Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 80 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Action and protest |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary to do with action and protest. • Do a questionnaire on attitudes to taking action. • Learn the use of will and might. • Practise using will, won’t, might and might not to make predictions. |
||
|
Value links |
Hospitality: Traditionally a nomadic culture, hospitality has always been an important part of Kazakh culture. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they watch the news or read newspapers. Ask them what issues in the world they care about. Elicit some examples, such as climate change, animal experiments, etc. • Ask students what they can do to change situations. Elicit some ideas. Encourage students to join in and express their opinions; there are no right or wrong answers. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:92 • If necessary, allow students to use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the new words. • When checking answers, model and drill pronunciation of the words, paying attention to the change of stress between some nouns and verbs such as organize / organization. • Ask students to do the questionnaire individually, then compare their answers with a partner and discuss which is the best plan of action in each case. • Ask some students to report back to the class on their discussions. Encourage other students to agree or disagree with them. Ex: 2 P:92 • In a weaker class, help students understand the meaning of each sentence by reading through them all with the class and answering the question in the instructions before students listen. • In a stronger class, allow students time to read through the options before listening. Follow up by answering the question in the instructions. Ex: 3 P:92 • After students have completed the key phrases, read through them with the class. • After saying each phrase, elicit whether it is used to make a suggestion, or comment on a suggestion. Make suggestions: Let’s (organize a meeting). How about (starting an email campaign)? I think we should try … Why don’t we (boycott the shops)? I think the best thing to do is … We could write to the council Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the table with the words in blue in the Plan of action questionnaire. Answers: 1 meeting 2 organize 3 march 4 donate 5 collection 6 protest 7 volunteer 8 supporter 9 sponsor 10 petition 11 ban 12 boycott 13 campaign Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to two people discussing questionnaire. Match opinions with dialogues Answers: 1 e 2 a 3 c 4 d 5 b Sentences which express certainty: b, d and e Students complete the key phrases with the words in the box. Descriptor: - complete the key phrases Answers: 1 idea 2 help 3 about 4 think 5 don’t 6 work 7 thing 8 could |
Descriptor: - model and drill pronunciation of the words - complete the table with the words in blue Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen to two people discussing questionnaire - Match opinions with dialogues Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the key phrases Total: 1 point . |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 81 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The food waste scandal |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a text about freegans and food waste. • Read for general meaning and specific details. • Learn about negative prefixes un-, in- and im-. • Express opinions about a campaign against food waste. |
||
|
Value links |
Tradition: Kazakh traditions and culture have been passed on from one generation to another through oral histories told by traditional Kazakh tribal leaders and elders. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, write the word food waste on the board. Ask students what they understand by the expression. • Elicit ideas about food waste issues, for example, food mountains, sell-by dates on food. Ask students to express their opinions on these issues, using L1 if necessary. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:94 • Refer students to the title and photos and discuss what the photos show. • Ask students to discuss the questions in pairs. You can discuss ideas with the class before playing the CD. • Students read and listen, and check whether their guesses were correct Ex: 2 P:94 • Encourage students to prepare by reading through the questions before they read the text again. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes before you check with the class Ex: 3 P:94 • Read through the words with the class and explain that the opposite of each word is in the text. Students should read the text again quickly to find the correct words. • Check answers with the class, and check that students understand the meaning of the adjectives. In a weaker class, ask for translations, then encourage students to put the new adjectives into sentences for context. In a stronger class, ask students to put the words into new sentences to show understanding. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the title of the text and photos and answer the questions. Then read and listen to the text. Answers: 1 The photos show: a person with a bag of food that has been thrown away, to show the quantity of food that is wasted. people who work on a food-sharing campaign. volunteers organizing food boxes so food can be redistributed. 2 Supermarkets throw food away if it is imperfect, for example, not all the same size, or if it doesn’t look nice. 3 Freegans are people who believe it is wrong to throw food away and who get most of their food from supermarket waste. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the text again and choose the correct answers. Answers: 1 c 2 a 3 c 4 c 5 c 6 a Students build their vocabulary Answers: 1 imperfect 2 unacceptable 3 insensitive 4 unnecessary |
Descriptor: - discuss the questions in pairs. - read and answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the text again - choose the correct answers Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
|
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 82 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: First conditional review |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.6.17.1 use if / unless/ if only in second conditional clauses and wish [that] clauses [present reference]; use a growing variety of relative clauses including why clauses on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the form and use of the first conditional. • Practise using the first conditional. |
||
|
Value links |
Freedom: Freedom is the major value of the civil society being formed in Kazakhstan. This must provide everyone with the possibility of creative self-realization. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Refer students back to the text, and ask: Does the writer want supermarkets to change? (Yes.) Ask students to look at the last paragraph of the text and find a sentence which says what people can do to make supermarkets change. (If we all boycott the supermarkets, they’ll listen to us.) • Ask students to translate this sentence into their L1. Elicit that the sentence is referring to a future possibility |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:95 • Students complete the tables in pairs. • After checking answers, draw attention to the question in the instructions and ensure students understand that the comma is used when the if-clause is written first Ex: 2 P:95 • In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs. Then, after checking answers, return to the table in exercise 1. Highlight which parts of the conditional sentences describe the action (using the present simple) and which parts describe the result (using will / won’t). • In a stronger class, ask students to find another example of the first conditional in the text (You’ll find more information and an online petition if you look on our website.). Ask students to identify the action and result clause, and the tenses used. Repeat this with the sentences in the table in exercise . Ex: 3 P:95 • Do the first sentence as an example if necessary. • Remind students to read the sentences carefully to check they understand the context before completing each one Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the first conditional sentences from the text. Answers: 1 boycott 2 ’ll listen 3 won’t change 4 protest Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students study the sentences and complete the rules. Use will, won’t and the present simple. Answers: 2 the present simple 3 will, won’t Students complete the sentences with the first conditional form of the verbs in brackets Answers: 1 supports, will win 2 ask, will volunteer 3 will boycott, sells won’t know, don’t organize 5 ban, won’t be 6 won’t sponsor, don’t finish |
Descriptor: - complete the tables in pairs. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - identify the action and result clause - Use will, won’t and the present simple. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the sentences carefully Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 83 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 04.04.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Phrasal verbs: a campaign |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn phrasal verbs relating to campaigning. • Learn how to make your own examples. • Listen to an interview with a campaigner who wants to save the rainforests. |
||
|
Value links |
Hospitality: Traditionally a nomadic culture, hospitality has always been an important part of Kazakh culture. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, write the word rainforest on the board. Ask students where you can find rainforests in the world. • Ask students what they know about rainforests and elicit some ideas. • Elicit that people are destroying rainforests and ask students if they feel strongly about this issue. Encourage students to participate and express their opinions |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:96 • Students read and listen to the text, then use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the phrasal verbs before matching them to the synonyms. It may help to point out that in most dictionaries phrasal verbs are listed under the main verb form, at the end of that entry. Ex: 2 P:96 • Students complete the sentences individually. • Ask individual students to read out some of their sentences and check that they have understood the meaning of the phrasal verbs correctly. • Put students into pairs to compare their sentences and choose the best ones to memorize. • Tell students they have two minutes to memorize their sentences. • After two minutes, with books closed, ask students to say one of their sentences from memory. • Encourage students to update their notebooks with example sentences regularly. Suggest that they try to learn new vocabulary and grammar, using examples, on a weekly basis. Ex: 3 P:96 • Ask individual students which two sentences they think are not in the interview. • Students then listen and check their answers. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students read and listen to the text and check the meaning of the verbs in blue. Answers: 1 end up 2 set up 3 carry on 4 look after 5 find out 6 wipe out 7 join in 8 sign up fo Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students complete the sentences with your own examples. Answers: Students’ own answers Students answer the question Answers: Questions 3 and 7 are not in the interview. |
Descriptor: - read and listen to the text - match them to the synonyms Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences individually. - complete the sentences with your own examples Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen and check their answers. Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 84 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: Be going to and will |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 8.6.8.1 use a growing variety of future forms including present continuous and present simple with future meaning on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn be going to and will for plans and intentions. • Learn the difference between be going to and will. • Practise using be going to to talk about plans and intentions, and will to talk about predictions and instant decisions. • Practise using be going to and will to talk about the future |
||
|
Value links |
Tradition: Kazakh traditions and culture have been passed on from one generation to another through oral histories told by traditional Kazakh tribal leaders and elders. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Refer students back to the text on page 62. Elicit that it all refers to the future. • Ask students to find sentences in which Molly talks about her plans, for example, I’m going to set up a campaign, I’m going to swim … . Elicit that the sentences use be going to. • Refer students back to the questions in exercise 3 on page 62. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:97 • Read the rules with the class, then ask them to complete the sentences LANGUAGE
NOTE Students often
omit the appropriate form of be in sentences with be going
to Ex: 2 P:97 • Encourage students to identify the plans and predictions before completing the text. • In a weaker class, you could ask them to go through the text first and decide which parts are plans and which parts are predictions. Discuss their answers as a class before they write the sentences. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes before you check with the class. Ex: 3 P:97 • Read the situation with the class. • Students write the questions and answers individually. • Ask individual students to read out some of the questions to the class, and correct any mistakes in the question formation before they invent answers. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the sentences from the text and match with rules. Answers: a will b won’t c ’m going to d Is, going to e ’ll f will Rules 1 c, d 2 a, b, e, f Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students complete the text with be going to or will / won’t Answers: 1 are going to run 2 will sponsor 3 ’ll make 4 will be 5 ’re going to start 6 ’s going to run 7 ’ll train Students read the situation. Then complete the questions and invent answer with be going to or will. Answers: 1 is, going to 2 are 3 will 4 are, going to, going to 5 ’ll 6 will Students’ own answers |
Descriptor: - complete the sentences from the text - match them with rules Total: 1 point Descriptor: - identify the plans and predictions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the situation Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 85 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Plans and arrangements |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 8.2.5.1 recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) with little or no support in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a dialogue in which someone talks about their plan to do a sponsored event. • Learn key phrases for talking about donating money. • Learn the use of the present continuous for future arrangements. • Practise talking about your plans and arrangements. |
||
|
Value links |
Freedom: Freedom is the major value of the civil society being formed in Kazakhstan. This must provide everyone with the possibility of creative self-realization. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students what their plans are for the weekend. Elicit a few ideas, making sure that students use be going to rather than will. • Write the words plan and arrangement on the board and elicit or explain the difference (a plan is something you intend to do; an arrangement is something that is already agreed, planned and arranged) |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:98 • Refer students to the photo and ask them what they think is happening. Elicit some answers from the class, but do not confirm or reject any at this stage. Ex: 2 P:98 • Read the question with the class and elicit or explain that at this stage, students should listen for the general meaning of the dialogue, and try to pick out the amount of money which Adam thinks he’ll raise. • When students have listened to the CD, ask for their ideas. • Confirm or reject students’ predictions about what Adam was asking the man (He was asking Mr Johnson to sponsor him to do a run for charity.) Ex: 3 P:98 • Ask students to complete the key phrases individually, then read them through with the class. • Ask students to identify who says the key phrases in the dialogue. Then play the CD for them to check their answers. • Students practise the dialogue in pairs. Ex: 3 P:98 • Read the rule with the class, then students identify the structures. • Ask students to find more examples of be going to for plans and the present continuous for future arrangements in the dialogue in exercise 2. Clarify the difference between a plan and an arrangement in each case. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the photo and answer the question. Answers: Students’ own answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to the dialogue. Answers: Adam thinks he’ll raise £150 Students complete the key phrases from the dialogue. Then practise the dialogue with a partner. .Answers: 1 minute (Adam) 2 do (Mr Johnson) . 3 for (Mr Johnson) 4 for (Adam) 5 to raise (Adam) 6 like (Mr Johnson) Students read the rule. Which structures are in sentences a and b? Answers: a present continuous b be going to |
