Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: ___ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: ___ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Vocabulary and language focus: Attributes and personality. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.3.3.1 explain and justify their own point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.6.3.1 use a variety of compound adjectives and adjectives as participles and a variety of comparative structures to indicate degree on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.6.12.1 use an increased variety of comparative degree adverb structures with regular and irregular adverbs use a variety of pre-verbal, post-verbal and end-position adverbs on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment Good afternoon, dear students and guests! Welcome to our English lesson The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up 3-4 minutes Describe the (imaginary) Picture\ With books closed, ask: How would you describe your personality? Elicit a few ideas from individual students. • Put students into pairs to write down as many words they can think of associated with personality. • Write attributes on the board and ask students if they think people with certain attributes are suited to particular hobbies. Ask: What kind of people are suited to playing chess? Accept all answers. Lead - In 1 What are you passionate about? 2 What are attributes? 3 Who was famous in the 1960s? |
Students respond to greetings. Describe your personality Students express their ideas The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere ANSWERS 1 Students’ own answers. 2 An attribute is a quality or characteristic of someone. 3 Students’ own answers. |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Pre-text discussion (pairwork!): consider letting the students share previous experiences in similar situation. Exercise 1 • In a weaker class, ask for translations. In a stronger class, encourage students to put the words into sentences to show understanding. ANSWERS 1 generous 2 passion 3 moody 4 anxious 5 pessimistic 6 optimism 7 responsibility 8 respect 9 enthusiasm 10 confidence 11 frustrated Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Exercise 2 • In a weaker class, you could help students to prepare for the task by deciding together whether the missing words are adjectives or nouns. • In a stronger class, ask students to give reasons and justify their opinion. • Ask some students to compare their answers and report back to the class on how similar or different they and their partner are Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students express their ideas
Students complete the table. Which adjectives are negative? Negative adjectives: moody, anxious, pessimistic, frustrated Students complete the sentences with your own ideas using words in exercise 1. ANSWERS Students’ own answers |
Assessment criteria - Recognize and use nouns and adjectives of attributes and personality. Descriptor: - recognize the nouns - Can use an adjectives Total: 1 point Assessment criteria: - Make adverbs from adjectives. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - can use adverbs from adjectives |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P:6 Complete the definitions with the words in the box. |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. Teacher asks students to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success Ladder. |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Comparing adjectives and adverbs |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.4.9.1 recognise inconsistencies in argument in extended texts on a range of general and curricular topics 9.6.14.1 use an increased variety of prepositions before nouns and adjectives use a growing number of dependent prepositions following nouns and adjectives and an increased variety of dependent prepositions following verbs on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Pantomime: 'What do you like? Play the game in 2 groups. One pupil from each group comes to the board and mimes a hobby. The other group tries to guess the hobby. If they guess correctly, they win one point. At the end of the game, the group with the most points is the winner. Lead - In Write on the board: In life, it’s best not to act too … Elicit possible endings for the sentence (quickly, carefully, etc.).
In differentiation part«Think and share» method was used to check up student’s vocabulary knowledge. After that T introduces the aim and theme of the lesson. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 4
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words. Exercise 5 • In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs to write their sentences. • Ask some students to write some of their sentences on the board. Discuss if they are logical and correctly formed. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Exercise 6 • Focus on the example and elicit one or two more examples from the class. Check answers. Make sure students understand we use less, the least, more, the most to form comparative and superlative forms of adverbs. |
Students complete the examples and the rules in the table Students write six sentences describing how you do different things. Use the verbs in the first box and adverbs formed from the adjectives in the second box. Students complete the table with the words in blue |
Assessment criteria - Recognize and use nouns and adjectives of attributes and personality. Descriptor: - recognize the nouns - Can use an adjectives Assessment criteria: - Make adverbs from adjectives. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - can use adverbs from adjectives |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Home task: WB p.6, ex.1-3 p.7 |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading: Comparing generations. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 9.6.14.1 use an increased variety of prepositions before nouns and adjectives use a growing number of dependent prepositions following nouns and adjectives and an increased variety of dependent prepositions following verbs on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.W3 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
Express their opinions about different generations building extended sentences. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre-teaching vocabulary Warm-up 1/ Describe the given picture. 2/ What is the message conveyed by it? • With books closed, ask students if they have seen photographs of their parents and grandparents when they were young. Lead – In What do you think life was like in the 1950s? Which of these things do you think were common in the 1950s? Which are common now? In differentiation part«Think and share» method was used to check up student’s vocabulary knowledge. .
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Pre- Reading Activity. Predictions. Elicitation Predicting and guessing. Students skimming the text "My generation" quickly Students express their ideas Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. While-reading Exercise 1 • Read through the items in the list with the class and check that students understand them. In a weaker class, allow students to use dictionaries In a stronger class, elicit suggestions and guesses for unfamiliar vocabulary, and then discuss again after the first reading, encouraging students to use context to work out the meaning. Exercise 2 -In a weaker class, encourage students to underline the parts of the text where they found the answers. In a stronger class, encourage students to identify the false sentences and correct them from memory. Then they should read again and confirm Exercise 3 Ask students to complete the sentences with the correct prepositions Peer testing. Students work in pairs or groups They have to prepare questions about the text they have just read. The members of each pair or each group will have to answer. |
Students express their ideas Students read, listen and compare their answers with the text.
ANSWERS More common in the 1950s ballrooms, big bands, black-and-white TV More common now mobile phones, computers, jobs for women, discos, bad language Students read the text again. Write true or false. Correct the false sentences ANSWERS 1 False. The cinema was popular in the fifties. 2 False. A family in her street bought a TV. 3 True. 4 False. She really likes the fashions. 5 True. 6 True |
Assessment criteria - understand specific information and detail in texts Descriptor: -finds necessary information in the text and completes the task. Assessment criteria: -Identify particular information and details in reading passage. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - analyses the information in the text and gives the right answers. |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB p.10 Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: ___ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Past perfect and past simple |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.6.9.1 use appropriately an increased variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books close, ask the SS what they remember about the reading text from last lesson. Write on the board the example I visited my gran last weekend and she'd found some of her old photos. Underline she'd found. Ask: When did I visit my gran? (last weekend). When did she find the photos, before or after I visited? (before I visited). Tell SS that this tense is called the past perfect. Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students write down the rules |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 • Ask students to open their books and look at the timeline. Tell them to read the sentence again and match the events to the diagram. • Ask students to translate the examples into their own language. Discuss how the equivalent tense is formed in the students’ own language, and whether this is similar to English Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Exercise 2 • Read the example with the class and ask: Which action happened first? (I saw the film) Focus on the next sentence and ask Which action happened first? (Alice didn’t have many hobbies when she was a child). Elicit which verb should be in the past perfect (have) and which in the past simple (tell). Exercise 3 Ask students to complete the sentences with the correct prepositions explain that prepositions are words like in, from, to, in front of, at and on, which are usually used before a noun or pronoun to show place |
Students write the events in the correct place on the timeline
ANSWERS Recent past: I visited my gran Earlier past: she’d found some of her old photos Rules: a before b past simple c had Students complete the sentences. Use the past perfect and the past simple in each sentence ANSWERS 1 told, hadn’t had 2 got, went, hadn’t seen 3 hadn’t invented, was 4 was, had left, had found 5 hadn’t started, arrived 6 wanted, had had |
Assessment criteria - Apply correctly active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in the context. Descriptor: - uses tense forms correctly; Assessment criteria: -Demonstrate the ability to write grammatically correct sentences on familiar topics. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: -fills in the sentences according to the grammar rule. |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB ex.4-5 p.7 |
Self-assessment. How well do I understand? 4 - I can do this and explain it to someone else. 3 - I understand and can do this by myself. 2 - I need more practice. 1 - I don't understand this yet. |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: ___ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: ___ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Past perfect and past simple Diagnostic test |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.6.9.1 use appropriately an increased variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books close, ask the SS what they remember about the reading text from last lesson. Write on the board the example I visited my gran last weekend and she'd found some of her old photos. Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students write down the rules |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 4 Remind students to use the both the positive and the negative – to talk about things they had and had not done. • In a weaker class, allow students time to prepare some notes and questions individually, then ask and answer their questions in pairs. In a stronger class, encourage students to ask and answer spontaneously. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text.
|
Students work in pairs. Find out what your partner had or hadn’t done before arriving at school today ANSWERS Students’ own answers Students complete the sentences. Use the past perfect and the past simple in each sentence ANSWERS 1 told, hadn’t had 2 got, went, hadn’t seen 3 hadn’t invented, was 4 was, had left, had found 5 hadn’t started, arrived 6 wanted, had had |
Assessment criteria - Apply correctly active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in the context. Descriptor: - uses tense forms correctly; Assessment criteria: -Demonstrate the ability to write grammatically correct sentences on familiar topics. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: -fills in the sentences according to the grammar rule. |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB ex.4-5 p.7 |
Self-assessment. How well do I understand? 4 - I can do this and explain it to someone else. 3 - I understand and can do this by myself. 2 - I need more practice. 1 - I don't understand this yet. |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: ___ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: ___ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Uses of get |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.2.1 understand most specific information in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks 9.6.1.1 use a growing variety of abstract compound nouns and complex noun phrases on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Write make, do, collect and write on the board as headings. With books closed, students work in pairs and brainstorm words you use with each Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students write down the rules |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 • In a weaker class, elicit translations of the collocations and make example sentences as a class. In a stronger class, encourage students to record the new phrases in their own example sentences. • Point out that students can use diagrams like these to record other collocations. They could also turn the diagrams into spidergrams if they prefer Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Exercise 2 • Students complete the questions individually In differentiation part «Discussion» method was used to check up student’s vocabulary knowledge. Exercise 3 Students listen and match the words with the people. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Ss use new words in the sentences. Exercise 4 Allow students time to read the questions. Encourage them to make notes from the first listening, which they can confirm when listening again. |
Students complete the diagram with the words in the box ANSWERS 1 model planes 2 clothes 3 music 4 puzzles 5 woodwork 6 sports 7 badges 8 stamps 9 football cards 10 blogs 11 poetry 12 short stories Students choose the correct words to complete the questions. Then ask and answer in pairs ANSWERS 1 collect 2 write 3 make 4 make 5 written 6 do 7 do, make Students’ own answers. Students listen to the dialogues. Match two words with each of the people in the photos 1–4 ANSWERS 1 Michael: money, test 2 Maxine: uniform, upset 3 Clare: party, married 4 Joey: uncle, tickets Students listen again and choose the correct answers ANSWERS 1 c 2 a 3 b 4 c 5 a
|
Assessment criteria -Identify facts and details in extended talkswith little support. Descriptor: - can make collocations -can classifying words Assessment criteria: - Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. -Make CCQ questions Descriptor: - asks complex questions to get information |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB p.8. |
Self-assessment. How well do I understand? 4 - I can do this and explain it to someone else. 3 - I understand and can do this by myself. 2 - I need more practice. 1 - I don't understand this yet. |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: ___ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: ___ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Past simple and continuous |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks 9.5.2.1 write independently about factual and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.6.9.1 use appropriately an increased variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Refer students back to the photos on page 12. Ask What was Clare doing when she first heard the music? • Elicit the answer (she was dancing) and write the sentence on the board: She was dancing when she heard the music. • Underline the verbs and elicit that they are in the past continuous and past simple. • Ask: Which action happened first? (she was dancing); Did she continue dancing when she heard it? (yes) Lead – In Ask questions |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students write down the rules |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 Students work in pairs to study the sentences and match them to the descriptions. • Check answers with the class. Elicit which tenses are used Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Exercise 3 Students continue writing their questions individually. Check answers as a class Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Ss use new words in the sentences. Exercise 4 Students complete the questions individually or in pairs |
Students match sentences 1–3 from the listening on page 12 with descriptions a–c. Which tenses do we use in each sentence? ANSWERS b (past continuous) 2 c (past continuous and past simple) 3 a (past simple) Students complete the questions in the History quiz with a past simple and a past continuous form ANSWERS What new invention was Alexander Bell using when he said, ‘Mr Watson, come here. I want to see you’? (the telephone) Students complete the questions using the correct form of the verbs in the box. ANSWERS 1 did, do 4 were, thinking, got 2 did, meet 5 were, doing 3 did, use 6 did, do
|
Assessment criteria - Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation.
