Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Creativity |
Lesson 53 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
|
||
|
Learning objectives |
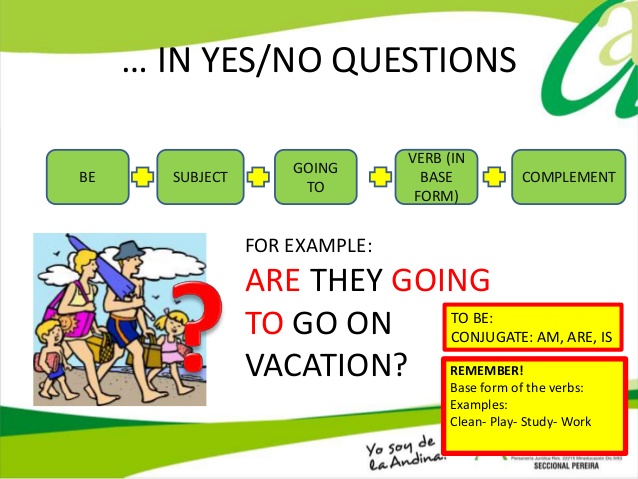
5.3.4.1 respond with limited flexibility at sentence level to unexpected comments on an increasing range of general and curricular topics; 5.4.1.1 understand the main points in a limited range of short simple texts on general and curricular topics; 5.6.3.1 use a structure to be going to (questions) to ask about plans. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise using be going to question forms. • Using be going to to ask about plans |
||
|
Value links |
Generosity – This may be a core value of yours if you cherish people who will give their time and resources to people in need. You may consider yourself to be a generous person if you find joy and meaning in giving to others. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask the class to think of things they are going to do next week. Write them on the board, e.g. go to school, play football. Ask students to make affirmative and negative sentences using the ideas. Ask the class to suggest corrections if they hear a mistake. Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 101 • Explain the task. Give students a few minutes to work individually reading and filling in the table. • Students check their answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:101 • Put students in pairs. Explain the task. When the students have completed the sentences tell them to practise saying the sentences together. • Monitor the students as they speak, making a note of any errors you would like to address later. Ex: 3 P:101 • Draw students’ attention to the example. Ask students to explain the rule for making questions with be going to (Answer: the correct form of be followed by the subject). Ask if we use the short form of be in short answers (Answer: no). •
Explain the task. Students work individually and
then check their answers in pairs. Circulate and monitor. |
Students complete the table with the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 Are 2 am 3 isn’t 4 is Students complete the questions and answers ANSWERS: 1 am 2 Is, isn’t 3 are, ’re 4 we, aren’t 5 Is, is 6 ’m not 7 ’re 8 ’s, is Students make the sentences into questions and short answers ANSWERS: 1 Is she going to save her friends? Yes, she is. 2 Are the princess and the beast going to fall in love? Yes, they are. 3 Are we going to find my sister? Yes, we are. 4 Are the criminals going to win? No, they aren’t. 5 Are you going to find your son? Yes, I am. 6 Is the evil wizard going to die? Yes, he is. 7 Is winter going to end soon? No, it isn’t. 8 Are the fish going to escape? Yes, they are. |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise using be going to question forms. Descriptor: - complete the table with the words in the box. Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Using be going to to ask about plans Descriptor: - complete the questions and answers Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 4 P: 59 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
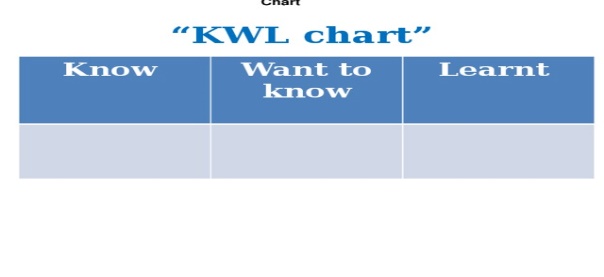
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Creativity |
Lesson 54 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Film Review |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.8.1 recount basic story and events on a range of general and curricular topics 5.5.6.1 link, with some support, sentences into coherent paragraphs using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -Learn and practise nouns -Learn and practise verbs to talk about plans. -Learn and practise vocabulary to talk about films |
||
|
Value links |
Integrity – Integrity is the quality of having strong moral principles. So, a person with integrity will always act with honesty and adhere to their own moral code regardless of what others do. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask the class to think of as many films as they can in one minute. After a minute ask for contributions and write them on the board. Ask the class to talk briefly about the type of films they are and which countries they are from. Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 102 Explain the task and do an example together to make sure students know what they have to do, pointing out that only one of the words on the left matches a word on the right. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:102 Explain the task. Students complete the activity individually and check their answers in pairs Ex: 3 P:102 • Explain the task and do an example together to make sure students know what they have to do, pointing out that only one of the words on the left matches a word on the right. • Explain the task and do an example with the class. Make sure the whole class understand the word sightseeing. |
Students match the things with the places ANSWERS: 1 painting 2 show 3 book 4 film 5 play 6 exhibit Students choose the correct words. ANSWERS: 1 borrow 2 look at 3 watch 4 study 5 listen to 6 go Students match the two part of the phrase ANSWERS: 1 river 2 hall 3 deck 4 resort 5 hall 6 gallery |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise nouns Descriptor: - match the things with the places Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: -Learn and practise verbs to talk about plans. Descriptor: - match the places with the things Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 5 P: 102 SB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Creativity |
Lesson 55 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Unit Review-8 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics; 5.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics; 5.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise using be going to question forms. • Using be going to to ask about plans • Learn and practise vocabulary to talk about films and stories. |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask the class to think of as many films as they can in one minute. After a minute ask for contributions and write them on the board. Ask the class to talk briefly about the type of films they are and which countries they are from. Lead – In
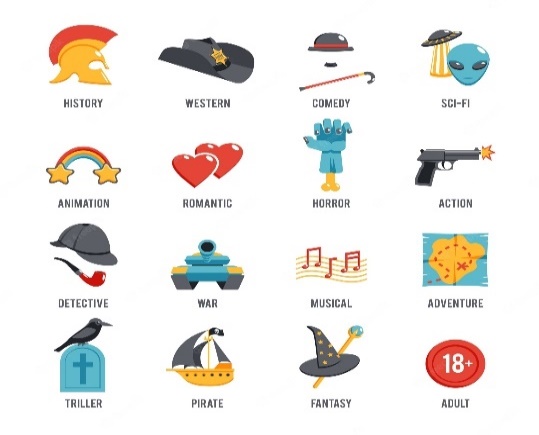
Movie genres vector icons. Movie film genres, comedy genre, war and romance genres, history drama film genre illustration |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 4 P: 102 • Explain the task. Make sure students understand the meaning of alien, ghost, monster, knight and wizard. • Circulate and monitor. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 5 P:102 • Explain the task and ask students to do it individually. Ex: 6 P:102 • Put students in pairs. Explain the task. When the students have completed the sentences tell them to practise saying the sentences together. • Monitor the students as they speak, making a note of any errors you would like to address later. Ex: 7 P:102 • Do the first sentence with the class. Write the sentence on the board as a model for weaker students. • Make sure students write the sentences as they will need them in the next exercise. • Get the students to read out their questions when they are ready.
|
Students match the films with the things ANSWERS: 1 a 2 d 3 f 4 e 5 c 6 g 7 h 8 b Students choose the correct words ANSWERS: 1 to walk 2 ’m y 3 ’s 4 not going to 5 ’re 6 ’re Students complete the questions and answers ANSWERS: 1 am 2 Is, isn’t 3 are, ’re 4 we, aren’t 5 Is, is 6 ’m not 7 ’re 8 ’s, is Students complete the questions and answers with going to ANSWERS: 1 Are you going to watch a film this week? 2 Where are you going to go on holiday this year? 3 How many books are you going to read this month? 4 Are you going to play football tomorrow? 5 What are you going to eat for supper tonight? 6 Are you going to do your homework on time? |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise using be going to question forms. Descriptor: - complete the table with the words in the box. Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Using be going to to ask about plans Descriptor: - complete the questions and answers Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 59 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Creativity |
Lesson 56 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Biography of an actor. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.3.1 Give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics; 5.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: Read the story about first President. Understand the key words and phrases Give reasons |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask the students to tell you what they know about the president of Kazakhstan, e.g. where he is from, his family, what he does, his early life. Ask the class if they know or have watched the film ‘The Sky of My Childhood’. If any students have seen the film, ask them to tell the rest of the class about the story. If there are no students who have seen the film, ask them if they know any films about other people’s lives. L The childhood story of Nursultan Nazarbayev, the first president of the Republic of Kazakhstan. ead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 103 • Ask students to look quickly through the story and find the four words. Discuss as a class which descriptions match the words. • Ask students to think of more words in the Kazakh language that they can explain in English. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:103 • Tell students to work individually and read the story carefully to answer the questions. • Circulate and monitor. Check that any weaker students understand the key words and phrases, e.g. horseback, falconry, high flier, attack and hunting. Make sure students write whole sentence answers. • Check the answers. Ask individual students to read out their sentences. Ex: 3 P:101 • Discuss the question with the whole class. Make sure students give reasons, either positive or negative. |
Students find these words in the story and match words with descriptions ANSWERS: Student’s own answer Students read the information about the film and answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 The story starts in 1940. 2 He lives with his mother, father and grandmother. 3 He enjoys galloping on horseback, learning falconry and playing the dombyra. He also likes playing with friends. 4 Yes, he was. He was a high flier. 5 Three actors played Nazarbayev. This was to show him as a young boy, a youth, and a young man. 6 Yes, he does. He says it is a beautiful film. It has excellent music. Some scenes are very exciting. Students give three reasons for their answer ANSWERS: Student’s own answer |
Assessment criteria - read the text and discuss about first President Descriptor: - read the story and find the four words Assessment criteria: - understand the key words and phrases Descriptor: - give three reasons for their answer Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 4 P: 59 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Reading for pleasure. |
Lesson 57 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Types of writing |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics 5.4.3.1 understand the detail of an argument on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of writing. • Practise asking questions about stories.
|
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask students to work in pairs to tell each other about the last three books they read. They should give details about the title, the author, and what kind of books they were. • After about two minutes, stop the students. Get feedback by asking a few pairs to describe one of the books they talked about Lead – In
In the English language there are a variety of different writing types, knowing when to use the right one will not only make your writing look and sound better but will also help you to create more fitting documents. In this article, we are going to take a look at the various different types of writing in a little more detail. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 104 • Focus students’ attention on the quiz on page 105. Ask the class who they can see in the photos (Answers: Abay Qunanbayuli who they talked about in unit 8; Oliver Twist; and Akira.) • Allow students a few minutes to answer the quiz questions. Tell them to write their answers on a separate piece of paper. Weaker students can work in pairs. • Ask the students to give their answer sheet to another student. Go through the quiz answers with the class. Make sure they keep the score – one point for a correct answer, no points for a wrong answer. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:104 • Explain the task and do an example together to make sure students know what they have to do, pointing out that only one item on the left matches an item on the right. • In a stronger class, ask students to do the activity individually before checking their answers in pairs. In a weaker class, check their understanding of the vocabulary and ask them to do the task in pairs. • Check answers as a class. Ask students to think of more examples of each type of writing. Ex: 4 P:104 • Explain the task and do the first question with the class. If necessary, review when we use wh- questions, e.g. Ask the class ‘Who is your maths teacher?’ (person) ‘When is your Geography class? (time), etc. • Circulate and monitor. Give assistance where necessary. |
Students do the quiz and check their score ANSWERS: 1 b 2 b 3 a 4 b 5 a 6 b 7 b 8 b Students look at the phrases in blue in the quiz. Math the types of writing with the names of the characters ANSWERS: 1 c 2 f 3 d 4 g 5 a 6 h 7 b 8 e Students complete the questions with a wh- or how question word ANSWERS: 1 What 2 Why 3 Who 4 Where 5 When 6 Which 7 How |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of writing. Descriptor: - do the quiz and check their score Assessment criteria: - Practise asking questions about stories. Descriptor: - complete the questions with a wh- or how question word Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 60 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Reading for pleasure. |
Lesson 58 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A Famous story |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.4.3.1 understand the detail of an argument on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics; 5.3.3.1 Give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics. 5.6.1.1 Use Past Simple to tell a story. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise verbs to talk about the past. • Understand stories written in the past tense.
|
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask the class what they know about the Kozy-Korpesh and Bayan-Sulu story. Ask students why the story is so famous. Lead – In
The ancient legend tells that two childhood friends, Syrybay and Karabay, decided to marry their children, who had been engaged even before they were born. Unfortunately, Syrybai died while hunting before his son was born. Growing up, Kozy and Bayan met and fell in love with each other, which made their families very happy. Having grown up, Kozy and Bayan-Sulu do end up falling in love with each other |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 106 • Do the exercise with the whole class. Make sure students understand warrior (a person who fights in battle). Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:106 • Explain the task. Make sure students understand these words before they start reading: steppe, rescue, revenge, stab. • Give students plenty of time to read the story and find the answers. • Go through the answers. In a stronger class, ask students to read the part of the story that answers the question, e.g. for question 1 ‘Karabay had a daughter called Bayan.’ If any sentences are false, ask students to make a true sentence. • In a weaker class, read the story to the class and stop at the sentence which helps answer the question.
