Куприянова (разнообразные сведения для начинающих энтомологовhttp://tinea.narod.ru/
19.Энциклопедия насекомых - большой сайт с разнообразной информацией (классификация, краткие описания видов, фотографии, определители) http://www.coleop123.narod.ru/
20. ДәуітбаеваК.Ә.«Омыртқасыздар зоологиясы» // Алматы. 1-кітап. -2004. – 374 б
21. Оразымбетова Б.Б., Көбеев М.С. «Жануартану пәнінде көрнекілікті қолдану» // Методикалық оқулық. Қостанай. - 2003.
22. Проценко А.И.К изучению энтомофауны Кустанайской области.Лесные экосистемы Тургайской впадины (тезисы докладов). Кустанай 1993 С. 56-59.
23.ТілменбаевӘ.Т.,ЖармұхамедоваГ.Э.Энтомология.Алматы,Кайнар, 19947 -336б.
24.Осмоловский Г.Е., Бондаренко Н.В. Энтомология. - Л.,«Колос», 1980. -360с.
25.Матпаева Б.Б., Тілменбаев Ә.Т.Ауыл шаруашылығына пайдалы жәндіктер.-Алматы:Қайнар,1973.20.Методы сбора и учетов численности насекомых. Е.А.Дунаев, А.С.Боголюбов.- М: Экосистема, 1996. - 25 с.
26.Методы исследований зообентоса и оценки экологического состояния водоемов (сост. А.С.Боголюбов). - М.: Экосистема, 1997 - 17 с.
27. Методы сбора и учетов численности насекомых. Е.А.Дунаев, А.С.Боголюбов.- М: Экосистема, 1996. - 25 с.
28.Методы исследований зообентоса и оценки экологического состояния водоемов (сост. А.С.Боголюбов). - М.: Экосистема, 1997 - 17 с.

шағым қалдыра аласыз
















