Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 49 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Books and films: genres |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.15.1 use infinitive forms after a limited number of verbs and adjectives; use gerund forms after a limited variety of verbs and prepositions; use some prepositional verbs and begin to use common phrasal verbs on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary of film genres. • Do a questionnaire on books and films. • Learn verbs that are followed by -ing or to. |
||
|
Value links |
Family – Family values are moral and ethical principles of typical family life, including sacrificing for loved ones, putting your loved ones first, and keeping your loved ones at the centre of your thoughts and actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students what films they have seen recently. Ask if they enjoyed the film and why, or why not. Encourage students to express their opinions. • Ask students what kinds of films and books they enjoy the most, and try to elicit some genres. Lead - In
If you're anything like us, you probably like to read the book before seeing the movie. This year, as usual, Hollywood is adapting a slew of books—fiction and nonfiction—into films. If you want to prepare yourself for these literary movies, look no further: |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
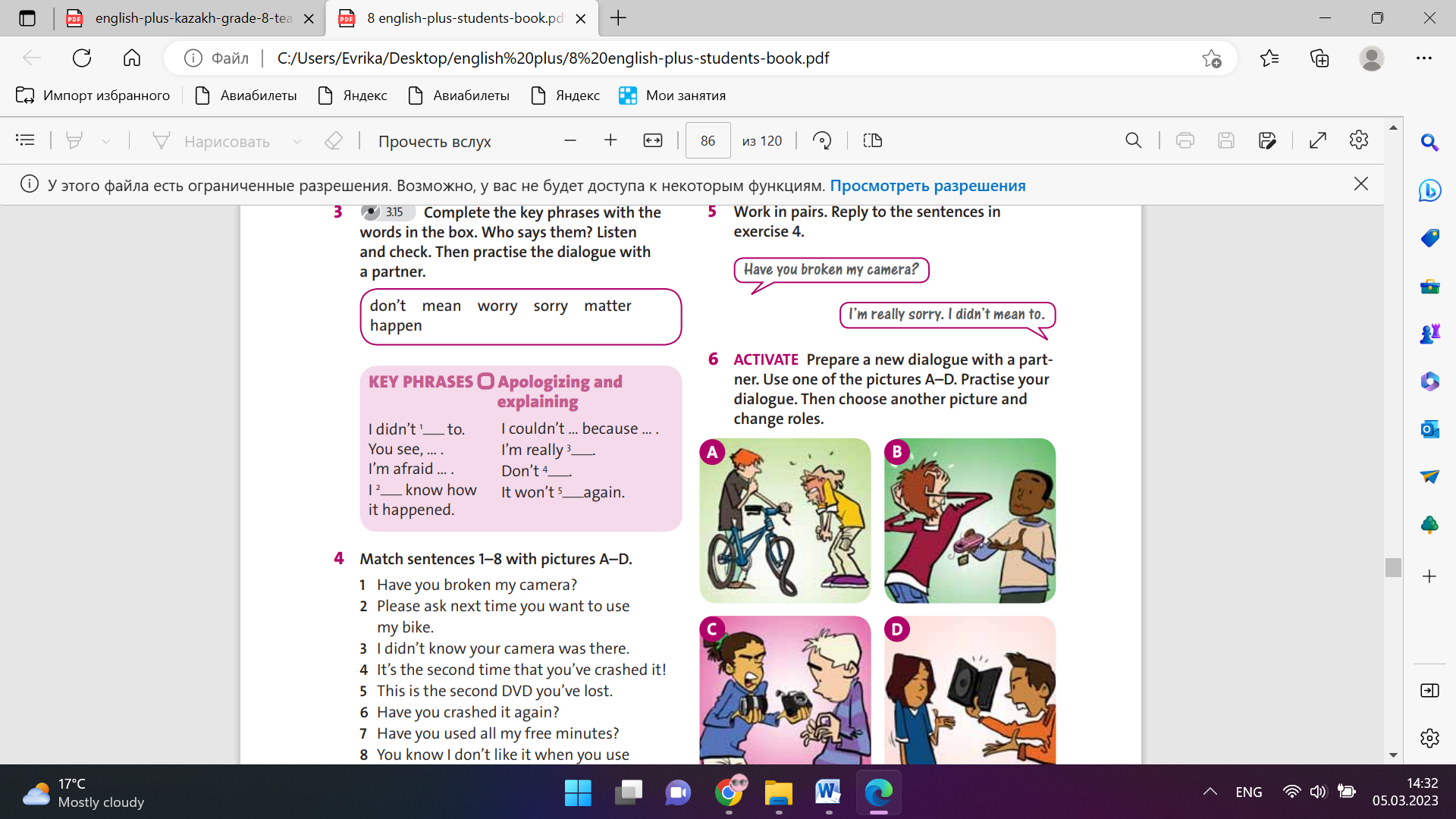
Ex: 1 p:56 • Focus students on the books and films pictured. Then, in pairs, students match them with the words. • While checking answers, model and drill the pronunciation if necessary. • Follow up by focusing on the genres which were not illustrated. Ask students to think of films or stories which match these categories. Ex: 2 p:56 • Read the example with the class and elicit one or two more possible titles from the class before they write their titles individually. • Once students have guessed genres, ask them to report back on their partner’s titles and genres
Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples By task – more motivated learners can do task without support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location Ex: 4 p:56 • To introduce this point, refer students back to question 6 in the questionnaire. Ask some students to give an answer to this question. Ask students to translate the answer, I enjoy doing unusual things, into their own language. • Elicit some answers to question 5, focusing students on the third sentence. Ask students to translate I’d like to work with people into their own language. • Point out that in question 6 option b the verb like is followed by the -ing form of the verb, but in question 5 it is followed by to + an infinitive. |
Students match the words in the boxes with the books and films in the pictures ANSWERS : 1 a detective story 2 a romance 3 a horror story 4 a fantasy 5 a comedy 6 a musical 7 an adventure story / film 8 a science fiction story / film
Students invent titles for books and films using the words and phrases in the boxes. ANSWERS : Students’ own answers. Students complete the sentences from the questionnaire ANSWERS: 1 being 2 reading 3 don’t 4 want 5 to work 6 wouldn’t Negative form of would: wouldn’t Short forms of would: I’d, you’d, he’d, she’d, it’d, we’d, they’d
|
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary of film genres.
Descriptor: - match the words in the boxes with the books and films in the pictures Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Learn verbs that are followed by -ing or to Descriptor: - complete the sentences from the questionnaire -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 40 WB |
|
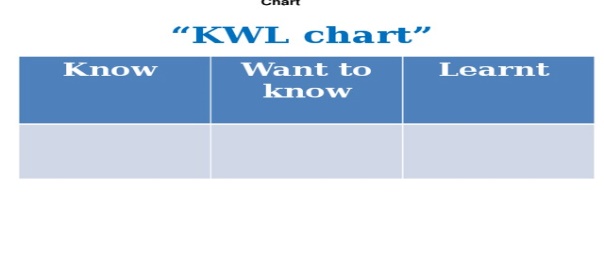
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 50 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 10.01.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Movie technology. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.4.1 read a growing range of extended fiction and non-fiction texts on familiar and some unfamiliar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about the use of technology in the movies. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Learn how to find specific information. • Learn about the suffixes -er and -or. |
||
|
Value links |
Loyalty – Loyalty might be a core personal value to you if you highly prize friends that are reliable and trustworthy. You might put your friends or chosen family first, always being there for them when they need you. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students what they know about the history of cinema. • Ask them when people made the first films, and if students have seen any very old films. Ask what the films were like. • Elicit that very early films were silent, and were in black and white. • Ask how films are continuing to improve now. • Elicit ideas and encourage students to join in and contribute ideas or express opinions. Lead - In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
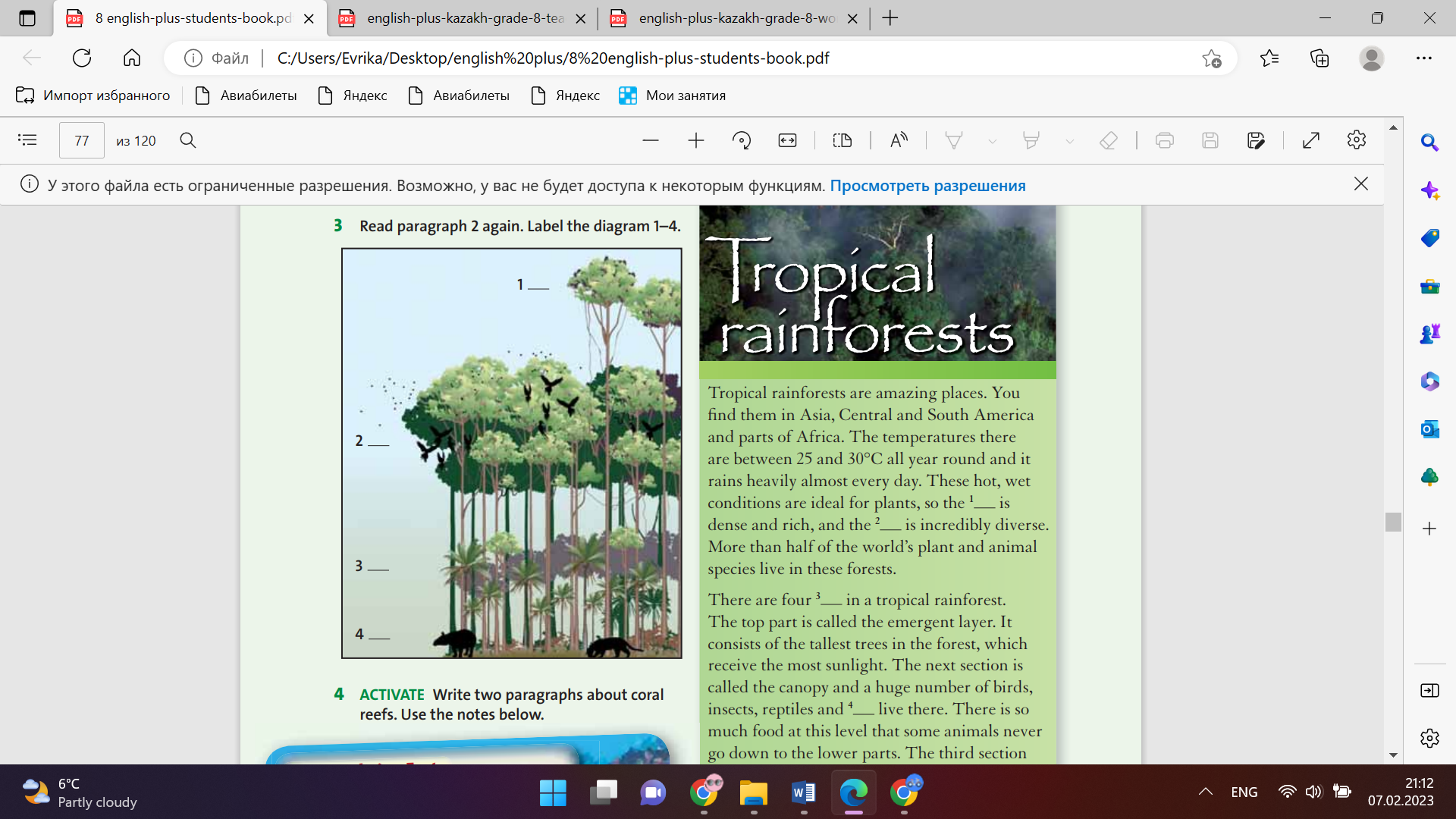
Ex: 1 p:58 • Read through the words in the box with the class and elicit or explain the meaning. • Students guess the order of the words on the timeline in pairs. • Students can check their answers by reading and listening to the text. When they have done this, ask round the class to find out if they guessed correctly. Ex: 2 p:58 • Allow students time to read the study strategy carefully. In a weaker class, go through each point and check understanding. In a stronger class, ask students if this is something they do already. • Students read the text again and answer the questions. Encourage all students to follow the tip step-by-step, by underlining the key words in the questions then looking for these in the text.
Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples By task – more motivated learners can do task without support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location Ex: 3 p:58 • Do the first item with the class by asking students to read the text, and to put their hand up when they find the correct word (viewer). • Check answers and spelling by asking students to come up and write the words on the board |
Students look at the words in the box and guess the correct order on the timeline ANSWERS : 1 colour 2 sound 3 3D 4 surround-sound 5 computer-generated images 6 digital projectors
Students find the answers to these questions ANSWERS : 1 In 1902. 2 There were more than 4,000. 3 They listened to a pianist. 4 Some actors lost their jobs because they didn’t have good voices or because they could not act and speak at the same time. 5 Surround-sound became popular in the 1970s. 6 With future technology it is possible that we will be able to feel a character’s emotions by connecting our bodies to special cinema seats. Students look at verbs and find corresponding nouns in the text. ANSWERS: 1 viewer 2 producer 3 actor 4 projector |
Assessment criteria - Read about the use of technology in the movies.
Descriptor: - look at the words in the box and guess the correct order on the timeline Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Read for general meaning and specific information. Descriptor: - look at verbs and find corresponding nouns in the text. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 40 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 51 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
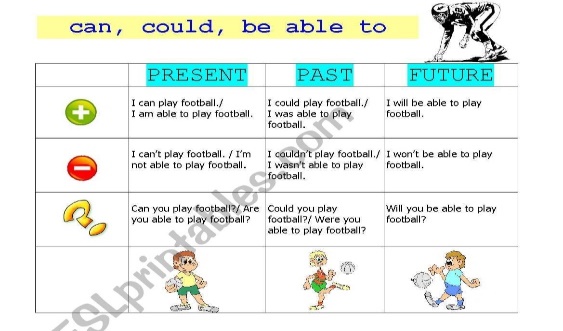
Could, can, will be able to |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.3.1 give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the use of could, can and will be able to. • Practise using could, can and will be able to to talk about ability in the past, present and future. |
||
|
Value links |
Fairness – If you value fairness, you might be highly sensitive to situations at school or in the workplace where a teacher or a peer has exhibited favoritism or allowed someone to get away with living by a different set of rules to everyone else. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, check students’ understanding of the text. Ask the class, Can we create realistic special effects now? (Yes, we can.) Can we feel the same emotions as the characters on the screen now? (No, we can’t.) • Explain that this lesson introduces ways to talk about ability and possibility in the past, present and future. Lead - In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:59 • To introduce this point, write these questions on the board, and ask students to find the answers in the text about cinema: What was possible in the 1930s? What is possible now? What will be possible in the future? • Elicit sentences from the text that give the answers and write them on the board (producers could include songs …, film makers can now create special effects …, we’ll be able to connect our bodies …). Underline can, could and will be able to and elicit that they refer to possibility or ability in the past, present and future. Ex: 2 p:59 • Students complete the sentences individually, then compare their answers in pairs. Ask them to help each other correct any mistakes before you check with the class. • In a weaker class, when checking answers highlight the tense in each sentence so students understand why each form was used. Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples By task – more motivated learners can do task without support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location Ex: 3 p:59 Focus on the title and ask students to predict what the text will be about. If they find this difficult, translate senses and ask them to think about what senses were mentioned in the first reading text (sight, hearing, smell). • Students complete the text with the verbs and the correct forms of could, can and will be able to. |
Students complete the sentences from the text ANSWERS : 1 could 2 can 3 be able to 1 Ability and possibility. 2 Film producers couldn’t include songs. They can’t create very realistic special effects. We won’t be able to feel the character’s emotions. 3 Yes, they do
Students complete the sentences with could, can ANSWERS : 1 can’t 4 couldn’t 2 can 5 could 3 won’t be able to 6 ’ll be able to Students complete the text with the verbs in the box ANSWERS: 1 could smell 4 can enjoy 2 couldn’t hear 5 ’ll be able to feel 3 couldn’t wear 6 ’ll be able to connect |
Assessment criteria - Learn the use of could, can and will be able to.
Descriptor: - complete the sentences from the text Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Practise using could, can and will be able to to talk about ability in the past, present and future. Descriptor: - complete the sentences with could, can -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 52 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
S. Murataliyeva |
||
|
Date: |
15.01.2024 |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Books and films: features |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.7.1 develop and sustain a consistent argument when speaking or writing 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary of the features of books and films. • Listen to a radio interview about books. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. • Talk about films and books |
||
|
Value links |
Honesty – You may highly value telling people the truth. This one gets tricky when being honest can be hurtful to others. So, a person who really puts honesty first might be the sort of person who will tell the truth even if it hurts to do so. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students what their favourite film is. Elicit some ideas and ask students to say what they like about the film in particular. Ask which part of the film they like best and which character. • Ask students what their favourite book is and why. Ask who wrote the book, then ask where the story happens and who the characters are. Ask which part of the book they like best. Lead - In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:60 • After students have checked the meaning of the words and completed the table, check answers with the class and check that students understand the meaning of all the new vocabulary. Model and drill the pronunciation of special effects, blockbuster, theme, scene and character. Ex: 2 p:60 • In a weaker class, students match the definitions with the words in pairs. In a stronger class, students work individually, then check their answers in pairs Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples By task – more motivated learners can do task without support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location Ex: 4 p:60 • Focus students’ attention on the topics in the box and refer back to the vocabulary on page 68 if necessary. • Students listen to the speakers and match the topics |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box and complete the table ANSWERS : Books only: novelist, best-seller, publisher Films only: special effects, film director, subtitles, blockbuster, scene, cast, script Both books and films: beginning, ending, theme, plot, character, biography, setting
Students match the definitions with words in exercise 1 ANSWERS : 1 cast 2 blockbuster 3 novelist 4 best-seller 5 biography 6 script 7 subtitles 8 setting Students listen to a radio programme. Match the topics in the box with the speakers. ANSWERS: 1 plot, characters 2 characters, ending 3 plot 4 crime, setting, characters |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary of the features of books and films.
Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words in the box and complete the table Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Listen to a radio interview about books Descriptor: - listen to a radio programme. Match the topics in the box with the speakers. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 53 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Date: |
17.01.2024 |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus Second conditional |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.6.17.1 use if / unless/ if only in second conditional clauses and wish [that] clauses [present reference]; use a growing variety of relative clauses including why clauses on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the form and use of the second conditional. • Practise using the second conditional to talk about imaginary situations. |
||
|
Value links |
Generosity – This may be a core value of yours if you cherish people who will give their time and resources to people in need. You may consider yourself to be a generous person if you find joy and meaning in giving to others. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to think again about the interview with Joe. Ask: Where would he go if he had a time machine? • Write the question on the board and elicit the answer (he would go to the past), then focus on the question. Ask: Does it refer to a real or imaginary situation? (imaginary). • Tell students that this type of sentence is called the second conditional.. Lead - In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:61 • Read the examples in the table with the class. • In a weaker class, once the rules have been completed and checked, demonstrate the structure of the second conditional example sentences with reference to the rules. • In a stronger class, encourage students to identify the tenses used in the second conditional example sentences. Ex: 2 p:61 • Remind students to read the sentences carefully to ensure they understand the context before they choose which verb form to use in each gap. • Students complete the sentences with the correct form of the verbs. Tell students to use the table in exercise 1 to help them. • Let students compare answers in pairs, then check answers by asking students to read out their completed sentences Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Ex: 4 p:61 • Do one or two examples with the whole class. • Students write the questions individually. • Check that students have formed the questions correctly. • Allow students time to prepare their answers individually, then put them into pairs to ask and answer the questions. • Ask some students to write their answers on the board. In a weaker class, correct mistakes as a class. In a stronger class, encourage students to correct the sentences individually first, then ask one or two students to correct the sentences on the board |
Students complete the second conditional sentences with the words in the box. ANSWERS : 1 did 2 had 3 would 4 ’d 5 wouldn’t Rules 2 past simple 3 would, wouldn’t
Students complete the sentences with the second conditional form of the verbs in brackets ANSWERS : 1 ’d enjoy; liked 4 would be; changed 2 had; wouldn’t believe 5 wouldn’t be; didn’t go 3 wouldn’t watch; hated 6 bought; ’d come Students write questions using second conditional ANSWERS: 1 What would you do if you became invisible? 2 If you had a time machine, where would you go? 3 If you went to the past, who would you meet? 4 If you had a special power, what would it be? 5 If you were a superhero, would you tell your friends? 6 Would you love a person if you discovered he or she was a vampire? Students’ own answers. |
Assessment criteria Learn the form and use of the second conditional. Descriptor: - complete the second conditional sentences with the words in the box. Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Practise using the second conditional to talk about imaginary situations Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the second conditional form of the verbs in brackets -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 54 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
18.01.2024 |
||
|
Date: 19.01.23 |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
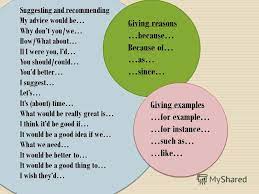
Expressing preferences and recommending |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 8.2.5.1 recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) with little or no support in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a dialogue in which people express preferences and recommend. • Learn key phrases for expressing preferences and recommending. • Practise recommending films to a friend. |
||
|
Value links |
Integrity – Integrity is the quality of having strong moral principles. So, a person with integrity will always act with honesty and adhere to their own moral code regardless of what others do. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, ask students who has seen a good film recently. Elicit some titles. Ask: Would you recommend this film? Explain the meaning of the question if necessary. • Choose one of the titles, and ask who has not seen this film. Ask the class: Do you think … would enjoy this film? • Ask students what they can say to someone if they want to recommend a film. • Elicit some ideas, but do not accept or reject any suggestions at this stage. Lead - In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:62 • Refer students to the photo and ask them to discuss where Tom and Caitlin could be. Ex: 2 p:62 • Read the task with the class and ensure students understand the information they should listen for. Clarify that this task only asks for the general meaning of the dialogue, and they should not worry about understanding every word at this stage. • Students read and listen, and answer the question in the instructions Ex: 3 p:62 • Allow time for students to read the key phrases and identify which ones respond to recommendations. • Ask students if they can remember who said each phrase. • After students have listened to the key phrases, ask them to find the key phrases in the dialogue and translate them into their own language. • Students practise the dialogue in pairs. |
Students look at the photo where Tom and Caitlin ANSWERS : Tom and Caitlin are in the library. They are choosing a film.
Students listen to the dialogue what type of film does Tom choose? ANSWERS : Tom chooses a comedy Students study the key phrases ANSWERS: Respond to recommendations: I don’t fancy that. I’m not a big fan of … Tom: What about this one?, I don’t fancy that. I’m not a big fan of … Caitlin: I’d only recommend that if … , If they had (Avatar), I’d recommend that. You might like … , Try this one. |
Assessment criteria -Listen to a dialogue in which people express preferences and recommend
Descriptor: - listen to the dialogue what type of film does Tom choose? Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for expressing preferences and recommending. Descriptor: - study the key phrases -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 55 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
22.01.2024 |
||
|
Date |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A review of a book or a film |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7,.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics 8.4.4.1 read a growing range of extended fiction and non-fiction texts on familiar and some unfamiliar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model book review. • Learn key phrases to express facts and opinions for a review of a book or film. • Learn about paragraphs and topic sentences. |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students how they decide which films they want to see or which books they want to read. • Elicit some ideas. If students mention reviews, write the word on the board. If they don’t mention reviews, ask What can you read to find information about a book or film? Elicit or teach the word review and write it on the board. • Explain to students that they are going to write a review of a book or film. Lead - In My Book Of Film Review: Write Review And Keep A Record Of All The Movies You Have Watched, A Perfect Book Gift For Movie Lovers, Film Log, Movie ... Boys Girls |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:63 • Refer students to the title of the model text and the photo. Ask students if they have read the book and what they know about it. • Students compare their ideas in pairs before you check answers with the class. ` Ex: 2 p:63 • Ask students to find the key phrases in the model text and translate them into their own language before identifying what each phrase introduces Ex: 3 p:63 • Read the task with the class. In a weaker class, explain that a topic sentence is one which summarizes what each paragraph is going to be about. Do the first item as an example. Identify the topic sentence in the first paragraph. (I have recently read a book called …) Then ask students to read through each option and say which one could replace it (e). • In a stronger class, ask for a definition of a topic sentence by encouraging them to work out the function of sentences a–e. Check understanding, then let students complete the task individually. • Point out that sentences a–e provide alternative phrases to introduce opinions and facts |
Students read the model text and answer the question ANSWERS : 1 Paragraphs 1 and 2 express facts; paragraphs 3 and 4 express opinions. 2 Paragraph 2 describes the setting and characters. 3 Paragraph 3 describes the theme. 4 People who enjoy drama and realism would enjoy this novel. 5 The plot is simple because a child narrates the story
Students study the key phrases. Which phrases introduce an opinion ANSWERS : Phrases which introduce an opinion: I’d like to recommend … , I particularly enjoyed … , All in all, I (really enjoyed) … , I’d / I wouldn’t change it. Phrases which introduce a fact: I have recently read … , The main characters are … , The setting is … . Students find the topic in each paragraph in the model text then replace the topic sentences. ANSWERS: a I particularly enjoyed the characters and the theme of friendship in the novel. (Paragraph 3) b I’d like to recommend this book to people who enjoy drama and realism. (Paragraph 2) c All in all, I really enjoyed the novel and I wouldn’t change the plot or characters. (Paragraph 4) d Not used. e I have recently read a book called The Boy in the Striped Pyjamas. (Paragraph 1) |
Assessment criteria - Study a model book review. Descriptor: - read the model text and answer the question Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases to express facts and opinions for a review of a book or film. Descriptor: - study the key phrases. Which phrases introduce an opinion -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 56 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Date: |
24.01.2024 |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Reading for pleasure |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Understand a legend about a Kazakh hero. • Review how to form adjectives and adverbs. • Review use of comparatives and superlatives. |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to look at the photo and guess who is on the photo. • Get students to say what they think the legend will be about. Lead – In Alpamys BatyrThe legend of the Alpamys batyr is rooted in the distant past of the Kazakh people, this legend reflects their ancient ideas about beauty, generosity, wisdom and courage. Baybori from the konrat clan owns countless riches. But he does not have the most important thing - children. Baybori and his wife Analik, in their declining years, make a pilgrimage to the mausoleum of St. Azret in the hope of begging for a child. And - about a miracle! They have a son, and then a daughter. The parents call the son Alpamys, and the daughter gets the name Karlygash.
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:62 • Put students into pairs. Ask students to read through the names in the box and discuss whether they know anything about the people. • If they have access to the internet they can search for more information about each character Ex: 2 p:62 • Explain that the story is divided into two parts, the first is a reading text and the second is a listening text that they will hear in exercise 5. • Ask students to read the first part of the story and put the events in the correct order. • Discuss with students what message from Gulbarshin says. They should use the information in the story so far to explain their answer. They will be able to check their answer when they listen to the second part of the story in exercise 5 Ex: 3 p:62 • Write recent on the board and ask students what type of word it is (adjective). • Get students to scan the text to find the adverbial form of recent – recently on line 6. • Ask the students to scan the rest of the text to find the other adverbial forms and complete the table. |
Students work in pairs. Do you know any legends about these people. ANSWERS : Student’s own answer.
Students read part 1 of the story and put the events in the correct order. ANSWERS : 1 Bayburi’s wife gave birth to a boy, Alpamys. 2 Bayburi invited Baysari to a big feast. 3 Baysari and Bayburi played a game of kokpar. 4 Baysari went to live in the Kalmyk country. 5 Alpamys rode the horse Baychobar. 6 Alpamys found a message from Gulbarshin. Students complete the table with the adverbs from the story. ANSWERS: recently, gladly, well, unfairly, far, fearlessly, fast, finally, clearly The adverbs well, far and fast are irregular (they don’t end in -ly). |
Assessment criteria - Understand a legend about a Kazakh hero.
Descriptor: - work in pairs. Do you know any legends about these people. Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Review how to form adjectives and adverbs. Descriptor: - complete the table with the adverbs from the story. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 57 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL Language and literature: Word building-nouns |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.9.1use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 8.4.4.1 read a growing range of extended fiction and non-fiction texts on familiar and some unfamiliar general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn about forming nouns from verbs and adjectives. • Practise forming nouns from verbs and adjectives. • Read an extract from The Time Machine by H. G. Wells |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, remind students of the conversation they listened to about the book The Time Machine. • Ask students if they would like to travel in a time machine and why. • Ask if they would like to travel to the future, and ask what they think people would be like in the future. Elicit some ideas, and encourage students to join in and express their opinions Lead - In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:62 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. In a weaker class, accept translations. In a stronger class, encourage students to contextualize the words in example sentences. • Students read the text and complete it with the missing words. Tell students that they should read the text quickly and not worry if they do not understand every word. • Do not check answers at this stage. Ex: 2 p:62 After they have checked their answers to exercise 1, ask students if they would like to read the rest of this book and ask them to give reasons. Ex: 3 p:62 • After they have completed the summary, check answers by asking individual students to read out one completed sentence each. |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box. ANSWERS : Student’s own answer
Students read and listen to the text. ANSWERS : 1 wavy 4 pointed 2 chins 5 thunder 3 softly 6 fools Students read the text again and choose the correct words to complete the summary. ANSWERS: 1 forward 4 friendly and cheerful 2 the same 5 future 3 attractive 6 intelligent |
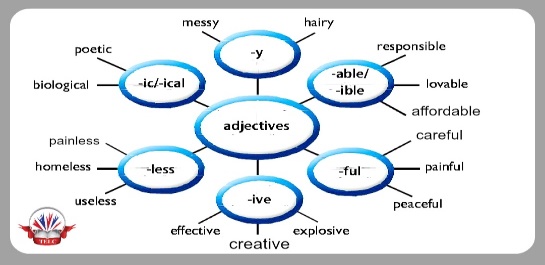
Assessment criteria - Learn about forming nouns from verbs and adjectives. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words in the box. Assessment criteria: - Practise forming nouns from verbs and adjectives. Descriptor: - read the text again and choose the correct words to complete the summary -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 58 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Unit Review 5 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.6.17.1 use if / unless/ if only in second conditional clauses and wish [that] clauses [present reference] use a growing variety of relative clauses including why clauses on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.2.7.1(8.L7) Recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level of a growing range of spoken genres 8.3.3.1(8.S3) Give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - show control of their own learning - use 'I wish/if only' to express wishes related to the present or future -identify discourse markers, supporting details, specific examples and concluding ideas - support talk with specific examples, facts and arguments |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students what films they have seen recently. Ask if they enjoyed the film and why, or why not. Encourage students to express their opinions. • Ask students what kinds of films and books they enjoy the most, and try to elicit some genres. Lead - In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!”Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:66 • Focus students on the books and films pictured. Then, in pairs, students match them with the words. • While checking answers, model and drill the pronunciation if necessary Ex: 2 p:66 • Students complete the text with the words in the box. • students use the words about films and books features.
Summative Assessment for the unit «The Natural World»
Listening
Task 1. Answer the questions about the interview. CD2. Tapescript 3. And transcript for listening task can be found after the rubrics. Write 3 facts about his mother.
Speaking
Task 2. Discuss the questions in a class. Learners discuss questions in a class. They answer the questions presenting logically connected information and use arguments to support their ideas. They express agreement, negotiation and disagreement on questions using given phrases. “The Natural World” what does it mean to you?
|
Students match the sentences with words in the box ANSWERS : 1 comedy 2 fantasy 3 horror 4 adventure 5 science fiction 6 musical Students complete the text with words in thebox ANSWERS : 1 novelist 2 best-seller 3 character 4 setting 5 beginning 6 themes 7 ending 8 reader Students listen the task and do the test ANSWERS: 1 C 2 B 3 C 4 B 5 C A learner should write only 3 facts about Mile’s mother. Possible answers: She is a zoologist. She has worked at universities studying animals. She is studying South African tortoises. Students discuss the questions in a class and answer them using given phrases. |
Assessment criteria - show control of their own learning Descriptor: - match the sentences with words in the box Assessment criteria: - identify discourse markers, supporting details, specific examples and concluding ideas Descriptor: - listen the task and do the test -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 59 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project: A film poster |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.5.1 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a film poster to find out information. • Produce a film poster |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students to name the most successful films that have been released recently. Lead - In
Rebirth of a nation. Not since Genghis Khan has anyone united the Kazakh tribes. Jungar tribesmen of Mongolia rule Kazakh land, but a prophecy has it that a descendant of Genghis will unite his people. Oraz the Wise travels the land looking for the child who will fulfill the prophecy. He finds that infant and protects him from the warriors of Galdan, the Jungar king. Oraz recruits one lad from each Kazakh tribe and teaches them the art of war, loyalty, and camaraderie. Two are the best: Mansur and Erali. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:67 • Look at the poster with the class and ask students to identify the film. Find out how many students have seen it. • Allow students time to read through the poster for Nomad the Warrior and find the information for the rubric task. Ex: 2 p:67 • Students read and follow the steps in the project checklist. • Students can work individually for this task, so encourage them to think about the film they have chosen in as much detail as possible. • Alternatively, ask students to work in groups. First groups must decide on which film to illustrate. Encourage students to choose a film which they are all interested in. Suggest they cast votes if they find it difficult to agree on a film. • Encourage students to delegate work. The initial research should be shared equally, with one student finding out about the director, another about the special effects, etc. • Go round and help as students are working. Encourage them to answer the questions in the checklist to help them structure their work. • Encourage students to do their research in English. It is an ideal opportunity to exploit the internet. • When students come to write their descriptions and information, encourage all to participate. A stronger student might take the lead, but all students should write something. The group could work cooperatively to correct each other’s work. • Suggest students research and write for homework, but allow time in the next class for students to develop their work together. |
Students look at the film poster. Find out who directed the film and who wrote the music for it? ANSWERS : The film was directed by Sergei Bodrov, Ivan Passer and Talgat Temenov and the music was written by Carlo Siliotto.
Students make a poster for a film. Follow the steps in the projects checklist. 1 Choose a film you have seen or would you like to see. 2 Find information about it on the winternet ANSWERS : Student’s own answers.
|
Assessment criteria - Study a film poster to find out information.
