Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 81 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
People in sport |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 7.2.4.1 understand with limited support the main points of extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 7.3.3.1 give an opinion at sentence and discourse level on an increasing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for people in sport. • Play the Team Manager game. • Learn about imperatives. • Practise using imperatives to give advice |
||
|
Value links |
Hospitality: Traditionally a nomadic culture, hospitality has always been an important part of Kazakh culture. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
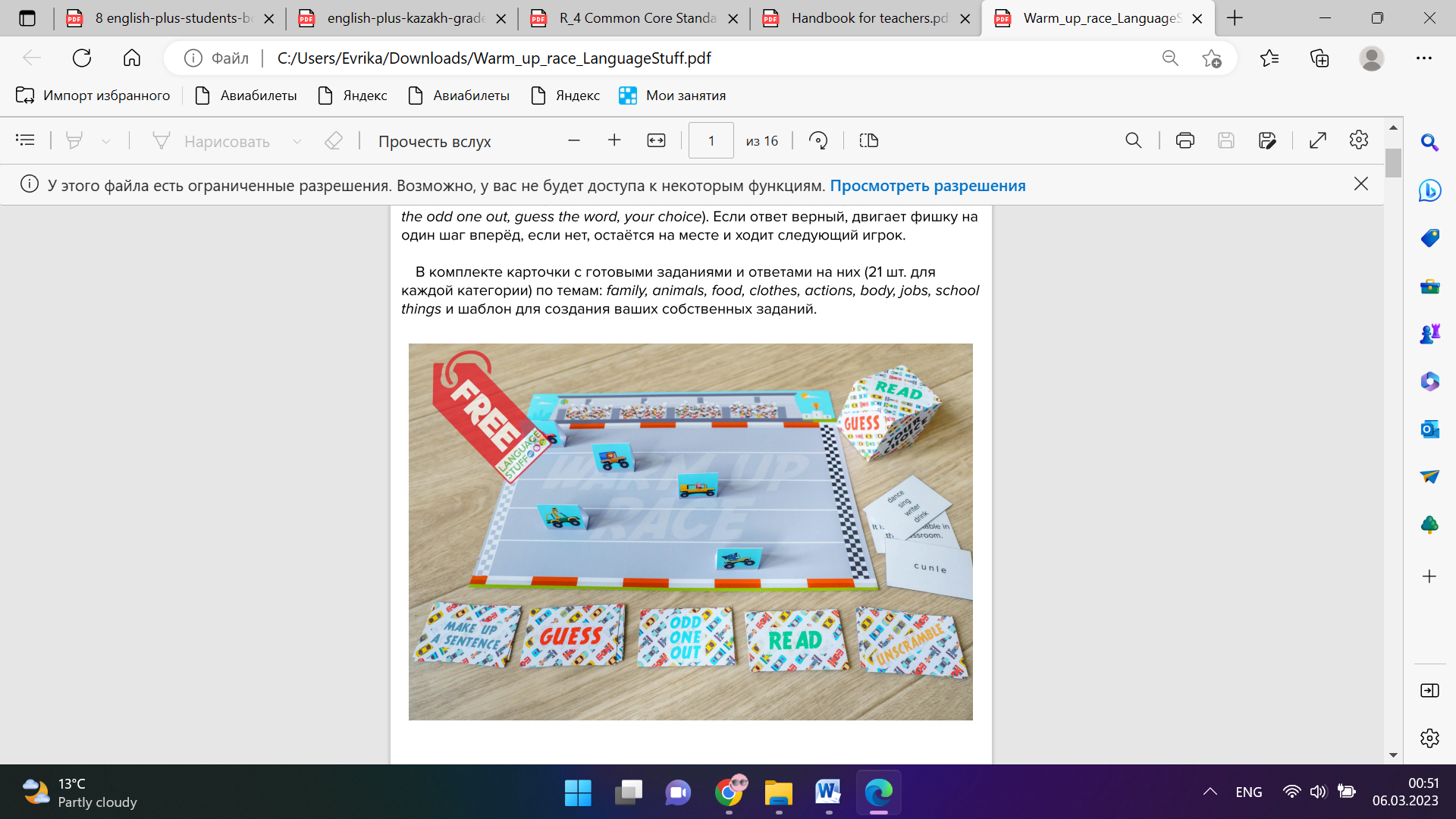
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, write the word sport on the board. • Put students into pairs and ask them to write down as many names of sports as they can in two minutes. • Ask students to call out sports they have written down. Write them on the board. • Ask students if they know any words for people in sport. Elicit a few words and write them on the board |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:92 • Students match the words with the photos. • Check answers with the class, and model and drill pronunciation of any words that are new to students. Ex: 2 P:92 • Students complete the sentences with their own ideas. This activity is based on general knowledge. In some classes you may need to group students who do not know much about sport with those who do. • Ask students to check their answers in pairs. Then ask some students to read their answers to the class. Ex: 3 P:92 • Look at the title and ask if anyone can explain what it means. Confirm that a team manager decides what the team should do in a variety of situations. • Students play the Team Manager game individually, then compare their answers in pairs. • Ask some students to report their own results and their partner’s results. Ask whether they agree with the results. • In a stronger class, go through each question and elicit why each option implies good or bad management skills. Follow up by asking for adjectives which describe a good manager. • In a weaker class, ask for adjectives which can describe good and bad managers. Students can refer to the key to help them. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students match photos with six of the words. Answers: 1 referee 2 supporter 3 TV reporter 4 captain 5 champion 6 loser Students complete the sentences with your own ideas. Answers: Students’ own answers Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students work in pairs. Answers: Students’ own answers. |
Descriptor: - match the words with the photos Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences with their own ideas. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - play the Team Manager game individually - describe good and bad managers Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 82 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Women in sport |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.3.3.1 give an opinion at sentence and discourse level on an increasing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about a female racing driver. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Give your opinions about sport |
||
|
Value links |
Tradition: Kazakh traditions and culture have been passed on from one generation to another through oral histories told by traditional Kazakh tribal leaders and elders. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, write Formula 1 on the board. Elicit the meaning and ask students what they know about the sport. • Ask students if they know any Formula 1 drivers, then ask if they think that women also race Formula 1 cars |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:94 • Read the task with the class and ask students for their ideas. Ask students to justify their ideas with reasons. • You could ask whether the situation is the same in all sports, comparing football with athletics, for example.
Ex: 2 P:94 • Read through the interview questions with the class and clarify that the text is a transcript of the interviewee’s answers. • in a stronger class, ask students to say which part of the answers they used to make their choices. In a weaker class, help them identify the areas of the text which dictate which choices to make. Ex: 3 P:94 • Students read the text again more carefully and complete the sentences. Note that sometimes more than one word is needed Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students sportsmen are often more famous than sportswomen. Answers: Students’ own answers Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the interview and match interview questions with answers in the text. Answers: 1 B 2 A 3 G 4 D 5 F 6 E Students read the text again and complete the sentences with one, two or three words Answers: 1 watched 2 rally cars 3 massive / popular 4 competitors 5 money 6 sponsors |
Descriptor: - answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the interview - match interview questions with answers in the text. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences with one, two or three words Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 83 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
be going to |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 7.6.8.1 use future form will to make offers, promises, and predictions on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn be going to for plans and intentions. • Write about plans and intentions using be going to. |
||
|
Value links |
Freedom: Freedom is the major value of the civil society being formed in Kazakhstan. This must provide everyone with the possibility of creative self-realization. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Refer students back to the reading text on page 70. Ask students to look in the first paragraph of the text and ask: What is Karen going to do next year? • Elicit the sentence: She’s going to try Formula 3. Write the sentence on the board and underline going to. Elicit that be going to refers to future plans. • Ask students to find more examples of be going to in the text. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:95 • Encourage students to check their answers in the text before completing the rule..
LANGUAGE NOTE We use be going to + infinitive: I’m going to play football. NOT I’m going to playing football. In the negative form, we use not + going to: He isn’t going to come. NOT He don’t going to come
Ex: 2 P:95 • Once students have completed the sentences ask them to compare answers in pairs Ex: 3 P:95 • Remind students they are writing about their own plans. In a stronger class, ask them to write true sentences using their own verbs Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students order the words to make sentences. Choose the correct words. Answers: 1 I’m going to have a go at Formula 3. 2 I’m not going to stop racing. 3 He’s going to contact more sponsors. 4 My sponsors aren’t going to give me much money Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students study the information and complete the sentences with your own ideas Answers: 1 are going to buy 2 is going to race 3 isn’t going to race 4 is going to contact 5 isn’t going to contact 6 aren’t going to look for Students write sentences about your plans using affirmative and negative form of to be going to. Answers: Students’ own answers |
Descriptor: - order the words to make sentences - choose the correct words Total: 1 point Descriptor: - study the information - complete the sentences Total: 1 point Descriptor: - write sentences about your plans - use affirmative and negative form of to be going to Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 84 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Will and be going to |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 7.6.8.1 use future form will to make offers, promises, and predictions on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the difference between will and be going to. • Write sentences using will and be going to. • Learn how to remember grammar with examples |
||
|
Value links |
Hospitality: Traditionally a nomadic culture, hospitality has always been an important part of Kazakh culture. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Refer students back to the reading text on page 70. Ask students to look in the first paragraph of the text and ask: What is Karen going to do next year? • Elicit the sentence: She’s going to try Formula 3. Write the sentence on the board and underline going to. Elicit that be going to refers to future plans. • Ask students to find more examples of be going to in the text. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 4 P:95 • Study the examples with the class and elicit the answer to the question in the instructions. LANGUAGE NOTE We use
be going to when we have already decided and planned something: I’m
going to watch the match tonight. NOT Ex: 5 P:95 • Remind students to read the sentences carefully and check they understand the context. In a weaker class, you could decide as a class which are plans and which are predictions before students complete the sentences. Ex: 6 P:95 • Point out to students that it is much easier to remember grammar through examples rather than rules. • Read through the instructions with the class, then ask students to write four example sentences. Tell them to use examples that they will find easy to remember, for example, by using a sport that interests them, or a famous person they admire. • Encourage students to test themselves on these examples regularly and to do this with other new grammar points Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students study the examples. Which sentence is a plan and which is a prediction? Answers: 1 plan 2 prediction Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students write the sentences with be going to or will Answers: 1 are going to meet 2 will be 3 are going to play 4 ’ll be 5 is going to leave Students read the study strategy. Then write examples of two plans and two predations. Answers: Students’ own answers |