Descriptor: - look at photo and discuss Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen for the general meaning of the dialogue Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the key phrases from the dialogue Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the rule Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 86 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 11.04.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A formal letter |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.7.1 develop and sustain a consistent argument when speaking or writing 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model formal letter. • Learn key phrases for writing a formal letter. • Learn how to explain things. • Write a formal letter |
||
|
Value links |
Hospitality: Traditionally a nomadic culture, hospitality has always been an important part of Kazakh culture. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students what things they can do if they care about an issue such as those mentioned in the unit. • Elicit various ideas. You could use this as an opportunity to revise the vocabulary on action and protest from page 58. • If no one suggests writing a letter to someone in authority, suggest it and ask who they might write to. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:99 • Read the task with the class and check understanding. Encourage students to read through options a–d first, then check understanding of these. In a weaker class, give an explanation in L1 if necessary. • Explain that this task will help them learn about the purpose and structure of the letter Ex: 2 P:99 • Students read the model letter more carefully and answer the questions Ex: 3 P:99 • Read through the key phrases with the class, and refer students back to the paragraph topics before they do the matching. Ex: 4 P:99 In a weaker class, elicit or explain the function of the words in the box. For example, because and as introduce a reason; therefore and for this reason indicate an action or opinion based on a given situation. In a stronger class, elicit this information and ask students to use the words in sentences of their own. • Ask some students to read out their sentences, and check they have used the explaining words and phrases correctly. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students read the model text and match paragraphs. Answers: The purpose of the letter is to ask the supermarket to display a poster and help publicize the protest. 1 d 2 a 3 c Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students answer the questions. Answers: 1 James West, Students Against Nuclear Energy, 8 Dene Gardens, Halford HA3 8HB 2 Morrisey’s Supermarket, High Street, Halford HA3 7RD 3 Dear Sir or Madam; Yours faithfully 4 The plans to build a nuclear power station in the area Students match the key phrases with the three correct paragraph. Answers: 1 a 2 d 3 c 4 a 5 c |
Descriptor: - read the model text Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the model again and answer the questions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - match the key phrases Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 87 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Food and drink: Record-breaking food |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.2.5.1 recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) with little or no support in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.3.1 use a growing variety of compound adjectives and adjectives as participles and some comparative structures including not as…as, much …than to indicate degree on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Review and learn vocabulary related to cooking and food. • Review how to use as, like, such, so, because |
||
|
Value links |
Tradition: Kazakh traditions and culture have been passed on from one generation to another through oral histories told by traditional Kazakh tribal leaders and elders. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Ask students what traditional food they like or don’t like. • Ask students to describe how the food is prepared and eaten. Encourage them to use cooking verbs and nouns, for example, fry / frying pan |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
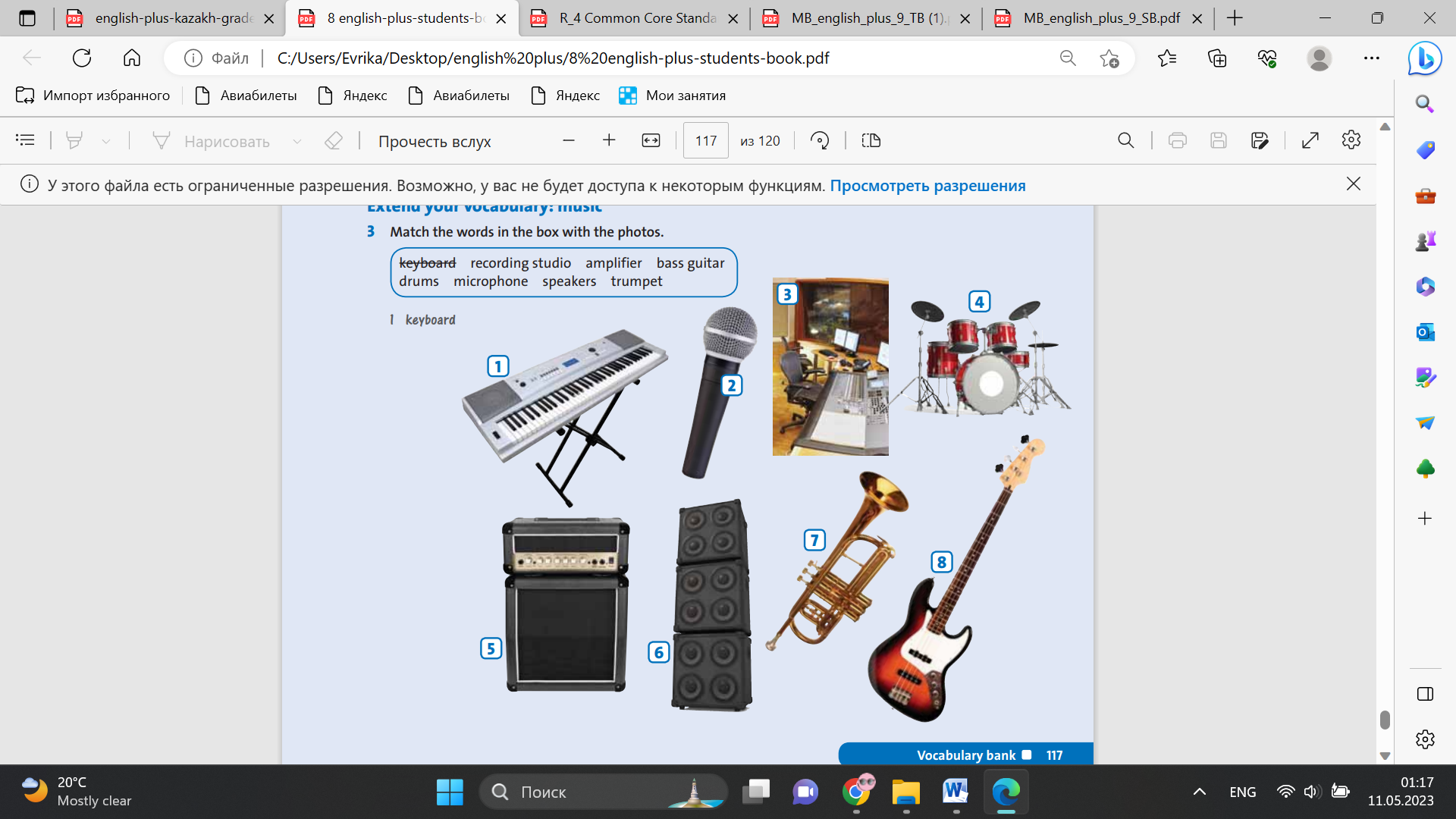
Ex: 1 P:100 • Read the sentences with the class. Ask students to explain the words in blue. Help them with the meaning if they are not sure. • Get students to guess whether the sentences are true or false. • Play the CD as students read the text and check if their guesses were correct. • Play the CD again so that they can correct the false sentences Ex: 2 P:100 • Ask students to scan the text for the words in the box and then complete the rules. • Note that so can be used as an adverb, ‘It’s so big it won’t fit in my bag.’ This is the so in paragraph one of the text. It can also be used as a conjunction: ‘It was cold so I put a jacket on.’ This is the so in the final paragraph. Ex: 3 P:100 • Ask students to complete the sentences using the correct word. • When you go through the answers with the class ask students to explain their answers by referring to the relevant rule Ex: 4 P:100 • Put students into pairs or small groups to do the activity. • Get students to use the internet or school library if there is one available. • Ask students to write about half a page, or longer if there is enough time. Walk round and help with ideas and language. Encourage students to use the vocabulary they have learnt in the lesson. • Get pairs or groups to read their descriptions out for the rest of the class Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students check the meaning of the words in blue in the sentences. Then read and listen to the text. Write true or false. Answers: 1 false – The world’s largest serving of beshbarmak weighed 736.5 kilograms. 2 false – The nomads didn’t use cutlery – they ate beshbarmak with their hands. 3 true 4 false – The meat, vegetables and spices are boiled together, but the nooodles are cooked separately. 5 false – Baursaks are also popular in other countries in Central Asia and in the Middle East. 6 true Students find these words and phrases in the text. Then complete the rules. Answers: 1 a 2 like 3 so, such a 4 because, since, as Students choose the correct words. Answers: 1 as 2 because 3 so 4 like 5 Since 6 such |
Descriptor: -read and listen to the text - write true or false Total: 1 point Descriptor: - scan the text for the words in the box and then complete the rules. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 88 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL Science: The future of food |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary of natural environments. • Read a text about tropical rainforests. • Write about coral reefs |
||
|
Value links |
Freedom: Freedom is the major value of the civil society being formed in Kazakhstan. This must provide everyone with the possibility of creative self-realization. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, write the word rainforest on the board. Ask students what they know about tropical rainforests. • Elicit a variety of ideas, then ask what they know about the conditions in a rainforest. Ask what types of animals and plants there are, and where they live in the forest. • Elicit a variety of responses, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:101 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. In a weaker class, accept translations, then encourage students to contextualize the words in examples sentences. In a stronger class, encourage them to contextualize the words directly. • Students read the text and complete it with the missing words. Tell students that they should read the text quickly and not worry if they do not understand every word. • Do not check answers at this stage Ex: 2 P:101 • Ask students to listen and read the text, and check their answers to exercise 1. Ex: 3 P:101 • After students have labelled the diagram, check answers and ask what the layers of a rainforest are called in their language Ex: 4 P:100 • Allow students time to read the notes. Elicit or explain that coral reefs are made up of lots of tiny animals. Encourage students to use dictionaries to look up any words they do not know. • Ask one or two students to read their paragraphs to the class. • In a weaker class, ask students to exchange their texts for correction. In a stronger class, ask them to exchange texts for correction. Then, in small groups, ask students to identify common errors. Finish by finding out what the most common errors are in the class and encourage students to revise these areas Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box. Answers: Students’ own answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read and listen to the text. Answers: 1 vegetation 2 wildlife 3 layers 4 mammals 5 shrubs 6 natura Students read the text again. Choose the correct answers Answers: 1 emergent layer 2 canopy 3 understorey 4 forest floor |
Descriptor: - read the text and complete - complete it with the missing words Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen and read the text Total: 1 point Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
”
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 89 |
||
|
Teacher’r name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Unit Review 8 SAU1 for the unit “Food and drink” |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.C5 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 8.W3 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.4.5.1(8.R5) Deduce meaning from context in short texts and some extended texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.3.2.1(8.S2) Ask more complex questions to get information about a growing range of general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Identify the meaning and details of the reading texts on familiar topics • Formulate and ask questions that are more complex to get information about the topic |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they watch the news or read newspapers. Ask them what issues in the world they care about. Elicit some examples, such as climate change, animal experiments, etc. • Ask students what they can do to change situations. Elicit some ideas. Encourage students to join in and express their opinions; there are no right or wrong answers |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:102 • ask students to write the nouns from these verbs. Check their answers in pairs and write them individually. Ex: 2 P:102 • Ask students to complete the text with the verbs in the box. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes before you check with the class Summative assessment for the unit «Food and Drink» Reading Task 1. Read the text and answer the questions Write the correct letter. One restaurant is extra. You don’t need to use. Speaking Task 2. Discuss the questions in a class. Task 2. Discuss the questions in a class. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students write the nouns from these verbs Descriptor: - write the nouns Students’ own answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students to complete the text with the verbs Descriptor: - listen and read the text Students read the text and answer the questions Descriptor: - read the text Students discuss the questions |
-can write the nouns from these verbs Total: 1 point Answers: 1 meeting 2 donation 3 campaign 4 organization 5 collection 6 ban 7 publicity 8 supporter -can listen and read the text Total: 1 point Answers: 1 look after 4 sign up 2 carry on 5 join in 3 wipe out 6 find out |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 91 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review language focus reference |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.C5 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 8.W3 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.4.5.1(8.R5) Deduce meaning from context in short texts and some extended texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.3.2.1(8.S2) Ask more complex questions to get information about a growing range of general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Identify the meaning and details of the reading texts on familiar topics • Formulate and ask questions that are more complex to get information about the topic |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they watch the news or read newspapers. Ask them what issues in the world they care about. Elicit some examples, such as climate change, animal experiments, etc. • Ask students what they can do to change situations. Elicit some ideas. Encourage students to join in and express their opinions; there are no right or wrong answers |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:102 • ask students to write the nouns from these verbs. Check their answers in pairs and write them individually. Ex: 2 P:102 • Ask students to complete the text with the verbs in the box. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes before you check with the class Summative assessment for the unit «Food and Drink» Reading Task 1. Read the text and answer the questions Write the correct letter. One restaurant is extra. You don’t need to use. Speaking Task 2. Discuss the questions in a class. Task 2. Discuss the questions in a class. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students write the nouns from these verbs Descriptor: - write the nouns Students’ own answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students to complete the text with the verbs Descriptor: - listen and read the text Students read the text and answer the questions Descriptor: - read the text Students discuss the questions |
-can write the nouns from these verbs Total: 1 point Answers: 1 meeting 2 donation 3 campaign 4 organization 5 collection 6 ban 7 publicity 8 supporter -can listen and read the text Total: 1 point Answers: 1 look after 4 sign up 2 carry on 5 join in 3 wipe out 6 find out |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
Lesson 92 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
School life: verbs |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn verbs to do with school life. • Do a questionnaire on attitudes to school. • Learn the form and use of should and must. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to tell you something they like and something they dislike about their school. Encourage students to join in and contribute ideas. • Ask students what kind of things they do at school. Elicit ideas, and write the verbs on the board (for example, study, work, do homework, make friends).. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:104 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words and expressions in the questionnaire. • Remind students to think carefully about using the infinitive form each time and to use this form in their table. • Encourage students to work individually, then compare answers in pairs. Then check as a class to ensure everyone has agreed on which column the words go in. • In a weaker class, ask students to put the words in new sentences to check understanding. In a stronger class, ask students to define the verbs. Ex: 2 P:104 • Students do the questionnaire. They can read the questions and options in pairs, but they should put answers that reflect their own ideas. • In a weaker class, encourage students to work out unfamiliar words from the context. • Ask students whether they agree with what the key says about them. • In a stronger class, you could ask students to prepare a short summary based on their answers to the questionnaire and the key. This could start, for example: I’ve got a good attitude to school because I get good marks and I make friends too, Ex: 3 P:104 • Read through the questions with the class and check understanding. If students find any of the questions difficult, ask if other students can offer a translation or explanation. • Allow students time to prepare their answers to the questions individually. • Put students in pairs to ask and answer the questions. Go round and listen as they are talking. Check they are using the present perfect correctly, and help with vocabulary. • Ask some students to report back to the class on their partner’s answers |
Students check the meaning of the words and phrases in blue. Then complete the table with the infinitive forms of the verbs. Descriptor: - complete the table with the infinitive forms of the verbs Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text.