Descriptor: - look at the film poster. Find out who directed the film and who wrote the music for it? Assessment criteria: - Produce a film poster Descriptor: - make a poster for a film. Follow the steps in the projects checklist. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit: 6 The natural world |
Lesson 60 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Nouns: art |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.9.1 use appropriately a variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.8.1 spell most high-frequency vocabulary accurately for a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn nouns related to art. • Do a quiz on art. |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, put students into pairs and tell them they have two minutes to think of as many words as they can to do with art. Tell students they can use their dictionaries if they like. • When time is up, elicit words from the class and write them on the board. Ask students to explain any words they give that other students do not understand. Lead - In
Do you know any artists or paintings? What are the most important art gallery in your town or country? |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:68 • Once students have completed the table with the words in the box in pairs, check answers with the class, and check that students understand the new vocabulary. • In a weaker class, ask for translations. In a stronger class, encourage students to put the words into sentences to show understanding. Model and drill pronunciation of any words that you think students will find difficult, for example auction, museum and exhibition. • Ask students to do the quiz individually, then compare their answers with a partner and discuss any differences. • Do not confirm or deny their answers at this stage Ex: 2 p:68 • Tell students that you will play the recording twice, and that they should listen carefully to check their answers. • When students have listened, find out how many answered correctly Ex: 3 p:68 • Go through the example with the class. Ask two students to read out the exchange, then ask students to think of another example. • Students prepare their definitions individually before working in pairs to guess the words. • Ask some students to report back on how many words they guessed correctly. |
Students complete the table with words in the box. Which word doesn’t go in any list? ANSWERS : Places: gallery, museum People: critic, collector Works of art: painting, sculpture, landscape, masterpiece, portrait Events: auction, exhibition Not in any list: art movement
Students listen and check your answers to the quiz. How many did you answer correctly? ANSWERS : 1 a 2 b 3 c 4 a 5 b 6 b Students write definitions of six of the words from exercise 1 ANSWERS: Student’s own answers. |
Assessment criteria - Learn nouns related to art. Descriptor: - complete the table with words in the box. Which word doesn’t go in any list? Assessment criteria: - Do a quiz on art. Descriptor: - listen and check your answers to the quiz. How many did you answer correctly? -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit: 6 The natural world |
Lesson 61 |
||
|
Teacher name: Kaltaeva D.A. |
|
||
|
Date: 02.02.2024 |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 «З» |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The lost world; Past passive |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.7.1 develop and sustain a consistent argument when speaking or writing 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a text about endangered and extinct species. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Learn about synonyms. • Express opinions about endangered species |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In
The final days of the last isolated woolly mammoths on Earth were filled with genetic misfortune |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 70 • Encourage students to scan the text quickly to find the blue words. Allow them time to look them up in a dictionary if there are any they do not know. • Check that students understand the new vocabulary. In a weaker class, accept translations. In a stronger class, encourage students to use the words in a sentence for context. Model and drill pronunciation of any words that you think students will find difficult. • Allow students to compare their opinions on the animals on this page with a partner, then ask a few students to share their ideas. Encourage them to give reasons for their opinions Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:70 • Read the questions with the class and ask students to guess the answers before they read and listen to the text. Ex: 3 P:70 • Students read the text again more carefully to decide if the sentences are true or false. Remind them to correct the false sentences |
Students check the meaning of the words in blue in the text. Then look at the photos. What kind of animals of these? What do you think happened of them? ANSWERS: Woolly mammoths, they became extinct because they were hunted Students read and listen to the text and check your answers in exercise 1. ANSWERS: 1 c 2 b Students read the text again. Write true or false. Correct the false sentences. ANSWERS: 1 False. They are already extinct. 2 True. 3 False. They study the fossils of animals that lived a long time ago. 4 True. 5 False. 6 True. |
Assessment criteria - Read a text about endangered and extinct species
Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words in blue in the text Assessment criteria: - Read for general meaning and specific information
Descriptor: - read and listen to the text and check your answers
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 53 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 62 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Past Passive: affirmative and negative |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.6.9.1 use appropriately a variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn how to change sentences from active to passive. • Practise changing sentences from active to passive. • Practise forming affirmative and negative passive sentences |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Refer students back to the text on endangered animals and ask them to find examples of passive verbs. • Elicit the passive verbs in the text. Ask students to try to change them so that they are active sentences. Elicit ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 71 • Read the first sentence with the class, and elicit the subject, the active verb and the object. • Ask the class to change the sentence to a passive sentence (Dada was started by a group of artists), and then give the negative past passive sentence (Dada wasn’t started by a group of artists). • Elicit the answer to the question in the instructions. • In pairs, students complete the rules Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:71 • Remind students to read the prompts carefully to choose the correct affirmative or negative form. Students complete the sentences individually, then compare their answers in pairs. • Correct any mistakes before you check with the class. • In a stronger class, ask students to transform the sentences to active examples Ex: 3 P:71 • Go through the example with the class. In a weaker class, do further examples if necessary. • Students work individually to choose a piece of art and make passive sentences, before guessing which pieces of art their partner’s sentences relate to. • Ask students to read some sentences for the whole class to guess |
Students study the sentences in the tables. How do we form past passive sentences? Complete the rules. ANSWERS: The negative of past passive sentences has the same structure as the affirmative, but was / were is replaced by wasn’t / weren’t. Rules: 1 subject 2 agent 3 active 4 by Students complete the passive sentences with the verbs in brackets. ANSWERS: 1 were influenced 4 was made 2 were created 5 wasn’t painted 3 was started 6 wasn’t shown Students make passive sentences using the verbs in the box. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers |
Assessment criteria - Learn how to change sentences from active to passive.
Descriptor: - study the sentences in the tables. How do we form past passive sentences? Complete the rules. Assessment criteria: - Practise changing sentences from active to passive
Descriptor: - complete the passive sentences with the verbs in brackets.
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 53 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 63 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Adjectives: describing art |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.5.1 recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) with little or no support in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn adjectives for describing art. • Learn how to mark word stress. • Listen to a podcast about the Turner Prize. • Listen for general meaning and specific details.
|
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Refer students back to the photographs in the Art Quiz on page 78. • Elicit some adjectives that can be used to describe the paintings. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 72 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. • Model pronunciation of one or two of the words, and ask students to identify which syllables are stressed. • After students have listened and underlined the stressed syllables, play the CD again for them to listen and repeat the words. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:72 • Students write their sentences individually, then compare their answers in pairs and say whether they agree with their partner’s sentences. • Ask some students to read their sentences to the class, and check that they are using the adjectives correctly. • In a weaker class, you could write students’ sentences on the board for the class to correct if necessary. Encourage students to copy the correct sentences into their notebooks Ex: 3 P:72 • Focus on the pictures. Before students listen and answer the questions in the instructions, ask them what they think each picture shows, and to try to predict what words they might hear to describe each one.
\Ex: 4 P:72 • Before they listen, allow students time to read the questions and options. Remind them that in a multiplechoice task they should check all the options carefully before they listen and think about which answers might fit. They should also look carefully at the pictures for any clues. |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box. Then listen and underline the stressed syllable in each word. ANSWERS: beautiful, controversial, amusing, shocking, imaginative, ridiculous, traditional, dull, colourful, original, strange, provocative Students choose six adjectives. Write sentences about things they can describe. ANSWERS: Students own answer. Students look at the photos. Then listen to the podcast. Answer the question. ANSWERS: 1 C 2 D 3 A 4 B No, the Turner Prize isn’t always given to a painter Students listen again and choose the correct answer ANSWERS: 1 b 2 c 3 b 4 a 5 b |
Assessment criteria - Learn how to change sentences from active to passive. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words - listen and underline the stressed syllable in each word Total: 2 point Descriptor: - choose six adjectives - write sentences Total: 2 point
Descriptor: - look at the photos. - Answer the question. Total: 2 point Descriptor: - listen again - choose the correct answer Total: 2 point Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket Home task: Ex: 3 P: 51 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 65 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Expressing doubt |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and disussion 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics 8.4.8.1 use familiar and some unfamiliar paper and digital reference resources to check meaning and extend understanding |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a dialogue in which people express opinions and doubts. • Learn key phrases for expressing opinions and doubts. • Practise expressing opinions and doubts |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Write the word opinion on the board. Elicit or explain the meaning. Ask students when they might try to persuade someone. Elicit ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. • With books closed, write the word doubt on the board. Elicit or explain the meaning. Ask students when they might express doubts. Again, elicit some ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 74 • Ask the class whether or not they like the painting in the photo. Ask students to give reasons for their opinions. • You could ask the class to vote on whether they like the painting or not. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:74 • Students read, listen and answer the question Ex: 3 P:74 • After listening to the key phrases, ask students to find them in the dialogue. In a weaker class, students can translate them into their own language. In a stronger class, ask students to explain what the phrases mean and use them in example sentences. • Students practise the dialogue in pairs
Ex: 3 P:74 • Refer students to the words in blue in the dialogue in exercise 2. Elicit translations of the phrases in L1. • Check the meanings with the class before students complete the mini-dialogue. Remind them to think about whether they need to transform the verb look in the third person. |
Students look at the photo. What kind of art is the painting? ANSWERS: The painting is an example of abstract art. Students’ own answers. Students listen to the dialogue. Why does Lucy dislike the painting? ANSWERS: Lucy dislikes the picture because she thinks the face is a bit mad, as if a child painted it. Students study the key phrases then listen and check. ANSWERS: Lucy says all the phrases. Students look at the words in blue in the dialogue in exercise 1. ANSWERS: look = see here look like = resemble looks = appears to be looks as if = seems as though 1 Look 2 looks 3 looks like 4 looks like |
Assessment criteria - Learn how to change sentences from active to passive.
Descriptor: - study the sentences in the tables. How do we form past passive sentences? Complete the rules. Assessment criteria: - Practise changing sentences from active to passive
Descriptor: - complete the passive sentences with the verbs in brackets.
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 51 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 66 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A description of a piece of art |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics 8.2.5.1 recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) with little or no support in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model text about a piece of art. • Learn key phrases for describing a painting. • Learn how to use synonyms. • Write about a piece of art. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wish lamp Lead – In Refer students back to the Art Quiz on pages 78–79. • Put students into pairs and tell them to take turns to describe one of the pictures to their partner. Tell them they should talk about what they can see and should also add any information they can about the artist and the style of the work of art. • Allow students a few minutes to describe some of the art, then ask some students to report back on how easy or difficult it was to talk about them. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 75 • Look at the piece of art shown with the text and ask if any of the students recognize or can say who it was painted by. • Ask students to read the title, and elicit guesses about what this refers to (It is the title of the painting, by Dalí). • Allow students time to read the model text and match the paragraphs and topics Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:75 • Students read the text again in more detail and answer the questions. Ask students to compare their answers in pairs before you check with the class Ex: 3 P:75 • Read through the key phrases with the class. • Ask students to find the key phrases in the model text and translate them into their own language. • Students identify the phrases which describe the painting. |
Students read the model text and match the paragraphs with the topics. There is one topic that you don’t need. ANSWERS: 1 d 2 a 3 b Students answer the questions. ANSWERS: 1 In 1931. 2 Melting watches. 3 Unusual, intense, bizarre, imaginative. 4 In 1931. 5 In the Museum of Modern Art in New York. Students study the key phrases. Which phrases describe the painting. ANSWERS: The scenery / composition includes …, … in the foreground / background …, (The Persistence of Memory) was first exhibited … |
Assessment criteria - Study a model text about a piece of art.
Descriptor: - read the model text and match the paragraphs with the topics. Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for describing a painting
Descriptor: - study the key phrases. Which phrases describe the painting
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 53 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 67 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Tamgaly petroglyphs: Rock art |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics 8.4.8.1 use familiar and some unfamiliar paper and digital reference resources to check meaning and extend understanding |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Understand the history of rock art in Kazakhstan. • Review how to use much, many, most, a little, a few, less, fewer, none |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Ask students to look at the photo and guess where it is and what they can see on the rock on the left side of the photo. • Get students to guess who carved or painted these images |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 76 • Check if students already know some of these words and, if they do, ask them to explain to the rest of the class. • Get students to use a dictionary to check the more difficult words. • Look at the photo together and get students to name all the things they can see Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:76 • Play the CD while students read the text and answer the questions. • Give students time to check their answers in pairs. • Go through the answers making sure students have all found the right answers Ex: 3 P:76 • Write ‘much’ on the board and ask students what the comparative and superlative forms are (more and most). • Get students to add these to the table and use the highlighted words in the text to complete the rest of the table. • When they have completed the table, check their answers and then ask them to complete the rules. • Go through the rules with the whole class. When you have finished, ask a few checking questions, for example, ‘Do we use ‘few’ with countable nouns?’ |
Students check the meaning of these words in a dictionary. Which of the things can you see in the photo? ANSWERS: petroglyphs, bull, gorge, slope Students read andlisten to the text. Answer the questions. ANSWERS: 1 In the south-east of Kazakhstan. 2 They were discovered in 1957. 3 There are more than 5,000 petroglyphs. 4 They used tools made of stone and metal. 5 Because for the people who lived in the Bronze Age, the bull was a symbol of power Students study the words in blue in the text and complete the table ANSWERS: much / many – more – (the most) (a) little – less – (the) least (a) few – fewer – (the) fewest 1 quantity 2 before, after 3 uncountable, countable, 4 than 5 not an |
Assessment criteria - Understand the history of rock art in Kazakhstan.
Descriptor: - check the meaning of these words in a dictionary. Which of the things can you see in the photo? Assessment criteria: - Review how to use much, many, most, a little, a few, less, fewer, none
Descriptor: - study the words in blue in the text and complete the table
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 54 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 68 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL Natural environments: Tropical rainforests |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.1.1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary of natural environments. • Read a text about tropical rainforests. • Write about coral reefs |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, write the word rainforest on the board. Ask students what they know about tropical rainforests. • Elicit a variety of ideas, then ask what they know about the conditions in a rainforest. Ask what types of animals and plants there are, and where they live in the forest. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 77 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. In a weaker class, accept translations, then encourage students to contextualize the words in examples sentences. In a stronger class, encourage them to contextualize the words directly. • Students read the text and complete it with the missing words. Tell students that they should read the text quickly and not worry if they do not understand every word. • Do not check answers at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:77 • Ask students to listen and read the text, and check their answers to exercise 1. Ex: 3 P:77 • After students have labelled the diagram, check answers and ask what the layers of a rainforest are called in their language. |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box. Then complete the text. ANSWERS: Students read and listen to the text. Check your answer in exercise 1. ANSWERS: 1 vegetation 2 wildlife 3 layers 4 mammals 5 shrubs 6 natural Students read paragraph 2 again. Label the diagram. ANSWERS: 1 emergent layer 2 canopy 3 understorey 4 forest floor
|
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary of natural environments.
Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words in the box. Then complete the text. Assessment criteria: - Read a text about tropical rainforests
Descriptor: - read paragraph 2 again. Label the diagram. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 5 P: 55 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 69 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Unit Review 6 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.5.1 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 8.2.5.1 recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) with little or no support in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.6.9.1 use appropriately a variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use nouns related to art • Use adjectives for describing art. • Write the form of present and past passive form |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, put students into pairs and tell them they have two minutes to think of as many words as they can to do with art. Tell students they learned all these words. • When time is up, elicit words from the class and write them on the board. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 77 • Once students have completed the sentences choose the words, check answers with the class, and check that students understand the vocabulary. • Ask students to do individually, then compare their answers with a partner and discuss any differences. • Do not confirm or deny their answers at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:77 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. • Ask students match adjectives with the sentences, then compare their answers with a partner and discuss any differences. Ex: 3 P:77 • Ask students to write the sentences put the verbs in brackets into the present or past passive. • Check answers with the class, writing each correct verbs. |
Students choose the correct words. ANSWERS: 1 an auction 2 critics 3 portrait 4 an art movement 5 a gallery 6 sculptures Students match adjectives with the sentences ANSWERS: 1 original 2 dull 3 strange 4 colourful 5 traditional 6 shocking 7 amusing 8 ridiculous 9 provocative Students complete the sentences with the present or past passive. ANSWERS: 1 was painted 2 aren’t accepted 3 was opened 4 wasn’t bought 5 were hidden 6 wasn’t mentioned 7 are owned 8 is appreciated |
Assessment criteria - Use nouns related to art
Descriptor: - choose the correct words Assessment criteria: - Use adjectives for describing art.
