Lesson plan Grade 8
|
Lesson plan |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Unit of a long term plan: Travel and transport |
School:Sirdaria |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: Rakisheva Z. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASS: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson title |
Youth travel.Modern nomads |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Learning objectives(s) that this lesson is contributing to (link to the Subject programme) . |
8.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.6.14.1 use some prepositions
before nouns and adjectives 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson objectives |
All learners will be able to: -translate the new words -read the text -Guess the characters’ names -name places of interest in KZ Most learners will be able to: -Answer for the gift questions -play the Bub Match game -complete the text with appropriate prepositions -fill in graphic organizer -speak about places of interest Some learners will be able to: -complete the text without support -fill in graphic organizer giving information about yourselves -give more useful information about interesting sights of our country |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Assessment criteria |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Values links |
Common history, culture & language. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Effective teaching and learning |
Collaborative work. Differentiation, Modeling, Use e- learning and new technology. Active learning. Responding to leaners needs |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Level of thinking skills |
Understanding and application, Higher order thinking skills |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cross-curricular links |
History, Geography, Art |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Plan |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Planned timings |
Planned activities (replace the notes below with your planned activities)
|
Resources |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Start 2 minutes |
Organization moment Greeting. Checking attendance |
Pictures of transport, slides |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Middle 3minute
5minute 5minute
7 min
3 min
10 min
3 min |
Lesson hook . Brainstorming. Teacher explains the rebus . Guessing the rebus learners open the theme of the lesson.
Gift questions:
Pre-reading tasks . Semantic map
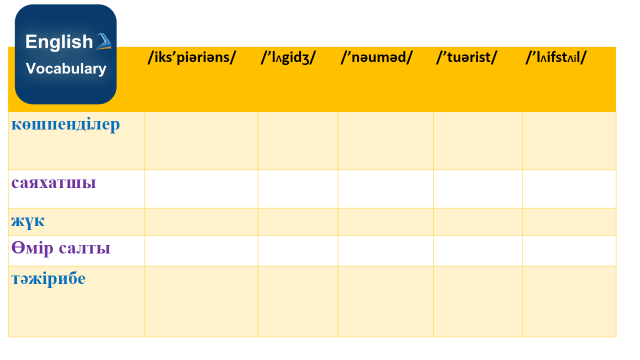
1.a person who does not stay long in the same place;-nomad 2.a particular place or position-location 3.staying alive-survival 4.the way in which a person lives-lifestyle 5. knowledge or skill from doing, seeing..-experience Descriptors: - work in group - Translate the words into English -complete the semantic map -choose right words Differentiation: by resource- learners use dictionaries to get the meaning of the words; By teacher support: TML, reformulation- teacher reformulates the words comprehensible to the learners.
Assessment : Self -assessment by checking correctness of answers looking at the keys.
While reading. Collaborative work. TML. Students put some prepositions before nouns and adjectives The life of modern nomads The modern nomad constantly changes locations, switching from one place to another. Most nomads have some kind of _place that they call home, which is usually where they pack and unpack their luggage, but they wouldn’t spend more than a few months a year there. Nor would they settle down in a new home, they just keep on changing a place, never feeling really at home, change is home. Nomads usually are quite smart, with fresh perspectives. The reason for that is that they are exposed to many lifestyles, cultures and situations. This constant process of change is a great learning experience, and when you learn, you become smarter. As 21st century nomads, we’ve evolved from traveling for the sake of survival to traveling in search of beauty and happiness. International tourism is one of the world’s fastest-growing industries. In 2016, over 1.2 billion people chose to go on holiday abroad. Youth travel is also on the rise – more than 22% of these travellers were between 15 and 29 years old. A recent survey about young people’s travel preferences has shown that this trend is likely to continue. While beach holidays and skiing trips are still popular with young travellers, more than 50% of the participants in the survey said that they had travelled for educational purposes. For 16-year-old Peter Jones from the USA, travelling abroad is a way to practise his language skills. He told researchers that he was studying French at school, but he also wanted to learn Spanish, so he had visited Mexico and Canada several times. Other common reasons why young people travel are to experience new cultures and exploring exotic destinations. . In search of new experiences, many tourists prefer to go off the beaten track and explore places like Africa and Asia.. Others choose a holiday in their home country over foreign travel. Maral Akhmadieva, a 15-year-old student from Kazakhstan, believes that travellers should get to know their own country before going abroad. She said that she had visited all the regions of Kazakhstan by the age of 14 and she would visit China in the near future. Descriptors: -work in group -read the text -put the prepositions -complete the graphic organizer Differentiation: by peer support. More abled learners assist less abled learners with the meaning of the text By resource- teacher gives extra sheets with prepositions
Assessment criteria:
Post-reading . Graphic organizer
Descriptors: - work in group - complete the chat -add information about yourself
Differentiation: By recourses - learners use the text to fill the table By peer support: While working in group work or pair work more abled learners help less abled learners .
Assessment criteria:
Speaking Task. Further practice. Active learning. Game : “I am a guide” Prompt: Teacher Shows video”Places to visit in Kazakhstan”
I’m………. I want to recomendate…. Because of……… It is located…… You can get there …….. It cost…..
