

TEXTBOOK
C H O — NAN 0
Kanat 8aikenov Temirlan Khassen Nurbolat Zhumagulov Dauren Kaliyev Olzhas Yussnpov
A by lay S amatov Abdrfrrahman Sel Ali for
Approved by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan
CHEMISTRY
Grade 9
1' EOJTION
ACTAI-IA
Astana 2018
UOC 373 167.1
LBC 24 a 72 Ch S1
K. Baikenov
OJEXtISTAY, Glade 9: Tex&oak / Kanat Baikenov, TemidBo Khassg , Nurbolat Ch S1 Zhumagulov, Dauren Kaliyev, Olzhas Yussupov, Abyby Samatov, Abdurrahman
Sel, Ali Tor
— Almaty: Aczaua-Kilan, 176 p. - 2018 ISBN 978-601-7415-83-9
UDC 373.167.1
LBC 24 n 72
ISBN 978-601-7415-83-9
Copyright notice @ AczaHa-riiau. 2018 All Rights Reserved
PREFACE
Natural science is an exciting and very useful subject. This textbook will show you all the beauty of it and will help you become true explorers. The main aim of this book is to answer the fundamental question: “What is science and what is its importance in our life?”
Starting from the first pages, you will realise that this textbook is completely different from any other usual textbook full of theoretical passages and formulas. Every chapter contains useful information, curious facts, tasks for individual and group work. You will also learn how to conduct research and experiments yourselves, search for information, make your own discoveries.
One more valuable feature of this textbook is the language. Every sentence has been carefully chosen so that it is not difficult for you to understand science in the English language. Each page contains translations of all the important terms, both in Kazakh and Russian. This textbook will not only help you improve your English, but it will also make you a part of a big international science community.
Please pay attention to the structure of this textbook. Remember: a textbook is no longer the only source of information in the modern world. With the help of carefully selected tasks, you are going to learn such important skills as critical thinking, problem solving, information analysis, creativity, imagination, teamwork, digital literacy etc.
If you have any questions, suggestions or ideas regarding the contents of this book, please feel free to contact us:
via email: admin@astanakitap.kz
via telegram app: @astanakitap
Best regards, team of authors, “Астана-кітап”
Preface
Chapter 1. Electrolytic dissosiation
Chapter 2. Qualitative analysis of inorganic compounds 1. Qualitative reactions for cations
-
Qualitative reactions for anions
Chapter 3. Qualitative analysis of inorganic compounds 1. Qualitative reactions for cations
Chapter 4. Chemical equilibrium 1. Chemical equilibrium
2. Factors affecting equilibrium
Chapter 5. Oxidation-reduction reactions
Chapter 6. Metals and metal alloys 1. General properties of metals
Chapter 7. 1,2,13 group elements and their compounds 1. Alkali metals and their compounds
Chapter 8. 16,17 group elements, their compounds 1. Halogens
Chapter 9. Elements and compounds of 14 and 15 groups 1. Nitrogen
Chapter 10. Macro- and micro elements in human body and environment
Chapter 11. Introduction to Organic Chemistry
Chapter 12. Hydrocarbons. Fuels 1. Alkanes
Chapter 13. Oxygen and Nitrogen containing organic compounds 1. Alcohols
Solubility table Periodic Table Glossary
CHAPTER 1: ELECTROLYTIC DISSOCIATION
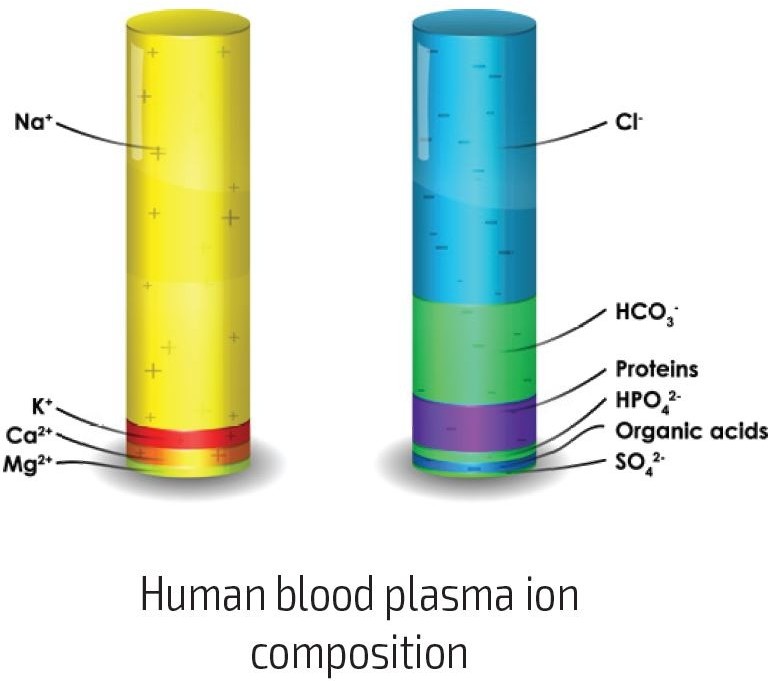
How does a human body conduct an electric current?
![]()
You
will:
![]()
![]() know what electrolytes and nonelectrolytes are;
explain the dependence of electrical conductivity
on a type of chemical
bond;
know what electrolytes and nonelectrolytes are;
explain the dependence of electrical conductivity
on a type of chemical
bond;
![]()
![]() know the electrolytic dissociation theory;
understand the mechanism of electrolytic
dissociation.
know the electrolytic dissociation theory;
understand the mechanism of electrolytic
dissociation.
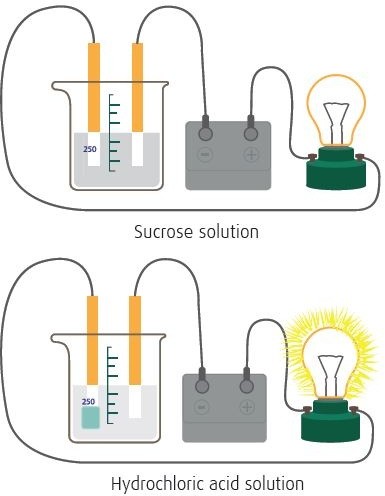
The conductivity of a solution depends on the solute. The more ions a solution contains, the greater its conductivity. Substances which dissolve in water by producing ions are called electrolytes. Solutions of electrolytes conduct electricity due to ions.
However, nonelectrolytes do not form ions in solution. Therefore, they do not conduct electricity.
How does a car battery work?
A car battery is a device used to power lighting, accessories and other electrical systems. The main components of the car battery are sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and lead (Pb) plate. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid and a good conductor of electricity.