Descriptor: -discusses questions and answers the questions -can classifying words Assessment criteria: -Write sentences about real and imaginary past events connecting them into paragraphs. . -Make CCQ questions Descriptor: - writes about past activities |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB p.9 |
Self-assessment. How well do I understand? 4 - I can do this and explain it to someone else. 3 - I understand and can do this by myself. 2 - I need more practice. 1 - I don't understand this yet. |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: ___ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talking about past events |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics 9.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in extended texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, ask students what important days they can remember from the past. • Elicit some answers, e.g. the first day at a new school, a holiday, Christmas day, etc. Ask students to describe what they remember and how they felt Lead – In Look at the photo. What do you think the relationship between Colin and Dean is? What are they looking at? In differentiation part«Think and share» method was used to check up student’s vocabulary knowledge. After that T introduces the aim and theme of the lesson. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Exercise 2 Tell students they are going to hear parts of a dialogue, and they must choose the most appropriate responses. Students listen and answer individually. • Play the CD again and elicit the answers
Exercise 4 • In a weaker class, encourage students to underline the parts of the text where they found the answers. In a stronger class, encourage students to identify the false sentences and correct them from memory. Then they should read again and confirm Exercise 3 Ask students to complete the sentences with the correct prepositions explain that prepositions are words like in, from, to, in front of, at and on, which are usually used before a noun or pronoun to show place |
Students express their ideas Students listen to the dialogue. Which part of the festival did Colin enjoy most?
ANSWERS The end of the last day Students listen and choose the correct answers. ANSWERS 1 b 2 b 3 a 4 b |
Assessment criteria - Identify the main idea in extended talk. Descriptor:
Assessment criteria: - Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor:
|
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB p.10 Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Describing a decade p.15 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics 9.5.2.1 write independently about factual and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model account of a decade. • Learn key phrases for writing about a decade. • Learn about giving examples. • Write an account of a decade. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Ask students what they think all these events have in common. If necessary, tell them that they all happened in the same decade and invite students to guess which one. Confirm that it is the 1960s Lead – In Answer the questions Why do people remember the seventies? What were the memorable events? What music, films and fashions were popular Do you like or dislike anything from the seventies? In differentiation part«Think and share» method was used to check up student’s vocabulary knowledge. After that T introduces the aim and theme of the lesson. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT CD1 |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 Read through the questions and make sure everyone understands. In a weaker class, students can compare answers in pairs before checking as a class. In a stronger class, set a short time limit and tell students to skim read the text for the information in the questions Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Exercise 2 • Read through the key phrases with the class. • Ask students to find the key phrases in the model text and translate them into their own language Exercise 3 Look at the words in blue in the model text. Elicit what their role is (to introduce examples).. • Point out the use of commas with for instance and for example |
Students rad the model text and answer the questions. ANSWERS 1 a 2 Paragraph 2 3 Paragraph 4 Students study the key phrases. Which phrases introduce the paragraphs in the text?
ANSWERS Paragraph 1: The … was a decade which … Paragraph 2: In the world of fashion … Paragraph 3: One of the most memorable … Paragraph 5: By the end of the decade Students study the words in blue in the model text. ANSWERS Students’ own answers |
Assessment criteria -. Study a model account of a decade. Descriptor: -read the model text Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for writing about a decade. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: -find the key phrases in the model text |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB p.10 Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Comparing generations p.16 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 9..3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to work in pairs and talk about what they know about their grandparents as young people. What jobs did they do and what did they do in their free time? Lead – In Look at the photo and describe.
How old are the people in the photo?
How old are the people in the photo? |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 • Draw students’ attention to the photos and ask them what they know about the people’s hobbies from the photos. Encourage students to describe the photos using the present continuous Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Exercise 2 • Before reading and listening students look at the true / false questions and guess the answers. Ask them to discuss the reason for their decisions in pairs
Exercise 3 Students look through the text and complete the exercise. Exercise 4 • Allow students time to think about the adjectives in relation to the people listed |
Students look at the photos. What are the people doing? What do you think their hobbies are? Students read and listen to the text. Are the sentences true or false?
Students match the words to make compound adjectives
|
Assessment criteria - Form ideas effectively and demonstrate the ability to express them clearly. Descriptor:
Assessment criteria: - Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - Match the words to make compound adjectives |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB p.10 Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. The British sense of humour p.17 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.5.1 recognize the opinion of the speaker(s) in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – teach vocabulary Warm-up With books closed, ask students what makes them laugh. Elicit ideas about films, books, TV programmes, etc. and encourage students to express their opinions. • Ask students if they know the character Mr Bean. Ask: Do you find him funny? Elicit a range of answers Lead – In Background Mr Bean, mentioned in the text, first appeared in a British TV comedy series in the early 1990s. The character was created by Rowan Atkinson, who has described Mr Bean as ‘a child in a grown man’s body’. Mr Bean has appeared in two feature films and also an animated cartoon
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Yes, I do No, I don’t His teddy |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise:1 In a weaker class, remind students to note the part of speech as well as the meaning for the words In a stronger class, check understanding of the new words by eliciting example sentences Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Exercise 2 Students listen, read and check their answers to exercise 1
Exercise 3 • Allow students time to compare their answers in pairs and discuss any differences before you check with the class. As usual, in a stronger class, encourage full, complete answers in the students’ own words. |
Students check the meaning of the words and phrases Students read and listen to the text. ANSWERS 1 good sense of humour 4 sarcasm 2 comedians 5 make fun of 3 laughter 6 bizarre Students read the text again and answer the questions ANSWERS Students’ own answers. |
Assessment criteria - Recognize and use vocabulary to do with humour Descriptor: -uses appropriate subject-specific vocabulary while speaking. Assessment criteria: - Identify the meaning of the text about the British sense of humour. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: -finds necessary information in the text and completes the task. |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 3 p:12 wb |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review. Unit 1. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.6.3.1 use a variety of compound adjectives and adjectives as participles and a variety of comparative structures to indicate degree on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.6.9.1 use appropriately an increased variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to work in pairs and talk about what they know about their grandparents as young people. What jobs did they do and what did they do in their free time? Lead – In
I want to do a course in Math. He may be able to do a good job, but I doubt it. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 Write the adverbs for these adjectives Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Exercise 2 Choose the correct words
Exercise 3 Complete the sentences with correct tense of the words in the box. Exercise 4 Choose the correct words |
Students write the adverbs for these adjectives ANSWERS 1 angrily 4 politely 2 well 5 optimistically 3 carefully 6 firmly Students choose the correct words ANSWERS 1 beautifully 4 optimistic 2 the hardest, successful 5 well, best 3 noisily, happily Students match the words to make compound adjectives
|
Assessment criteria -Make adverbs from adjectives Descriptor: -write the adverbs for these adjectives Assessment criteria: - |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book |
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex:6 p:18 st Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project. An interview summary: teenage years p.19 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.3.3.1 explain and justify their own point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in extended texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a summary of an interview with a family member. • Interview an older person about their teenage years and their generation. • Write a summary of your interview about an older person’s youth. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, write My teenage years on the board and elicit or explain the meaning If students are struggling, give them some categories and decades and brainstorm associations, for example, fashion and hair styles in the 1980s, music in the 1960s, exciting new technology in the 1990s Lead – In Background The word teenager to describe a person between the ages of 13–19 originated in the 1950s. Prior to that, this age group was not a clearly defined demographic grouping. In the 1950s adolescents began to stand out as a group of people for whom modern music, fashions and trends were very important. They had more freedom than previous generations, and more money to spend. They rebelled against the norms of their parents, creating what became recognized as the ‘generation gap’. Over the next couple of decades, the teenage years became a recognized life stag |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 Look at the photographs and elicit what they show. Ask students to guess the decade, then read the text quickly and check their guesses Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Exercise 2 • In a weaker class, brainstorm other questions or topics that students could ask about. Tell them to choose five questions and point out or elicit that this means their summary will have five paragraphs.
Exercise 3 • Find out which generation was the most researched and whether people had the same experiences. Ask students whether they would rather be teenagers now, or in another decade. Have a vote for the most popular decade. |
Students read the interview summary. Match paragraphs A–E with interview questions 1–5 ANSWERS 1 E 2 A 3 D 4 B 5 C Students write about an older person’s teenage years ANSWERS : Students’ own answers Students share your interview summary with the rest of the class. Did any other students find out similar information? |
Assessment criteria - Read a summary of an interview with a family member Descriptor: read the interview Assessment criteria: -Interview an older person about their teenage years and their generation. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - write about an older person’s teenage years |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book |
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB p.10 Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Medical science |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.8.1 begin to recognise inconsistencies in argument in extended talk on a growing range of general and curricular subjects 9.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn nouns and verbs related to the health benefits of exercise. • Do a health and exercise quiz. • Talk about the benefits of doing sport and exercise. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write health and exercise on the board and elicit the connection between the two. • Ask: Can you be healthy without doing exercise? Lead – In
3 What are the secrets of a long life? |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 P:20 Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the nouns in the quiz. If you want to speed this up, put them in pairs and ask each student to find half the words Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex:2 P:20 Tell students to look at the text and find the verbs that are used with the nouns in the text and write the nouns and the related verb phrase
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text
Ex:3 P:20 • Put students into pairs to read the sentences in the Health and exercise quiz and decide whether they are true or false • Find out who got the most answers right. Were there any answers that really surprised students? |
Students check the meaning of the nouns in blue in the Health and exercise quiz. Which words are about mental attitude, and which are about physical health? ANSWERS: Mental attitude: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 Physical health: 6, 10, 11, 12 Students read the text again and complete the table with nouns 1–12 from exercise 1 and the verbs used with them.
ANSWERS: 1 have commitment 2 build self-esteem 3 have determination 4 develop self-reliance 5 have discipline 6 improve stamina 7 involve team work 8 improve concentration 9 boost (your) mood 10 increase endorphins 11 increase (your) energy 12 raise (your) blood pressure Students do the Health and exercise quiz. Decide if the sentences are true or false. Then listen and check ANSWERS: 1 True. 2 True 3 False 4 False. 5 True. 6 True 7 False 8 False. 9 False |
Assessment criteria - Learn nouns and verbs related to the health benefits of exercise. Descriptor: check the meaning of the nouns in blue in the Health and exercise quiz. Assessment criteria: - Talk about the benefits of doing sport and exercise -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - write the nouns and the related verb phrase |
CD 1 Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex:3 P:14 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
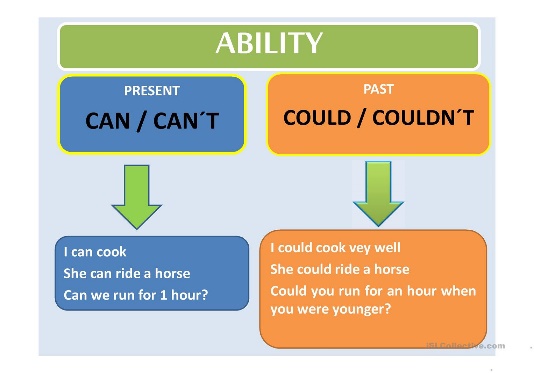
Сould, can , will be able to |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.3.3.1 explain and justify their own point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 9.6.1.1 use a growing variety of abstract compound nouns and complex noun phrases on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the use of could, can and will be able to. • Practise using could, can and will be able to to talk about ability in the past, present and future
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • • With books closed, write health and exercise on the board and elicit the connection between the two. • Ask: Can you be healthy without doing exercise? Lead – In
We sometimes use be able to instead of "can" or "could" for ability. Be able to is possible in all tenses - but "can" is possible only in the present and "could" is possible only in the past for ability. In addition, "can" and "could" have no infinitive form |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:5 P:21 Ask students to look at the quiz again and find an example of can and will be able to. Ask what are they used to express (ability). Play the audio again and ask students to listen for examples of can, could and will be able to in the affirmative and negative Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 6 P:21 Ask students to read the text through quickly, ignoring the gaps. Ask: What problem did Jed have? (He fell down a hole and damaged his feet and knees.)
