ГУ « Зангарская СОШ»
Biology
Class 8
Topic: Structure and function of the skin
Tuimebaeva Altynay Turakulovna
Pavlodar.2019
|
Class 8 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Topic: Structure and function of the skin |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson aim is to study structure and functions of skin Tasks: Educational: to generate knowledge in schoolchildren about the structure and functions of the skin: epidermis, dermis, hypodermis; Sweat, sebaceous glands, skin vessels, its receptors, their functions; Give an idea of the types of skin: oily, dry, normal, teach how to properly care for the skin, Developing: develop intellectual abilities, logical thinking, speech, attention and memory; formulate methods of generalization and analysis, highlighting the main. Educational: the formation of a careful attitude towards one's health through the realization of scientifically grounded negative influence of harmful habits of man on the structure and functioning of the skin |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Expected results: should know: the structure of the skin, the appendages of the skin and its types understand: the barrier role of skin and care for it to be able: to use the acquired knowledge in life and at home |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Teacher activity |
The activities of students |
Graphially |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
10 min |
I. Organizational - motivational stage. 1) Greetings. Teacher: Hello guys, before you are cards with greetings in different languages. Let us read and add our greetings in other languages.
2) Psychological mood of students.We all want to catch a "goldfish" that would fulfill all our desires. I'll ask everyone to go to the aquarium and catch their "goldfish". Make a wish for today's lesson. Now try to make from small fish one huge goldfish. And let all the desires that you have made will come true. And with the help of this "goldfish" to us in the lesson will be accompanied by luck and success! 3)Аctualization knowledge. BrainstormTranslate the term "skin" into Kazakh The problematic question: Why do you think the skin is called the mirror of our body? In order to answer this question correctly, what do you think is the theme of our lesson? Let's form the purpose of the lesson. I suggest you find yourself and paint the little man on the tree in orange: Where are you on this topic at this stage (find yourself). |
Students comprehend the goal. Children are called greetings in other languages.
Students make wishes for the lesson and Glue small fish that serve as scales
Students respond to teacher questions and form the purpose of the lesson
|
Cards
Aquarium, fish from cardboard
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
25 min
|
II Operationally - executive stage. 1) The new material study. Glossary of essential terms for you know [1].
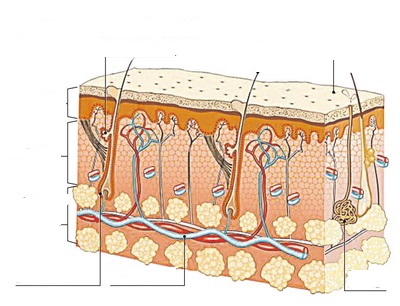
The division of class into groups, using a mosaic (the image of a bird and a frog). 1 st group: skin structure (work with text 2nd group-function of the skin (work with text) Text. Skin is the integument of the human body. The area of the skin of an adult is 1.5–1.6 m2. Skin consists of three layers: 1. Epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin composed of squamous cells. This layer is characterized into two distinct types: thick skin and thin skin. 2. Dermis is the thickest layer of skin that lies beneath and supports the epidermis. 3. Hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue) lowermost layer of the body integument that helps to insulate the body and cushion internal organs. Other components of the skin are hair, nails, sweat glands, oil glands, blood vessels, lymph vessels, nerves and muscles. The epidermis is formed by epithelial tissue. Its thickness is 0.07–2.5 mm. The outer layer of the epidermis is the stratum corneum (keratinocytes), the internal one is the basal layer (consists of basal cells and melanocytes). The stratum corneum consists of dead cells. Basal layer is below the stratum corneum. It consists of living cells. These cells constantly divide to produce new cells that are pushed upward to the layers above. Basal cells become new keratinocytes, which replace the older ones that die and are shed. Within the basal layer are melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanin is a pigment that helps to protect the skin from harmful ultraviolet solar radiation. The epidermis has sensory nerve terminals (receptors). Derivatives of stratum corneum are nails. The dermis is the thickest layer of skin (0.5 to 5 mm). There are papillary and reticular layers in the dermis. The papillary layer consists of loose fibrous connective tissue and form protrusions into the epidermis. It contains blood and lymph vessels, receptors, fibers that give strength and elasticity to the skin. Under the papillary layer is a reticular layer. It contains sebaceous (oil) glands, sweat glands, hair follicles. Sweat glands regulate body temperature by transporting water to the skin’s surface where it can evaporate to cool down the skin. Such gland consists of a body and excretory duct which opens on the surface of the skin. The human organism have 2–3 million sweat glands. A lot of them are on the face and hands. Sweat glands secrete sweat. Sweat contains