Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 49 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Sherlock Holmes: The Blue Diamond |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 7.4.4.1 read independently a limited range of short simple fiction and non-fiction texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading. • Practise asking questions about stories |
||
|
Value links |
Family – Family values are moral and ethical principles of typical family life, including sacrificing for loved ones, putting your loved ones first, and keeping your loved ones at the centre of your thoughts and actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask students what they know about the Sherlock Holmes stories. Write their ideas on the board and include these details: • Sherlock Holmes is a private detective. • Dr Watson is his assistant. • They solve crimes in London at the end of the 19th century. • Famous stories include Hound of the Baskervilles and Sign of Four. Lead - In
The fate of the allied forces lies in the hands of Joanna and the Watsons in the next Daughter of Sherlock Holmes mystery from USA Today bestselling author Leonard Goldberg. |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
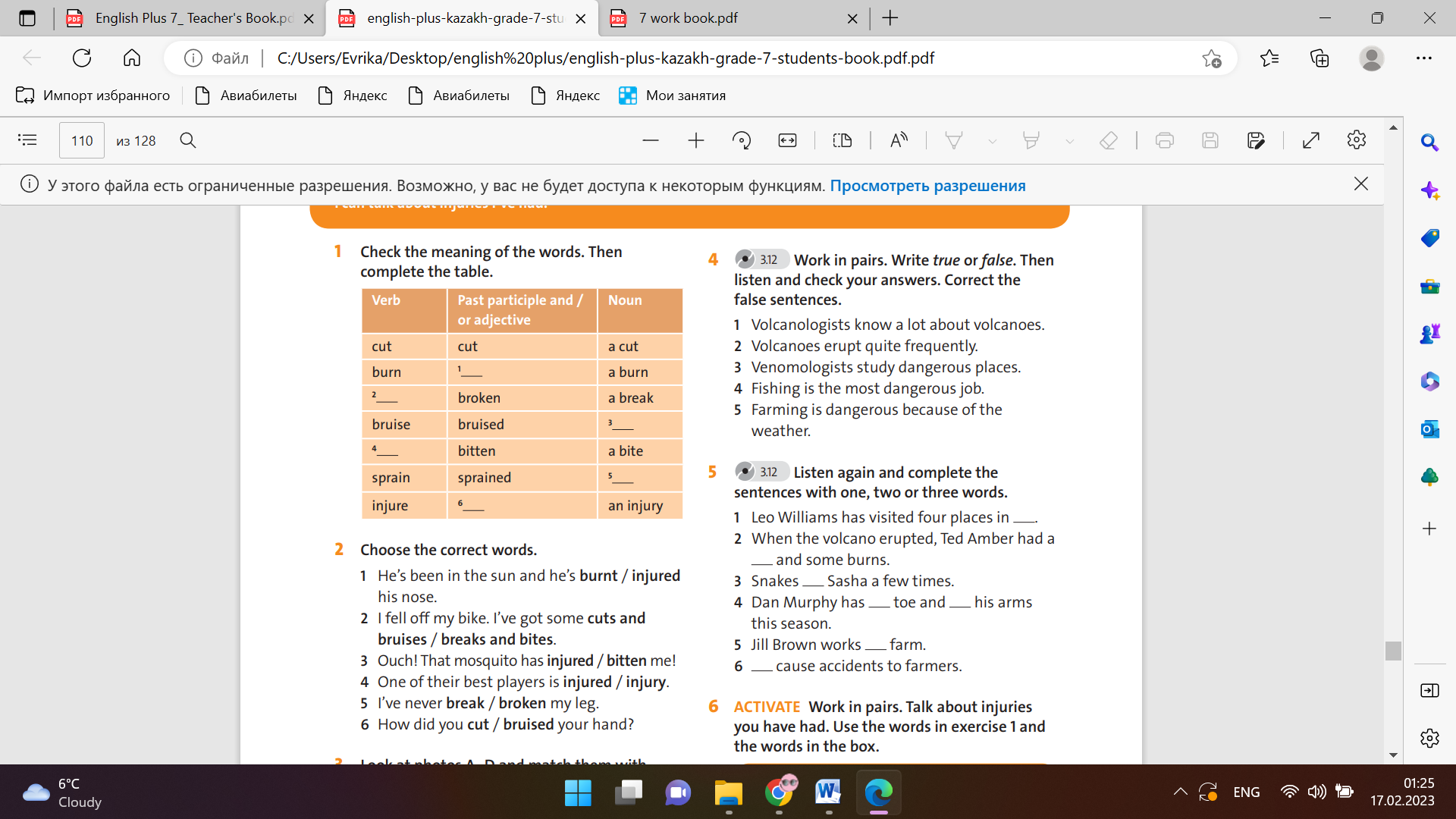
Ex:1 P:120 • Tell students to look at the pictures and make a list of things they can see. Start the list by writing these items on the board: a goose, a blue diamond, an advertisement • After three minutes, ask students for their ideas and write them on the board. • Go through the pictures with students identifying the main elements, e.g. picture A – goose, man wearing a suit, etc. • Tell students to read all the story sections and match the sections to the pictures Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 120 Ask the class which section is the first and explain their reasoning. Use prompt questions if necessary, e.g. What is main event in the story? When does the main event occur? Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 120 • Explain the task. Tell students to pay attention to the use of ‘a’ (for the first time an element of the story is introduced) and ‘the’ (when we already know who or what is being referred to). In a stronger class, let students work individually. Give them about five minutes to put the pictures in order. In a weaker class, put the students in pairs and monitor their progress, helping out if necessary. |
Students read the story and match them to the pictures ANSWERS 1 E 2 H 3 F 4 G 5 C . 6 A 7 D 8 B Students look at the again. Which section do you think is the start of the story ANSWERS The start of the story is section 3 – the blue diamond is missing. The end of the story is section 6 – Ryder admits he stole it. Students read the section again and put them in order to make the story ANSWERS . 1 section 3 2 section 5 3 section 2 4 section 4 5 section 1 6 section 8 7 section 7 8 section 6 |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading Descriptor: - read the story and match them to the pictures Assessment criteria: - Practise asking questions about stories. Descriptor: - look at the again. Which section do you think is the start of the story -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 88 WB |
|
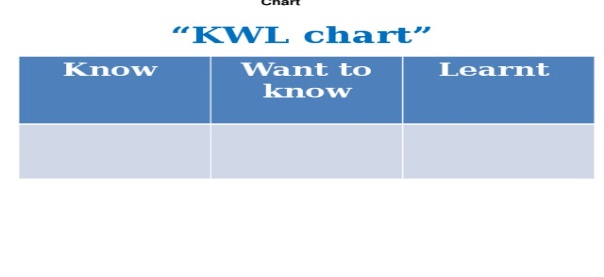
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 50 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talk about it |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 7.3.3.1 give an opinion at sentence and discourse level on an increasing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading. • Practise asking questions about stories. |
||
|
Value links |
Loyalty – Loyalty might be a core personal value to you if you highly prize friends that are reliable and trustworthy. You might put your friends or chosen family first, always being there for them when they need you. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask students what they know about the Sherlock Holmes stories. Write their ideas on the board and include these details: • Sherlock Holmes is a private detective. • Dr Watson is his assistant. • They solve crimes in London at the end of the 19th century. • Famous stories include Hound of the Baskervilles and Sign of Four. Lead - In
The fate of the allied forces lies in the hands of Joanna and the Watsons in the next Daughter of Sherlock Holmes mystery from USA Today bestselling author Leonard Goldberg. |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:4 P:121 • Put student in pairs. Give students time to make a note of who the people are, what happened at each place, and events related to the verbs and nouns. • When students are ready, without looking at p121, students take turns to tell the story. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 6 P: 121 • Tell students to listen to James Ryder and choose the correct words to complete the sentences. • Play the recording. • Go through the answers with the class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 7 P: 121 • Explain the task. Then play the recording. • Discuss the ending with students. |
Students use the pictures and the words in the boxes to tell the story to your partner. ANSWERS Students’ own answers. Students listen to James Ryder talk about his story. ANSWERS 1 Horner 2 sister’s 3 Maudsley 4 geese 5 black 6 Maudsley’s 7 didn’t find 8 two 9 would not Students listen to the end of the story. ANSWERS Students’ own answers. |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading Descriptor: - read the story and match them to the pictures Assessment criteria: - Practise asking questions about stories. Descriptor: - look at the again. Which section do you think is the start of the story -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 88 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 51 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The Lost World |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.4.1 read independently a limited range of short simple fiction and non-fiction texts 6.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading. • Practise asking questions about stories. |
||
|
Value links |
Fairness – If you value fairness, you might be highly sensitive to situations at school or in the workplace where a teacher or a peer has exhibited favoritism or allowed someone to get away with living by a different set of rules to everyone else. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Ask students to look at the book cover and characters in the pictures and guess what the story is about Lead - In
In this story, Edward Malone is a young journalist who is sent to interview the bizarre claims made by Professor George Edward Challenger, who claims to have made an exciting discovery in South America |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:122 • Tell students to work individually and write adjectives they can use to describe the six characters in the pictures, e.g. A – young, pretty, well-dressed. Students write the notes on the note pad. Tell students not to write the name of the characters. • Put students in pairs. Tell them to share their adjectives and ask their partner which character they think the adjectives refer to. Circulate and monitor. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 122 • Explain the task. Make sure students know zoologist (someone who studies animals). In a weaker class, do the first description with the whole class.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 122 • Explain the task. Ask a student to read the first quote and the rest of the class to guess who it is. • Make sure they use the clues in the quote. |
Students think of adjectives to describe the six people in the pictures. ANSWERS Students’ own answers. Students read the descriptions of some of the characters from the book. ANSWERS 1 D 2 A 3 E 4 F 5 C 6 B Students look at the descriptions and the pictures again. Which characters say these things, do you think ANSWERS 1 Gladys Hungerton 2 Ned Malone 3 Mr McArdle 4 Lord John Roxton 5 Professor Summerlee |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading Descriptor: - to describe the six people in the pictures. Assessment criteria: - Practise asking questions about stories. Descriptor: - look at the again. Which section do you think is the start of the story -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 88 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 52 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Date: |
16.01.2024 |
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The Last of the Mohicans |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 7.4.4.1 read independently a limited range of short simple fiction and non-fiction texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading. • Practise asking questions about stories. |
||
|
Value links |
Generosity – This may be a core value of yours if you cherish people who will give their time and resources to people in need. You may consider yourself to be a generous person if you find joy and meaning in giving to others. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to look at the book cover and characters in the pictures and guess what the story is about. Lead - In
Last of the Mohicans tells the seminal story of a race on the brink of disappearance due to the inexorable push of civilization into the wilderness of the New World. It's a tale that will touch readers of every age with both its timeless realization of an important historical period-and with its powerful action and adventure! |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:124 • Explain the task. Tell the students to use the visual information in the book cover and pictures • to answer the questions. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 124 • Draw students’ attention to the map and ask which part of the world it shows. Explain the task. • Go through the answers.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 124 • Ask the students what sort of hairstyles and clothes Europeans and Native Americans had. • Explain the task. • Go through the answers. |
Students look at the front cover of the book and the pictures of the characters. Choose the correct words to complete the sentences. ANSWERS 1 South 2 1757 3 French and the British 4 before 5 tribes 6 land 7 French 8 British Students the Last of the Mohicans takes place in North America. Label the map of North America today ANSWERS 1 Canada 2 United States of America 3 Mexico 4 Lake Champlain 5 udson River Students look at some of the characters in the story. Put the characters into the group they belong to. ANSWERS Europeans Alice Montcalm Cora Munro American Indian Chingachgook Magua Uncas Tamenund |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading Descriptor: - Choose the correct words to complete the sentences. Assessment criteria: - Practise asking questions about stories. Descriptor: - Label the map of North America today -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 88 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 53 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Date: |
17.01.2024 |
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The Last of the Mohicans |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 7.3.3.1 give an opinion at sentence and discourse level on an increasing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading. • Practise asking questions about stories. |
||
|
Value links |
Integrity – Integrity is the quality of having strong moral principles. So, a person with integrity will always act with honesty and adhere to their own moral code regardless of what others do. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to look at the book cover and characters in the pictures and guess what the story is about. Lead - In
Last of the Mohicans tells the seminal story of a race on the brink of disappearance due to the inexorable push of civilization into the wilderness of the New World. It's a tale that will touch readers of every age with both its timeless realization of an important historical period-and with its powerful action and adventure! |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:4 P:125 • Ask students to think of as many names of Native American tribes as they can, e.g. Comanche, Sioux, Cheyenne. Explain the task. • Go through the answers. Ask students to correct any false sentences. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 5 P: 125 • Explain the task. • Go through the answers.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 6 P: 125 • Put students in pairs. If possible. draw or describe an example of a totem. • Explain the task. If internet is accessible, ask students to do online research to answer the questions. |
Students read about Ojibwa tribe. Are the sentences true or false ANSWERS 1 false 2 false 3 true 4 true 5 false 6 true 7 true 8 false Students put the words from the story into the correct category in the table. ANSWERS European American Indian Army tribe Fort tomahawk Officer moccasin Church totem Hymn Great spirit King warrior General magic Feathers Chief Canoe Students ask and answer the questions about American Indians with your partner ANSWERS 1 A totem is an animal or natural
object that is a special symbol of the community. They are
important to American 2 The Great Spirit is a universal force or supreme being. 3 Tribal chief. 4 They wear feathers in their headdress. 5 A tomahawk is a type of axe. |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading Descriptor: - read about Ojibwa tribe. Are the sentences true or false Assessment criteria: - Practise asking questions about stories. Descriptor: - put the words from the story into the correct category in the table. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 88 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 55 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Nicholas Nickleby |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 7.4.4.1 read independently a limited range of short simple fiction and non-fiction texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - apply appropriate descriptive language to create different types of (grade-appropriate) texts and speeches -identify the differences between fiction and non-fiction |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to look at the book cover and characters in the pictures and guess what the story is about. Lead - In
Nicholas Nickleby is the tale of a young man whose father has died leaving his family penniless. Nicholas must find a job to support his mother and sister, Kate. The family turns for help to their uncle, Ralph Nickleby, a ruthless businessman, who has taken a dislike to his relatives. Nicholas, aided by many diverse characters, must protect his family from his uncle’s machinations. |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P: 88 WB • Explain the task. Tell students before complete the paragraph with the words below. Then read the first extract. • Students work in pairs to complete the paragraph with the words in the box. • Read through the first extract together and check for understanding. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 88 Wb • Tell students to read the first extract, ask to work individually to choose the correct words. • Check answers by asking individual students to read out their sentences
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 4 P: 88 Wb • Explain students should read the second extract then write sentences are true or false. • Check answers by asking students to read out their answers, making sure that they read them correctly. |
Students complete the paragraph with the words in the box and read the first extract. ANSWERS 1 dies 2 uncle 3 like 4 boarding 5 better 6 travels Students read the first extract then choose the correct words ANSWERS 1 doesn’t look 2 isn’t 3 animals 4 money 5 little Students read the second extract then write true or false ANSWERS 1 f 2 t 3 f 4 t 5 f 6 t |
Assessment criteria - apply appropriate descriptive language to create different types of (grade-appropriate) texts and speeches Descriptor: - complete the paragraph with the words in the box - read the first extract Assessment criteria: - identify the differences between fiction and non-fiction Descriptor: - read the second extract - write true or false -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 88 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 56 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Romeo and Juliet |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 7.4.4.1 read independently a limited range of short simple fiction and non-fiction texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - apply appropriate descriptive language to create different types of (grade-appropriate) texts and speeches -identify the differences between fiction and non-fiction |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask students what they know about the Romeo and Juliet stories. Write their ideas on the board and include these details: • Romeo and Juliet belongs to a tradition of tragic romances Lead - In