Ex: 3 P:106 • Tell students to look quickly at the story again and find the five words. • In a weaker class, stand up in front of the class and point to your hair, waist, neck. Ask the class to say each time what you are pointing at. Mime combing, tidying, wearing (round the neck and waist), and cutting (hair with a knife). • Go through the answers.
|
Students identify who are characters in the story. Match the names with the roles. ANSWERS: 1 daughter 2 lover 3 father 4 warrior Students read the text and write true or false. ANSWERS: 1 true 2 false 3 false 4 true 5 true 6 false 7 false 8 true Students find these words in the text. Match the words with definitions. ANSWERS: 1 c 2 e 3 a 4 d 5 b |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise verbs to talk about the past. Descriptor: - identify who are characters in the story. Match the names with the roles. Assessment criteria: - Understand stories written in the past tense.. Descriptor: - find these words in the text. Match the words with definitions. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 60 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Reading for pleasure. |
Lesson 59 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus: Past Simple |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.6.1.1 use Past Simple (negative and questions) to speak about past events tell; 5.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics; 5.3.3.1 Give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise past simple regular and irregular forms. • Use the past simple to talk about events in the past.
|
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Write watch on the board and ask the students what the past simple form is (watched). Then write go on the board and ask what the past simple form is (went). Draw students’ attention to the table in exercise 1 and ask which group watch belongs to (regular) and go (irregular). Lead – In
Past Simple Tense! When talking about an action which has happened in the past, you will need to use the past simple tense. However, before you can begin confidently using this tense, it is important to learn the rules which surround it. As with any part of English grammar, the rules of the past simple tense should be applied each time it is used in order to ensure that you are forming grammatically correct sentences. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 107 • Tell the class to read the story on page 106 again and find the regular verbs in the past simple. Make sure they do not read the story again but ‘scan’ the text for the words. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:107 • Explain the task. In a weaker class, do the first sentence together and draw students’ attention to the table in exercise 1 which has the past simple forms. Circulate and monitor. • Check answers as a class.
Ex: 3 P:107 • Explain the task. Remind students to use the table in exercise 1 to help them. • Students complete the activity individually and check their answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class. |
Students find the past simple forms in the text. ANSWERS: help – helped, want – wanted, follow – followed, ask – asked, die – died, climb – climbed, love – loved Rules -d, different Students complete the sentences with the past simple forms of the verbs in brackets. ANSWERS: 1 wanted 2 was 3 asked 4 were 5 took 6 died 7 followed 8 cut Students complete the text. Use the correct forms of the verbs in the box ANSWERS: 1 lived 2 was 3 loved 4 came 5 told 6 wanted 7 left 8 followed 9 took 10 climbed |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise past simple regular and irregular forms. Descriptor: - find the past simple forms in the text. Assessment criteria: - Use the past simple to talk about events in the past. Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the past simple forms of the verbs in brackets. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 61 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Reading for pleasure. |
Lesson 60 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Biography of a writer |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 5.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects; 5.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise vocabulary to talk about people’s lives. • Understand a famous person’s biography.
|
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask the class to name some big events in their life so far, e.g. I started school, I went on holiday, I learned to ride a bike. Write the ideas on the board and ask students to put them in the order the events occurred in their lives. Lead – In
Abai Kunanbaev Kazakh writer, poet, lyricist, social philosopher. Born in Kazakhstan in Semey province, Abai Kunanbaev was educated at home and then sen |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 108 • Explain the task. Circulate and monitor. • Check answers as a class. • Get students to close their books. For further practice, tell the students you are going to say a word from the lifeline and they have to say the next stage, e.g. born – go to school. • In a stronger class, say a verb and ask students to finish the phrase, e.g. take – exams. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:108 • Do the exercise quickly with the whole class. Ex: 3 P:108 • Tell the students to read the questions and discuss possible answers. • In a weaker class, ask more questions to guide students, e.g. Was he famous? Which country is he from? Was he born 300 years ago, 150 years ago? • Do not go through the answers at this stage. Students will listen for the answers in the next exercise. Ex: 4 P:108 • Play the recording. Pause at the relevant points to allow students to write the answers. • Tell students to check in pairs. Circulate and monitor. If students have blank or wrong answers, play the recording again |
Students put the words in correct place in the lifeline. ANSWERS: 1 go to school 2 graduate from college 3 start a job 4 have children Students write the past simple form of the verb ANSWERS: 1 was 2 went 3 got 4 started 5 retired 6 died 7 graduated Students answer the questions. What do theu know about Abay Qunanbayuli? ANSWERS: Student’s own answer Students listen to the interview about Abay Qunanbayuli. ANSWERS: 1 He was one of the great poets and philosophers of Kazakhstan. 2 He was born on August 10, 1845. 3 He was from Karauyl in East Kazakhstan. 4 In English ‘abay’ means ‘careful’ 5 He was a great poet. He was also a translator, philosopher and composer. 6 He had four children. 7 He wrote poems such as Spring and he wrote books such as The Book of Words. 8 He died on 6 July 1904. |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise vocabulary to talk about people’s lives. Descriptor: - put the words in correct place in the lifeline. Assessment criteria: - Understand a famous person’s biography Descriptor: - answer the questions. What do theu know about Abay Qunanbayuli? Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 61 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Reading for pleasure. |
Lesson 61 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus: Past Simple. Question and negative form |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.3.1 Give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics; 5.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects 5.6.1.1 use Past Simple (negative and questions) to speak about past events tell; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise using questions in the past simple. • Use negative forms in the past simple.
|
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up • Books closed. Write ‘I got up this morning at …’, ‘I left home at …’, ‘I got to school at …’. Tell students to write down the three times on a piece of paper. Nominate a student to ask another student a question using Did, e.g. ‘Did you get up at 6.30?’. The other student answers ‘Yes, I did.’ or ‘No, I didn’t.’ Students score one point for every question they get right Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the pictur |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 109 • Explain the task. Give students a few minutes to work individually completing the rules. • Students check their answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:109 • Put students in pairs. Explain the task. When students have completed the sentences, tell them to practise saying the sentences together. • Monitor the students as they speak, making a note of any errors you would like to address later. Ex: 3 P:109 • Explain the task. Students work individually and then check their answers in pairs. Circulate and monitor. Make sure students understand that the wh- question word comes at the beginning of the sentence. • Check answers as a class. • Put students in pairs and tell them to ask and answer each other the questions. The answers should be based on the truth. |
Students look at the table and complete the rules. ANSWERS: did, didn’t Students complete the questions and answers ANSWERS: 1 Did 2 you, didn’t, 3 Did, he 4 Did she, didn’t 5 Did, I did 6 What, did, got 7 Where, did,
went Students order the words to make questions. The ask your partner the questions ANSWERS: 1 What did you do yesterday? 2 How did you get to school today? 3 Where did you go yesterday? 4 What time did you get up yesterday? 5 Where did you have lunch yesterday? 6 Who did you talk to yesterday? |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise using questions in the past simple.
Descriptor: - complete the rules in the past Assessment criteria: - Use negative forms in the past simple Descriptor: - complete the questions and answers Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 4 P: 109 SB write sentences about your studies last week. |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Reading for pleasure. |
Lesson 63 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Unit Review -9 Summative assessment for the unit “Creativity” |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.6.1.1 use Past Simple (negative and questions) to speak about past events tell; 5.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which 5.L4 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics; 5.L5 Understand most specific information and detail of short, supported talk on a wide range of familiar topics 5.S8 Recount basic stories and events on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use and practise nouns to talk about types of writing. • Practise asking questions about stories. • Recognize detailed information in a short conversation with some support • Retell short stories and episodes on a given topic |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wish lamp Lead – In Review previos lesson asking vocabulary. Legend, fairy tale, poem, |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 110 • Explain the task. Remind students to use with the words in the box. . • Students complete the sentences individually and check their answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:110 • Explain the task. Draw students’ attention to the example sentences. • Get the students to read out their sentences when they are ready. Summative assessment for the unit “Creativity” Listening Task 1. Listen to the story and fill in the gaps with the words from the box. One word is odd.CD2. Tapescript2 Speaking Task 2. Look at the pictures bellow, choose one and answer the following questions. What do you know about cartoons below? Speak about one of the cartoons. The following questions will help you to organize the speech: 1 Why do you like this cartoon? 2 Who are the main heroes? 3 What is this cartoon about? 4 Which part do you like most and why? |
Students complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 horror 2 fairy 3 poem 4 play 5 comic 6 classic 7 crime 8 legend Students put the words in the correct order and answer the questions. ANSWERS: 1 What is your favorite story? 2 Why do you like it? 3 Where is the location of the story? 4 Who is the hero? 5 When does the story take place? 6 Which character do you like? 7 How many times have you read it? Students listen to the story and fill in the gaps. ANSWERS: 1 a lovely garden 2 a wall 3 winter 4 a hole 5 spring Students look at the pictures and choose one of cartoon. Answer the questions ANSWERS: Student’s own answer |
Assessment criteria - Use and practise nouns to talk about types of writing.
Descriptor: -Use nouns - complete the sentences Assessment criteria: - Retell short stories and episodes on a given topic Descriptor: -answers questions -speaks with grammar accuracy Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 5 P: 110 SB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Reading for pleasure. |
Lesson 64 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A Book festival. Kazakh famous writers and poets. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics; 5.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects 5.3.3.1 Give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - use simple context clues strategies to identify meaning of unknown words from the contex - write a short text (e.g. a description of the room, hobby, or a friend) - give a limited response showing their opinion, preferences, agreement or disagreement |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wish lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Ask the students to tell you what they know about book festivals. Who goes to a book festival? What can they do there? Who can they see? |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 111 • Draw the students’ attention to the poster. Ask some quick questions, e.g. Where is the festival? (Answer: London, UK), When does it start? (Answer: Saturday 12 August), How many main events are there on Saturday? (Answer: three). • Tell students to read questions 1-5 and find the answers in the poster. For fast finishers, ask them to correct any false sentences. • In a stronger class, tell the students use other information in the poster to make true and false sentence. Students read the sentence to a partner who says if it is true or false and corrects any false sentences Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:111 • Explain the task. Give students five minutes to choose a book and write between three and five sentences. • Ask some students to read out their sentences for the class. Ex: 3 P:111 • Tell the students to read the questions and discuss possible answers. • In a weaker class, ask more questions to guide students, e.g. Was he famous? Which country is he from? Was he born 300 years ago, 150 years ago? • Do not go through the answers at this stage. Students will listen for the answers in the next exercise. |
Students read the information in the poster and write true or false for each sentence ANSWERS: 1 true 2 false 3 true 4 true 5 false Students write the past simple form of the verb ANSWERS: 1 was 2 went 3 got 4 started 5 retired 6 died 7 graduated Students think of a book you know very well. Write some sentences to describe the story and the characters. ANSWERS: Student’s own answer Students say which authors would they like to meet? ANSWERS: Student’s own answer |
Assessment criteria - use simple context clues strategies to identify meaning of unknown words from the contex
Descriptor: - read the information in the poster and write true or false for each sentence Assessment criteria: - write a short text (e.g. a description of the room, hobby, or a friend)
Descriptor: - Write some sentences to describe the story and the characters. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 61 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 65 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
People and places |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics; 5.1.4.1 evaluate and respond constructively to feedback from others; 5.6.6.1 use plural form of nouns talking about people and places; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise basic vocabulary. • Learn how to form plurals. |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wish lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Write the following words on the board in random order: country, village, city, town. Tell students to work in pairs to put these places in order of size, starting with the largest. Ask them to think of an example of each place from their own country. • After about 1 minute, stop the students. Get feedback from each pair. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
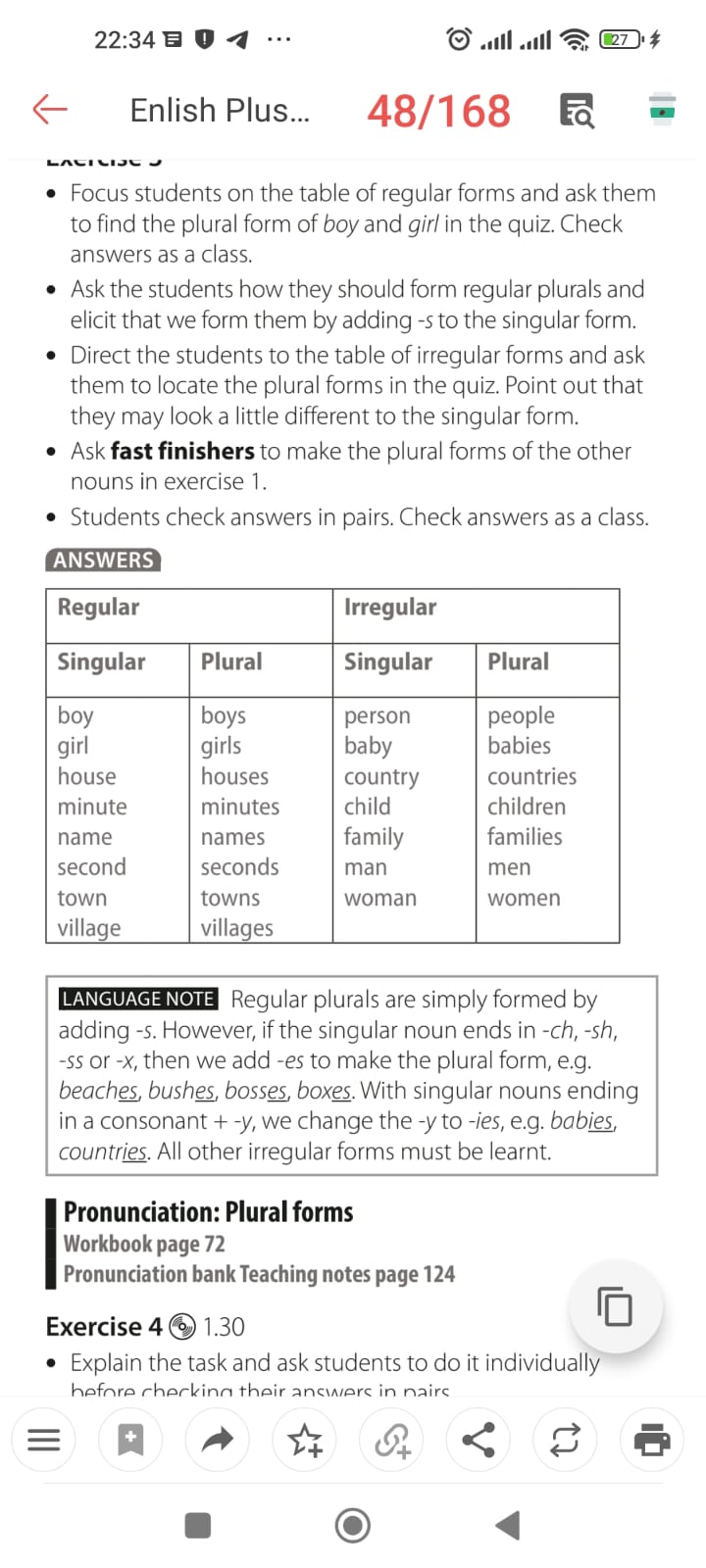
Ex: 1 P: 26 • Focus students’ attention on the words in the box. If you have done the warm-up activity, they will already be familiar with country, town, city and village. • In a weaker class, ask students to work in pairs, using page 77 of the Workbook to help them. In a stronger class, encourage students to complete the lists by themselves. • Students check answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:26 • Refer students to the quiz on page 23. Look at the photos and ask students to identify words from exercise 1 (people, baby, city, village, house). • Explain the task and play the recording. Students work individually and then check their answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class. Do any of the facts surprise them? What is the most interesting fact? Ex: 3 P:26 • Focus students on the table of regular forms and ask them to find the plural form of boy and girl in the quiz. Check answers as a class. • Ask the students how they should form regular plurals and elicit that we form them by adding -s to the singular form. • Direct the students to the table of irregular forms and ask them to locate the plural forms in the quiz. Point out that they may look a little different to the singular form. • Ask fast finishers to make the plural forms of the other nouns in exercise 1 |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box in the wordlist in the workbook ANSWERS: Places: city, house, town, village People: child, family, man, person, woman Students do the Our World quiz. Then listen and check your answers. ANSWERS: 1 a 2 a 3 a 4 a 5 b 6 b 7 a Students complete the lists with plural forms in the Our World quiz. ANSWERS:
|
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise basic vocabulary.
Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words in the box Assessment criteria: - Learn how to form plurals.
Descriptor: - complete the lists with plural forms Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 18 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 66 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
An article about two places. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in short, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topics; 5.3.6.1 communicate meaning clearly at sentence level during, pair, group and whole class exchanges; 5.4.1.1 understand the main points in a limited range of short simple texts on general and curricular topics. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about two different places. • Learn and use new vocabulary to describe places in towns. • Practise speaking about a town. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Write Hollywood on the board. • Ask the class to brainstorm what they know about Hollywood, which country it is in, what it’s famous for, etc. Accept any feedback they give you and put any interesting facts and new vocabulary on the board. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 28 • Focus on the three pictures and explain the task. Allow students about 2–3 minutes to compare the pictures in pairs. • When they are ready, they choose adjectives to match each location. Ask them to match the pictures to the locations as well. • Check answers as a class. In a stronger class, encourage students to give reasons for choosing their adjectives Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:28 • Refer students to the texts and play the recording. • In pairs, students do the task. • Check answers as a class. You could ask fast finishers to underline the adjectives used in the text to describe the two locations (fast, noisy, famous, big, expensive, small, quiet, nice, interesting) Ex: 3 P:28 • Draw students’ attention to the questions. In a stronger class, ask the students to complete the activity individually before checking their answers in pairs. Encourage them to guess the meaning of any new vocabulary from the context. • In a weaker class, read the questions together, explaining any new vocabulary and checking for understanding. Do the first questions together as an example. • Remind students to write full sentences in their answers. • Students check answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. |
Students look at the pictures in the text. Guess which adjectives in the box describe Hollywood, USA and which describe Hollywood, Ireland ANSWERS: Students’ own answers Students read and listen. Check your answers to exercise 1 ANSWERS: Hollywood, USA: famous, noisy Hollywood, Ireland: quiet, small Students read the text again and answer the question. ANSWERS: 1 No, it isn’t. It’s part of Los Angeles. 2 No, it isn’t. It’s part of a city. 3 No, it isn’t. It’s a noisy place. 4 No, it isn’t. It’s a small place. 5 There are many interesting places near the village. 6 Yes, it is. The city of Dublin is forty-two kilometres from the village. |
Assessment criteria - Read about two different places. Descriptor: - read and listen Assessment criteria: - Learn and use new vocabulary to describe places in towns. - Practise speaking about a town.
Descriptor: - read the text again and answer the question. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 18 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 67 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus: there is/ there are/ some and any |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.5.8.1 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics; 5.6.1.1 use appropriate countable and uncountable nouns, including common noun phrases and a structure there is/ there are describing times and location, on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics; 5.6.14.1 use prepositions to talk about time and location and some/ any/no; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise the affirmative and negative forms of there is, there are, some and any. • Practise describing towns and cities. |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Tell the students you are going to say the name of a city and they should write down the first thing – a building, a place, a person, anything they like – they can think of in relation to that city. • Say London. Students write down the first thing they think of. Don’t allow them any more than 30 seconds for this. • Get feedback from a few students in the class and put their ideas on the board. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 29 • Focus students on the tables and the rules. In a stronger class, ask the students to go ahead and complete the rules based on the examples in the table. They check answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. • In a weaker class, go through the table with the students, pointing out the plural and singular sections in the positive and the negative. Complete the rules together with the class. LANGUAGE NOTE We can use some and any with both countable and uncountable nouns. However, with uncountable nouns we always use the singular form of the verb be, e.g. There are some chairs in the room; There aren’t any students in the school; There’s some milk in the fridge; There isn’t any coffee left. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:29 • Tell the class to try to remember the information in the text about Hollywood in Ireland on page 24 of the book. Refer them to the sentences and explain the task. • In a weaker class, ask students to complete the activity in pairs. Encourage students in a stronger class to do the task individually. Ex: 3 P:29 • Refer students to the information about the two places and allow them a few minutes to look through it. • Ask students to complete the task individually and then to compare their answers in pairs. Check the answers all together as a class. |
Students study the tables. Then choose the correct words to complete the rules. ANSWERS: In plural sentences we use some in the affirmative. We use any in negative sentences. Students correct the sentences ANSWERS: 1 There aren’t any discos. 2 There are some interesting places near the village. 3 There isn’t an Armani shop. 4 There is a small shop. 5 There are 100 people in the village. 6 There aren’t any famous people Students write the sentences about London in England and London in the South Pacific. ANSWERS: London, England: There are some museums in London. There are four airports in London. There aren’t any long houses in London. London, Kiritimati Island, South Pacific: There are 1,000 people in London. There is one hotel in London. There aren’t any cinemas in London. There are some shops in London. |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise the affirmative and negative forms of there is, there are, some and any.
Descriptor: - study the tables. Then choose the correct words to complete the rules. Assessment criteria: - Practise describing towns and cities.
Descriptor: - write the sentences about London in England and London in the South Pacific. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 19 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 68 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Shops. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary to talk about a limited range of general topics; 5.6.1.1 use appropriate countable and uncountable nouns, including common noun phrases and a structure there is/ there are describing times and location, on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics; 5.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in short, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topics; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary to describe different shops. • Practise talking about favourite shops. |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Ask students to work in pairs and think about the last thing they bought and to tell their partners about it – what it was and where they bought it from. • Get some feedback from the class by asking a few students to describe what their partner last bought. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 30 • Draw students’ attention to the ten pictures and to the words in the box. Explain the task. • Tell students to match the pictures with the shops that they recognize first, and encourage them to try to guess the others. • Students check their answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. • You could ask fast finishers to think about other types of shops that are not included and to check their names in a dictionary. Ex: 2 P:30 • Go through the vocabulary in the box with the class and check for understanding. • Students do the task in pairs. Check answers as a class. • Divide students into pairs and allow them 2–3 minutes to think of a few examples of items from the other shops in exercise 1. • Get feedback from each pair and put their ideas on the board for the whole class to see. Background information Dubai is a big, modern city in the United Arab Emirates. It is known as the ‘shopping capital of the Middle East’ because of it’s large number of shopping malls – over 70 of them – built with the aim of increasing Dubai’s tourist industry. Of these, the ‘Dubai mall’ is the largest. Apart from 1,200 shops and gigantic cinema, its attractions include an aquarium, a spectacular fountain, an indoor theme park and a children’s entertainment centre Ex: 4 P:30 • Discuss the photo at the bottom of the page with the students. Ask them if they know anything about Dubai and elicit any feedback from the students. • Draw students’ attention to the numbers and ask them to say them. • Explain the task and play the recording. Students check answers in pairs. |
Students match pictures with the shops in the box. ANSWERS: 1 bookshop 2 chemist’s 3 newsagent’s 4 clothes shop 5 games shop 6 supermarket 7 sports shop 8 pet shop 9 computer shop 10 shoe shop Students think of more adjectives from each shop. What shops are the objects in the box from? ANSWERS: 1 supermarket 2 clothes shop / sports shop \ 3 pet shop 4 newsagent’s / supermarket 5 shoe shop 6 games shop / computer shop
Students say the numbers. Listen to Fiona and Sophie talking about Dubai Mall. Order the numbers as you hear them. ANSWERS: 1 d 2 a 3 b 4 c |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary to describe different shops.
Descriptor: - match pictures with the shops in the box. Assessment criteria: - Practise talking about favourite shops. Descriptor: - think of more adjectives from each shop. What shops are the objects in the box from? Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 20 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 69 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
There is/ there are and short answers. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.6.14.1 use prepositions to talk about time and location and some/ any/no; 5.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics; 5.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn how to use there is and there are in questions and short answers. • Learn and practise using prepositions of place. • Further practice describing towns and shops. |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Remind students about the shopping centre in Dubai from page 26 and ask them to work in pairs to briefly discuss whether they would prefer to go shopping in a big shopping centre or in small shops in a town. • After about 2 minutes, stop the students and get some feedback from a few pairs. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 31 • Explain the task. In a stronger class, ask students to complete the task individually. In a weaker class, students complete the task in pairs. • Ask the students how they can make the question form of there is and there are and elicit that we invert the verb be and there. Point out that with How many we put the verb be and there at the end of the question. LANGUAGE NOTE We almost always use any in negative and questions forms. An exception to this is when we make an offer or a request, e.g. Would you like some coffee? Could I have some bread, please? Ex: 2 P:31 • Refer students to the questions and explain the task. They complete the activity individually. • Point out that students should check carefully whether they are talking about a singular or plural noun before they choose their answers. Ex: 3 P:31 • Refer students to the dialogue and ask them to read it quickly, ignoring the gaps. Ask the class what Lucy and Jared are talking about and elicit that they are talking about shops in their town • Students complete the task individually, though in a weaker class you could ask students to do the activity in pairs. Ex: 4 P:31 • Refer students to the words in the box and explain that these are prepositions (students already met the prepositions on and at on page 15). • Focus the student on the six pictures and ask them what they think these prepositions are being used for. Elicit that they are used to describe where something is and that they are prepositions of place |
Students complete the questions in the table with words from exercise 5 page 30 ANSWERS: 1 Is 2 Are 3 are there Students choose the correct words. Then write short amswers. ANSWERS: 1 Is 2 Is 3 Are 4 are 5 Is 6 Is 7 Is 8 are Students complete the dialogue. Then listen and check. ANSWERS: 1 There are 2 there is 3 How many 4 There are 5 Is there 6 there isn’t 7 Are there 8 there are Students study the prepositions. Then look at the picture and complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 in 2 on 3 under 4 next to 5 opposite 6 near 1 people / balls, sports shop 2 boys, door 3 shoes 4 balls, bags 5 t-shirts 6 bag |
Assessment criteria - Learn how to use there is and there are in questions and short answers.
Descriptor: - complete the questions in the table Assessment criteria: - Learn and practice using prepositions of place.
