Lesson title Across curriculum: Sound and hearing
Short term plan: term 2
|
Unit 3 Entertainment and media |
Lesson 34 |
|
|
Teacher name: |
|
|
|
Date: |
|
|
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
Lesson title |
Across curriculum: Sound and hearing |
|
|
Learning objectives |
8.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
|
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
|
|
Plan |
||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min Pre-learning «Brainstorming» method 7 min. |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warming up Guess the Word Instructions: Teacher gives a description or action, students guess the word. Divide the class into teams and give points for correct answers.
Lead – In
Answers
Checking homework 1 p |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Learners find mime an action associated with one of the places Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
The teacher to assess learners for their ability. “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment Good job! Descriptor: -know key phrases - can make sentence - know vocabulary of previous lesson Assessment criteria - Learners have met the learning objectives if they can: |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 30 min |
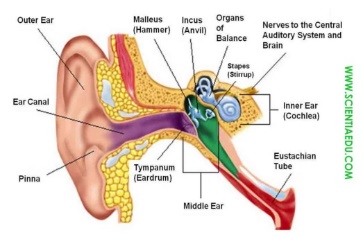
Ex:1 P:38 • Introduce the topic and listen and read for specific information • Ask Ss to read the statements 1-4. Elicit Ss’ guesses as to which one is incorrect. • Play the recording. Ss listen and read the text to check if their guesses were correct. Ex: 2 P: 38 • Read for order • Ask Ss to read statements 1-5. • Give Ss time to read the text again and complete the task. • Check Ss’ answers around the class. Ex: 3 P: 38 • consolidate comprehension of a text • Give Ss time to read the text again and label the diagram writing their answers in the notebook. • Check Ss’ answers. Answer the questions 1. What part of the ear do we see? 2. What happens when sound waves hit our eardrum? 3. What are the names of the three little bones in the ear? 1. What kind of sounds do we hear all day long? A) Only sounds we enjoy B) Only sounds we don’t like C) Both sounds we enjoy and sounds we don’t like D) No sounds at all 2. What happens when sound waves hit the eardrum? A) The eardrum gets damaged B) The eardrum vibrates and moves three little bones C) The sound stops D) The eardrum turns into liquid 3. What are the names of the three little bones in the ear? A) The hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup B) The hammer, the spoon, and the stirrup C) The anvil, the nail, and the stirrup D) The hammer, the nail, and the wheel 4. What does the cochlea look like? A) A small, curled tube that looks like a snail shell B) A flat circle C) A long, straight tube D) A square box Ex: 4 P: 38 • Prepare a monologue; to consolidate information from a text • Ask Ss to use the diagram to prepare a monologue. • Then ask various Ss to give their monologue to the class about how we hear. • Record the monologues. |
• Pupils read the following statements about sound. ANSWERS 4 is incorrect • Pupils read the text and put the sentences in the correct order ANSWERS 3, 5, 1, 2, 4 • Pupils use words from the text to label the diagram ANSWERS 1 eardrum 2 stirrup [ˈstɪrəp] 3 cochlea[kɔˈleːa] • Pupils look at the diagram above and tell the class how we hear.
C) Both sounds we enjoy and sounds we don’t like B) The eardrum vibrates and moves three little bones A) The hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup A) A small, curled tube that looks like a snail shell ANSWERS Sound travels in waves and these are collected in the outer ear. Then they go through the ear canal and hit the eardrum which vibrates. This moves some little bones in our ears called the hammer, the anvil and the stirrup which bump against each other and move the sound along into the cochlea. This is a curved tube that looks like a snail shell. The sound waves move to the nerves here that create signals to tell the brain what we can hear. |
Descriptor: - read the following statements Mutual assessment Descriptor: - read the text - put the sentences in the correct order Peer assessemnt Descriptor: - use words from the text - label the diagram Self assessment Descriptor:
Total 7 p Descriptor: - look at the diagram - tell the class how we hear Total: 2 points
|
Students book |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. Ex: Home task: |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comprehension Questions
-
How does sound travel to our ears?
Answer: Sound travels in waves. -
What part of the ear do we see?
Answer: The outer ear. -
What happens when sound waves hit the eardrum?
Answer: The eardrum vibrates and moves three little bones: the hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup. -
What are the names of the three little bones in the middle ear?
Answer: Hammer, anvil, and stirrup. -
What is the cochlea and what does it look like?
Answer: The cochlea is a small, curled tube that looks like a snail shell. -
What is inside the cochlea?
Answer: Liquid and nerves. -
How do the nerves inside the cochlea help us hear?
Answer: When the stirrup moves, it creates waves in the liquid, which move the nerves. The nerves create signals that the brain understands, so we can hear. -
Why are the nerves in the cochlea important?