The story of Romeo and Juliet has everything that a reader could want. Like many of Shakespeare’s works, it has comedy and tragedy, but it also has love, family, duals, good and evil. |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P: 90 WB • Explain the task. Tell students before complete the paragraph with the words below. Then read the first extract. • Students work in pairs to complete the paragraph with the words in the box. • Read through the first extract together and check for understanding. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 90 Wb • Explain students should read the first extract then write sentences are true or false. • Check answers by asking students to read out their answers, making sure that they read them correctly.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 4 P: 90 Wb • Explain students should read the second extract then complete the sentences with one word • Check answers by asking students to read out their answers, making sure that they read them correctly. |
Students complete the paragraph with the words in the box and read the first extract. ANSWERS 1 families 2 enemies 3 fight 4 party 5 marry 6 man 7 masks Students read the first extract then write true or false ANSWERS 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 t 5 t 6 f 7 t Students read the second extract then complete the sentences with one word. ANSWERS 1 mother 2 enemy 3 never 4 wife 5 hated |
Assessment criteria - apply appropriate descriptive language to create different types of (grade-appropriate) texts and speeches Descriptor: - complete the paragraph with the words in the box - read the first extract Assessment criteria: - identify the differences between fiction and non-fiction Descriptor: - read the second extract - complete the sentences with one word -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 88 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 57 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Emma |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 7.4.4.1 read independently a limited range of short simple fiction and non-fiction texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - apply appropriate descriptive language to create different types of (grade-appropriate) texts and speeches -identify the differences between fiction and non-fiction |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to look at the book cover and characters in the pictures and guess what the story is about. Lead - In
The young beauty Emma Woodhouse believes that she is well versed in human characters and therefore can play the role of a matchmaker for her friends and young people. She dissuades her friend, the modest girl Harriet Smith, from marrying a farmer and elects a vicar for her , Mr. Elton. However, he falls in love with Emma herself. |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P: 91 WB • Explain students read the first extract then write sentences are true or false. • Check answers by asking students to read out their answers, making sure that they read them correctly. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 91 Wb • Tell students to read the second extract, ask to work individually to choose the correct words. • Check answers by asking individual students to read out their sentences
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 4 P: 91 Wb • Explain students read the second extract again then answer the question • Check answers by asking students to read out their answers, making sure that they read them correctly. |
Students read the first extract then write true or false ANSWERS 1 t 2 f 3 t 4 f 5 t Students read the second extract then choose the correct words ANSWERS 1 doesn’t have 2 is 3 talks 4 clergyman 5 Elton 6 isn’t Students read the second extract again then answer the question ANSWERS 1 she was friendly and kind 2 they met Mr Martin 3 she planned lots of ways for them to meet 4 started to visit |
Assessment criteria - apply appropriate descriptive language to create different types of (grade-appropriate) texts and speeches Descriptor: - complete the paragraph with the words in the box - read the first extract Assessment criteria: - identify the differences between fiction and non-fiction Descriptor: - read the second extract - write true or false -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 88 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Entertainment and media |
Lesson 58 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Skills and people |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 7.6.1.1 begin to use basic abstract nouns and compound nouns and noun phrases describing times and location on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.2.3.1 understand more complex supported questions on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for skills and people. • Do a quiz on talented people. • Learn how to learn words in groups. • Learn phrases for expressing knowledge. |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the word clever on the board and elicit the meaning. • Name a few famous artists, musicians or scientists and ask students if these people are / were clever. • Ask students to name some more clever people. Lead - In
In Rich Dad Poor Dad, Kiyosaki names the following seven skills as being prime skills to help you become wealthy |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:64 • Look at the title of the quiz and elicit that it is going to be about famous people who showed their talents when they were children. • Explain that this is a general knowledge quiz. Students should work in pairs. • After checking answers, find out who got the most correct answers. • In a stronger class, ask students if they know anything else about the people in the quiz. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 64 • Focus on the table with the class, then ask students to read the quiz to find the missing words to complete the table. • Play the CD so that students can check their answers. Drill the pronunciation of the new words if necessary. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 64 • Point out that it is a good idea to learn new vocabulary in groups. • Focus on the example, then ask students to work individually to add the related words. To extend the activity, refer students back to the table in exercise 2 and elicit the activity nouns associated with those words. • In a stronger class, you could also ask students to look up more words to add to the list and write each form in their notebooks Ex: 3 P: 64 • Students complete the phrases. Check understanding by asking students to translate them into their own language. In a weaker class, say some names of topics or famous people and ask students to respond by using the key phrases |
Students work in pairs. Do the Clever kids quiz ANSWERS 1 a Salvador Dalí 2 b Henry Ford 3 b karate 4 a prince 5 c Oliver Twist 6 a lens 7 c Chinese 8 b The X factor Students complete the table with verbs and nouns from the Clever kids quiz. Then listen and check. ANSWERS 1 composer 2 swimmer 3 play 4 writer 5 winner 6 program 7 singer Students complete the table with related words. Then listen and check. ANSWERS 1 actor 4 dancer 2 acting 5 cook 3 dance 6 cooking Students use key phrases in the box. ANSWERS 1 a bit, a lot 2 anything, much |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for skills and people. - Do a quiz on talented people. Descriptor: - work in pairs. Do the Clever kids quiz. Assessment criteria: - Learn how to learn words in groups Descriptor: - complete the table with related words. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 48 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit of a long term plan: Entertainment and media |
Lesson 59 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Date: |
23.01.2024 |
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Whizz-kids |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.1.1 understand the main points in a growing range of short, simple texts on general and curricular topics 7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at discourse level on a range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about prodigies. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Talk about topics raised in the text |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students back to the Clever Kids quiz on page 49. Ask students to think about the people in the quiz. Ask what links all the people mentioned (they were all exceptionally talented from a very early age). • Ask students if they know anyone like this, or whether they can name any other famous prodigies. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:66 • Focus on the title of the text and the photo. Elicit or explain the meaning of prodigy. • Ask students what kinds of things prodigies can do. Accept all ideas at this stage Background In British schools, children who are recognized as ‘gifted’ or exceptionally talented are sometimes given extra lessons by their school, or may attend special classes for similarly gifted children after school or during school holidays. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 66 • Tell students to read through the summaries. Clarify that only one of these fits the text correctly. • Play the CD. Students, read, listen and choose the correct summary. In a stronger class, ask them to explain their choice in English. Ex: 3 P: 66 • After closely reading the text, students complete the sentences. Ex: 4 P: 66 • Students read the text again and complete the phrases with the correct words. • In a weaker class, check understanding of the words and phrases, for example, by asking students to translate them. In a stronger class, ask students to put the phrases into a sentence to show they have understood. • Explain that these phrases are very common and useful to learn. In a stronger class, elicit or explain some other related phrases, for example, set a record, take a decision |
Students look at photo and discuss about what does prodigy mean ANSWERS A prodigy is a child with incredible talents. Students read and listen to the text. Then choose the correct summary ANSWERS a) Students read the text again and complete the sentences with one, two or three words. ANSWERS 1 of twelve 2 children 3 university at seven 4 they help 5 160 Students find and complete the phrases with the verbs in the box. ANSWERS 1 break 2 take 3 take 4 make 5 make |
Assessment criteria - Read about prodigies. Descriptor: - look at photo and discuss about what does prodigy mean Assessment criteria: - Read for general meaning and specific information Descriptor: - read and listen to the text. Then choose the correct summary -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 48 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit of a long term plan: Entertainment and media |
Lesson 56 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Date: |
24.01.2024 |
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
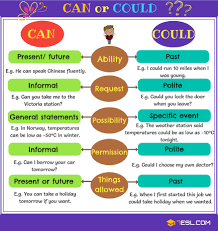
Ability: can, could. Questions with How...? |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.5.1 use questions including questions with whose, how often , how long and a growing range of tag questions on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.6.13.1 use modal forms including mustn’t (prohibition), need (necessity) should (for advice) on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn can and could for ability in the present and past. • Learn about questions using How ...? • Practise asking and answering questions using can, could and How ...? |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students back to the reading text on page 50. Read the first sentence with the class and ask which verb refers to ability (could). • Elicit or explain that we use can to talk about ability in the present, and could to talk about ability in the past. Lead - In Pupils watch video about differences can and could
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students watch video and say different words from the differences can and could |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet https://youtu.be/BBq0hWsrC6o Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:67 • Explain that students are going to focus on can and could in the context of the text LANGUAGE NOTE We use can for ability in the present and could for ability in the past: I can swim now. I could swim when I was three. NOT I can swim when I was three. The verbs can and could do not add -s after he, she and it: He can dance. NOT He cans dance. After can and could, we use the infinitive without to: I can speak English. NOT I can to speak English. Point out that the negative forms are can’t and couldn’t: He can’t paint. NOT He doesn’t can paint Ex: 2 P: • Students choose the correct words to complete the rules. In a weaker class, do this as a class activity for support. • In a stronger class, ask for an example of what students could / couldn’t do in the past and what they can / can’t do now. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 67 • Tell students to read all the sentences carefully before they start to complete them to check they understand the context. They should think about whether the sentences refer to the present or the past. Ex: 4 P: 67 • Once students have matched the question halves, check answers and ask students to ask and answer pairs. |
Students complete the sentences. ANSWERS 1 can’t do 2 could 3 couldn’t Students choose the correct words ANSWERS 1 without 2 can 3 can’t 4 present 5 past Students complete the sentences with the words in the box. ANSWERS 1 could 2 couldn’t 3 can 4 couldn’t 5 can’t Students match and make questions. Then ask and answer questions with a partner. ANSWERS 1 e How far can you swim? 2 f How strict is your teacher? 3 b How often do you go to the cinema? 4 g How intelligent are your friends? 5 a How many people are in your class? 6 c How much cola do you drink? 7 d How tall are you? |
Assessment criteria - Learn can and could for ability in the present and past. Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the can and could Assessment criteria: - Learn about questions using How ...? Descriptor: - match and make questions. Then ask and answer questions -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 49 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Entertainment and media |
Lesson 61 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Adjectives: qualities |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.C6 organize and present information clearly to others 7.6.3.1 use common participles as adjectives and order adjectives correctly in front of nouns on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn adjectives used to describe animals. • Listen to a conversation about animals. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students to work in pairs and write down as many animals in English as they can in two minutes. • Elicit names of animals from the class and write them on the board. . • Point to one of the words and ask students what they know about this animal. Elicit some adjectives to describe it and write them on the board. Do the same with two or three more of the animal words. • Ask students which animals they think are clever. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:68 • Focus on the example. Ask students to work in pairs to find pairs of adjectives . • In a weaker class, check that students understand all the adjectives, for example by asking them to translate the words into their own language. In a stronger class, encourage students to put the words into a sentence to show understanding. • Model and drill the pronunciation of any new adjectives. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 68 • Read the instructions with the class. Check that students understand the animal words, and check that they understand the difference between not very, quite, very and really. • Students prepare their sentences in pairs. Ask students to report back to the class on how they described the animals
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 68 • Explain to students that they are going to listen to two people talking about animals. Before you play the CD, look at the photos and identify the animal in each one. • Tell students that there is one extra animal in the conversation which is not pictured. |