Descriptor: - match adjectives with the sentences Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 5 P: 55 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 70 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Skills round-up: Welcome – Unit 6 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.4.8.1 use familiar and some unfamiliar paper and digital reference resources to check meaning and extend understanding. 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -Listen to a conversation - Prepare a conversation using questions |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 79 • Focus students on the photos and discuss what each one shows. Elicit suggestions and ask students to give reasons for their answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:79 • Explain that students are going to listen to two people talking and that the first time they listen, they should pick out where the people are Ex: 3 P:79 • Students listen again for more specific details. Allow students time to read through the sentences carefully first. • Students could try to complete some gaps from memory if possible. • Let students listen to the CD twice before checking answers. Ex: 4 P:79 • Read the task with the class and check understanding. • Encourage students to discuss their ideas in pairs, following the prompts. • Suggest students to refer back to the photos to give them ideas if they find this difficult. • Go round and listen as students are working. Check for correct use of past tenses and for a wide variety of adjectives |
Students look at the photos and answer the questions ANSWERS: Students’ own answer Students listen to a conversation. Where are Jenny and Joe? ANSWERS: Jenny and Joe are in the National Gallery. Students listen again and complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 English 2 Jenny 3 conceptual 4 statue 5 1762 6 masterpiece 7 exhibition 8 colourful 9 boring 10 poster Students work in pairs and prepare a conversation. Imagine you went to a nature reserve a zoo, a museum or a gallery in your country. Use the questions ANSWERS: Students’ own answer |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a conversation
Descriptor: - listen to a conversation - identify where are Jenny and Joe? Assessment criteria: - Prepare a Conversation using questions
Descriptor: - work in pairs and prepare a conversation - Use the questions Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 8 P: 55 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 71 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Transport: nouns |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.7.1 use a variety of simple perfect forms to express recent, indefinite and unfinished past on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn verbs to do with travelling and transport. • Do a questionnaire about famous explorers. • Learn the form of the past perfect. • Practise using the past perfect to talk about past events |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to tell you about how they get around and the kind of transport they use, e.g. bicycles, trains, cars. Encourage students to join in and contribute ideas. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 80 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words in the box and write the words in the correct part of the table. • In a weaker class, explain the more difficult words such as submarine, helicopter, and spacecraft. In a stronger class, ask students to talk about the benefits and dangers of each type of transport. • Model and drill the pronunciation of longer words. Make sure students can pronounce the words with the correct word stress, for example, submarine. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:80 • Students do the questionnaire. They can work in pairs or individually. Encourage students to guess if they do not know the answer. Do not give students the answers at this stage. • When the students have answered all the questions, play the CD for the students to listen and check their answers. In a weaker class, play the CD twice so that students can also write the correct answers if they have made a mistake. In a stronger class, students should check and correct at the same time. Ex: 3 P:80 • Allow students time to read the texts in detail and find the information they need to match the texts with the pictures. • Ask some students to report back to the class on their answers. Encourage them to explain how they chose their answers referring to details in the text (for example, Marco Polo travelled in the 13th century so his picture must be the oldest). • Discuss with the class which journey they think was the most difficult and make sure students give their reasons (for example, Roald Amundsen’s journey was the hardest because it was so cold) |
Students complete the table with the words in the box. ANSWERS: Land: bus, camel, car, bicycle, train, horse, lorry, tram Water: boat, ship, submarine Air: plane, helicopter, spacecraft, airship Marco Polo photo - camels; Amelia Earhart photo – plane; Roald Amundsen photo - ship Students do the Explorers quiz. Then listen and check your answers. ANSWERS: 1 c 2 c 3 a 4 b 5 b Students match the text with photos. Which explorer’s journey do you think was the most difficult? ANWERS: [TBC] |
Assessment criteria - Learn verbs to do with travelling and transport.
Descriptor: - complete the table with the words in the box. Assessment criteria: - Do a questionnaire about famous explorers.
Descriptor: - do the Explorers quiz - listen and check your answers Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket Home task: Ex: 2 P: 56 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 72 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Youth travel. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.3.1 give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.6.14.1 use some prepositions before nouns and adjectives |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about why young people travel, where they go, what they do. • Discuss your own ideas about travel and transport. • Learn vocabulary with prepositions by, off, in and on. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, write the word nomad on the board and ask students what they think it means. • Ask students to say what they think the difference is between a traditional nomad and a modern nomad. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 82 • Discuss the question with the whole class and get students to explain their answers using the pictures, the title and the sub-headings. • When you have elicited some students’ ideas, get them to read the text quickly (not in detail) and check their answers Ex: 2 P:82 • Students read the text again this time more slowly so that they can find the details they need to answer the question. • In a weaker class, do the first question together and help students find the relevant sentence in the second paragraph. • In a stronger class, get students to make a note of or underline the relevant part of the text, for example, ‘… more than 50% of the participants in the survey said that they had travelled for educational purposes’ is the relevant part for question 1. Ex: 3 P:82 • Explain to the class that the phrases come from the text. Give them a few minutes to think about the answers before they read the text and find the relevant phrases. • When students have read the text, they can check their answers in pairs. Finally, go through the answers with the whole class Ex: 4 P:82 • Explain that we can use by, off, in and on in a wide variety of common phrases. • For further practice in a weaker class, ask students questions using some of the phrases, for example, ‘Do you prefer to study on your own or with friends? and ‘What sort of people are on the move all day?’ • For further practice in a stronger class, ask students to work in pairs and think of their own questions or sentences using the prepositions. You could also ask them to brainstorm other phrases they know (or can find) using the prepositions |
Students look at the photos and the title of the text. Which of the topics do you think the text mentions? Read the text and check your answers. ANSWERS: 2, 4, 6 Students read the text. Who said these things? ANSWERS: 1 more than 50% of the participants in the survey 2 Peter Jones 3 Peter Jones 4 Peter Jones 5 Maral Akhmadieva 6 Maral Akhmadieva 7 25% of the participants in the survey Students complete the phrases with by, of, in or on. Then check your answers in the text. ANWERS: 1 on 2 on 3 in 4 in 5 off 6 by Students choose the correct words ANWERS: 1 on 2 By 3 on 4 in 5 off 6 in |
Assessment criteria - Read about why young people travel, where they go, what they do.
Descriptor: - look at the photos and the title of the text. Assessment criteria: - Learn vocabulary with prepositions by, off, in and on.
Descriptor: - complete the phrases with by, of, in or on. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket Home task: |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 74 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The future of transport |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.6.11.1 use some reported speech forms for statements, questions and commands: say, ask, tell including reported requests on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.6.1 link, independently, sentences into coherent paragraphs using a variety of basic connectors on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn verbs describing movement. • Identify forms of transport discussed in a radio programme. • Listen for specific details. • Discuss various forms of transport and their benefits and drawbacks |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to think of examples of recent examples of new forms of transport (for example, electric cars, drones, etc.). • Ask students what they think the advantages and disadvantages of these new forms of transport might be. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 84 Ask students to use their dictionaries or portable devices to check the meaning of the verbs in the box. Give students time to complete the sentences and check in pairs Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:84 Get students to describe what they can see in the pictures. Elicit flying bicycle, solar-powered car, and solar-powered plane, driverless car and space elevator. Explain that they are going to listen to a radio programme. Tell students to listen and identify the forms of transported discussed Ex: 3 P:84 • Tell students to read sentences 1–6. • Play the CD again so that the students can identify the correct phrases to complete the sentences. • In a weaker class, stop the CD after each sentence to give students time to choose the correct answers. • In a stronger class, play the CD without stopping. |
Students check the meaning of the verbs in the box. Then complete the sentences with the correct form of six of the verbs. ANSWERS: 1 stopped off 2 takes off / will take off / is going to take off 3 turn back 4 set off 5 pull off 6 went up Students look at the photos and listen to the radio proggrame. Which forms of transport do the people mention? ANSWERS: a – solar-powered car d – driverless car e – space elevator Students listen again and choose the correct answers ANWERS: 1 a 2 b 3 a 4 b 5 b 6 b |
Assessment criteria - Identify forms of transport discussed in a radio programme.
Descriptor: - look at the photos and listen to the radio proggrame. Which forms of transport do the people mention Assessment criteria: - Listen for specific details
Descriptor: - listen again and choose the correct answers Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket Home task: Ex: P: WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 75 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reported questions, commands and requests |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 8.6.11.1 use some reported speech forms for statements, questions and commands: say, ask, tell including reported requests on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.6.1 link, independently, sentences into coherent paragraphs using a variety of basic connectors on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics 8.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Identify direct speech and reported speech. • Learn the tense changes we use in reported speech. • Practise changing direct speech into reported speech |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Ask students to quickly read (scan) the text for examples of said and told. • Ask students what word often comes after said (that). |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 83 • Tell students to look again at exercise 2 on the previous page. Ask them to find the reported speech in the text that relates to each item and get them to focus on the difference in tenses between the two. • Give students time to work individually to complete the table. • In a weaker class, walk round checking students’ progress and give help where needed. • In a stronger class, get students to write down examples of the tense changes. • When students have finished completing the table, ask them to complete the rules on the right side of the page Ex: 2 P:83 • Allow students time to complete the sentences. Walk round and remind students to refer to the RULES box if they are having difficulty. • Go through the answers with the whole class. Ask students to explain their answers. For example, the answer to question 1 is told because it is followed by reference to a person – i.e. a noun (see Rule 3). Ex: 3 P:83 Check that students know what to do by going through the example and eliciting the changes that have been made: we to they, can’t to couldn’t, adding that • In a weaker class, put students into pairs to do the exercise. Go round the class and check each pair can make the changes following the example. • In a stronger class, students can work individually then check their answers in pairs. • Go through the answers with the class and write the complete sentences on the board. |
Students complete the direct speech and the reported speech in the text. How does the tense change? Complete the table and rules. ANSWERS: present simple - past simple present continuous- past continuous present perfect - past perfect past simple - past perfect will - would 1 past 2 pronouns 3 say Students complete the sentences with said or told. ANSWERS: 1 told 2 said 3 told 4 said 5 said Students rewrite the sentences using reported speech. ANWERS: 1 Assel told us that she was writing a book about the travels of the Moroccan explorer Ibn Battuta. 2 Ilyas and Maxim said that they always read online reviews before they booked a holiday. 3 Jake said that he had never tried koumiss before. 4 The reporter said that about five million people had travelled to Kazakhstan in 2017. 5 The tourists said that they would buy some souvenirs from the bazaar. 6 Yerzhan told his sister that he had lost the guidebook that she had given to him. |
Assessment criteria - Identify direct speech and reported speech.
Descriptor: - complete the direct speech and the reported speech in the text Assessment criteria: - Learn the tense changes we use in reported speech
Descriptor: - rewrite the sentences using reported speech. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket Home task: Ex: P: WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 76 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Apologizing and explaining |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.7.1 develop and sustain a consistent argument when speaking or writing 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a dialogue in which people apologize and explain. • Learn phrases for apologizing and explaining. • Practise apologizing and explaining. |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, write the words apology and apologize on the board and elicit the difference between the two words (apology is the noun, and apologize is the verb). Check students’ pronunciation of both words. • Ask students to think of last time they apologized. Who did they apologize to and what did they apologize for? |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets.
|
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 86 • Ask students to say what they can see in the photo. Encourage them to describe Jane’s and Mark’s face and body language and use this to guess the situation. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:86 • Tell students to listen to the conversation between Jane and Mark to understand the situation and find out why Mark didn’t call Jane. • Play the CD without stopping and get students to discuss their answers before checking with the whole class. Ex: 3 P:86 Draw students’ attention to KEY PHRASES box and point out the five gaps in the phrases. Ensure that students understand they need to use the words in the box in exercise 3 to complete the gaps. Give them a few a few minutes to complete the phrases and then play the CD again so that they can check their answers. Get individual students to say each phrase. Model and correct students’ pronunciation as necessary.
|
Students look at the photo. How do you think Jane is feeling? ANSWERS: Jane is not looking at Mark and her facial expression suggests she is not happy. Mark is looking sympathetic or apologetic with his hand on Jane’s arm. Students listen to the dialogue. Why didn’t Mark call Jane? ANSWERS: Mark couldn’t call Jane because he hadn’t charged his phone. He had lost the helmet Jane bought him and broke his skateboard.
Students complete the key phrases with the words in the box. Who says them? Listen and check. ANSWERS: 1 mean (Mark) 2 don’t (Mark) 3 sorry (Mark) 4 worry (Mark) 5 happen (Mark |
• In a weaker class, translate these words in L1. Helmet, skateboard, upset, • In a weaker class, complete the key phrases with the words in the box with teacher’s support |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a dialogue in which people apologize and explain
Descriptor: - look at the photo. How do you think Jane is feeling?\ Assessment criteria: - Learn phrases for apologizing and explaining.
Descriptor: - complete the key phrases with the words in the box. Who says them? Make CCQ questions Yes / No
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 77 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A memorable journey |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 8.6.11.1 use some reported speech forms for statements, questions and commands: say, ask, tell including reported requests on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a text that tells a story. • Learn time phrases with prepositions. • Practise time phrases in direct and reported speech.
|
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, write Bayanaul and Lake Zhasybay on the board and ask them what they know about these places – what there is to see and do, where it is, etc. Ask if these are good places to go to on a school trip. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets.
|
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 87 Ask students the questions about school trips and encourage them to give details of places and times. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:87 • Read the title of the text and look at the picture with the class. Ask students to describe what they can see in photo. • Students then read the text and look for any sentences or phrases that suggest whether the reader enjoyed the trip or not. • Check answers as a class and ask students to read the relevant phrases out loud. Ex: 3 P:87 • Focus students’ attention on the Key Phrases box. • In a stronger class, get students to complete the phrases before they check the text for the answers |
Students answer the questions. Do you enjoy going on school trips? What trips have you been on recently? ANSWERS: Students own answers Students read the story. Did the writer enjoy the trip? ANSWERS: Yes, the writer enjoyed the trip. Key sentences and phrases: I was very excited, amazing, beautiful, I was tired but really happy, I learnt a lot, made some new friends.
Students complete the key phrases with the correct prepositions. Then read the model text. ANSWERS: 1 from 2 to 3 by 4 on 5 By 6 A |
• In a weaker class, tell students to use the text to complete the key phrases. |
Assessment criteria - Study a text that tells a story.
Descriptor: - answer the questions. Do you enjoy going on school trips? What trips have you been on recently? Assessment criteria: - Learn time phrases with prepositions.
Descriptor: - complete the key phrases with the correct prepositions.
Make CCQ questions Yes / No
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 78 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Almaty Metro: Going underground |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a text about the metro system in Astana. • Learn adjectives to describe a transport system. • Review the use of the present simple to talk about timetables and schedules. • Practise prepositions off, at, in.
|
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Draw students’ attention to the photo and ask them where they think it is and what their opinion is – what do they like or dislike about it? |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets.
|
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 87 • Ask students if they ever use the metro system or trains to other cities. Get them to think of adjectives to describe the trains and the system, for example, quiet or noisy, on time or late, etc. • When the students have matched the words with the opposite meaning, go through the answers making sure students can pronounce the words correctly. Drill the longer words if necessary. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:87 • Tell students to follow the text as you play the CD. They should listen only to check whether the sentences are true or false. • In a stronger class, play the CD straight through. Ex: 3 P:87 • Read through the sentences with students and then give them a few minutes to complete the rules. • Ask students to think of other examples of using the present simple, for example, ‘This class ends at …’
|
Students match adjectives in the box with their opposites. Which adjectives would you use to describe the transport system in your town or city? ANSWERS: 1 convenient 2 safe 3 comfortable 4 cheap 5 fast 6 reliable 7 clean 8 modern Students read and listen to the text. Write true or false. Correct the false sentences. ANSWERS: 1 true 2 false – In future, the Almaty Metro will have 45 kilometres of track. 3 false – Yeldos said that the trains were always on time. 4 true 5 false – Tolkyn said she liked all the stations
Students study the sentence below then choose the correct words to complete the rules. ANSWERS: 1 present 2 time |
• In a weaker class, match adjectives in the box with their opposites with teacher’s support • In a weaker class, pause the CD after the sentence that provides the information for each true / false question. |
Assessment criteria - Study a text about the metro system in Astana
Descriptor: - match adjectives in the box with their opposites. Assessment criteria: - Learn adjectives to describe a transport system.
Descriptor: - to describe the transport system in your town or city
Make CCQ questions Yes / No
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 79 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL Language and literature: Adventure stories |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics 8.6.14.1 use some prepositions before nouns and
adjectives |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Understand an extract from a classic work of literature. • Review the use of prepositions. \ • Discuss an adventure story and analyse the style and content |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Ask students to talk about books they have read recently, giving details of the author, the characters, and the story. Ask if the story was written in the first person (‘I was born in … I went to school …’ etc.) or the third person (‘Yeldos was born in … he went to school …’ etc.) |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:88 • Ask students to describe what they can see in the photo and guess where and when the story is set and who the characters are. • Get students to read the summary and answer the question. Note that there are two parts to the answer, one for Huckleberry and one for Jim. Answers: Huckleberry is running away from his father and Jim is a runaway slave that people are looking for Ex: 2 P:88 • Ask students to read the text again and put the prepositions from the box into the correct sentences. • Make it clear to students that each preposition can be used in two sentences. • Play the audio for students to check answers. Answers: (1 on 2 On 3 to 4 in 5 of 6 at 7 off 8 out 9 to 10 out 11 of 12 at 13 off 14 in) Ex: 3 P:88 • Ask students to read the text one more time to check their detailed understanding of the story. Answers: 1 false 2 true 3 false 4 don’t know 5 don’t know 6 true 7 false 8 false |
Students look at the photo from a film adaptation of an American novel, then read the summary below. Why do Huckleberry Finn Jim decide to go on journey? Descriptor: - work in groups - read the text -discuss about text Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students complete the text with the prepositions in the box. Use each preposition twice. Then read and listen to the text. Descriptor: - complete the text with the prepositions - read and listen to the text Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students read the text again and write true, false or don’t know Descriptor: - read the text again - write true, false or don’t know |
-can discuss about text Total: 1 point -can complete the text with the prepositions Total: 1 point -can write true, false or don’t know Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 78 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative Assessment for term 3 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.14.1 use some prepositions before nouns and adjectives |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to recall the previous lesson (Speaking, page 86) and elicit what they remember about the scenario. • Ask: Where was the woman? (In a shop.) What was she doing? (Returning a record.) What did she want? (To change it.) Did she get what she wanted? |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
LISTENING Task. Listen to five people talking about different celebrations. Match the halves of the sentences (1-4) with the opinions (A-F) to make true sentences. ONE argument is extra. CD3 Tapescript3
Task. Choose and circle the correct answer A, B or C
READING Task. Paraphrase the given sentences so it has similar meaning. Use the given beginnings of sentences. Example, No kitchen was needed to prepare popcorn. Preparation _________________________. Answer, Preparation of popcorn did not need any kitchen Task. Answer the questions. 5. Why have cinemas sold popcorn since the 19th century? 6. Why cannot popcorn be dissapperead from cinemas?