Car battery
In 1897 Svante Arrhenius introduced his electrolytic dissociation theory that explained the properties of electrolytes. Postulates of Arrhenius theory:
-
Molecules of electrolytes (acids, bases, and salts) dissociate into oppositely charged ions:
![]()
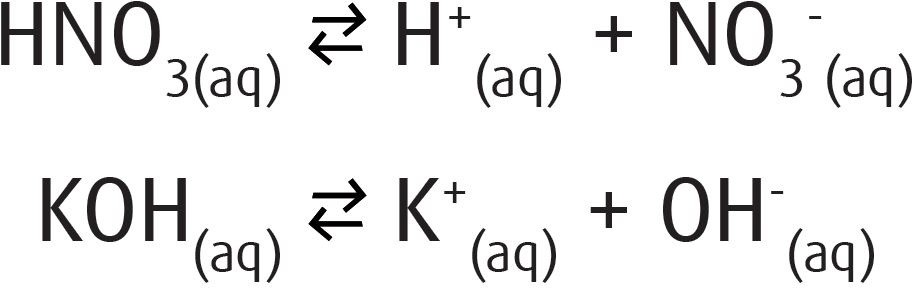
-
Electrolytes (molten compounds) conduct electric current due to produced ions. This is the mechanism of electrolytic dissociation.
![]()
Keep in
mind:
Electrolytic dissociation - the separation of a compound into ions in water.
Electrolytes form electrically conducting solutions in water due to produced ions.
Nonelectrolytes do not conduct electric current because of absence of ions.

Literacy
-
Why do table salt solutions conduct electricity well, while sugar solutions do not?
-
What is the difference between tap water and distilled water? Which of these two solutions conducts electricity? Why?
-
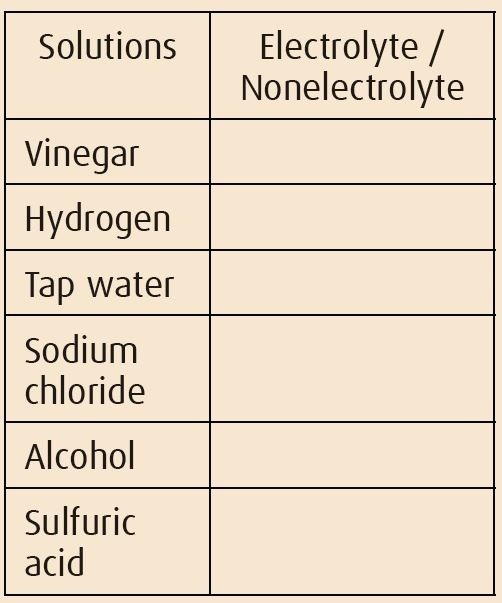
Which of the followings are electrolytes?