Students find pairs of opposite adjectives ANSWERS aggressive – peaceful common – rare domesticated – wild fast – slow heavy – light intelligent – stupid Students work in pairs. Write sentences about each animal using three adjectives from exercise 1 ANSWERS Students’ own answers Students listen to Sophie and Joe talking about animals ANSWERS Monkeys |
Assessment criteria - Learn adjectives used to describe animals Descriptor: - find pairs of opposite adjectives Assessment criteria: - Listen to a conversation about animals. Descriptor: - listen to Sophie and Joe talking about animals -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 50 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Entertainment and media |
Lesson 62 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Comparative and Superlative adjectives |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics, and some curricular topics 7.6.3.1 use common participles as adjectives and order adjectives correctly in front of nouns on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.5.2.1 write with some support about real and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a limited range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn comparative and superlative forms of adjectives. • Make sentences using comparative and superlative adjectives. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the words elephant and monkey on the board. • Write the adjectives big and intelligent on the board and ask students how they can compare the two animals using the adjectives on the board. • Refer students back to exercise 5 on page 52 and ask them to find examples of how we can compare things in English. Lead – In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:69 • Students copy the table and complete the missing forms. Point out that only regular forms are gapped. LANGUAGE NOTE We do not use more and most with short adjectives: An elephant is bigger than a monkey. NOT An elephant is more big than a monkey. Some adjectives are irregular, for example, bad, worse, worst. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 69 • Refer students back to the table in exercise 1 and to the example sentences. Allow students time to look at the forms, then ask them to complete the rules.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 69 • Explain to students that there are spelling rules for forming regular comparative and superlative adjectives, which are summarized in the table. • Ask students to apply what they have covered and to complete the rules. In a weaker class, ask them to do this in pairs. |
Students complete the table with comparative and superlative adjectives ANSWERS 1 faster 4 more artistic 2 bigger 5 the most intelligent 3 noisiest Students study the example sentences and the table in exercise 1 ANSWERS 1 than 2 the Students study the table in exercise 1 again. Complete the spelling rules and add examples. ANSWERS 1 fastest 2 rarer 3 bigger |
Assessment criteria - Learn comparative and superlative forms of adjectives Descriptor: - complete the table with comparative and superlative adjectives Assessment criteria: - Make sentences using comparative and superlative adjectives. Descriptor: - study the example sentences and the table -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 51 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Entertainment and media |
Lesson 63 |
||
|
Teacher name: Kaltaeva D.A. |
|
||
|
Date: 02.02.2024 |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 «Г» |
Number present: 12 |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Choosing a present |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.13.1 use modal forms including mustn’t (prohibition), need (necessity) should (for advice) on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a conversation about comparing ideas for a present. • Learn key phrases for choosing a present. • Learn how to use should and must. • Practise comparing ideas for a present. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they ever buy presents. Ask them when and where they buy them. • Ask them to think about the last present they bought and say why they chose that present. • Ask if they ever buy a present with another person. Lead - In
If kids are big enough to understand Christmas and presents, let them choose what they like. This way you can be sure they get something they really want. You will avoid long walks around the shops choosing Christmas present when you have no clue what’s “in” and what could be boring for them. |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:70 • Discuss the questions as a class. Find out how many artists students can name and who the most popular artists are. • In a stronger class, encourage them to describe briefly the artist and their work using adjectives, and comparative and superlative forms from the previous lessons in the unit. • Explain that Shaun and Gemma are looking at posters of works by famous artists. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 70 • Play the CD. Students read and listen to find out the answer to the question in the instructions. In a stronger class, encourage students to listen with books closed. • Ask students if Gemma agrees with Shaun about the posters
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 70 • Read through the key phrases with the class and the questions below each one. • Ask students to listen to the key phrases and find them in the dialogue. They answer the questions based on their understanding of the dialogue. • Play the CD. Students listen and answer the questions. In a weaker class, it may help to write the key phrases on the board, underlining the word(s) they need to define. Then, using the printed dialogue for support, help students work out what is being referred to in each case. |
Students discuss who are the most famous artists from your country? Have you got any posters of their work. ANSWERS Student’s own answers Students listen to the dialogue. Does Gemma agree with Shaun about the posters ANSWERS Yes, she does. Students listen to the key phrases. Then answer the question. ANSWERS 1 Gemma’s dad 2 van Gogh 3 Starry Night 4 the poster of the painting by Picasso |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a conversation about comparing ideas for a present. Descriptor: -listen to the dialogue. Does Gemma agree with Shaun about the posters Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for choosing a present Descriptor: - listen to the key phrases. Then answer the question. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 51 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Entertainment and media |
Lesson 64 |
||
|
Teacher name: Kaltaeva D.A. |
|
||
|
Date: 02.02.2024 |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 «Ж» |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Biographies |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with some support on a growing range of general and curricular topics 6.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 6.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model text. • Learn key phrases to link events in a biography. • Write a biography of a famous writer and artist. |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, write the word biography on the board and elicit the meaning. • Ask students if they ever read biographies of famous people. • Ask what kinds of information you usually find in a biography. Elicit ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 71 • Read the title of the text and look at the picture with the class. Ask students if they have heard of this writer, and whether they can name any of her books (for example, Emma, Pride and Prejudice, Sense and Sensibility, Mansfield Park). • Students read the text, then match four of the five headings to the paragraphs. Tell them not to worry about the blue words at this stage • In a weaker class, demonstrate how to find clues in the text. In a stronger class, ask students which parts of the text helped them identify which heading to choose Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:71 • Focus students on the blue words in the text and explain that they are used to convey the time expression in a sentence. • Students match the sentences from the text. In a weaker class, ask them to do this in pairs. • In a stronger class, check answers by asking individuals to read out the complete sentence. Ex: 3 P:71 • Read the task with the class and refer students to the biographical information and the book covers. • Students use the questions to make notes and plan their biographies individually. • Students write their biographies. This can be set for homework. • Tell students to check their work, and check they have used comparative and superlative forms, and time expressions correctly |
Students read the model text. Then match headings with paragraphs. There is one heading that you don’t need. ANSWERS: 1 B 2 C 4 D 5 A Students study the model text and find the time expressions in blue. Then match. ANSWERS: 1 e 2 d 3 f 4 c 5 a 6 b Students write a biography. Use the notes on Herge or detail about another writer you admire. ANSWERS: 1 She was born in Warsaw. 2 A year later, he got married. 3 She lived in Paris for five years. 4 By the age of twenty, he was studying at university. 5 She died in 1824 |
Assessment criteria - Study a model text. Descriptor: - read the model text. Then match headings with paragraphs. There is one heading that you don’t need. Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases to link events in a biography Descriptor: - study the model text and find the time expressions in blue. Then match. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 53 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Entertainment and media |
Lesson 65 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Entertainment and media |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.3.1 use common participles as adjectives and order adjectives correctly in front of nouns on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.6.17.1 use subordinate clauses following think know believe hope, say , tell use subordinate clauses following sure, certain; use defining relative clauses with which who that where on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with some support on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about films. • Learn about adjectives ending in -ing and -ed. • Learn and practise using relative clauses. • Write a film review. |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, divide students into pairs and ask them to tell each other about their favourite film. Encourage them to give reasons for their choice. • Ask a few students to describe their partner’s preferences |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 75 • Focus students’ attention on the words in the box. Encourage them to try to guess the meaning of all the words before they look them up in a dictionary. • Ask students to name a film for each genre. • Model and drill the pronunciation of the words Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:75 • Play the recording and ask students to listen and read the text. • Allow students time to read the questions. In a weaker class, pre-teach the following words and phrases: relationship, based on, star (verb), brave and recommend. • Ask them to read the text again and answer the questions. • Check answers as a class Ex: 3 P:75 • Draw students’ attention to the words in blue. Ask them to find the word or phrase that the each blue word refers to in the text and underline them (The Old Man and the Sea, shepherd, town, actors, film, anyone). • Students complete the rules and check their answers. |
Students work in pairs. Check the meaning of these words in a dictionary. Then write the name of a film for each genre. ANSWERS: Student’s own answers. Students read and listen to the film review. Answer the question. ANSWERS: 1 The title of the film is The Old Man. 2 It’s a drama. 3 It’s about family relationships and the relationship between people and nature. 4 Yes, it’s based on a book by the American writer Ernest Hemingway. 5 It’s set in Kazakhstan 6 Yerbulat Toguzakov plays the main role. 7 Her favourite character is Kassym. She likes him because he is brave. 8 She thinks that it is a great film. She would recommend it to anyone who likes adventure stories Students look at the words in blue in the text. Then choose the correct words in the rules. ANSWERS: 1 who 2 which 3 where |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for talking about films. Descriptor: - Check the meaning of these words in a dictionary. Assessment criteria: - Learn about adjectives ending in -ing and -ed. Descriptor: - read and listen to the film review. Answer the question Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 53 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Entertainment and media |
Lesson 66 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Buying tickets |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for buying tickets. • Listen to a conversation about buying tickets. • Practise buying tickets |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, ask students: When do you buy tickets? Elicit some answers. • Ask: When you buy tickets at a theatre, what information do you give? Elicit ideas such as which day you want to go, where you want to sit, how much you want to pay, etc. • Tell students they are going to practise buying tickets. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 73 • Students work in pairs to match the types of show to the posters. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:73 • After students have listened to the exchange, ask them what type of show Tom is buying tickets for Ex: 3 P:73 • Read through the key phrases with the class. Check that students understand row and model the pronunciation, /rəʊ/. • Ask students to copy the ticket. • Students listen again and complete the ticket with the correct information Ex: 4 P:73 • Tell students they are going to listen to some more seat and row numbers. • Students write down the letters and numbers they hear. • Check answers, then play the CD again for students to listen and repeat. |
Students match posters with the types of show in the box. ANSWERS: 1 ballet 2 musical 3 play Students look at the posters and listen to the conversation. Which type of show is Tom buying tickets for? ANSWERS: A musical (We will Rock You) Students study the key phrases. Then listen to the conversation again. Complete the ticket with the correct information. ANSWERS: 1 We Will Rock You 2 18th 3 11 4 12 5 V 6 £46.00 Students listen and write the numbers and letters. Then listen and repeat. ANSWERS: 1 seats 9 and 10 in row R 2 seats 24, 25 and 26 in row H 3 seats 16–19 in row J 4 seats 30–32 in row E |
Assessment criteria - Learn key phrases for buying tickets Descriptor: - study the key phrases. Then listen to the conversation again. Complete the ticket with the correct information Assessment criteria: - Listen to a conversation about buying tickets. Descriptor: - look at the posters and listen to the conversation. Which type of show is Tom buying tickets for? Make CCQ questions Yes / No
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 53 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Entertainment and media |
Lesson 67 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL: Natural science: Adapting to the environment |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with some support on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about animal adaptations and migrations. • Read a text about animal migrations. • Practise talking about animals migrations. |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, write polar bear and camel on the board. • Check that students understand the words, then ask where these animals live. Ask why polar bears are able to live in very cold conditions. • Elicit some ideas, then write the word adapt on the board. Ask how camels have adapted to living in very hot, dry conditions. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 74 • Refer students to the pictures and elicit or teach the names of the animals (arctic fox, snake, salmon, butterfly). • Play the CD, and ask students to listen and read the text. • Students match the words in blue with the definitions. • Check answers, and make sure that students understand the meaning of the blue words, for example, by asking them to translate them into their own language. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:74 • Focus on the map and the pictures. Model pronunciation of grey whale and arctic tern. • Play the CD and ask students to read and listen, and choose the correct migration routes.