Students work in pairs and do the questionnaire Descriptor: - do the questionnaire Students ask and answer the questions with a partner. Then compare their answers with the class. Descriptor: - Read the questions - answers to the questions individually |
-can understand the meaning of the words and phrases in blue Total: 1 point Answers: Positive: make friends, get good marks, pass exams, get a qualification Neutral: revise for a test, do your homework, take the exam, leave school Negative: play truant, cheat in exams, fail an exam, copy a friend’s work, get a bad mark, bully, suspend, expel -can read the questions Total: 1 point Answers: Students’ own answers. -can answers to the questions individually Total: 1 point Answers: Students’ own answers |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
9 The world of work |
Lesson 93 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Cheating |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about cheating in exams. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Learn some American English vocabulary. • Learn key phrases for agreeing and disagreeing |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, write the word cheat on the board and elicit the meaning. • Ask students to think about the different ways in which people can cheat. • Ask students to give their opinions on the topic of cheating. Try to elicit different ideas and encourage students to join in and give their opinions. • Ask students if they can guess what percentage of school students cheat in tests and exams. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:106 • In a weaker class, help students to read through the sentences. Explain that they should give their opinion, as there may be a difference between what different people would describe as cheating. • In a stronger class, students read the sentences and decide in pairs which of the things they think are cheating. • Ask some students to report back to the class on their discussions, and ask other students whether they agree. • Students read the text and identify which of the items are mentioned. Tell them to ignore the gaps at this stage. Ex: 2 P:106 • Explain to the class that five of the sentences a–f can be used to complete the gaps in the text. • Explain that students will need to read the text again more carefully to complete the gaps. They can work individually or in pairs. • When students listen to the text, encourage them to correct any mistakes they may have made. Ex: 3 P:106 • Explain to the class that there are many vocabulary differences between British and American English. Ask if students can think of any examples, such as chips / fries, pavement / sidewalk, etc. • Students find the American English words in the text. Ex: 4 P:106 • In a weaker class, ask for translations of the words in the box before students start the exercise. In a stronger class, ask students to define the words. • After students have matched the words, encourage them to record the words in sentences in their notebooks. |
Students read the text and tick the things that are mentioned. Descriptor: - read the sentences and decide in pairs which of the things they think are cheating. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the text again and complete the gaps. There is one sentence that you don’t need. Then listen to the text and check the answer. Descriptor: - read the text again more carefully to complete the gaps Students find the American English words in the text. Descriptor: - find the American English words in the text. Students match the British English words in the box with the American English words in the box. Descriptor: -translate the words in the box |
-can read the sentences Total: 1 point Answers: 1, 2, 4, 5 and 7 are cheating. 1, 2, 4 and 5 are mentioned in the text. -can complete the gaps Total: 1 point Answers: 1 b 2 a 3 e 4 f 5 c -can find the American English words in the text. Total: 1 point Answers: 1 grades 2 cell phones 3 principal -can translate the words in the box Total: 1 point Answers: 1 petrol 2 film 3 rubbish 4 motorway 5 shop 6 trousers 7 biscuit 8 pavement 9 lorry 10 sweet |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
Lesson 94 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: Have t;;;o and don't have to |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.3.3.1 give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.6.13.1 use a growing variety of modal forms for different functions: obligation, necessity, possibility, permission, requests, suggestions, prohibition on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: Learn the form and use of have to and don’t have to. • Practise using have to and don’t have to to talk about things that are necessary or not necessary. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Ask students to find a phrase in paragraph 2 in the text on page 50 meaning ‘it’s necessary to cheat’ (they have to cheat). Ask them to find a phrase in paragraph 5 on page 51 meaning ‘it isn’t necessary to cheat’ (they don’t have to cheat). • Ask students what other things it is necessary to do at school (for example, work hard, come to classes, wear a uniform). |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:107 • Refer students back to the text to complete the sentences, then ask them to study these and use their answers to help them complete the rules. Ex: 2 P:107 • Check students’ understanding of the word order in questions by asking them to write these individually. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes before you check with the class. • Explain that questions start with a negative auxiliary when we are asking for clarification. So for item 3 the speaker was surprised to see some students out of uniform. In a weaker class, explain that the speaker could have said, I thought they had to wear uniforms. In a stronger class, encourage students to think of alternative ways of clarifying the situations in items 3 and 4 to check they have understood the use of the negative auxiliary, don’t / doesn’t Ex: 3 P:107 • Allow students time to read through the list of things to do. • Explain that students are going to listen to an interview with a girl who is talking about what she has to and does not have to do. Students listen and tick the things that Laura has to do, then write sentences. • Let students listen to the CD twice, then ask them to compare their sentences in pairs. |
Students complete the sentences from the text. Then choose the correct words in the rules. Descriptor: - complete the rules. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students order the words to make questions Descriptor: - make questions compare their sentences in pairs. Students listen to a interview with Laura. Then write sentences with have to and don’t have to Descriptor: - listen and tick the things that Laura has to do |
-can complete the rules. Total: 1 point Answers: 1 have to 2 have to 3 don’t have to Rules 1 have to 2 don’t have to -can make questions Total: 1 point Answers: 1 Do we have to walk to school? 2 Does the teacher have to prepare lessons? 3 Don’t they have to wear a uniform? 4 Doesn’t Francis have to study? 5 Does he have to see the head teacher? 6 Do you have to go home? -can. listen and tick the things that Laura has to do Total: 1 point Answers: 1 ✓ Laura has to walk to school. 2 ✓ Laura has to wear a uniform. 3 Laura doesn’t have to eat at the canteen. 4 ✓ Laura has to do her homework before she goes out. 5 Laura doesn’t have to help make dinner every evening. 6 Laura doesn’t have to stay at home on school days. |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
Lesson 95 |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
School life: nouns |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.3.1 give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn nouns relating to school life. • Listen to three teenagers talking about their schools. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. • Discuss opinions about different kinds of school. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to say what kind of school they go to. Ask if there are other kinds of school in their country, and ask students to say what the differences are. • Ask what the advantages are of the school they go to, and also what the disadvantages are. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
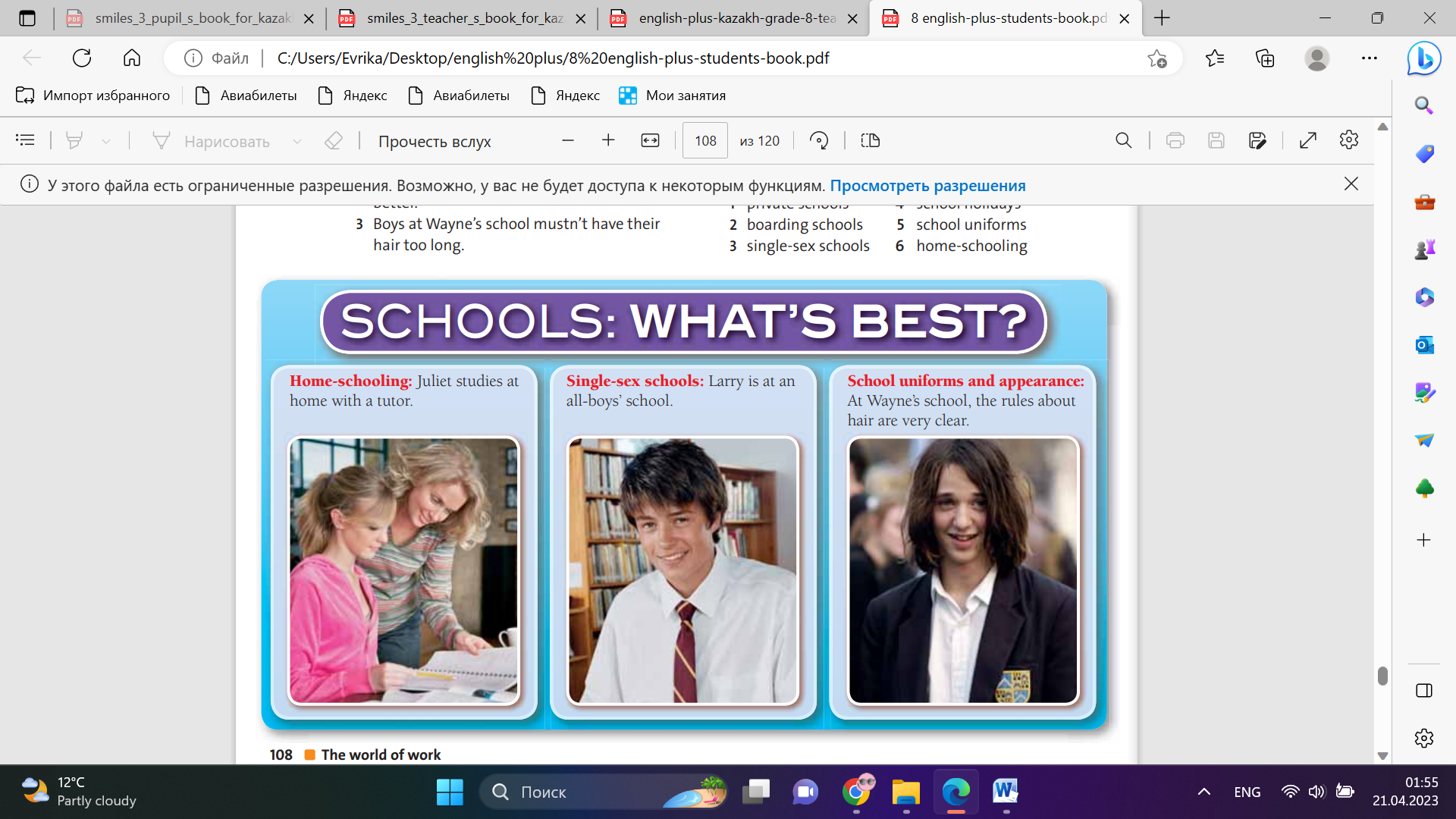
Ex: 1 P:108 • Ask students to read through the sentences and think about the meaning of the words in blue. • Read the table headings and check understanding. In a weaker class, do another example under each heading. • Once students have completed the table, check answers before students move on. • Students answer the questions with their own ideas. Go round and listen as they are working, and help as necessary Ex: 2 P:108 • Explain to students that they are going to listen to four people talking about school, and that they should identify which type of school each of them goes to. Ex: 3 P:108 • Explain that this exercise is designed to help students predict information. • Elicit ideas, but do not confirm or reject them at this stage. Students listen to the CD to check their answers. Ask round the class to find out how many answered.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the table with the words in blue. Then answer the questions with a partner Descriptor: - read the sentences - complete the table Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to four people Descriptor: - listen to four people talking about school Students look at the photos. Are the sentences true or false? Descriptor: - discuss about photos |
-can complete the table Total: 1 point Answers: Types of school: mixed school, single-sex school, state school, private school, primary school, secondary school, boarding school Other collocations: school-leaving age, school uniform, school rules, school holidays, school subjects, school-leaving exams Students’ own answers. -can talk about school Total: 1 point Answers: 1 boarding school 2 secondary 3 single-sex school school 4 state schoo -can discuss about photos Total: 1 point Answers: 1 True. 2 False. 3 True. |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work Lesson 96 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: Should, must and have to |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.3.3.1 give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.6.13.1 use a growing variety of modal forms for different functions: obligation, necessity, possibility, permission, requests, suggestions, prohibition on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the difference between should, must and have to. • Learn how to improve your English. • Practise using should, must and have to to make recommendations and talk about school |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Ask students to look back through the unit and find examples of should, must and have to. • Elicit some simple sentences and write them on the board. • Underline the verbs and ask students to translate the sentences into their own language. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:109 • Point out the difference in meaning between mustn’t and don’t have to. • After completing the table, students can compare answers in pairs before you check with the class. Then refer back to the warm-up examples on the board and ask students to classify them LANGUAGE NOTE Students
often confuse the meanings of mustn’t (= prohibition) and don’t
have to (= no obligation). Typical errors might be:
Ex: 2 P:109 • Encourage students to read through the whole text to get an idea of the context before they complete the activity. • Allow students time to choose the correct words before they listen to the CD and check their answers Ex: 3 P:109 • Refer students back to the table in exercise 1 to help them choose the correct verbs. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes. • Hold a feedback session with the whole class to ensure students are making the correct distinctions in the use of the modals. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the sentences from the listening with words in the box. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the text and choose the correct words Descriptor: - read the text - choose the correct words Students write true sentences using have to Descriptor: - write true sentences using have to |
Descriptor: - complete the table - ask students to classify them Total: 1 point -can choose the correct words Total: 1 point Answers: 1 don’t have to 2 mustn’t 3 must 4 don’t have to 5 should 6 have to 7 mustn’t 8 shouldn’t 9 must 10 have to -can write true sentences using have to Total: 1 point Answers: Students’ own answers |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work Lesson 97 |
|
||
|
Date: 03.05.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Asking for and giving advice |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a dialogue in which people ask for and give advice. • Learn key phrases for asking for and giving advice. • Practise asking for and giving advice |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, write the word advice on the board and elicit the meaning. In a weaker class, ask students to translate the word into their own language if necessary. • Ask them when they ask for advice, and who they ask. • Ask students when they give advice and to whom. Elicit some ideas and encourage students to contribute. • Ask students what they would say in English to ask for advice or give someone advice. Elicit ideas, but do not confirm or reject any at this stage |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:110 • Refer students to the photo, and ask them to work in pairs to discuss what could be happening. • Elicit ideas, but do not confirm or deny them at this stage. Ex: 2 P:110 • Read the question with the class and elicit or explain that the first time students hear the recording, they should concentrate on getting the general meaning of the conversation, and three specific pieces of advice. Ex: 3 P:110 • Students work individually to complete the key phrases, then check their answers by listening to the CD. • You could ask students to find the key phrases in the dialogue and translate them into their own language. • Go round and listen as students practise the dialogue in pairs. Help with pronunciation as necessary Ex: 3 P:110 • Students work individually to match the sentences and responses. Remind them that there is one response they do not need. • In a weaker class, you could ask students to practise the sentences and responses in pairs. In a stronger class, encourage students to think of a context for each exchange. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the photo. What is Adam doing? Answers: Adam is reading a text message on his mobile Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to the dialogue. What three things does Lucy advise? Answers: Lucy advises Adam not to cheat, to tell his teacher, and to tell the boy what he thinks. Answers: 1 matter 2 should 3 do 4 for . 5 you Students complete the key phrases from the dialogue. Then listen and check. Answers: 1 d 2 b 3 g 4 c 5 e 6 a |
Descriptor: - discuss about the photo Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the question - answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the key phrases Total: 1 point 6 sure -can match sentences with responses Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
Lesson 98 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
An opinion essay |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.1.1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model opinion essay. • Learn key phrases for an opinion essay. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they are in favour of school uniforms. Ask them to explain their answers. • Write the words opinion essay on the board. Elicit or explain that in an opinion essay, you give your own opinion and the reasons for your opinion, rather than arguing the advantages and disadvantages of something. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:111 • After students have read the model text and answered the questions, check answers with the class. Point out that in an opinion essay you can use contractions. Ex: 2 P:111 • Read through the key phrases with the class and check understanding. Then check the answer to the question in the instructions Ex: 3 P:111 • Refer students back to the model text. In a weaker class, point out that we use the linkers at the beginning of a sentence and they are followed by a comma. In a stronger class, elicit this information. • Ask some students to read their paragraphs to the class and check that they have used the linkers correctly Ex: 3 P:110 • Students work individually to match the sentences and responses. Remind them that there is one response they do not need. • In a weaker class, you could ask students to practise the sentences and responses in pairs. In a stronger class, encourage students to think of a context for each exchange. Ex: 4 P:110 • Read the task with the class. • Students think and plan their essays individually. If some students are struggling to think of ideas, you could brainstorm some ideas about boarding schools with the whole class. • Students write their essays. This can be set for homework. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students read the model text and answer the questions Answers: 1 The writer gives four arguments in favour of school uniforms. 2 Paragraph 3. 3 School uniforms are compulsory at the writer’s school, but at most schools in the same area they are not. 4 They like to choose their own clothes. 5 Students’ own answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students study the key phrases Answers: All in all, … . / In conclusion, … Students look at sentences and choose the four best reasons for learning English. Then write a paragraph using the linkers in the box. Answers: Students’ own answers. |