WRITING Choose ONE of the topics and write. Topic 1. You are a blogger who shares with own experience. Write a story about a concert you have been to. Include the following information in your review:. • The concert; when? / where? • The band: people in the band/ kind of music/ songs played • The audience: how many people / their reaction • Problems: the music/ the sound quality/ the time • Suggestions: different place / different time / different kind of music
SPEAKING Task. You are given questions to speak about for 2-3 minutes. Before you speak you have one minute to think about what you are going to say. |
Students Listen to five people talking about different celebrations then match Descriptor: - listen and match Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students Descriptor: - Paraphrase the given sentences so it has similar meaning Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students choose ONE of the topics and write. Descriptor: - Write a story about a concert Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
-can match the halves of the sentences Total: 1 point -can paraphrase the given sentences Total: 1 point -can write a story about a concert Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 79 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review unit 7 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.8.1 recount some extended stories and events on a range of general and curricular topics 8.4.4.1 read a growing range of extended fiction and non-fiction texts on familiar and some unfamiliar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use verbs to do with travelling and transport • Use vocabulary with prepositions by, off, in and on. • Identify direct speech and reported speech. |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Focus students’ attention on the picture. Ask them what sort of story they think the text is. (A folk tale) • Ask them what sort of things usually happen in such stories. (There’s often romance, a search for something that involves a long journey, or a problem to be overcome. There is also often a sense of good versus bad.) |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:90 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words in the box and write the words in the correct part of the table. • Encourage students to work individually, then compare answers in pairs. Then check as a class to ensure everyone has agreed which column the words go in. • In a weaker class, explain the more difficult words such as submarine, helicopter, and spacecraft. In a stronger class, ask students to talk about the benefits and dangers of each type of transport. • Model and drill the pronunciation of longer words. Make sure students can pronounce the words with the correct word stress, for example, submarine Answers: Students’ own answers Ex: 2 P:90 Ask students if they know the story of Kyz-Zhibek and what they know about it. • Focus students’ attention on the questions and give them a minute to read them before you play the recording for them to listen to while they read. • Students work through the answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class. Ask students what they think about the story and whether they prefer stories with happy or sad endings. Answers: (1 It was first told in the 16th century. 2 Bararbai and his wife had 11 children. 3 Tulgen went on a long journey because he wanted to meet and marry Kyz-Zhibek. 4 When Tulgen met Kyz-Zhibek they fell in love. 5 He wanted to marry Kyz-Zhibek and challenged Tulgen to a fight. 6 She killed herself..) Ex: 3 P:90 • Focus students on the blue words in the text. Ask a couple of students to read them out. • Students complete the sentences in the exercise. . Answers: 1 north 2 war 3 son 4 thunder 5 goddess Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students work in pairs. Make a list of the folktale names and the main characters. Which folktales do you know? Descriptor: - work in pairs - make a list of the folktale names Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read and listen to the story. Answer the question Descriptor: -listen the dialogue -answer the question Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students find the phrases in blue the story and complete the sentences. Then complete the rules. Descriptor: - find the phrases in blue - complete the sentences. Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
-can make a list of the folktale names Total: 1 point -can read and listen the story Total: 1 point -can find phrases in blue the story Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
ҚМЖ Eng Plus gr 8 term 3
ҚМЖ Eng Plus gr 8 term 3
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 49 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Books and films: genres |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.15.1 use infinitive forms after a limited number of verbs and adjectives; use gerund forms after a limited variety of verbs and prepositions; use some prepositional verbs and begin to use common phrasal verbs on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary of film genres. • Do a questionnaire on books and films. • Learn verbs that are followed by -ing or to. |
||
|
Value links |
Family – Family values are moral and ethical principles of typical family life, including sacrificing for loved ones, putting your loved ones first, and keeping your loved ones at the centre of your thoughts and actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students what films they have seen recently. Ask if they enjoyed the film and why, or why not. Encourage students to express their opinions. • Ask students what kinds of films and books they enjoy the most, and try to elicit some genres. Lead - In
If you're anything like us, you probably like to read the book before seeing the movie. This year, as usual, Hollywood is adapting a slew of books—fiction and nonfiction—into films. If you want to prepare yourself for these literary movies, look no further: |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:56 • Focus students on the books and films pictured. Then, in pairs, students match them with the words. • While checking answers, model and drill the pronunciation if necessary. • Follow up by focusing on the genres which were not illustrated. Ask students to think of films or stories which match these categories. Ex: 2 p:56 • Read the example with the class and elicit one or two more possible titles from the class before they write their titles individually. • Once students have guessed genres, ask them to report back on their partner’s titles and genres
Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples By task – more motivated learners can do task without support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location Ex: 4 p:56 • To introduce this point, refer students back to question 6 in the questionnaire. Ask some students to give an answer to this question. Ask students to translate the answer, I enjoy doing unusual things, into their own language. • Elicit some answers to question 5, focusing students on the third sentence. Ask students to translate I’d like to work with people into their own language. • Point out that in question 6 option b the verb like is followed by the -ing form of the verb, but in question 5 it is followed by to + an infinitive. |
Students match the words in the boxes with the books and films in the pictures ANSWERS : 1 a detective story 2 a romance 3 a horror story 4 a fantasy 5 a comedy 6 a musical 7 an adventure story / film 8 a science fiction story / film
Students invent titles for books and films using the words and phrases in the boxes. ANSWERS : Students’ own answers. Students complete the sentences from the questionnaire ANSWERS: 1 being 2 reading 3 don’t 4 want 5 to work 6 wouldn’t Negative form of would: wouldn’t Short forms of would: I’d, you’d, he’d, she’d, it’d, we’d, they’d
|
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary of film genres.
Descriptor: - match the words in the boxes with the books and films in the pictures Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Learn verbs that are followed by -ing or to Descriptor: - complete the sentences from the questionnaire -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 40 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 50 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 10.01.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Movie technology. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.4.1 read a growing range of extended fiction and non-fiction texts on familiar and some unfamiliar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about the use of technology in the movies. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Learn how to find specific information. • Learn about the suffixes -er and -or. |
||
|
Value links |
Loyalty – Loyalty might be a core personal value to you if you highly prize friends that are reliable and trustworthy. You might put your friends or chosen family first, always being there for them when they need you. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students what they know about the history of cinema. • Ask them when people made the first films, and if students have seen any very old films. Ask what the films were like. • Elicit that very early films were silent, and were in black and white. • Ask how films are continuing to improve now. • Elicit ideas and encourage students to join in and contribute ideas or express opinions. Lead - In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:58 • Read through the words in the box with the class and elicit or explain the meaning. • Students guess the order of the words on the timeline in pairs. • Students can check their answers by reading and listening to the text. When they have done this, ask round the class to find out if they guessed correctly. Ex: 2 p:58 • Allow students time to read the study strategy carefully. In a weaker class, go through each point and check understanding. In a stronger class, ask students if this is something they do already. • Students read the text again and answer the questions. Encourage all students to follow the tip step-by-step, by underlining the key words in the questions then looking for these in the text.
Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples By task – more motivated learners can do task without support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location Ex: 3 p:58 • Do the first item with the class by asking students to read the text, and to put their hand up when they find the correct word (viewer). • Check answers and spelling by asking students to come up and write the words on the board |
Students look at the words in the box and guess the correct order on the timeline ANSWERS : 1 colour 2 sound 3 3D 4 surround-sound 5 computer-generated images 6 digital projectors
Students find the answers to these questions ANSWERS : 1 In 1902. 2 There were more than 4,000. 3 They listened to a pianist. 4 Some actors lost their jobs because they didn’t have good voices or because they could not act and speak at the same time. 5 Surround-sound became popular in the 1970s. 6 With future technology it is possible that we will be able to feel a character’s emotions by connecting our bodies to special cinema seats. Students look at verbs and find corresponding nouns in the text. ANSWERS: 1 viewer 2 producer 3 actor 4 projector |
Assessment criteria - Read about the use of technology in the movies.
Descriptor: - look at the words in the box and guess the correct order on the timeline Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Read for general meaning and specific information. Descriptor: - look at verbs and find corresponding nouns in the text. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 3 P: 40 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 51 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Could, can, will be able to |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.3.1 give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the use of could, can and will be able to. • Practise using could, can and will be able to to talk about ability in the past, present and future. |
||
|
Value links |
Fairness – If you value fairness, you might be highly sensitive to situations at school or in the workplace where a teacher or a peer has exhibited favoritism or allowed someone to get away with living by a different set of rules to everyone else. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, check students’ understanding of the text. Ask the class, Can we create realistic special effects now? (Yes, we can.) Can we feel the same emotions as the characters on the screen now? (No, we can’t.) • Explain that this lesson introduces ways to talk about ability and possibility in the past, present and future. Lead - In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:59 • To introduce this point, write these questions on the board, and ask students to find the answers in the text about cinema: What was possible in the 1930s? What is possible now? What will be possible in the future? • Elicit sentences from the text that give the answers and write them on the board (producers could include songs …, film makers can now create special effects …, we’ll be able to connect our bodies …). Underline can, could and will be able to and elicit that they refer to possibility or ability in the past, present and future. Ex: 2 p:59 • Students complete the sentences individually, then compare their answers in pairs. Ask them to help each other correct any mistakes before you check with the class. • In a weaker class, when checking answers highlight the tense in each sentence so students understand why each form was used. Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples By task – more motivated learners can do task without support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location Ex: 3 p:59 Focus on the title and ask students to predict what the text will be about. If they find this difficult, translate senses and ask them to think about what senses were mentioned in the first reading text (sight, hearing, smell). • Students complete the text with the verbs and the correct forms of could, can and will be able to. |
Students complete the sentences from the text ANSWERS : 1 could 2 can 3 be able to 1 Ability and possibility. 2 Film producers couldn’t include songs. They can’t create very realistic special effects. We won’t be able to feel the character’s emotions. 3 Yes, they do
Students complete the sentences with could, can ANSWERS : 1 can’t 4 couldn’t 2 can 5 could 3 won’t be able to 6 ’ll be able to Students complete the text with the verbs in the box ANSWERS: 1 could smell 4 can enjoy 2 couldn’t hear 5 ’ll be able to feel 3 couldn’t wear 6 ’ll be able to connect |
Assessment criteria - Learn the use of could, can and will be able to.
Descriptor: - complete the sentences from the text Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Practise using could, can and will be able to to talk about ability in the past, present and future. Descriptor: - complete the sentences with could, can -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 52 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
S. Murataliyeva |
||
|
Date: |
15.01.2024 |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Books and films: features |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.7.1 develop and sustain a consistent argument when speaking or writing 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary of the features of books and films. • Listen to a radio interview about books. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. • Talk about films and books |
||
|
Value links |
Honesty – You may highly value telling people the truth. This one gets tricky when being honest can be hurtful to others. So, a person who really puts honesty first might be the sort of person who will tell the truth even if it hurts to do so. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students what their favourite film is. Elicit some ideas and ask students to say what they like about the film in particular. Ask which part of the film they like best and which character. • Ask students what their favourite book is and why. Ask who wrote the book, then ask where the story happens and who the characters are. Ask which part of the book they like best. Lead - In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:60 • After students have checked the meaning of the words and completed the table, check answers with the class and check that students understand the meaning of all the new vocabulary. Model and drill the pronunciation of special effects, blockbuster, theme, scene and character. Ex: 2 p:60 • In a weaker class, students match the definitions with the words in pairs. In a stronger class, students work individually, then check their answers in pairs Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples By task – more motivated learners can do task without support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location Ex: 4 p:60 • Focus students’ attention on the topics in the box and refer back to the vocabulary on page 68 if necessary. • Students listen to the speakers and match the topics |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box and complete the table ANSWERS : Books only: novelist, best-seller, publisher Films only: special effects, film director, subtitles, blockbuster, scene, cast, script Both books and films: beginning, ending, theme, plot, character, biography, setting
Students match the definitions with words in exercise 1 ANSWERS : 1 cast 2 blockbuster 3 novelist 4 best-seller 5 biography 6 script 7 subtitles 8 setting Students listen to a radio programme. Match the topics in the box with the speakers. ANSWERS: 1 plot, characters 2 characters, ending 3 plot 4 crime, setting, characters |
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary of the features of books and films.
Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words in the box and complete the table Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Listen to a radio interview about books Descriptor: - listen to a radio programme. Match the topics in the box with the speakers. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 53 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Date: |
17.01.2024 |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus Second conditional |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.6.17.1 use if / unless/ if only in second conditional clauses and wish [that] clauses [present reference]; use a growing variety of relative clauses including why clauses on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the form and use of the second conditional. • Practise using the second conditional to talk about imaginary situations. |
||
|
Value links |
Generosity – This may be a core value of yours if you cherish people who will give their time and resources to people in need. You may consider yourself to be a generous person if you find joy and meaning in giving to others. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to think again about the interview with Joe. Ask: Where would he go if he had a time machine? • Write the question on the board and elicit the answer (he would go to the past), then focus on the question. Ask: Does it refer to a real or imaginary situation? (imaginary). • Tell students that this type of sentence is called the second conditional.. Lead - In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:61 • Read the examples in the table with the class. • In a weaker class, once the rules have been completed and checked, demonstrate the structure of the second conditional example sentences with reference to the rules. • In a stronger class, encourage students to identify the tenses used in the second conditional example sentences. Ex: 2 p:61 • Remind students to read the sentences carefully to ensure they understand the context before they choose which verb form to use in each gap. • Students complete the sentences with the correct form of the verbs. Tell students to use the table in exercise 1 to help them. • Let students compare answers in pairs, then check answers by asking students to read out their completed sentences Differentiation: Modelling- teacher gives clear description of the task with examples Ex: 4 p:61 • Do one or two examples with the whole class. • Students write the questions individually. • Check that students have formed the questions correctly. • Allow students time to prepare their answers individually, then put them into pairs to ask and answer the questions. • Ask some students to write their answers on the board. In a weaker class, correct mistakes as a class. In a stronger class, encourage students to correct the sentences individually first, then ask one or two students to correct the sentences on the board |
Students complete the second conditional sentences with the words in the box. ANSWERS : 1 did 2 had 3 would 4 ’d 5 wouldn’t Rules 2 past simple 3 would, wouldn’t
Students complete the sentences with the second conditional form of the verbs in brackets ANSWERS : 1 ’d enjoy; liked 4 would be; changed 2 had; wouldn’t believe 5 wouldn’t be; didn’t go 3 wouldn’t watch; hated 6 bought; ’d come Students write questions using second conditional ANSWERS: 1 What would you do if you became invisible? 2 If you had a time machine, where would you go? 3 If you went to the past, who would you meet? 4 If you had a special power, what would it be? 5 If you were a superhero, would you tell your friends? 6 Would you love a person if you discovered he or she was a vampire? Students’ own answers. |
Assessment criteria Learn the form and use of the second conditional. Descriptor: - complete the second conditional sentences with the words in the box. Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Practise using the second conditional to talk about imaginary situations Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the second conditional form of the verbs in brackets -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 54 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
18.01.2024 |
||
|
Date: 19.01.23 |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Expressing preferences and recommending |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.1.1 use speaking and listening skills to solve problems creatively and cooperatively in groups 8.2.5.1 recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) with little or no support in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a dialogue in which people express preferences and recommend. • Learn key phrases for expressing preferences and recommending. • Practise recommending films to a friend. |
||
|
Value links |
Integrity – Integrity is the quality of having strong moral principles. So, a person with integrity will always act with honesty and adhere to their own moral code regardless of what others do. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up With books closed, ask students who has seen a good film recently. Elicit some titles. Ask: Would you recommend this film? Explain the meaning of the question if necessary. • Choose one of the titles, and ask who has not seen this film. Ask the class: Do you think … would enjoy this film? • Ask students what they can say to someone if they want to recommend a film. • Elicit some ideas, but do not accept or reject any suggestions at this stage. Lead - In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:62 • Refer students to the photo and ask them to discuss where Tom and Caitlin could be. Ex: 2 p:62 • Read the task with the class and ensure students understand the information they should listen for. Clarify that this task only asks for the general meaning of the dialogue, and they should not worry about understanding every word at this stage. • Students read and listen, and answer the question in the instructions Ex: 3 p:62 • Allow time for students to read the key phrases and identify which ones respond to recommendations. • Ask students if they can remember who said each phrase. • After students have listened to the key phrases, ask them to find the key phrases in the dialogue and translate them into their own language. • Students practise the dialogue in pairs. |
Students look at the photo where Tom and Caitlin ANSWERS : Tom and Caitlin are in the library. They are choosing a film.