Ex: 3 P:74 • Allow time for students to read the table. • Play the CD again, and ask students to listen and complete the table. • Ask students to compare answers in pairs, then check answers with the class. |
Students read and listen to the text. Then match the words in blue with definitions. ANSWERS: 1 breed 2 habitat 3 migrate 4 feed 5 adapt Students look at the map. Then listen and choose the correct migration route for the grey whale and the arctic tern. ANSWERS: grey whale b arctic tern c
Students listen again and complete the table. ANSWERS: 1 Bering Sea, Arctic 2 3 3 Antarctic 4 20,000 |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for talking about animal adaptations and migrations Descriptor: - read and listen to the text. Then match the words in blue with definitions. Assessment criteria: - Read a text about animal migrations. Descriptor: - look at the map. Then listen and choose the correct migration route for the grey whale and the arctic tern. Make CCQ questions Yes / No 1 Do animals adapt to their environment in different way? Yes 2 Do polar bears live in Indian ocean? No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 54 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Entertainment and media |
Lesson 68 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review unit 5 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use vocabulary for skills and people. • Write adjectives used to describe animals • Learn can and could for ability in the present and past. |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 76 • Ask students to complete the sentences with the missing words. • Check their answers. Drill the pronunciation of the new words if necessary. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:76 • Focus on the example. Ask students to work in pairs to complete the adjectives with a, o, I, o and u. Then find pairs of opposites. • In a weaker class, check that students understand all the adjectives, for example by asking them to translate the words into their own language. In a stronger class, encourage students to put the words into a sentence to show understanding. • Model and drill the pronunciation of any new adjectives Ex: 3 P:76 Tell students to read all the sentences carefully before they start to complete them to check they understand the context. They should think about whether the sentences refer to the present or the past. |
Students complete the sentences with the correct form of the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 writer, wrote 2 composer, composed 3 dancer, dance 4 cook, cook 5 paints, painter Students complete the adjectives with a, e, I, o and u. Then find pairs of opposites. ANSWERS: 1 slow – f fast 2 domesticated – c wild 3 stupid – b intelligent 4 light – e heavy 5 common – d rare 6 aggressive – a peaceful Students complete the sentences with the words in the box ANSWERS: 1 must 2 Could, couldn’t 3 How many, can, can’t 4 should |
Assessment criteria - Use vocabulary for skills and people. Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the correct form of the words in the box. Assessment criteria: - Write adjectives used to describe animals Descriptor: - complete the adjectives with a, e, I, o and u. Then find pairs of opposites. Make CCQ questions Yes / No 1 Did J. K. Rowling become a writer in 2004? No 2 Did she write five books? Yes |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 69 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Feelings |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 7.4.1.1 understand the main points in a growing range of short, simple texts on general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Do a quiz about risks and dangers. • Learn how to use modifiers with different adjectives. • Learn how to express emotions |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, write the words risk and danger on the board and elicit the meanings. • Ask students if they do any things that are dangerous. Elicit some ideas. • Ask students if they enjoy taking risks. Elicit a variety of responses |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 106 • Read the title of the quiz and look at the photos. Ask students if they think the things pictured are scary. • Students do the quiz individually and look at the key. • They discuss their results with a partner, giving reasons for their ideas. • Ask one or two students to report back to the class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:106 • Explain that each of the adjectives can be used with one of the prepositions to give a particular meaning. Ex: 3 P:106 Students read the phrases again and think about the emotion they express. If they are not sure, refer them back to the quiz to check the context and any other supporting words that might help. • Ask students to use the phrases in sentences. In a weaker class, ask students to work in pairs and write new sentences using the phrases in context. Monitor students as they do this. In a stronger class, ask students to say new sentences with the phrases as a whole-class activity. |
Students do the Risks and danger questionnaire. Then look at the key. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers Students add about, at, in or of to each adjective. Then check your answers in the questionnaire. ANSWERS: 1 at 2 of 3 at 4 about 5 in 6 about 7 of 8 about Students are the phrases in exercise 2 positive or negative? ANSWERS: 1 negative 2 positive 3 positive 4 positive 5 positive 6 negative 7 negative 8 negative |
Assessment criteria - Do a quiz about risks and dangers. Descriptor: - do the Risks and danger questionnaire. Then look at the key. Assessment criteria: - Learn how to use modifiers with different adjectives. Descriptor: - add about, at, in or of to each adjective. Then check your answers in the questionnaire. Make CCQ questions |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 54 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 70 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Arachnophobia |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.1.1 understand the main points in a growing range of short, simple texts on general and curricular topics 7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about phobias. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Talk about fears and phobias. |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, draw a picture of a spider on the board. Ask students to identify the animal and say how it makes them feel. • Then draw a picture of a snake. Repeat the activity and find out if any of the students are scared of snakes. • Ask students to suggest other things that could scare people. Elicit some ideas, then write the word phobia on the board. Ask students what it means. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 108 • Read the questions with the class and discuss their ideas. Ask students if they are frightened of anything. • Ask students if they know anyone who has a phobia. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:108 • Read the question with the class before they read and listen to the text. Ex: 3 P:108 • Explain that students should now read for detail so that they can decide if the sentences are true or false. Remind them to correct the false sentences
Ex: 4 P:108 • Refer students back to the text to find the blue adjectives. In a weaker class, students can match these in pairs. • Remind students that there is one definition they do not need to use. |
Students answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 Students’ own answers. 2 Students’ own answers. 3 The difference between a fear and a phobia is that a phobia can seem irrational but is very strong and has to be treated like an illness. Students read and listen to the text. How can you cure a phobia? ANSWERS: Exposure therapy. Students read the text again and write true or false. Correct false sentences. ANSWERS: 1 True. 2 False. Mark Tanner has helped a lot of patients with phobias. 3 True. 4 False. Georgia’s family hid plastic spiders at home. 5 True. 6 False. Georgia may touch a spider. Students find adjectives in blue in the text. Then match them with definitions. There is one definition you do not need. ANSWERS: 1 d 2 f 3 e 4 a 5 b |
Assessment criteria - Read about phobias. Descriptor: - answer the questions Assessment criteria: - Read for General meaning and specific information. Descriptor: - read the text again and write true or false. Correct false sentences. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 54 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 71 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Present Perfect: affirmative and negative |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 7.6.7.1 use simple perfect forms to express indefinite and unfinished past with for and since] on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the affirmative and negative forms of the present perfect. • Read about school phobia. • Use the present perfect to talk about experiences. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Refer students back to the text on page 80. Focus on the final paragraph and the sentence I’ve looked at hundreds of spiders with Mark. • Ask: Is Georgia talking about an event at a specific time in the past, or about an experience at some time in the past? • Elicit that she is talking about an experience at some time in the past. Tell students that we use the present perfect to talk about experiences. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 109 • Students use the sentences in the text as examples to help them complete the rules. In a stronger class, let them do this individually, otherwise, in pairs. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. LANGUAGE NOTE We use ’ve or ’s before the past
participle: I’ve been to England. NOT Ex: 2 P:109 • Refer students to the Irregular verbs list on page 104 of the Workbook to help them decide which verbs are irregular. They may need further reference material to complete the table Ex: 4 P:109 • Students complete the sentences. In a weaker class, remind them to refer back to exercise 2 for the past participles. In a stronger class, encourage them to try to remember these |
Students complete the sentences from the text. Then choose the correct answers in the rules. ANSWERS: 1 ’s helped 2 ’ve seen 3 ’s made 4 ’ve seen Rules ANSWERS 1 past, now 2 don’t say 3 have Students complete the table with the past simple and past participle forms of the verbs in the box. ANSWERS: Regular: look – looked – looked, play – played – played, stay – stayed – stayed, touch – touched – touched, visit – visited – visited Irregular: speak – spoke – spoken, find – found – found, go – went – been/gone, see – saw – seen, make – made – made Students complete the sentences using the present perfect form of the verbs. ANSWERS: 1 ’ve seen 2 haven’t spoken 3 haven’t stayed 4 ’ve looked 5 hasn’t touched |
Assessment criteria - Learn the affirmative and negative forms of the present perfect. Descriptor: - complete the sentences from the text. Then choose the correct answers in the rules. Assessment criteria: - Use the present perfect to talk about experiences. Descriptor: - complete the sentences using the present perfect form of the verbs. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 78 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 72 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Injuries |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 7.2.4.1 understand with limited support the main points of extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 7.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary of injuries. • Listen to people talking about dangerous jobs. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, write the word injury on the board and elicit or explain the meaning. • Ask students for examples of injuries and ask if they have ever had any injuries. • Ask students what injuries people sometimes get at work. • Ask what jobs students think are dangerous and why. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 110 • Once students have completed the table, model and drill the pronunciation of the words. Check that students understand them, for example, by asking them to translate the words into their own language.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:110 • Students choose the correct words in the sentences individually. Ex: 3 P:110 • Before students match the photos and the jobs mentioned in the programme guide text, ask them if they can guess the jobs from the pictures Ex: 4 P:108 • Students read the sentences to find out how much they already know about the dangerous jobs before they listen to the recording. They discuss in pairs whether the sentences are true or false. In a weaker class, discuss as a group which jobs are likely to be dangerous and why. • Play the CD. Students listen and check their answers. Play the CD again, and ask students to correct the sentences which were false. In a stronger class, students could correct false sentences before listening again |
Students check the meaning of the words. Then complete the table. ANSWERS: 1 burnt 2 break 3 a bruise 4 bite 5 a sprain 6 injured Students choose the correct words. ANSWERS: 1 burnt 2 cuts and bruises 3 bitten 4 injured 5 broken 6 cut Students look at the photos and match them with jobs in the programme guide. ANSWERS: A 2 B 1 C 4 D 3 Students work in pairs. Write true or false. Then listen and check your answers. ANSWERS: 1 True. 2 False. Volcanoes don’t erupt very often. 3 False. Venomologists study venom. 4 True. 5 False. Farming is dangerous because of the big machines. |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary of injuries. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words. Then complete the table. Assessment criteria: - Listen to people talking about dangerous jobs Descriptor: - look at the photos and match them with jobs in the programme guide. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 80 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 73 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Present Perfect: questions |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.7.1 use simple perfect forms to express indefinite and unfinished past [with for and since] on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the question forms of the present perfect. • Practise writing questions using the present perfect. • Learn key phrases for reacting to what people say. • Practise reacting to what people say. |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Ask students to recap what the present perfect tense is used for (to talk about experiences in the past). Remind students that they have covered the affirmative and negative forms of this tense. • Tell students they are going to study present perfect questions. Ask them what they think might change in the question form. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets. |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 111 • Explain that the completed sentences provide a context for working out the rule. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. LANGUAGE NOTE In present perfect questions, have / has
comes before the subject: Have you injured your arm? NOT
It is the past participle, not the past simple
form, which is used in present perfect questions: Has she seen that
film? NOT Ex: 2 P:111 • Ask students to work individually to choose the correct words. • Check answers by asking individual students to read out their sentences. Ex: 3 P:111 • Focus on the information in the table. Check that students understand stunt person and bodyguard. • Focus on the task and example and do another example with the whole class if necessary. • Once students have individually written the questions and answers, ask them to compare their answers in pairs. Then check answers with the class. |
Students complete the sentences with the words in the box. Then choose the correct words in the rule. ANSWERS: 1 has 2 ever, No 3 Have, they Rule answers. past participle Students choose the correct words ANSWERS: 1 Have, have 2 had, hasn’t 3 Has, has 4 Have, haven’t 5 broken, haven’t Students write questions and answers ANSWERS: 1 Has Vin broken a bone? No, he hasn’t. 2 Has Bess jumped off a building? Yes, she has. 3 Has Bess met the president? No, she hasn’t. 4 Has Vin met the president? Yes, he has. 5 Have they driven at 200kph? Yes, they have. |
• In a weaker class, you may need to provide more examples of questions to help them understand the structure. • In a weaker class, choose the correct words with teacher’s support |
Assessment criteria - Learn the question forms of the present perfect. Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the words in the box. Then choose the correct words in the rule. Assessment criteria: - Practise writing questions using the present perfect. Descriptor: - write questions and answers Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 74 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 09.03.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Helping with problems |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a conversation about an injury. • Learn key phrases for helping someone who is hurt. • Practise suggesting how to help someone. |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, tell students you are going to mime one of the injuries from the vocabulary section of this unit. Mime spraining your ankle and get students to guess the injury. • Ask students to imagine their friend has sprained his/her ankle. Ask: What would you say to your friend? |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets. |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 112 • Look at the photo with the class and ask students to guess what has happened to Leah. • Play the CD. Students read and listen, and answer the question in the instructions. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:112 • Ask students to read the key phrases and match them to make mini-dialogues. • Ask students to find the key phrases in the dialogue and translate them into their own language. Ex: 3 P:112 • In a stronger class, ask students to close their books. You point to the body parts to find out if students already know the vocabulary. • Check answers and model pronunciation of the words. |
Students look at the picture. What has happened? Listen to the dialogue then practice the dialogue with your partner. ANSWERS: Leah has cut her arm. Students match the key phrases ANSWERS: 1 b 2 d 3 c 4 a Students match photos with with words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 shoulder 2 wrist 3 ankle 4 elbow 5 neck 6 toe 7 finger 8 knee |
• In a weaker class, match the key phrases with teacher’s support • In a weaker class, students match the words with the photos |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a conversation about an injury. Descriptor: - look at the picture. What has happened? Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for helping someone who is hurt Descriptor: - match the key phrases Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 75 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 14.03.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL: Reading for pleasure: Stories |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.3.8.1 recount some extended stories and events on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a folk story from Kazakhstan . • Learn about different types of adverbs. • Learn how to use for and since with the present perfect. • Write a summary of a folk story or a legend. |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, divide students into pairs and ask them to think about the most beautiful garden they have ever seen. Tell them to describe it to their partner. • Get feedback from the class by asking a few students to describe their partner’s preferences. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:114 • Tell students they are going to read a Kazakh folk story. Draw their attention to the photo and the title. • Students discuss their ideas. Get some feedback from the class, but do not confirm or reject any ideas at this stage. Answers: Students’ own answers Ex: 2 P:114 • Refer students to Part 1 of the story. In a weaker class, preteach the following words and phrases: pot, buried, wise, argue, rest, seeds, gates, merchant, gull, swallow, lark. • In pairs, students put the events in the correct order. • Check answers as a class. Allow students one or two minutes to discuss their ideas about the ending of the story, then elicit some ideas Answers: 1 the shepherd’s sheep died 2 the farmer gave the shepherd some land 3 the shepherd found a pot of gold coins 4 the farmer and the shepherd argued 5 they asked a wise man for advice 6 the student travelled to the city 7 the student met some merchants Ex: 3 P:114 • Tell students they are going to hear the ending of the story. Explain they have to listen and decide whether it’s a happy ending or not. They should focus on listening for the general meaning. • Play the recording. • In pairs, students discuss the ending and compare it with their ideas in exercise 2 Answers: The story has a happy ending. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the photo and the title of the story. What do you think the story is about? Descriptor: - look at the photo - discuss their ideas Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students work in pairs. Read the story and put the events in the correct order. Descriptor: -work in pairs - put the events in the correct order. Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students listen the story. Does it have a happy ending? Descriptor: - listen the story - answer the question Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
-can discuss with their ideas Total: 1 point -can read the story and put the events in the correct order. Total: 1 point -can answer the question Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Holidays |
Lesson 76 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative Assessment for term 3 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.L4 Understand with little support some of the implied meaning in extended talk on a limited range of general and curricular topics. 7.R6 Recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer on a range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics 7.W1 Plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with some support on a range of general and curricular topics. 7.S4 Respond with some flexibility at both sentence and discourse level to unexpected comments on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to recall the previous lesson (Speaking, page 86) and elicit what they remember about the scenario. • Ask: Where was the woman? (In a shop.) What was she doing? (Returning a record.) What did she want? (To change it.) Did she get what she wanted? |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