Demonstration
№ 1. Electrolytic dissociation of ionic and covalent
compounds. Materials:
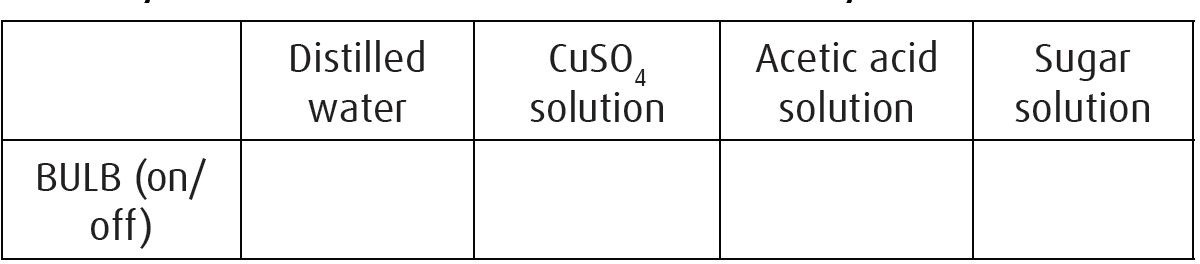
beaker 250 ml (4), 6V bulb, plug-in bulb mouth, steel electrode (2), crocodile leads (2), power supply (12V), acetic acid (vinegar) solution, copper sulfate solution, sugar solution, distilled water.
Procedure:
-
Pour distilled water, copper sulfate, vinegar and sugar solutions into four different 250 ml beakers.
-
Arrange the circuit as shown in the fi gure for distilled water.
-
Switch the power supply to 6V. Observe if the bulb is lightening or not. Record your observation.
-
Place the electrodes in copper sulfate, acetic acid, sugar solutions and repeat.
Write your observations on the conductivity table below:
Observation & questions:

![]()
Terminology
![]()
![]() solute - ерiген зат / растворенное вещество;
solution - ерітінді / раствор;
solute - ерiген зат / растворенное вещество;
solution - ерітінді / раствор;
Жүктеу
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
Обобщение опыта " Преподавание химии на английском языке в 8 классе"
Обобщение опыта " Преподавание химии на английском языке в 8 классе"

TEXTBOOK
C H O — NAN 0
Kanat 8aikenov Temirlan Khassen Nurbolat Zhumagulov Dauren Kaliyev Olzhas Yussnpov
A by lay S amatov Abdrfrrahman Sel Ali for
Approved by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan
CHEMISTRY
Grade 9
1' EOJTION
ACTAI-IA
Astana 2018
UOC 373 167.1
LBC 24 a 72 Ch S1
K. Baikenov
OJEXtISTAY, Glade 9: Tex&oak / Kanat Baikenov, TemidBo Khassg , Nurbolat Ch S1 Zhumagulov, Dauren Kaliyev, Olzhas Yussupov, Abyby Samatov, Abdurrahman
Sel, Ali Tor
— Almaty: Aczaua-Kilan, 176 p. - 2018 ISBN 978-601-7415-83-9
UDC 373.167.1
LBC 24 n 72
ISBN 978-601-7415-83-9
Copyright notice @ AczaHa-riiau. 2018 All Rights Reserved
PREFACE
Natural science is an exciting and very useful subject. This textbook will show you all the beauty of it and will help you become true explorers. The main aim of this book is to answer the fundamental question: “What is science and what is its importance in our life?”
Starting from the first pages, you will realise that this textbook is completely different from any other usual textbook full of theoretical passages and formulas. Every chapter contains useful information, curious facts, tasks for individual and group work. You will also learn how to conduct research and experiments yourselves, search for information, make your own discoveries.
One more valuable feature of this textbook is the language. Every sentence has been carefully chosen so that it is not difficult for you to understand science in the English language. Each page contains translations of all the important terms, both in Kazakh and Russian. This textbook will not only help you improve your English, but it will also make you a part of a big international science community.
Please pay attention to the structure of this textbook. Remember: a textbook is no longer the only source of information in the modern world. With the help of carefully selected tasks, you are going to learn such important skills as critical thinking, problem solving, information analysis, creativity, imagination, teamwork, digital literacy etc.
If you have any questions, suggestions or ideas regarding the contents of this book, please feel free to contact us:
via email: admin@astanakitap.kz
via telegram app: @astanakitap
Best regards, team of authors, “Астана-кітап”
Preface
Chapter 1. Electrolytic dissosiation
Chapter 2. Qualitative analysis of inorganic compounds 1. Qualitative reactions for cations
-
Qualitative reactions for anions
Chapter 3. Qualitative analysis of inorganic compounds 1. Qualitative reactions for cations
Chapter 4. Chemical equilibrium 1. Chemical equilibrium
2. Factors affecting equilibrium
Chapter 5. Oxidation-reduction reactions
Chapter 6. Metals and metal alloys 1. General properties of metals
Chapter 7. 1,2,13 group elements and their compounds 1. Alkali metals and their compounds
Chapter 8. 16,17 group elements, their compounds 1. Halogens
Chapter 9. Elements and compounds of 14 and 15 groups 1. Nitrogen
Chapter 10. Macro- and micro elements in human body and environment
Chapter 11. Introduction to Organic Chemistry
Chapter 12. Hydrocarbons. Fuels 1. Alkanes
Chapter 13. Oxygen and Nitrogen containing organic compounds 1. Alcohols
Solubility table Periodic Table Glossary
CHAPTER 1: ELECTROLYTIC DISSOCIATION
How does a human body conduct an electric current?
![]()
You
will:
![]()
![]() know what electrolytes and nonelectrolytes are;
explain the dependence of electrical conductivity
on a type of chemical
bond;
know what electrolytes and nonelectrolytes are;
explain the dependence of electrical conductivity
on a type of chemical
bond;
![]()
![]() know the electrolytic dissociation theory;
understand the mechanism of electrolytic
dissociation.
know the electrolytic dissociation theory;
understand the mechanism of electrolytic
dissociation.
The conductivity of a solution depends on the solute. The more ions a solution contains, the greater its conductivity. Substances which dissolve in water by producing ions are called electrolytes. Solutions of electrolytes conduct electricity due to ions.
However, nonelectrolytes do not form ions in solution. Therefore, they do not conduct electricity.