Descriptor: - answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - write the sentences - identify to be going to or will Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the study strategy - write examples of two plans and two predations Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 85 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 05.04.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Compound nouns |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.1.1 begin to use basic abstract nouns and compound nouns and noun phrases describing times and location on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.2.4.1 understand with limited support the main points of extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 7.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn compound nouns related to sport. • Listen to three people talking about sport for the disabled. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. |
||
|
Value links |
Tradition: Kazakh traditions and culture have been passed on from one generation to another through oral histories told by traditional Kazakh tribal leaders and elders. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to name some people in sport. Write their names on the board and ask: What is this person? Elicit the compound nouns tennis / football player and write them on the board. • Focus on the compound nouns and tell students they are going to learn more compound nouns to do with sport. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
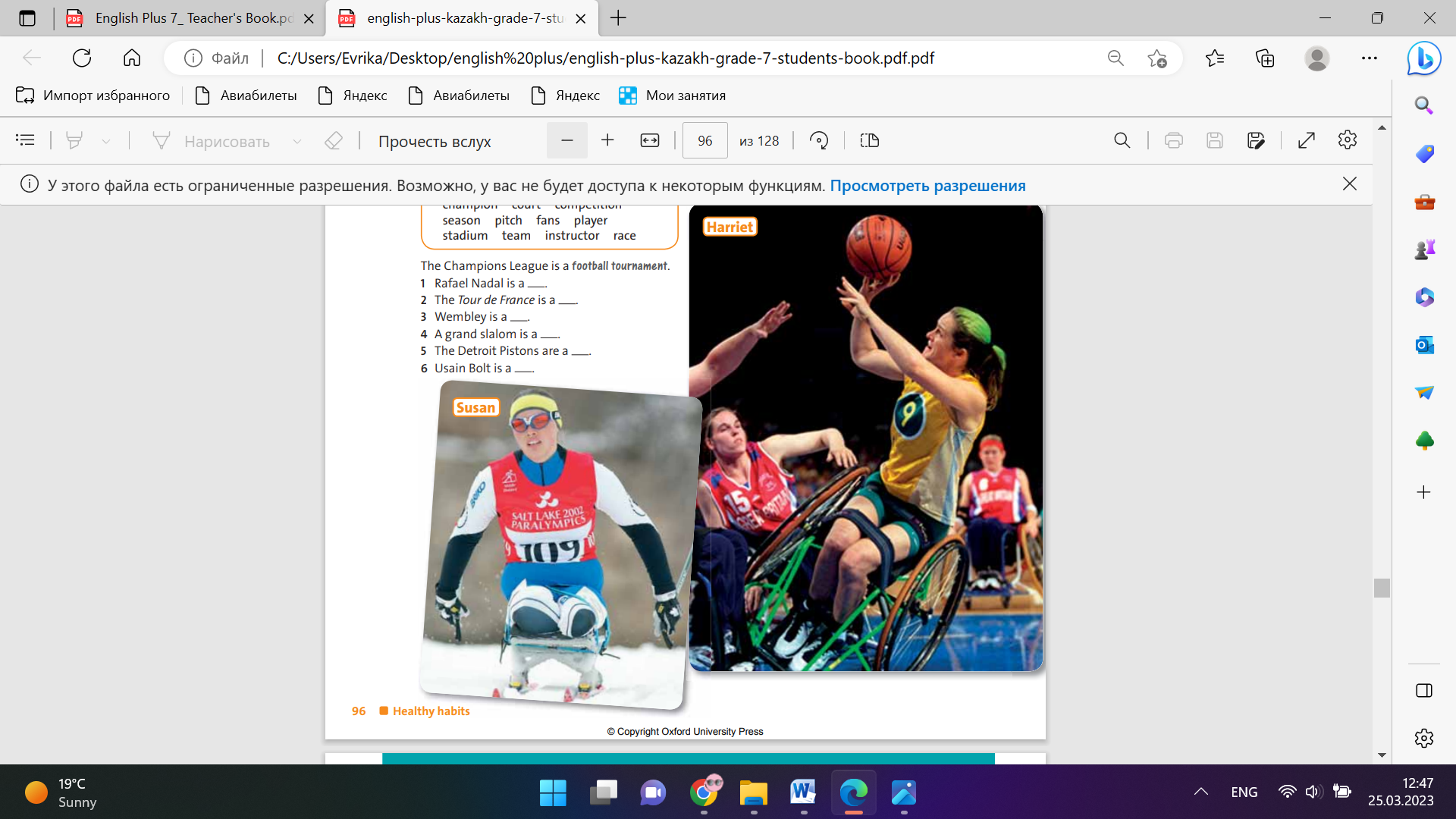
Ex: 1 P:96 • Allow students time to read the sentences and choose the correct answers. Encourage them to guess if they aren’t sure. • Play the CD. Students listen and check their answers. In a stronger class, ask where the stress falls. In a weaker class, point out that in compound nouns, the stress falls on the first word, not the second word. Model and drill some of the pronunciations Ex: 2 P:96 • Read the instructions and the example sentence with the class. Then, in pairs, students form compound nouns and complete the sentences. Ex: 3 P:96 • Focus on the photos and elicit or explain the meaning of disabled. • Play the CD. Students listen and check their answer. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students choose the correct words. the correct answers Answers: 1 tennis tournament 2 rugby match 3 football team 4 swimming champion 5 athletics stadium 6 team manager Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students work in pairs. Complete the sentences with a word in the box from A and a word from box B Answers: 1 tennis player / champion 2 cycling competition 3 football stadium 4 skiing tournament 5 basketball team 6 running champion Students look at the photos and listen to three interviews about disabled people and sport. Answers: Oscar Pistorius |
Descriptor: - read the sentences - choose Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen to three interviews about disabled people and sport. Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 86 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Be going to and Present Continuous |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 7.6.8.1 use future form will to make offers, promises, and predictions on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the question form of be going to. • Write questions using be going to. • Learn the use of present continuous for future arrangements. • Practise asking about future arrangements using the present continuous. |
||
|
Value links |
Freedom: Freedom is the major value of the civil society being formed in Kazakhstan. This must provide everyone with the possibility of creative self-realization. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Revise statements with be going to with the class. Ask them to form affirmative or negative sentences with be going to. Try to elicit a variety of forms, using I / he / she / we / you / they, etc. • Ask: Does the word order usually change in questions in English? Do not confirm or reject any ideas at this stage. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:97 • Focus students on the questions and ask them to complete them with the words in the box. They should read them carefully to choose the correct question words LANGUAGE NOTE The forms am / is / are come before the subject in questions with be going to: Is he going to leave school? NOT He is going to leave school? Ex: 2 P:97 • Students order the words and write the questions individually
Ex: 3 P:97 • Go round and listen as students ask and answer. Encourage them to give answers that are true for them, or to make answers up to fit the topic if they prefer. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students complete the questions from the interviews with the words in the box. Answers: 1 What 2 Where 3 going to 4 Is, is 5 How Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students order the words to make questions Answers: 1 Are you going to play tennis later? 2 Are you and your friends going to join any teams next year? 3 Are you going to go to any tournaments this year? 4 Is your friend going to go cycling this weekend? 5 What sport are you going to play next week? Students work in pairs and answer the question Answers: Students’ own answers |
Descriptor: - read the sentences - complete the questions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - order the words to make questions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work in pairs - answer the question Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 87 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Be going to and Present Continuous |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 7.6.8.1 use future form will to make offers, promises, and predictions on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the question form of be going to. • Wr read and complete the dialogue.ite questions using be going to. • Learn the use of present continuous for future arrangements. • Practise asking about future arrangements using the present continuous. |
||
|
Value links |
Freedom: Freedom is the major value of the civil society being formed in Kazakhstan. This must provide everyone with the possibility of creative self-realization. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Revise statements with be going to with the class. Ask them to form affirmative or negative sentences with be going to. Try to elicit a variety of forms, using I / he / she / we / you / they, etc. • Ask: Does the word order usually change in questions in English? Do not confirm or reject any ideas at this stage. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 4 P:97 • Allow students time to read the sentences through the mini-dialogues, then match each one to the rule that describes its function. In a stronger class, ask if students can describe the difference in function without looking at the rules. LANGUAGE NOTE We use the present continuous for definite arrangements that are planned and agreed for the future: I’m going to London on Saturday. NOT I will go to London on Saturday. The taxi is coming to collect us at six o’clock. NOT The taxi will come to collect us at six o’clock Ex: 5 P:97 • Students analyse the meaning of the tense in each sentence. Remind them to look carefully at any time markers that might give them clues. • In a weaker class, provide more examples for students to identify Ex: 6 P:97 • If necessary refer back to the spelling rules on page 21. • Students read and complete the dialogue. Explain that they do not need to worry about the blue words at this stage Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students study mini dialogues and match them with rules. Answers: 1 a 2 b Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students study the sentences. Then write action in progress or future arrangement. Answers: 1 future arrangement 2 action in progress 3 future arrangement Students complete the mini dialogue. Answers: 1 ’re practising 2 ’re cycling 3 ’m visiting 4 Are, doing, ’m swimming 5 ’m watching |
Descriptor: -read the mini-dialogues, - match each one to the rule Total: 1 point Descriptor: - write action in progress or future arrangement. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read and complete the dialogue.Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 88 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Making plans and arrangements |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.6.1 use a variety of personal, demonstrative and quantitative pronouns including someone, somebody, everybody , no-one on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a conversation about plans and arrangements. • Learn key phrases for talking about plans and arrangements. • Learn about indefinite pronouns. • Practise talking about plans and arrangements |
||
|
Value links |
Respect: Respect of elders and of the spiritual freedom of other nations are principal values. It is important to develop a productive dialogue between confessions and to acknowledge religion as an element of civil society. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they ever meet their friends at the weekend. Ask where they go and what they do. • Ask when they make their plans for the weekend and how they make the arrangements. • Ask them to imagine that they want to meet some friends and go to a football match. Ask: What things do you need to talk about with your friends? • Elicit that they will talk about where they should meet and what time they should meet. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:98 • Ask students to listen for where and when Callum and Gemma are meeting. Ex: 2 P:98 • Read through the key phrases with the class. • Ask students to think about the dialogue and recall who says each one. Remind them to think about whether the speaker is making or responding to an invitation. • Play the CD and ask students to listen and check. Ex: 3 P:98 • Students complete the dialogue with the key phrases. When they have checked their answers, ask them to practise with a partner. • Ask them to perform the dialogue a couple of times, then swap roles and go through it again. Ex: 4 P:98 • Allow students time to read through the examples, then ask the question in the instructions. • Explain that indefinite pronouns are used to ask or talk about a person or place without saying specifically who or what it is Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students listen and read the dialogue. Where and when are Callum and Gemma meeting? Answers: They’re meting outside the sports centre at about 7.30. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students study the key phrases Answers: 1 Callum 2 Gemma 3 Gemma 4 Callum 5 Callum 6 Gemma Students complete the dialogue with the key phrases Answers: 1 b Are you doing anything this evening? 2 d No, nothing special. 3 a What are you up to? 4 c if you’re interested. . 5 f It’s on at 6 e Shall I meet you outside … ? Students study the examples. When do they use some and any? Answers: We use any- in negative sentences or questions, and some- in affirmative statements. |