Descriptor: - read the model text Total: 1 point Descriptor: - study the key phrases Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work individually - write a paragraph using the linkers in the box. |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
Lesson 99 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country. The world of work |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.W1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics 8.UE17 use if / unless/ if only in second conditional clauses and wish [that] clauses [present reference]; use a growing variety of relative clauses including why clauses on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Review and learn vocabulary related to jobs • Review how to use I wish and If only to talk about wishes and regrets |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Ask students which jobs in Kazakhstan are the most popular, the best paid, the most interesting, and the most common. • Find out which jobs students think they would do, or which jobs members of their famiies do |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:112 • Look at the photos as a class and guess what the people’s jobs are. • Get students to talk about details in the photos that helped them guess, for example, Arslan’s white shirt and bow tie are typical of a waiter. • Play the CD for students to listen to the text. Students can follow the written text and check their answer Ex: 2 P:112 • Get students to read the sentences first and then play the CD. • Note that the answers are not in the order of the script and students will have to infer the answers from what each person says, for example, Arslan says ‘Maybe I’ll become a famous writer’ suggests he hasn’t decided what job he wants to do Ex: 3 P:112 • Ask students to find the three phrases in the texts and use them to work out the rules. Check students understand by giving them example sentences and asking them if they are correct, for example, ‘I wish I can speak English.’ • Explain that wishes can also be negative, for example, ‘I wish I didn’t have a test tomorrow.’ • Ensure students understand the meaning of the phrases using check questions, for example, ‘Does Arslan have as much free time as he wants?’ Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the photos and match the people with three of the jobs below. Then listen and check your answers Descriptor: - read the model text and answer the questions Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen again. Match the people with the statement. Write A (Arslan), Z (Zhibek) or N (Nursultan) Descriptor: - match the people with the statement. Students study the phrases in blue in the text. Then choose the correct words to complete the rules. Descriptor: - work individually - complete the rules. |
-can read the model text and answer the questions Total: 1 point Answers: Arslan – waiter, Zhibek – artist, Nursultan – doctor -can match the people with the statement. Total: 1 point Answers: 1 Zhibek 2 Arslan 3 Arslan 4 Nursultan 5 Zhibek -can complete the rules. Answers: 1 present, were 2 present or future, if not |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
Lesson 100 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: 11.05.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL History: Child labour in Victorian Britain. Summative Assessment for the unit “The world of work” |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.R1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.W1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a text about the school community. \ • Discuss students’ rights and responsibilities in the classroom. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, write the word community on the board and elicit or explain the meaning (a group of people who have something in common and feel that they belong together). • Ask students what different types of community there are (a town / village community, a work community, a religious community, clubs, organizations, etc). Ask students if they think their school is a community |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:113 • Read through the headings with the class and make sure that students understand them. In a weaker class, students can translate the headings. In a stronger class, encourage students to define the headings in English. • Students read the text and match the headings with the paragraphs. Point out to students that they should read the text quickly at this stage, and not worry if they do not understand every word. • Do not check answers at this stage. Ex: 2 P:113 • Students listen and read the text, and check their answers to exercise 1 Summative Assessment for the unit “The world of work” Listening Task 1. Listen to the description of the jobs and complete the chart. Write what the job is and the key words that help you to guess what it is. CD2. Tapescript 4. And transcript for listening task can be found after the rubrics. Writing Task 2. Think about ONE job. Write the description of the job without naming what the job is. Describe the place where the person works, qualities or skills that are required for the job. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students check the meaning of the words in the table. Then write the missing words. Answers: Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to the text and check your answers. Answers: Paragraph 1 d Paragraph 2 a Paragraph 3 b Paragraph 4 e Paragraph 5 c Students listen to the description of the jobs and complete the chart Answers: Students write the description of the job without naming what the job is Answers: |
-can match the headings with the paragraphs Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the text - check your answers. Total: 1 point -can complete the chart Total: 8 point Descriptor: - complete the chart Total: 5 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work Lesson 101 |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project. A survey. A survey about career choices |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.R1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.W1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a survey about school life. • Write a survey about school life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, write the word community on the board and elicit or explain the meaning (a group of people who have something in common and feel that they belong together). • Ask students what different types of community there are (a town / village community, a work community, a religious community, clubs, organizations, etc). Ask students if they think their school is a community |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:115 • Students read the survey and answer the questions, then compare their answers with the results in the survey Ex: 2 P:115 • Students read and follow the steps in the project checklist. • They could work individually for this task. Read through the task and explain that they need to think of four potential answers for each one. They should model this on the survey above, by reflecting a range of opinions in the answers. • Alternatively, students could work in pairs or small groups. Encourage all students to work cooperatively and say that each one should make suggestions for the options in the survey. • Suggest that students take turns to write down the questions and options. Weaker students can be supported by stronger ones, who can help with accuracy. • Go round and help as students are working. Encourage them to follow the points in the checklist to help them structure their work. • Set aside time in class for students to carry out their surveys. They can write up the results and summary for homework Ex: 3 P:115 • In the following lesson, ask students to present their surveys, and discuss the findings as a class. • Ask students to assess how well they feel they performed the task, whether as individuals or in groups. • Ask if they would change their approach if they had to do another survey in the future. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students read the survey and questions. Are your answers the same as the most popular ones? Answers: Students’ own answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students write a survey about school life. Follow the steps in the project Answers: Students’ own answers. Students exchange your survey with the rest of the class. Answers: Students’ own answers. |
Descriptor: - read the survey - answer the questions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work individually - write a survey about school life Total: 1 point Descriptor: - exchange your survey Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Vocabulary Bank/ Compound Nouns/ Waste |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.L1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.W3 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.UE13 use a growing variety of modal forms for different functions: obligation, necessity, possibility, permission, requests, suggestions, prohibition on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -recount and interpret the main points of the listening -proofread and edit own and others’ writing for grammar |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In
|
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:116 • Read the instructions with the class and make seven more compound nouns with words from A and B • Students work in pairs to make as many compound nouns as possible. Then they read the text and compare it with their lists. • Check answers and expand the list with any more compound nouns from the text Ex: 2 P:116 • Ask students to complete the task individually,then label the photos using compound nouns. • Elicit answers from the class, and encourage students to discuss any differences of opinion. Ex: 3 P:116 • In the following lesson, ask students to label the photos with the words in the box. • Ask students to assess how well they feel they performed the task, whether as individuals or in groups. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students make seven more compound nouns with words from A and B Answers: 1 art gallery 2 shopping basket 3 pencil case 4 tennis racket 5 video camera 6 paper clip 7 water bottle 8 chocolate cake Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students label the photos using compound nouns Answers: 2 key ring 3 birthday card 4 train station 5 football stadium 6 door handle 7 letter box Students label the photos with the words in the box Answers: 1 litter bin 2 waste-paper basket 3 skip 4 landfill tip 5 refuse sack 6 dustbins 7 recycling centre |
Descriptor: -make seven more compound nouns Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work individually - label the photos using compound nouns Total: 1 point Descriptor: - label the photos with the words Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Prefixes and suffixes |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.R1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.W1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - explain the topical word by giving definition/synonym - identify the central idea, the intended audience and the author’s purpose |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In
|
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:117 • Allow students time to compare their answers in pairs before you check with the class. Discuss what helped students make their choices. Ask students to choose the correct prefixes and suffixes Ex: 2 P:117 • Ask students to complete the task individually, then add prefixes and suffixes to the words in the box. • Students study the examples in pairs and complete the words. • Check answers with the class Ex: 3 P:117 • Students match the words in the box with the photos. Allow students to use their dictionaries if necessary. • Check answers with the class. • In the following lesson, ask students to label the photos with the words in the box.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students choose the correct prefixes and suffixes Answers: 1 peaceful 2 unfriendly 3 understandable 4 homeless 5 wonderful 6 unhappy 7 childless 8 noticeable Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students add prefixes and suffixes to the words in the box Answers: 1 endless 2 playful 3 breakable 4 unusual 5 drinkable 6 lifeless 7 unlucky 8 spiteful Students match the words in the box with the photos Answers: 2 microphone 3 recording studio 4 drums 5 amplifier 6 speakers 7 trumpet 8 bass guitar |
Descriptor: - choose the correct prefixes and suffixes Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work individually Total: 1 point Descriptor: - match the words Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative Assessment for the 4th term |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.2.4.1 (8.L5) Recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) with little or no support in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics. 8.4.6.1(8.R6) Recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.5.1.1(8.W1) Plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a growing range of general and curricular topics. 8.3.5.1(8.S5) Interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - explain the topical word by giving definition/synonym - identify the central idea, the intended audience and the author’s purpose |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Listening Task. You will hear a radio interview with a famous cardiologist. Decide whether the statements are TRUE or FALSE. Transcript for listening task can be found after the mark scheme. Example: Heart attacks are more common now than they were in the past. True Listen and complete the sentences with NO MORE THAN TWO words. Example: Dr. Shaw gives some advice on how to keep our hearts in good condition. Reading Task. Read the text about Kenneth. Mark the sentences TRUE or FALSE according to the context. Writing Task. Choose ONE of the topics to write. Topic 1. Write an essay about the following topic: Nowadays food has become easier to prepare. Has this change improved the way people live? Give reasons for your answer using your own ideas Topic 2. Write an essay about the following topic: Doctors, nurses and teachers make a great contribution to society and should be paid more than entertainment and sports celebrities. Do you agree or disagree? Give reasons for your answer using your own ideas SPEAKING Task. Work in pairs. Choose one of the cards and answer the questions. You have 1 minute to prepare and 3 minutes to speak. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students listen and complete the sentences Answers: Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the text about Kenneth Answers: Students write an essay Answers: Students work in pairs. choose one of the cards and answer the questions Answers: |
Descriptor: - decide whether the statements are TRUE or FALSE Total: 6 point Descriptor: - work individually - read the text about Kenneth Total: 6 point Descriptor: - write an essay about the following topic Total: 6 point Descriptor: choose one of the cards and answer the questions Total: 6 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
ҚМЖ жинағы English Plus 8-сынып 4-тоқсан
ҚМЖ жинағы English Plus 8-сынып 4-тоқсан
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 80 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Action and protest |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.9.1 use imagination to express thoughts, ideas, experiences and feelings 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary to do with action and protest. • Do a questionnaire on attitudes to taking action. • Learn the use of will and might. • Practise using will, won’t, might and might not to make predictions. |
||
|
Value links |