LISTENING Task. Listen to the recording twice and answer the questions. Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS or A NUMBER.CD3. Tapescript 3.OR Go to this link to listen information Example: 0. Was she happy in her marriage? No, she was not. READING Task. Read the text carefully and answer the questions. __ Part 1. Choose the correct answer Part 2. Find some inconsistences in the statements. Mark these sentences Yes, No, Not Given. 3. Fishermen all over the world know when hurricanes start 4. Hurricanes usually start in the steppe 5. The best place to hide from hurricane is indoors _______________________. WRITING Task. Look at the films below. Choose one of them to write a review about. Use linking words and connectors in sentences to make some coherent paragraphs. You can use prompts for your answer SPEAKING Task. You will be given a card which asks you to retell a short story about a particular situation. You should include your ideas while telling it. You will be given 1 minute to prepare your talk and then 1-2 minutes to speak. Your classmates prepare the questions to ask you on the topic. Learners take turns in retelling the stories from the cards |
Students listen to the recording twice and answer the questions Descriptor: - listen and match Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students Read the text carefully and answer the questions Descriptor: - Paraphrase the given sentences so it has similar meaning Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students choose ONE of the topics and write. Descriptor: - Write a story about a concert Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
-can match the halves of the sentences Total: 1 point -can paraphrase the given sentences Total: 1 point -can write a story about a concert Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 77 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Phoning a medical helpline |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.3.8.1 recount some extended stories and events on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for phoning a medical helpline. • Listen to someone phoning a medical helpline. • Practise phoning a medical helpline |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In With books closed, ask: Have you ever had an accident? What happened? • Elicit some answers, then ask: What do you do when someone has an accident? • Elicit some answers, then write Medical helpline on the board. Elicit that this is a helpline you can phone when you hurt yourself and need advice |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:115 • Students work in pairs to match the instructions with the pictures. Answers: 1 B 2 E 3 A 4 F 5 D 6 C Ex: 2 P:115 • Play the CD. Students listen and say which instructions they hear. Answers: Put it under cold water. Put some ice on it. Take an aspirin. Ex: 3 P:115 • Read through the key phrases with the class. Point out that we use the present perfect, not the past simple, when talking about injuries that happened very recently. • Allow students time to read the questions. • Play the CD again. Students listen and answer the questions individually, then compare their answers in pairs. Answers: 1 She has burnt her hand. 2 She was making lunch. She was taking some hot soup out of the microwave and it went on her hand. 3 It really hurts. 4 She’s fallen over and bruised her knee. 5 She is going to play badminton. 6 She mustn’t move her leg a lot. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students match instructions with pictures Descriptor: - work in pairs -match instruction with pictures Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to two telephone calls to a medical helpline. Which instructions from exercise 1 do you hear? Descriptor: - listen to two telephone calls to a medical helpline Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students study the key phrases. Then listen to the telephone calls again and answer the question Descriptor: - listen the story - answer the question Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
-can discuss with their ideas Total: 1 point -can read the story and put the events in the correct order. Total: 1 point -can answer the question Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
ҚМЖ Eng Plus gr 7 term 3
ҚМЖ Eng Plus gr 7 term 3
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 49 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Sherlock Holmes: The Blue Diamond |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 7.4.4.1 read independently a limited range of short simple fiction and non-fiction texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading. • Practise asking questions about stories |
||
|
Value links |
Family – Family values are moral and ethical principles of typical family life, including sacrificing for loved ones, putting your loved ones first, and keeping your loved ones at the centre of your thoughts and actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask students what they know about the Sherlock Holmes stories. Write their ideas on the board and include these details: • Sherlock Holmes is a private detective. • Dr Watson is his assistant. • They solve crimes in London at the end of the 19th century. • Famous stories include Hound of the Baskervilles and Sign of Four. Lead - In
The fate of the allied forces lies in the hands of Joanna and the Watsons in the next Daughter of Sherlock Holmes mystery from USA Today bestselling author Leonard Goldberg. |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:120 • Tell students to look at the pictures and make a list of things they can see. Start the list by writing these items on the board: a goose, a blue diamond, an advertisement • After three minutes, ask students for their ideas and write them on the board. • Go through the pictures with students identifying the main elements, e.g. picture A – goose, man wearing a suit, etc. • Tell students to read all the story sections and match the sections to the pictures Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 120 Ask the class which section is the first and explain their reasoning. Use prompt questions if necessary, e.g. What is main event in the story? When does the main event occur? Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 120 • Explain the task. Tell students to pay attention to the use of ‘a’ (for the first time an element of the story is introduced) and ‘the’ (when we already know who or what is being referred to). In a stronger class, let students work individually. Give them about five minutes to put the pictures in order. In a weaker class, put the students in pairs and monitor their progress, helping out if necessary. |
Students read the story and match them to the pictures ANSWERS 1 E 2 H 3 F 4 G 5 C . 6 A 7 D 8 B Students look at the again. Which section do you think is the start of the story ANSWERS The start of the story is section 3 – the blue diamond is missing. The end of the story is section 6 – Ryder admits he stole it. Students read the section again and put them in order to make the story ANSWERS . 1 section 3 2 section 5 3 section 2 4 section 4 5 section 1 6 section 8 7 section 7 8 section 6 |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading Descriptor: - read the story and match them to the pictures Assessment criteria: - Practise asking questions about stories. Descriptor: - look at the again. Which section do you think is the start of the story -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 88 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 50 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talk about it |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 7.3.3.1 give an opinion at sentence and discourse level on an increasing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading. • Practise asking questions about stories. |
||
|
Value links |
Loyalty – Loyalty might be a core personal value to you if you highly prize friends that are reliable and trustworthy. You might put your friends or chosen family first, always being there for them when they need you. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask students what they know about the Sherlock Holmes stories. Write their ideas on the board and include these details: • Sherlock Holmes is a private detective. • Dr Watson is his assistant. • They solve crimes in London at the end of the 19th century. • Famous stories include Hound of the Baskervilles and Sign of Four. Lead - In
The fate of the allied forces lies in the hands of Joanna and the Watsons in the next Daughter of Sherlock Holmes mystery from USA Today bestselling author Leonard Goldberg. |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:4 P:121 • Put student in pairs. Give students time to make a note of who the people are, what happened at each place, and events related to the verbs and nouns. • When students are ready, without looking at p121, students take turns to tell the story. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 6 P: 121 • Tell students to listen to James Ryder and choose the correct words to complete the sentences. • Play the recording. • Go through the answers with the class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 7 P: 121 • Explain the task. Then play the recording. • Discuss the ending with students. |
Students use the pictures and the words in the boxes to tell the story to your partner. ANSWERS Students’ own answers. Students listen to James Ryder talk about his story. ANSWERS 1 Horner 2 sister’s 3 Maudsley 4 geese 5 black 6 Maudsley’s 7 didn’t find 8 two 9 would not Students listen to the end of the story. ANSWERS Students’ own answers. |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading Descriptor: - read the story and match them to the pictures Assessment criteria: - Practise asking questions about stories. Descriptor: - look at the again. Which section do you think is the start of the story -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 88 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 51 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The Lost World |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.4.1 read independently a limited range of short simple fiction and non-fiction texts 6.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading. • Practise asking questions about stories. |
||
|
Value links |
Fairness – If you value fairness, you might be highly sensitive to situations at school or in the workplace where a teacher or a peer has exhibited favoritism or allowed someone to get away with living by a different set of rules to everyone else. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up Ask students to look at the book cover and characters in the pictures and guess what the story is about Lead - In
In this story, Edward Malone is a young journalist who is sent to interview the bizarre claims made by Professor George Edward Challenger, who claims to have made an exciting discovery in South America |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:122 • Tell students to work individually and write adjectives they can use to describe the six characters in the pictures, e.g. A – young, pretty, well-dressed. Students write the notes on the note pad. Tell students not to write the name of the characters. • Put students in pairs. Tell them to share their adjectives and ask their partner which character they think the adjectives refer to. Circulate and monitor. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 122 • Explain the task. Make sure students know zoologist (someone who studies animals). In a weaker class, do the first description with the whole class.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 122 • Explain the task. Ask a student to read the first quote and the rest of the class to guess who it is. • Make sure they use the clues in the quote. |
Students think of adjectives to describe the six people in the pictures. ANSWERS Students’ own answers. Students read the descriptions of some of the characters from the book. ANSWERS 1 D 2 A 3 E 4 F 5 C 6 B Students look at the descriptions and the pictures again. Which characters say these things, do you think ANSWERS 1 Gladys Hungerton 2 Ned Malone 3 Mr McArdle 4 Lord John Roxton 5 Professor Summerlee |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading Descriptor: - to describe the six people in the pictures. Assessment criteria: - Practise asking questions about stories. Descriptor: - look at the again. Which section do you think is the start of the story -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 88 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 52 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Date: |
16.01.2024 |
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The Last of the Mohicans |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 7.4.4.1 read independently a limited range of short simple fiction and non-fiction texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading. • Practise asking questions about stories. |
||
|
Value links |
Generosity – This may be a core value of yours if you cherish people who will give their time and resources to people in need. You may consider yourself to be a generous person if you find joy and meaning in giving to others. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to look at the book cover and characters in the pictures and guess what the story is about. Lead - In
Last of the Mohicans tells the seminal story of a race on the brink of disappearance due to the inexorable push of civilization into the wilderness of the New World. It's a tale that will touch readers of every age with both its timeless realization of an important historical period-and with its powerful action and adventure! |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:124 • Explain the task. Tell the students to use the visual information in the book cover and pictures • to answer the questions. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 124 • Draw students’ attention to the map and ask which part of the world it shows. Explain the task. • Go through the answers.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 124 • Ask the students what sort of hairstyles and clothes Europeans and Native Americans had. • Explain the task. • Go through the answers. |
Students look at the front cover of the book and the pictures of the characters. Choose the correct words to complete the sentences. ANSWERS 1 South 2 1757 3 French and the British 4 before 5 tribes 6 land 7 French 8 British Students the Last of the Mohicans takes place in North America. Label the map of North America today ANSWERS 1 Canada 2 United States of America 3 Mexico 4 Lake Champlain 5 udson River Students look at some of the characters in the story. Put the characters into the group they belong to. ANSWERS Europeans Alice Montcalm Cora Munro American Indian Chingachgook Magua Uncas Tamenund |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading Descriptor: - Choose the correct words to complete the sentences. Assessment criteria: - Practise asking questions about stories. Descriptor: - Label the map of North America today -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 88 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 53 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Date: |
17.01.2024 |
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The Last of the Mohicans |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 7.3.3.1 give an opinion at sentence and discourse level on an increasing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading. • Practise asking questions about stories. |
||
|
Value links |
Integrity – Integrity is the quality of having strong moral principles. So, a person with integrity will always act with honesty and adhere to their own moral code regardless of what others do. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to look at the book cover and characters in the pictures and guess what the story is about. Lead - In
Last of the Mohicans tells the seminal story of a race on the brink of disappearance due to the inexorable push of civilization into the wilderness of the New World. It's a tale that will touch readers of every age with both its timeless realization of an important historical period-and with its powerful action and adventure! |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:4 P:125 • Ask students to think of as many names of Native American tribes as they can, e.g. Comanche, Sioux, Cheyenne. Explain the task. • Go through the answers. Ask students to correct any false sentences. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 5 P: 125 • Explain the task. • Go through the answers.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 6 P: 125 • Put students in pairs. If possible. draw or describe an example of a totem. • Explain the task. If internet is accessible, ask students to do online research to answer the questions. |
Students read about Ojibwa tribe. Are the sentences true or false ANSWERS 1 false 2 false 3 true 4 true 5 false 6 true 7 true 8 false Students put the words from the story into the correct category in the table. ANSWERS European American Indian Army tribe Fort tomahawk Officer moccasin Church totem Hymn Great spirit King warrior General magic Feathers Chief Canoe Students ask and answer the questions about American Indians with your partner ANSWERS 1 A totem is an animal or natural
object that is a special symbol of the community. They are
important to American 2 The Great Spirit is a universal force or supreme being. 3 Tribal chief. 4 They wear feathers in their headdress. 5 A tomahawk is a type of axe. |
Assessment criteria - Learn and practise nouns to talk about types of reading Descriptor: - read about Ojibwa tribe. Are the sentences true or false Assessment criteria: - Practise asking questions about stories. Descriptor: - put the words from the story into the correct category in the table. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 88 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 55 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Nicholas Nickleby |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 7.4.4.1 read independently a limited range of short simple fiction and non-fiction texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - apply appropriate descriptive language to create different types of (grade-appropriate) texts and speeches -identify the differences between fiction and non-fiction |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to look at the book cover and characters in the pictures and guess what the story is about. Lead - In
Nicholas Nickleby is the tale of a young man whose father has died leaving his family penniless. Nicholas must find a job to support his mother and sister, Kate. The family turns for help to their uncle, Ralph Nickleby, a ruthless businessman, who has taken a dislike to his relatives. Nicholas, aided by many diverse characters, must protect his family from his uncle’s machinations. |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P: 88 WB • Explain the task. Tell students before complete the paragraph with the words below. Then read the first extract. • Students work in pairs to complete the paragraph with the words in the box. • Read through the first extract together and check for understanding. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 88 Wb • Tell students to read the first extract, ask to work individually to choose the correct words. • Check answers by asking individual students to read out their sentences
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 4 P: 88 Wb • Explain students should read the second extract then write sentences are true or false. • Check answers by asking students to read out their answers, making sure that they read them correctly. |
Students complete the paragraph with the words in the box and read the first extract. ANSWERS 1 dies 2 uncle 3 like 4 boarding 5 better 6 travels Students read the first extract then choose the correct words ANSWERS 1 doesn’t look 2 isn’t 3 animals 4 money 5 little Students read the second extract then write true or false ANSWERS 1 f 2 t 3 f 4 t 5 f 6 t |
Assessment criteria - apply appropriate descriptive language to create different types of (grade-appropriate) texts and speeches Descriptor: - complete the paragraph with the words in the box - read the first extract Assessment criteria: - identify the differences between fiction and non-fiction Descriptor: - read the second extract - write true or false -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 88 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 56 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Romeo and Juliet |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 7.4.4.1 read independently a limited range of short simple fiction and non-fiction texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - apply appropriate descriptive language to create different types of (grade-appropriate) texts and speeches -identify the differences between fiction and non-fiction |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Books closed. Ask students what they know about the Romeo and Juliet stories. Write their ideas on the board and include these details: • Romeo and Juliet belongs to a tradition of tragic romances Lead - In
The story of Romeo and Juliet has everything that a reader could want. Like many of Shakespeare’s works, it has comedy and tragedy, but it also has love, family, duals, good and evil. |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P: 90 WB • Explain the task. Tell students before complete the paragraph with the words below. Then read the first extract. • Students work in pairs to complete the paragraph with the words in the box. • Read through the first extract together and check for understanding. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 90 Wb • Explain students should read the first extract then write sentences are true or false. • Check answers by asking students to read out their answers, making sure that they read them correctly.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 4 P: 90 Wb • Explain students should read the second extract then complete the sentences with one word • Check answers by asking students to read out their answers, making sure that they read them correctly. |