Descriptor: -listen and read the dialogues, - answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - recall who says each one. Total: 1 point . Descriptor: - complete the dialogue with the key phrases Total: 1 point Descriptor: -read the examples Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 89 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A formal letter |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with some support on a growing range of general and curricular topics 6.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 6.3.2.1 ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model formal letter. • Learn about layout and language in a formal letter. • Learn key phrases for writing a formal letter. • Write a formal letter |
||
|
Value links |
Respect - treating people with respect, value and courtesy. Especially apologising to them where the situation calls for it. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they ever write letters. Ask who they write letters to, and why. • Ask if they ever write formal letters. Ask who they might write a formal letter to and why
|
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:99 • Ask students to read the model letter quickly and then ask: What does the person who wrote this letter want? (They want money for a sports tournament.) • Students read the letter again and answer the questions. Ex: 2 P:99 • Read through the questions with the class. Explain that these questions cover the structure of the letter and the language used in detail. • Students look at the model text again and find the information. Ask students if the layout of a formal letter is the same in their language. Ex: 3 P:99 • Read through the key phrases with the class. Ask students to find the key phrases in the model letter and translate them into their own language before ordering them. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students read the model text and answer the question Answers: 1 Mary Grant 2 No. 3 Paragraph C 4 Paragraph B 5 Paragraph A Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students study the text again and answer the question Answers: 1 At the top of the letter. 2 Under the address of the person who is going to receive the letter. 3 At the top left of the letter. 4 Full forms: I am; we are. 5 Formal: Dear Sir or Madam; I am writing to you because; Please contact me; I look forward to hearing from you; Yours faithfully Students study the key phrases. Then order them. Answers: 1 Dear Sir or Madam 2 I am writing to you because … 3 Please contact me … 4 I look forward to hearing from you.. 5 Yours faithfull |
Descriptor: - read the model letter for gist - answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the model text again and find the information Total: 1 point Descriptor: - find the key phrases in the model letter Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 90 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Healthy habits |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.1.1 begin to use basic abstract nouns and compound nouns and noun phrases describing times and location on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.6.8.1 use future form will to make offers, promises, and predictions on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn abstract nouns related to health and lifestyle. • Talk about healthy habits. • Learn how to use will for offers and promises. • Learn and practise using tag questions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to name the oldest person they know. • Elicit some names, then ask for more details, e.g. how old is the person, where do they live, how they spend their time, do they have any unusual habits. • Ask students what they think the secret to a long and healthy life is. Elicit some ideas, but do not confirm or reject any at this stage. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:100 • Explain the task. In pairs, students discuss the different options and decide which ones are healthier. • Get some feedback from a few students and encourage them to give reasons for their answers Ex: 2 P:100 • Read the instructions and draw students’ attention to the word in the box. Ask students what part of speech they are and elicit that they are all nouns. Then ask: Do they refer to material objects or abstract ideas? Elicit answers and explain that nouns like these are called abstract nouns. In a stronger class, you could point out that most (but not all) abstract nouns are uncountable. • Students work in pairs to complete the text. Play the recording for them to listen and check their answers. Ex: 3 P:100 • Ask students to read the dialogue again and decide if the sentences are true or false. Encourage them to underline the parts of the dialogue where they find their answers. • Check answers as a class. Then draw students’ attention to the note about will and won’t. Ask them to find five examples in the dialogue (I’ll ask my grandparents …, I’ll help you …, I’ll call my grandmother …, I’ll be there …, I’ll make sandwiches …) Ex: 4 P:100 • Read through the instructions together. Draw students’ attention to the words in blue in the dialogue and point out that these are tag questions. Explain that they aren’t real questions – they are usually used to check that the listener agrees with what the speaker has said. Highlight that tag questions are very commonly used in spoken English, but not in formal written English Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students work in pairs. Look at the list and choose the options which you think are healthier Answers: Students’ own answers Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students check the meaning of these nouns in a dictionary. Complete the dialogue with five of the nouns. Answers: 1 habits 2 lifestyle 3 humour 4 education 5 idea. Students read the dialogue again. Are the sentences true or false? Answers: 1 False 2 True 3 True 4 False 5 False Students Highlight that tag questions are very commonly used in spoken English Answers: 1 the same as 2 positive, negative |
Descriptor: - discuss the different options and decide which ones are healthier Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the dialogue with five of the nouns Total: 1 point Descriptor: - decide if the sentences are true or false Total: 1 point Descriptor: -can attention to the words in blue Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 91 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talking about scores |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for talking about scores. • Listen to a conversation about scores. • Practise talking about scores. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills. Lead – In • With books closed, ask students: Do you like watching sport on TV? • Ask what sports they like watching. • Ask what was the last football match they watched on TV. Ask who was playing and what the score was. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:101 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words then complete the sentences. • Check answers and model pronunciation of the words. Ex: 2 P:101 • Refer students to the picture. Tell students they are going to listen to a conversation between people who are watching a match. • After students have listened to the dialogue, ask which match Paula and Andy are watching. • Elicit the answer, then write Liverpool vs Roma on the board. Point out that we use vs (versus) to mean ‘against’ when we are talking about football matches. Ex: 3 P:101 • Read through the key phrases with the class, pointing out that we say three all (not three-three) and one nil (not one zero). • Explain the meaning of draw if necessary. • Allow time for students to read the sentences. • Students listen again and correct the false sentences. Ex: 4 P:101 • Students read and listen to the dialogue. Tell them not to worry about the blue words at this stage. • Students practise the dialogue with a partner. Remind them to swap roles and practise it again. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box. Then complete the sentences with the words. Answers: 1 fan 2 score 3 goal 4 match Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to the conversation. Which match are Paula and Andy watching? Answers: They are watching Liverpool vs Roma. Students study the key phrases. Then listen to a conversation again and write true or false. and write true or false Answers: 1 False. The match started twenty minutes ago. 2 True. 3 True. 4 False. The score is one all, so it is a draw at the moment 5 False. Paula thinks that Liverpool will win this match and the Champions League. Students listen to the dialogue. Then practise the dialogue with a partner. Answers: Students’ own answers |
Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the words Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen to a conversation between people who are watching a match Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen to a conversation again Total: 1 point Descriptor: - practise the dialogue with a partner Total: 1 point . |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 92 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL: Maths: Average speed |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about average speed. • Read statistics about average speed. • Practise calculating average speed in English. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students some questions about journey distances and times. For example, name two large cities in the area and ask: How far is it from X to Y? How long does it take by train? How far is it from here to the next town? How long does it take to drive? • Write some of their answers on the board, then focus on some of the figures of distance and time and ask: What is the average speed for this journey? • Elicit some answers, but do not confirm or reject any at this stage |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
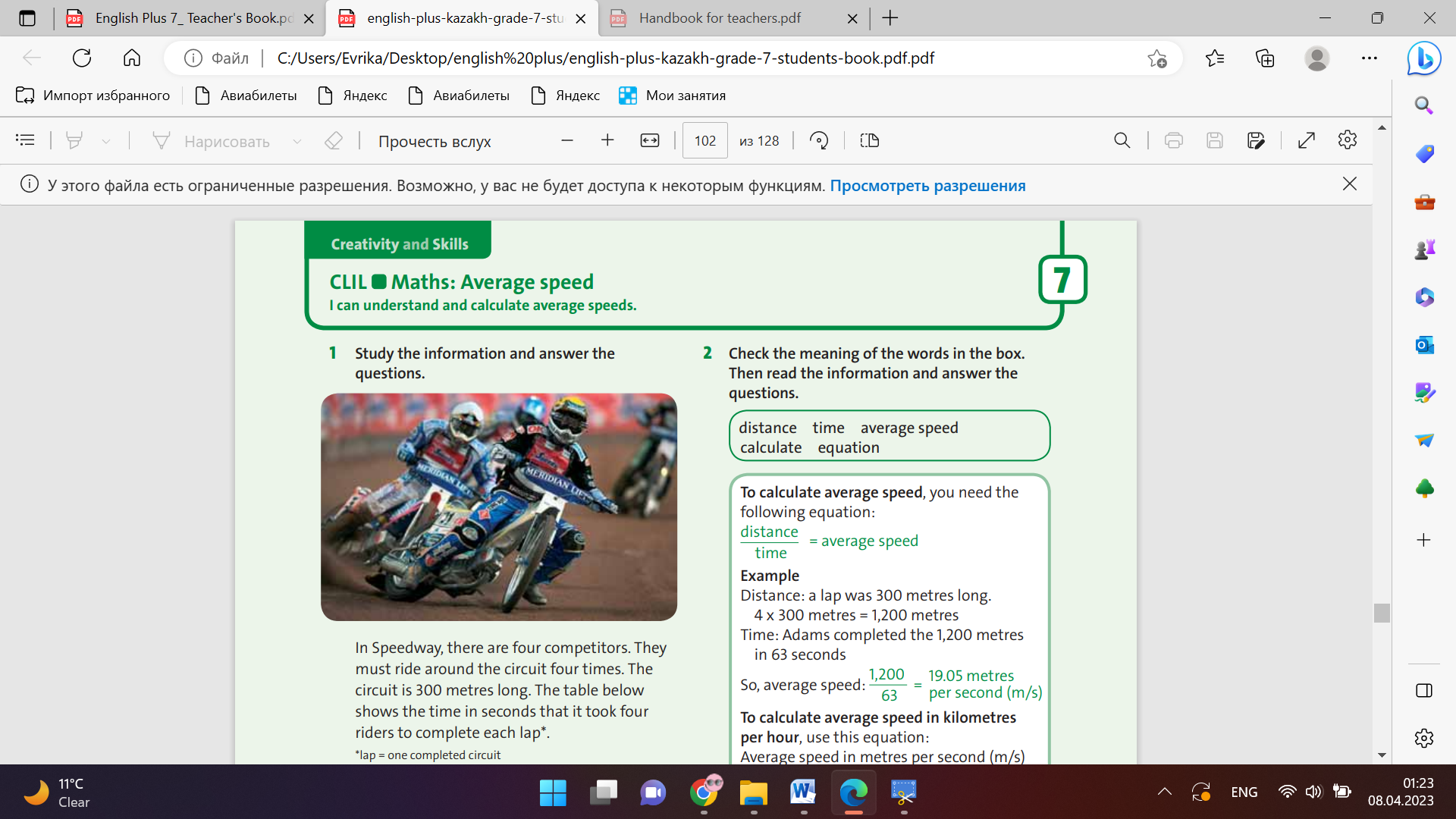
Ex: 1 P:102 • Focus on the picture and tell students that this kind of racing is called Speedway. • Read the instructions with the class and make sure that students understand the word lap. • Students study the information and answer the questions.
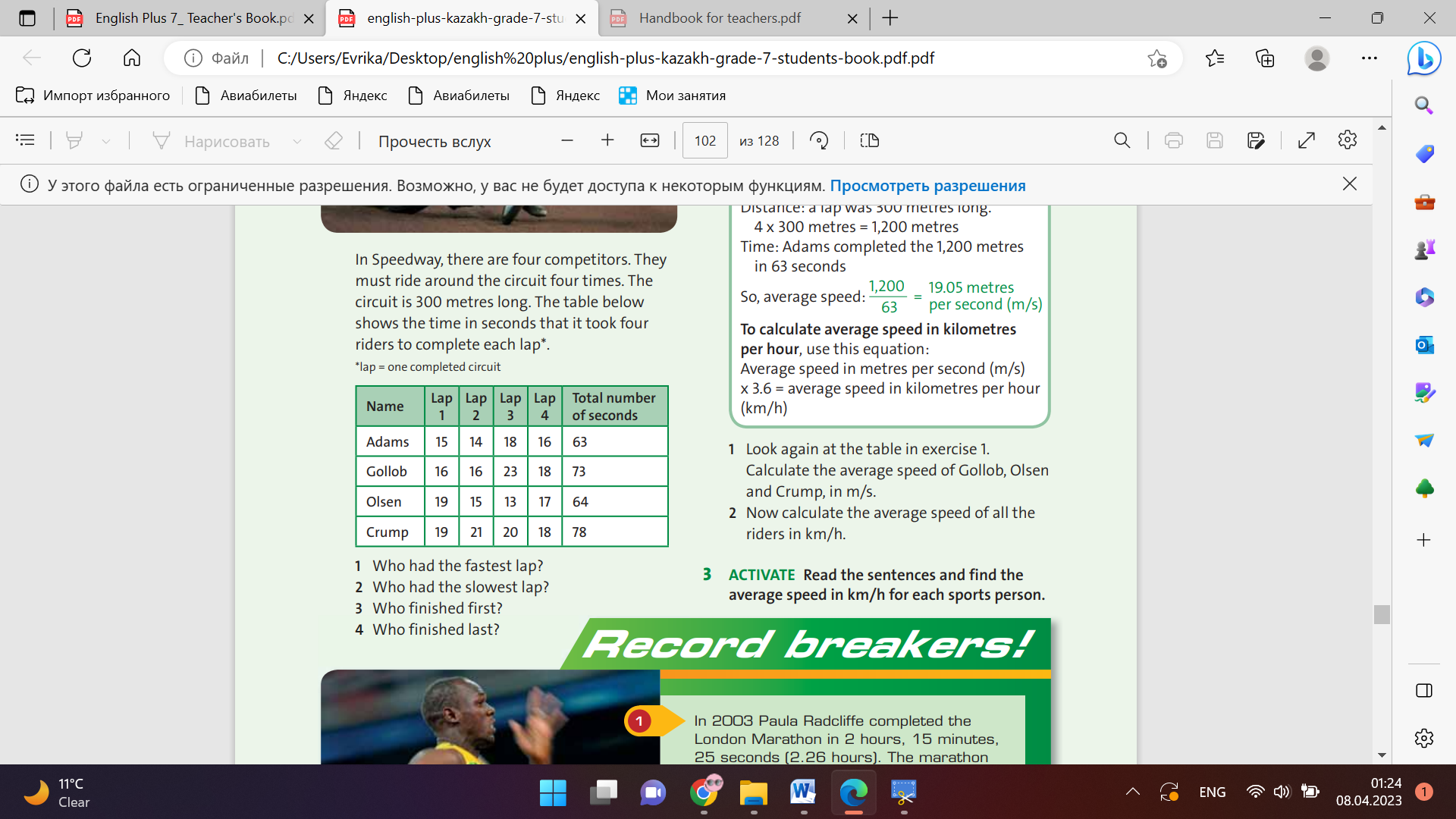
Ex: 2 P:102 • Allow students time to check the meaning of the words in their dictionaries. • Read the information with the class. • Point out the spoken form of distance / time (distance over time), m/s (metres per second), x 3.6 (times three point six) and km/h (kilometres per hour). • Students work in pairs to answer the questions.