Students listen to the dialogue what type of film does Tom choose? ANSWERS : Tom chooses a comedy Students study the key phrases ANSWERS: Respond to recommendations: I don’t fancy that. I’m not a big fan of … Tom: What about this one?, I don’t fancy that. I’m not a big fan of … Caitlin: I’d only recommend that if … , If they had (Avatar), I’d recommend that. You might like … , Try this one. |
Assessment criteria -Listen to a dialogue in which people express preferences and recommend
Descriptor: - listen to the dialogue what type of film does Tom choose? Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for expressing preferences and recommending. Descriptor: - study the key phrases -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 55 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
22.01.2024 |
||
|
Date |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A review of a book or a film |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7,.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics 8.4.4.1 read a growing range of extended fiction and non-fiction texts on familiar and some unfamiliar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model book review. • Learn key phrases to express facts and opinions for a review of a book or film. • Learn about paragraphs and topic sentences. |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students how they decide which films they want to see or which books they want to read. • Elicit some ideas. If students mention reviews, write the word on the board. If they don’t mention reviews, ask What can you read to find information about a book or film? Elicit or teach the word review and write it on the board. • Explain to students that they are going to write a review of a book or film. Lead - In My Book Of Film Review: Write Review And Keep A Record Of All The Movies You Have Watched, A Perfect Book Gift For Movie Lovers, Film Log, Movie ... Boys Girls |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:63 • Refer students to the title of the model text and the photo. Ask students if they have read the book and what they know about it. • Students compare their ideas in pairs before you check answers with the class. ` Ex: 2 p:63 • Ask students to find the key phrases in the model text and translate them into their own language before identifying what each phrase introduces Ex: 3 p:63 • Read the task with the class. In a weaker class, explain that a topic sentence is one which summarizes what each paragraph is going to be about. Do the first item as an example. Identify the topic sentence in the first paragraph. (I have recently read a book called …) Then ask students to read through each option and say which one could replace it (e). • In a stronger class, ask for a definition of a topic sentence by encouraging them to work out the function of sentences a–e. Check understanding, then let students complete the task individually. • Point out that sentences a–e provide alternative phrases to introduce opinions and facts |
Students read the model text and answer the question ANSWERS : 1 Paragraphs 1 and 2 express facts; paragraphs 3 and 4 express opinions. 2 Paragraph 2 describes the setting and characters. 3 Paragraph 3 describes the theme. 4 People who enjoy drama and realism would enjoy this novel. 5 The plot is simple because a child narrates the story
Students study the key phrases. Which phrases introduce an opinion ANSWERS : Phrases which introduce an opinion: I’d like to recommend … , I particularly enjoyed … , All in all, I (really enjoyed) … , I’d / I wouldn’t change it. Phrases which introduce a fact: I have recently read … , The main characters are … , The setting is … . Students find the topic in each paragraph in the model text then replace the topic sentences. ANSWERS: a I particularly enjoyed the characters and the theme of friendship in the novel. (Paragraph 3) b I’d like to recommend this book to people who enjoy drama and realism. (Paragraph 2) c All in all, I really enjoyed the novel and I wouldn’t change the plot or characters. (Paragraph 4) d Not used. e I have recently read a book called The Boy in the Striped Pyjamas. (Paragraph 1) |
Assessment criteria - Study a model book review. Descriptor: - read the model text and answer the question Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases to express facts and opinions for a review of a book or film. Descriptor: - study the key phrases. Which phrases introduce an opinion -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
Тексерілді: Қ. Байсеитов
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 56 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
Murataliyeva S |
||
|
Date: |
24.01.2024 |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Reading for pleasure |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Understand a legend about a Kazakh hero. • Review how to form adjectives and adverbs. • Review use of comparatives and superlatives. |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • Ask students to look at the photo and guess who is on the photo. • Get students to say what they think the legend will be about. Lead – In Alpamys BatyrThe legend of the Alpamys batyr is rooted in the distant past of the Kazakh people, this legend reflects their ancient ideas about beauty, generosity, wisdom and courage. Baybori from the konrat clan owns countless riches. But he does not have the most important thing - children. Baybori and his wife Analik, in their declining years, make a pilgrimage to the mausoleum of St. Azret in the hope of begging for a child. And - about a miracle! They have a son, and then a daughter. The parents call the son Alpamys, and the daughter gets the name Karlygash.
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:62 • Put students into pairs. Ask students to read through the names in the box and discuss whether they know anything about the people. • If they have access to the internet they can search for more information about each character Ex: 2 p:62 • Explain that the story is divided into two parts, the first is a reading text and the second is a listening text that they will hear in exercise 5. • Ask students to read the first part of the story and put the events in the correct order. • Discuss with students what message from Gulbarshin says. They should use the information in the story so far to explain their answer. They will be able to check their answer when they listen to the second part of the story in exercise 5 Ex: 3 p:62 • Write recent on the board and ask students what type of word it is (adjective). • Get students to scan the text to find the adverbial form of recent – recently on line 6. • Ask the students to scan the rest of the text to find the other adverbial forms and complete the table. |
Students work in pairs. Do you know any legends about these people. ANSWERS : Student’s own answer.
Students read part 1 of the story and put the events in the correct order. ANSWERS : 1 Bayburi’s wife gave birth to a boy, Alpamys. 2 Bayburi invited Baysari to a big feast. 3 Baysari and Bayburi played a game of kokpar. 4 Baysari went to live in the Kalmyk country. 5 Alpamys rode the horse Baychobar. 6 Alpamys found a message from Gulbarshin. Students complete the table with the adverbs from the story. ANSWERS: recently, gladly, well, unfairly, far, fearlessly, fast, finally, clearly The adverbs well, far and fast are irregular (they don’t end in -ly). |
Assessment criteria - Understand a legend about a Kazakh hero.
Descriptor: - work in pairs. Do you know any legends about these people. Peer assessment: answer key Assessment criteria: - Review how to form adjectives and adverbs. Descriptor: - complete the table with the adverbs from the story. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 57 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL Language and literature: Word building-nouns |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.9.1use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 8.4.4.1 read a growing range of extended fiction and non-fiction texts on familiar and some unfamiliar general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn about forming nouns from verbs and adjectives. • Practise forming nouns from verbs and adjectives. • Read an extract from The Time Machine by H. G. Wells |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, remind students of the conversation they listened to about the book The Time Machine. • Ask students if they would like to travel in a time machine and why. • Ask if they would like to travel to the future, and ask what they think people would be like in the future. Elicit some ideas, and encourage students to join in and express their opinions Lead - In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:62 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. In a weaker class, accept translations. In a stronger class, encourage students to contextualize the words in example sentences. • Students read the text and complete it with the missing words. Tell students that they should read the text quickly and not worry if they do not understand every word. • Do not check answers at this stage. Ex: 2 p:62 After they have checked their answers to exercise 1, ask students if they would like to read the rest of this book and ask them to give reasons. Ex: 3 p:62 • After they have completed the summary, check answers by asking individual students to read out one completed sentence each. |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box. ANSWERS : Student’s own answer
Students read and listen to the text. ANSWERS : 1 wavy 4 pointed 2 chins 5 thunder 3 softly 6 fools Students read the text again and choose the correct words to complete the summary. ANSWERS: 1 forward 4 friendly and cheerful 2 the same 5 future 3 attractive 6 intelligent |
Assessment criteria - Learn about forming nouns from verbs and adjectives. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words in the box. Assessment criteria: - Practise forming nouns from verbs and adjectives. Descriptor: - read the text again and choose the correct words to complete the summary -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 58 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Unit Review 5 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.6.17.1 use if / unless/ if only in second conditional clauses and wish [that] clauses [present reference] use a growing variety of relative clauses including why clauses on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.2.7.1(8.L7) Recognise typical features at word, sentence and text level of a growing range of spoken genres 8.3.3.1(8.S3) Give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - show control of their own learning - use 'I wish/if only' to express wishes related to the present or future -identify discourse markers, supporting details, specific examples and concluding ideas - support talk with specific examples, facts and arguments |
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students what films they have seen recently. Ask if they enjoyed the film and why, or why not. Encourage students to express their opinions. • Ask students what kinds of films and books they enjoy the most, and try to elicit some genres. Lead - In
|
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!”Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:66 • Focus students on the books and films pictured. Then, in pairs, students match them with the words. • While checking answers, model and drill the pronunciation if necessary Ex: 2 p:66 • Students complete the text with the words in the box. • students use the words about films and books features.
Summative Assessment for the unit «The Natural World»
Listening
Task 1. Answer the questions about the interview. CD2. Tapescript 3. And transcript for listening task can be found after the rubrics. Write 3 facts about his mother.
Speaking
Task 2. Discuss the questions in a class. Learners discuss questions in a class. They answer the questions presenting logically connected information and use arguments to support their ideas. They express agreement, negotiation and disagreement on questions using given phrases. “The Natural World” what does it mean to you?
|
Students match the sentences with words in the box ANSWERS : 1 comedy 2 fantasy 3 horror 4 adventure 5 science fiction 6 musical Students complete the text with words in thebox ANSWERS : 1 novelist 2 best-seller 3 character 4 setting 5 beginning 6 themes 7 ending 8 reader Students listen the task and do the test ANSWERS: 1 C 2 B 3 C 4 B 5 C A learner should write only 3 facts about Mile’s mother. Possible answers: She is a zoologist. She has worked at universities studying animals. She is studying South African tortoises. Students discuss the questions in a class and answer them using given phrases. |
Assessment criteria - show control of their own learning Descriptor: - match the sentences with words in the box Assessment criteria: - identify discourse markers, supporting details, specific examples and concluding ideas Descriptor: - listen the task and do the test -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit: 5 Reading for pleasure |
Lesson 59 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project: A film poster |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.5.1 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a film poster to find out information. • Produce a film poster |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, ask students to name the most successful films that have been released recently. Lead - In
Rebirth of a nation. Not since Genghis Khan has anyone united the Kazakh tribes. Jungar tribesmen of Mongolia rule Kazakh land, but a prophecy has it that a descendant of Genghis will unite his people. Oraz the Wise travels the land looking for the child who will fulfill the prophecy. He finds that infant and protects him from the warriors of Galdan, the Jungar king. Oraz recruits one lad from each Kazakh tribe and teaches them the art of war, loyalty, and camaraderie. Two are the best: Mansur and Erali. |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:67 • Look at the poster with the class and ask students to identify the film. Find out how many students have seen it. • Allow students time to read through the poster for Nomad the Warrior and find the information for the rubric task. Ex: 2 p:67 • Students read and follow the steps in the project checklist. • Students can work individually for this task, so encourage them to think about the film they have chosen in as much detail as possible. • Alternatively, ask students to work in groups. First groups must decide on which film to illustrate. Encourage students to choose a film which they are all interested in. Suggest they cast votes if they find it difficult to agree on a film. • Encourage students to delegate work. The initial research should be shared equally, with one student finding out about the director, another about the special effects, etc. • Go round and help as students are working. Encourage them to answer the questions in the checklist to help them structure their work. • Encourage students to do their research in English. It is an ideal opportunity to exploit the internet. • When students come to write their descriptions and information, encourage all to participate. A stronger student might take the lead, but all students should write something. The group could work cooperatively to correct each other’s work. • Suggest students research and write for homework, but allow time in the next class for students to develop their work together. |
Students look at the film poster. Find out who directed the film and who wrote the music for it? ANSWERS : The film was directed by Sergei Bodrov, Ivan Passer and Talgat Temenov and the music was written by Carlo Siliotto.
Students make a poster for a film. Follow the steps in the projects checklist. 1 Choose a film you have seen or would you like to see. 2 Find information about it on the winternet ANSWERS : Student’s own answers.
|
Assessment criteria - Study a film poster to find out information.
Descriptor: - look at the film poster. Find out who directed the film and who wrote the music for it? Assessment criteria: - Produce a film poster Descriptor: - make a poster for a film. Follow the steps in the projects checklist. -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit: 6 The natural world |
Lesson 60 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Nouns: art |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.9.1 use appropriately a variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.8.1 spell most high-frequency vocabulary accurately for a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn nouns related to art. • Do a quiz on art. |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. Warm-up • With books closed, put students into pairs and tell them they have two minutes to think of as many words as they can to do with art. Tell students they can use their dictionaries if they like. • When time is up, elicit words from the class and write them on the board. Ask students to explain any words they give that other students do not understand. Lead - In
Do you know any artists or paintings? What are the most important art gallery in your town or country? |
The aim: To develop Ss speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students introduce themselves Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment T tries to award active Ss. «The praise» method is used to evaluate Ss with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures PPT Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 p:68 • Once students have completed the table with the words in the box in pairs, check answers with the class, and check that students understand the new vocabulary. • In a weaker class, ask for translations. In a stronger class, encourage students to put the words into sentences to show understanding. Model and drill pronunciation of any words that you think students will find difficult, for example auction, museum and exhibition. • Ask students to do the quiz individually, then compare their answers with a partner and discuss any differences. • Do not confirm or deny their answers at this stage Ex: 2 p:68 • Tell students that you will play the recording twice, and that they should listen carefully to check their answers. • When students have listened, find out how many answered correctly Ex: 3 p:68 • Go through the example with the class. Ask two students to read out the exchange, then ask students to think of another example. • Students prepare their definitions individually before working in pairs to guess the words. • Ask some students to report back on how many words they guessed correctly. |
Students complete the table with words in the box. Which word doesn’t go in any list? ANSWERS : Places: gallery, museum People: critic, collector Works of art: painting, sculpture, landscape, masterpiece, portrait Events: auction, exhibition Not in any list: art movement
Students listen and check your answers to the quiz. How many did you answer correctly? ANSWERS : 1 a 2 b 3 c 4 a 5 b 6 b Students write definitions of six of the words from exercise 1 ANSWERS: Student’s own answers. |
Assessment criteria - Learn nouns related to art. Descriptor: - complete the table with words in the box. Which word doesn’t go in any list? Assessment criteria: - Do a quiz on art. Descriptor: - listen and check your answers to the quiz. How many did you answer correctly? -Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
Home task: Ex: 1 P: 42 WB |
|
Poster KWL chart |
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit: 6 The natural world |
Lesson 61 |
||
|
Teacher name: Kaltaeva D.A. |
|
||
|
Date: 02.02.2024 |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 «З» |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The lost world; Past passive |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.7.1 develop and sustain a consistent argument when speaking or writing 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a text about endangered and extinct species. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Learn about synonyms. • Express opinions about endangered species |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In
The final days of the last isolated woolly mammoths on Earth were filled with genetic misfortune |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 70 • Encourage students to scan the text quickly to find the blue words. Allow them time to look them up in a dictionary if there are any they do not know. • Check that students understand the new vocabulary. In a weaker class, accept translations. In a stronger class, encourage students to use the words in a sentence for context. Model and drill pronunciation of any words that you think students will find difficult. • Allow students to compare their opinions on the animals on this page with a partner, then ask a few students to share their ideas. Encourage them to give reasons for their opinions Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:70 • Read the questions with the class and ask students to guess the answers before they read and listen to the text. Ex: 3 P:70 • Students read the text again more carefully to decide if the sentences are true or false. Remind them to correct the false sentences |
Students check the meaning of the words in blue in the text. Then look at the photos. What kind of animals of these? What do you think happened of them? ANSWERS: Woolly mammoths, they became extinct because they were hunted Students read and listen to the text and check your answers in exercise 1. ANSWERS: 1 c 2 b Students read the text again. Write true or false. Correct the false sentences. ANSWERS: 1 False. They are already extinct. 2 True. 3 False. They study the fossils of animals that lived a long time ago. 4 True. 5 False. 6 True. |
Assessment criteria - Read a text about endangered and extinct species
Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words in blue in the text Assessment criteria: - Read for general meaning and specific information
Descriptor: - read and listen to the text and check your answers
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 53 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 62 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Past Passive: affirmative and negative |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.6.9.1 use appropriately a variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn how to change sentences from active to passive. • Practise changing sentences from active to passive. • Practise forming affirmative and negative passive sentences |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Refer students back to the text on endangered animals and ask them to find examples of passive verbs. • Elicit the passive verbs in the text. Ask students to try to change them so that they are active sentences. Elicit ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 71 • Read the first sentence with the class, and elicit the subject, the active verb and the object. • Ask the class to change the sentence to a passive sentence (Dada was started by a group of artists), and then give the negative past passive sentence (Dada wasn’t started by a group of artists). • Elicit the answer to the question in the instructions. • In pairs, students complete the rules Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:71 • Remind students to read the prompts carefully to choose the correct affirmative or negative form. Students complete the sentences individually, then compare their answers in pairs. • Correct any mistakes before you check with the class. • In a stronger class, ask students to transform the sentences to active examples Ex: 3 P:71 • Go through the example with the class. In a weaker class, do further examples if necessary. • Students work individually to choose a piece of art and make passive sentences, before guessing which pieces of art their partner’s sentences relate to. • Ask students to read some sentences for the whole class to guess |
Students study the sentences in the tables. How do we form past passive sentences? Complete the rules. ANSWERS: The negative of past passive sentences has the same structure as the affirmative, but was / were is replaced by wasn’t / weren’t. Rules: 1 subject 2 agent 3 active 4 by Students complete the passive sentences with the verbs in brackets. ANSWERS: 1 were influenced 4 was made 2 were created 5 wasn’t painted 3 was started 6 wasn’t shown Students make passive sentences using the verbs in the box. ANSWERS: Students’ own answers |
Assessment criteria - Learn how to change sentences from active to passive.
Descriptor: - study the sentences in the tables. How do we form past passive sentences? Complete the rules. Assessment criteria: - Practise changing sentences from active to passive
Descriptor: - complete the passive sentences with the verbs in brackets.
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 53 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 63 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Adjectives: describing art |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.5.1 recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) with little or no support in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn adjectives for describing art. • Learn how to mark word stress. • Listen to a podcast about the Turner Prize. • Listen for general meaning and specific details.
|
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Refer students back to the photographs in the Art Quiz on page 78. • Elicit some adjectives that can be used to describe the paintings. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 72 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. • Model pronunciation of one or two of the words, and ask students to identify which syllables are stressed. • After students have listened and underlined the stressed syllables, play the CD again for them to listen and repeat the words. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:72 • Students write their sentences individually, then compare their answers in pairs and say whether they agree with their partner’s sentences. • Ask some students to read their sentences to the class, and check that they are using the adjectives correctly. • In a weaker class, you could write students’ sentences on the board for the class to correct if necessary. Encourage students to copy the correct sentences into their notebooks Ex: 3 P:72 • Focus on the pictures. Before students listen and answer the questions in the instructions, ask them what they think each picture shows, and to try to predict what words they might hear to describe each one.