Descriptor: - study the prepositions. Then look at the picture and complete the sentences Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 21 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 70 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Asking about places in a town |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in short, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topics; 5.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 5.3.6.1 communicate meaning clearly at sentence level during, pair, group and whole class exchanges |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Practise asking for information about places. • Learn and practise phrases for asking for information. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Draw a rough map of a few streets in the area of the school on the board. Write school on the map to show the students where they are. • Draw a few empty boxes at different places on the streets to represent some of the shops or other buildings in the area. Ask the students to tell you what they are and write the names of the places in the boxes |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 32 • Focus on the photo and discuss it with the class. Ask the students what they can see and elicit that there is girl and a woman in the picture. • They answer the questions in pairs. Get feedback from a few pairs of students Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:32 Draw students’ attention to the map at the bottom of the page. Allow them a minute or two to familiarize themselves with it and ask them a couple of questions to check they can follow it properly. For example, ask: Is there a restaurant? Are there any shops? How many shops are there? • Explain the task and play the recording. Students complete the dialogue and check answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. • For further practice, you could divide students into pairs and allocate each student the role of Rosa and the woman. Ask the students to practise the dialogue in pairs Ex: 3 P:32 • Refer students to the key phrases and explain the task. Point out the arrows at the end of the phrases and explain that we raise our intonation when asking for something. • Play the recording. Pause after each phrase and ask the students to repeat. Model the phrases yourself, making sure to raise or lower your intonation as appropriate. Exaggerate your intonation a little so that the students notice the difference |
Students look at the photo. Where are the people. Is the girl from this town? ANSWERS: The people are in a town. The girl is not from the town.
Students look at the map and listen to the dialogue. What are the missing word? ANSWERS: 1 sports shop 2 sports shop Students listen to the key phrases and practise the pronunciation. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers
|
Assessment criteria - Practise asking for information about places.
Descriptor: -look at the photo. Where are the people. Is the girl from this town? Assessment criteria: - Learn and practise phrases for asking for information. Descriptor: - look at the map and listen to the dialogue. What are the missing word? Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 4 P: 21 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 71 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A brochure about your town |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 5.3.6.1 communicate meaning clearly at sentence level during, pair, group and whole class exchanges 5.5.8.1 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the structure of a brochure about a town or city. • Learn and practise how to use be + also. • Practise writing a brochure about a town. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Students work in pairs to think of things to say in English about their home town / city. • After about 2 minutes, stop the students and get some feedback from each pair
|
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 33 • Focus on the photos and the flag and ask students if they recognize the country. Elicit that it is Canada. • Explain the task and allow students time to answer the questions based on the text
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:33 • Refer students to the example and do the task together as a class. Point out that we use also to give further information about something. It helps to link two things together and makes descriptions sound more natural. • Students find the other example of also in the text LANGUAGE NOTE While also comes after the verb be, it usually comes before all other verbs. For example, I also like to play football or She also eats a lot of chocolate. Ex: 3 P:33 • Refer students to the sentences and explain the task. Students check answers in pairs. Ex: 4 P:33 • Draw students’ attention to the key phrases that can be used to describe a town or a city. Read through them with the class and check for understanding. • Tell students to think about their own town or city and explain the task. Check answers as a class. |
Students read the model text and answer the questions. ANSWERS: 1 The capital of Canada is Ottawa. 2 Ice hockey, skating and American football are popular sports in Canada. 3 Quebec is 275
kilometres from Montreal. Students look at the examples. Is also before or after the verb be? Find another example of also in the brochure about Montreal. ANSWERS: Also is after the verb be. There are also interesting museums here Students rewrite the blue sentences. Include also in each sentence. ANSWERS: 1 There’s also a museum. 2 There are also bookshops. 3 There are also two parks. 4 There’s also a restaurant. 5 There’s also an airport. Students substitute words in the box for the words in blue in the key phrases and change the names of the places. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers |
Assessment criteria - Learn the structure of a brochure about a town or city.
Descriptor: - look at the examples. Is also before or after the verb be? Find another example of also in the brochure about Montreal. Assessment criteria: - Practise writing a brochure about a town. Descriptor: - rewrite the blue sentences. Include also in each sentence. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 22 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 72 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country. My world Summative assessment for the unit ”Fantasy world” |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics; 5.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in short, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topic; 5.4.1.1 Understand the main points in a limited range of short simple texts on general and curricular topics; 5.5.4.1. Write with support a sequence of extended sentences in a paragraph to give basic personal information. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about geographical features. • Read a text about geographical features in Kazakhstan. Write short sentences on familiar topics with support Connect sentences into a paragraph |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
||
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Allow students about 2 minutes to tell each other their favourite thing about the countryside.
|
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
||
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 34 • Draw students’ attention to the words in the box and to the pictures 1–6. • Check answers as a class Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:34 • Focus students’ attention on the map and the compass. Explain that a compass tells you what direction you are facing. Draw a compass on the board and write the directions: north, south, east, west, north-west, north-east, south-west, and south-east. Ask students to find their hometown on the map and say whether it is in the north, north-east, west, etc.
Summative assessment for the unit ”Fantasy world” Writing Task 1. Look at the map and choose ONE of the buildings bellow and describe your route from the shop to that building: Reading Task 2. Read the text and identify the writer’s opinion and write Yes or No next to the given statements as in the example. Task 3. Write Yes or No next to the statements as in the example:
|
Students check the meaning of the words. Then match words with pictures. ANSWERS: 1 forest 2 mountain 3 river 4 desert 5 steppe 6 lake Students look at the map of Kazakhstan and choose the correct word in the text. Then listen and check. ANSWERS: 1 forests 2 steppe 3 desert 4 rivers 5 lake 6 mountains gives a full answer using linking words and basic connectors writes with grammar accuracy (allowed to make 2 errors); 1 Yes 2 Yes 3 No 4 Yes 5 No |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for talking about geographical features.
Descriptor: -check the meaning of the words. Then match words with pictures.
Assessment criteria: - Write short sentences on familiar topics with support
Descriptor: - writes with grammar accuracy (allowed to make 2 errors);
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards
Worksheets
|
||
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 23 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 73 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Shopping |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.2.7.1 recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) in basic, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topics; 5.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics; 5.5.6.1 link, with some support, sentences into coherent paragraphs using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn how to use prices. • Understand a conversation in a shop. • Practise asking for prices and buying things. |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Tell students to imagine they have €100 to spend on anything they like. • In pairs, students tell each other what they would spend their money on. Get some feedback from a few pairs by asking students what their partner would spend the money on. Put their ideas on the board, explaining any new vocabulary |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 35 • Focus students’ attention on the two columns. Ask them what the currency symbol £ represents and elicit that it represents pounds, the currency used in the UK. Point out that there are 100 pence in one pound. If you can, tell students how much £1 is worth in their currency. • Explain the task. Students complete it individually and check their answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. • Model the prices for pronunciation and ask students to repeat Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:35 • Explain the task. Ask students to write the prices down in two ways (numbers and words). • Pause after each price to allow students time to write it down. • Students compare their prices in pairs. Check answers as a class. • Play the recording again and pause after each price to allow students time to repeat Ex: 3 P:35 • Explain the task and draw students’ attention to the question. Check they understand what the four different places are by quickly eliciting from the students some example of the different things you can buy in each. • Play the recording. Students check their answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. |
Students match 1 – 6 with a – f. then listen and check. ANSWERS: 1 c 2 e 3 a 4 f 5 b 6 d Students listen and write the prices you hear. Then listen and repeat. ANSWERS: 1 32p, thirty-two pence 2 75p, seventy-five pence 3 £3.20, three pounds twenty 4 £8, eight pounds 5 £15, fifteen pounds 6 £7.50, seven pounds fifty
Students listen to a conversation. Where is Jared? ANSWERS: Jared is in a souvenir shop |
Assessment criteria - Learn how to use prices.
Descriptor: - match 1 – 6 with a – f. then listen and check Assessment criteria: - Understand a conversation in a shop.
Descriptor: - listen to a conversation. Where is Jared? Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 24 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 74 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 06.03.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Fantasy world |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.4.6.1 recognize the attitude or opinion of the writer in short texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics; 5.5.6.1 link, with some support, sentences into coherent paragraphs using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics 5.3.2.1 ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general topic. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a Kazakh folk story. • Write a story and make a poster |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
||
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Books closed. Write folk story on the board. Explain or elicit that a folk story is a traditional story from a particular country or place that was originally passed on to people in a spoken form. • Ask students if they know any folk stories from Kazakhstan or from other countries. Ask if they enjoy reading folk stories and why. • Get feedback from the class and elicit the titles of some popular folk stories. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets. |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
||
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 36 • Focus students’ attention on the names in the box and ask them what they know about these people. Elicit any information you can from the students by asking them some questions, e.g. Why is this person famous? What did they do? When did they live? Have you read any stories about them? • Ask students what their favourite folk story is. Elicit some ideas and encourage students to give reasons for their answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:36 • Refer students to the text and ask them to read the paragraphs quickly and say which of the people in exercise 1 is the main character in the story • Students work in pairs to put the paragraphs in the correct order. • Check answers as a class. Ex: 3 P:36 Read through the instructions together and make sure students understand what they have to do. • Give students a few minutes to identify the main events in the story. In a stronger class, ask students to summarize each event in one sentence, e.g. • Students work in pairs to complete the task. Monitor as they retell the story and remind them to use the past simple tense |
Students answer the questions. Who are these people? Do you know any stories about them? Which story is your favourite? ANSWERS: Students’ own answer. Students read the paragraphs and put them in the correct order to make a story. ANSWERS: A 4 B 1 C 3 D 5 E 2 The story is about Aldar Kose Students work in pairs. Make a list of the main events in the story. Draw a picture to illustrate each event. Then retell the story using the pictures ANSWERS: Students’ own answers Aldar Kose was cold and unhappy because his coat had holes in it and his horse was slow. When he saw the bai in the distance, he took off his coat and his hat and started singing cheerfully. When the bai heard about Aldar Kose’s magic coat, he wanted to buy it. He gave Aldar his fur coat, his beautiful white horse, and a bag of gold. Aldar Kose jumped on the horse and rode off as quickly as he could. |
• In a weaker class, pre-teach the following words and phrases: ride, fur coat, holes, in the distance, recognize. • In a weaker class, This task differentiated by the students abilities. Less able students define words with the help of prompt cards which written the new words. |
Assessment criteria - Read a Kazakh folk story.
Descriptor: - answer the questions Assessment criteria: - Write a story and make a poster
Descriptor: - Make a list of the main events in the story -Write a story about one of the people Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
||
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
|||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 75 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Vocabulary puzzles: People and places. shops |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics; 5.5.6.1 link, with some support, sentences into coherent paragraphs using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use and practise basic vocabulary • Use vocabulary to describe different shops. • Write the affirmative and negative forms of there is, |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Books closed. Ask students to work in pairs and think about the last thing they bought and to tell their partners about it – what it was and where they bought it from. • Get some feedback from the class by asking a few students to describe what their partner last bought |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets. |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 37 • Focus students’ attention on the words in the puzzle. If you have done the warm-up activity, they will already be familiar with country, town, city and village. Find ten words for people and places. • In a stronger class, encourage students to complete the lists by themselves. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:37 • Draw students’ attention to the five pictures. Explain the task. • Tell students to match the pictures with the shops that they recognize first, and encourage them to try to guess the others. Ex: 3 P:37 • Focus the student on the two pictures and ask them what they think these there is, there are are being used for. Elicit that they are used to describe two differences pictures of Tinford town centre. |
Students find ten words for people and places. Use the green letters to spell a place. ANSWERS: Country Person People City Students complete the puzzle with the shops ANSWERS: 1 bookshop 2 chemist’s 3 pet shop 4 supermarket 5 shoe shop The spot the difference. Look at the two pictures of Tinford town centre. Write the shops that are different in picture 2. What shops are the same? ANSWERS: |
• In a weaker class, ask students to work in pairs, • In a weaker class, pre-teach the following words and phrases: bookshop, supermarket |
Assessment criteria - Read a Kazakh folk story.
Descriptor: - answer the questions Assessment criteria: - Write a story and make a poster
Descriptor: - Make a list of the main events in the story -Write a story about one of the people Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 76 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review. Unit-3 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.4.1.1 understand the main points in a limited range of short simple texts (a poem) on general and curricular topics; 5.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - talk about people and places. - understand an article about a shopping centre. - ask for information about places in a town |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Books closed. Write the following words on the board in random order: country, village, city, town. Tell students to work in pairs to put these places in order of size, starting with the largest. Ask them to think of an example of each place from their own country |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets. |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 38 • Read through the instructions together and make sure students understand what they have to do. • Check answers as a class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:38 • Focus students’ attention on the two columns. There is one shop you don’t need. • Explain the task. Students complete it individually and check their answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. Ex: 3 P:37 • Refer students to the questions and explain the task. They complete the activity individually. • Point out that students should check carefully whether they are talking about a singular or plural noun before they choose their answers. • Students check answers in pairs. Check answers as a class |
Students complete the sentences with the singular or plural forms of the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 cities 2 people 3 baby 4 children 5 women 6 countries Students match objects with shops. There is one shop you don’t need. ANSWERS: 1 f 2 e 3 b 4 a 5 d 6 c Students choose the correct words ANSWERS: 1 ’s 2 aren’t 3 isn’t 4 ’s 5 any 6 some |
In a weaker class, revise the rules for forming plural nouns. • In a weaker class, pre-teach the following words and phrases: Computer shop Sport shop Aspirin |
Assessment criteria - talk about people and places.
Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the singular or plural forms of the words in the box. Assessment criteria: - ask for information about places in a town
Descriptor: match objects with shops. There is one shop you don’t need. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 77 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
People and places |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics; 5.6.6.1 use plural form of nouns talking about people and places; 5.6.5.1 use numbers to complete the fact file of a country; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use and practise basic vocabulary. • Use and practise the affirmative and negative forms of there is, there are, some and any |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Books closed. Write the following words on the board in random order: country, village, city, town. Tell students to work in pairs to put these places in order of size, starting with the largest. Ask them to think of an example of each place from their own country. • After about 1 minute, stop the students. Get feedback from each pair. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:38 • Read through the instructions together and make sure students understand what they have to do. In a weaker class, revise the rules for forming plural nouns. • Check answers as a class. Ex: 2 P:38 • Focus on the table and on the words in the left-hand column. Read through them with the class, checking for understanding. • Students do the task in pairs. Encourage students to match the words they recognize first Ex: 3 P:38 • Tell students to work in pairs to choose the correct words. Check answers as a class. • Students complete the rest of the task individually, though you could ask students to do it in pairs in a weaker class. Check answers as a class. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the sentences with the singular or plural form of the words in the box Descriptor: -finds out the right place. -use singular or plural form (1 cities 2 people 3 baby 4 children 5 women 6 countries) Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students match objects with shops. There is one shop you don’t need Descriptor:
(1 f 2 e 3 b 4 a 5 d 6 c) Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students choose the correct words Descriptor:
Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
-remember simple words - can complete sentence - know vocabulary Total: 2 point -can match -know vocabulary Total: 2 point -can complete the sentences Total: 2 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 80 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative control work for the 3rd term |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.2.4.1 Understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics. 5.4.2.1 Understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics. 5.5.6.1 Link, with some support, sentences into coherent paragraphs using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics. 5.3.1.1 Provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - summarize the main idea with the limited support of details they hear or write down -identify the details of a text - use simple transitional phrases (firstly, secondly…, in conclusion, then, but) -convey ideas and basic information (age, hobbies, interests, family and educational background) |
||
|
Plan |
|||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 81 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Revision |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.2.4.1 Understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics. 5.4.2.1 Understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - summarize the main idea with the limited support of details they hear or write down -identify the details of a text |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Books closed. Write the following words on the board in random order: country, village, city, town. Tell students to work in pairs to put these places in order of size, starting with the largest. Ask them to think of an example of each place from their own country. • After about 1 minute, stop the students. Get feedback from each pair. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria Use the information to write sentences which describe people, places and objects |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students listen to the recording and write the name of each room Descriptor: - write the names of each room. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students Read the text and complete the sentences using the words from the box Descriptor: -read the text -complete the sentences Students describe the places and write using the following questions. Descriptor: - describe the places Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students choose one card to speak about the topic Descriptor: - speak using questions Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
- can write the names of each room. Total: 5 point -can read the text Total: 5 point -can describe the places Total: 5 point -can speak using questions Total: 5 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
Means of transport
Means of transport
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Creativity |
Lesson 53 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
|
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.4.1 respond with limited flexibility at sentence level to unexpected comments on an increasing range of general and curricular topics; 5.4.1.1 understand the main points in a limited range of short simple texts on general and curricular topics; 5.6.3.1 use a structure to be going to (questions) to ask about plans. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise using be going to question forms. • Using be going to to ask about plans |
||
|
Value links |
Generosity – This may be a core value of yours if you cherish people who will give their time and resources to people in need. You may consider yourself to be a generous person if you find joy and meaning in giving to others. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask the class to think of things they are going to do next week. Write them on the board, e.g. go to school, play football. Ask students to make affirmative and negative sentences using the ideas. Ask the class to suggest corrections if they hear a mistake. Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 101 • Explain the task. Give students a few minutes to work individually reading and filling in the table. • Students check their answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:101 • Put students in pairs. Explain the task. When the students have completed the sentences tell them to practise saying the sentences together. • Monitor the students as they speak, making a note of any errors you would like to address later. Ex: 3 P:101 • Draw students’ attention to the example. Ask students to explain the rule for making questions with be going to (Answer: the correct form of be followed by the subject). Ask if we use the short form of be in short answers (Answer: no). •
Explain the task. Students work individually and
then check their answers in pairs. Circulate and monitor. |
Students complete the table with the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 Are 2 am 3 isn’t 4 is Students complete the questions and answers ANSWERS: 1 am 2 Is, isn’t 3 are, ’re 4 we, aren’t 5 Is, is 6 ’m not 7 ’re 8 ’s, is Students make the sentences into questions and short answers ANSWERS: 1 Is she going to save her friends? Yes, she is. 2 Are the princess and the beast going to fall in love? Yes, they are. 3 Are we going to find my sister? Yes, we are. 4 Are the criminals going to win? No, they aren’t. 5 Are you going to find your son? Yes, I am. 6 Is the evil wizard going to die? Yes, he is. 7 Is winter going to end soon? No, it isn’t. 8 Are the fish going to escape? Yes, they are. |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise using be going to question forms. Descriptor: - complete the table with the words in the box. Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Using be going to to ask about plans Descriptor: - complete the questions and answers Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 4 P: 59 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Creativity |
Lesson 54 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Film Review |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.8.1 recount basic story and events on a range of general and curricular topics 5.5.6.1 link, with some support, sentences into coherent paragraphs using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -Learn and practise nouns -Learn and practise verbs to talk about plans. -Learn and practise vocabulary to talk about films |
||
|
Value links |
Integrity – Integrity is the quality of having strong moral principles. So, a person with integrity will always act with honesty and adhere to their own moral code regardless of what others do. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask the class to think of as many films as they can in one minute. After a minute ask for contributions and write them on the board. Ask the class to talk briefly about the type of films they are and which countries they are from. Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 102 Explain the task and do an example together to make sure students know what they have to do, pointing out that only one of the words on the left matches a word on the right. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:102 Explain the task. Students complete the activity individually and check their answers in pairs Ex: 3 P:102 • Explain the task and do an example together to make sure students know what they have to do, pointing out that only one of the words on the left matches a word on the right. • Explain the task and do an example with the class. Make sure the whole class understand the word sightseeing. |
Students match the things with the places ANSWERS: 1 painting 2 show 3 book 4 film 5 play 6 exhibit Students choose the correct words. ANSWERS: 1 borrow 2 look at 3 watch 4 study 5 listen to 6 go Students match the two part of the phrase ANSWERS: 1 river 2 hall 3 deck 4 resort 5 hall 6 gallery |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise nouns Descriptor: - match the things with the places Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: -Learn and practise verbs to talk about plans. Descriptor: - match the places with the things Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 5 P: 102 SB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Creativity |
Lesson 55 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Unit Review-8 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics; 5.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics; 5.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise using be going to question forms. • Using be going to to ask about plans • Learn and practise vocabulary to talk about films and stories. |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask the class to think of as many films as they can in one minute. After a minute ask for contributions and write them on the board. Ask the class to talk briefly about the type of films they are and which countries they are from. Lead – In
Movie genres vector icons. Movie film genres, comedy genre, war and romance genres, history drama film genre illustration |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 4 P: 102 • Explain the task. Make sure students understand the meaning of alien, ghost, monster, knight and wizard. • Circulate and monitor. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 5 P:102 • Explain the task and ask students to do it individually. Ex: 6 P:102 • Put students in pairs. Explain the task. When the students have completed the sentences tell them to practise saying the sentences together. • Monitor the students as they speak, making a note of any errors you would like to address later. Ex: 7 P:102 • Do the first sentence with the class. Write the sentence on the board as a model for weaker students. • Make sure students write the sentences as they will need them in the next exercise. • Get the students to read out their questions when they are ready.
|
Students match the films with the things ANSWERS: 1 a 2 d 3 f 4 e 5 c 6 g 7 h 8 b Students choose the correct words ANSWERS: 1 to walk 2 ’m y 3 ’s 4 not going to 5 ’re 6 ’re Students complete the questions and answers ANSWERS: 1 am 2 Is, isn’t 3 are, ’re 4 we, aren’t 5 Is, is 6 ’m not 7 ’re 8 ’s, is Students complete the questions and answers with going to ANSWERS: 1 Are you going to watch a film this week? 2 Where are you going to go on holiday this year? 3 How many books are you going to read this month? 4 Are you going to play football tomorrow? 5 What are you going to eat for supper tonight? 6 Are you going to do your homework on time? |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise using be going to question forms. Descriptor: - complete the table with the words in the box. Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Using be going to to ask about plans Descriptor: - complete the questions and answers Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 59 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Creativity |
Lesson 56 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Biography of an actor. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.3.1 Give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics; 5.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: Read the story about first President. Understand the key words and phrases Give reasons |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask the students to tell you what they know about the president of Kazakhstan, e.g. where he is from, his family, what he does, his early life. Ask the class if they know or have watched the film ‘The Sky of My Childhood’. If any students have seen the film, ask them to tell the rest of the class about the story. If there are no students who have seen the film, ask them if they know any films about other people’s lives. L The childhood story of Nursultan Nazarbayev, the first president of the Republic of Kazakhstan. ead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 103 • Ask students to look quickly through the story and find the four words. Discuss as a class which descriptions match the words. • Ask students to think of more words in the Kazakh language that they can explain in English. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:103 • Tell students to work individually and read the story carefully to answer the questions. • Circulate and monitor. Check that any weaker students understand the key words and phrases, e.g. horseback, falconry, high flier, attack and hunting. Make sure students write whole sentence answers. • Check the answers. Ask individual students to read out their sentences. Ex: 3 P:101 • Discuss the question with the whole class. Make sure students give reasons, either positive or negative. |
Students find these words in the story and match words with descriptions ANSWERS: Student’s own answer Students read the information about the film and answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 The story starts in 1940. 2 He lives with his mother, father and grandmother. 3 He enjoys galloping on horseback, learning falconry and playing the dombyra. He also likes playing with friends. 4 Yes, he was. He was a high flier. 5 Three actors played Nazarbayev. This was to show him as a young boy, a youth, and a young man. 6 Yes, he does. He says it is a beautiful film. It has excellent music. Some scenes are very exciting. Students give three reasons for their answer ANSWERS: Student’s own answer |
Assessment criteria - read the text and discuss about first President Descriptor: - read the story and find the four words Assessment criteria: - understand the key words and phrases Descriptor: - give three reasons for their answer Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 4 P: 59 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Reading for pleasure. |
Lesson 57 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Types of writing |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics 5.4.3.1 understand the detail of an argument on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of writing. • Practise asking questions about stories.
|
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask students to work in pairs to tell each other about the last three books they read. They should give details about the title, the author, and what kind of books they were. • After about two minutes, stop the students. Get feedback by asking a few pairs to describe one of the books they talked about Lead – In
In the English language there are a variety of different writing types, knowing when to use the right one will not only make your writing look and sound better but will also help you to create more fitting documents. In this article, we are going to take a look at the various different types of writing in a little more detail. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 104 • Focus students’ attention on the quiz on page 105. Ask the class who they can see in the photos (Answers: Abay Qunanbayuli who they talked about in unit 8; Oliver Twist; and Akira.) • Allow students a few minutes to answer the quiz questions. Tell them to write their answers on a separate piece of paper. Weaker students can work in pairs. • Ask the students to give their answer sheet to another student. Go through the quiz answers with the class. Make sure they keep the score – one point for a correct answer, no points for a wrong answer. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:104 • Explain the task and do an example together to make sure students know what they have to do, pointing out that only one item on the left matches an item on the right. • In a stronger class, ask students to do the activity individually before checking their answers in pairs. In a weaker class, check their understanding of the vocabulary and ask them to do the task in pairs. • Check answers as a class. Ask students to think of more examples of each type of writing. Ex: 4 P:104 • Explain the task and do the first question with the class. If necessary, review when we use wh- questions, e.g. Ask the class ‘Who is your maths teacher?’ (person) ‘When is your Geography class? (time), etc. • Circulate and monitor. Give assistance where necessary. |
Students do the quiz and check their score ANSWERS: 1 b 2 b 3 a 4 b 5 a 6 b 7 b 8 b Students look at the phrases in blue in the quiz. Math the types of writing with the names of the characters ANSWERS: 1 c 2 f 3 d 4 g 5 a 6 h 7 b 8 e Students complete the questions with a wh- or how question word ANSWERS: 1 What 2 Why 3 Who 4 Where 5 When 6 Which 7 How |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of writing. Descriptor: - do the quiz and check their score Assessment criteria: - Practise asking questions about stories. Descriptor: - complete the questions with a wh- or how question word Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 60 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Reading for pleasure. |
Lesson 58 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A Famous story |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.4.3.1 understand the detail of an argument on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics; 5.3.3.1 Give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics. 5.6.1.1 Use Past Simple to tell a story. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise verbs to talk about the past. • Understand stories written in the past tense.
|
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask the class what they know about the Kozy-Korpesh and Bayan-Sulu story. Ask students why the story is so famous. Lead – In
The ancient legend tells that two childhood friends, Syrybay and Karabay, decided to marry their children, who had been engaged even before they were born. Unfortunately, Syrybai died while hunting before his son was born. Growing up, Kozy and Bayan met and fell in love with each other, which made their families very happy. Having grown up, Kozy and Bayan-Sulu do end up falling in love with each other |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 106 • Do the exercise with the whole class. Make sure students understand warrior (a person who fights in battle). Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:106 • Explain the task. Make sure students understand these words before they start reading: steppe, rescue, revenge, stab. • Give students plenty of time to read the story and find the answers. • Go through the answers. In a stronger class, ask students to read the part of the story that answers the question, e.g. for question 1 ‘Karabay had a daughter called Bayan.’ If any sentences are false, ask students to make a true sentence. • In a weaker class, read the story to the class and stop at the sentence which helps answer the question.