Hospitality: Traditionally a nomadic culture, hospitality has always been an important part of Kazakh culture. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they watch the news or read newspapers. Ask them what issues in the world they care about. Elicit some examples, such as climate change, animal experiments, etc. • Ask students what they can do to change situations. Elicit some ideas. Encourage students to join in and express their opinions; there are no right or wrong answers. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:92 • If necessary, allow students to use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the new words. • When checking answers, model and drill pronunciation of the words, paying attention to the change of stress between some nouns and verbs such as organize / organization. • Ask students to do the questionnaire individually, then compare their answers with a partner and discuss which is the best plan of action in each case. • Ask some students to report back to the class on their discussions. Encourage other students to agree or disagree with them. Ex: 2 P:92 • In a weaker class, help students understand the meaning of each sentence by reading through them all with the class and answering the question in the instructions before students listen. • In a stronger class, allow students time to read through the options before listening. Follow up by answering the question in the instructions. Ex: 3 P:92 • After students have completed the key phrases, read through them with the class. • After saying each phrase, elicit whether it is used to make a suggestion, or comment on a suggestion. Make suggestions: Let’s (organize a meeting). How about (starting an email campaign)? I think we should try … Why don’t we (boycott the shops)? I think the best thing to do is … We could write to the council Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the table with the words in blue in the Plan of action questionnaire. Answers: 1 meeting 2 organize 3 march 4 donate 5 collection 6 protest 7 volunteer 8 supporter 9 sponsor 10 petition 11 ban 12 boycott 13 campaign Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to two people discussing questionnaire. Match opinions with dialogues Answers: 1 e 2 a 3 c 4 d 5 b Sentences which express certainty: b, d and e Students complete the key phrases with the words in the box. Descriptor: - complete the key phrases Answers: 1 idea 2 help 3 about 4 think 5 don’t 6 work 7 thing 8 could |
Descriptor: - model and drill pronunciation of the words - complete the table with the words in blue Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen to two people discussing questionnaire - Match opinions with dialogues Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the key phrases Total: 1 point . |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 81 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
The food waste scandal |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.2.1 understand specific information and detail in texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a text about freegans and food waste. • Read for general meaning and specific details. • Learn about negative prefixes un-, in- and im-. • Express opinions about a campaign against food waste. |
||
|
Value links |
Tradition: Kazakh traditions and culture have been passed on from one generation to another through oral histories told by traditional Kazakh tribal leaders and elders. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, write the word food waste on the board. Ask students what they understand by the expression. • Elicit ideas about food waste issues, for example, food mountains, sell-by dates on food. Ask students to express their opinions on these issues, using L1 if necessary. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:94 • Refer students to the title and photos and discuss what the photos show. • Ask students to discuss the questions in pairs. You can discuss ideas with the class before playing the CD. • Students read and listen, and check whether their guesses were correct Ex: 2 P:94 • Encourage students to prepare by reading through the questions before they read the text again. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes before you check with the class Ex: 3 P:94 • Read through the words with the class and explain that the opposite of each word is in the text. Students should read the text again quickly to find the correct words. • Check answers with the class, and check that students understand the meaning of the adjectives. In a weaker class, ask for translations, then encourage students to put the new adjectives into sentences for context. In a stronger class, ask students to put the words into new sentences to show understanding. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the title of the text and photos and answer the questions. Then read and listen to the text. Answers: 1 The photos show: a person with a bag of food that has been thrown away, to show the quantity of food that is wasted. people who work on a food-sharing campaign. volunteers organizing food boxes so food can be redistributed. 2 Supermarkets throw food away if it is imperfect, for example, not all the same size, or if it doesn’t look nice. 3 Freegans are people who believe it is wrong to throw food away and who get most of their food from supermarket waste. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the text again and choose the correct answers. Answers: 1 c 2 a 3 c 4 c 5 c 6 a Students build their vocabulary Answers: 1 imperfect 2 unacceptable 3 insensitive 4 unnecessary |
Descriptor: - discuss the questions in pairs. - read and answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the text again - choose the correct answers Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
|
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 82 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: First conditional review |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.6.17.1 use if / unless/ if only in second conditional clauses and wish [that] clauses [present reference]; use a growing variety of relative clauses including why clauses on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the form and use of the first conditional. • Practise using the first conditional. |
||
|
Value links |
Freedom: Freedom is the major value of the civil society being formed in Kazakhstan. This must provide everyone with the possibility of creative self-realization. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Refer students back to the text, and ask: Does the writer want supermarkets to change? (Yes.) Ask students to look at the last paragraph of the text and find a sentence which says what people can do to make supermarkets change. (If we all boycott the supermarkets, they’ll listen to us.) • Ask students to translate this sentence into their L1. Elicit that the sentence is referring to a future possibility |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:95 • Students complete the tables in pairs. • After checking answers, draw attention to the question in the instructions and ensure students understand that the comma is used when the if-clause is written first Ex: 2 P:95 • In a weaker class, allow students to work in pairs. Then, after checking answers, return to the table in exercise 1. Highlight which parts of the conditional sentences describe the action (using the present simple) and which parts describe the result (using will / won’t). • In a stronger class, ask students to find another example of the first conditional in the text (You’ll find more information and an online petition if you look on our website.). Ask students to identify the action and result clause, and the tenses used. Repeat this with the sentences in the table in exercise . Ex: 3 P:95 • Do the first sentence as an example if necessary. • Remind students to read the sentences carefully to check they understand the context before completing each one Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the first conditional sentences from the text. Answers: 1 boycott 2 ’ll listen 3 won’t change 4 protest Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students study the sentences and complete the rules. Use will, won’t and the present simple. Answers: 2 the present simple 3 will, won’t Students complete the sentences with the first conditional form of the verbs in brackets Answers: 1 supports, will win 2 ask, will volunteer 3 will boycott, sells won’t know, don’t organize 5 ban, won’t be 6 won’t sponsor, don’t finish |
Descriptor: - complete the tables in pairs. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - identify the action and result clause - Use will, won’t and the present simple. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the sentences carefully Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 83 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 04.04.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Phrasal verbs: a campaign |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn phrasal verbs relating to campaigning. • Learn how to make your own examples. • Listen to an interview with a campaigner who wants to save the rainforests. |
||
|
Value links |
Hospitality: Traditionally a nomadic culture, hospitality has always been an important part of Kazakh culture. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, write the word rainforest on the board. Ask students where you can find rainforests in the world. • Ask students what they know about rainforests and elicit some ideas. • Elicit that people are destroying rainforests and ask students if they feel strongly about this issue. Encourage students to participate and express their opinions |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:96 • Students read and listen to the text, then use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the phrasal verbs before matching them to the synonyms. It may help to point out that in most dictionaries phrasal verbs are listed under the main verb form, at the end of that entry. Ex: 2 P:96 • Students complete the sentences individually. • Ask individual students to read out some of their sentences and check that they have understood the meaning of the phrasal verbs correctly. • Put students into pairs to compare their sentences and choose the best ones to memorize. • Tell students they have two minutes to memorize their sentences. • After two minutes, with books closed, ask students to say one of their sentences from memory. • Encourage students to update their notebooks with example sentences regularly. Suggest that they try to learn new vocabulary and grammar, using examples, on a weekly basis. Ex: 3 P:96 • Ask individual students which two sentences they think are not in the interview. • Students then listen and check their answers. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students read and listen to the text and check the meaning of the verbs in blue. Answers: 1 end up 2 set up 3 carry on 4 look after 5 find out 6 wipe out 7 join in 8 sign up fo Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students complete the sentences with your own examples. Answers: Students’ own answers Students answer the question Answers: Questions 3 and 7 are not in the interview. |
Descriptor: - read and listen to the text - match them to the synonyms Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the sentences individually. - complete the sentences with your own examples Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen and check their answers. Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 84 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: Be going to and will |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.6.1 organize and present information clearly to others 8.6.8.1 use a growing variety of future forms including present continuous and present simple with future meaning on a range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn be going to and will for plans and intentions. • Learn the difference between be going to and will. • Practise using be going to to talk about plans and intentions, and will to talk about predictions and instant decisions. • Practise using be going to and will to talk about the future |
||
|
Value links |
Tradition: Kazakh traditions and culture have been passed on from one generation to another through oral histories told by traditional Kazakh tribal leaders and elders. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Refer students back to the text on page 62. Elicit that it all refers to the future. • Ask students to find sentences in which Molly talks about her plans, for example, I’m going to set up a campaign, I’m going to swim … . Elicit that the sentences use be going to. • Refer students back to the questions in exercise 3 on page 62. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:97 • Read the rules with the class, then ask them to complete the sentences LANGUAGE
NOTE Students often
omit the appropriate form of be in sentences with be going
to Ex: 2 P:97 • Encourage students to identify the plans and predictions before completing the text. • In a weaker class, you could ask them to go through the text first and decide which parts are plans and which parts are predictions. Discuss their answers as a class before they write the sentences. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes before you check with the class. Ex: 3 P:97 • Read the situation with the class. • Students write the questions and answers individually. • Ask individual students to read out some of the questions to the class, and correct any mistakes in the question formation before they invent answers. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the sentences from the text and match with rules. Answers: a will b won’t c ’m going to d Is, going to e ’ll f will Rules 1 c, d 2 a, b, e, f Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students complete the text with be going to or will / won’t Answers: 1 are going to run 2 will sponsor 3 ’ll make 4 will be 5 ’re going to start 6 ’s going to run 7 ’ll train Students read the situation. Then complete the questions and invent answer with be going to or will. Answers: 1 is, going to 2 are 3 will 4 are, going to, going to 5 ’ll 6 will Students’ own answers |
Descriptor: - complete the sentences from the text - match them with rules Total: 1 point Descriptor: - identify the plans and predictions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the situation Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 85 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Plans and arrangements |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 8.2.5.1 recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) with little or no support in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a dialogue in which someone talks about their plan to do a sponsored event. • Learn key phrases for talking about donating money. • Learn the use of the present continuous for future arrangements. • Practise talking about your plans and arrangements. |
||
|
Value links |
Freedom: Freedom is the major value of the civil society being formed in Kazakhstan. This must provide everyone with the possibility of creative self-realization. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students what their plans are for the weekend. Elicit a few ideas, making sure that students use be going to rather than will. • Write the words plan and arrangement on the board and elicit or explain the difference (a plan is something you intend to do; an arrangement is something that is already agreed, planned and arranged) |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:98 • Refer students to the photo and ask them what they think is happening. Elicit some answers from the class, but do not confirm or reject any at this stage. Ex: 2 P:98 • Read the question with the class and elicit or explain that at this stage, students should listen for the general meaning of the dialogue, and try to pick out the amount of money which Adam thinks he’ll raise. • When students have listened to the CD, ask for their ideas. • Confirm or reject students’ predictions about what Adam was asking the man (He was asking Mr Johnson to sponsor him to do a run for charity.) Ex: 3 P:98 • Ask students to complete the key phrases individually, then read them through with the class. • Ask students to identify who says the key phrases in the dialogue. Then play the CD for them to check their answers. • Students practise the dialogue in pairs. Ex: 3 P:98 • Read the rule with the class, then students identify the structures. • Ask students to find more examples of be going to for plans and the present continuous for future arrangements in the dialogue in exercise 2. Clarify the difference between a plan and an arrangement in each case. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the photo and answer the question. Answers: Students’ own answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to the dialogue. Answers: Adam thinks he’ll raise £150 Students complete the key phrases from the dialogue. Then practise the dialogue with a partner. .Answers: 1 minute (Adam) 2 do (Mr Johnson) . 3 for (Mr Johnson) 4 for (Adam) 5 to raise (Adam) 6 like (Mr Johnson) Students read the rule. Which structures are in sentences a and b? Answers: a present continuous b be going to |