\Ex: 4 P:72 • Before they listen, allow students time to read the questions and options. Remind them that in a multiplechoice task they should check all the options carefully before they listen and think about which answers might fit. They should also look carefully at the pictures for any clues. |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box. Then listen and underline the stressed syllable in each word. ANSWERS: beautiful, controversial, amusing, shocking, imaginative, ridiculous, traditional, dull, colourful, original, strange, provocative Students choose six adjectives. Write sentences about things they can describe. ANSWERS: Students own answer. Students look at the photos. Then listen to the podcast. Answer the question. ANSWERS: 1 C 2 D 3 A 4 B No, the Turner Prize isn’t always given to a painter Students listen again and choose the correct answer ANSWERS: 1 b 2 c 3 b 4 a 5 b |
Assessment criteria - Learn how to change sentences from active to passive. Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words - listen and underline the stressed syllable in each word Total: 2 point Descriptor: - choose six adjectives - write sentences Total: 2 point
Descriptor: - look at the photos. - Answer the question. Total: 2 point Descriptor: - listen again - choose the correct answer Total: 2 point Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket Home task: Ex: 3 P: 51 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 65 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Expressing doubt |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and disussion 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics 8.4.8.1 use familiar and some unfamiliar paper and digital reference resources to check meaning and extend understanding |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a dialogue in which people express opinions and doubts. • Learn key phrases for expressing opinions and doubts. • Practise expressing opinions and doubts |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Write the word opinion on the board. Elicit or explain the meaning. Ask students when they might try to persuade someone. Elicit ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. • With books closed, write the word doubt on the board. Elicit or explain the meaning. Ask students when they might express doubts. Again, elicit some ideas, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 74 • Ask the class whether or not they like the painting in the photo. Ask students to give reasons for their opinions. • You could ask the class to vote on whether they like the painting or not. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:74 • Students read, listen and answer the question Ex: 3 P:74 • After listening to the key phrases, ask students to find them in the dialogue. In a weaker class, students can translate them into their own language. In a stronger class, ask students to explain what the phrases mean and use them in example sentences. • Students practise the dialogue in pairs
Ex: 3 P:74 • Refer students to the words in blue in the dialogue in exercise 2. Elicit translations of the phrases in L1. • Check the meanings with the class before students complete the mini-dialogue. Remind them to think about whether they need to transform the verb look in the third person. |
Students look at the photo. What kind of art is the painting? ANSWERS: The painting is an example of abstract art. Students’ own answers. Students listen to the dialogue. Why does Lucy dislike the painting? ANSWERS: Lucy dislikes the picture because she thinks the face is a bit mad, as if a child painted it. Students study the key phrases then listen and check. ANSWERS: Lucy says all the phrases. Students look at the words in blue in the dialogue in exercise 1. ANSWERS: look = see here look like = resemble looks = appears to be looks as if = seems as though 1 Look 2 looks 3 looks like 4 looks like |
Assessment criteria - Learn how to change sentences from active to passive.
Descriptor: - study the sentences in the tables. How do we form past passive sentences? Complete the rules. Assessment criteria: - Practise changing sentences from active to passive
Descriptor: - complete the passive sentences with the verbs in brackets.
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 51 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 66 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A description of a piece of art |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics 8.2.5.1 recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) with little or no support in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model text about a piece of art. • Learn key phrases for describing a painting. • Learn how to use synonyms. • Write about a piece of art. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wish lamp Lead – In Refer students back to the Art Quiz on pages 78–79. • Put students into pairs and tell them to take turns to describe one of the pictures to their partner. Tell them they should talk about what they can see and should also add any information they can about the artist and the style of the work of art. • Allow students a few minutes to describe some of the art, then ask some students to report back on how easy or difficult it was to talk about them. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 75 • Look at the piece of art shown with the text and ask if any of the students recognize or can say who it was painted by. • Ask students to read the title, and elicit guesses about what this refers to (It is the title of the painting, by Dalí). • Allow students time to read the model text and match the paragraphs and topics Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:75 • Students read the text again in more detail and answer the questions. Ask students to compare their answers in pairs before you check with the class Ex: 3 P:75 • Read through the key phrases with the class. • Ask students to find the key phrases in the model text and translate them into their own language. • Students identify the phrases which describe the painting. |
Students read the model text and match the paragraphs with the topics. There is one topic that you don’t need. ANSWERS: 1 d 2 a 3 b Students answer the questions. ANSWERS: 1 In 1931. 2 Melting watches. 3 Unusual, intense, bizarre, imaginative. 4 In 1931. 5 In the Museum of Modern Art in New York. Students study the key phrases. Which phrases describe the painting. ANSWERS: The scenery / composition includes …, … in the foreground / background …, (The Persistence of Memory) was first exhibited … |
Assessment criteria - Study a model text about a piece of art.
Descriptor: - read the model text and match the paragraphs with the topics. Assessment criteria: - Learn key phrases for describing a painting
Descriptor: - study the key phrases. Which phrases describe the painting
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 2 P: 53 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 67 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Tamgaly petroglyphs: Rock art |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics 8.4.8.1 use familiar and some unfamiliar paper and digital reference resources to check meaning and extend understanding |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Understand the history of rock art in Kazakhstan. • Review how to use much, many, most, a little, a few, less, fewer, none |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Ask students to look at the photo and guess where it is and what they can see on the rock on the left side of the photo. • Get students to guess who carved or painted these images |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 76 • Check if students already know some of these words and, if they do, ask them to explain to the rest of the class. • Get students to use a dictionary to check the more difficult words. • Look at the photo together and get students to name all the things they can see Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:76 • Play the CD while students read the text and answer the questions. • Give students time to check their answers in pairs. • Go through the answers making sure students have all found the right answers Ex: 3 P:76 • Write ‘much’ on the board and ask students what the comparative and superlative forms are (more and most). • Get students to add these to the table and use the highlighted words in the text to complete the rest of the table. • When they have completed the table, check their answers and then ask them to complete the rules. • Go through the rules with the whole class. When you have finished, ask a few checking questions, for example, ‘Do we use ‘few’ with countable nouns?’ |
Students check the meaning of these words in a dictionary. Which of the things can you see in the photo? ANSWERS: petroglyphs, bull, gorge, slope Students read andlisten to the text. Answer the questions. ANSWERS: 1 In the south-east of Kazakhstan. 2 They were discovered in 1957. 3 There are more than 5,000 petroglyphs. 4 They used tools made of stone and metal. 5 Because for the people who lived in the Bronze Age, the bull was a symbol of power Students study the words in blue in the text and complete the table ANSWERS: much / many – more – (the most) (a) little – less – (the) least (a) few – fewer – (the) fewest 1 quantity 2 before, after 3 uncountable, countable, 4 than 5 not an |
Assessment criteria - Understand the history of rock art in Kazakhstan.
Descriptor: - check the meaning of these words in a dictionary. Which of the things can you see in the photo? Assessment criteria: - Review how to use much, many, most, a little, a few, less, fewer, none
Descriptor: - study the words in blue in the text and complete the table
Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 1 P: 54 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 68 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL Natural environments: Tropical rainforests |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.1.1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary of natural environments. • Read a text about tropical rainforests. • Write about coral reefs |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, write the word rainforest on the board. Ask students what they know about tropical rainforests. • Elicit a variety of ideas, then ask what they know about the conditions in a rainforest. Ask what types of animals and plants there are, and where they live in the forest. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 77 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. In a weaker class, accept translations, then encourage students to contextualize the words in examples sentences. In a stronger class, encourage them to contextualize the words directly. • Students read the text and complete it with the missing words. Tell students that they should read the text quickly and not worry if they do not understand every word. • Do not check answers at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:77 • Ask students to listen and read the text, and check their answers to exercise 1. Ex: 3 P:77 • After students have labelled the diagram, check answers and ask what the layers of a rainforest are called in their language. |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box. Then complete the text. ANSWERS: Students read and listen to the text. Check your answer in exercise 1. ANSWERS: 1 vegetation 2 wildlife 3 layers 4 mammals 5 shrubs 6 natural Students read paragraph 2 again. Label the diagram. ANSWERS: 1 emergent layer 2 canopy 3 understorey 4 forest floor
|
Assessment criteria - Learn vocabulary of natural environments.
Descriptor: - check the meaning of the words in the box. Then complete the text. Assessment criteria: - Read a text about tropical rainforests
Descriptor: - read paragraph 2 again. Label the diagram. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 5 P: 55 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 69 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Unit Review 6 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.5.1 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 8.2.5.1 recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) with little or no support in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.6.9.1 use appropriately a variety of active and passive simple present and past forms and past perfect simple forms in narrative and reported speech on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use nouns related to art • Use adjectives for describing art. • Write the form of present and past passive form |
||
|
Value links |
Thoughtfulness – You may highly value people who are thoughtful. If this is you, then you might find yourself rolling your eyes at people who are full of bluster and never stop to reflect on their own actions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, put students into pairs and tell them they have two minutes to think of as many words as they can to do with art. Tell students they learned all these words. • When time is up, elicit words from the class and write them on the board. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 77 • Once students have completed the sentences choose the words, check answers with the class, and check that students understand the vocabulary. • Ask students to do individually, then compare their answers with a partner and discuss any differences. • Do not confirm or deny their answers at this stage. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:77 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. • Ask students match adjectives with the sentences, then compare their answers with a partner and discuss any differences. Ex: 3 P:77 • Ask students to write the sentences put the verbs in brackets into the present or past passive. • Check answers with the class, writing each correct verbs. |
Students choose the correct words. ANSWERS: 1 an auction 2 critics 3 portrait 4 an art movement 5 a gallery 6 sculptures Students match adjectives with the sentences ANSWERS: 1 original 2 dull 3 strange 4 colourful 5 traditional 6 shocking 7 amusing 8 ridiculous 9 provocative Students complete the sentences with the present or past passive. ANSWERS: 1 was painted 2 aren’t accepted 3 was opened 4 wasn’t bought 5 were hidden 6 wasn’t mentioned 7 are owned 8 is appreciated |
Assessment criteria - Use nouns related to art
Descriptor: - choose the correct words Assessment criteria: - Use adjectives for describing art.
Descriptor: - match adjectives with the sentences Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 5 P: 55 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 6 The natural world |
Lesson 70 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Skills round-up: Welcome – Unit 6 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.4.8.1 use familiar and some unfamiliar paper and digital reference resources to check meaning and extend understanding. 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -Listen to a conversation - Prepare a conversation using questions |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In
|
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 79 • Focus students on the photos and discuss what each one shows. Elicit suggestions and ask students to give reasons for their answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:79 • Explain that students are going to listen to two people talking and that the first time they listen, they should pick out where the people are Ex: 3 P:79 • Students listen again for more specific details. Allow students time to read through the sentences carefully first. • Students could try to complete some gaps from memory if possible. • Let students listen to the CD twice before checking answers. Ex: 4 P:79 • Read the task with the class and check understanding. • Encourage students to discuss their ideas in pairs, following the prompts. • Suggest students to refer back to the photos to give them ideas if they find this difficult. • Go round and listen as students are working. Check for correct use of past tenses and for a wide variety of adjectives |
Students look at the photos and answer the questions ANSWERS: Students’ own answer Students listen to a conversation. Where are Jenny and Joe? ANSWERS: Jenny and Joe are in the National Gallery. Students listen again and complete the sentences ANSWERS: 1 English 2 Jenny 3 conceptual 4 statue 5 1762 6 masterpiece 7 exhibition 8 colourful 9 boring 10 poster Students work in pairs and prepare a conversation. Imagine you went to a nature reserve a zoo, a museum or a gallery in your country. Use the questions ANSWERS: Students’ own answer |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a conversation
Descriptor: - listen to a conversation - identify where are Jenny and Joe? Assessment criteria: - Prepare a Conversation using questions
Descriptor: - work in pairs and prepare a conversation - Use the questions Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket This is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 8 P: 55 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 71 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Transport: nouns |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.7.1 use a variety of simple perfect forms to express recent, indefinite and unfinished past on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn verbs to do with travelling and transport. • Do a questionnaire about famous explorers. • Learn the form of the past perfect. • Practise using the past perfect to talk about past events |
||
|
Value links |
Patience – A person who has patience as a core personal value is going to prioritize giving their time to others. They will sit down and be calm while waiting for others. This is a great trait for a teacher. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to tell you about how they get around and the kind of transport they use, e.g. bicycles, trains, cars. Encourage students to join in and contribute ideas. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 80 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words in the box and write the words in the correct part of the table. • In a weaker class, explain the more difficult words such as submarine, helicopter, and spacecraft. In a stronger class, ask students to talk about the benefits and dangers of each type of transport. • Model and drill the pronunciation of longer words. Make sure students can pronounce the words with the correct word stress, for example, submarine. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:80 • Students do the questionnaire. They can work in pairs or individually. Encourage students to guess if they do not know the answer. Do not give students the answers at this stage. • When the students have answered all the questions, play the CD for the students to listen and check their answers. In a weaker class, play the CD twice so that students can also write the correct answers if they have made a mistake. In a stronger class, students should check and correct at the same time. Ex: 3 P:80 • Allow students time to read the texts in detail and find the information they need to match the texts with the pictures. • Ask some students to report back to the class on their answers. Encourage them to explain how they chose their answers referring to details in the text (for example, Marco Polo travelled in the 13th century so his picture must be the oldest). • Discuss with the class which journey they think was the most difficult and make sure students give their reasons (for example, Roald Amundsen’s journey was the hardest because it was so cold) |
Students complete the table with the words in the box. ANSWERS: Land: bus, camel, car, bicycle, train, horse, lorry, tram Water: boat, ship, submarine Air: plane, helicopter, spacecraft, airship Marco Polo photo - camels; Amelia Earhart photo – plane; Roald Amundsen photo - ship Students do the Explorers quiz. Then listen and check your answers. ANSWERS: 1 c 2 c 3 a 4 b 5 b Students match the text with photos. Which explorer’s journey do you think was the most difficult? ANWERS: [TBC] |
Assessment criteria - Learn verbs to do with travelling and transport.
Descriptor: - complete the table with the words in the box. Assessment criteria: - Do a questionnaire about famous explorers.
Descriptor: - do the Explorers quiz - listen and check your answers Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket Home task: Ex: 2 P: 56 WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 72 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Youth travel. |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.3.1 give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.6.14.1 use some prepositions before nouns and adjectives |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about why young people travel, where they go, what they do. • Discuss your own ideas about travel and transport. • Learn vocabulary with prepositions by, off, in and on. |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, write the word nomad on the board and ask students what they think it means. • Ask students to say what they think the difference is between a traditional nomad and a modern nomad. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 82 • Discuss the question with the whole class and get students to explain their answers using the pictures, the title and the sub-headings. • When you have elicited some students’ ideas, get them to read the text quickly (not in detail) and check their answers Ex: 2 P:82 • Students read the text again this time more slowly so that they can find the details they need to answer the question. • In a weaker class, do the first question together and help students find the relevant sentence in the second paragraph. • In a stronger class, get students to make a note of or underline the relevant part of the text, for example, ‘… more than 50% of the participants in the survey said that they had travelled for educational purposes’ is the relevant part for question 1. Ex: 3 P:82 • Explain to the class that the phrases come from the text. Give them a few minutes to think about the answers before they read the text and find the relevant phrases. • When students have read the text, they can check their answers in pairs. Finally, go through the answers with the whole class Ex: 4 P:82 • Explain that we can use by, off, in and on in a wide variety of common phrases. • For further practice in a weaker class, ask students questions using some of the phrases, for example, ‘Do you prefer to study on your own or with friends? and ‘What sort of people are on the move all day?’ • For further practice in a stronger class, ask students to work in pairs and think of their own questions or sentences using the prepositions. You could also ask them to brainstorm other phrases they know (or can find) using the prepositions |
Students look at the photos and the title of the text. Which of the topics do you think the text mentions? Read the text and check your answers. ANSWERS: 2, 4, 6 Students read the text. Who said these things? ANSWERS: 1 more than 50% of the participants in the survey 2 Peter Jones 3 Peter Jones 4 Peter Jones 5 Maral Akhmadieva 6 Maral Akhmadieva 7 25% of the participants in the survey Students complete the phrases with by, of, in or on. Then check your answers in the text. ANWERS: 1 on 2 on 3 in 4 in 5 off 6 by Students choose the correct words ANWERS: 1 on 2 By 3 on 4 in 5 off 6 in |
Assessment criteria - Read about why young people travel, where they go, what they do.
Descriptor: - look at the photos and the title of the text. Assessment criteria: - Learn vocabulary with prepositions by, off, in and on.