H2O, ammonia, urea, mineral salts. Sebaceous (oil) glands secret oil that helps to waterproof the skin and protect it against microbes. They are attached to hair follicles. Hairs are derivatives of skin. A hair consists of a hair bulb, root and stem. Hair follicles are tube-shaped cavities that enclose the hair root and providenourishment to the hair. Vessels and nerves enters the hair follicle. Muscles attached to the hair follicle raises the hair. The hypodermis is composed of fat and loose connective tissues; this layer of the skin insulates the body and cushions and protects internal organs from injury. Functions of the skin: ‒ protection of the organism from the harmful mechanical, chemical, microbiological external factors; ‒ thermoregulation; ‒ metabolic (involved in metabolism of vitamin D, urea, water and salt balance); ‒ it is the organ responsible for the sense of touch (due to tactile, thermal and pain receptors)[2]. Creating a poster and its protection. The roles are distributed in the group; the rules of work in the group are repeated. Group rating: 2 star reception, 1 wish Distribute roles in a group (card) reader reads aloud; secretary - records something on behalf of the group; the speaker at the blackboard tells what the band has decided; scheduler-examines the conditions of the task and plans work; Time-speaker - keeps track of time. Rules of work in a group (card) Be active. Listen to a friend without interrupting. Speak calmly and clearly; Speak only on business; speak in turn; react with gestures and signs; objecting or agreeing, look at the speaker; make sure everyone participates in the conversation; turn to a friend by name Relate the terms (work in pairs)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
5 min |
Fixing material. Writing the skin structure in three languages (Russian, English, Kazakh)[3].
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
5 min . |
Reflection Feedback
|
sticker |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Список литературы
1. Воеводина О.С., Нестерова О.Ю., Садыкова А.Р. English for Biotechnologists and Biologists (Английский язык для биотехнологов и биологов) /учебное пособие. — Ижевск: Удмуртский государственный университет, 2012. —с. 375
2. Биология для слушателей подготовительного отделения иностранных учащихся обуч. на англ. яз. = Biology for English studying international students of preparatory department : учеб.-метод. пособие / В. Э. Бутвиловский [идр.]. – Минск : БГМУ, 2016. – 164 с
3.Биология = Biology : практикум для слушателей подготовительного отделения иностранных учащихся, обучающихся на английском языке / В. Э. Бутвиловский [и др.]. – Минск : БГМУ, 2016. – 132 с
5
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
Topic: Structure and function of the skin
Topic: Structure and function of the skin
ГУ « Зангарская СОШ»
Biology
Class 8
Topic: Structure and function of the skin
Tuimebaeva Altynay Turakulovna
Pavlodar.2019
|
Class 8 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Topic: Structure and function of the skin |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lesson aim is to study structure and functions of skin Tasks: Educational: to generate knowledge in schoolchildren about the structure and functions of the skin: epidermis, dermis, hypodermis; Sweat, sebaceous glands, skin vessels, its receptors, their functions; Give an idea of the types of skin: oily, dry, normal, teach how to properly care for the skin, Developing: develop intellectual abilities, logical thinking, speech, attention and memory; formulate methods of generalization and analysis, highlighting the main. Educational: the formation of a careful attitude towards one's health through the realization of scientifically grounded negative influence of harmful habits of man on the structure and functioning of the skin |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Expected results: should know: the structure of the skin, the appendages of the skin and its types understand: the barrier role of skin and care for it to be able: to use the acquired knowledge in life and at home |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Teacher activity |
The activities of students |
Graphially |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
10 min |
I. Organizational - motivational stage. 1) Greetings. Teacher: Hello guys, before you are cards with greetings in different languages. Let us read and add our greetings in other languages.
2) Psychological mood of students.We all want to catch a "goldfish" that would fulfill all our desires. I'll ask everyone to go to the aquarium and catch their "goldfish". Make a wish for today's lesson. Now try to make from small fish one huge goldfish. And let all the desires that you have made will come true. And with the help of this "goldfish" to us in the lesson will be accompanied by luck and success! 3)Аctualization knowledge. BrainstormTranslate the term "skin" into Kazakh The problematic question: Why do you think the skin is called the mirror of our body? In order to answer this question correctly, what do you think is the theme of our lesson? Let's form the purpose of the lesson. I suggest you find yourself and paint the little man on the tree in orange: Where are you on this topic at this stage (find yourself). |
Students comprehend the goal. Children are called greetings in other languages.