Descriptor: - look at photo and discuss Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen for the general meaning of the dialogue Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the key phrases from the dialogue Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the rule Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 86 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: 11.04.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
A formal letter |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.7.1 develop and sustain a consistent argument when speaking or writing 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model formal letter. • Learn key phrases for writing a formal letter. • Learn how to explain things. • Write a formal letter |
||
|
Value links |
Hospitality: Traditionally a nomadic culture, hospitality has always been an important part of Kazakh culture. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students what things they can do if they care about an issue such as those mentioned in the unit. • Elicit various ideas. You could use this as an opportunity to revise the vocabulary on action and protest from page 58. • If no one suggests writing a letter to someone in authority, suggest it and ask who they might write to. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:99 • Read the task with the class and check understanding. Encourage students to read through options a–d first, then check understanding of these. In a weaker class, give an explanation in L1 if necessary. • Explain that this task will help them learn about the purpose and structure of the letter Ex: 2 P:99 • Students read the model letter more carefully and answer the questions Ex: 3 P:99 • Read through the key phrases with the class, and refer students back to the paragraph topics before they do the matching. Ex: 4 P:99 In a weaker class, elicit or explain the function of the words in the box. For example, because and as introduce a reason; therefore and for this reason indicate an action or opinion based on a given situation. In a stronger class, elicit this information and ask students to use the words in sentences of their own. • Ask some students to read out their sentences, and check they have used the explaining words and phrases correctly. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students read the model text and match paragraphs. Answers: The purpose of the letter is to ask the supermarket to display a poster and help publicize the protest. 1 d 2 a 3 c Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students answer the questions. Answers: 1 James West, Students Against Nuclear Energy, 8 Dene Gardens, Halford HA3 8HB 2 Morrisey’s Supermarket, High Street, Halford HA3 7RD 3 Dear Sir or Madam; Yours faithfully 4 The plans to build a nuclear power station in the area Students match the key phrases with the three correct paragraph. Answers: 1 a 2 d 3 c 4 a 5 c |
Descriptor: - read the model text Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the model again and answer the questions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - match the key phrases Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 87 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country: Food and drink: Record-breaking food |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.2.5.1 recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) with little or no support in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.6.3.1 use a growing variety of compound adjectives and adjectives as participles and some comparative structures including not as…as, much …than to indicate degree on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Review and learn vocabulary related to cooking and food. • Review how to use as, like, such, so, because |
||
|
Value links |
Tradition: Kazakh traditions and culture have been passed on from one generation to another through oral histories told by traditional Kazakh tribal leaders and elders. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • Ask students what traditional food they like or don’t like. • Ask students to describe how the food is prepared and eaten. Encourage them to use cooking verbs and nouns, for example, fry / frying pan |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:100 • Read the sentences with the class. Ask students to explain the words in blue. Help them with the meaning if they are not sure. • Get students to guess whether the sentences are true or false. • Play the CD as students read the text and check if their guesses were correct. • Play the CD again so that they can correct the false sentences Ex: 2 P:100 • Ask students to scan the text for the words in the box and then complete the rules. • Note that so can be used as an adverb, ‘It’s so big it won’t fit in my bag.’ This is the so in paragraph one of the text. It can also be used as a conjunction: ‘It was cold so I put a jacket on.’ This is the so in the final paragraph. Ex: 3 P:100 • Ask students to complete the sentences using the correct word. • When you go through the answers with the class ask students to explain their answers by referring to the relevant rule Ex: 4 P:100 • Put students into pairs or small groups to do the activity. • Get students to use the internet or school library if there is one available. • Ask students to write about half a page, or longer if there is enough time. Walk round and help with ideas and language. Encourage students to use the vocabulary they have learnt in the lesson. • Get pairs or groups to read their descriptions out for the rest of the class Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students check the meaning of the words in blue in the sentences. Then read and listen to the text. Write true or false. Answers: 1 false – The world’s largest serving of beshbarmak weighed 736.5 kilograms. 2 false – The nomads didn’t use cutlery – they ate beshbarmak with their hands. 3 true 4 false – The meat, vegetables and spices are boiled together, but the nooodles are cooked separately. 5 false – Baursaks are also popular in other countries in Central Asia and in the Middle East. 6 true Students find these words and phrases in the text. Then complete the rules. Answers: 1 a 2 like 3 so, such a 4 because, since, as Students choose the correct words. Answers: 1 as 2 because 3 so 4 like 5 Since 6 such |
Descriptor: -read and listen to the text - write true or false Total: 1 point Descriptor: - scan the text for the words in the box and then complete the rules. Total: 1 point Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 88 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL Science: The future of food |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.10.1 use talk or writing as a means of reflecting on and exploring a range of perspectives on the world 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn vocabulary of natural environments. • Read a text about tropical rainforests. • Write about coral reefs |
||
|
Value links |
Freedom: Freedom is the major value of the civil society being formed in Kazakhstan. This must provide everyone with the possibility of creative self-realization. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, write the word rainforest on the board. Ask students what they know about tropical rainforests. • Elicit a variety of ideas, then ask what they know about the conditions in a rainforest. Ask what types of animals and plants there are, and where they live in the forest. • Elicit a variety of responses, but do not accept or reject any at this stage. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:101 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words. In a weaker class, accept translations, then encourage students to contextualize the words in examples sentences. In a stronger class, encourage them to contextualize the words directly. • Students read the text and complete it with the missing words. Tell students that they should read the text quickly and not worry if they do not understand every word. • Do not check answers at this stage Ex: 2 P:101 • Ask students to listen and read the text, and check their answers to exercise 1. Ex: 3 P:101 • After students have labelled the diagram, check answers and ask what the layers of a rainforest are called in their language Ex: 4 P:100 • Allow students time to read the notes. Elicit or explain that coral reefs are made up of lots of tiny animals. Encourage students to use dictionaries to look up any words they do not know. • Ask one or two students to read their paragraphs to the class. • In a weaker class, ask students to exchange their texts for correction. In a stronger class, ask them to exchange texts for correction. Then, in small groups, ask students to identify common errors. Finish by finding out what the most common errors are in the class and encourage students to revise these areas Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students check the meaning of the words in the box. Answers: Students’ own answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read and listen to the text. Answers: 1 vegetation 2 wildlife 3 layers 4 mammals 5 shrubs 6 natura Students read the text again. Choose the correct answers Answers: 1 emergent layer 2 canopy 3 understorey 4 forest floor |
Descriptor: - read the text and complete - complete it with the missing words Total: 1 point Descriptor: - listen and read the text Total: 1 point Descriptor: - choose the correct words Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
”
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 89 |
||
|
Teacher’r name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Unit Review 8 SAU1 for the unit “Food and drink” |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.C5 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 8.W3 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.4.5.1(8.R5) Deduce meaning from context in short texts and some extended texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.3.2.1(8.S2) Ask more complex questions to get information about a growing range of general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Identify the meaning and details of the reading texts on familiar topics • Formulate and ask questions that are more complex to get information about the topic |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they watch the news or read newspapers. Ask them what issues in the world they care about. Elicit some examples, such as climate change, animal experiments, etc. • Ask students what they can do to change situations. Elicit some ideas. Encourage students to join in and express their opinions; there are no right or wrong answers |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:102 • ask students to write the nouns from these verbs. Check their answers in pairs and write them individually. Ex: 2 P:102 • Ask students to complete the text with the verbs in the box. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes before you check with the class Summative assessment for the unit «Food and Drink» Reading Task 1. Read the text and answer the questions Write the correct letter. One restaurant is extra. You don’t need to use. Speaking Task 2. Discuss the questions in a class. Task 2. Discuss the questions in a class. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students write the nouns from these verbs Descriptor: - write the nouns Students’ own answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students to complete the text with the verbs Descriptor: - listen and read the text Students read the text and answer the questions Descriptor: - read the text Students discuss the questions |
-can write the nouns from these verbs Total: 1 point Answers: 1 meeting 2 donation 3 campaign 4 organization 5 collection 6 ban 7 publicity 8 supporter -can listen and read the text Total: 1 point Answers: 1 look after 4 sign up 2 carry on 5 join in 3 wipe out 6 find out |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 8 Food and drink |
Lesson 91 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Review language focus reference |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.C5 use feedback to set personal learning objectives 8.W3 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.4.5.1(8.R5) Deduce meaning from context in short texts and some extended texts on a growing range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.3.2.1(8.S2) Ask more complex questions to get information about a growing range of general topics and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Identify the meaning and details of the reading texts on familiar topics • Formulate and ask questions that are more complex to get information about the topic |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up
Fasten your seat belts and get ready for the all-round race Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they watch the news or read newspapers. Ask them what issues in the world they care about. Elicit some examples, such as climate change, animal experiments, etc. • Ask students what they can do to change situations. Elicit some ideas. Encourage students to join in and express their opinions; there are no right or wrong answers |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:102 • ask students to write the nouns from these verbs. Check their answers in pairs and write them individually. Ex: 2 P:102 • Ask students to complete the text with the verbs in the box. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes before you check with the class Summative assessment for the unit «Food and Drink» Reading Task 1. Read the text and answer the questions Write the correct letter. One restaurant is extra. You don’t need to use. Speaking Task 2. Discuss the questions in a class. Task 2. Discuss the questions in a class. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students write the nouns from these verbs Descriptor: - write the nouns Students’ own answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students to complete the text with the verbs Descriptor: - listen and read the text Students read the text and answer the questions Descriptor: - read the text Students discuss the questions |
-can write the nouns from these verbs Total: 1 point Answers: 1 meeting 2 donation 3 campaign 4 organization 5 collection 6 ban 7 publicity 8 supporter -can listen and read the text Total: 1 point Answers: 1 look after 4 sign up 2 carry on 5 join in 3 wipe out 6 find out |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
Lesson 92 |
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
School life: verbs |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.6.1 organise and present information clearly to others 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn verbs to do with school life. • Do a questionnaire on attitudes to school. • Learn the form and use of should and must. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to tell you something they like and something they dislike about their school. Encourage students to join in and contribute ideas. • Ask students what kind of things they do at school. Elicit ideas, and write the verbs on the board (for example, study, work, do homework, make friends).. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:104 • Students use their dictionaries to check the meaning of the words and expressions in the questionnaire. • Remind students to think carefully about using the infinitive form each time and to use this form in their table. • Encourage students to work individually, then compare answers in pairs. Then check as a class to ensure everyone has agreed on which column the words go in. • In a weaker class, ask students to put the words in new sentences to check understanding. In a stronger class, ask students to define the verbs. Ex: 2 P:104 • Students do the questionnaire. They can read the questions and options in pairs, but they should put answers that reflect their own ideas. • In a weaker class, encourage students to work out unfamiliar words from the context. • Ask students whether they agree with what the key says about them. • In a stronger class, you could ask students to prepare a short summary based on their answers to the questionnaire and the key. This could start, for example: I’ve got a good attitude to school because I get good marks and I make friends too, Ex: 3 P:104 • Read through the questions with the class and check understanding. If students find any of the questions difficult, ask if other students can offer a translation or explanation. • Allow students time to prepare their answers to the questions individually. • Put students in pairs to ask and answer the questions. Go round and listen as they are talking. Check they are using the present perfect correctly, and help with vocabulary. • Ask some students to report back to the class on their partner’s answers |
Students check the meaning of the words and phrases in blue. Then complete the table with the infinitive forms of the verbs. Descriptor: - complete the table with the infinitive forms of the verbs Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text.