Descriptor: - complete the phrases with by, of, in or on. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket Home task: |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 74 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The future of transport |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.6.11.1 use some reported speech forms for statements, questions and commands: say, ask, tell including reported requests on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.6.1 link, independently, sentences into coherent paragraphs using a variety of basic connectors on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn verbs describing movement. • Identify forms of transport discussed in a radio programme. • Listen for specific details. • Discuss various forms of transport and their benefits and drawbacks |
||
|
Value links |
Open-Mindedness – An open-minded person is someone who is always willing to hear new points of view and even change their own point of view if new arguments are highly convincing. It’s the opposite of stubbornness. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to think of examples of recent examples of new forms of transport (for example, electric cars, drones, etc.). • Ask students what they think the advantages and disadvantages of these new forms of transport might be. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 84 Ask students to use their dictionaries or portable devices to check the meaning of the verbs in the box. Give students time to complete the sentences and check in pairs Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:84 Get students to describe what they can see in the pictures. Elicit flying bicycle, solar-powered car, and solar-powered plane, driverless car and space elevator. Explain that they are going to listen to a radio programme. Tell students to listen and identify the forms of transported discussed Ex: 3 P:84 • Tell students to read sentences 1–6. • Play the CD again so that the students can identify the correct phrases to complete the sentences. • In a weaker class, stop the CD after each sentence to give students time to choose the correct answers. • In a stronger class, play the CD without stopping. |
Students check the meaning of the verbs in the box. Then complete the sentences with the correct form of six of the verbs. ANSWERS: 1 stopped off 2 takes off / will take off / is going to take off 3 turn back 4 set off 5 pull off 6 went up Students look at the photos and listen to the radio proggrame. Which forms of transport do the people mention? ANSWERS: a – solar-powered car d – driverless car e – space elevator Students listen again and choose the correct answers ANWERS: 1 a 2 b 3 a 4 b 5 b 6 b |
Assessment criteria - Identify forms of transport discussed in a radio programme.
Descriptor: - look at the photos and listen to the radio proggrame. Which forms of transport do the people mention Assessment criteria: - Listen for specific details
Descriptor: - listen again and choose the correct answers Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket Home task: Ex: P: WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan : term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 75 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Reported questions, commands and requests |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 8.6.11.1 use some reported speech forms for statements, questions and commands: say, ask, tell including reported requests on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.6.1 link, independently, sentences into coherent paragraphs using a variety of basic connectors on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular topics 8.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Identify direct speech and reported speech. • Learn the tense changes we use in reported speech. • Practise changing direct speech into reported speech |
||
|
Value links |
Perseverance – People who value perseverance will work through adversity and be determined to get a result. This is a great treat for employees and entrepreneurs alike. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
students wish each other by holding a wishes lamp Lead – In • Ask students to quickly read (scan) the text for examples of said and told. • Ask students what word often comes after said (that). |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 83 • Tell students to look again at exercise 2 on the previous page. Ask them to find the reported speech in the text that relates to each item and get them to focus on the difference in tenses between the two. • Give students time to work individually to complete the table. • In a weaker class, walk round checking students’ progress and give help where needed. • In a stronger class, get students to write down examples of the tense changes. • When students have finished completing the table, ask them to complete the rules on the right side of the page Ex: 2 P:83 • Allow students time to complete the sentences. Walk round and remind students to refer to the RULES box if they are having difficulty. • Go through the answers with the whole class. Ask students to explain their answers. For example, the answer to question 1 is told because it is followed by reference to a person – i.e. a noun (see Rule 3). Ex: 3 P:83 Check that students know what to do by going through the example and eliciting the changes that have been made: we to they, can’t to couldn’t, adding that • In a weaker class, put students into pairs to do the exercise. Go round the class and check each pair can make the changes following the example. • In a stronger class, students can work individually then check their answers in pairs. • Go through the answers with the class and write the complete sentences on the board. |
Students complete the direct speech and the reported speech in the text. How does the tense change? Complete the table and rules. ANSWERS: present simple - past simple present continuous- past continuous present perfect - past perfect past simple - past perfect will - would 1 past 2 pronouns 3 say Students complete the sentences with said or told. ANSWERS: 1 told 2 said 3 told 4 said 5 said Students rewrite the sentences using reported speech. ANWERS: 1 Assel told us that she was writing a book about the travels of the Moroccan explorer Ibn Battuta. 2 Ilyas and Maxim said that they always read online reviews before they booked a holiday. 3 Jake said that he had never tried koumiss before. 4 The reporter said that about five million people had travelled to Kazakhstan in 2017. 5 The tourists said that they would buy some souvenirs from the bazaar. 6 Yerzhan told his sister that he had lost the guidebook that she had given to him. |
Assessment criteria - Identify direct speech and reported speech.
Descriptor: - complete the direct speech and the reported speech in the text Assessment criteria: - Learn the tense changes we use in reported speech
Descriptor: - rewrite the sentences using reported speech. Make CCQ questions Yes / No |
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticket Home task: Ex: P: WB |
|
Students use their stickers to show their knowledge according to the lesson. |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 76 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Apologizing and explaining |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.7.1 develop and sustain a consistent argument when speaking or writing 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.5.1 interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a dialogue in which people apologize and explain. • Learn phrases for apologizing and explaining. • Practise apologizing and explaining. |
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, write the words apology and apologize on the board and elicit the difference between the two words (apology is the noun, and apologize is the verb). Check students’ pronunciation of both words. • Ask students to think of last time they apologized. Who did they apologize to and what did they apologize for? |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets.
|
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 86 • Ask students to say what they can see in the photo. Encourage them to describe Jane’s and Mark’s face and body language and use this to guess the situation. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:86 • Tell students to listen to the conversation between Jane and Mark to understand the situation and find out why Mark didn’t call Jane. • Play the CD without stopping and get students to discuss their answers before checking with the whole class. Ex: 3 P:86 Draw students’ attention to KEY PHRASES box and point out the five gaps in the phrases. Ensure that students understand they need to use the words in the box in exercise 3 to complete the gaps. Give them a few a few minutes to complete the phrases and then play the CD again so that they can check their answers. Get individual students to say each phrase. Model and correct students’ pronunciation as necessary.
|
Students look at the photo. How do you think Jane is feeling? ANSWERS: Jane is not looking at Mark and her facial expression suggests she is not happy. Mark is looking sympathetic or apologetic with his hand on Jane’s arm. Students listen to the dialogue. Why didn’t Mark call Jane? ANSWERS: Mark couldn’t call Jane because he hadn’t charged his phone. He had lost the helmet Jane bought him and broke his skateboard.
Students complete the key phrases with the words in the box. Who says them? Listen and check. ANSWERS: 1 mean (Mark) 2 don’t (Mark) 3 sorry (Mark) 4 worry (Mark) 5 happen (Mark |
• In a weaker class, translate these words in L1. Helmet, skateboard, upset, • In a weaker class, complete the key phrases with the words in the box with teacher’s support |
Assessment criteria - Listen to a dialogue in which people apologize and explain
Descriptor: - look at the photo. How do you think Jane is feeling?\ Assessment criteria: - Learn phrases for apologizing and explaining.
Descriptor: - complete the key phrases with the words in the box. Who says them? Make CCQ questions Yes / No
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 77 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A memorable journey |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 8.6.11.1 use some reported speech forms for statements, questions and commands: say, ask, tell including reported requests on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a text that tells a story. • Learn time phrases with prepositions. • Practise time phrases in direct and reported speech.
|
||
|
Value links |
Self-Discipline – If you value self-discipline, you might be a person who wakes up early, exercises daily, and doesn’t get distracted by vices. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, write Bayanaul and Lake Zhasybay on the board and ask them what they know about these places – what there is to see and do, where it is, etc. Ask if these are good places to go to on a school trip. |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets.
|
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 87 Ask students the questions about school trips and encourage them to give details of places and times. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:87 • Read the title of the text and look at the picture with the class. Ask students to describe what they can see in photo. • Students then read the text and look for any sentences or phrases that suggest whether the reader enjoyed the trip or not. • Check answers as a class and ask students to read the relevant phrases out loud. Ex: 3 P:87 • Focus students’ attention on the Key Phrases box. • In a stronger class, get students to complete the phrases before they check the text for the answers |
Students answer the questions. Do you enjoy going on school trips? What trips have you been on recently? ANSWERS: Students own answers Students read the story. Did the writer enjoy the trip? ANSWERS: Yes, the writer enjoyed the trip. Key sentences and phrases: I was very excited, amazing, beautiful, I was tired but really happy, I learnt a lot, made some new friends.
Students complete the key phrases with the correct prepositions. Then read the model text. ANSWERS: 1 from 2 to 3 by 4 on 5 By 6 A |
• In a weaker class, tell students to use the text to complete the key phrases. |
Assessment criteria - Study a text that tells a story.
Descriptor: - answer the questions. Do you enjoy going on school trips? What trips have you been on recently? Assessment criteria: - Learn time phrases with prepositions.
Descriptor: - complete the key phrases with the correct prepositions.
Make CCQ questions Yes / No
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 78 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Almaty Metro: Going underground |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a text about the metro system in Astana. • Learn adjectives to describe a transport system. • Review the use of the present simple to talk about timetables and schedules. • Practise prepositions off, at, in.
|
||
|
Value links |
Humility – You might highly value humility if you find yourself disgusted by people who are arrogant or braggadocious, and instead find yourself gravitating to people who are always expressing their gratefulness for the blessings in their life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
A student with special educational needs |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Draw students’ attention to the photo and ask them where they think it is and what their opinion is – what do they like or dislike about it? |
The aim: To develop pupils speaking skills and create friendly atmosphere Efficiency: By telling the wishes they show their appreciations . Students of the class are listed. Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students analyze the given pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and purpose of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
A pupil greets.
|
At the organization moment teacher tries to award active pupils. «The praise» method is used to evaluate pupils with phrases like: “Good job! Well done!” Formative Assessment
Good job! |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P: 87 • Ask students if they ever use the metro system or trains to other cities. Get them to think of adjectives to describe the trains and the system, for example, quiet or noisy, on time or late, etc. • When the students have matched the words with the opposite meaning, go through the answers making sure students can pronounce the words correctly. Drill the longer words if necessary. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Ex: 2 P:87 • Tell students to follow the text as you play the CD. They should listen only to check whether the sentences are true or false. • In a stronger class, play the CD straight through. Ex: 3 P:87 • Read through the sentences with students and then give them a few minutes to complete the rules. • Ask students to think of other examples of using the present simple, for example, ‘This class ends at …’
|
Students match adjectives in the box with their opposites. Which adjectives would you use to describe the transport system in your town or city? ANSWERS: 1 convenient 2 safe 3 comfortable 4 cheap 5 fast 6 reliable 7 clean 8 modern Students read and listen to the text. Write true or false. Correct the false sentences. ANSWERS: 1 true 2 false – In future, the Almaty Metro will have 45 kilometres of track. 3 false – Yeldos said that the trains were always on time. 4 true 5 false – Tolkyn said she liked all the stations
Students study the sentence below then choose the correct words to complete the rules. ANSWERS: 1 present 2 time |
• In a weaker class, match adjectives in the box with their opposites with teacher’s support • In a weaker class, pause the CD after the sentence that provides the information for each true / false question. |
Assessment criteria - Study a text about the metro system in Astana
Descriptor: - match adjectives in the box with their opposites. Assessment criteria: - Learn adjectives to describe a transport system.
Descriptor: - to describe the transport system in your town or city
Make CCQ questions Yes / No
|
Cards Worksheets |
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. The exit ticketThis is a way for students to self-reflect on their progress in the lesson. Home task: Ex: 3 P: 56 WB |
|
Poster
|
|
||
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 79 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL Language and literature: Adventure stories |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics 8.6.14.1 use some prepositions before nouns and
adjectives |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Understand an extract from a classic work of literature. • Review the use of prepositions. \ • Discuss an adventure story and analyse the style and content |
||
|
Value links |
Kindness – If you value kindness, you’ll likely always be respectful of people around you, be gentle with criticism, and always willing to welcome people with open arms. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Ask students to talk about books they have read recently, giving details of the author, the characters, and the story. Ask if the story was written in the first person (‘I was born in … I went to school …’ etc.) or the third person (‘Yeldos was born in … he went to school …’ etc.) |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:88 • Ask students to describe what they can see in the photo and guess where and when the story is set and who the characters are. • Get students to read the summary and answer the question. Note that there are two parts to the answer, one for Huckleberry and one for Jim. Answers: Huckleberry is running away from his father and Jim is a runaway slave that people are looking for Ex: 2 P:88 • Ask students to read the text again and put the prepositions from the box into the correct sentences. • Make it clear to students that each preposition can be used in two sentences. • Play the audio for students to check answers. Answers: (1 on 2 On 3 to 4 in 5 of 6 at 7 off 8 out 9 to 10 out 11 of 12 at 13 off 14 in) Ex: 3 P:88 • Ask students to read the text one more time to check their detailed understanding of the story. Answers: 1 false 2 true 3 false 4 don’t know 5 don’t know 6 true 7 false 8 false |
Students look at the photo from a film adaptation of an American novel, then read the summary below. Why do Huckleberry Finn Jim decide to go on journey? Descriptor: - work in groups - read the text -discuss about text Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students complete the text with the prepositions in the box. Use each preposition twice. Then read and listen to the text. Descriptor: - complete the text with the prepositions - read and listen to the text Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students read the text again and write true, false or don’t know Descriptor: - read the text again - write true, false or don’t know |
-can discuss about text Total: 1 point -can complete the text with the prepositions Total: 1 point -can write true, false or don’t know Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 78 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative Assessment for term 3 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.14.1 use some prepositions before nouns and adjectives |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to:
|
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to recall the previous lesson (Speaking, page 86) and elicit what they remember about the scenario. • Ask: Where was the woman? (In a shop.) What was she doing? (Returning a record.) What did she want? (To change it.) Did she get what she wanted? |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
LISTENING Task. Listen to five people talking about different celebrations. Match the halves of the sentences (1-4) with the opinions (A-F) to make true sentences. ONE argument is extra. CD3 Tapescript3
Task. Choose and circle the correct answer A, B or C
READING Task. Paraphrase the given sentences so it has similar meaning. Use the given beginnings of sentences. Example, No kitchen was needed to prepare popcorn. Preparation _________________________. Answer, Preparation of popcorn did not need any kitchen Task. Answer the questions. 5. Why have cinemas sold popcorn since the 19th century? 6. Why cannot popcorn be dissapperead from cinemas?
WRITING Choose ONE of the topics and write. Topic 1. You are a blogger who shares with own experience. Write a story about a concert you have been to. Include the following information in your review:. • The concert; when? / where? • The band: people in the band/ kind of music/ songs played • The audience: how many people / their reaction • Problems: the music/ the sound quality/ the time • Suggestions: different place / different time / different kind of music
SPEAKING Task. You are given questions to speak about for 2-3 minutes. Before you speak you have one minute to think about what you are going to say. |
Students Listen to five people talking about different celebrations then match Descriptor: - listen and match Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students Descriptor: - Paraphrase the given sentences so it has similar meaning Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students choose ONE of the topics and write. Descriptor: - Write a story about a concert Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
-can match the halves of the sentences Total: 1 point -can paraphrase the given sentences Total: 1 point -can write a story about a concert Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Travel and transport |
Lesson 79 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review unit 7 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
8.3.8.1 recount some extended stories and events on a range of general and curricular topics 8.4.4.1 read a growing range of extended fiction and non-fiction texts on familiar and some unfamiliar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use verbs to do with travelling and transport • Use vocabulary with prepositions by, off, in and on. • Identify direct speech and reported speech. |
||
|
Value links |
Gratitude – You value gratitude if you find yourself respecting people who say please and thank you. If you’re a religious person who values gratitude, you may always insist on praying before eating your dinner. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Focus students’ attention on the picture. Ask them what sort of story they think the text is. (A folk tale) • Ask them what sort of things usually happen in such stories. (There’s often romance, a search for something that involves a long journey, or a problem to be overcome. There is also often a sense of good versus bad.) |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture
|
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support
|
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min
|
Ex: 1 P:90 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words in the box and write the words in the correct part of the table. • Encourage students to work individually, then compare answers in pairs. Then check as a class to ensure everyone has agreed which column the words go in. • In a weaker class, explain the more difficult words such as submarine, helicopter, and spacecraft. In a stronger class, ask students to talk about the benefits and dangers of each type of transport. • Model and drill the pronunciation of longer words. Make sure students can pronounce the words with the correct word stress, for example, submarine Answers: Students’ own answers Ex: 2 P:90 Ask students if they know the story of Kyz-Zhibek and what they know about it. • Focus students’ attention on the questions and give them a minute to read them before you play the recording for them to listen to while they read. • Students work through the answers in pairs. • Check answers as a class. Ask students what they think about the story and whether they prefer stories with happy or sad endings. Answers: (1 It was first told in the 16th century. 2 Bararbai and his wife had 11 children. 3 Tulgen went on a long journey because he wanted to meet and marry Kyz-Zhibek. 4 When Tulgen met Kyz-Zhibek they fell in love. 5 He wanted to marry Kyz-Zhibek and challenged Tulgen to a fight. 6 She killed herself..) Ex: 3 P:90 • Focus students on the blue words in the text. Ask a couple of students to read them out. • Students complete the sentences in the exercise. . Answers: 1 north 2 war 3 son 4 thunder 5 goddess Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students work in pairs. Make a list of the folktale names and the main characters. Which folktales do you know? Descriptor: - work in pairs - make a list of the folktale names Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read and listen to the story. Answer the question Descriptor: -listen the dialogue -answer the question Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs Students find the phrases in blue the story and complete the sentences. Then complete the rules. Descriptor: - find the phrases in blue - complete the sentences. Differentiation by support Less motivated learners will be given prompts to find the correct location of the text() paragraphs |
-can make a list of the folktale names Total: 1 point -can read and listen the story Total: 1 point -can find phrases in blue the story Total: 1 point
|
Cards Worksheets
|
|
End of the lesson 5 min
|
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|

шағым қалдыра аласыз