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Ex: 7 P:21 Make sure students understand what they have to do. If necessary, do the first sentence as an example |
Students look at the sentences from the quiz and the listening. Complete them with can / can’t or will / won’t be able to ANSWERS: 1 will be able to 2 can’t 3 won’t be able to 4 will be able to 5 won’t be able to
Students complete the text with the affirmative and negative forms of can, could and will be able to. ANSWERS: 1 can’t 5 will be able to 2 couldn’t 6 will be able to 3 couldn’t 7 won’t be able to 4 can
|
Assessment criteria - Learn the use of could, can and will be able to. Descriptor: Complete them with can / can’t or will / won’t be able to Assessment criteria: - Practise using could, can and will be able to to talk about ability in the past, present and future -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - read the text through quickly, ignoring the gaps. |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex:3 P:15 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Alternative therapy |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 9.6.1.1 use a growing variety of abstract compound nouns and complex noun phrases on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about exercise as a cure. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Express your own opinions on exercise as an alternative medical treatment. • Learn about and practise noun suffixes
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the quote from Hippocrates Walking is man’s best medicine on the board and ask students what they think it means. Elicit or explain that it probably means that keeping active improves your health Lead – In Background Hippocrates lived between 460–370 BCE and was possibly the first person to think disease and illness was the result of natural causes and not a punishment from the gods. He believed lifestyle, diet and environment all had a part in people’ s health and that health could be improved by improving these factors
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:22 • Draw students’ attention to the photos and elicit a description. In a weaker class, encourage students to participate by accepting factual descriptions. In a stronger class, ask students to speculate about and explain their answers Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 2 P:22 • Read the instructions and make sure students understand what they have to do. Tell them to use context and meaning, but also to look at structural elements like tenses or words such as however
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Ex: 3 P:22 In a stronger class, ask students to predict or guess the noun form and share ideas as a class |
Students look at the photos and the title of the text, and answer the questions. Then read the text and check your answers ANSWERS: Exercise reduces pain, helps people with depression and reduces loneliness Students complete the text with sentences a–e. Listen and check your answers. ANSWERS: 1 b 2 d 3 c 4 e 5 c Students complete the table with words from the text. What suffixes are used to form the nouns? ANSWERS: 1 medication 2 treatment 3 infection 4 illness 5 reduction 6 depression 7 loneliness |
Assessment criteria - Read about exercise as a cure Descriptor: to participate by accepting factual descriptions Assessment criteria: - Read for general meaning and specific information -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - use context and meaning, |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 4 P:15 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
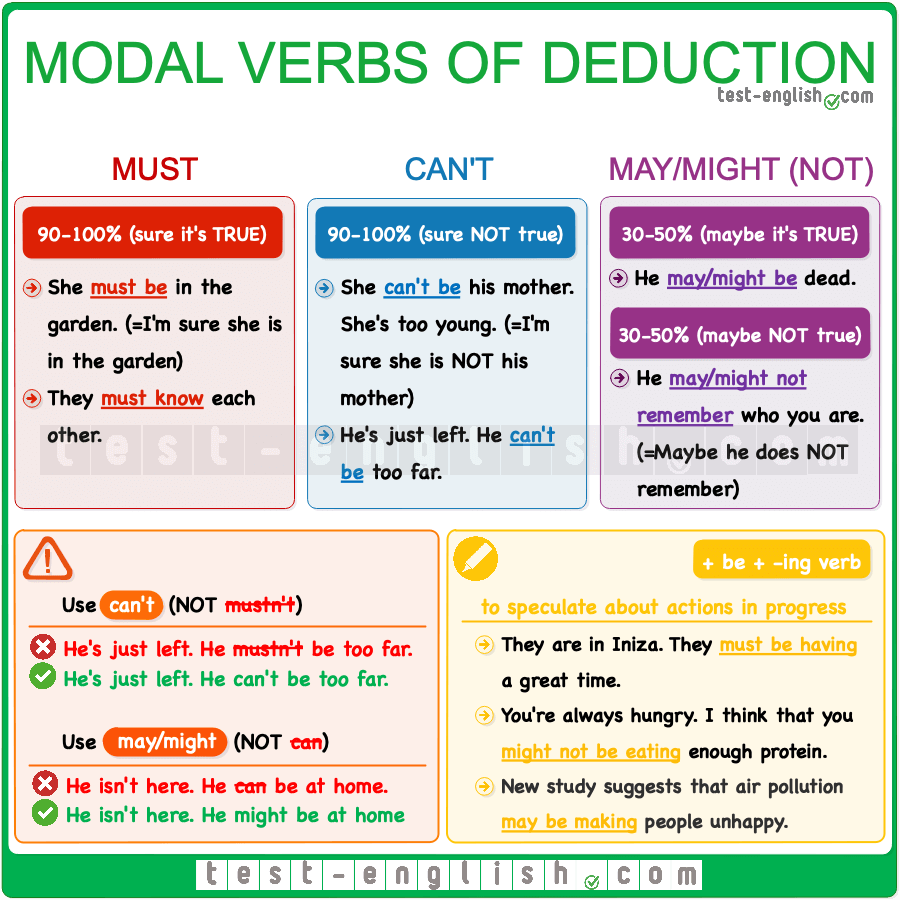
May, might, could, must, can't |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 9.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 9.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the use of may, might, could, must and can’t for possibility and certainty. • Practise using may, might, could, must and can’t to express possibility and certainty in opinions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Refer students back to the text on pages 22–23 and ask: Do you think that swimming in cold water helps depression? Elicit a range of ideas, including the idea that it is possible it works Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:23 Students study the examples in pairs and complete the rules Point out that we don’t usually use can to express possibility Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 2 P:23 Allow students time to compare their answers in pairs before you check with the class. Discuss what helped students make their choices Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P:23 In a weaker class, do a few examples and discuss them before students continue in pairs. In a stronger class, ask students to provide not just one sentence for each item, but all the possible sentences for each item. |
Students study the modal forms in blue in sentences 1–5. Then choose the correct options in the rules. ANSWERS: a possibility b are c don’t Students сhoose the correct words ANSWERS: 1 might 4 must 2 can’t 5 might 3 may 6 might Students make sentences using the modal verbs in exercise 1 and the words in brackets ANSWERS: 1 He / She may / might / could have flu. 2 He must be tired. 3 They may / might / could be Mexican. 4 He / She can’t be angry. 5 She must be ill. 6 He may / might / could be a surgeon
|
Assessment criteria - Learn the use of may, might, could, must and can’t for possibility and certainty. Descriptor: study the modal forms in blue Assessment criteria: - Practise using may, might, could, must and can’t to express possibility and certainty in opinions. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - make sentences using the modal verbs |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 41 P:17 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Phrasal verbs |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.3.3.1 explain and justify their own point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn phrasal verbs about health and lifestyle. • Read an eight-point health plan. • Listen to a conversation about living longer. . • Learn how to prepare for listening tasks |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write health and lifestyle on the board and elicit or teach the meaning. • Ask: How can your lifestyle affect your health? Elicit some ideas. • Ask: How can you change your lifestyle to make you healthier? Elicit a range of ideas Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:24 • Read the eight-point health plan together and see if any of the students’ ideas from the warm-up are mentioned. • Students match the phrasal verbs with their synonyms. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 3 P:24 Focus on the photos and the title Live longer, live better. Ask How old do you think the people are? What are they doing? Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Ex: 4 P:24 Look at the statements and tell students they should prepare to listen by following the advice in the study strategy. Give them some time to read the statements and underline key words. |
Students match the phrasal verbs in blue in The eight-point health plan with synonyms ANSWERS: 1 h 2 c 3 g 4 a 5 d 6f 7 b 8 e Students read the introduction to the Live longer, live better article. Then listen. What is a centenarian? ANSWERS: A centenarian is a person who is over a hundred years old
Students Listen again and write true or false ANSWERS: 1 True. 2 False. 3 False. 4 False. 5 True. 6 True.
|
Assessment criteria - Learn phrasal verbs about health and lifestyle. Descriptor: match the phrasal verbs in blue in Assessment criteria: - Read an eight-point health plan. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - read the introduction to the Live longer |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 3 P:16 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
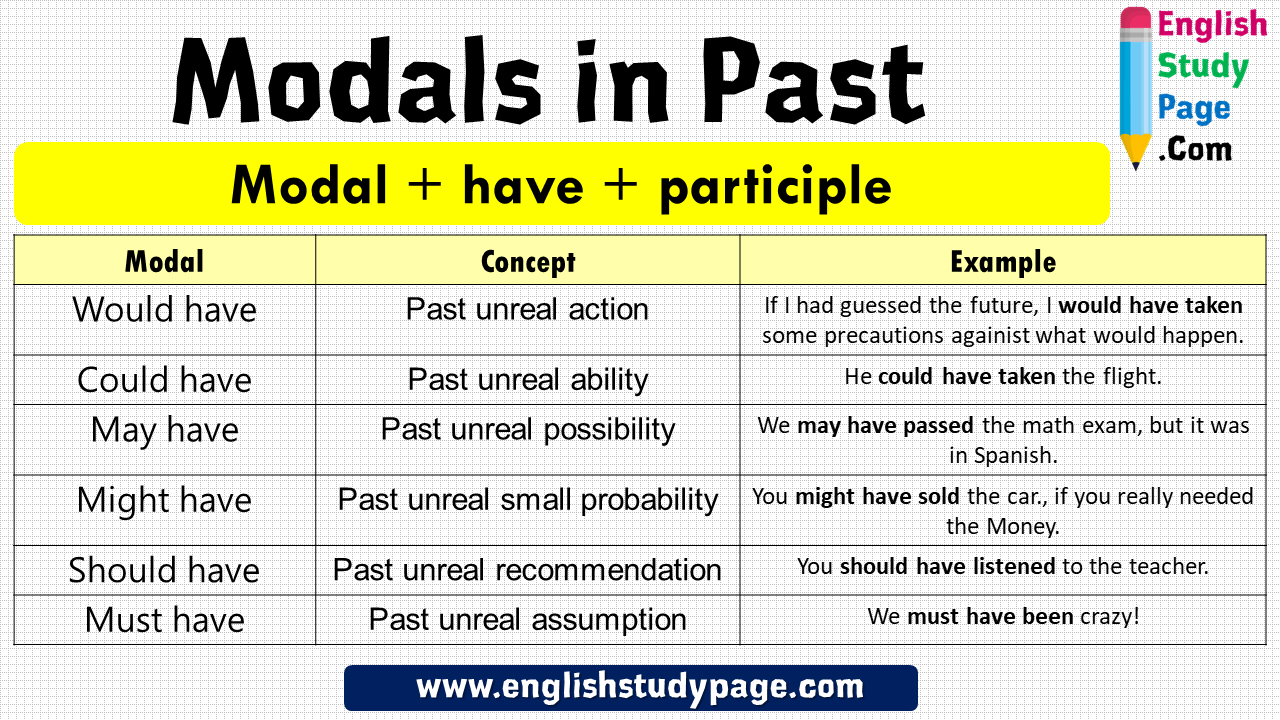
Past modals |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.4.1 understand most of the implied meaning in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.5.2.1 write independently about factual and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the use of must have, can’t have, could have and might have to speculate about the past. • Practise speculating about the past using past modals. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, ask students to remember how we express possibility in the present. Give them some scenarios and elicit sentences using may, might, could and must, can’t. For example, say: Joe’s doing his driving test after only three lessons. (He can’t be ready / must be very confident.) Look, it’s getting cloudy. (It may / might rain this afternoon.), etc Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:25 • Students read the sentences and answer the questions. • Check answers and remind students what past participles are Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 2 P:25 Remind students that some verbs have irregular past participles. Tell them to look up any they are not sure of in the irregular verbs list on page 126 of the Student’s Book
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Ex: 3 P:25 • Students complete the sentences with the correct modals. • Check answers by asking some students to read out their sentences and asking the class to say whether they are correct or not. |
Students sudy the modal forms in blue i ANSWERS: a must, can’t, could / might b have . Students rewrite the sentences in the past form ANSWERS: 1 They could have been seventy years old. 2 He can’t have been a hundred years old. He was still working. 3 She might have cut down on chocolate. 4 He must have worked out a lot. 5 She could have gone without dessert. 6 They might have taken up basketball Students choose the correct words ANSWERS: 1 might 2 must 3 could 4 can’t 5 must 6 can’t |
Assessment criteria - Learn the use of must have, can’t have, could have and might have to speculate about the past.
Descriptor: rewrite the sentences in the past form Assessment criteria: -Practise speculating about the past using past modals. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the correct modals |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 1 P:17 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Exchanging opinions p.26 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.5.1 recognize the opinion of the speaker(s) in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organize priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a conversation in which people exchange opinions. • Learn key phrases for exchanging opinions. • Learn how to use should, must, have to • Practise exchanging opinions.