Students make wishes for the lesson and Glue small fish that serve as scales
Students respond to teacher questions and form the purpose of the lesson
|
Cards
Aquarium, fish from cardboard
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
25 min
|
II Operationally - executive stage. 1) The new material study. Glossary of essential terms for you know [1].
The division of class into groups, using a mosaic (the image of a bird and a frog). 1 st group: skin structure (work with text 2nd group-function of the skin (work with text) Text. Skin is the integument of the human body. The area of the skin of an adult is 1.5–1.6 m2. Skin consists of three layers: 1. Epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin composed of squamous cells. This layer is characterized into two distinct types: thick skin and thin skin. 2. Dermis is the thickest layer of skin that lies beneath and supports the epidermis. 3. Hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue) lowermost layer of the body integument that helps to insulate the body and cushion internal organs. Other components of the skin are hair, nails, sweat glands, oil glands, blood vessels, lymph vessels, nerves and muscles. The epidermis is formed by epithelial tissue. Its thickness is 0.07–2.5 mm. The outer layer of the epidermis is the stratum corneum (keratinocytes), the internal one is the basal layer (consists of basal cells and melanocytes). The stratum corneum consists of dead cells. Basal layer is below the stratum corneum. It consists of living cells. These cells constantly divide to produce new cells that are pushed upward to the layers above. Basal cells become new keratinocytes, which replace the older ones that die and are shed. Within the basal layer are melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanin is a pigment that helps to protect the skin from harmful ultraviolet solar radiation. The epidermis has sensory nerve terminals (receptors). Derivatives of stratum corneum are nails. The dermis is the thickest layer of skin (0.5 to 5 mm). There are papillary and reticular layers in the dermis. The papillary layer consists of loose fibrous connective tissue and form protrusions into the epidermis. It contains blood and lymph vessels, receptors, fibers that give strength and elasticity to the skin. Under the papillary layer is a reticular layer. It contains sebaceous (oil) glands, sweat glands, hair follicles. Sweat glands regulate body temperature by transporting water to the skin’s surface where it can evaporate to cool down the skin. Such gland consists of a body and excretory duct which opens on the surface of the skin. The human organism have 2–3 million sweat glands. A lot of them are on the face and hands. Sweat glands secrete sweat. Sweat contains H2O, ammonia, urea, mineral salts. Sebaceous (oil) glands secret oil that helps to waterproof the skin and protect it against microbes. They are attached to hair follicles. Hairs are derivatives of skin. A hair consists of a hair bulb, root and stem. Hair follicles are tube-shaped cavities that enclose the hair root and providenourishment to the hair. Vessels and nerves enters the hair follicle. Muscles attached to the hair follicle raises the hair. The hypodermis is composed of fat and loose connective tissues; this layer of the skin insulates the body and cushions and protects internal organs from injury. Functions of the skin: ‒ protection of the organism from the harmful mechanical, chemical, microbiological external factors; ‒ thermoregulation; ‒ metabolic (involved in metabolism of vitamin D, urea, water and salt balance); ‒ it is the organ responsible for the sense of touch (due to tactile, thermal and pain receptors)[2]. Creating a poster and its protection. The roles are distributed in the group; the rules of work in the group are repeated. Group rating: 2 star reception, 1 wish Distribute roles in a group (card) reader reads aloud; secretary - records something on behalf of the group; the speaker at the blackboard tells what the band has decided; scheduler-examines the conditions of the task and plans work; Time-speaker - keeps track of time. Rules of work in a group (card) Be active. Listen to a friend without interrupting. Speak calmly and clearly; Speak only on business; speak in turn; react with gestures and signs; objecting or agreeing, look at the speaker; make sure everyone participates in the conversation; turn to a friend by name Relate the terms (work in pairs)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
5 min |
Fixing material. Writing the skin structure in three languages (Russian, English, Kazakh)[3].
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
5 min . |
Reflection Feedback
|
sticker |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Список литературы
1. Воеводина О.С., Нестерова О.Ю., Садыкова А.Р. English for Biotechnologists and Biologists (Английский язык для биотехнологов и биологов) /учебное пособие. — Ижевск: Удмуртский государственный университет, 2012. —с. 375
2. Биология для слушателей подготовительного отделения иностранных учащихся обуч. на англ. яз. = Biology for English studying international students of preparatory department : учеб.-метод. пособие / В. Э. Бутвиловский [идр.]. – Минск : БГМУ, 2016. – 164 с
3.Биология = Biology : практикум для слушателей подготовительного отделения иностранных учащихся, обучающихся на английском языке / В. Э. Бутвиловский [и др.]. – Минск : БГМУ, 2016. – 132 с
5

шағым қалдыра аласыз