Ex: 3 P:102 • Students work in pairs to read the sentences and find the average speed for each sports person. • Check answers by asking students to read out their answers, making sure that they read them correctly. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students study the information and answer the question. Answers: 1 Olsen y 2 Gollob 3 Adams 4 Crump Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students check the meaning of the words in the box. Then read the information and answer the question. Answers: 1 Gollob: 1,200 73 = 16.44 Olsen: 1,200 64 = 18.75 Crump: 1,200 78 = 15.38 2 Adams: 19.05 x 3.6 = 68.58 Gollob: 16.44 x 3.6 = 59.18 Olsen: 18.75 x 3.6 = 67.5 Crump: 15.38 x 3.6 =55.37 Students read the sentences and find the average speed in km/h for each sports person. Answers: 1 Paula Radcliffe: 42.19 (km) 2.26 (hours) = 18.67 km/h 2 Lance Armstrong: 3,870 (km) = 46.86km/h 82.59 (hours) 3 Usain Bolt: 100 (m) = 10.44 m/s 9.58 (s) 10.44 x 3.6 = 37.58 km/h 4 Michael Phelps: 200 (m) = 1.94 m/s 103 (s) 1.94 x 3.6 = 6.98 km/h |
Descriptor: - study the information and answer the questions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work in pairs to answer the questions. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - find the average speed for each sports person Total: 1 point 1.94 x 3.6 = 6.98 km/h |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 93 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review 7 Summative assessment for the unit “Healthy Habits” |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.8.1 use future form will to make offers, promises, and predictions on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.2.6.1 Deduce meaning from context with little support in extended talk on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.5.5.1 Develop with some support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a limited range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -Figure out the content of a conversation with some support in extended talk -Use punctuation marks in a piece of writing |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students some questions about journey distances and times. For example, name two large cities in the area and ask: How far is it from X to Y? How long does it take by train? How far is it from here to the next town? How long does it take to drive? |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 2 P:104 • Allow students time to read the sentences and choose the correct answers. Encourage them to guess if they aren’t sure. Ex: 4 P:104 • Focus students on the questions and ask them to complete them with the words in the box. They should read them carefully to choose the correct question words Summative assessment for the unit “Healthy Habits” Listening Task 1. Listen to the conversation and fill in the gaps. Use NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS. CD2. Tapescript4
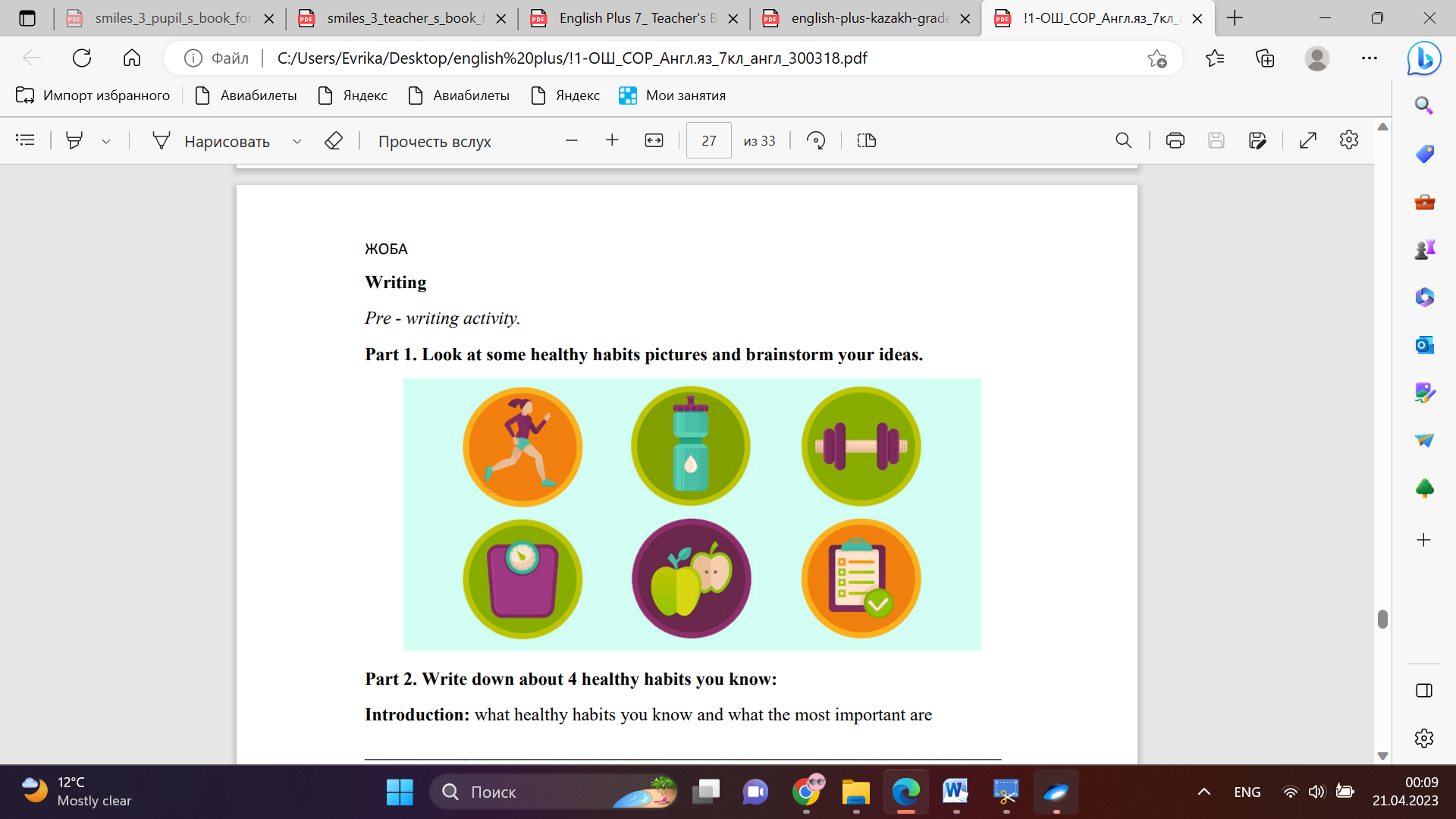
Writing Part 1. Look at some healthy habits pictures and brainstorm your ideas.
Part 2. Write down about 4 healthy habits you know: Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students choose the correct words Answers: 1 matches 2 atmosphere 3 stadium 4 supporters 5 referee’s Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students write sentences using to be going to or will Answers: 1 I think my favourite team will win the league next year. 2 Who is going to win the match tomorrow? 3 I’m going to the cinema with Nick later. 4 They aren’t going to play tennis tomorrow. They’re going to play football. 5 The PE teacher is going to train us tonight. |
Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point Descriptor: - write sentences using to be going to or will Total: 1 point - |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 94 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project proposal |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a proposal about sport in a neighbourhood. • Write a proposal for improving sports facilities in your town |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students what sporting facilities are like in their town. Ask if they think these could be improved. • Ask students how important they think it is to have good sports facilities in a town and how much money people should spend on them. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:105 • Students read the proposal. Ask them to discuss their opinions of Yernur’s solutions in pairs. They can use the opinion icons to help them. Ex: 2 P:105 • Read through the project checklist with the class. • Students prepare their proposals individually. They can work in class, or complete the proposal for homework. • Alternatively, use the project as an opportunity to promote groupwork. In a weaker class, once students have decided upon their three sports facilities, help them structure their thoughts. Encourage them to think of for and against arguments for each proposal. When writing, remind students to use the present simple to talk about the current situation and will for predictions and outcomes of their plans. Ex: 3 P:105 • Put students into pairs, and ask them to exchange proposals and give their opinions on their partner’s proposal. If students have worked in groups, allow them to evaluate another group’s work. • When students have finished, ask them to change partners (or groups) and repeat the process four or five times. • Ask students which proposals they thought were the best. • See page 33 in this guide for ideas about how students can assess their work Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students read the proposal. What is your opinion of Yernur’s sollutions Answers: Students’ own answers Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students make a proposal for sports facilities in your neighbourhood or town. Answers: Students’ own answers Students exchange your proposal with the rest of the class. |
Descriptor: - read the proposal Total: 1 point Descriptor: - make a proposal for sports Total: 1 point Answers: Students’ own answers |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 95 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Adjectives: feeling and events |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 7.6.14.1 use an increased variety of prepositions of time, location and directionuse by and with to denote agent and instrument; use prepositions before nouns and adjectives in common prepositional phrases on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for feelings and events. • Do a quiz about memory. • Talk about feelings |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they can remember their first day at school. • Ask students what they did and what things happened. Ask what it was like and how they felt. They can discuss this in L1 at first, but elicit as many words in English as possible. Write these on the board. • Find out how many students enjoyed their first day at school and how many did not enjoy it. Ask those who enjoyed it to think of positive adjectives, and those who did not to think of negative adjectives. Write these on the board as separate categories. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:36 • Read the task with the class. You may need to translate or pre-teach the word, memory. • In a weaker class, encourage students to make notes about each question before you discuss their ideas. In a stronger class, encourage them to go into more detail in their answers by explaining why they felt the way they did on this occasion. • Discuss ideas as a class. Students can use their own language for any ideas that they find difficult to express in English. However, encourage them to give simple answers to the questions if they can Ex: 2 P:36 • Allow students time to look at the photos and match them to the phrases. • If they do not know the adjectives, encourage them to make guesses based on the nouns they recognize. • Once students have matched the photos and the adjectives, check answers by calling out a number and asking for the correct phrase Ex: 3 P:36 • Students read through the sentences and choose the correct words to complete them. Encourage students to think about the context given by the sentences before choosing their answers. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students think about their first memory and answer the questions. Answers: Students’ own answers . Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students match photos with the phrases in the box. Answers: 1 a cute baby 2 a naughty boy 3 a nervous teenager 4 an upset baby 5 a lucky girl 6 a scary film 7 a lonely dog Students choose the correct words. Answers: 1 nervous 4 cute 2 lucky 5 upset, naughty 3 scary 6 lonely |
. Descriptor: - translate or pre-teach the word, memory Total: 1 point Descriptor: - match photos with the phrases Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read through the sentences and choose the correct words Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 96 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Remember this! |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.1.1 understand the main points in a growing range of short, simple texts on general and curricular topics 7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about people with very good memories. • Read for general meaning and specific information.. • Talk about memory |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to work individually and write down as many objects in the photos as they can remember from the quiz on page 29. • Set a strict time limit of one minute and then see who has remembered the most. • Write the word memory on the board and elicit or explain the meaning. Tell students they are going to read about some people with very good memories. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Background Stephen Wiltshire is unusual in that he could not speak as a young child and was diagnosed with autism. He was sent to a special school and learned to talk at the age of nine. He started drawing when he was still a child and was encouraged by his teachers. He has since been to art college and graduated with a degree. He has published several books of his drawings. Ex: 1 P:38 • Do the task as a fun way to test students’ memory. • Find out how many students could remember half of the numbers. Could anyone remember all of them? Ex: 2 P:38 • Read the title of the text with the class and ask students what they think the text will be about. • Then read the task and clarify that students should listen for four different names. Point out that students do not need to understand everything in the text at this stage. • Once students have read and listened to the text, elicit answers to the questions Ex: 3 P:38 • Tell students to read through all the sentences before reading the text again more carefully to decide whether the sentences are true or false. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students study the numbers for fifteen seconds. Then close your books. How many can you remember? Answers: Students’ own answers Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read and listen to the text. Which four people does the text mention Answers: Stephen Wiltshire, Mahavir Jain, Akira Haraguchi, Dominic O’Brien They all have good memories. Students read the text again. Write true or false. Answers: 1 False. Stephen doesn’t know the city. He drew a picture of it from memory. 2 False. Stephen was in a helicopter. 3 True. 4 False. He recited 100,000 digits of pi in 16 hours. 5 False. He was World Memory Champion |
Descriptor: - study the numbers Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the title of the text Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the text - write true or false. Total: 1 point eight times. |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 97 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Was, were |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 7.6.9.1 use appropriately an increased variety of present and past simple active and some passive forms on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn was and were to talk about the past. • Talk about the past using was and were. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Ask students to think about how they were feeling yesterday, last week, and last month. Ask for ideas about specific events that happened and ask students to say whether they felt happy, sad, excited, etc. • Encourage students to use the adjectives from page 28 if they can, for example, nervous, lonely or lucky. • Explain to the class that they are going to learn how to describe events in the past. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:39 • Explain that students are using sentences in context to deduce the rules. • Once students have completed the rules, check answers by asking students to read them out. • In a weaker class, ensure students understand that was is for the first and third person, and were is for the rest. In a stronger class, ask students to find more sentences using was, wasn’t, were or weren’t in the text. LANGUAGE NOTE We use
was for I, he, she, it and were for you, they: I was happy. They
were happy. NOT Ex: 2 P:39 • Students complete the sentences. If they are not sure about the information, encourage them to make a guess, although they should be careful to use the correct form of was, were. Ex: 3 P:39 • Students ask and answer in pairs. Refer them back to the rules section if they need help forming the short answers. • Ask some students to read some of their questions to the class and report back on their partner.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
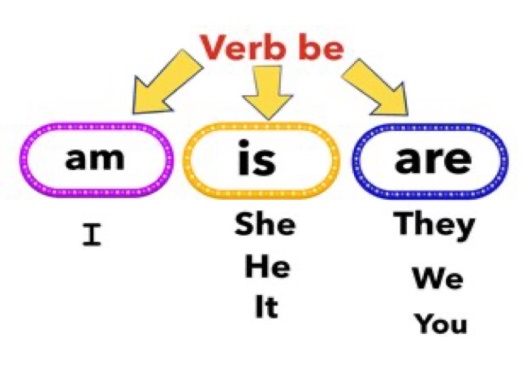
Students look at the text and complete the sentences with the words in the box. h the words in the box Answers: 1 were 2 wasn’t 3 Was 4 was Rules 1 were 2 wasn’t 3 was 4 was Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students complete the sentences using the correct form of was and were. Answers: 1 wasn’t 2 was 3 weren’t 4 were 5 wasn’t / was Students work in pairs. Ask and answer questions about the sentences using was and were Answers: 1 Was the football world cup in 2008? No, it wasn’t. 2 Was Michael Jackson an American singer? Yes, he was. 3 Were DVDs popular in 1980? No, they weren’t. 4 Were Robert Pattinson and Kristen Stewart in the Twilight films? Yes, they were. \ 5 Was I at school in 2001? Yes, I was. / No, I wasn’t. |
Descriptor: - completed the rules -complete the sentences wit Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences -use correct form of was and were Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work in pairs - answer the questions Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 98 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Milestones |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.3.1 use common participles as adjectives and order adjectives correctly in front of nouns on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.2.4.1 understand with limited support the main points of extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 7.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn adjectives used to talk about life events. • Listen to details about events in the lives of famous people. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to name a few famous people and write their names on the board. • Ask students what information they know about the people. • Elicit some ideas, for example he / she is married, he / she has two children, etc. Write vocabulary to do with life events on the board. • Ask students what other important things can happen to your in your life, and write useful vocabulary on the board. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:40 • Students choose the correct words to complete the phrases. In a weaker class, encourage them to guess if they are not sure, or to compare ideas with a partner. • Play the CD for students to check their answers. Ex: 2 P:40 • Students work in pairs to identify the people in the photos. Encourage them to use sentences to express their ideas, as in the example. • Once students have listened and checked their answers, find out how many they guessed correctly. Ex: 3 P:40 • Tell students to read through the sentences carefully. In a stronger class, if they can remember any information from the first time they listened, they can complete it now. Ensure students understand that they may need more than one word. • Play the CD again and ask students to complete the sentences