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Ask where students come across advice about health. Elicit suggestions for how the government and schools can communicate with young people about health issues Lead – In Using drugs in sport undermines values like fair play and teamwork. When sportspeople use drugs, they not only might damage their own health, they also give sport a bad reputation and set a poor example to others. So-called 'performance-enhancing drugs' or 'performance and image-enhancing drugs' are banned in sports because they could give a sportsperson an unfair advantage over other competitors. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!”
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:26 Focus on the photo. Ask: What are Marie and Dean looking at? What do the posters show? Elicit ideas and then ask: Which poster do you prefer? Why? Elicit a range of opinions
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words inthe text. Ex: 2 P:26 n a stronger class, tell students to cover the dialogue and just listen. Play the CD once and ask whether Marie and Dean agree about the posters.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words inthe text. Ex: 3 P:26 • Ask students to find the key phrases in the dialogue and translate them into their own language. • Students practise the dialogue in pairs |
Students look at the posters. What are they campaigning against? ANSWERS: They are campaigning against drugs. Students listen to the dialogue. Which poster has got the clearest message? ANSWERS: Marie thinks the poster with the photo has a clearer message, but Dean prefers the poster with a more positive message Students listen to the key phrases. Which phrase expresses a strong opinion? Practise the dialogue ANSWERS: It should definitely … expresses a strong opinion.
|
Assessment criteria - Listen to a conversation in which people exchange opinions
Descriptor: -look at the posters. What are they campaigning against? Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for exchanging opinions. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - listen to the key phrases. |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 1 P:19 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading. Health advice / A discussion essay |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9..3.7. 1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics 9.4.6.1 recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer in extended texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary to do with nutrition and healthy eating. • Read a text about healthy eating. • Talk about diet and ways it could be improved. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, write An apple a day keeps the doctor away on the board. Explain that this is an old proverb and ask students what it means. Lead – In
When it comes to overall health and weight loss, there’s an excess of advice out there. Unfortunately, most of it is terrible, misguided, outdated and scientifically disproven.
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas Students share with their opinions how to keep healthy life. |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!”
Good job! |
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:29 • Students match the definitions with the blue words. Allow students to use their dictionaries if necessary. • Check answers with the class Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text.
Ex: 2 P:29 Students listen and read. Ask the question to the whole clas
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 3 P:29 • Remind students to look carefully at the whole question, and watch out for little words or negatives that change the meaning of the sentences, e.g. question 5 (Which fats are not good for us?). • Students read the text again and answer the questions. |
Students match definitions 1–5 with the words in blue in the text. ANSWERS: 1 dairy 2 processed 3 tissues 4 evidence 5 fibre Students read and listen to the text. How does healthy eating affect our lives? ANSWERS: Healthy eating affects our physical and mental health. It can reduce the risk of serious illnesses such as heart disease, diabetes and possibly also mental illness, like depression. Eating regular meals can help with energy, as well as mood and memory Students read the text again and choose the correct answers ANSWERS: 1 a 2 c 3 b 4 b 5 a 6 b |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary to do with nutrition and healthy eating.
Descriptor: -match definitions with the words in blue in the text Assessment criteria: - Read a text about healthy eating. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - read and listen to the text. How does healthy eating affect our lives?
|
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 1 P:17 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative assessment for the 1st unit. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.1.1 Understand the main points in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.4.1.1 Understand the main points in extended texts on a range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics 9.5.2.1 Write independently about factual and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.3.1.1 Use formal and informal registers in their talk on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - Recognise the main points in unsupported extended talk; -Identify specific information and detail in texts; -Write with moderate grammatical accuracy; -Use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax in a talk; |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. LISTENING Task. Listen to the dialogues. Six people talk about sport they like. Match each speaker with his or her reason, A-F. CD3 Tapescript1. 1. Speaker 1______ A) There are friendly people who go there, so it’s a good place to meet people. [1] 2. Speaker 2______ B) It’s a great way to keep fit. It’s better than going to a health club. [1] 3. Speaker 3______ C) There’s hardly anyone there and you can listen to the ocean as you do it. [1] 4. Speaker 4______ D) It’s a good exercise because you have to walk a lot. [1] 5. Speaker 5______ E) It’s really fun! But, it’s not as easy as it looks. [1] |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students listen to the dialogues and match each speaker with his or her reason ANSWERS: 1 A 2 C 3 F 4 E 5 B 6 D |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!”
Good job! |
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
6. Speaker 6______ F) I have no trouble to finding somewhere to play. [1]
READING Task. Read the text and identify in which paragraph (A-D) the writer does these things. 1. Establishes the emotional importance of baseball for fans. Paragraph ________[1] 2. The origins of baseball. Paragraph ________[1]
Task. Match the headings 3-6 with the paragraphs A-D 3. The rules of playing the game ______ [1] 4. The facilities ______ [1] 5. The changes happening to baseball ______ [1] 6. Part of people’s life ______ [1] WRITING Choose ONE of the topics and write Topic 1. Write an article to a newspaper describing the most popular hobby in Kazakhstan nowadays using appropriate grammar. Try to mention these questions: Topic 2. Write an article to a newspaper describing the recent Sport Olympiad where Kazakhstan sportsmen participated (in country or abroad) using appropriate grammar. Try to mention these questions: SPEAKING Task. You are given quetsions to speak about for 2-3 minutes. Before you speak you have one minute to think about what you are going to say and you can make notes if you wish. |
Students . Read the text and identify in which paragraph (A-D) the writer does these things. ANSWERS: 1 B 2 C 3 D 4 C 5 A 6 B Students Choose ONE of the topics and write ANSWERS: Students own answers
Students answer the questions ANSWERS: Students own answers
|
Assessment criteria - Study a model discussion essay.
Descriptor: read the model text and answer the questions. Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for a discussion essay. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - complete the key phrases. Then read the model text and check
|
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 3 P:19 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country. Exercise and sport |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.3.3.1 explain and justify their own point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.4.9.1 recognise inconsistencies in argument in extended texts on a range of general and curricular topics 9.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics.S3 explain and justify their own point of view on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a text about Kazakh sports stars. • Learn vocabulary connected to success in sports. • Learn the difference between could, was / were able to and managed to. • Write sentences about famous sportspeople in Kazakhstan. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Have a race to find which group can list the most Kazakh sportspeople in two minutes. • After two minutes, find out which group had the longest list and declare them the winner Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!”
Good job! |
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:28 • Draw students’ attention to the photos. Ask them if they can identify who they are. • In pairs, students discuss what they know about the sportspeople Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 2 P:28 • Tell students to listen to and read the text and see if it contains the information they talked about. • In a stronger class, play the recording with books closed to see how much they understand and for them to check whether the information they talked about is mentioned Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Ex: 3 P:28 • Focus students’ attention on the verbs. • Ask students to note down what they think the nouns are. • Then tell them to check their answers in the text and correct any they have got wrong. • Students underline the suffixes. • Check answers as a class. |
Students look at the photos. Who are these people? What do you know about them? ANSWERS: Kazhymukan Munaitpasov Denis Ten Zarina Diyas Students’ own answers Students read and listen to the text. Complete the sentences with the names of the people ANSWERS: 1 Zarina Diyas (Czech Republic) 2 Kazhymukan Munaitpasov 3 Denis Ten (shopping mall) 4 Kazhymukan Munaitpasov 5 Denis Ten 6 Zarina Diyas Students complete the table with nouns from the text. What suffixes are used to form the nouns? ANSWERS: 1 wrestling 2 performance 3 failure 4 achievement 5 competition 6 injury |
Assessment criteria - Read a text about Kazakh sports stars. Descriptor: discuss what they know about the sportspeople Assessment criteria: -Learn vocabulary connected to success in sports -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - read and listen to the text |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 5 P:21 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
,
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Healthy eating |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.4.6.1 recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer in extended texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary to do with nutrition and healthy eating. • Read a text about healthy eating. • Talk about diet and ways it could be improved
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write An apple a day keeps the doctor away on the board. Explain that this is an old proverb and ask students what it means. • Elicit that the proverb is not meant literally, but suggests that if we eat healthy foods, like fruit, we will not get ill. Lead – In
There is one thing that we all have in common….. no matter where you live….. and that is the basic human need for good health and well-being. The links below will focus on eating healthy, maintaining fitness, proper diet, natural energy, and health safety issues. New content is added from time to time so keep checking back. Many of the posts below have had steady stream of daily visitors over the last several months. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas Students discuss then write an essay |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!”
Good job! |
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:29 • Students match the definitions with the blue words. Allow students to use their dictionaries if necessary. • Check answers with the class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 2 P:29 • Students listen and read. Ask the question to the whole class
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Ex: 3 P:29 Remind students to look carefully at the whole question, and watch out for little words or negatives that change the meaning of the sentences, e.g. question 5 (Which fats are not good for us?) |
Students match definitions 1–5 with the words in blue in the text. ANSWERS: 1 dairy 2 processed 3 tissues 4 evidence 5 fibre Students read and listen to the text. How does healthy eating affect our lives? ANSWERS: Healthy eating affects our physical and mental health. It can reduce the risk of serious illnesses such as heart disease, diabetes and possibly also mental illness, like depression. Eating regular meals can help with energy, as well as mood and memory Students read the text again and choose the correct answers ANSWERS: 1 a 2 c 3 b 4 b 5 a 6 b |
Assessment criteria - Study a model discussion essay.
Descriptor: read the model text and answer the questions. Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for a discussion essay. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - complete the key phrases. Then read the model text and check
|
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 3 P:22 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
ҚМЖ 9 сынып 1 тоқсан English Plus кітабы бойынша
ҚМЖ 9 сынып 1 тоқсан English Plus кітабы бойынша
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: ___ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: ___ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Vocabulary and language focus: Attributes and personality. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.3.3.1 explain and justify their own point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.6.3.1 use a variety of compound adjectives and adjectives as participles and a variety of comparative structures to indicate degree on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.6.12.1 use an increased variety of comparative degree adverb structures with regular and irregular adverbs use a variety of pre-verbal, post-verbal and end-position adverbs on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
Organization moment Good afternoon, dear students and guests! Welcome to our English lesson The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up 3-4 minutes Describe the (imaginary) Picture\ With books closed, ask: How would you describe your personality? Elicit a few ideas from individual students. • Put students into pairs to write down as many words they can think of associated with personality. • Write attributes on the board and ask students if they think people with certain attributes are suited to particular hobbies. Ask: What kind of people are suited to playing chess? Accept all answers. Lead - In 1 What are you passionate about? 2 What are attributes? 3 Who was famous in the 1960s? |
Students respond to greetings. Describe your personality Students express their ideas The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere ANSWERS 1 Students’ own answers. 2 An attribute is a quality or characteristic of someone. 3 Students’ own answers. |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Pre-text discussion (pairwork!): consider letting the students share previous experiences in similar situation. Exercise 1 • In a weaker class, ask for translations. In a stronger class, encourage students to put the words into sentences to show understanding. ANSWERS 1 generous 2 passion 3 moody 4 anxious 5 pessimistic 6 optimism 7 responsibility 8 respect 9 enthusiasm 10 confidence 11 frustrated Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Exercise 2 • In a weaker class, you could help students to prepare for the task by deciding together whether the missing words are adjectives or nouns. • In a stronger class, ask students to give reasons and justify their opinion. • Ask some students to compare their answers and report back to the class on how similar or different they and their partner are Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions |
Students express their ideas
Students complete the table. Which adjectives are negative? Negative adjectives: moody, anxious, pessimistic, frustrated Students complete the sentences with your own ideas using words in exercise 1. ANSWERS Students’ own answers |
Assessment criteria - Recognize and use nouns and adjectives of attributes and personality. Descriptor: - recognize the nouns - Can use an adjectives Total: 1 point Assessment criteria: - Make adverbs from adjectives. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - can use adverbs from adjectives |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Home task: Ex: 2 P:6 Complete the definitions with the words in the box. |
The Ladder method was used as a reflection. Teacher asks students to stick their stickers to the Success Ladder. |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success Ladder. |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Comparing adjectives and adverbs |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.4.9.1 recognise inconsistencies in argument in extended texts on a range of general and curricular topics 9.6.14.1 use an increased variety of prepositions before nouns and adjectives use a growing number of dependent prepositions following nouns and adjectives and an increased variety of dependent prepositions following verbs on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Pantomime: 'What do you like? Play the game in 2 groups. One pupil from each group comes to the board and mimes a hobby. The other group tries to guess the hobby. If they guess correctly, they win one point. At the end of the game, the group with the most points is the winner. Lead - In Write on the board: In life, it’s best not to act too … Elicit possible endings for the sentence (quickly, carefully, etc.).