Students work in pairs and do the questionnaire Descriptor: - do the questionnaire Students ask and answer the questions with a partner. Then compare their answers with the class. Descriptor: - Read the questions - answers to the questions individually |
-can understand the meaning of the words and phrases in blue Total: 1 point Answers: Positive: make friends, get good marks, pass exams, get a qualification Neutral: revise for a test, do your homework, take the exam, leave school Negative: play truant, cheat in exams, fail an exam, copy a friend’s work, get a bad mark, bully, suspend, expel -can read the questions Total: 1 point Answers: Students’ own answers. -can answers to the questions individually Total: 1 point Answers: Students’ own answers |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
9 The world of work |
Lesson 93 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Cheating |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read about cheating in exams. • Read for general meaning and specific information. • Learn some American English vocabulary. • Learn key phrases for agreeing and disagreeing |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
|
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, write the word cheat on the board and elicit the meaning. • Ask students to think about the different ways in which people can cheat. • Ask students to give their opinions on the topic of cheating. Try to elicit different ideas and encourage students to join in and give their opinions. • Ask students if they can guess what percentage of school students cheat in tests and exams. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:106 • In a weaker class, help students to read through the sentences. Explain that they should give their opinion, as there may be a difference between what different people would describe as cheating. • In a stronger class, students read the sentences and decide in pairs which of the things they think are cheating. • Ask some students to report back to the class on their discussions, and ask other students whether they agree. • Students read the text and identify which of the items are mentioned. Tell them to ignore the gaps at this stage. Ex: 2 P:106 • Explain to the class that five of the sentences a–f can be used to complete the gaps in the text. • Explain that students will need to read the text again more carefully to complete the gaps. They can work individually or in pairs. • When students listen to the text, encourage them to correct any mistakes they may have made. Ex: 3 P:106 • Explain to the class that there are many vocabulary differences between British and American English. Ask if students can think of any examples, such as chips / fries, pavement / sidewalk, etc. • Students find the American English words in the text. Ex: 4 P:106 • In a weaker class, ask for translations of the words in the box before students start the exercise. In a stronger class, ask students to define the words. • After students have matched the words, encourage them to record the words in sentences in their notebooks. |
Students read the text and tick the things that are mentioned. Descriptor: - read the sentences and decide in pairs which of the things they think are cheating. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the text again and complete the gaps. There is one sentence that you don’t need. Then listen to the text and check the answer. Descriptor: - read the text again more carefully to complete the gaps Students find the American English words in the text. Descriptor: - find the American English words in the text. Students match the British English words in the box with the American English words in the box. Descriptor: -translate the words in the box |
-can read the sentences Total: 1 point Answers: 1, 2, 4, 5 and 7 are cheating. 1, 2, 4 and 5 are mentioned in the text. -can complete the gaps Total: 1 point Answers: 1 b 2 a 3 e 4 f 5 c -can find the American English words in the text. Total: 1 point Answers: 1 grades 2 cell phones 3 principal -can translate the words in the box Total: 1 point Answers: 1 petrol 2 film 3 rubbish 4 motorway 5 shop 6 trousers 7 biscuit 8 pavement 9 lorry 10 sweet |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
Lesson 94 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: Have t;;;o and don't have to |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.3.3.1 give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.6.13.1 use a growing variety of modal forms for different functions: obligation, necessity, possibility, permission, requests, suggestions, prohibition on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: Learn the form and use of have to and don’t have to. • Practise using have to and don’t have to to talk about things that are necessary or not necessary. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Ask students to find a phrase in paragraph 2 in the text on page 50 meaning ‘it’s necessary to cheat’ (they have to cheat). Ask them to find a phrase in paragraph 5 on page 51 meaning ‘it isn’t necessary to cheat’ (they don’t have to cheat). • Ask students what other things it is necessary to do at school (for example, work hard, come to classes, wear a uniform). |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:107 • Refer students back to the text to complete the sentences, then ask them to study these and use their answers to help them complete the rules. Ex: 2 P:107 • Check students’ understanding of the word order in questions by asking them to write these individually. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes before you check with the class. • Explain that questions start with a negative auxiliary when we are asking for clarification. So for item 3 the speaker was surprised to see some students out of uniform. In a weaker class, explain that the speaker could have said, I thought they had to wear uniforms. In a stronger class, encourage students to think of alternative ways of clarifying the situations in items 3 and 4 to check they have understood the use of the negative auxiliary, don’t / doesn’t Ex: 3 P:107 • Allow students time to read through the list of things to do. • Explain that students are going to listen to an interview with a girl who is talking about what she has to and does not have to do. Students listen and tick the things that Laura has to do, then write sentences. • Let students listen to the CD twice, then ask them to compare their sentences in pairs. |
Students complete the sentences from the text. Then choose the correct words in the rules. Descriptor: - complete the rules. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students order the words to make questions Descriptor: - make questions compare their sentences in pairs. Students listen to a interview with Laura. Then write sentences with have to and don’t have to Descriptor: - listen and tick the things that Laura has to do |
-can complete the rules. Total: 1 point Answers: 1 have to 2 have to 3 don’t have to Rules 1 have to 2 don’t have to -can make questions Total: 1 point Answers: 1 Do we have to walk to school? 2 Does the teacher have to prepare lessons? 3 Don’t they have to wear a uniform? 4 Doesn’t Francis have to study? 5 Does he have to see the head teacher? 6 Do you have to go home? -can. listen and tick the things that Laura has to do Total: 1 point Answers: 1 ✓ Laura has to walk to school. 2 ✓ Laura has to wear a uniform. 3 Laura doesn’t have to eat at the canteen. 4 ✓ Laura has to do her homework before she goes out. 5 Laura doesn’t have to help make dinner every evening. 6 Laura doesn’t have to stay at home on school days. |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
Lesson 95 |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
School life: nouns |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.1.8.1 develop intercultural awareness through reading and discussion 8.2.2.1 understand with little or no support most specific information in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.3.3.1 give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn nouns relating to school life. • Listen to three teenagers talking about their schools. • Listen for general meaning and specific details. • Discuss opinions about different kinds of school. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students to say what kind of school they go to. Ask if there are other kinds of school in their country, and ask students to say what the differences are. • Ask what the advantages are of the school they go to, and also what the disadvantages are. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:108 • Ask students to read through the sentences and think about the meaning of the words in blue. • Read the table headings and check understanding. In a weaker class, do another example under each heading. • Once students have completed the table, check answers before students move on. • Students answer the questions with their own ideas. Go round and listen as they are working, and help as necessary Ex: 2 P:108 • Explain to students that they are going to listen to four people talking about school, and that they should identify which type of school each of them goes to. Ex: 3 P:108 • Explain that this exercise is designed to help students predict information. • Elicit ideas, but do not confirm or reject them at this stage. Students listen to the CD to check their answers. Ask round the class to find out how many answered.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the table with the words in blue. Then answer the questions with a partner Descriptor: - read the sentences - complete the table Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to four people Descriptor: - listen to four people talking about school Students look at the photos. Are the sentences true or false? Descriptor: - discuss about photos |
-can complete the table Total: 1 point Answers: Types of school: mixed school, single-sex school, state school, private school, primary school, secondary school, boarding school Other collocations: school-leaving age, school uniform, school rules, school holidays, school subjects, school-leaving exams Students’ own answers. -can talk about school Total: 1 point Answers: 1 boarding school 2 secondary 3 single-sex school school 4 state schoo -can discuss about photos Total: 1 point Answers: 1 True. 2 False. 3 True. |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work Lesson 96 |
School: |
||
|
Date: |
Teacher name: |
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Language focus: Should, must and have to |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.3.3.1 give an opinion at discourse level on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.6.13.1 use a growing variety of modal forms for different functions: obligation, necessity, possibility, permission, requests, suggestions, prohibition on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Learn the difference between should, must and have to. • Learn how to improve your English. • Practise using should, must and have to to make recommendations and talk about school |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Ask students to look back through the unit and find examples of should, must and have to. • Elicit some simple sentences and write them on the board. • Underline the verbs and ask students to translate the sentences into their own language. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:109 • Point out the difference in meaning between mustn’t and don’t have to. • After completing the table, students can compare answers in pairs before you check with the class. Then refer back to the warm-up examples on the board and ask students to classify them LANGUAGE NOTE Students
often confuse the meanings of mustn’t (= prohibition) and don’t
have to (= no obligation). Typical errors might be:
Ex: 2 P:109 • Encourage students to read through the whole text to get an idea of the context before they complete the activity. • Allow students time to choose the correct words before they listen to the CD and check their answers Ex: 3 P:109 • Refer students back to the table in exercise 1 to help them choose the correct verbs. • Ask students to compare their answers in pairs and correct any mistakes. • Hold a feedback session with the whole class to ensure students are making the correct distinctions in the use of the modals. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students complete the sentences from the listening with words in the box. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the text and choose the correct words Descriptor: - read the text - choose the correct words Students write true sentences using have to Descriptor: - write true sentences using have to |
Descriptor: - complete the table - ask students to classify them Total: 1 point -can choose the correct words Total: 1 point Answers: 1 don’t have to 2 mustn’t 3 must 4 don’t have to 5 should 6 have to 7 mustn’t 8 shouldn’t 9 must 10 have to -can write true sentences using have to Total: 1 point Answers: Students’ own answers |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work Lesson 97 |
|
||
|
Date: 03.05.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Asking for and giving advice |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.2.1.1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.5.3.1 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Listen to a dialogue in which people ask for and give advice. • Learn key phrases for asking for and giving advice. • Practise asking for and giving advice |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, write the word advice on the board and elicit the meaning. In a weaker class, ask students to translate the word into their own language if necessary. • Ask them when they ask for advice, and who they ask. • Ask students when they give advice and to whom. Elicit some ideas and encourage students to contribute. • Ask students what they would say in English to ask for advice or give someone advice. Elicit ideas, but do not confirm or reject any at this stage |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:110 • Refer students to the photo, and ask them to work in pairs to discuss what could be happening. • Elicit ideas, but do not confirm or deny them at this stage. Ex: 2 P:110 • Read the question with the class and elicit or explain that the first time students hear the recording, they should concentrate on getting the general meaning of the conversation, and three specific pieces of advice. Ex: 3 P:110 • Students work individually to complete the key phrases, then check their answers by listening to the CD. • You could ask students to find the key phrases in the dialogue and translate them into their own language. • Go round and listen as students practise the dialogue in pairs. Help with pronunciation as necessary Ex: 3 P:110 • Students work individually to match the sentences and responses. Remind them that there is one response they do not need. • In a weaker class, you could ask students to practise the sentences and responses in pairs. In a stronger class, encourage students to think of a context for each exchange. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the photo. What is Adam doing? Answers: Adam is reading a text message on his mobile Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to the dialogue. What three things does Lucy advise? Answers: Lucy advises Adam not to cheat, to tell his teacher, and to tell the boy what he thinks. Answers: 1 matter 2 should 3 do 4 for . 5 you Students complete the key phrases from the dialogue. Then listen and check. Answers: 1 d 2 b 3 g 4 c 5 e 6 a |
Descriptor: - discuss about the photo Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the question - answer the question Total: 1 point Descriptor: - complete the key phrases Total: 1 point 6 sure -can match sentences with responses Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
Lesson 98 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
An opinion essay |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.3.7.1 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.4.1.1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.5.1.1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Study a model opinion essay. • Learn key phrases for an opinion essay. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, ask students if they are in favour of school uniforms. Ask them to explain their answers. • Write the words opinion essay on the board. Elicit or explain that in an opinion essay, you give your own opinion and the reasons for your opinion, rather than arguing the advantages and disadvantages of something. |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:111 • After students have read the model text and answered the questions, check answers with the class. Point out that in an opinion essay you can use contractions. Ex: 2 P:111 • Read through the key phrases with the class and check understanding. Then check the answer to the question in the instructions Ex: 3 P:111 • Refer students back to the model text. In a weaker class, point out that we use the linkers at the beginning of a sentence and they are followed by a comma. In a stronger class, elicit this information. • Ask some students to read their paragraphs to the class and check that they have used the linkers correctly Ex: 3 P:110 • Students work individually to match the sentences and responses. Remind them that there is one response they do not need. • In a weaker class, you could ask students to practise the sentences and responses in pairs. In a stronger class, encourage students to think of a context for each exchange. Ex: 4 P:110 • Read the task with the class. • Students think and plan their essays individually. If some students are struggling to think of ideas, you could brainstorm some ideas about boarding schools with the whole class. • Students write their essays. This can be set for homework. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students read the model text and answer the questions Answers: 1 The writer gives four arguments in favour of school uniforms. 2 Paragraph 3. 3 School uniforms are compulsory at the writer’s school, but at most schools in the same area they are not. 4 They like to choose their own clothes. 5 Students’ own answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students study the key phrases Answers: All in all, … . / In conclusion, … Students look at sentences and choose the four best reasons for learning English. Then write a paragraph using the linkers in the box. Answers: Students’ own answers. |