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
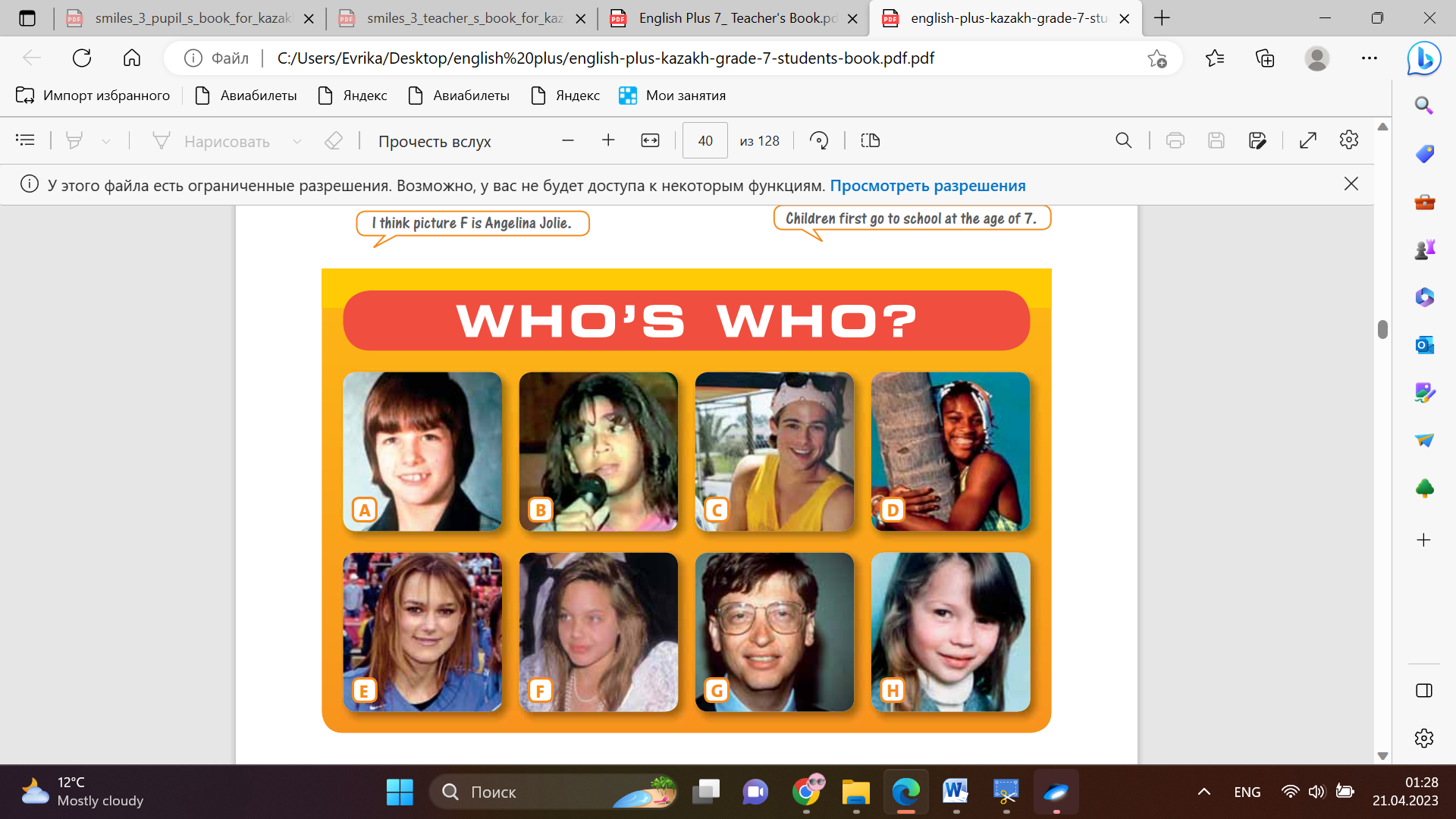
Students choose the correct verbs. Answers: 1 become 2 have 3 be 4 get 5 go 6 learn 7 leave 8 do 9 buy 10 graduate 11 win 12 leave 13 move 14 start 15 get Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students work in pairs. Match the names to the pictures Answers: A Tom B Beyoncé Cruise C Brad D Serena Williams E Keira Knightley F Angelina Jolie Pitt G Bill Gates H Kate Moss Students listen and complete the sentences with one or two words. Answers: 1 became a model 2 become 3 a big house 4 graduate 5 a job 6 drive 7 married 8 didn’t go |
Descriptor: - choose the correct words to complete the phrases Total: 1 point 16 become Descriptor: - read the sentences carefully - match the names to the pictures Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work in pairs - complete the sentences Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 99 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Past Simple |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 7.8.9.1 use appropriately an increased variety of present and past simple active and some passive forms on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the affirmative, negative and question forms of the past simple. • Use the past simple to talk about past events. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Refer students back to the reading text on page 30 and ask them to find examples of affirmative and negative forms of the past simple. • Elicit verb forms and write them on the board. Ask students what difference they notice between the affirmative and negative forms. Elicit ideas, but do not give an explanation at this stage. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:41 • Once students have copied and completed the table, check answers with the class LANGUAGE NOTE The
past simple affirmative forms are the same for all persons: I left,
she left, we left, etc. In the past simple negative form, we use
didn’t and the infinitive form of the verb, not the past simple
form: She didn’t leave school. NOT Ex: 2 P:41 • Students complete the sentences individually. In a weaker class, discuss questions a–c as a whole class activity. • In a stronger class, once students have finished, ask them to think of a new sentence for each of the past simple forms in the box. Check they have formed these correctly. Ex: 3 P:41 • Remind students to read all the options carefully before they match them. • In a weaker class, revise why questions 1 and 2 need information answers, and why question 3 requires a short answer Ex: 4 P:41 • Allow students time to study exercises 2 and 3 before they complete the rules. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abili1ies |
Students look at the verbs in the box and complete the table. Answers: Regular: learn – learned Irregular: buy – bought, get – got, go – went, become – became Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students complete the sentences with the words in the box. Answers: 1 played 2 didn’t go , 3 taught a 1 b 3 c 2 Students match questions with answers Answers: 1 c 2 a 3 b Students study the examples then choose the correct words in the rules. Answers: 1 same 2 base form 3 base form |
Descriptor: - complete the table Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences individually Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work in pairs - complete the sentences Total: 1 point Descriptor: - choose the correct words in the rules. Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 100 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: 23.05.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL: Folk stories. Summative assessment for the unit “Clothes and Fashion” |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.5.7.1 use with some support appropriate layout at text level for a growing range of written genres on familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a folk story. • Learn about first person and third person narrators. • Practise writing a story as a first person narrator. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students what kind of stories they enjoy reading. • Elicit some answers, then write folk story on the board. Ask students if they have read any folk stories. Elicit the names of some folk stories that students know. • Tell students they are going to read a folk story in English. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:46 • Students work in pairs to put the pictures in the correct order. • Play the CD. Students read and listen to the story, and check their answers Ex: 2 P:46 • Students read the story again and answer the questions. Summative assessment for the unit “Clothes and Fashion” Reading Task 1. Read the definitions below. Find the proper word in the text and insert it into the table. Look up the words in the dictionary and check the answers. Speaking Task 2. Choose the question and be ready to answer it after the teacher starts the conversation. You should add your ideas to the class discussion. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abili1ies |
Students look at the pictures and put them in the correct order Answers: 1 D 2 C 3 B 4 A Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the story again and answer the question Answers: 1 There weren’t any other elephants around. The elephant was lonely. 2 The bird looked for the other elephants and took the young elephant to them. 3 Because the bird had helped it twenty years ago, and the elephant remembered. 4 a Students Read the definitions below Answers: 1 uniform 2 girlish 3 casual 4 emblem 5 comfortabl |
- Descriptor: - work in pairs - put the pictures in the correct order. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the story again - answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - Find the proper word in the text Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 101 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative Control work for the term 4 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.2.5.1 Recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) in supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 7.4.2.1 Understand specific information and detail in texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics. 7.5.6.1 Link with little or no support, sentences into coherent paragraphs using a variety of basic connectors on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular 7.3.7.1 Use appropriate subjectspecific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a growing range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - understand specific details through the keywords, style, intonation and repetition -pronounce words and phrases correctly -formulate a simple character outline |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Listening Task. Listen and choose between A, B, C or D. CD3. Tapescript 4. Use the link to listen information 1) Continue listening to tape and fill in the gaps with NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS: 2) Choose the correct answer. Reading Task. Read the text and fill in the table below with necessary information. Answer the questions. Writing Task. Topic1. Fill in all the spaces provided. You can write more than one idea. Topic 2. When we talk about fashion we usually mean the popular style in dress or behavior. For most modern people fashion is a method of wearing to express themselves. What do you think about it? Write 80-90 words SPEAKING Task. Choose the card. Work individually. Look at the picture and make up a story for 1-2 minutes. Use the questions from the card. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abili1ies |
Students Listen and choose between A, B, C or D. Answers: 1 B 2 D 3 expensive 4 brands 5 B 6 D Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the text and fill in the table below with necessary information. Answers: Student’s own answer Students choose one topic and write more than one idea. Anwers: Student’s own answer Students Choose the card Anwers: Student’s own answer |
Descriptor: - work individually - Use the link to listen information Total: 6 point Descriptor: - read the text - fill in the table Total: 6 point Descriptor: - choose one topic -write the topic Total: 6 point Descriptor: - choose the card -answer the question Total: 6 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 102 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.5.7.1 use with some support appropriate layout at text level for a growing range of written genres on familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use vocabulary for feelings and events. • Use adjectives used to talk about life events |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they can remember their first day at school. • Ask students what they did and what things happened. Ask what it was like and how they felt. They can discuss this in L1 at first, but elicit as many words in English as possible. Write these on the board. • Find out how many students enjoyed their first day at school and how many did not enjoy it. Ask those who enjoyed it to think of positive adjectives, and those who did not to think of negative adjectives. Write these on the board as separate categories |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:48 • Students choose the correct words to complete the phrases. In a weaker class, encourage them to guess if they are not sure, or to compare ideas with a partner. Ex: 2 P:48 • Students complete the phrases with the verbs. In a weaker class, ask them to do this in pairs. In a stronger class, ask students there is one verb you don’t need. Ex: 3 P:48 Explain the students complete the dialogue with the affirmative or negative form of was and were Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abili1ies |
Students choose the correct words Answers: 1 nervous 2 scary 3 lucky 4 naughty 5 upset 6 cute Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students complete the phrases with the verbs in the box. There is one verb you don’t need. Answers: 1 become 2 go 3 have 4 buy 5 do 6 graduate Students complete the dialogue with the affirmative or negative form of was and were Anwers: 1 was 2 was 3 wasn’t 4 were 5 wasn’t 6 were 7 weren’t 8 was |
Descriptor: - work individually - choose the correct words Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the phrases with the verbs Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the dialogue Total: 6 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
ҚМЖ жинағы English Plus 7-сынып 4-тоқсан
ҚМЖ жинағы English Plus 7-сынып 4-тоқсан
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 81 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
People in sport |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 7.2.4.1 understand with limited support the main points of extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 7.3.3.1 give an opinion at sentence and discourse level on an increasing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for people in sport. • Play the Team Manager game. • Learn about imperatives. • Practise using imperatives to give advice |
||
|
Value links |
Hospitality: Traditionally a nomadic culture, hospitality has always been an important part of Kazakh culture. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, write the word sport on the board. • Put students into pairs and ask them to write down as many names of sports as they can in two minutes. • Ask students to call out sports they have written down. Write them on the board. • Ask students if they know any words for people in sport. Elicit a few words and write them on the board |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:92 • Students match the words with the photos. • Check answers with the class, and model and drill pronunciation of any words that are new to students. Ex: 2 P:92 • Students complete the sentences with their own ideas. This activity is based on general knowledge. In some classes you may need to group students who do not know much about sport with those who do. • Ask students to check their answers in pairs. Then ask some students to read their answers to the class. Ex: 3 P:92 • Look at the title and ask if anyone can explain what it means. Confirm that a team manager decides what the team should do in a variety of situations. • Students play the Team Manager game individually, then compare their answers in pairs. • Ask some students to report their own results and their partner’s results. Ask whether they agree with the results. • In a stronger class, go through each question and elicit why each option implies good or bad management skills. Follow up by asking for adjectives which describe a good manager. • In a weaker class, ask for adjectives which can describe good and bad managers. Students can refer to the key to help them. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students match photos with six of the words. Answers: 1 referee 2 supporter 3 TV reporter 4 captain 5 champion 6 loser Students complete the sentences with your own ideas. Answers: Students’ own answers Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students work in pairs. Answers: Students’ own answers. |
Descriptor: - match the words with the photos Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences with their own ideas. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - play the Team Manager game individually - describe good and bad managers Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 82 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Women in sport |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.3.3.1 give an opinion at sentence and discourse level on an increasing range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about a female racing driver. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Give your opinions about sport |
||
|
Value links |
Tradition: Kazakh traditions and culture have been passed on from one generation to another through oral histories told by traditional Kazakh tribal leaders and elders. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, write Formula 1 on the board. Elicit the meaning and ask students what they know about the sport. • Ask students if they know any Formula 1 drivers, then ask if they think that women also race Formula 1 cars |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:94 • Read the task with the class and ask students for their ideas. Ask students to justify their ideas with reasons. • You could ask whether the situation is the same in all sports, comparing football with athletics, for example.