In differentiation part«Think and share» method was used to check up student’s vocabulary knowledge. After that T introduces the aim and theme of the lesson. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 4
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words. Exercise 5 • In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs to write their sentences. • Ask some students to write some of their sentences on the board. Discuss if they are logical and correctly formed. Differentiation:Support; learners are arranged to interact in mixed groups. Topic vocabulary is used while responding to the given questions Exercise 6 • Focus on the example and elicit one or two more examples from the class. Check answers. Make sure students understand we use less, the least, more, the most to form comparative and superlative forms of adverbs. |
Students complete the examples and the rules in the table Students write six sentences describing how you do different things. Use the verbs in the first box and adverbs formed from the adjectives in the second box. Students complete the table with the words in blue |
Assessment criteria - Recognize and use nouns and adjectives of attributes and personality. Descriptor: - recognize the nouns - Can use an adjectives Assessment criteria: - Make adverbs from adjectives. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - can use adverbs from adjectives |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Home task: WB p.6, ex.1-3 p.7 |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading: Comparing generations. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 9.6.14.1 use an increased variety of prepositions before nouns and adjectives use a growing number of dependent prepositions following nouns and adjectives and an increased variety of dependent prepositions following verbs on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.W3 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
Express their opinions about different generations building extended sentences. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre-teaching vocabulary Warm-up 1/ Describe the given picture. 2/ What is the message conveyed by it? • With books closed, ask students if they have seen photographs of their parents and grandparents when they were young. Lead – In What do you think life was like in the 1950s? Which of these things do you think were common in the 1950s? Which are common now? In differentiation part«Think and share» method was used to check up student’s vocabulary knowledge. .
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Pre- Reading Activity. Predictions. Elicitation Predicting and guessing. Students skimming the text "My generation" quickly Students express their ideas Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. While-reading Exercise 1 • Read through the items in the list with the class and check that students understand them. In a weaker class, allow students to use dictionaries In a stronger class, elicit suggestions and guesses for unfamiliar vocabulary, and then discuss again after the first reading, encouraging students to use context to work out the meaning. Exercise 2 -In a weaker class, encourage students to underline the parts of the text where they found the answers. In a stronger class, encourage students to identify the false sentences and correct them from memory. Then they should read again and confirm Exercise 3 Ask students to complete the sentences with the correct prepositions Peer testing. Students work in pairs or groups They have to prepare questions about the text they have just read. The members of each pair or each group will have to answer. |
Students express their ideas Students read, listen and compare their answers with the text.
ANSWERS More common in the 1950s ballrooms, big bands, black-and-white TV More common now mobile phones, computers, jobs for women, discos, bad language Students read the text again. Write true or false. Correct the false sentences ANSWERS 1 False. The cinema was popular in the fifties. 2 False. A family in her street bought a TV. 3 True. 4 False. She really likes the fashions. 5 True. 6 True |
Assessment criteria - understand specific information and detail in texts Descriptor: -finds necessary information in the text and completes the task. Assessment criteria: -Identify particular information and details in reading passage. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - analyses the information in the text and gives the right answers. |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB p.10 Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: ___ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Past perfect and past simple |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.6.9.1 use appropriately an increased variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books close, ask the SS what they remember about the reading text from last lesson. Write on the board the example I visited my gran last weekend and she'd found some of her old photos. Underline she'd found. Ask: When did I visit my gran? (last weekend). When did she find the photos, before or after I visited? (before I visited). Tell SS that this tense is called the past perfect. Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students write down the rules |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 • Ask students to open their books and look at the timeline. Tell them to read the sentence again and match the events to the diagram. • Ask students to translate the examples into their own language. Discuss how the equivalent tense is formed in the students’ own language, and whether this is similar to English Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Exercise 2 • Read the example with the class and ask: Which action happened first? (I saw the film) Focus on the next sentence and ask Which action happened first? (Alice didn’t have many hobbies when she was a child). Elicit which verb should be in the past perfect (have) and which in the past simple (tell). Exercise 3 Ask students to complete the sentences with the correct prepositions explain that prepositions are words like in, from, to, in front of, at and on, which are usually used before a noun or pronoun to show place |
Students write the events in the correct place on the timeline
ANSWERS Recent past: I visited my gran Earlier past: she’d found some of her old photos Rules: a before b past simple c had Students complete the sentences. Use the past perfect and the past simple in each sentence ANSWERS 1 told, hadn’t had 2 got, went, hadn’t seen 3 hadn’t invented, was 4 was, had left, had found 5 hadn’t started, arrived 6 wanted, had had |
Assessment criteria - Apply correctly active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in the context. Descriptor: - uses tense forms correctly; Assessment criteria: -Demonstrate the ability to write grammatically correct sentences on familiar topics. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: -fills in the sentences according to the grammar rule. |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB ex.4-5 p.7 |
Self-assessment. How well do I understand? 4 - I can do this and explain it to someone else. 3 - I understand and can do this by myself. 2 - I need more practice. 1 - I don't understand this yet. |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: ___ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: ___ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Past perfect and past simple Diagnostic test |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.6.9.1 use appropriately an increased variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books close, ask the SS what they remember about the reading text from last lesson. Write on the board the example I visited my gran last weekend and she'd found some of her old photos. Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students write down the rules |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 4 Remind students to use the both the positive and the negative – to talk about things they had and had not done. • In a weaker class, allow students time to prepare some notes and questions individually, then ask and answer their questions in pairs. In a stronger class, encourage students to ask and answer spontaneously. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text.
|
Students work in pairs. Find out what your partner had or hadn’t done before arriving at school today ANSWERS Students’ own answers Students complete the sentences. Use the past perfect and the past simple in each sentence ANSWERS 1 told, hadn’t had 2 got, went, hadn’t seen 3 hadn’t invented, was 4 was, had left, had found 5 hadn’t started, arrived 6 wanted, had had |
Assessment criteria - Apply correctly active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in the context. Descriptor: - uses tense forms correctly; Assessment criteria: -Demonstrate the ability to write grammatically correct sentences on familiar topics. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: -fills in the sentences according to the grammar rule. |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB ex.4-5 p.7 |
Self-assessment. How well do I understand? 4 - I can do this and explain it to someone else. 3 - I understand and can do this by myself. 2 - I need more practice. 1 - I don't understand this yet. |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: ___ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: ___ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Uses of get |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.2.1 understand most specific information in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks 9.6.1.1 use a growing variety of abstract compound nouns and complex noun phrases on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Write make, do, collect and write on the board as headings. With books closed, students work in pairs and brainstorm words you use with each Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students write down the rules |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 • In a weaker class, elicit translations of the collocations and make example sentences as a class. In a stronger class, encourage students to record the new phrases in their own example sentences. • Point out that students can use diagrams like these to record other collocations. They could also turn the diagrams into spidergrams if they prefer Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Exercise 2 • Students complete the questions individually In differentiation part «Discussion» method was used to check up student’s vocabulary knowledge. Exercise 3 Students listen and match the words with the people. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Ss use new words in the sentences. Exercise 4 Allow students time to read the questions. Encourage them to make notes from the first listening, which they can confirm when listening again. |
Students complete the diagram with the words in the box ANSWERS 1 model planes 2 clothes 3 music 4 puzzles 5 woodwork 6 sports 7 badges 8 stamps 9 football cards 10 blogs 11 poetry 12 short stories Students choose the correct words to complete the questions. Then ask and answer in pairs ANSWERS 1 collect 2 write 3 make 4 make 5 written 6 do 7 do, make Students’ own answers. Students listen to the dialogues. Match two words with each of the people in the photos 1–4 ANSWERS 1 Michael: money, test 2 Maxine: uniform, upset 3 Clare: party, married 4 Joey: uncle, tickets Students listen again and choose the correct answers ANSWERS 1 c 2 a 3 b 4 c 5 a
|
Assessment criteria -Identify facts and details in extended talkswith little support. Descriptor: - can make collocations -can classifying words Assessment criteria: - Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. -Make CCQ questions Descriptor: - asks complex questions to get information |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB p.8. |
Self-assessment. How well do I understand? 4 - I can do this and explain it to someone else. 3 - I understand and can do this by myself. 2 - I need more practice. 1 - I don't understand this yet. |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: ___ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: ___ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Past simple and continuous |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks 9.5.2.1 write independently about factual and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.6.9.1 use appropriately an increased variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Refer students back to the photos on page 12. Ask What was Clare doing when she first heard the music? • Elicit the answer (she was dancing) and write the sentence on the board: She was dancing when she heard the music. • Underline the verbs and elicit that they are in the past continuous and past simple. • Ask: Which action happened first? (she was dancing); Did she continue dancing when she heard it? (yes) Lead – In Ask questions |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students write down the rules |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 Students work in pairs to study the sentences and match them to the descriptions. • Check answers with the class. Elicit which tenses are used Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Exercise 3 Students continue writing their questions individually. Check answers as a class Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Ss use new words in the sentences. Exercise 4 Students complete the questions individually or in pairs |
Students match sentences 1–3 from the listening on page 12 with descriptions a–c. Which tenses do we use in each sentence? ANSWERS b (past continuous) 2 c (past continuous and past simple) 3 a (past simple) Students complete the questions in the History quiz with a past simple and a past continuous form ANSWERS What new invention was Alexander Bell using when he said, ‘Mr Watson, come here. I want to see you’? (the telephone) Students complete the questions using the correct form of the verbs in the box. ANSWERS 1 did, do 4 were, thinking, got 2 did, meet 5 were, doing 3 did, use 6 did, do
|
Assessment criteria - Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation.
Descriptor: -discusses questions and answers the questions -can classifying words Assessment criteria: -Write sentences about real and imaginary past events connecting them into paragraphs. . -Make CCQ questions Descriptor: - writes about past activities |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB p.9 |
Self-assessment. How well do I understand? 4 - I can do this and explain it to someone else. 3 - I understand and can do this by myself. 2 - I need more practice. 1 - I don't understand this yet. |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: ___ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talking about past events |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics 9.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in extended texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, ask students what important days they can remember from the past. • Elicit some answers, e.g. the first day at a new school, a holiday, Christmas day, etc. Ask students to describe what they remember and how they felt Lead – In Look at the photo. What do you think the relationship between Colin and Dean is? What are they looking at? In differentiation part«Think and share» method was used to check up student’s vocabulary knowledge. After that T introduces the aim and theme of the lesson. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Exercise 2 Tell students they are going to hear parts of a dialogue, and they must choose the most appropriate responses. Students listen and answer individually. • Play the CD again and elicit the answers
Exercise 4 • In a weaker class, encourage students to underline the parts of the text where they found the answers. In a stronger class, encourage students to identify the false sentences and correct them from memory. Then they should read again and confirm Exercise 3 Ask students to complete the sentences with the correct prepositions explain that prepositions are words like in, from, to, in front of, at and on, which are usually used before a noun or pronoun to show place |
Students express their ideas Students listen to the dialogue. Which part of the festival did Colin enjoy most?
ANSWERS The end of the last day Students listen and choose the correct answers. ANSWERS 1 b 2 b 3 a 4 b |
Assessment criteria - Identify the main idea in extended talk. Descriptor:
Assessment criteria: - Demonstrate the ability to participate in a conversation. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor:
|
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB p.10 Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Describing a decade p.15 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics 9.5.2.1 write independently about factual and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model account of a decade. • Learn key phrases for writing about a decade. • Learn about giving examples. • Write an account of a decade. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Ask students what they think all these events have in common. If necessary, tell them that they all happened in the same decade and invite students to guess which one. Confirm that it is the 1960s Lead – In Answer the questions Why do people remember the seventies? What were the memorable events? What music, films and fashions were popular Do you like or dislike anything from the seventies? In differentiation part«Think and share» method was used to check up student’s vocabulary knowledge. After that T introduces the aim and theme of the lesson. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT CD1 |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 Read through the questions and make sure everyone understands. In a weaker class, students can compare answers in pairs before checking as a class. In a stronger class, set a short time limit and tell students to skim read the text for the information in the questions Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Exercise 2 • Read through the key phrases with the class. • Ask students to find the key phrases in the model text and translate them into their own language Exercise 3 Look at the words in blue in the model text. Elicit what their role is (to introduce examples).. • Point out the use of commas with for instance and for example |
Students rad the model text and answer the questions. ANSWERS 1 a 2 Paragraph 2 3 Paragraph 4 Students study the key phrases. Which phrases introduce the paragraphs in the text?