Descriptor: - read the model text Total: 1 point Descriptor: - study the key phrases Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work individually - write a paragraph using the linkers in the box. |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
Lesson 99 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
My country. The world of work |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.W1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics 8.UE17 use if / unless/ if only in second conditional clauses and wish [that] clauses [present reference]; use a growing variety of relative clauses including why clauses on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Review and learn vocabulary related to jobs • Review how to use I wish and If only to talk about wishes and regrets |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • Ask students which jobs in Kazakhstan are the most popular, the best paid, the most interesting, and the most common. • Find out which jobs students think they would do, or which jobs members of their famiies do |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:112 • Look at the photos as a class and guess what the people’s jobs are. • Get students to talk about details in the photos that helped them guess, for example, Arslan’s white shirt and bow tie are typical of a waiter. • Play the CD for students to listen to the text. Students can follow the written text and check their answer Ex: 2 P:112 • Get students to read the sentences first and then play the CD. • Note that the answers are not in the order of the script and students will have to infer the answers from what each person says, for example, Arslan says ‘Maybe I’ll become a famous writer’ suggests he hasn’t decided what job he wants to do Ex: 3 P:112 • Ask students to find the three phrases in the texts and use them to work out the rules. Check students understand by giving them example sentences and asking them if they are correct, for example, ‘I wish I can speak English.’ • Explain that wishes can also be negative, for example, ‘I wish I didn’t have a test tomorrow.’ • Ensure students understand the meaning of the phrases using check questions, for example, ‘Does Arslan have as much free time as he wants?’ Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students look at the photos and match the people with three of the jobs below. Then listen and check your answers Descriptor: - read the model text and answer the questions Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen again. Match the people with the statement. Write A (Arslan), Z (Zhibek) or N (Nursultan) Descriptor: - match the people with the statement. Students study the phrases in blue in the text. Then choose the correct words to complete the rules. Descriptor: - work individually - complete the rules. |
-can read the model text and answer the questions Total: 1 point Answers: Arslan – waiter, Zhibek – artist, Nursultan – doctor -can match the people with the statement. Total: 1 point Answers: 1 Zhibek 2 Arslan 3 Arslan 4 Nursultan 5 Zhibek -can complete the rules. Answers: 1 present, were 2 present or future, if not |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
Lesson 100 |
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: 11.05.23 |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
CLIL History: Child labour in Victorian Britain. Summative Assessment for the unit “The world of work” |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.R1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.W1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a text about the school community. \ • Discuss students’ rights and responsibilities in the classroom. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, write the word community on the board and elicit or explain the meaning (a group of people who have something in common and feel that they belong together). • Ask students what different types of community there are (a town / village community, a work community, a religious community, clubs, organizations, etc). Ask students if they think their school is a community |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:113 • Read through the headings with the class and make sure that students understand them. In a weaker class, students can translate the headings. In a stronger class, encourage students to define the headings in English. • Students read the text and match the headings with the paragraphs. Point out to students that they should read the text quickly at this stage, and not worry if they do not understand every word. • Do not check answers at this stage. Ex: 2 P:113 • Students listen and read the text, and check their answers to exercise 1 Summative Assessment for the unit “The world of work” Listening Task 1. Listen to the description of the jobs and complete the chart. Write what the job is and the key words that help you to guess what it is. CD2. Tapescript 4. And transcript for listening task can be found after the rubrics. Writing Task 2. Think about ONE job. Write the description of the job without naming what the job is. Describe the place where the person works, qualities or skills that are required for the job. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students check the meaning of the words in the table. Then write the missing words. Answers: Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students listen to the text and check your answers. Answers: Paragraph 1 d Paragraph 2 a Paragraph 3 b Paragraph 4 e Paragraph 5 c Students listen to the description of the jobs and complete the chart Answers: Students write the description of the job without naming what the job is Answers: |
-can match the headings with the paragraphs Total: 1 point Descriptor: - read the text - check your answers. Total: 1 point -can complete the chart Total: 8 point Descriptor: - complete the chart Total: 5 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work Lesson 101 |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Project. A survey. A survey about career choices |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.R1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.W1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: • Read a survey about school life. • Write a survey about school life. |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In • With books closed, write the word community on the board and elicit or explain the meaning (a group of people who have something in common and feel that they belong together). • Ask students what different types of community there are (a town / village community, a work community, a religious community, clubs, organizations, etc). Ask students if they think their school is a community |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:115 • Students read the survey and answer the questions, then compare their answers with the results in the survey Ex: 2 P:115 • Students read and follow the steps in the project checklist. • They could work individually for this task. Read through the task and explain that they need to think of four potential answers for each one. They should model this on the survey above, by reflecting a range of opinions in the answers. • Alternatively, students could work in pairs or small groups. Encourage all students to work cooperatively and say that each one should make suggestions for the options in the survey. • Suggest that students take turns to write down the questions and options. Weaker students can be supported by stronger ones, who can help with accuracy. • Go round and help as students are working. Encourage them to follow the points in the checklist to help them structure their work. • Set aside time in class for students to carry out their surveys. They can write up the results and summary for homework Ex: 3 P:115 • In the following lesson, ask students to present their surveys, and discuss the findings as a class. • Ask students to assess how well they feel they performed the task, whether as individuals or in groups. • Ask if they would change their approach if they had to do another survey in the future. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students read the survey and questions. Are your answers the same as the most popular ones? Answers: Students’ own answers. Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students write a survey about school life. Follow the steps in the project Answers: Students’ own answers. Students exchange your survey with the rest of the class. Answers: Students’ own answers. |
Descriptor: - read the survey - answer the questions Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work individually - write a survey about school life Total: 1 point Descriptor: - exchange your survey Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Vocabulary Bank/ Compound Nouns/ Waste |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.L1 understand with little or no support the main points in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics 8.W3 write with moderate grammatical accuracy on a limited range of familiar general and curricular topics 8.UE13 use a growing variety of modal forms for different functions: obligation, necessity, possibility, permission, requests, suggestions, prohibition on a range of familiar general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: -recount and interpret the main points of the listening -proofread and edit own and others’ writing for grammar |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In
|
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:116 • Read the instructions with the class and make seven more compound nouns with words from A and B • Students work in pairs to make as many compound nouns as possible. Then they read the text and compare it with their lists. • Check answers and expand the list with any more compound nouns from the text Ex: 2 P:116 • Ask students to complete the task individually,then label the photos using compound nouns. • Elicit answers from the class, and encourage students to discuss any differences of opinion. Ex: 3 P:116 • In the following lesson, ask students to label the photos with the words in the box. • Ask students to assess how well they feel they performed the task, whether as individuals or in groups. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students make seven more compound nouns with words from A and B Answers: 1 art gallery 2 shopping basket 3 pencil case 4 tennis racket 5 video camera 6 paper clip 7 water bottle 8 chocolate cake Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students label the photos using compound nouns Answers: 2 key ring 3 birthday card 4 train station 5 football stadium 6 door handle 7 letter box Students label the photos with the words in the box Answers: 1 litter bin 2 waste-paper basket 3 skip 4 landfill tip 5 refuse sack 6 dustbins 7 recycling centre |
Descriptor: -make seven more compound nouns Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work individually - label the photos using compound nouns Total: 1 point Descriptor: - label the photos with the words Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
|
||
|
Teacher’s name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Prefixes and suffixes |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.S7 use appropriate subject-specific vocabulary and syntax to talk about a range of general topics, and some curricular topics 8.R1 understand the main points in texts on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.W1 plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a range of general and curricular topics |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - explain the topical word by giving definition/synonym - identify the central idea, the intended audience and the author’s purpose |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In
|
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Ex: 1 P:117 • Allow students time to compare their answers in pairs before you check with the class. Discuss what helped students make their choices. Ask students to choose the correct prefixes and suffixes Ex: 2 P:117 • Ask students to complete the task individually, then add prefixes and suffixes to the words in the box. • Students study the examples in pairs and complete the words. • Check answers with the class Ex: 3 P:117 • Students match the words in the box with the photos. Allow students to use their dictionaries if necessary. • Check answers with the class. • In the following lesson, ask students to label the photos with the words in the box.
Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students choose the correct prefixes and suffixes Answers: 1 peaceful 2 unfriendly 3 understandable 4 homeless 5 wonderful 6 unhappy 7 childless 8 noticeable Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students add prefixes and suffixes to the words in the box Answers: 1 endless 2 playful 3 breakable 4 unusual 5 drinkable 6 lifeless 7 unlucky 8 spiteful Students match the words in the box with the photos Answers: 2 microphone 3 recording studio 4 drums 5 amplifier 6 speakers 7 trumpet 8 bass guitar |
Descriptor: - choose the correct prefixes and suffixes Total: 1 point Descriptor: - work individually Total: 1 point Descriptor: - match the words Total: 1 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|
Short term plan: term 4
|
Unit 9 The world of work |
|
||
|
Teacher name: |
|
||
|
Date: |
|
||
|
Grade: 8 |
Number present: |
absent: |
|
|
Lesson title |
Summative Assessment for the 4th term |
||
|
Learning objectives
|
8.2.4.1 (8.L5) Recognise the opinion of the speaker(s) with little or no support in extended talk on a wide range of general and curricular topics. 8.4.6.1(8.R6) Recognise the attitude or opinion of the writer on a growing range of unfamiliar general and curricular topics, including some extended texts 8.5.1.1(8.W1) Plan, write, edit and proofread work at text level with little support on a growing range of general and curricular topics. 8.3.5.1(8.S5) Interact with peers to negotiate, agree and organise priorities and plans for completing classroom tasks. |
||
|
Lesson objectives |
Learners will be able to: - explain the topical word by giving definition/synonym - identify the central idea, the intended audience and the author’s purpose |
||
|
Plan |
|||
|
Stages / Time |
Teachers’ actions |
Students’ actions |
Assessment criteria |
Resources |
|
Beginning of the lesson 5 min |
Organization moment 1.Greeting. Ask about the weather. The teacher sets the lesson objectives, letting students know what to anticipate from the lesson. Warm-up Method speaking phone was used to develop speaking skills.
Lead – In |
Students' attention is drawn to the lesson. Students discuss the pictures in pairs. Determines the topic and aim of the lesson Students say different words from the picture |
Formative Assessment
Good job! Assessment criteria -Identify detailed information in extended conversation with support |
Pictures Student’s book |
|
Middle of the lesson Presentation part. 35 min |
Listening Task. You will hear a radio interview with a famous cardiologist. Decide whether the statements are TRUE or FALSE. Transcript for listening task can be found after the mark scheme. Example: Heart attacks are more common now than they were in the past. True Listen and complete the sentences with NO MORE THAN TWO words. Example: Dr. Shaw gives some advice on how to keep our hearts in good condition. Reading Task. Read the text about Kenneth. Mark the sentences TRUE or FALSE according to the context. Writing Task. Choose ONE of the topics to write. Topic 1. Write an essay about the following topic: Nowadays food has become easier to prepare. Has this change improved the way people live? Give reasons for your answer using your own ideas Topic 2. Write an essay about the following topic: Doctors, nurses and teachers make a great contribution to society and should be paid more than entertainment and sports celebrities. Do you agree or disagree? Give reasons for your answer using your own ideas SPEAKING Task. Work in pairs. Choose one of the cards and answer the questions. You have 1 minute to prepare and 3 minutes to speak. Conclusion during the lesson some tasks differentiated by outcomes of the students and by their abilities. |
Students listen and complete the sentences Answers: Differentiation: «Verbal support» method is used to help Students use new words in the text. Students read the text about Kenneth Answers: Students write an essay Answers: Students work in pairs. choose one of the cards and answer the questions Answers: |
Descriptor: - decide whether the statements are TRUE or FALSE Total: 6 point Descriptor: - work individually - read the text about Kenneth Total: 6 point Descriptor: - write an essay about the following topic Total: 6 point Descriptor: choose one of the cards and answer the questions Total: 6 point |
Cards Worksheets |
|
End of the lesson 5 min |
FEEDBACK Learners provide feedback on what they have learned at the lesson. |
|
Students evaluate each other and encourage classmate with phrases like: Well done! Brilliant! Good job! I like it! . |
Poster
|

шағым қалдыра аласыз