Ex: 2 P:94 • Read through the interview questions with the class and clarify that the text is a transcript of the interviewee’s answers. • in a stronger class, ask students to say which part of the answers they used to make their choices. In a weaker class, help them identify the areas of the text which dictate which choices to make. Ex: 3 P:94 • Students read the text again more carefully and complete the sentences. Note that sometimes more than one word is needed Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students sportsmen are often more famous than sportswomen. Answers: Students’ own answers Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the interview and match interview questions with answers in the text. Answers: 1 B 2 A 3 G 4 D 5 F 6 E Students read the text again and complete the sentences with one, two or three words Answers: 1 watched 2 rally cars 3 massive / popular 4 competitors 5 money 6 sponsors |
Descriptor: - answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the interview - match interview questions with answers in the text. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences with one, two or three words Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 3
|
Unit of a long term plan: Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 83 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
be going to |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 7.6.8.1 use future form will to make offers, promises, and predictions on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn be going to for plans and intentions. • Write about plans and intentions using be going to. |
||
|
Value links |
Freedom: Freedom is the major value of the civil society being formed in Kazakhstan. This must provide everyone with the possibility of creative self-realization. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Refer students back to the reading text on page 70. Ask students to look in the first paragraph of the text and ask: What is Karen going to do next year? • Elicit the sentence: She’s going to try Formula 3. Write the sentence on the board and underline going to. Elicit that be going to refers to future plans. • Ask students to find more examples of be going to in the text. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:95 • Encourage students to check their answers in the text before completing the rule..
LANGUAGE NOTE We use be going to + infinitive: I’m going to play football. NOT I’m going to playing football. In the negative form, we use not + going to: He isn’t going to come. NOT He don’t going to come
Ex: 2 P:95 • Once students have completed the sentences ask them to compare answers in pairs Ex: 3 P:95 • Remind students they are writing about their own plans. In a stronger class, ask them to write true sentences using their own verbs Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students order the words to make sentences. Choose the correct words. Answers: 1 I’m going to have a go at Formula 3. 2 I’m not going to stop racing. 3 He’s going to contact more sponsors. 4 My sponsors aren’t going to give me much money Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students study the information and complete the sentences with your own ideas Answers: 1 are going to buy 2 is going to race 3 isn’t going to race 4 is going to contact 5 isn’t going to contact 6 aren’t going to look for Students write sentences about your plans using affirmative and negative form of to be going to. Answers: Students’ own answers |
Descriptor: - order the words to make sentences - choose the correct words Total: 1 point Descriptor: - study the information - complete the sentences Total: 1 point Descriptor: - write sentences about your plans - use affirmative and negative form of to be going to Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 84 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Will and be going to |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 7.6.8.1 use future form will to make offers, promises, and predictions on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the difference between will and be going to. • Write sentences using will and be going to. • Learn how to remember grammar with examples |
||
|
Value links |
Hospitality: Traditionally a nomadic culture, hospitality has always been an important part of Kazakh culture. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Refer students back to the reading text on page 70. Ask students to look in the first paragraph of the text and ask: What is Karen going to do next year? • Elicit the sentence: She’s going to try Formula 3. Write the sentence on the board and underline going to. Elicit that be going to refers to future plans. • Ask students to find more examples of be going to in the text. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 4 P:95 • Study the examples with the class and elicit the answer to the question in the instructions. LANGUAGE NOTE We use
be going to when we have already decided and planned something: I’m
going to watch the match tonight. NOT Ex: 5 P:95 • Remind students to read the sentences carefully and check they understand the context. In a weaker class, you could decide as a class which are plans and which are predictions before students complete the sentences. Ex: 6 P:95 • Point out to students that it is much easier to remember grammar through examples rather than rules. • Read through the instructions with the class, then ask students to write four example sentences. Tell them to use examples that they will find easy to remember, for example, by using a sport that interests them, or a famous person they admire. • Encourage students to test themselves on these examples regularly and to do this with other new grammar points Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students study the examples. Which sentence is a plan and which is a prediction? Answers: 1 plan 2 prediction Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students write the sentences with be going to or will Answers: 1 are going to meet 2 will be 3 are going to play 4 ’ll be 5 is going to leave Students read the study strategy. Then write examples of two plans and two predations. Answers: Students’ own answers |
Descriptor: - answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - write the sentences - identify to be going to or will Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the study strategy - write examples of two plans and two predations Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 85 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 05.04.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Compound nouns |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.1.1 begin to use basic abstract nouns and compound nouns and noun phrases describing times and location on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.2.4.1 understand with limited support the main points of extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 7.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn compound nouns related to sport. • Listen to three people talking about sport for the disabled. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. |
||
|
Value links |
Tradition: Kazakh traditions and culture have been passed on from one generation to another through oral histories told by traditional Kazakh tribal leaders and elders. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to name some people in sport. Write their names on the board and ask: What is this person? Elicit the compound nouns tennis / football player and write them on the board. • Focus on the compound nouns and tell students they are going to learn more compound nouns to do with sport. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:96 • Allow students time to read the sentences and choose the correct answers. Encourage them to guess if they aren’t sure. • Play the CD. Students listen and check their answers. In a stronger class, ask where the stress falls. In a weaker class, point out that in compound nouns, the stress falls on the first word, not the second word. Model and drill some of the pronunciations Ex: 2 P:96 • Read the instructions and the example sentence with the class. Then, in pairs, students form compound nouns and complete the sentences. Ex: 3 P:96 • Focus on the photos and elicit or explain the meaning of disabled. • Play the CD. Students listen and check their answer. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students choose the correct words. the correct answers Answers: 1 tennis tournament 2 rugby match 3 football team 4 swimming champion 5 athletics stadium 6 team manager Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students work in pairs. Complete the sentences with a word in the box from A and a word from box B Answers: 1 tennis player / champion 2 cycling competition 3 football stadium 4 skiing tournament 5 basketball team 6 running champion Students look at the photos and listen to three interviews about disabled people and sport. Answers: Oscar Pistorius |
Descriptor: - read the sentences - choose Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen to three interviews about disabled people and sport. Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 86 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Be going to and Present Continuous |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 7.6.8.1 use future form will to make offers, promises, and predictions on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the question form of be going to. • Write questions using be going to. • Learn the use of present continuous for future arrangements. • Practise asking about future arrangements using the present continuous. |
||
|
Value links |
Freedom: Freedom is the major value of the civil society being formed in Kazakhstan. This must provide everyone with the possibility of creative self-realization. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Revise statements with be going to with the class. Ask them to form affirmative or negative sentences with be going to. Try to elicit a variety of forms, using I / he / she / we / you / they, etc. • Ask: Does the word order usually change in questions in English? Do not confirm or reject any ideas at this stage. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:97 • Focus students on the questions and ask them to complete them with the words in the box. They should read them carefully to choose the correct question words LANGUAGE NOTE The forms am / is / are come before the subject in questions with be going to: Is he going to leave school? NOT He is going to leave school? Ex: 2 P:97 • Students order the words and write the questions individually
Ex: 3 P:97 • Go round and listen as students ask and answer. Encourage them to give answers that are true for them, or to make answers up to fit the topic if they prefer. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students complete the questions from the interviews with the words in the box. Answers: 1 What 2 Where 3 going to 4 Is, is 5 How Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students order the words to make questions Answers: 1 Are you going to play tennis later? 2 Are you and your friends going to join any teams next year? 3 Are you going to go to any tournaments this year? 4 Is your friend going to go cycling this weekend? 5 What sport are you going to play next week? Students work in pairs and answer the question Answers: Students’ own answers |
Descriptor: - read the sentences - complete the questions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - order the words to make questions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work in pairs - answer the question Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 87 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Be going to and Present Continuous |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 7.6.8.1 use future form will to make offers, promises, and predictions on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the question form of be going to. • Wr read and complete the dialogue.ite questions using be going to. • Learn the use of present continuous for future arrangements. • Practise asking about future arrangements using the present continuous. |
||
|
Value links |
Freedom: Freedom is the major value of the civil society being formed in Kazakhstan. This must provide everyone with the possibility of creative self-realization. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Revise statements with be going to with the class. Ask them to form affirmative or negative sentences with be going to. Try to elicit a variety of forms, using I / he / she / we / you / they, etc. • Ask: Does the word order usually change in questions in English? Do not confirm or reject any ideas at this stage. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 4 P:97 • Allow students time to read the sentences through the mini-dialogues, then match each one to the rule that describes its function. In a stronger class, ask if students can describe the difference in function without looking at the rules. LANGUAGE NOTE We use the present continuous for definite arrangements that are planned and agreed for the future: I’m going to London on Saturday. NOT I will go to London on Saturday. The taxi is coming to collect us at six o’clock. NOT The taxi will come to collect us at six o’clock Ex: 5 P:97 • Students analyse the meaning of the tense in each sentence. Remind them to look carefully at any time markers that might give them clues. • In a weaker class, provide more examples for students to identify Ex: 6 P:97 • If necessary refer back to the spelling rules on page 21. • Students read and complete the dialogue. Explain that they do not need to worry about the blue words at this stage Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students study mini dialogues and match them with rules. Answers: 1 a 2 b Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students study the sentences. Then write action in progress or future arrangement. Answers: 1 future arrangement 2 action in progress 3 future arrangement Students complete the mini dialogue. Answers: 1 ’re practising 2 ’re cycling 3 ’m visiting 4 Are, doing, ’m swimming 5 ’m watching |
Descriptor: -read the mini-dialogues, - match each one to the rule Total: 1 point Descriptor: - write action in progress or future arrangement. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read and complete the dialogue.Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 88 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Making plans and arrangements |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.6.1 use a variety of personal, demonstrative and quantitative pronouns including someone, somebody, everybody , no-one on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a conversation about plans and arrangements. • Learn key phrases for talking about plans and arrangements. • Learn about indefinite pronouns. • Practise talking about plans and arrangements |
||
|
Value links |