ANSWERS Paragraph 1: The … was a decade which … Paragraph 2: In the world of fashion … Paragraph 3: One of the most memorable … Paragraph 5: By the end of the decade Students study the words in blue in the model text. ANSWERS Students’ own answers |
Assessment criteria -. Study a model account of a decade. Descriptor: -read the model text Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for writing about a decade. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: -find the key phrases in the model text |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB p.10 Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Comparing generations p.16 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 9..3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to work in pairs and talk about what they know about their grandparents as young people. What jobs did they do and what did they do in their free time? Lead – In Look at the photo and describe.
How old are the people in the photo?
How old are the people in the photo? |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 • Draw students’ attention to the photos and ask them what they know about the people’s hobbies from the photos. Encourage students to describe the photos using the present continuous Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Exercise 2 • Before reading and listening students look at the true / false questions and guess the answers. Ask them to discuss the reason for their decisions in pairs
Exercise 3 Students look through the text and complete the exercise. Exercise 4 • Allow students time to think about the adjectives in relation to the people listed |
Students look at the photos. What are the people doing? What do you think their hobbies are? Students read and listen to the text. Are the sentences true or false?
Students match the words to make compound adjectives
|
Assessment criteria - Form ideas effectively and demonstrate the ability to express them clearly. Descriptor:
Assessment criteria: - Apply topic related vocabulary in speech appropriately arranging words and phrases into well-formed sentences -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - Match the words to make compound adjectives |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB p.10 Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. The British sense of humour p.17 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.5.1 recognize the opinion of the speaker(s) in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Pre – teach vocabulary Warm-up With books closed, ask students what makes them laugh. Elicit ideas about films, books, TV programmes, etc. and encourage students to express their opinions. • Ask students if they know the character Mr Bean. Ask: Do you find him funny? Elicit a range of answers Lead – In Background Mr Bean, mentioned in the text, first appeared in a British TV comedy series in the early 1990s. The character was created by Rowan Atkinson, who has described Mr Bean as ‘a child in a grown man’s body’. Mr Bean has appeared in two feature films and also an animated cartoon
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
Yes, I do No, I don’t His teddy |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise:1 In a weaker class, remind students to note the part of speech as well as the meaning for the words In a stronger class, check understanding of the new words by eliciting example sentences Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Exercise 2 Students listen, read and check their answers to exercise 1
Exercise 3 • Allow students time to compare their answers in pairs and discuss any differences before you check with the class. As usual, in a stronger class, encourage full, complete answers in the students’ own words. |
Students check the meaning of the words and phrases Students read and listen to the text. ANSWERS 1 good sense of humour 4 sarcasm 2 comedians 5 make fun of 3 laughter 6 bizarre Students read the text again and answer the questions ANSWERS Students’ own answers. |
Assessment criteria - Recognize and use vocabulary to do with humour Descriptor: -uses appropriate subject-specific vocabulary while speaking. Assessment criteria: - Identify the meaning of the text about the British sense of humour. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: -finds necessary information in the text and completes the task. |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 3 p:12 wb |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review. Unit 1. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.6.3.1 use a variety of compound adjectives and adjectives as participles and a variety of comparative structures to indicate degree on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.6.9.1 use appropriately an increased variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to work in pairs and talk about what they know about their grandparents as young people. What jobs did they do and what did they do in their free time? Lead – In
I want to do a course in Math. He may be able to do a good job, but I doubt it. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 Write the adverbs for these adjectives Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Exercise 2 Choose the correct words
Exercise 3 Complete the sentences with correct tense of the words in the box. Exercise 4 Choose the correct words |
Students write the adverbs for these adjectives ANSWERS 1 angrily 4 politely 2 well 5 optimistically 3 carefully 6 firmly Students choose the correct words ANSWERS 1 beautifully 4 optimistic 2 the hardest, successful 5 well, best 3 noisily, happily Students match the words to make compound adjectives
|
Assessment criteria -Make adverbs from adjectives Descriptor: -write the adverbs for these adjectives Assessment criteria: - |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book |
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex:6 p:18 st Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 1 "Hobbies and qualities"
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project. An interview summary: teenage years p.19 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.3.3.1 explain and justify their own point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.4.5.1 deduce meaning from context in extended texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a summary of an interview with a family member. • Interview an older person about their teenage years and their generation. • Write a summary of your interview about an older person’s youth. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, write My teenage years on the board and elicit or explain the meaning If students are struggling, give them some categories and decades and brainstorm associations, for example, fashion and hair styles in the 1980s, music in the 1960s, exciting new technology in the 1990s Lead – In Background The word teenager to describe a person between the ages of 13–19 originated in the 1950s. Prior to that, this age group was not a clearly defined demographic grouping. In the 1950s adolescents began to stand out as a group of people for whom modern music, fashions and trends were very important. They had more freedom than previous generations, and more money to spend. They rebelled against the norms of their parents, creating what became recognized as the ‘generation gap’. Over the next couple of decades, the teenage years became a recognized life stag |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Exercise 1 Look at the photographs and elicit what they show. Ask students to guess the decade, then read the text quickly and check their guesses Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Exercise 2 • In a weaker class, brainstorm other questions or topics that students could ask about. Tell them to choose five questions and point out or elicit that this means their summary will have five paragraphs.
Exercise 3 • Find out which generation was the most researched and whether people had the same experiences. Ask students whether they would rather be teenagers now, or in another decade. Have a vote for the most popular decade. |
Students read the interview summary. Match paragraphs A–E with interview questions 1–5 ANSWERS 1 E 2 A 3 D 4 B 5 C Students write about an older person’s teenage years ANSWERS : Students’ own answers Students share your interview summary with the rest of the class. Did any other students find out similar information? |
Assessment criteria - Read a summary of an interview with a family member Descriptor: read the interview Assessment criteria: -Interview an older person about their teenage years and their generation. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - write about an older person’s teenage years |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book |
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. WB p.10 Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Medical science |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.8.1 begin to recognise inconsistencies in argument in extended talk on a growing range of general and curricular subjects 9.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn nouns and verbs related to the health benefits of exercise. • Do a health and exercise quiz. • Talk about the benefits of doing sport and exercise. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write health and exercise on the board and elicit the connection between the two. • Ask: Can you be healthy without doing exercise? Lead – In
3 What are the secrets of a long life? |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex: 1 P:20 Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the nouns in the quiz. If you want to speed this up, put them in pairs and ask each student to find half the words Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex:2 P:20 Tell students to look at the text and find the verbs that are used with the nouns in the text and write the nouns and the related verb phrase
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text
Ex:3 P:20 • Put students into pairs to read the sentences in the Health and exercise quiz and decide whether they are true or false • Find out who got the most answers right. Were there any answers that really surprised students? |
Students check the meaning of the nouns in blue in the Health and exercise quiz. Which words are about mental attitude, and which are about physical health? ANSWERS: Mental attitude: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 Physical health: 6, 10, 11, 12 Students read the text again and complete the table with nouns 1–12 from exercise 1 and the verbs used with them.
ANSWERS: 1 have commitment 2 build self-esteem 3 have determination 4 develop self-reliance 5 have discipline 6 improve stamina 7 involve team work 8 improve concentration 9 boost (your) mood 10 increase endorphins 11 increase (your) energy 12 raise (your) blood pressure Students do the Health and exercise quiz. Decide if the sentences are true or false. Then listen and check ANSWERS: 1 True. 2 True 3 False 4 False. 5 True. 6 True 7 False 8 False. 9 False |
Assessment criteria - Learn nouns and verbs related to the health benefits of exercise. Descriptor: check the meaning of the nouns in blue in the Health and exercise quiz. Assessment criteria: - Talk about the benefits of doing sport and exercise -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - write the nouns and the related verb phrase |
CD 1 Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex:3 P:14 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Сould, can , will be able to |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.3.3.1 explain and justify their own point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 9.6.1.1 use a growing variety of abstract compound nouns and complex noun phrases on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the use of could, can and will be able to. • Practise using could, can and will be able to to talk about ability in the past, present and future
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • • With books closed, write health and exercise on the board and elicit the connection between the two. • Ask: Can you be healthy without doing exercise? Lead – In
We sometimes use be able to instead of "can" or "could" for ability. Be able to is possible in all tenses - but "can" is possible only in the present and "could" is possible only in the past for ability. In addition, "can" and "could" have no infinitive form |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:5 P:21 Ask students to look at the quiz again and find an example of can and will be able to. Ask what are they used to express (ability). Play the audio again and ask students to listen for examples of can, could and will be able to in the affirmative and negative Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 6 P:21 Ask students to read the text through quickly, ignoring the gaps. Ask: What problem did Jed have? (He fell down a hole and damaged his feet and knees.)
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Ex: 7 P:21 Make sure students understand what they have to do. If necessary, do the first sentence as an example |
Students look at the sentences from the quiz and the listening. Complete them with can / can’t or will / won’t be able to ANSWERS: 1 will be able to 2 can’t 3 won’t be able to 4 will be able to 5 won’t be able to
Students complete the text with the affirmative and negative forms of can, could and will be able to. ANSWERS: 1 can’t 5 will be able to 2 couldn’t 6 will be able to 3 couldn’t 7 won’t be able to 4 can
|
Assessment criteria - Learn the use of could, can and will be able to. Descriptor: Complete them with can / can’t or will / won’t be able to Assessment criteria: - Practise using could, can and will be able to to talk about ability in the past, present and future -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - read the text through quickly, ignoring the gaps. |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex:3 P:15 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Alternative therapy |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 9.6.1.1 use a growing variety of abstract compound nouns and complex noun phrases on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about exercise as a cure. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Express your own opinions on exercise as an alternative medical treatment. • Learn about and practise noun suffixes
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the quote from Hippocrates Walking is man’s best medicine on the board and ask students what they think it means. Elicit or explain that it probably means that keeping active improves your health Lead – In Background Hippocrates lived between 460–370 BCE and was possibly the first person to think disease and illness was the result of natural causes and not a punishment from the gods. He believed lifestyle, diet and environment all had a part in people’ s health and that health could be improved by improving these factors
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:22 • Draw students’ attention to the photos and elicit a description. In a weaker class, encourage students to participate by accepting factual descriptions. In a stronger class, ask students to speculate about and explain their answers Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 2 P:22 • Read the instructions and make sure students understand what they have to do. Tell them to use context and meaning, but also to look at structural elements like tenses or words such as however
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Ex: 3 P:22 In a stronger class, ask students to predict or guess the noun form and share ideas as a class |
Students look at the photos and the title of the text, and answer the questions. Then read the text and check your answers ANSWERS: Exercise reduces pain, helps people with depression and reduces loneliness Students complete the text with sentences a–e. Listen and check your answers. ANSWERS: 1 b 2 d 3 c 4 e 5 c Students complete the table with words from the text. What suffixes are used to form the nouns? ANSWERS: 1 medication 2 treatment 3 infection 4 illness 5 reduction 6 depression 7 loneliness |
Assessment criteria - Read about exercise as a cure Descriptor: to participate by accepting factual descriptions Assessment criteria: - Read for general meaning and specific information -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - use context and meaning, |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 4 P:15 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
May, might, could, must, can't |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 9.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 9.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a wide range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the use of may, might, could, must and can’t for possibility and certainty. • Practise using may, might, could, must and can’t to express possibility and certainty in opinions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Refer students back to the text on pages 22–23 and ask: Do you think that swimming in cold water helps depression? Elicit a range of ideas, including the idea that it is possible it works Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:23 Students study the examples in pairs and complete the rules Point out that we don’t usually use can to express possibility Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 2 P:23 Allow students time to compare their answers in pairs before you check with the class. Discuss what helped students make their choices Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P:23 In a weaker class, do a few examples and discuss them before students continue in pairs. In a stronger class, ask students to provide not just one sentence for each item, but all the possible sentences for each item. |
Students study the modal forms in blue in sentences 1–5. Then choose the correct options in the rules. ANSWERS: a possibility b are c don’t Students сhoose the correct words ANSWERS: 1 might 4 must 2 can’t 5 might 3 may 6 might Students make sentences using the modal verbs in exercise 1 and the words in brackets ANSWERS: 1 He / She may / might / could have flu. 2 He must be tired. 3 They may / might / could be Mexican. 4 He / She can’t be angry. 5 She must be ill. 6 He may / might / could be a surgeon
|
Assessment criteria - Learn the use of may, might, could, must and can’t for possibility and certainty. Descriptor: study the modal forms in blue Assessment criteria: - Practise using may, might, could, must and can’t to express possibility and certainty in opinions. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - make sentences using the modal verbs |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 41 P:17 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Phrasal verbs |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.6.1 deduce meaning from context in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.3.3.1 explain and justify their own point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn phrasal verbs about health and lifestyle. • Read an eight-point health plan. • Listen to a conversation about living longer. . • Learn how to prepare for listening tasks |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write health and lifestyle on the board and elicit or teach the meaning. • Ask: How can your lifestyle affect your health? Elicit some ideas. • Ask: How can you change your lifestyle to make you healthier? Elicit a range of ideas Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:24 • Read the eight-point health plan together and see if any of the students’ ideas from the warm-up are mentioned. • Students match the phrasal verbs with their synonyms. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 3 P:24 Focus on the photos and the title Live longer, live better. Ask How old do you think the people are? What are they doing? Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Ex: 4 P:24 Look at the statements and tell students they should prepare to listen by following the advice in the study strategy. Give them some time to read the statements and underline key words. |
Students match the phrasal verbs in blue in The eight-point health plan with synonyms ANSWERS: 1 h 2 c 3 g 4 a 5 d 6f 7 b 8 e Students read the introduction to the Live longer, live better article. Then listen. What is a centenarian? ANSWERS: A centenarian is a person who is over a hundred years old
Students Listen again and write true or false ANSWERS: 1 True. 2 False. 3 False. 4 False. 5 True. 6 True.