Descriptors:
Differentiation: by support: Teacher models the task with examples and prompts by resourse: learners use internet to get information
Assessment: Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз Lesson plan Grade 8
Lesson
plan Unit of a long term
plan: Travel and
transport School:Sirdaria Date: Teacher name: Rakisheva
Z. CLASS:
8 Number
present: absent: Lesson
title Youth travel.Modern
nomads Learning objectives(s) that
this lesson is contributing to (link to the Subject
programme) . 8.4.2.1 understand specific information and
detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and
curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.6.14.1 use some prepositions
before nouns and adjectives 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and
syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular
topics Lesson
objectives All learners will be able
to: -translate the new
words -read the
text -Guess the characters’
names -name places of interest in
KZ Most learners will be able
to: -Answer for the gift
questions -play the Bub Match
game -complete the text with
appropriate prepositions -fill in graphic
organizer -speak about places of
interest Some learners will be able
to: -complete the text without
support -fill in graphic organizer
giving information about yourselves -give more useful information
about interesting sights of our country Assessment criteria Recognize specific details of
the text “The modern nomads” Use prepositions appropriate
grammar assurance Speak using the specific
vocabulary and give information for foreign
tourists Values links Common history, culture &
language. Effective teaching and
learning Collaborative work.
Differentiation, Modeling, Use e- learning and new
technology. Active learning. Responding to leaners
needs Level of thinking skills Understanding and application,
Higher order thinking skills Cross-curricular
links History,
Geography, Art Plan Planned timings Planned activities (replace
the notes below with your planned
activities)
Resources Start 2
minutes Organization
moment Greeting. Checking
attendance Pictures of transport,
slides Middle 3minute
5minute 5minute
7 min
3 min 10
min 3 min Lesson
hook .
Brainstorming. Teacher explains the rebus .
Guessing the rebus learners open the theme of the
lesson. Gift
questions: What does the word
"nomad " mean? What is the
difference between a traditional nomad and a modern
nomad? Would you like to
be modern nomads? What would you
enjoy? Pre-reading tasks . Semantic
map 1.a person who does not stay long in the same
place;-nomad 2.a particular place or
position-location 3.staying
alive-survival 4.the way in which a person
lives-lifestyle 5. knowledge or skill from doing,
seeing..-experience Descriptors: - work in
group - Translate the words into
English -complete the semantic
map -choose right
words Differentiation: by
resource- learners use dictionaries to
get the meaning of the words; By teacher
support: TML, reformulation- teacher
reformulates the words comprehensible to the
learners.
Assessment
: Self -assessment by checking
correctness of answers looking at the
keys.
While
reading. Collaborative work.
TML. Students put
some prepositions before nouns and adjectives The life of modern
nomads
The modern nomad constantly
changes locations, switching from one place to another. Most nomads
have some kind of _place that they call home,
which is usually where they pack and unpack their luggage, but they
wouldn’t spend more than a few months a year there. Nor would they
settle down in a new home, they just keep on
changing a place, never feeling really
at home, change is
home.
Nomads usually are quite
smart, with fresh perspectives. The reason
for that is that they are exposed to many lifestyles, cultures and
situations. This constant process
of change is a great learning
experience, and when you learn, you become
smarter.
As 21st century nomads, we’ve
evolved from traveling for the sake of
survival to traveling in
search of beauty and
happiness.
International tourism is
one of the world’s fastest-growing
industries. In 2016, over 1.2 billion people
chose to go on holiday abroad. Youth travel
is also on the rise – more than 22% of
these travellers were between 15 and 29 years old. A recent survey
about young people’s travel preferences has shown that this trend
is likely to continue. While beach holidays and
skiing trips are still popular with young travellers, more than
50% of the participants in the survey
said that they had travelled for educational purposes. For
16-year-old Peter Jones from the USA, travelling abroad is a way to
practise his language skills. He told researchers that he was
studying French at school, but he also wanted to
learn Spanish, so he had visited Mexico and Canada several times.
Other common reasons why young people travel are to experience new
cultures and exploring exotic
destinations.
.
In search of new experiences,
many tourists prefer to go off the beaten track and explore
places like Africa and Asia.. Others choose a holiday in their home
country over foreign travel. Maral Akhmadieva, a 15-year-old
student from Kazakhstan, believes that travellers should
get to know their own country
before going abroad. She said that she had visited all the
regions of Kazakhstan by the
age of 14 and she would visit
China in the near
future. Descriptors: -work in
group -read the
text -put the
prepositions -complete the graphic
organizer Differentiation: by peer
support. More abled learners assist
less abled learners with the meaning of the
text By
resource- teacher gives extra sheets
with prepositions Assessment
criteria: Use prepositions appropriate
grammar assurance Post-reading .
Graphic
organizer Character Country Age Reasons for
travelling Countries they had
been Want to
visit Descriptors: - work in
group - complete the
chat -add information about
yourself
Differentiation: By
recourses - learners use the text to
fill the table
By peer
support: While working in
group work or pair work more abled learners help less abled
learners .
Assessment
criteria: Recognize specific details of
the text “The modern nomads”
Speaking Task. Further
practice. Active learning. Game : “I am a
guide” Prompt: Teacher Shows
video”Places to visit in Kazakhstan”
I’m………. I want to
recomendate…. Because of……… It is located…… You can get there
…….. It cost…..
Descriptors: Work in a
group Show more places of visit in
map of Kazakhstan Give more information about
those places Give reasons to visit
them Speak
clearly
Differentiation:
by
support: Teacher models the
task with examples and prompts by
resourse: learners use internet to get
information
Assessment: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||