Respect: Respect of elders and of the spiritual freedom of other nations are principal values. It is important to develop a productive dialogue between confessions and to acknowledge religion as an element of civil society. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they ever meet their friends at the weekend. Ask where they go and what they do. • Ask when they make their plans for the weekend and how they make the arrangements. • Ask them to imagine that they want to meet some friends and go to a football match. Ask: What things do you need to talk about with your friends? • Elicit that they will talk about where they should meet and what time they should meet. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:98 • Ask students to listen for where and when Callum and Gemma are meeting. Ex: 2 P:98 • Read through the key phrases with the class. • Ask students to think about the dialogue and recall who says each one. Remind them to think about whether the speaker is making or responding to an invitation. • Play the CD and ask students to listen and check. Ex: 3 P:98 • Students complete the dialogue with the key phrases. When they have checked their answers, ask them to practise with a partner. • Ask them to perform the dialogue a couple of times, then swap roles and go through it again. Ex: 4 P:98 • Allow students time to read through the examples, then ask the question in the instructions. • Explain that indefinite pronouns are used to ask or talk about a person or place without saying specifically who or what it is Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students listen and read the dialogue. Where and when are Callum and Gemma meeting? Answers: They’re meting outside the sports centre at about 7.30. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students study the key phrases Answers: 1 Callum 2 Gemma 3 Gemma 4 Callum 5 Callum 6 Gemma Students complete the dialogue with the key phrases Answers: 1 b Are you doing anything this evening? 2 d No, nothing special. 3 a What are you up to? 4 c if you’re interested. . 5 f It’s on at 6 e Shall I meet you outside … ? Students study the examples. When do they use some and any? Answers: We use any- in negative sentences or questions, and some- in affirmative statements. |
Descriptor: -listen and read the dialogues, - answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - recall who says each one. Total: 1 point . Descriptor: - complete the dialogue with the key phrases Total: 1 point Descriptor: -read the examples Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 89 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A formal letter |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with some support on a growing range of general and curricular topics 6.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 6.3.2.1 ask simple questions to get information about a limited range of general topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model formal letter. • Learn about layout and language in a formal letter. • Learn key phrases for writing a formal letter. • Write a formal letter |
||
|
Value links |
Respect - treating people with respect, value and courtesy. Especially apologising to them where the situation calls for it. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they ever write letters. Ask who they write letters to, and why. • Ask if they ever write formal letters. Ask who they might write a formal letter to and why
|
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:99 • Ask students to read the model letter quickly and then ask: What does the person who wrote this letter want? (They want money for a sports tournament.) • Students read the letter again and answer the questions. Ex: 2 P:99 • Read through the questions with the class. Explain that these questions cover the structure of the letter and the language used in detail. • Students look at the model text again and find the information. Ask students if the layout of a formal letter is the same in their language. Ex: 3 P:99 • Read through the key phrases with the class. Ask students to find the key phrases in the model letter and translate them into their own language before ordering them. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students read the model text and answer the question Answers: 1 Mary Grant 2 No. 3 Paragraph C 4 Paragraph B 5 Paragraph A Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students study the text again and answer the question Answers: 1 At the top of the letter. 2 Under the address of the person who is going to receive the letter. 3 At the top left of the letter. 4 Full forms: I am; we are. 5 Formal: Dear Sir or Madam; I am writing to you because; Please contact me; I look forward to hearing from you; Yours faithfully Students study the key phrases. Then order them. Answers: 1 Dear Sir or Madam 2 I am writing to you because … 3 Please contact me … 4 I look forward to hearing from you.. 5 Yours faithfull |
Descriptor: - read the model letter for gist - answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the model text again and find the information Total: 1 point Descriptor: - find the key phrases in the model letter Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 90 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Healthy habits |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.1.1 begin to use basic abstract nouns and compound nouns and noun phrases describing times and location on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.6.8.1 use future form will to make offers, promises, and predictions on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn abstract nouns related to health and lifestyle. • Talk about healthy habits. • Learn how to use will for offers and promises. • Learn and practise using tag questions. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to name the oldest person they know. • Elicit some names, then ask for more details, e.g. how old is the person, where do they live, how they spend their time, do they have any unusual habits. • Ask students what they think the secret to a long and healthy life is. Elicit some ideas, but do not confirm or reject any at this stage. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:100 • Explain the task. In pairs, students discuss the different options and decide which ones are healthier. • Get some feedback from a few students and encourage them to give reasons for their answers Ex: 2 P:100 • Read the instructions and draw students’ attention to the word in the box. Ask students what part of speech they are and elicit that they are all nouns. Then ask: Do they refer to material objects or abstract ideas? Elicit answers and explain that nouns like these are called abstract nouns. In a stronger class, you could point out that most (but not all) abstract nouns are uncountable. • Students work in pairs to complete the text. Play the recording for them to listen and check their answers. Ex: 3 P:100 • Ask students to read the dialogue again and decide if the sentences are true or false. Encourage them to underline the parts of the dialogue where they find their answers. • Check answers as a class. Then draw students’ attention to the note about will and won’t. Ask them to find five examples in the dialogue (I’ll ask my grandparents …, I’ll help you …, I’ll call my grandmother …, I’ll be there …, I’ll make sandwiches …) Ex: 4 P:100 • Read through the instructions together. Draw students’ attention to the words in blue in the dialogue and point out that these are tag questions. Explain that they aren’t real questions – they are usually used to check that the listener agrees with what the speaker has said. Highlight that tag questions are very commonly used in spoken English, but not in formal written English Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students work in pairs. Look at the list and choose the options which you think are healthier Answers: Students’ own answers Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students check the meaning of these nouns in a dictionary. Complete the dialogue with five of the nouns. Answers: 1 habits 2 lifestyle 3 humour 4 education 5 idea. Students read the dialogue again. Are the sentences true or false? Answers: 1 False 2 True 3 True 4 False 5 False Students Highlight that tag questions are very commonly used in spoken English Answers: 1 the same as 2 positive, negative |
Descriptor: - discuss the different options and decide which ones are healthier Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the dialogue with five of the nouns Total: 1 point Descriptor: - decide if the sentences are true or false Total: 1 point Descriptor: -can attention to the words in blue Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 91 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Talking about scores |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn key phrases for talking about scores. • Listen to a conversation about scores. • Practise talking about scores. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills. Lead – In • With books closed, ask students: Do you like watching sport on TV? • Ask what sports they like watching. • Ask what was the last football match they watched on TV. Ask who was playing and what the score was. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:101 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words then complete the sentences. • Check answers and model pronunciation of the words. Ex: 2 P:101 • Refer students to the picture. Tell students they are going to listen to a conversation between people who are watching a match. • After students have listened to the dialogue, ask which match Paula and Andy are watching. • Elicit the answer, then write Liverpool vs Roma on the board. Point out that we use vs (versus) to mean ‘against’ when we are talking about football matches. Ex: 3 P:101 • Read through the key phrases with the class, pointing out that we say three all (not three-three) and one nil (not one zero). • Explain the meaning of draw if necessary. • Allow time for students to read the sentences. • Students listen again and correct the false sentences. Ex: 4 P:101 • Students read and listen to the dialogue. Tell them not to worry about the blue words at this stage. • Students practise the dialogue with a partner. Remind them to swap roles and practise it again. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box. Then complete the sentences with the words. Answers: 1 fan 2 score 3 goal 4 match Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to the conversation. Which match are Paula and Andy watching? Answers: They are watching Liverpool vs Roma. Students study the key phrases. Then listen to a conversation again and write true or false. and write true or false Answers: 1 False. The match started twenty minutes ago. 2 True. 3 True. 4 False. The score is one all, so it is a draw at the moment 5 False. Paula thinks that Liverpool will win this match and the Champions League. Students listen to the dialogue. Then practise the dialogue with a partner. Answers: Students’ own answers |
Descriptor: - complete the sentences with the words Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen to a conversation between people who are watching a match Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen to a conversation again Total: 1 point Descriptor: - practise the dialogue with a partner Total: 1 point . |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 92 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL: Maths: Average speed |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for talking about average speed. • Read statistics about average speed. • Practise calculating average speed in English. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students some questions about journey distances and times. For example, name two large cities in the area and ask: How far is it from X to Y? How long does it take by train? How far is it from here to the next town? How long does it take to drive? • Write some of their answers on the board, then focus on some of the figures of distance and time and ask: What is the average speed for this journey? • Elicit some answers, but do not confirm or reject any at this stage |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:102 • Focus on the picture and tell students that this kind of racing is called Speedway. • Read the instructions with the class and make sure that students understand the word lap. • Students study the information and answer the questions.
Ex: 2 P:102 • Allow students time to check the meaning of the words in their dictionaries. • Read the information with the class. • Point out the spoken form of distance / time (distance over time), m/s (metres per second), x 3.6 (times three point six) and km/h (kilometres per hour). • Students work in pairs to answer the questions.
Ex: 3 P:102 • Students work in pairs to read the sentences and find the average speed for each sports person. • Check answers by asking students to read out their answers, making sure that they read them correctly. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students study the information and answer the question. Answers: 1 Olsen y 2 Gollob 3 Adams 4 Crump Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students check the meaning of the words in the box. Then read the information and answer the question. Answers: 1 Gollob: 1,200 73 = 16.44 Olsen: 1,200 64 = 18.75 Crump: 1,200 78 = 15.38 2 Adams: 19.05 x 3.6 = 68.58 Gollob: 16.44 x 3.6 = 59.18 Olsen: 18.75 x 3.6 = 67.5 Crump: 15.38 x 3.6 =55.37 Students read the sentences and find the average speed in km/h for each sports person. Answers: 1 Paula Radcliffe: 42.19 (km) 2.26 (hours) = 18.67 km/h 2 Lance Armstrong: 3,870 (km) = 46.86km/h 82.59 (hours) 3 Usain Bolt: 100 (m) = 10.44 m/s 9.58 (s) 10.44 x 3.6 = 37.58 km/h 4 Michael Phelps: 200 (m) = 1.94 m/s 103 (s) 1.94 x 3.6 = 6.98 km/h |
Descriptor: - study the information and answer the questions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work in pairs to answer the questions. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - find the average speed for each sports person Total: 1 point 1.94 x 3.6 = 6.98 km/h |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 93 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review 7 Summative assessment for the unit “Healthy Habits” |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.8.1 use future form will to make offers, promises, and predictions on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.2.6.1 Deduce meaning from context with little support in extended talk on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.5.5.1 Develop with some support coherent arguments supported when necessary by examples and reasons for a limited range of written genres in familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -Figure out the content of a conversation with some support in extended talk -Use punctuation marks in a piece of writing |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students some questions about journey distances and times. For example, name two large cities in the area and ask: How far is it from X to Y? How long does it take by train? How far is it from here to the next town? How long does it take to drive? |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 2 P:104 • Allow students time to read the sentences and choose the correct answers. Encourage them to guess if they aren’t sure. Ex: 4 P:104 • Focus students on the questions and ask them to complete them with the words in the box. They should read them carefully to choose the correct question words Summative assessment for the unit “Healthy Habits” Listening Task 1. Listen to the conversation and fill in the gaps. Use NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS. CD2. Tapescript4
Writing Part 1. Look at some healthy habits pictures and brainstorm your ideas.