Ex: 3 P:106 • Tell students to look quickly at the story again and find the five words. • In a weaker class, stand up in front of the class and point to your hair, waist, neck. Ask the class to say each time what you are pointing at. Mime combing, tidying, wearing (round the neck and waist), and cutting (hair with a knife). • Go through the answers.
|
Students identify who are characters in the story. Match the names with the roles. ANSWERS: 1 daughter 2 lover 3 father 4 warrior Students read the text and write true or false. ANSWERS: 1 true 2 false 3 false 4 true 5 true 6 false 7 false 8 true Students find these words in the text. Match the words with definitions. ANSWERS: 1 c 2 e 3 a 4 d 5 b |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise verbs to talk about the past. Descriptor: - identify who are characters in the story. Match the names with the roles. Assessment criteria: - Understand stories written in the past tense.. Descriptor: - find these words in the text. Match the words with definitions. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 60 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Reading for pleasure. |
Lesson 59 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus: Past Simple |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.6.1.1 use Past Simple (negative and questions) to speak about past events tell; 5.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with support on a limited range of general and curricular topics; 5.3.3.1 Give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise past simple regular and irregular forms. • Use the past simple to talk about events in the past.
|
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Write watch on the board and ask the students what the past simple form is (watched). Then write go on the board and ask what the past simple form is (went). Draw students’ attention to the table in exercise 1 and ask which group watch belongs to (regular) and go (irregular). Lead – In
Past Simple Tense! When talking about an action which has happened in the past, you will need to use the past simple tense. However, before you can begin confidently using this tense, it is important to learn the rules which surround it. As with any part of English grammar, the rules of the past simple tense should be applied each time it is used in order to ensure that you are forming grammatically correct sentences. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 107 • Tell the class to read the story on page 106 again and find the regular verbs in the past simple. Make sure they do not read the story again but ‘scan’ the text for the words. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:107 • Explain the task. In a weaker class, do the first sentence together and draw students’ attention to the table in exercise 1 which has the past simple forms. Circulate and monitor. • Check answers as a class.
Ex: 3 P:107 • Explain the task. Remind students to use the table in exercise 1 to help them. • Students complete the activity individually and check their answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class. |
Students find the past simple forms in the text. ANSWERS: help – helped, want – wanted, follow – followed, ask – asked, die – died, climb – climbed, love – loved Rules -d, different Students complete the sentences with the past simple forms of the verbs in brackets. ANSWERS: 1 wanted 2 was 3 asked 4 were 5 took 6 died 7 followed 8 cut Students complete the text. Use the correct forms of the verbs in the box ANSWERS: 1 lived 2 was 3 loved 4 came 5 told 6 wanted 7 left 8 followed 9 took 10 climbed |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise past simple regular and irregular forms. Descriptor: - find the past simple forms in the text. Assessment criteria: - Use the past simple to talk about events in the past. Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the past simple forms of the verbs in brackets. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 61 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Reading for pleasure. |
Lesson 60 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Biography of a writer |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 5.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects; 5.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise vocabulary to talk about people’s lives. • Understand a famous person’s biography.
|
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask the class to name some big events in their life so far, e.g. I started school, I went on holiday, I learned to ride a bike. Write the ideas on the board and ask students to put them in the order the events occurred in their lives. Lead – In
Abai Kunanbaev Kazakh writer, poet, lyricist, social philosopher. Born in Kazakhstan in Semey province, Abai Kunanbaev was educated at home and then sen |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students say about different questions |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 108 • Explain the task. Circulate and monitor. • Check answers as a class. • Get students to close their books. For further practice, tell the students you are going to say a word from the lifeline and they have to say the next stage, e.g. born – go to school. • In a stronger class, say a verb and ask students to finish the phrase, e.g. take – exams. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:108 • Do the exercise quickly with the whole class. Ex: 3 P:108 • Tell the students to read the questions and discuss possible answers. • In a weaker class, ask more questions to guide students, e.g. Was he famous? Which country is he from? Was he born 300 years ago, 150 years ago? • Do not go through the answers at this stage. Students will listen for the answers in the next exercise. Ex: 4 P:108 • Play the recording. Pause at the relevant points to allow students to write the answers. • Tell students to check in pairs. Circulate and monitor. If students have blank or wrong answers, play the recording again |
Students put the words in correct place in the lifeline. ANSWERS: 1 go to school 2 graduate from college 3 start a job 4 have children Students write the past simple form of the verb ANSWERS: 1 was 2 went 3 got 4 started 5 retired 6 died 7 graduated Students answer the questions. What do theu know about Abay Qunanbayuli? ANSWERS: Student’s own answer Students listen to the interview about Abay Qunanbayuli. ANSWERS: 1 He was one of the great poets and philosophers of Kazakhstan. 2 He was born on August 10, 1845. 3 He was from Karauyl in East Kazakhstan. 4 In English ‘abay’ means ‘careful’ 5 He was a great poet. He was also a translator, philosopher and composer. 6 He had four children. 7 He wrote poems such as Spring and he wrote books such as The Book of Words. 8 He died on 6 July 1904. |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise vocabulary to talk about people’s lives. Descriptor: - put the words in correct place in the lifeline. Assessment criteria: - Understand a famous person’s biography Descriptor: - answer the questions. What do theu know about Abay Qunanbayuli? Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 61 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Reading for pleasure. |
Lesson 61 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus: Past Simple. Question and negative form |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.3.1 Give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics; 5.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects 5.6.1.1 use Past Simple (negative and questions) to speak about past events tell; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise using questions in the past simple. • Use negative forms in the past simple.
|
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up • Books closed. Write ‘I got up this morning at …’, ‘I left home at …’, ‘I got to school at …’. Tell students to write down the three times on a piece of paper. Nominate a student to ask another student a question using Did, e.g. ‘Did you get up at 6.30?’. The other student answers ‘Yes, I did.’ or ‘No, I didn’t.’ Students score one point for every question they get right Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the pictur |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 109 • Explain the task. Give students a few minutes to work individually completing the rules. • Students check their answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:109 • Put students in pairs. Explain the task. When students have completed the sentences, tell them to practise saying the sentences together. • Monitor the students as they speak, making a note of any errors you would like to address later. Ex: 3 P:109 • Explain the task. Students work individually and then check their answers in pairs. Circulate and monitor. Make sure students understand that the wh- question word comes at the beginning of the sentence. • Check answers as a class. • Put students in pairs and tell them to ask and answer each other the questions. The answers should be based on the truth. |
Students look at the table and complete the rules. ANSWERS: did, didn’t Students complete the questions and answers ANSWERS: 1 Did 2 you, didn’t, 3 Did, he 4 Did she, didn’t 5 Did, I did 6 What, did, got 7 Where, did,
went Students order the words to make questions. The ask your partner the questions ANSWERS: 1 What did you do yesterday? 2 How did you get to school today? 3 Where did you go yesterday? 4 What time did you get up yesterday? 5 Where did you have lunch yesterday? 6 Who did you talk to yesterday? |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise using questions in the past simple.
Descriptor: - complete the rules in the past Assessment criteria: - Use negative forms in the past simple Descriptor: - complete the questions and answers Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 4 P: 109 SB write sentences about your studies last week. |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Reading for pleasure. |
Lesson 63 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Unit Review -9 Summative assessment for the unit “Creativity” |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.6.1.1 use Past Simple (negative and questions) to speak about past events tell; 5.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which 5.L4 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics; 5.L5 Understand most specific information and detail of short, supported talk on a wide range of familiar topics 5.S8 Recount basic stories and events on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use and practise nouns to talk about types of writing. • Practise asking questions about stories. • Recognize detailed information in a short conversation with some support • Retell short stories and episodes on a given topic |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wish lamp Lead – In Review previos lesson asking vocabulary. Legend, fairy tale, poem, |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 110 • Explain the task. Remind students to use with the words in the box. . • Students complete the sentences individually and check their answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:110 • Explain the task. Draw students’ attention to the example sentences. • Get the students to read out their sentences when they are ready. Summative assessment for the unit “Creativity” Listening Task 1. Listen to the story and fill in the gaps with the words from the box. One word is odd.CD2. Tapescript2 Speaking Task 2. Look at the pictures bellow, choose one and answer the following questions. What do you know about cartoons below? Speak about one of the cartoons. The following questions will help you to organize the speech: 1 Why do you like this cartoon? 2 Who are the main heroes? 3 What is this cartoon about? 4 Which part do you like most and why? |
Students complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 horror 2 fairy 3 poem 4 play 5 comic 6 classic 7 crime 8 legend Students put the words in the correct order and answer the questions. ANSWERS: 1 What is your favorite story? 2 Why do you like it? 3 Where is the location of the story? 4 Who is the hero? 5 When does the story take place? 6 Which character do you like? 7 How many times have you read it? Students listen to the story and fill in the gaps. ANSWERS: 1 a lovely garden 2 a wall 3 winter 4 a hole 5 spring Students look at the pictures and choose one of cartoon. Answer the questions ANSWERS: Student’s own answer |
Assessment criteria - Use and practise nouns to talk about types of writing.
Descriptor: -Use nouns - complete the sentences Assessment criteria: - Retell short stories and episodes on a given topic Descriptor: -answers questions -speaks with grammar accuracy Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 5 P: 110 SB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 9 Reading for pleasure. |
Lesson 64 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A Book festival. Kazakh famous writers and poets. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics; 5.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects 5.3.3.1 Give an opinion at sentence level on a limited range of general and curricular topics. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - use simple context clues strategies to identify meaning of unknown words from the contex - write a short text (e.g. a description of the room, hobby, or a friend) - give a limited response showing their opinion, preferences, agreement or disagreement |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wish lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Ask the students to tell you what they know about book festivals. Who goes to a book festival? What can they do there? Who can they see? |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 111 • Draw the students’ attention to the poster. Ask some quick questions, e.g. Where is the festival? (Answer: London, UK), When does it start? (Answer: Saturday 12 August), How many main events are there on Saturday? (Answer: three). • Tell students to read questions 1-5 and find the answers in the poster. For fast finishers, ask them to correct any false sentences. • In a stronger class, tell the students use other information in the poster to make true and false sentence. Students read the sentence to a partner who says if it is true or false and corrects any false sentences Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:111 • Explain the task. Give students five minutes to choose a book and write between three and five sentences. • Ask some students to read out their sentences for the class. Ex: 3 P:111 • Tell the students to read the questions and discuss possible answers. • In a weaker class, ask more questions to guide students, e.g. Was he famous? Which country is he from? Was he born 300 years ago, 150 years ago? • Do not go through the answers at this stage. Students will listen for the answers in the next exercise. |
Students read the information in the poster and write true or false for each sentence ANSWERS: 1 true 2 false 3 true 4 true 5 false Students write the past simple form of the verb ANSWERS: 1 was 2 went 3 got 4 started 5 retired 6 died 7 graduated Students think of a book you know very well. Write some sentences to describe the story and the characters. ANSWERS: Student’s own answer Students say which authors would they like to meet? ANSWERS: Student’s own answer |
Assessment criteria - use simple context clues strategies to identify meaning of unknown words from the contex
Descriptor: - read the information in the poster and write true or false for each sentence Assessment criteria: - write a short text (e.g. a description of the room, hobby, or a friend)
Descriptor: - Write some sentences to describe the story and the characters. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 61 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster KWL chart
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 65 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
People and places |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.2.4.1 understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics; 5.1.4.1 evaluate and respond constructively to feedback from others; 5.6.6.1 use plural form of nouns talking about people and places; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise basic vocabulary. • Learn how to form plurals. |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wish lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Write the following words on the board in random order: country, village, city, town. Tell students to work in pairs to put these places in order of size, starting with the largest. Ask them to think of an example of each place from their own country. • After about 1 minute, stop the students. Get feedback from each pair. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 26 • Focus students’ attention on the words in the box. If you have done the warm-up activity, they will already be familiar with country, town, city and village. • In a weaker class, ask students to work in pairs, using page 77 of the Workbook to help them. In a stronger class, encourage students to complete the lists by themselves. • Students check answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:26 • Refer students to the quiz on page 23. Look at the photos and ask students to identify words from exercise 1 (people, baby, city, village, house). • Explain the task and play the recording. Students work individually and then check their answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class. Do any of the facts surprise them? What is the most interesting fact? Ex: 3 P:26 • Focus students on the table of regular forms and ask them to find the plural form of boy and girl in the quiz. Check answers as a class. • Ask the students how they should form regular plurals and elicit that we form them by adding -s to the singular form. • Direct the students to the table of irregular forms and ask them to locate the plural forms in the quiz. Point out that they may look a little different to the singular form. • Ask fast finishers to make the plural forms of the other nouns in exercise 1 |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box in the wordlist in the workbook ANSWERS: Places: city, house, town, village People: child, family, man, person, woman Students do the Our World quiz. Then listen and check your answers. ANSWERS: 1 a 2 a 3 a 4 a 5 b 6 b 7 a Students complete the lists with plural forms in the Our World quiz. ANSWERS:
|
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise basic vocabulary.
Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words in the box Assessment criteria: - Learn how to form plurals.