|
Assessment criteria - Learn phrasal verbs about health and lifestyle. Descriptor: match the phrasal verbs in blue in Assessment criteria: - Read an eight-point health plan. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - read the introduction to the Live longer |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 3 P:16 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Past modals |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.4.1 understand most of the implied meaning in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.5.2.1 write independently about factual and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the use of must have, can’t have, could have and might have to speculate about the past. • Practise speculating about the past using past modals. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, ask students to remember how we express possibility in the present. Give them some scenarios and elicit sentences using may, might, could and must, can’t. For example, say: Joe’s doing his driving test after only three lessons. (He can’t be ready / must be very confident.) Look, it’s getting cloudy. (It may / might rain this afternoon.), etc Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Good job!
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:25 • Students read the sentences and answer the questions. • Check answers and remind students what past participles are Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 2 P:25 Remind students that some verbs have irregular past participles. Tell them to look up any they are not sure of in the irregular verbs list on page 126 of the Student’s Book
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Ex: 3 P:25 • Students complete the sentences with the correct modals. • Check answers by asking some students to read out their sentences and asking the class to say whether they are correct or not. |
Students sudy the modal forms in blue i ANSWERS: a must, can’t, could / might b have . Students rewrite the sentences in the past form ANSWERS: 1 They could have been seventy years old. 2 He can’t have been a hundred years old. He was still working. 3 She might have cut down on chocolate. 4 He must have worked out a lot. 5 She could have gone without dessert. 6 They might have taken up basketball Students choose the correct words ANSWERS: 1 might 2 must 3 could 4 can’t 5 must 6 can’t |
Assessment criteria - Learn the use of must have, can’t have, could have and might have to speculate about the past.
Descriptor: rewrite the sentences in the past form Assessment criteria: -Practise speculating about the past using past modals. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the correct modals |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 1 P:17 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Exchanging opinions p.26 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.5.1 recognize the opinion of the speaker(s) in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organize priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks 9.6.13.1 use a variety of modal forms for different functions and a limited number of past modal forms including should/ shouldn’t have to express regret and criticism on range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a conversation in which people exchange opinions. • Learn key phrases for exchanging opinions. • Learn how to use should, must, have to • Practise exchanging opinions.
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Ask where students come across advice about health. Elicit suggestions for how the government and schools can communicate with young people about health issues Lead – In Using drugs in sport undermines values like fair play and teamwork. When sportspeople use drugs, they not only might damage their own health, they also give sport a bad reputation and set a poor example to others. So-called 'performance-enhancing drugs' or 'performance and image-enhancing drugs' are banned in sports because they could give a sportsperson an unfair advantage over other competitors. |
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations .
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!”
|
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:26 Focus on the photo. Ask: What are Marie and Dean looking at? What do the posters show? Elicit ideas and then ask: Which poster do you prefer? Why? Elicit a range of opinions
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words inthe text. Ex: 2 P:26 n a stronger class, tell students to cover the dialogue and just listen. Play the CD once and ask whether Marie and Dean agree about the posters.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words inthe text. Ex: 3 P:26 • Ask students to find the key phrases in the dialogue and translate them into their own language. • Students practise the dialogue in pairs |
Students look at the posters. What are they campaigning against? ANSWERS: They are campaigning against drugs. Students listen to the dialogue. Which poster has got the clearest message? ANSWERS: Marie thinks the poster with the photo has a clearer message, but Dean prefers the poster with a more positive message Students listen to the key phrases. Which phrase expresses a strong opinion? Practise the dialogue ANSWERS: It should definitely … expresses a strong opinion.
|
Assessment criteria - Listen to a conversation in which people exchange opinions
Descriptor: -look at the posters. What are they campaigning against? Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for exchanging opinions. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - listen to the key phrases. |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 1 P:19 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reading. Health advice / A discussion essay |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9..3.7. 1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a wide increased range of general and curricular topics 9.4.6.1 recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer in extended texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary to do with nutrition and healthy eating. • Read a text about healthy eating. • Talk about diet and ways it could be improved. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, write An apple a day keeps the doctor away on the board. Explain that this is an old proverb and ask students what it means. Lead – In
When it comes to overall health and weight loss, there’s an excess of advice out there. Unfortunately, most of it is terrible, misguided, outdated and scientifically disproven.
|
The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas Students share with their opinions how to keep healthy life. |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!”
Good job! |
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:29 • Students match the definitions with the blue words. Allow students to use their dictionaries if necessary. • Check answers with the class Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text.
Ex: 2 P:29 Students listen and read. Ask the question to the whole clas
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 3 P:29 • Remind students to look carefully at the whole question, and watch out for little words or negatives that change the meaning of the sentences, e.g. question 5 (Which fats are not good for us?). • Students read the text again and answer the questions. |
Students match definitions 1–5 with the words in blue in the text. ANSWERS: 1 dairy 2 processed 3 tissues 4 evidence 5 fibre Students read and listen to the text. How does healthy eating affect our lives? ANSWERS: Healthy eating affects our physical and mental health. It can reduce the risk of serious illnesses such as heart disease, diabetes and possibly also mental illness, like depression. Eating regular meals can help with energy, as well as mood and memory Students read the text again and choose the correct answers ANSWERS: 1 a 2 c 3 b 4 b 5 a 6 b |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary to do with nutrition and healthy eating.
Descriptor: -match definitions with the words in blue in the text Assessment criteria: - Read a text about healthy eating. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - read and listen to the text. How does healthy eating affect our lives?
|
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 1 P:17 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative assessment for the 1st unit. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.2.1.1 Understand the main points in unsupported extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 9.4.1.1 Understand the main points in extended texts on a range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics 9.5.2.1 Write independently about factual and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.3.1.1 Use formal and informal registers in their talk on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - Recognise the main points in unsupported extended talk; -Identify specific information and detail in texts; -Write with moderate grammatical accuracy; -Use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax in a talk; |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. LISTENING Task. Listen to the dialogues. Six people talk about sport they like. Match each speaker with his or her reason, A-F. CD3 Tapescript1. 1. Speaker 1______ A) There are friendly people who go there, so it’s a good place to meet people. [1] 2. Speaker 2______ B) It’s a great way to keep fit. It’s better than going to a health club. [1] 3. Speaker 3______ C) There’s hardly anyone there and you can listen to the ocean as you do it. [1] 4. Speaker 4______ D) It’s a good exercise because you have to walk a lot. [1] 5. Speaker 5______ E) It’s really fun! But, it’s not as easy as it looks. [1] |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students listen to the dialogues and match each speaker with his or her reason ANSWERS: 1 A 2 C 3 F 4 E 5 B 6 D |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!”
Good job! |
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
6. Speaker 6______ F) I have no trouble to finding somewhere to play. [1]
READING Task. Read the text and identify in which paragraph (A-D) the writer does these things. 1. Establishes the emotional importance of baseball for fans. Paragraph ________[1] 2. The origins of baseball. Paragraph ________[1]
Task. Match the headings 3-6 with the paragraphs A-D 3. The rules of playing the game ______ [1] 4. The facilities ______ [1] 5. The changes happening to baseball ______ [1] 6. Part of people’s life ______ [1] WRITING Choose ONE of the topics and write Topic 1. Write an article to a newspaper describing the most popular hobby in Kazakhstan nowadays using appropriate grammar. Try to mention these questions: Topic 2. Write an article to a newspaper describing the recent Sport Olympiad where Kazakhstan sportsmen participated (in country or abroad) using appropriate grammar. Try to mention these questions: SPEAKING Task. You are given quetsions to speak about for 2-3 minutes. Before you speak you have one minute to think about what you are going to say and you can make notes if you wish. |
Students . Read the text and identify in which paragraph (A-D) the writer does these things. ANSWERS: 1 B 2 C 3 D 4 C 5 A 6 B Students Choose ONE of the topics and write ANSWERS: Students own answers
Students answer the questions ANSWERS: Students own answers
|
Assessment criteria - Study a model discussion essay.
Descriptor: read the model text and answer the questions. Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for a discussion essay. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - complete the key phrases. Then read the model text and check
|
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 3 P:19 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country. Exercise and sport |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.3.3.1 explain and justify their own point of view on a range of general and curricular topics 9.4.9.1 recognise inconsistencies in argument in extended texts on a range of general and curricular topics 9.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics.S3 explain and justify their own point of view on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a text about Kazakh sports stars. • Learn vocabulary connected to success in sports. • Learn the difference between could, was / were able to and managed to. • Write sentences about famous sportspeople in Kazakhstan. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Have a race to find which group can list the most Kazakh sportspeople in two minutes. • After two minutes, find out which group had the longest list and declare them the winner Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!”
Good job! |
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:28 • Draw students’ attention to the photos. Ask them if they can identify who they are. • In pairs, students discuss what they know about the sportspeople Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 2 P:28 • Tell students to listen to and read the text and see if it contains the information they talked about. • In a stronger class, play the recording with books closed to see how much they understand and for them to check whether the information they talked about is mentioned Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Ex: 3 P:28 • Focus students’ attention on the verbs. • Ask students to note down what they think the nouns are. • Then tell them to check their answers in the text and correct any they have got wrong. • Students underline the suffixes. • Check answers as a class. |
Students look at the photos. Who are these people? What do you know about them? ANSWERS: Kazhymukan Munaitpasov Denis Ten Zarina Diyas Students’ own answers Students read and listen to the text. Complete the sentences with the names of the people ANSWERS: 1 Zarina Diyas (Czech Republic) 2 Kazhymukan Munaitpasov 3 Denis Ten (shopping mall) 4 Kazhymukan Munaitpasov 5 Denis Ten 6 Zarina Diyas Students complete the table with nouns from the text. What suffixes are used to form the nouns? ANSWERS: 1 wrestling 2 performance 3 failure 4 achievement 5 competition 6 injury |
Assessment criteria - Read a text about Kazakh sports stars. Descriptor: discuss what they know about the sportspeople Assessment criteria: -Learn vocabulary connected to success in sports -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - read and listen to the text |
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 5 P:21 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |
,
Short term plan
|
Term 1 Unit 2 " Exercise and sport "
|
School: _____ |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: _____ |
||
|
Grade: 9 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL. Healthy eating |
||
|
Learning objectives |
9.4.6.1 recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer in extended texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 9.5.5.1 develop with support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary to do with nutrition and healthy eating. • Read a text about healthy eating. • Talk about diet and ways it could be improved
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Start
|
1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write An apple a day keeps the doctor away on the board. Explain that this is an old proverb and ask students what it means. • Elicit that the proverb is not meant literally, but suggests that if we eat healthy foods, like fruit, we will not get ill. Lead – In
There is one thing that we all have in common….. no matter where you live….. and that is the basic human need for good health and well-being. The links below will focus on eating healthy, maintaining fitness, proper diet, natural energy, and health safety issues. New content is added from time to time so keep checking back. Many of the posts below have had steady stream of daily visitors over the last several months. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students express their ideas Students discuss then write an essay |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!”