Students complete the paragraph with the words in the box and read the first extract. ANSWERS 1 families 2 enemies 3 fight 4 party 5 marry 6 man 7 masks Students read the first extract then write true or false ANSWERS 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 t 5 t 6 f 7 t Students read the second extract then complete the sentences with one word. ANSWERS 1 mother 2 enemy 3 never 4 wife 5 hated |
Assessment criteria - apply appropriate descriptive language to create different types of (grade-appropriate) texts and speeches Descriptor: - complete the paragraph with the words in the box - read the first extract Assessment criteria: - identify the differences between fiction and non-fiction Descriptor: - read the second extract - complete the sentences with one word -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 88 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 57 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Emma |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 7.4.4.1 read independently a limited range of short simple fiction and non-fiction texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - apply appropriate descriptive language to create different types of (grade-appropriate) texts and speeches -identify the differences between fiction and non-fiction |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to look at the book cover and characters in the pictures and guess what the story is about. Lead - In
The young beauty Emma Woodhouse believes that she is well versed in human characters and therefore can play the role of a matchmaker for her friends and young people. She dissuades her friend, the modest girl Harriet Smith, from marrying a farmer and elects a vicar for her , Mr. Elton. However, he falls in love with Emma herself. |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P: 91 WB • Explain students read the first extract then write sentences are true or false. • Check answers by asking students to read out their answers, making sure that they read them correctly. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 91 Wb • Tell students to read the second extract, ask to work individually to choose the correct words. • Check answers by asking individual students to read out their sentences
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 4 P: 91 Wb • Explain students read the second extract again then answer the question • Check answers by asking students to read out their answers, making sure that they read them correctly. |
Students read the first extract then write true or false ANSWERS 1 t 2 f 3 t 4 f 5 t Students read the second extract then choose the correct words ANSWERS 1 doesn’t have 2 is 3 talks 4 clergyman 5 Elton 6 isn’t Students read the second extract again then answer the question ANSWERS 1 she was friendly and kind 2 they met Mr Martin 3 she planned lots of ways for them to meet 4 started to visit |
Assessment criteria - apply appropriate descriptive language to create different types of (grade-appropriate) texts and speeches Descriptor: - complete the paragraph with the words in the box - read the first extract Assessment criteria: - identify the differences between fiction and non-fiction Descriptor: - read the second extract - write true or false -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 88 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Entertainment and media |
Lesson 58 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Skills and people |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 7.6.1.1 begin to use basic abstract nouns and compound nouns and noun phrases describing times and location on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.2.3.1 understand more complex supported questions on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for skills and people. • Do a quiz on talented people. • Learn how to learn words in groups. • Learn phrases for expressing knowledge. |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the word clever on the board and elicit the meaning. • Name a few famous artists, musicians or scientists and ask students if these people are / were clever. • Ask students to name some more clever people. Lead - In
In Rich Dad Poor Dad, Kiyosaki names the following seven skills as being prime skills to help you become wealthy |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:64 • Look at the title of the quiz and elicit that it is going to be about famous people who showed their talents when they were children. • Explain that this is a general knowledge quiz. Students should work in pairs. • After checking answers, find out who got the most correct answers. • In a stronger class, ask students if they know anything else about the people in the quiz. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 64 • Focus on the table with the class, then ask students to read the quiz to find the missing words to complete the table. • Play the CD so that students can check their answers. Drill the pronunciation of the new words if necessary. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 64 • Point out that it is a good idea to learn new vocabulary in groups. • Focus on the example, then ask students to work individually to add the related words. To extend the activity, refer students back to the table in exercise 2 and elicit the activity nouns associated with those words. • In a stronger class, you could also ask students to look up more words to add to the list and write each form in their notebooks Ex: 3 P: 64 • Students complete the phrases. Check understanding by asking students to translate them into their own language. In a weaker class, say some names of topics or famous people and ask students to respond by using the key phrases |
Students work in pairs. Do the Clever kids quiz ANSWERS 1 a Salvador Dalí 2 b Henry Ford 3 b karate 4 a prince 5 c Oliver Twist 6 a lens 7 c Chinese 8 b The X factor Students complete the table with verbs and nouns from the Clever kids quiz. Then listen and check. ANSWERS 1 composer 2 swimmer 3 play 4 writer 5 winner 6 program 7 singer Students complete the table with related words. Then listen and check. ANSWERS 1 actor 4 dancer 2 acting 5 cook 3 dance 6 cooking Students use key phrases in the box. ANSWERS 1 a bit, a lot 2 anything, much |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for skills and people. - Do a quiz on talented people. Descriptor: - work in pairs. Do the Clever kids quiz. Assessment criteria: - Learn how to learn words in groups Descriptor: - complete the table with related words. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 48 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit of a long term plan: Entertainment and media |
Lesson 59 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Date: |
23.01.2024 |
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Whizz-kids |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.1.1 understand the main points in a growing range of short, simple texts on general and curricular topics 7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.3.1.1 provide basic information about themselves and others at discourse level on a range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about prodigies. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Talk about topics raised in the text |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students back to the Clever Kids quiz on page 49. Ask students to think about the people in the quiz. Ask what links all the people mentioned (they were all exceptionally talented from a very early age). • Ask students if they know anyone like this, or whether they can name any other famous prodigies. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:66 • Focus on the title of the text and the photo. Elicit or explain the meaning of prodigy. • Ask students what kinds of things prodigies can do. Accept all ideas at this stage Background In British schools, children who are recognized as ‘gifted’ or exceptionally talented are sometimes given extra lessons by their school, or may attend special classes for similarly gifted children after school or during school holidays. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 66 • Tell students to read through the summaries. Clarify that only one of these fits the text correctly. • Play the CD. Students, read, listen and choose the correct summary. In a stronger class, ask them to explain their choice in English. Ex: 3 P: 66 • After closely reading the text, students complete the sentences. Ex: 4 P: 66 • Students read the text again and complete the phrases with the correct words. • In a weaker class, check understanding of the words and phrases, for example, by asking students to translate them. In a stronger class, ask students to put the phrases into a sentence to show they have understood. • Explain that these phrases are very common and useful to learn. In a stronger class, elicit or explain some other related phrases, for example, set a record, take a decision |
Students look at photo and discuss about what does prodigy mean ANSWERS A prodigy is a child with incredible talents. Students read and listen to the text. Then choose the correct summary ANSWERS a) Students read the text again and complete the sentences with one, two or three words. ANSWERS 1 of twelve 2 children 3 university at seven 4 they help 5 160 Students find and complete the phrases with the verbs in the box. ANSWERS 1 break 2 take 3 take 4 make 5 make |
Assessment criteria - Read about prodigies. Descriptor: - look at photo and discuss about what does prodigy mean Assessment criteria: - Read for general meaning and specific information Descriptor: - read and listen to the text. Then choose the correct summary -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 48 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit of a long term plan: Entertainment and media |
Lesson 56 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Date: |
24.01.2024 |
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Ability: can, could. Questions with How...? |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.5.1 use questions including questions with whose, how often , how long and a growing range of tag questions on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.6.13.1 use modal forms including mustn’t (prohibition), need (necessity) should (for advice) on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn can and could for ability in the present and past. • Learn about questions using How ...? • Practise asking and answering questions using can, could and How ...? |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Refer students back to the reading text on page 50. Read the first sentence with the class and ask which verb refers to ability (could). • Elicit or explain that we use can to talk about ability in the present, and could to talk about ability in the past. Lead - In Pupils watch video about differences can and could
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students watch video and say different words from the differences can and could |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet https://youtu.be/BBq0hWsrC6o Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:67 • Explain that students are going to focus on can and could in the context of the text LANGUAGE NOTE We use can for ability in the present and could for ability in the past: I can swim now. I could swim when I was three. NOT I can swim when I was three. The verbs can and could do not add -s after he, she and it: He can dance. NOT He cans dance. After can and could, we use the infinitive without to: I can speak English. NOT I can to speak English. Point out that the negative forms are can’t and couldn’t: He can’t paint. NOT He doesn’t can paint Ex: 2 P: • Students choose the correct words to complete the rules. In a weaker class, do this as a class activity for support. • In a stronger class, ask for an example of what students could / couldn’t do in the past and what they can / can’t do now. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 67 • Tell students to read all the sentences carefully before they start to complete them to check they understand the context. They should think about whether the sentences refer to the present or the past. Ex: 4 P: 67 • Once students have matched the question halves, check answers and ask students to ask and answer pairs. |
Students complete the sentences. ANSWERS 1 can’t do 2 could 3 couldn’t Students choose the correct words ANSWERS 1 without 2 can 3 can’t 4 present 5 past Students complete the sentences with the words in the box. ANSWERS 1 could 2 couldn’t 3 can 4 couldn’t 5 can’t Students match and make questions. Then ask and answer questions with a partner. ANSWERS 1 e How far can you swim? 2 f How strict is your teacher? 3 b How often do you go to the cinema? 4 g How intelligent are your friends? 5 a How many people are in your class? 6 c How much cola do you drink? 7 d How tall are you? |
Assessment criteria - Learn can and could for ability in the present and past. Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the can and could Assessment criteria: - Learn about questions using How ...? Descriptor: - match and make questions. Then ask and answer questions -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 49 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Entertainment and media |
Lesson 61 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Adjectives: qualities |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.C6 organize and present information clearly to others 7.6.3.1 use common participles as adjectives and order adjectives correctly in front of nouns on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn adjectives used to describe animals. • Listen to a conversation about animals. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students to work in pairs and write down as many animals in English as they can in two minutes. • Elicit names of animals from the class and write them on the board. . • Point to one of the words and ask students what they know about this animal. Elicit some adjectives to describe it and write them on the board. Do the same with two or three more of the animal words. • Ask students which animals they think are clever. Lead - In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:68 • Focus on the example. Ask students to work in pairs to find pairs of adjectives . • In a weaker class, check that students understand all the adjectives, for example by asking them to translate the words into their own language. In a stronger class, encourage students to put the words into a sentence to show understanding. • Model and drill the pronunciation of any new adjectives. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 68 • Read the instructions with the class. Check that students understand the animal words, and check that they understand the difference between not very, quite, very and really. • Students prepare their sentences in pairs. Ask students to report back to the class on how they described the animals
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 68 • Explain to students that they are going to listen to two people talking about animals. Before you play the CD, look at the photos and identify the animal in each one. • Tell students that there is one extra animal in the conversation which is not pictured. |
Students find pairs of opposite adjectives ANSWERS aggressive – peaceful common – rare domesticated – wild fast – slow heavy – light intelligent – stupid Students work in pairs. Write sentences about each animal using three adjectives from exercise 1 ANSWERS Students’ own answers Students listen to Sophie and Joe talking about animals ANSWERS Monkeys |
Assessment criteria - Learn adjectives used to describe animals Descriptor: - find pairs of opposite adjectives Assessment criteria: - Listen to a conversation about animals. Descriptor: - listen to Sophie and Joe talking about animals -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 50 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Entertainment and media |
Lesson 62 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Comparative and Superlative adjectives |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a limited range of general topics, and some curricular topics 7.6.3.1 use common participles as adjectives and order adjectives correctly in front of nouns on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.5.2.1 write with some support about real and imaginary past events, activities and experiences on a limited range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn comparative and superlative forms of adjectives. • Make sentences using comparative and superlative adjectives. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, write the words elephant and monkey on the board. • Write the adjectives big and intelligent on the board and ask students how they can compare the two animals using the adjectives on the board. • Refer students back to exercise 5 on page 52 and ask them to find examples of how we can compare things in English. Lead – In
|
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:69 • Students copy the table and complete the missing forms. Point out that only regular forms are gapped. LANGUAGE NOTE We do not use more and most with short adjectives: An elephant is bigger than a monkey. NOT An elephant is more big than a monkey. Some adjectives are irregular, for example, bad, worse, worst. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 69 • Refer students back to the table in exercise 1 and to the example sentences. Allow students time to look at the forms, then ask them to complete the rules.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 69 • Explain to students that there are spelling rules for forming regular comparative and superlative adjectives, which are summarized in the table. • Ask students to apply what they have covered and to complete the rules. In a weaker class, ask them to do this in pairs. |
Students complete the table with comparative and superlative adjectives ANSWERS 1 faster 4 more artistic 2 bigger 5 the most intelligent 3 noisiest Students study the example sentences and the table in exercise 1 ANSWERS 1 than 2 the Students study the table in exercise 1 again. Complete the spelling rules and add examples. ANSWERS 1 fastest 2 rarer 3 bigger |
Assessment criteria - Learn comparative and superlative forms of adjectives Descriptor: - complete the table with comparative and superlative adjectives Assessment criteria: - Make sentences using comparative and superlative adjectives. Descriptor: - study the example sentences and the table -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 51 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Entertainment and media |
Lesson 63 |
||
|
Teacher name: Kaltaeva D.A. |
|
||
|
Date: 02.02.2024 |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 «Г» |
Number present: 12 |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Choosing a present |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.13.1 use modal forms including mustn’t (prohibition), need (necessity) should (for advice) on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a conversation about comparing ideas for a present. • Learn key phrases for choosing a present. • Learn how to use should and must. • Practise comparing ideas for a present. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers actions |
Students actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment : 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students if they ever buy presents. Ask them when and where they buy them. • Ask them to think about the last present they bought and say why they chose that present. • Ask if they ever buy a present with another person. Lead - In
If kids are big enough to understand Christmas and presents, let them choose what they like. This way you can be sure they get something they really want. You will avoid long walks around the shops choosing Christmas present when you have no clue what’s “in” and what could be boring for them. |
“The wish flower” method helps to start the lesson with good wishes to each other. The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create fndly atmosphere Efficiency: By wishing each other they feel better and feel the support of others Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures worksheet Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex:1 P:70 • Discuss the questions as a class. Find out how many artists students can name and who the most popular artists are. • In a stronger class, encourage them to describe briefly the artist and their work using adjectives, and comparative and superlative forms from the previous lessons in the unit. • Explain that Shaun and Gemma are looking at posters of works by famous artists. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P: 70 • Play the CD. Students read and listen to find out the answer to the question in the instructions. In a stronger class, encourage students to listen with books closed. • Ask students if Gemma agrees with Shaun about the posters
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 3 P: 70 • Read through the key phrases with the class and the questions below each one. • Ask students to listen to the key phrases and find them in the dialogue. They answer the questions based on their understanding of the dialogue. • Play the CD. Students listen and answer the questions. In a weaker class, it may help to write the key phrases on the board, underlining the word(s) they need to define. Then, using the printed dialogue for support, help students work out what is being referred to in each case. |
Students discuss who are the most famous artists from your country? Have you got any posters of their work. ANSWERS Student’s own answers Students listen to the dialogue. Does Gemma agree with Shaun about the posters ANSWERS Yes, she does. Students listen to the key phrases. Then answer the question. ANSWERS 1 Gemma’s dad 2 van Gogh 3 Starry Night 4 the poster of the painting by Picasso |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a conversation about comparing ideas for a present. Descriptor: -listen to the dialogue. Does Gemma agree with Shaun about the posters Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for choosing a present Descriptor: - listen to the key phrases. Then answer the question. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Card Worksheet Students book |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