Descriptor: - complete the lists with plural forms Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 18 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 66 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
An article about two places. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in short, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topics; 5.3.6.1 communicate meaning clearly at sentence level during, pair, group and whole class exchanges; 5.4.1.1 understand the main points in a limited range of short simple texts on general and curricular topics. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about two different places. • Learn and use new vocabulary to describe places in towns. • Practise speaking about a town. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Write Hollywood on the board. • Ask the class to brainstorm what they know about Hollywood, which country it is in, what it’s famous for, etc. Accept any feedback they give you and put any interesting facts and new vocabulary on the board. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 28 • Focus on the three pictures and explain the task. Allow students about 2–3 minutes to compare the pictures in pairs. • When they are ready, they choose adjectives to match each location. Ask them to match the pictures to the locations as well. • Check answers as a class. In a stronger class, encourage students to give reasons for choosing their adjectives Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:28 • Refer students to the texts and play the recording. • In pairs, students do the task. • Check answers as a class. You could ask fast finishers to underline the adjectives used in the text to describe the two locations (fast, noisy, famous, big, expensive, small, quiet, nice, interesting) Ex: 3 P:28 • Draw students’ attention to the questions. In a stronger class, ask the students to complete the activity individually before checking their answers in pairs. Encourage them to guess the meaning of any new vocabulary from the context. • In a weaker class, read the questions together, explaining any new vocabulary and checking for understanding. Do the first questions together as an example. • Remind students to write full sentences in their answers. • Students check answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. |
Students look at the pictures in the text. Guess which adjectives in the box describe Hollywood, USA and which describe Hollywood, Ireland ANSWERS: Students’ own answers Students read and listen. Check your answers to exercise 1 ANSWERS: Hollywood, USA: famous, noisy Hollywood, Ireland: quiet, small Students read the text again and answer the question. ANSWERS: 1 No, it isn’t. It’s part of Los Angeles. 2 No, it isn’t. It’s part of a city. 3 No, it isn’t. It’s a noisy place. 4 No, it isn’t. It’s a small place. 5 There are many interesting places near the village. 6 Yes, it is. The city of Dublin is forty-two kilometres from the village. |
Assessment criteria - Read about two different places. Descriptor: - read and listen Assessment criteria: - Learn and use new vocabulary to describe places in towns. - Practise speaking about a town.
Descriptor: - read the text again and answer the question. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 18 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 67 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language Focus: there is/ there are/ some and any |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.5.8.1 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics; 5.6.1.1 use appropriate countable and uncountable nouns, including common noun phrases and a structure there is/ there are describing times and location, on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics; 5.6.14.1 use prepositions to talk about time and location and some/ any/no; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise the affirmative and negative forms of there is, there are, some and any. • Practise describing towns and cities. |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Tell the students you are going to say the name of a city and they should write down the first thing – a building, a place, a person, anything they like – they can think of in relation to that city. • Say London. Students write down the first thing they think of. Don’t allow them any more than 30 seconds for this. • Get feedback from a few students in the class and put their ideas on the board. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 29 • Focus students on the tables and the rules. In a stronger class, ask the students to go ahead and complete the rules based on the examples in the table. They check answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. • In a weaker class, go through the table with the students, pointing out the plural and singular sections in the positive and the negative. Complete the rules together with the class. LANGUAGE NOTE We can use some and any with both countable and uncountable nouns. However, with uncountable nouns we always use the singular form of the verb be, e.g. There are some chairs in the room; There aren’t any students in the school; There’s some milk in the fridge; There isn’t any coffee left. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:29 • Tell the class to try to remember the information in the text about Hollywood in Ireland on page 24 of the book. Refer them to the sentences and explain the task. • In a weaker class, ask students to complete the activity in pairs. Encourage students in a stronger class to do the task individually. Ex: 3 P:29 • Refer students to the information about the two places and allow them a few minutes to look through it. • Ask students to complete the task individually and then to compare their answers in pairs. Check the answers all together as a class. |
Students study the tables. Then choose the correct words to complete the rules. ANSWERS: In plural sentences we use some in the affirmative. We use any in negative sentences. Students correct the sentences ANSWERS: 1 There aren’t any discos. 2 There are some interesting places near the village. 3 There isn’t an Armani shop. 4 There is a small shop. 5 There are 100 people in the village. 6 There aren’t any famous people Students write the sentences about London in England and London in the South Pacific. ANSWERS: London, England: There are some museums in London. There are four airports in London. There aren’t any long houses in London. London, Kiritimati Island, South Pacific: There are 1,000 people in London. There is one hotel in London. There aren’t any cinemas in London. There are some shops in London. |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise the affirmative and negative forms of there is, there are, some and any.
Descriptor: - study the tables. Then choose the correct words to complete the rules. Assessment criteria: - Practise describing towns and cities.
Descriptor: - write the sentences about London in England and London in the South Pacific. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 19 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 68 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Shops. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary to talk about a limited range of general topics; 5.6.1.1 use appropriate countable and uncountable nouns, including common noun phrases and a structure there is/ there are describing times and location, on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics; 5.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in short, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topics; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary to describe different shops. • Practise talking about favourite shops. |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Ask students to work in pairs and think about the last thing they bought and to tell their partners about it – what it was and where they bought it from. • Get some feedback from the class by asking a few students to describe what their partner last bought. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 30 • Draw students’ attention to the ten pictures and to the words in the box. Explain the task. • Tell students to match the pictures with the shops that they recognize first, and encourage them to try to guess the others. • Students check their answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. • You could ask fast finishers to think about other types of shops that are not included and to check their names in a dictionary. Ex: 2 P:30 • Go through the vocabulary in the box with the class and check for understanding. • Students do the task in pairs. Check answers as a class. • Divide students into pairs and allow them 2–3 minutes to think of a few examples of items from the other shops in exercise 1. • Get feedback from each pair and put their ideas on the board for the whole class to see. Background information Dubai is a big, modern city in the United Arab Emirates. It is known as the ‘shopping capital of the Middle East’ because of it’s large number of shopping malls – over 70 of them – built with the aim of increasing Dubai’s tourist industry. Of these, the ‘Dubai mall’ is the largest. Apart from 1,200 shops and gigantic cinema, its attractions include an aquarium, a spectacular fountain, an indoor theme park and a children’s entertainment centre Ex: 4 P:30 • Discuss the photo at the bottom of the page with the students. Ask them if they know anything about Dubai and elicit any feedback from the students. • Draw students’ attention to the numbers and ask them to say them. • Explain the task and play the recording. Students check answers in pairs. |
Students match pictures with the shops in the box. ANSWERS: 1 bookshop 2 chemist’s 3 newsagent’s 4 clothes shop 5 games shop 6 supermarket 7 sports shop 8 pet shop 9 computer shop 10 shoe shop Students think of more adjectives from each shop. What shops are the objects in the box from? ANSWERS: 1 supermarket 2 clothes shop / sports shop \ 3 pet shop 4 newsagent’s / supermarket 5 shoe shop 6 games shop / computer shop
Students say the numbers. Listen to Fiona and Sophie talking about Dubai Mall. Order the numbers as you hear them. ANSWERS: 1 d 2 a 3 b 4 c |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary to describe different shops.
Descriptor: - match pictures with the shops in the box. Assessment criteria: - Practise talking about favourite shops. Descriptor: - think of more adjectives from each shop. What shops are the objects in the box from? Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 20 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 69 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
There is/ there are and short answers. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.6.14.1 use prepositions to talk about time and location and some/ any/no; 5.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in short texts on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics; 5.5.3.1 write with support factual descriptions at text level which describe people, places and objects. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn how to use there is and there are in questions and short answers. • Learn and practise using prepositions of place. • Further practice describing towns and shops. |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Remind students about the shopping centre in Dubai from page 26 and ask them to work in pairs to briefly discuss whether they would prefer to go shopping in a big shopping centre or in small shops in a town. • After about 2 minutes, stop the students and get some feedback from a few pairs. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 31 • Explain the task. In a stronger class, ask students to complete the task individually. In a weaker class, students complete the task in pairs. • Ask the students how they can make the question form of there is and there are and elicit that we invert the verb be and there. Point out that with How many we put the verb be and there at the end of the question. LANGUAGE NOTE We almost always use any in negative and questions forms. An exception to this is when we make an offer or a request, e.g. Would you like some coffee? Could I have some bread, please? Ex: 2 P:31 • Refer students to the questions and explain the task. They complete the activity individually. • Point out that students should check carefully whether they are talking about a singular or plural noun before they choose their answers. Ex: 3 P:31 • Refer students to the dialogue and ask them to read it quickly, ignoring the gaps. Ask the class what Lucy and Jared are talking about and elicit that they are talking about shops in their town • Students complete the task individually, though in a weaker class you could ask students to do the activity in pairs. Ex: 4 P:31 • Refer students to the words in the box and explain that these are prepositions (students already met the prepositions on and at on page 15). • Focus the student on the six pictures and ask them what they think these prepositions are being used for. Elicit that they are used to describe where something is and that they are prepositions of place |
Students complete the questions in the table with words from exercise 5 page 30 ANSWERS: 1 Is 2 Are 3 are there Students choose the correct words. Then write short amswers. ANSWERS: 1 Is 2 Is 3 Are 4 are 5 Is 6 Is 7 Is 8 are Students complete the dialogue. Then listen and check. ANSWERS: 1 There are 2 there is 3 How many 4 There are 5 Is there 6 there isn’t 7 Are there 8 there are Students study the prepositions. Then look at the picture and complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 in 2 on 3 under 4 next to 5 opposite 6 near 1 people / balls, sports shop 2 boys, door 3 shoes 4 balls, bags 5 t-shirts 6 bag |
Assessment criteria - Learn how to use there is and there are in questions and short answers.
Descriptor: - complete the questions in the table Assessment criteria: - Learn and practice using prepositions of place.
Descriptor: - study the prepositions. Then look at the picture and complete the sentences Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 21 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 70 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Asking about places in a town |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in short, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topics; 5.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 5.3.6.1 communicate meaning clearly at sentence level during, pair, group and whole class exchanges |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Practise asking for information about places. • Learn and practise phrases for asking for information. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Draw a rough map of a few streets in the area of the school on the board. Write school on the map to show the students where they are. • Draw a few empty boxes at different places on the streets to represent some of the shops or other buildings in the area. Ask the students to tell you what they are and write the names of the places in the boxes |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 32 • Focus on the photo and discuss it with the class. Ask the students what they can see and elicit that there is girl and a woman in the picture. • They answer the questions in pairs. Get feedback from a few pairs of students Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:32 Draw students’ attention to the map at the bottom of the page. Allow them a minute or two to familiarize themselves with it and ask them a couple of questions to check they can follow it properly. For example, ask: Is there a restaurant? Are there any shops? How many shops are there? • Explain the task and play the recording. Students complete the dialogue and check answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. • For further practice, you could divide students into pairs and allocate each student the role of Rosa and the woman. Ask the students to practise the dialogue in pairs Ex: 3 P:32 • Refer students to the key phrases and explain the task. Point out the arrows at the end of the phrases and explain that we raise our intonation when asking for something. • Play the recording. Pause after each phrase and ask the students to repeat. Model the phrases yourself, making sure to raise or lower your intonation as appropriate. Exaggerate your intonation a little so that the students notice the difference |
Students look at the photo. Where are the people. Is the girl from this town? ANSWERS: The people are in a town. The girl is not from the town.
Students look at the map and listen to the dialogue. What are the missing word? ANSWERS: 1 sports shop 2 sports shop Students listen to the key phrases and practise the pronunciation. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers
|
Assessment criteria - Practise asking for information about places.
Descriptor: -look at the photo. Where are the people. Is the girl from this town? Assessment criteria: - Learn and practise phrases for asking for information. Descriptor: - look at the map and listen to the dialogue. What are the missing word? Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 4 P: 21 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 71 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A brochure about your town |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 5.3.6.1 communicate meaning clearly at sentence level during, pair, group and whole class exchanges 5.5.8.1 spell most high-frequency words accurately for a limited range of general topics; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the structure of a brochure about a town or city. • Learn and practise how to use be + also. • Practise writing a brochure about a town. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Students work in pairs to think of things to say in English about their home town / city. • After about 2 minutes, stop the students and get some feedback from each pair
|
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 33 • Focus on the photos and the flag and ask students if they recognize the country. Elicit that it is Canada. • Explain the task and allow students time to answer the questions based on the text
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:33 • Refer students to the example and do the task together as a class. Point out that we use also to give further information about something. It helps to link two things together and makes descriptions sound more natural. • Students find the other example of also in the text LANGUAGE NOTE While also comes after the verb be, it usually comes before all other verbs. For example, I also like to play football or She also eats a lot of chocolate. Ex: 3 P:33 • Refer students to the sentences and explain the task. Students check answers in pairs. Ex: 4 P:33 • Draw students’ attention to the key phrases that can be used to describe a town or a city. Read through them with the class and check for understanding. • Tell students to think about their own town or city and explain the task. Check answers as a class. |
Students read the model text and answer the questions. ANSWERS: 1 The capital of Canada is Ottawa. 2 Ice hockey, skating and American football are popular sports in Canada. 3 Quebec is 275
kilometres from Montreal. Students look at the examples. Is also before or after the verb be? Find another example of also in the brochure about Montreal. ANSWERS: Also is after the verb be. There are also interesting museums here Students rewrite the blue sentences. Include also in each sentence. ANSWERS: 1 There’s also a museum. 2 There are also bookshops. 3 There are also two parks. 4 There’s also a restaurant. 5 There’s also an airport. Students substitute words in the box for the words in blue in the key phrases and change the names of the places. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers |
Assessment criteria - Learn the structure of a brochure about a town or city.