Part 2. Write down about 4 healthy habits you know: Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students choose the correct words Answers: 1 matches 2 atmosphere 3 stadium 4 supporters 5 referee’s Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students write sentences using to be going to or will Answers: 1 I think my favourite team will win the league next year. 2 Who is going to win the match tomorrow? 3 I’m going to the cinema with Nick later. 4 They aren’t going to play tennis tomorrow. They’re going to play football. 5 The PE teacher is going to train us tonight. |
Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point Descriptor: - write sentences using to be going to or will Total: 1 point - |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 7 Healthy habits |
Lesson 94 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project proposal |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.2.1 use speaking and listening skills to provide sensitive feedback to peers |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a proposal about sport in a neighbourhood. • Write a proposal for improving sports facilities in your town |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students what sporting facilities are like in their town. Ask if they think these could be improved. • Ask students how important they think it is to have good sports facilities in a town and how much money people should spend on them. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:105 • Students read the proposal. Ask them to discuss their opinions of Yernur’s solutions in pairs. They can use the opinion icons to help them. Ex: 2 P:105 • Read through the project checklist with the class. • Students prepare their proposals individually. They can work in class, or complete the proposal for homework. • Alternatively, use the project as an opportunity to promote groupwork. In a weaker class, once students have decided upon their three sports facilities, help them structure their thoughts. Encourage them to think of for and against arguments for each proposal. When writing, remind students to use the present simple to talk about the current situation and will for predictions and outcomes of their plans. Ex: 3 P:105 • Put students into pairs, and ask them to exchange proposals and give their opinions on their partner’s proposal. If students have worked in groups, allow them to evaluate another group’s work. • When students have finished, ask them to change partners (or groups) and repeat the process four or five times. • Ask students which proposals they thought were the best. • See page 33 in this guide for ideas about how students can assess their work Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students read the proposal. What is your opinion of Yernur’s sollutions Answers: Students’ own answers Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students make a proposal for sports facilities in your neighbourhood or town. Answers: Students’ own answers Students exchange your proposal with the rest of the class. |
Descriptor: - read the proposal Total: 1 point Descriptor: - make a proposal for sports Total: 1 point Answers: Students’ own answers |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 95 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Adjectives: feeling and events |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 7.6.14.1 use an increased variety of prepositions of time, location and directionuse by and with to denote agent and instrument; use prepositions before nouns and adjectives in common prepositional phrases on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary for feelings and events. • Do a quiz about memory. • Talk about feelings |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they can remember their first day at school. • Ask students what they did and what things happened. Ask what it was like and how they felt. They can discuss this in L1 at first, but elicit as many words in English as possible. Write these on the board. • Find out how many students enjoyed their first day at school and how many did not enjoy it. Ask those who enjoyed it to think of positive adjectives, and those who did not to think of negative adjectives. Write these on the board as separate categories. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:36 • Read the task with the class. You may need to translate or pre-teach the word, memory. • In a weaker class, encourage students to make notes about each question before you discuss their ideas. In a stronger class, encourage them to go into more detail in their answers by explaining why they felt the way they did on this occasion. • Discuss ideas as a class. Students can use their own language for any ideas that they find difficult to express in English. However, encourage them to give simple answers to the questions if they can Ex: 2 P:36 • Allow students time to look at the photos and match them to the phrases. • If they do not know the adjectives, encourage them to make guesses based on the nouns they recognize. • Once students have matched the photos and the adjectives, check answers by calling out a number and asking for the correct phrase Ex: 3 P:36 • Students read through the sentences and choose the correct words to complete them. Encourage students to think about the context given by the sentences before choosing their answers. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students think about their first memory and answer the questions. Answers: Students’ own answers . Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students match photos with the phrases in the box. Answers: 1 a cute baby 2 a naughty boy 3 a nervous teenager 4 an upset baby 5 a lucky girl 6 a scary film 7 a lonely dog Students choose the correct words. Answers: 1 nervous 4 cute 2 lucky 5 upset, naughty 3 scary 6 lonely |
. Descriptor: - translate or pre-teach the word, memory Total: 1 point Descriptor: - match photos with the phrases Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read through the sentences and choose the correct words Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 96 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Remember this! |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.1.1 understand the main points in a growing range of short, simple texts on general and curricular topics 7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.3.5.1 keep interaction going in longer exchanges on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about people with very good memories. • Read for general meaning and specific information.. • Talk about memory |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to work individually and write down as many objects in the photos as they can remember from the quiz on page 29. • Set a strict time limit of one minute and then see who has remembered the most. • Write the word memory on the board and elicit or explain the meaning. Tell students they are going to read about some people with very good memories. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Background Stephen Wiltshire is unusual in that he could not speak as a young child and was diagnosed with autism. He was sent to a special school and learned to talk at the age of nine. He started drawing when he was still a child and was encouraged by his teachers. He has since been to art college and graduated with a degree. He has published several books of his drawings. Ex: 1 P:38 • Do the task as a fun way to test students’ memory. • Find out how many students could remember half of the numbers. Could anyone remember all of them? Ex: 2 P:38 • Read the title of the text with the class and ask students what they think the text will be about. • Then read the task and clarify that students should listen for four different names. Point out that students do not need to understand everything in the text at this stage. • Once students have read and listened to the text, elicit answers to the questions Ex: 3 P:38 • Tell students to read through all the sentences before reading the text again more carefully to decide whether the sentences are true or false. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students study the numbers for fifteen seconds. Then close your books. How many can you remember? Answers: Students’ own answers Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read and listen to the text. Which four people does the text mention Answers: Stephen Wiltshire, Mahavir Jain, Akira Haraguchi, Dominic O’Brien They all have good memories. Students read the text again. Write true or false. Answers: 1 False. Stephen doesn’t know the city. He drew a picture of it from memory. 2 False. Stephen was in a helicopter. 3 True. 4 False. He recited 100,000 digits of pi in 16 hours. 5 False. He was World Memory Champion |
Descriptor: - study the numbers Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the title of the text Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the text - write true or false. Total: 1 point eight times. |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 97 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Was, were |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 7.6.9.1 use appropriately an increased variety of present and past simple active and some passive forms on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn was and were to talk about the past. • Talk about the past using was and were. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Ask students to think about how they were feeling yesterday, last week, and last month. Ask for ideas about specific events that happened and ask students to say whether they felt happy, sad, excited, etc. • Encourage students to use the adjectives from page 28 if they can, for example, nervous, lonely or lucky. • Explain to the class that they are going to learn how to describe events in the past. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:39 • Explain that students are using sentences in context to deduce the rules. • Once students have completed the rules, check answers by asking students to read them out. • In a weaker class, ensure students understand that was is for the first and third person, and were is for the rest. In a stronger class, ask students to find more sentences using was, wasn’t, were or weren’t in the text. LANGUAGE NOTE We use
was for I, he, she, it and were for you, they: I was happy. They
were happy. NOT Ex: 2 P:39 • Students complete the sentences. If they are not sure about the information, encourage them to make a guess, although they should be careful to use the correct form of was, were. Ex: 3 P:39 • Students ask and answer in pairs. Refer them back to the rules section if they need help forming the short answers. • Ask some students to read some of their questions to the class and report back on their partner.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students look at the text and complete the sentences with the words in the box. h the words in the box Answers: 1 were 2 wasn’t 3 Was 4 was Rules 1 were 2 wasn’t 3 was 4 was Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students complete the sentences using the correct form of was and were. Answers: 1 wasn’t 2 was 3 weren’t 4 were 5 wasn’t / was Students work in pairs. Ask and answer questions about the sentences using was and were Answers: 1 Was the football world cup in 2008? No, it wasn’t. 2 Was Michael Jackson an American singer? Yes, he was. 3 Were DVDs popular in 1980? No, they weren’t. 4 Were Robert Pattinson and Kristen Stewart in the Twilight films? Yes, they were. \ 5 Was I at school in 2001? Yes, I was. / No, I wasn’t. |
Descriptor: - completed the rules -complete the sentences wit Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences -use correct form of was and were Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work in pairs - answer the questions Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 98 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Milestones |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.6.3.1 use common participles as adjectives and order adjectives correctly in front of nouns on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 7.2.4.1 understand with limited support the main points of extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 7.2.5.1 understand most specific information and detail of supported, extended talk on a range general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn adjectives used to talk about life events. • Listen to details about events in the lives of famous people. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to name a few famous people and write their names on the board. • Ask students what information they know about the people. • Elicit some ideas, for example he / she is married, he / she has two children, etc. Write vocabulary to do with life events on the board. • Ask students what other important things can happen to your in your life, and write useful vocabulary on the board. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:40 • Students choose the correct words to complete the phrases. In a weaker class, encourage them to guess if they are not sure, or to compare ideas with a partner. • Play the CD for students to check their answers. Ex: 2 P:40 • Students work in pairs to identify the people in the photos. Encourage them to use sentences to express their ideas, as in the example. • Once students have listened and checked their answers, find out how many they guessed correctly. Ex: 3 P:40 • Tell students to read through the sentences carefully. In a stronger class, if they can remember any information from the first time they listened, they can complete it now. Ensure students understand that they may need more than one word. • Play the CD again and ask students to complete the sentences
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities |
Students choose the correct verbs. Answers: 1 become 2 have 3 be 4 get 5 go 6 learn 7 leave 8 do 9 buy 10 graduate 11 win 12 leave 13 move 14 start 15 get Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students work in pairs. Match the names to the pictures Answers: A Tom B Beyoncé Cruise C Brad D Serena Williams E Keira Knightley F Angelina Jolie Pitt G Bill Gates H Kate Moss Students listen and complete the sentences with one or two words. Answers: 1 became a model 2 become 3 a big house 4 graduate 5 a job 6 drive 7 married 8 didn’t go |
Descriptor: - choose the correct words to complete the phrases Total: 1 point 16 become Descriptor: - read the sentences carefully - match the names to the pictures Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work in pairs - complete the sentences Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 99 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Past Simple |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 7.8.9.1 use appropriately an increased variety of present and past simple active and some passive forms on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the affirmative, negative and question forms of the past simple. • Use the past simple to talk about past events. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Refer students back to the reading text on page 30 and ask them to find examples of affirmative and negative forms of the past simple. • Elicit verb forms and write them on the board. Ask students what difference they notice between the affirmative and negative forms. Elicit ideas, but do not give an explanation at this stage. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:41 • Once students have copied and completed the table, check answers with the class LANGUAGE NOTE The
past simple affirmative forms are the same for all persons: I left,
she left, we left, etc. In the past simple negative form, we use
didn’t and the infinitive form of the verb, not the past simple
form: She didn’t leave school. NOT Ex: 2 P:41 • Students complete the sentences individually. In a weaker class, discuss questions a–c as a whole class activity. • In a stronger class, once students have finished, ask them to think of a new sentence for each of the past simple forms in the box. Check they have formed these correctly. Ex: 3 P:41 • Remind students to read all the options carefully before they match them. • In a weaker class, revise why questions 1 and 2 need information answers, and why question 3 requires a short answer Ex: 4 P:41 • Allow students time to study exercises 2 and 3 before they complete the rules. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abili1ies |
Students look at the verbs in the box and complete the table. Answers: Regular: learn – learned Irregular: buy – bought, get – got, go – went, become – became Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students complete the sentences with the words in the box. Answers: 1 played 2 didn’t go , 3 taught a 1 b 3 c 2 Students match questions with answers Answers: 1 c 2 a 3 b Students study the examples then choose the correct words in the rules. Answers: 1 same 2 base form 3 base form |
Descriptor: - complete the table Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences individually Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work in pairs - complete the sentences Total: 1 point Descriptor: - choose the correct words in the rules. Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 100 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: 23.05.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL: Folk stories. Summative assessment for the unit “Clothes and Fashion” |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.5.7.1 use with some support appropriate layout at text level for a growing range of written genres on familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a folk story. • Learn about first person and third person narrators. • Practise writing a story as a first person narrator. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students what kind of stories they enjoy reading. • Elicit some answers, then write folk story on the board. Ask students if they have read any folk stories. Elicit the names of some folk stories that students know. • Tell students they are going to read a folk story in English. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:46 • Students work in pairs to put the pictures in the correct order. • Play the CD. Students read and listen to the story, and check their answers Ex: 2 P:46 • Students read the story again and answer the questions. Summative assessment for the unit “Clothes and Fashion” Reading Task 1. Read the definitions below. Find the proper word in the text and insert it into the table. Look up the words in the dictionary and check the answers. Speaking Task 2. Choose the question and be ready to answer it after the teacher starts the conversation. You should add your ideas to the class discussion. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abili1ies |
Students look at the pictures and put them in the correct order Answers: 1 D 2 C 3 B 4 A Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the story again and answer the question Answers: 1 There weren’t any other elephants around. The elephant was lonely. 2 The bird looked for the other elephants and took the young elephant to them. 3 Because the bird had helped it twenty years ago, and the elephant remembered. 4 a Students Read the definitions below Answers: 1 uniform 2 girlish 3 casual 4 emblem 5 comfortabl |
- Descriptor: - work in pairs - put the pictures in the correct order. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the story again - answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - Find the proper word in the text Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 101 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative Control work for the term 4 |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.2.5.1 Recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) in supported extended talk on a range of general and curricular topics 7.4.2.1 Understand specific information and detail in texts on a range of familiar general and curricular topics. 7.5.6.1 Link with little or no support, sentences into coherent paragraphs using a variety of basic connectors on a range of familiar general topics and some curricular 7.3.7.1 Use appropriate subjectspecific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a growing range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - understand specific details through the keywords, style, intonation and repetition -pronounce words and phrases correctly -formulate a simple character outline |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Listening Task. Listen and choose between A, B, C or D. CD3. Tapescript 4. Use the link to listen information 1) Continue listening to tape and fill in the gaps with NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS: 2) Choose the correct answer. Reading Task. Read the text and fill in the table below with necessary information. Answer the questions. Writing Task. Topic1. Fill in all the spaces provided. You can write more than one idea. Topic 2. When we talk about fashion we usually mean the popular style in dress or behavior. For most modern people fashion is a method of wearing to express themselves. What do you think about it? Write 80-90 words SPEAKING Task. Choose the card. Work individually. Look at the picture and make up a story for 1-2 minutes. Use the questions from the card. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abili1ies |
Students Listen and choose between A, B, C or D. Answers: 1 B 2 D 3 expensive 4 brands 5 B 6 D Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the text and fill in the table below with necessary information. Answers: Student’s own answer Students choose one topic and write more than one idea. Anwers: Student’s own answer Students Choose the card Anwers: Student’s own answer |
Descriptor: - work individually - Use the link to listen information Total: 6 point Descriptor: - read the text - fill in the table Total: 6 point Descriptor: - choose one topic -write the topic Total: 6 point Descriptor: - choose the card -answer the question Total: 6 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 3 Clothes and Fashion |
Lesson 102 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 7 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review |
||
|
Learning objectives |
7.4.2.1 understand independently specific information and detail in short, simple texts on a limited range of general and curricular topics 7.5.7.1 use with some support appropriate layout at text level for a growing range of written genres on familiar general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Use vocabulary for feelings and events. • Use adjectives used to talk about life events |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they can remember their first day at school. • Ask students what they did and what things happened. Ask what it was like and how they felt. They can discuss this in L1 at first, but elicit as many words in English as possible. Write these on the board. • Find out how many students enjoyed their first day at school and how many did not enjoy it. Ask those who enjoyed it to think of positive adjectives, and those who did not to think of negative adjectives. Write these on the board as separate categories |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures
Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:48 • Students choose the correct words to complete the phrases. In a weaker class, encourage them to guess if they are not sure, or to compare ideas with a partner. Ex: 2 P:48 • Students complete the phrases with the verbs. In a weaker class, ask them to do this in pairs. In a stronger class, ask students there is one verb you don’t need. Ex: 3 P:48 Explain the students complete the dialogue with the affirmative or negative form of was and were Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abili1ies |
Students choose the correct words Answers: 1 nervous 2 scary 3 lucky 4 naughty 5 upset 6 cute Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students complete the phrases with the verbs in the box. There is one verb you don’t need. Answers: 1 become 2 go 3 have 4 buy 5 do 6 graduate Students complete the dialogue with the affirmative or negative form of was and were Anwers: 1 was 2 was 3 wasn’t 4 were 5 wasn’t 6 were 7 weren’t 8 was |
Descriptor: - work individually - choose the correct words Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the phrases with the verbs Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the dialogue Total: 6 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|

шағым қалдыра аласыз