Answer: They are important because they send signals to the brain, allowing us to hear sounds.
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
Lesson plan 8 grade Sound and hearing
Lesson plan 8 grade Sound and hearing
Lesson title Across curriculum: Sound and hearing
Short term plan: term 2
|
Unit 3 Entertainment and media |
Lesson 34 |
|
|
Teacher name: |
|
|
|
Date: |
|
|
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
Lesson title |
Across curriculum: Sound and hearing |
|
|
Learning objectives |
8.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
|
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
|
|
Plan |
||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Beginning of the lesson Warming-up 3 min Pre-learning «Brainstorming» method 7 min. |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warming up Guess the Word Instructions: Teacher gives a description or action, students guess the word. Divide the class into teams and give points for correct answers.
Lead – In
Answers
Checking homework 1 p |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Learners find mime an action associated with one of the places Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
The teacher to assess learners for their ability. “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment Good job! Descriptor: -know key phrases - can make sentence - know vocabulary of previous lesson Assessment criteria - Learners have met the learning objectives if they can: |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 30 min |
Ex:1 P:38 • Introduce the topic and listen and read for specific information • Ask Ss to read the statements 1-4. Elicit Ss’ guesses as to which one is incorrect. • Play the recording. Ss listen and read the text to check if their guesses were correct. Ex: 2 P: 38 • Read for order • Ask Ss to read statements 1-5. • Give Ss time to read the text again and complete the task. • Check Ss’ answers around the class. Ex: 3 P: 38 • consolidate comprehension of a text • Give Ss time to read the text again and label the diagram writing their answers in the notebook. • Check Ss’ answers. Answer the questions 1. What part of the ear do we see? 2. What happens when sound waves hit our eardrum? 3. What are the names of the three little bones in the ear? 1. What kind of sounds do we hear all day long? A) Only sounds we enjoy B) Only sounds we don’t like C) Both sounds we enjoy and sounds we don’t like D) No sounds at all 2. What happens when sound waves hit the eardrum? A) The eardrum gets damaged B) The eardrum vibrates and moves three little bones C) The sound stops D) The eardrum turns into liquid 3. What are the names of the three little bones in the ear? A) The hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup B) The hammer, the spoon, and the stirrup C) The anvil, the nail, and the stirrup D) The hammer, the nail, and the wheel 4. What does the cochlea look like? A) A small, curled tube that looks like a snail shell B) A flat circle C) A long, straight tube D) A square box Ex: 4 P: 38 • Prepare a monologue; to consolidate information from a text • Ask Ss to use the diagram to prepare a monologue. • Then ask various Ss to give their monologue to the class about how we hear. • Record the monologues. |
• Pupils read the following statements about sound. ANSWERS 4 is incorrect • Pupils read the text and put the sentences in the correct order ANSWERS 3, 5, 1, 2, 4 • Pupils use words from the text to label the diagram ANSWERS 1 eardrum 2 stirrup [ˈstɪrəp] 3 cochlea[kɔˈleːa] • Pupils look at the diagram above and tell the class how we hear.
C) Both sounds we enjoy and sounds we don’t like B) The eardrum vibrates and moves three little bones A) The hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup A) A small, curled tube that looks like a snail shell ANSWERS Sound travels in waves and these are collected in the outer ear. Then they go through the ear canal and hit the eardrum which vibrates. This moves some little bones in our ears called the hammer, the anvil and the stirrup which bump against each other and move the sound along into the cochlea. This is a curved tube that looks like a snail shell. The sound waves move to the nerves here that create signals to tell the brain what we can hear. |
Descriptor: - read the following statements Mutual assessment Descriptor: - read the text - put the sentences in the correct order Peer assessemnt Descriptor: - use words from the text - label the diagram Self assessment Descriptor:
Total 7 p Descriptor: - look at the diagram - tell the class how we hear Total: 2 points
|
Students book |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. Ex: Home task: |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comprehension Questions
-
How does sound travel to our ears?
Answer: Sound travels in waves. -
What part of the ear do we see?
Answer: The outer ear. -
What happens when sound waves hit the eardrum?
Answer: The eardrum vibrates and moves three little bones: the hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup. -
What are the names of the three little bones in the middle ear?
Answer: Hammer, anvil, and stirrup. -
What is the cochlea and what does it look like?
Answer: The cochlea is a small, curled tube that looks like a snail shell. -
What is inside the cochlea?
Answer: Liquid and nerves. -
How do the nerves inside the cochlea help us hear?
Answer: When the stirrup moves, it creates waves in the liquid, which move the nerves. The nerves create signals that the brain understands, so we can hear. -
Why are the nerves in the cochlea important?
Answer: They are important because they send signals to the brain, allowing us to hear sounds.

шағым қалдыра аласыз