Descriptor: - look at the examples. Is also before or after the verb be? Find another example of also in the brochure about Montreal. Assessment criteria: - Practise writing a brochure about a town. Descriptor: - rewrite the blue sentences. Include also in each sentence. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 22 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 72 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country. My world Summative assessment for the unit ”Fantasy world” |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics; 5.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in short, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topic; 5.4.1.1 Understand the main points in a limited range of short simple texts on general and curricular topics; 5.5.4.1. Write with support a sequence of extended sentences in a paragraph to give basic personal information. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about geographical features. • Read a text about geographical features in Kazakhstan. Write short sentences on familiar topics with support Connect sentences into a paragraph |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
||
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Allow students about 2 minutes to tell each other their favourite thing about the countryside.
|
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
||
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 34 • Draw students’ attention to the words in the box and to the pictures 1–6. • Check answers as a class Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:34 • Focus students’ attention on the map and the compass. Explain that a compass tells you what direction you are facing. Draw a compass on the board and write the directions: north, south, east, west, north-west, north-east, south-west, and south-east. Ask students to find their hometown on the map and say whether it is in the north, north-east, west, etc.
Summative assessment for the unit ”Fantasy world” Writing Task 1. Look at the map and choose ONE of the buildings bellow and describe your route from the shop to that building: Reading Task 2. Read the text and identify the writer’s opinion and write Yes or No next to the given statements as in the example. Task 3. Write Yes or No next to the statements as in the example:
|
Students check the meaning of the words. Then match words with pictures. ANSWERS: 1 forest 2 mountain 3 river 4 desert 5 steppe 6 lake Students look at the map of Kazakhstan and choose the correct word in the text. Then listen and check. ANSWERS: 1 forests 2 steppe 3 desert 4 rivers 5 lake 6 mountains gives a full answer using linking words and basic connectors writes with grammar accuracy (allowed to make 2 errors); 1 Yes 2 Yes 3 No 4 Yes 5 No |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for talking about geographical features.
Descriptor: -check the meaning of the words. Then match words with pictures.
Assessment criteria: - Write short sentences on familiar topics with support
Descriptor: - writes with grammar accuracy (allowed to make 2 errors);
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards
Worksheets
|
||
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 23 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 73 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Shopping |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.2.7.1 recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) in basic, supported talk on an increasing range of general and curricular topics; 5.4.2.1 understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics; 5.5.6.1 link, with some support, sentences into coherent paragraphs using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn how to use prices. • Understand a conversation in a shop. • Practise asking for prices and buying things. |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Books closed. Tell students to imagine they have €100 to spend on anything they like. • In pairs, students tell each other what they would spend their money on. Get some feedback from a few pairs by asking students what their partner would spend the money on. Put their ideas on the board, explaining any new vocabulary |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 35 • Focus students’ attention on the two columns. Ask them what the currency symbol £ represents and elicit that it represents pounds, the currency used in the UK. Point out that there are 100 pence in one pound. If you can, tell students how much £1 is worth in their currency. • Explain the task. Students complete it individually and check their answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. • Model the prices for pronunciation and ask students to repeat Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:35 • Explain the task. Ask students to write the prices down in two ways (numbers and words). • Pause after each price to allow students time to write it down. • Students compare their prices in pairs. Check answers as a class. • Play the recording again and pause after each price to allow students time to repeat Ex: 3 P:35 • Explain the task and draw students’ attention to the question. Check they understand what the four different places are by quickly eliciting from the students some example of the different things you can buy in each. • Play the recording. Students check their answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. |
Students match 1 – 6 with a – f. then listen and check. ANSWERS: 1 c 2 e 3 a 4 f 5 b 6 d Students listen and write the prices you hear. Then listen and repeat. ANSWERS: 1 32p, thirty-two pence 2 75p, seventy-five pence 3 £3.20, three pounds twenty 4 £8, eight pounds 5 £15, fifteen pounds 6 £7.50, seven pounds fifty
Students listen to a conversation. Where is Jared? ANSWERS: Jared is in a souvenir shop |
Assessment criteria - Learn how to use prices.
Descriptor: - match 1 – 6 with a – f. then listen and check Assessment criteria: - Understand a conversation in a shop.
Descriptor: - listen to a conversation. Where is Jared? Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 24 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 74 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 06.03.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Fantasy world |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.4.6.1 recognize the attitude or opinion of the writer in short texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics; 5.5.6.1 link, with some support, sentences into coherent paragraphs using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics 5.3.2.1 ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general topic. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a Kazakh folk story. • Write a story and make a poster |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
||
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Books closed. Write folk story on the board. Explain or elicit that a folk story is a traditional story from a particular country or place that was originally passed on to people in a spoken form. • Ask students if they know any folk stories from Kazakhstan or from other countries. Ask if they enjoy reading folk stories and why. • Get feedback from the class and elicit the titles of some popular folk stories. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets. |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
||
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 36 • Focus students’ attention on the names in the box and ask them what they know about these people. Elicit any information you can from the students by asking them some questions, e.g. Why is this person famous? What did they do? When did they live? Have you read any stories about them? • Ask students what their favourite folk story is. Elicit some ideas and encourage students to give reasons for their answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:36 • Refer students to the text and ask them to read the paragraphs quickly and say which of the people in exercise 1 is the main character in the story • Students work in pairs to put the paragraphs in the correct order. • Check answers as a class. Ex: 3 P:36 Read through the instructions together and make sure students understand what they have to do. • Give students a few minutes to identify the main events in the story. In a stronger class, ask students to summarize each event in one sentence, e.g. • Students work in pairs to complete the task. Monitor as they retell the story and remind them to use the past simple tense |
Students answer the questions. Who are these people? Do you know any stories about them? Which story is your favourite? ANSWERS: Students’ own answer. Students read the paragraphs and put them in the correct order to make a story. ANSWERS: A 4 B 1 C 3 D 5 E 2 The story is about Aldar Kose Students work in pairs. Make a list of the main events in the story. Draw a picture to illustrate each event. Then retell the story using the pictures ANSWERS: Students’ own answers Aldar Kose was cold and unhappy because his coat had holes in it and his horse was slow. When he saw the bai in the distance, he took off his coat and his hat and started singing cheerfully. When the bai heard about Aldar Kose’s magic coat, he wanted to buy it. He gave Aldar his fur coat, his beautiful white horse, and a bag of gold. Aldar Kose jumped on the horse and rode off as quickly as he could. |
• In a weaker class, pre-teach the following words and phrases: ride, fur coat, holes, in the distance, recognize. • In a weaker class, This task differentiated by the students abilities. Less able students define words with the help of prompt cards which written the new words. |
Assessment criteria - Read a Kazakh folk story.
Descriptor: - answer the questions Assessment criteria: - Write a story and make a poster
Descriptor: - Make a list of the main events in the story -Write a story about one of the people Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
||
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
|||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 75 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Vocabulary puzzles: People and places. shops |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics; 5.5.6.1 link, with some support, sentences into coherent paragraphs using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use and practise basic vocabulary • Use vocabulary to describe different shops. • Write the affirmative and negative forms of there is, |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Books closed. Ask students to work in pairs and think about the last thing they bought and to tell their partners about it – what it was and where they bought it from. • Get some feedback from the class by asking a few students to describe what their partner last bought |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets. |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 37 • Focus students’ attention on the words in the puzzle. If you have done the warm-up activity, they will already be familiar with country, town, city and village. Find ten words for people and places. • In a stronger class, encourage students to complete the lists by themselves. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:37 • Draw students’ attention to the five pictures. Explain the task. • Tell students to match the pictures with the shops that they recognize first, and encourage them to try to guess the others. Ex: 3 P:37 • Focus the student on the two pictures and ask them what they think these there is, there are are being used for. Elicit that they are used to describe two differences pictures of Tinford town centre. |
Students find ten words for people and places. Use the green letters to spell a place. ANSWERS: Country Person People City Students complete the puzzle with the shops ANSWERS: 1 bookshop 2 chemist’s 3 pet shop 4 supermarket 5 shoe shop The spot the difference. Look at the two pictures of Tinford town centre. Write the shops that are different in picture 2. What shops are the same? ANSWERS: |
• In a weaker class, ask students to work in pairs, • In a weaker class, pre-teach the following words and phrases: bookshop, supermarket |
Assessment criteria - Read a Kazakh folk story.
Descriptor: - answer the questions Assessment criteria: - Write a story and make a poster
Descriptor: - Make a list of the main events in the story -Write a story about one of the people Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 76 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review. Unit-3 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.4.1.1 understand the main points in a limited range of short simple texts (a poem) on general and curricular topics; 5.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - talk about people and places. - understand an article about a shopping centre. - ask for information about places in a town |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Books closed. Write the following words on the board in random order: country, village, city, town. Tell students to work in pairs to put these places in order of size, starting with the largest. Ask them to think of an example of each place from their own country |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets. |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 38 • Read through the instructions together and make sure students understand what they have to do. • Check answers as a class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:38 • Focus students’ attention on the two columns. There is one shop you don’t need. • Explain the task. Students complete it individually and check their answers in pairs. Check answers as a class. Ex: 3 P:37 • Refer students to the questions and explain the task. They complete the activity individually. • Point out that students should check carefully whether they are talking about a singular or plural noun before they choose their answers. • Students check answers in pairs. Check answers as a class |
Students complete the sentences with the singular or plural forms of the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 cities 2 people 3 baby 4 children 5 women 6 countries Students match objects with shops. There is one shop you don’t need. ANSWERS: 1 f 2 e 3 b 4 a 5 d 6 c Students choose the correct words ANSWERS: 1 ’s 2 aren’t 3 isn’t 4 ’s 5 any 6 some |
In a weaker class, revise the rules for forming plural nouns. • In a weaker class, pre-teach the following words and phrases: Computer shop Sport shop Aspirin |
Assessment criteria - talk about people and places.
Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the singular or plural forms of the words in the box. Assessment criteria: - ask for information about places in a town
Descriptor: match objects with shops. There is one shop you don’t need. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 77 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
People and places |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.3.5.1 keep interaction going in basic exchanges on a growing range of general and curricular topics; 5.6.6.1 use plural form of nouns talking about people and places; 5.6.5.1 use numbers to complete the fact file of a country; |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use and practise basic vocabulary. • Use and practise the affirmative and negative forms of there is, there are, some and any |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Books closed. Write the following words on the board in random order: country, village, city, town. Tell students to work in pairs to put these places in order of size, starting with the largest. Ask them to think of an example of each place from their own country. • After about 1 minute, stop the students. Get feedback from each pair. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:38 • Read through the instructions together and make sure students understand what they have to do. In a weaker class, revise the rules for forming plural nouns. • Check answers as a class. Ex: 2 P:38 • Focus on the table and on the words in the left-hand column. Read through them with the class, checking for understanding. • Students do the task in pairs. Encourage students to match the words they recognize first Ex: 3 P:38 • Tell students to work in pairs to choose the correct words. Check answers as a class. • Students complete the rest of the task individually, though you could ask students to do it in pairs in a weaker class. Check answers as a class. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the sentences with the singular or plural form of the words in the box Descriptor: -finds out the right place. -use singular or plural form (1 cities 2 people 3 baby 4 children 5 women 6 countries) Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students match objects with shops. There is one shop you don’t need Descriptor:
(1 f 2 e 3 b 4 a 5 d 6 c) Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students choose the correct words Descriptor:
Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
-remember simple words - can complete sentence - know vocabulary Total: 2 point -can match -know vocabulary Total: 2 point -can complete the sentences Total: 2 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 80 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative control work for the 3rd term |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.2.4.1 Understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics. 5.4.2.1 Understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics. 5.5.6.1 Link, with some support, sentences into coherent paragraphs using basic connectors on a limited range of familiar general topics. 5.3.1.1 Provide basic information about themselves and others at sentence level on an increasing range of general topics. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - summarize the main idea with the limited support of details they hear or write down -identify the details of a text - use simple transitional phrases (firstly, secondly…, in conclusion, then, but) -convey ideas and basic information (age, hobbies, interests, family and educational background) |
||
|
Plan |
|||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 3 Fantasy world |
Lesson 81 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 5 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Revision |
||
|
Learning objectives |
5.2.4.1 Understand the main points of supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics. 5.4.2.1 Understand with little support specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - summarize the main idea with the limited support of details they hear or write down -identify the details of a text |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Books closed. Write the following words on the board in random order: country, village, city, town. Tell students to work in pairs to put these places in order of size, starting with the largest. Ask them to think of an example of each place from their own country. • After about 1 minute, stop the students. Get feedback from each pair. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria Use the information to write sentences which describe people, places and objects |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students listen to the recording and write the name of each room Descriptor: - write the names of each room. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students Read the text and complete the sentences using the words from the box Descriptor: -read the text -complete the sentences Students describe the places and write using the following questions. Descriptor: - describe the places Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students choose one card to speak about the topic Descriptor: - speak using questions Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
- can write the names of each room. Total: 5 point -can read the text Total: 5 point -can describe the places Total: 5 point -can speak using questions Total: 5 point
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|

шағым қалдыра аласыз