Home task: Ex: 2 P: 51 WB |
|
Poster Success KWL chart
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Entertainment and media |
Lesson 64 |
||
|
Teacher name: Kaltaeva D.A. |
|
||
|
Date: 02.02.2024 |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 «Ж» |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Biographies |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with some support on a growing range of general and curricular topics 6.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 6.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model text. • Learn key phrases to link events in a biography. • Write a biography of a famous writer and artist. |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, write the word biography on the board and elicit the meaning. • Ask students if they ever read biographies of famous people. • Ask what kinds of information you usually find in a biography. Elicit ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 71 • Read the title of the text and look at the picture with the class. Ask students if they have heard of this writer, and whether they can name any of her books (for example, Emma, Pride and Prejudice, Sense and Sensibility, Mansfield Park). • Students read the text, then match four of the five headings to the paragraphs. Tell them not to worry about the blue words at this stage • In a weaker class, demonstrate how to find clues in the text. In a stronger class, ask students which parts of the text helped them identify which heading to choose Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:71 • Focus students on the blue words in the text and explain that they are used to convey the time expression in a sentence. • Students match the sentences from the text. In a weaker class, ask them to do this in pairs. • In a stronger class, check answers by asking individuals to read out the complete sentence. Ex: 3 P:71 • Read the task with the class and refer students to the biographical information and the book covers. • Students use the questions to make notes and plan their biographies individually. • Students write their biographies. This can be set for homework. • Tell students to check their work, and check they have used comparative and superlative forms, and time expressions correctly |
Students read the model text. Then match headings with paragraphs. There is one heading that you don’t need. ANSWERS: 1 B 2 C 4 D 5 A Students study the model text and find the time expressions in blue. Then match. ANSWERS: 1 e 2 d 3 f 4 c 5 a 6 b Students write a biography. Use the notes on Herge or detail about another writer you admire. ANSWERS: 1 She was born in Warsaw. 2 A year later, he got married. 3 She lived in Paris for five years. 4 By the age of twenty, he was studying at university. 5 She died in 1824 |
Assessment criteria - Study a model text. Descriptor: - read the model text. Then match headings with paragraphs. There is one heading that you don’t need. Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases to link events in a biography Descriptor: - study the model text and find the time expressions in blue. Then match. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 53 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Entertainment and media |
Lesson 65 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Entertainment and media |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.3.1 use common participles as adjectives and order adjectives correctly in front of nouns on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.6.17.1 use subordinate clauses following think know believe hope, say , tell use subordinate clauses following sure, certain; use defining relative clauses with which who that where on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with some support on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about films. • Learn about adjectives ending in -ing and -ed. • Learn and practise using relative clauses. • Write a film review. |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, divide students into pairs and ask them to tell each other about their favourite film. Encourage them to give reasons for their choice. • Ask a few students to describe their partner’s preferences |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 75 • Focus students’ attention on the words in the box. Encourage them to try to guess the meaning of all the words before they look them up in a dictionary. • Ask students to name a film for each genre. • Model and drill the pronunciation of the words Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:75 • Play the recording and ask students to listen and read the text. • Allow students time to read the questions. In a weaker class, pre-teach the following words and phrases: relationship, based on, star (verb), brave and recommend. • Ask them to read the text again and answer the questions. • Check answers as a class Ex: 3 P:75 • Draw students’ attention to the words in blue. Ask them to find the word or phrase that the each blue word refers to in the text and underline them (The Old Man and the Sea, shepherd, town, actors, film, anyone). • Students complete the rules and check their answers. |
Students work in pairs. Check the meaning of these words in a dictionary. Then write the name of a film for each genre. ANSWERS: Student’s own answers. Students read and listen to the film review. Answer the question. ANSWERS: 1 The title of the film is The Old Man. 2 It’s a drama. 3 It’s about family relationships and the relationship between people and nature. 4 Yes, it’s based on a book by the American writer Ernest Hemingway. 5 It’s set in Kazakhstan 6 Yerbulat Toguzakov plays the main role. 7 Her favourite character is Kassym. She likes him because he is brave. 8 She thinks that it is a great film. She would recommend it to anyone who likes adventure stories Students look at the words in blue in the text. Then choose the correct words in the rules. ANSWERS: 1 who 2 which 3 where |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for talking about films. Descriptor: - Check the meaning of these words in a dictionary. Assessment criteria: - Learn about adjectives ending in -ing and -ed. Descriptor: - read and listen to the film review. Answer the question Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 53 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Entertainment and media |
Lesson 66 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Buying tickets |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for buying tickets. • Listen to a conversation about buying tickets. • Practise buying tickets |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, ask students: When do you buy tickets? Elicit some answers. • Ask: When you buy tickets at a theatre, what information do you give? Elicit ideas such as which day you want to go, where you want to sit, how much you want to pay, etc. • Tell students they are going to practise buying tickets. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 73 • Students work in pairs to match the types of show to the posters. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:73 • After students have listened to the exchange, ask them what type of show Tom is buying tickets for Ex: 3 P:73 • Read through the key phrases with the class. Check that students understand row and model the pronunciation, /rəʊ/. • Ask students to copy the ticket. • Students listen again and complete the ticket with the correct information Ex: 4 P:73 • Tell students they are going to listen to some more seat and row numbers. • Students write down the letters and numbers they hear. • Check answers, then play the CD again for students to listen and repeat. |
Students match posters with the types of show in the box. ANSWERS: 1 ballet 2 musical 3 play Students look at the posters and listen to the conversation. Which type of show is Tom buying tickets for? ANSWERS: A musical (We will Rock You) Students study the key phrases. Then listen to the conversation again. Complete the ticket with the correct information. ANSWERS: 1 We Will Rock You 2 18th 3 11 4 12 5 V 6 £46.00 Students listen and write the numbers and letters. Then listen and repeat. ANSWERS: 1 seats 9 and 10 in row R 2 seats 24, 25 and 26 in row H 3 seats 16–19 in row J 4 seats 30–32 in row E |
Assessment criteria - Learn key phrases for buying tickets Descriptor: - study the key phrases. Then listen to the conversation again. Complete the ticket with the correct information Assessment criteria: - Listen to a conversation about buying tickets. Descriptor: - look at the posters and listen to the conversation. Which type of show is Tom buying tickets for? Make CCQ questions Yes / No
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 53 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Entertainment and media |
Lesson 67 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL: Natural science: Adapting to the environment |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with some support on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about animal adaptations and migrations. • Read a text about animal migrations. • Practise talking about animals migrations. |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, write polar bear and camel on the board. • Check that students understand the words, then ask where these animals live. Ask why polar bears are able to live in very cold conditions. • Elicit some ideas, then write the word adapt on the board. Ask how camels have adapted to living in very hot, dry conditions. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 74 • Refer students to the pictures and elicit or teach the names of the animals (arctic fox, snake, salmon, butterfly). • Play the CD, and ask students to listen and read the text. • Students match the words in blue with the definitions. • Check answers, and make sure that students understand the meaning of the blue words, for example, by asking them to translate them into their own language. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:74 • Focus on the map and the pictures. Model pronunciation of grey whale and arctic tern. • Play the CD and ask students to read and listen, and choose the correct migration routes.
Ex: 3 P:74 • Allow time for students to read the table. • Play the CD again, and ask students to listen and complete the table. • Ask students to compare answers in pairs, then check answers with the class. |
Students read and listen to the text. Then match the words in blue with definitions. ANSWERS: 1 breed 2 habitat 3 migrate 4 feed 5 adapt Students look at the map. Then listen and choose the correct migration route for the grey whale and the arctic tern. ANSWERS: grey whale b arctic tern c
Students listen again and complete the table. ANSWERS: 1 Bering Sea, Arctic 2 3 3 Antarctic 4 20,000 |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary for talking about animal adaptations and migrations Descriptor: - read and listen to the text. Then match the words in blue with definitions. Assessment criteria: - Read a text about animal migrations. Descriptor: - look at the map. Then listen and choose the correct migration route for the grey whale and the arctic tern. Make CCQ questions Yes / No 1 Do animals adapt to their environment in different way? Yes 2 Do polar bears live in Indian ocean? No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 54 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 5 Entertainment and media |
Lesson 68 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review unit 5 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use vocabulary for skills and people. • Write adjectives used to describe animals • Learn can and could for ability in the present and past. |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 76 • Ask students to complete the sentences with the missing words. • Check their answers. Drill the pronunciation of the new words if necessary. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:76 • Focus on the example. Ask students to work in pairs to complete the adjectives with a, o, I, o and u. Then find pairs of opposites. • In a weaker class, check that students understand all the adjectives, for example by asking them to translate the words into their own language. In a stronger class, encourage students to put the words into a sentence to show understanding. • Model and drill the pronunciation of any new adjectives Ex: 3 P:76 Tell students to read all the sentences carefully before they start to complete them to check they understand the context. They should think about whether the sentences refer to the present or the past. |
Students complete the sentences with the correct form of the words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 writer, wrote 2 composer, composed 3 dancer, dance 4 cook, cook 5 paints, painter Students complete the adjectives with a, e, I, o and u. Then find pairs of opposites. ANSWERS: 1 slow – f fast 2 domesticated – c wild 3 stupid – b intelligent 4 light – e heavy 5 common – d rare 6 aggressive – a peaceful Students complete the sentences with the words in the box ANSWERS: 1 must 2 Could, couldn’t 3 How many, can, can’t 4 should |
Assessment criteria - Use vocabulary for skills and people. Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the correct form of the words in the box. Assessment criteria: - Write adjectives used to describe animals Descriptor: - complete the adjectives with a, e, I, o and u. Then find pairs of opposites. Make CCQ questions Yes / No 1 Did J. K. Rowling become a writer in 2004? No 2 Did she write five books? Yes |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 69 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Feelings |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 7.4.1.1 understand the main points in a growing range of short, simple texts on general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Do a quiz about risks and dangers. • Learn how to use modifiers with different adjectives. • Learn how to express emotions |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, write the words risk and danger on the board and elicit the meanings. • Ask students if they do any things that are dangerous. Elicit some ideas. • Ask students if they enjoy taking risks. Elicit a variety of responses |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 106 • Read the title of the quiz and look at the photos. Ask students if they think the things pictured are scary. • Students do the quiz individually and look at the key. • They discuss their results with a partner, giving reasons for their ideas. • Ask one or two students to report back to the class. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:106 • Explain that each of the adjectives can be used with one of the prepositions to give a particular meaning. Ex: 3 P:106 Students read the phrases again and think about the emotion they express. If they are not sure, refer them back to the quiz to check the context and any other supporting words that might help. • Ask students to use the phrases in sentences. In a weaker class, ask students to work in pairs and write new sentences using the phrases in context. Monitor students as they do this. In a stronger class, ask students to say new sentences with the phrases as a whole-class activity. |
Students do the Risks and danger questionnaire. Then look at the key. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers Students add about, at, in or of to each adjective. Then check your answers in the questionnaire. ANSWERS: 1 at 2 of 3 at 4 about 5 in 6 about 7 of 8 about Students are the phrases in exercise 2 positive or negative? ANSWERS: 1 negative 2 positive 3 positive 4 positive 5 positive 6 negative 7 negative 8 negative |
Assessment criteria - Do a quiz about risks and dangers. Descriptor: - do the Risks and danger questionnaire. Then look at the key. Assessment criteria: - Learn how to use modifiers with different adjectives. Descriptor: - add about, at, in or of to each adjective. Then check your answers in the questionnaire. Make CCQ questions |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 54 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 70 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Arachnophobia |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.1.1 understand the main points in a growing range of short, simple texts on general and curricular topics 7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about phobias. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Talk about fears and phobias. |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, draw a picture of a spider on the board. Ask students to identify the animal and say how it makes them feel. • Then draw a picture of a snake. Repeat the activity and find out if any of the students are scared of snakes. • Ask students to suggest other things that could scare people. Elicit some ideas, then write the word phobia on the board. Ask students what it means. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 108 • Read the questions with the class and discuss their ideas. Ask students if they are frightened of anything. • Ask students if they know anyone who has a phobia. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:108 • Read the question with the class before they read and listen to the text. Ex: 3 P:108 • Explain that students should now read for detail so that they can decide if the sentences are true or false. Remind them to correct the false sentences
Ex: 4 P:108 • Refer students back to the text to find the blue adjectives. In a weaker class, students can match these in pairs. • Remind students that there is one definition they do not need to use. |
Students answer the questions ANSWERS: 1 Students’ own answers. 2 Students’ own answers. 3 The difference between a fear and a phobia is that a phobia can seem irrational but is very strong and has to be treated like an illness. Students read and listen to the text. How can you cure a phobia? ANSWERS: Exposure therapy. Students read the text again and write true or false. Correct false sentences. ANSWERS: 1 True. 2 False. Mark Tanner has helped a lot of patients with phobias. 3 True. 4 False. Georgia’s family hid plastic spiders at home. 5 True. 6 False. Georgia may touch a spider. Students find adjectives in blue in the text. Then match them with definitions. There is one definition you do not need. ANSWERS: 1 d 2 f 3 e 4 a 5 b |
Assessment criteria - Read about phobias. Descriptor: - answer the questions Assessment criteria: - Read for General meaning and specific information. Descriptor: - read the text again and write true or false. Correct false sentences. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 54 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 71 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Present Perfect: affirmative and negative |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 7.6.7.1 use simple perfect forms to express indefinite and unfinished past with for and since] on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the affirmative and negative forms of the present perfect. • Read about school phobia. • Use the present perfect to talk about experiences. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Refer students back to the text on page 80. Focus on the final paragraph and the sentence I’ve looked at hundreds of spiders with Mark. • Ask: Is Georgia talking about an event at a specific time in the past, or about an experience at some time in the past? • Elicit that she is talking about an experience at some time in the past. Tell students that we use the present perfect to talk about experiences. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 109 • Students use the sentences in the text as examples to help them complete the rules. In a stronger class, let them do this individually, otherwise, in pairs. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. LANGUAGE NOTE We use ’ve or ’s before the past
participle: I’ve been to England. NOT Ex: 2 P:109 • Refer students to the Irregular verbs list on page 104 of the Workbook to help them decide which verbs are irregular. They may need further reference material to complete the table Ex: 4 P:109 • Students complete the sentences. In a weaker class, remind them to refer back to exercise 2 for the past participles. In a stronger class, encourage them to try to remember these |
Students complete the sentences from the text. Then choose the correct answers in the rules. ANSWERS: 1 ’s helped 2 ’ve seen 3 ’s made 4 ’ve seen Rules ANSWERS 1 past, now 2 don’t say 3 have Students complete the table with the past simple and past participle forms of the verbs in the box. ANSWERS: Regular: look – looked – looked, play – played – played, stay – stayed – stayed, touch – touched – touched, visit – visited – visited Irregular: speak – spoke – spoken, find – found – found, go – went – been/gone, see – saw – seen, make – made – made Students complete the sentences using the present perfect form of the verbs. ANSWERS: 1 ’ve seen 2 haven’t spoken 3 haven’t stayed 4 ’ve looked 5 hasn’t touched |
Assessment criteria - Learn the affirmative and negative forms of the present perfect. Descriptor: - complete the sentences from the text. Then choose the correct answers in the rules. Assessment criteria: - Use the present perfect to talk about experiences. Descriptor: - complete the sentences using the present perfect form of the verbs. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 78 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 72 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Injuries |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers 7.2.4.1 understand with limited support the main points of extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 7.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary of injuries. • Listen to people talking about dangerous jobs. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, write the word injury on the board and elicit or explain the meaning. • Ask students for examples of injuries and ask if they have ever had any injuries. • Ask students what injuries people sometimes get at work. • Ask what jobs students think are dangerous and why. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 110 • Once students have completed the table, model and drill the pronunciation of the words. Check that students understand them, for example, by asking them to translate the words into their own language.
Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:110 • Students choose the correct words in the sentences individually. Ex: 3 P:110 • Before students match the photos and the jobs mentioned in the programme guide text, ask them if they can guess the jobs from the pictures Ex: 4 P:108 • Students read the sentences to find out how much they already know about the dangerous jobs before they listen to the recording. They discuss in pairs whether the sentences are true or false. In a weaker class, discuss as a group which jobs are likely to be dangerous and why. • Play the CD. Students listen and check their answers. Play the CD again, and ask students to correct the sentences which were false. In a stronger class, students could correct false sentences before listening again |
Students check the meaning of the words. Then complete the table. ANSWERS: 1 burnt 2 break 3 a bruise 4 bite 5 a sprain 6 injured Students choose the correct words. ANSWERS: 1 burnt 2 cuts and bruises 3 bitten 4 injured 5 broken 6 cut Students look at the photos and match them with jobs in the programme guide. ANSWERS: A 2 B 1 C 4 D 3 Students work in pairs. Write true or false. Then listen and check your answers. ANSWERS: 1 True. 2 False. Volcanoes don’t erupt very often. 3 False. Venomologists study venom. 4 True. 5 False. Farming is dangerous because of the big machines. |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary of injuries. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words. Then complete the table. Assessment criteria: - Listen to people talking about dangerous jobs Descriptor: - look at the photos and match them with jobs in the programme guide. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 80 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 73 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Present Perfect: questions |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.7.1 use simple perfect forms to express indefinite and unfinished past [with for and since] on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the question forms of the present perfect. • Practise writing questions using the present perfect. • Learn key phrases for reacting to what people say. • Practise reacting to what people say. |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Ask students to recap what the present perfect tense is used for (to talk about experiences in the past). Remind students that they have covered the affirmative and negative forms of this tense. • Tell students they are going to study present perfect questions. Ask them what they think might change in the question form. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets. |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 111 • Explain that the completed sentences provide a context for working out the rule. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. LANGUAGE NOTE In present perfect questions, have / has
comes before the subject: Have you injured your arm? NOT
It is the past participle, not the past simple
form, which is used in present perfect questions: Has she seen that
film? NOT Ex: 2 P:111 • Ask students to work individually to choose the correct words. • Check answers by asking individual students to read out their sentences. Ex: 3 P:111 • Focus on the information in the table. Check that students understand stunt person and bodyguard. • Focus on the task and example and do another example with the whole class if necessary. • Once students have individually written the questions and answers, ask them to compare their answers in pairs. Then check answers with the class. |
Students complete the sentences with the words in the box. Then choose the correct words in the rule. ANSWERS: 1 has 2 ever, No 3 Have, they Rule answers. past participle Students choose the correct words ANSWERS: 1 Have, have 2 had, hasn’t 3 Has, has 4 Have, haven’t 5 broken, haven’t Students write questions and answers ANSWERS: 1 Has Vin broken a bone? No, he hasn’t. 2 Has Bess jumped off a building? Yes, she has. 3 Has Bess met the president? No, she hasn’t. 4 Has Vin met the president? Yes, he has. 5 Have they driven at 200kph? Yes, they have. |
• In a weaker class, you may need to provide more examples of questions to help them understand the structure. • In a weaker class, choose the correct words with teacher’s support |
Assessment criteria - Learn the question forms of the present perfect. Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the words in the box. Then choose the correct words in the rule. Assessment criteria: - Practise writing questions using the present perfect. Descriptor: - write questions and answers Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 74 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 09.03.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Helping with problems |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a conversation about an injury. • Learn key phrases for helping someone who is hurt. • Practise suggesting how to help someone. |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, tell students you are going to mime one of the injuries from the vocabulary section of this unit. Mime spraining your ankle and get students to guess the injury. • Ask students to imagine their friend has sprained his/her ankle. Ask: What would you say to your friend? |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets. |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P: 112 • Look at the photo with the class and ask students to guess what has happened to Leah. • Play the CD. Students read and listen, and answer the question in the instructions. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:112 • Ask students to read the key phrases and match them to make mini-dialogues. • Ask students to find the key phrases in the dialogue and translate them into their own language. Ex: 3 P:112 • In a stronger class, ask students to close their books. You point to the body parts to find out if students already know the vocabulary. • Check answers and model pronunciation of the words. |
Students look at the picture. What has happened? Listen to the dialogue then practice the dialogue with your partner. ANSWERS: Leah has cut her arm. Students match the key phrases ANSWERS: 1 b 2 d 3 c 4 a Students match photos with with words in the box. ANSWERS: 1 shoulder 2 wrist 3 ankle 4 elbow 5 neck 6 toe 7 finger 8 knee |
• In a weaker class, match the key phrases with teacher’s support • In a weaker class, students match the words with the photos |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a conversation about an injury. Descriptor: - look at the picture. What has happened? Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for helping someone who is hurt Descriptor: - match the key phrases Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 75 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 14.03.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL: Reading for pleasure: Stories |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.3.8.1 recount some extended stories and events on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a folk story from Kazakhstan . • Learn about different types of adverbs. • Learn how to use for and since with the present perfect. • Write a summary of a folk story or a legend. |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, divide students into pairs and ask them to think about the most beautiful garden they have ever seen. Tell them to describe it to their partner. • Get feedback from the class by asking a few students to describe their partner’s preferences. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:114 • Tell students they are going to read a Kazakh folk story. Draw their attention to the photo and the title. • Students discuss their ideas. Get some feedback from the class, but do not confirm or reject any ideas at this stage. Answers: Students’ own answers Ex: 2 P:114 • Refer students to Part 1 of the story. In a weaker class, preteach the following words and phrases: pot, buried, wise, argue, rest, seeds, gates, merchant, gull, swallow, lark. • In pairs, students put the events in the correct order. • Check answers as a class. Allow students one or two minutes to discuss their ideas about the ending of the story, then elicit some ideas Answers: 1 the shepherd’s sheep died 2 the farmer gave the shepherd some land 3 the shepherd found a pot of gold coins 4 the farmer and the shepherd argued 5 they asked a wise man for advice 6 the student travelled to the city 7 the student met some merchants Ex: 3 P:114 • Tell students they are going to hear the ending of the story. Explain they have to listen and decide whether it’s a happy ending or not. They should focus on listening for the general meaning. • Play the recording. • In pairs, students discuss the ending and compare it with their ideas in exercise 2 Answers: The story has a happy ending. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the photo and the title of the story. What do you think the story is about? Descriptor: - look at the photo - discuss their ideas Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students work in pairs. Read the story and put the events in the correct order. Descriptor: -work in pairs - put the events in the correct order. Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students listen the story. Does it have a happy ending? Descriptor: - listen the story - answer the question Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
-can discuss with their ideas Total: 1 point -can read the story and put the events in the correct order. Total: 1 point -can answer the question Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Holidays |
Lesson 76 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative Assessment for term 3 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.L4 Understand with little support some of the implied meaning in extended talk on a limited range of general and curricular topics. 7.R6 Recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer on a range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics 7.W1 Plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with some support on a range of general and curricular topics. 7.S4 Respond with some flexibility at both sentence and discourse level to unexpected comments on a growing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to recall the previous lesson (Speaking, page 86) and elicit what they remember about the scenario. • Ask: Where was the woman? (In a shop.) What was she doing? (Returning a record.) What did she want? (To change it.) Did she get what she wanted? |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
LISTENING Task. Listen to the recording twice and answer the questions. Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS or A NUMBER.CD3. Tapescript 3.OR Go to this link to listen information Example: 0. Was she happy in her marriage? No, she was not. READING Task. Read the text carefully and answer the questions. __ Part 1. Choose the correct answer Part 2. Find some inconsistences in the statements. Mark these sentences Yes, No, Not Given. 3. Fishermen all over the world know when hurricanes start 4. Hurricanes usually start in the steppe 5. The best place to hide from hurricane is indoors _______________________. WRITING Task. Look at the films below. Choose one of them to write a review about. Use linking words and connectors in sentences to make some coherent paragraphs. You can use prompts for your answer SPEAKING Task. You will be given a card which asks you to retell a short story about a particular situation. You should include your ideas while telling it. You will be given 1 minute to prepare your talk and then 1-2 minutes to speak. Your classmates prepare the questions to ask you on the topic. Learners take turns in retelling the stories from the cards |
Students listen to the recording twice and answer the questions Descriptor: - listen and match Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students Read the text carefully and answer the questions Descriptor: - Paraphrase the given sentences so it has similar meaning Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students choose ONE of the topics and write. Descriptor: - Write a story about a concert Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
-can match the halves of the sentences Total: 1 point -can paraphrase the given sentences Total: 1 point -can write a story about a concert Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 8 Natural disasters |
Lesson 77 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 6 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Phoning a medical helpline |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.3.8.1 recount some extended stories and events on a limited range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for phoning a medical helpline. • Listen to someone phoning a medical helpline. • Practise phoning a medical helpline |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In With books closed, ask: Have you ever had an accident? What happened? • Elicit some answers, then ask: What do you do when someone has an accident? • Elicit some answers, then write Medical helpline on the board. Elicit that this is a helpline you can phone when you hurt yourself and need advice |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:115 • Students work in pairs to match the instructions with the pictures. Answers: 1 B 2 E 3 A 4 F 5 D 6 C Ex: 2 P:115 • Play the CD. Students listen and say which instructions they hear. Answers: Put it under cold water. Put some ice on it. Take an aspirin. Ex: 3 P:115 • Read through the key phrases with the class. Point out that we use the present perfect, not the past simple, when talking about injuries that happened very recently. • Allow students time to read the questions. • Play the CD again. Students listen and answer the questions individually, then compare their answers in pairs. Answers: 1 She has burnt her hand. 2 She was making lunch. She was taking some hot soup out of the microwave and it went on her hand. 3 It really hurts. 4 She’s fallen over and bruised her knee. 5 She is going to play badminton. 6 She mustn’t move her leg a lot. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students match instructions with pictures Descriptor: - work in pairs -match instruction with pictures Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to two telephone calls to a medical helpline. Which instructions from exercise 1 do you hear? Descriptor: - listen to two telephone calls to a medical helpline Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students study the key phrases. Then listen to the telephone calls again and answer the question Descriptor: - listen the story - answer the question Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
-can discuss with their ideas Total: 1 point -can read the story and put the events in the correct order. Total: 1 point -can answer the question Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|

шағым қалдыра аласыз