How does a car battery work?
A car battery is a device used to power lighting, accessories and other electrical systems. The main components of the car battery are sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and lead (Pb) plate. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid and a good conductor of electricity.

Car battery
In 1897 Svante Arrhenius introduced his electrolytic dissociation theory that explained the properties of electrolytes. Postulates of Arrhenius theory:
-
Molecules of electrolytes (acids, bases, and salts) dissociate into oppositely charged ions:
![]()
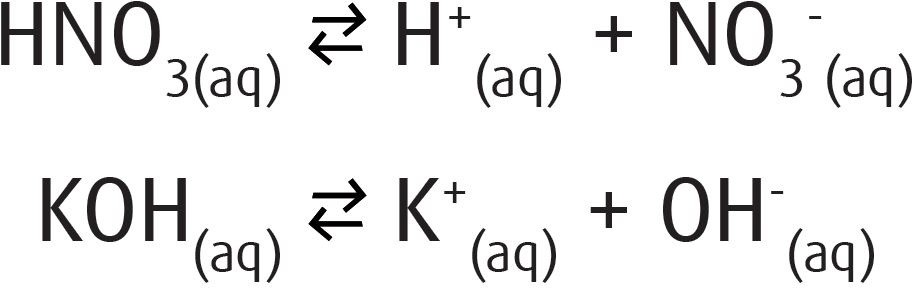
-
Electrolytes (molten compounds) conduct electric current due to produced ions. This is the mechanism of electrolytic dissociation.

![]()
Keep in
mind:
Electrolytic dissociation - the separation of a compound into ions in water.
Electrolytes form electrically conducting solutions in water due to produced ions.
Nonelectrolytes do not conduct electric current because of absence of ions.

Literacy
-
Why do table salt solutions conduct electricity well, while sugar solutions do not?
-
What is the difference between tap water and distilled water? Which of these two solutions conducts electricity? Why?
-
Which of the followings are electrolytes?


Demonstration
№ 1. Electrolytic dissociation of ionic and covalent
compounds. Materials:
beaker 250 ml (4), 6V bulb, plug-in bulb mouth, steel electrode (2), crocodile leads (2), power supply (12V), acetic acid (vinegar) solution, copper sulfate solution, sugar solution, distilled water.
Procedure:
-
Pour distilled water, copper sulfate, vinegar and sugar solutions into four different 250 ml beakers.
-
Arrange the circuit as shown in the fi gure for distilled water.
-
Switch the power supply to 6V. Observe if the bulb is lightening or not. Record your observation.
-
Place the electrodes in copper sulfate, acetic acid, sugar solutions and repeat.
Write your observations on the conductivity table below:
Observation & questions:


![]()
Terminology
![]()
![]() solute - ерiген зат / растворенное вещество;
solution - ерітінді / раствор;
solute - ерiген зат / растворенное вещество;
solution - ерітінді / раствор;

шағым қалдыра аласыз