Good job! |
Pictures PPT |
|
Main part
|
Ex:1 P:29 • Students match the definitions with the blue words. Allow students to use their dictionaries if necessary. • Check answers with the class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text.
Ex: 2 P:29 • Students listen and read. Ask the question to the whole class
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students ue new words in the text. Ex: 3 P:29 Remind students to look carefully at the whole question, and watch out for little words or negatives that change the meaning of the sentences, e.g. question 5 (Which fats are not good for us?) |
Students match definitions 1–5 with the words in blue in the text. ANSWERS: 1 dairy 2 processed 3 tissues 4 evidence 5 fibre Students read and listen to the text. How does healthy eating affect our lives? ANSWERS: Healthy eating affects our physical and mental health. It can reduce the risk of serious illnesses such as heart disease, diabetes and possibly also mental illness, like depression. Eating regular meals can help with energy, as well as mood and memory Students read the text again and choose the correct answers ANSWERS: 1 a 2 c 3 b 4 b 5 a 6 b |
Assessment criteria - Study a model discussion essay.
Descriptor: read the model text and answer the questions. Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for a discussion essay. -Make CCQ questions
Descriptor: - complete the key phrases. Then read the model text and check
|
Cards Student’s book Worksheets Student’s book
|
|
End
|
Giving the hometask. Ex: 3 P:22 wb Self-reflection |
Peer-assessment. Two stars and a wish.
Maybe you could ... |
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster Success |

шағым қалдыра аласыз



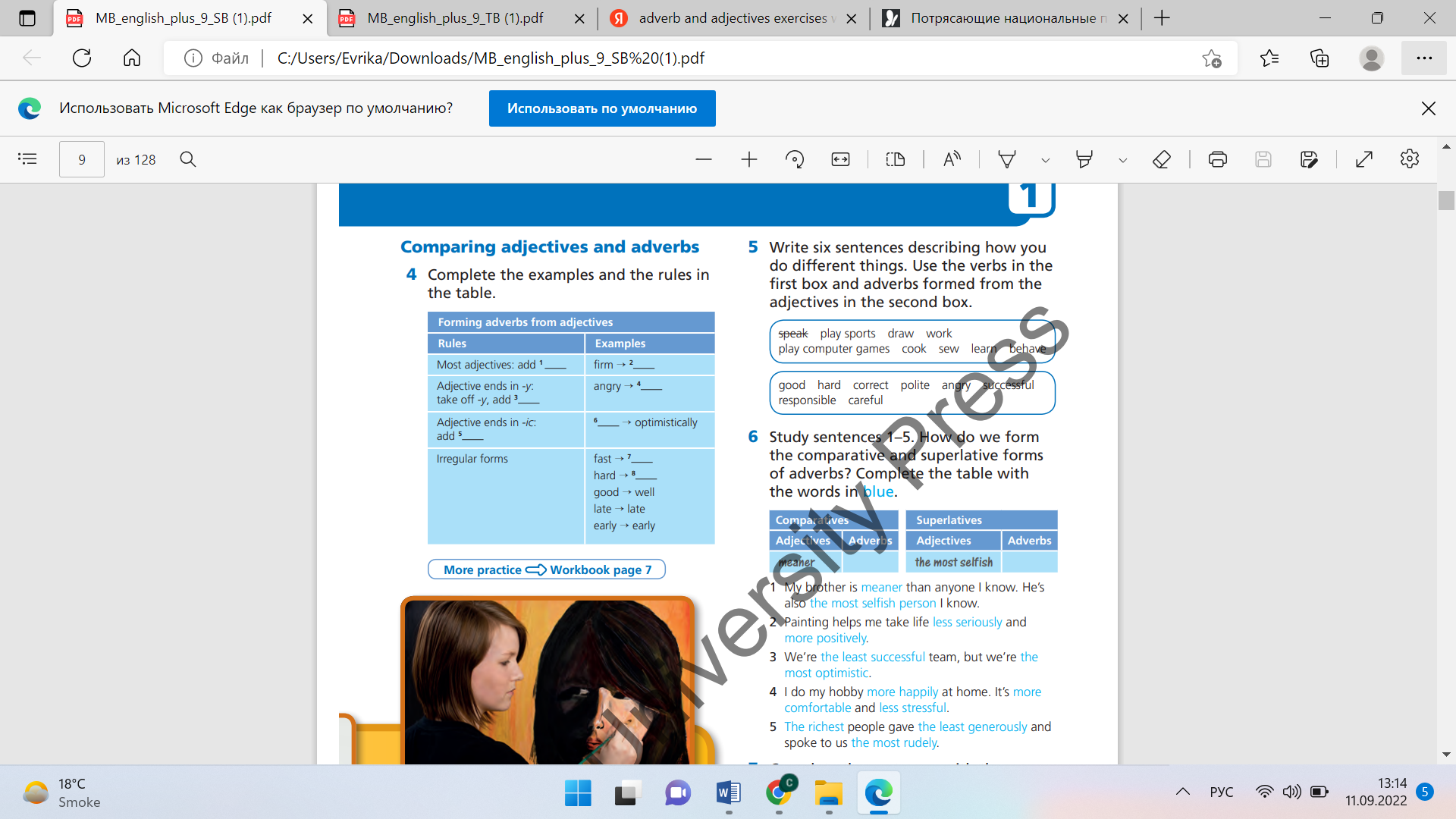
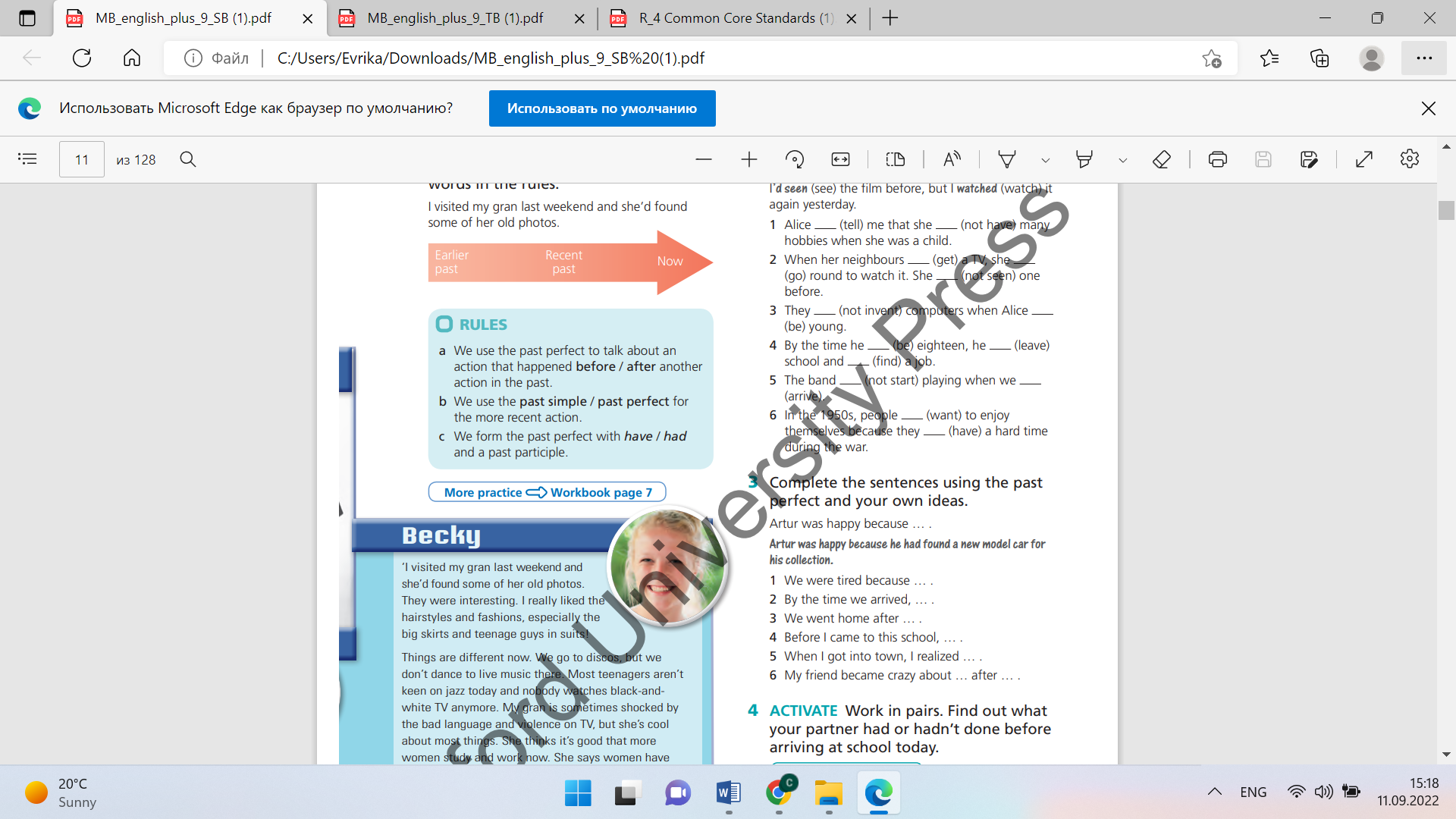
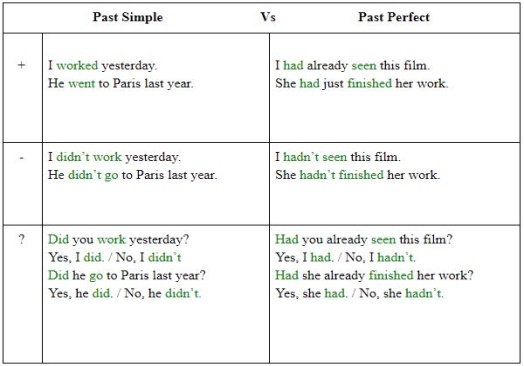
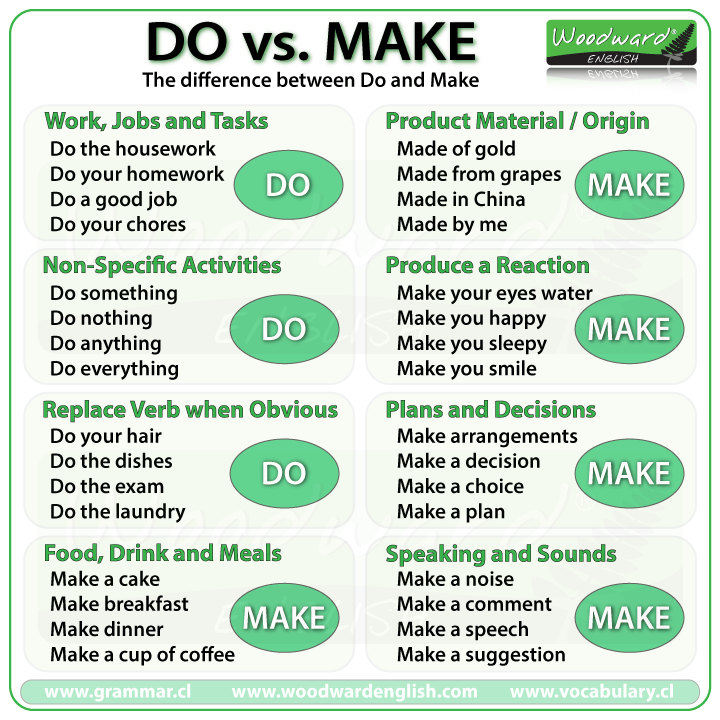




 1 Why
are team sports good for you? 2 What are the health benefits of
sport and exercise?
1 Why
are team sports good for you? 2 What are the health benefits of
sport and exercise?