
ЗЕРТТЕУ ЖҰМЫСЫНЫҢ ТАҚЫРЫБЫ:
Crab sticks - ways of making, benefits and harms
Секция: ағылшын тілі, ағылшын тілі
Тақырыбы: «Crab sticks - ways of making, benefits and harms»
«Краб таяқшаларының пайдасы мен зияны»
Оқушының толық аты:
Сынып:
Жетекшісі:
АННОТАЦИЯ
Краб таяқшалары - сурими балықтарының филесінен жасалған балық өнімі. Пішіні мен түсі бойынша таяқшалар краб етіне ұқсайды, сондықтанда атауы осыдан шыққан. Краб таяқшаларында краб еті жоқ ол тек сурими атты ақ мұхиттық балықтардың ұнтақталған филесінен ақуызды өңдеу арқылы алынады. Құрамына су, май, крахмал, жұмыртқа ақтығы, қант және тұз кіреді. Краб таяқшаларды жасау идеясы Жапониядан келді. Қазір краб таяқшалары бүкіл әлемде шығарылады, оларды шикі жеуге, салаттар мен тағамдарға қосуға болады. Краб таяқшалары - бұл қол жетімді және кең таралған өнім, кез-келген тоңазытқышта бар. Краб таяқшалары - жеуге дайын өнім, ұзын тіктөртбұрышты немесе ақ түсті цилиндрлі, жоғарғы бөлігі крабтың түсіне ұқсайтын қызғылт сары немесе қызыл түске боялған. Әрбір таяқшада жұқа полиэтиленнен жасалған жеке мөлдір қаптама бар. Краб таяқшалары жұқа қабаттардан тұрады, олар ораммен тығыз оралған, оны кескенде айқын көруге болады. Өнім серпімді құрылымға ие, дәмі мен иісі бойынша шаянтәрізділерге жақын.
АННОТАЦИЯ
Крабовые палочки — рыбий продукт из филе сурими рыбы. Получил свое обманчивое такое название засчет формы и цвета палочки, которая напоминает клешню краба. Палочки получаются путем обработки белков из филе белых океанических рыб и не содержат мяса. В состав также входит вода, масло, крахмал, яичный белок, сахар и соль. Идея создания палочек позрадилась в Японии. Сейчас палочки производятся во всем мире, их можно есть сырыми, добавлять в салаты и закуски. Крабовые палочки являются доступным и распространённым продуктом, практически в каждом холодильнике найдётся упаковка, приобретённая «на всякий случай». Крабовые палочки – это готовые к употреблению полностью продукты, представляющие собой длинные прямоугольники или цилиндры белого цвета, верхняя часть окрашена в оранжевый или красный цвет, имитирующий окраску краба. Каждая палочка имеет индивидуальную прозрачную упаковку из тонкого полиэтилена. На срезе это отчётливо видно крабовые палочки состоят из тонких пластов, туго свёрнутых рулетом. Продукт имеет упругую структуру, по вкусу и запаху близок к ракообразным.
ANNOTATION
Crab sticks are a fish product made from minced fish surimi. In shape and color, the sticks vaguely resemble a crab claw for which they received their deceptive name. The sticks do not contain crab meat at all and are obtained by processing protein from minced surimi — fillet of white oceanic fish. The composition also includes water, oil, starch, egg white, sugar and salt. The idea of creating sticks came from Japan. Now chopsticks are produced all over the world, they can be eaten raw, added to salads and snacks. Crab sticks are an affordable and common product, almost every refrigerator has a package purchased "just in case". Crab sticks are a completely ready–to-use product, they are long rectangles or cylinders of white color, the upper part is painted orange or red, imitating the color of a crab. Each stick has an individual transparent packaging made of thin polyethylene. Crab sticks consist of thin layers tightly rolled into a roll, this is clearly visible on the slice. The product has an elastic structure, tastes and smells close to crustaceans.
CONTENT OF THE SCIENTIFIC PROJECT
I. INTRODUCTION..............................................................................................
II. MAIN PART.....................................................................................................
2.1. Ways of making crab sticks
2.2. The emergence of interest in crab sticks
2.3. Calorie content and composition
2.4. Benefits and harms of crab sticks
2.5. Downsides and risks of crab sticks
2.6. Crab sticks in the diet
III. PRACTICAL PART.......................................................................................
3.1. Do students know about the benefits and harms of crab sticks?
3.2. Cooking crab sticks at home
IV. Conclusion........................................................................................................
LIST OF LITERATURE .....................................................................................
І. КІРІСПЕ
This crab stand-in has become popular over the past few decades and is commonly found in seafood salad, crab cakes, California sushi rolls and crab rangoons.
In short, imitation crab is processed fish meat — in fact, it’s sometimes called “the hot dog of the sea.” However, some people may still wonder what it’s made from and whether it’s healthy.
Purpose of the project: to determine the benefits and harms of crab sticks
Relevance of the chosen topic: Сrab sticks are known all over the world. Do people know what crab sticks are made of and their benefits to the body or harms?
Object of research: Crab sticks
Hypothesis: How healthful and harmful are crab sticks?
Responsibilities:
1. To analyze data from books and other information sources;
2. To make a plan for researching my topic;
3. To ask what our school students know about crab sticks;
4. To make a conclusion on the research topic.
Research methods:
1. To study special literature;
2. To watch videos;
3. To conduct a survey;
4. To analyze received data;
5. Generalization.
II. MAIN PART.
2.1.Ways of making crab sticks
Crab sticks! In fact, the product is not made from crab meat, but from minced fish. Therefore, they differ from natural crab meat in the same way as an artificial flower from a real one. Crab sticks are a fish product made from minced fish surimi.
One of the main ingredients of quality sticks is minced fish (surimi). Its recipe was invented in Japan in the 12th century. The inhabitants of the island noticed that the mass obtained from ground and squeezed out of the water fish has good taste, various figures can be molded from this mass to decorate the dish.
Japanese people failed to export surimi and products made from it for a long time. Americans and Europeans were not willing to buy the product. This continued until the Japanese technologists dyed the product with food coloring, applied a red stripe to them, after which the “imitation crab meat” product went on sale. In such packaging, they quickly flooded not only European and American markets, but became popular all over the world.


Minced fish for crab sticks is made from fish fillets that live in the ocean. It can be pollock, hake, herring or mackerel. The meat is minced and washed many times with water. Then the mass is placed in a centrifuge to remove excess water. The result is an almost tasteless mixture that the Japanese love, but residents of other countries do not. Therefore, minced fish had to be seasoned with salt, sugar, flavorings, and in order for the product to be well stored, preservatives were also added. Then apply a red stripe with food coloring and the product is ready for use.

Crab sticks are low-calorie foods. It will not be difficult to independently determine the calorie content of one stick - according to the same instructions on the pack.
Surimi was invented by the Japanese in order not to throw away food waste. According to historians, minced fish mixed with starch has been known in the land of the Rising Sun for more than 900 years. The first surviving mention of Japanese products from Surimi dates back to 1115.
Starting from the XIV century. in Japan, the kamaboko dish is eaten. For him, minced white fish with the addition of several more ingredients, primarily affecting the texture of the final mass, is turned into tortillas and usually steamed. Usually kamaboko is served on New Year's Eve. There is also a tikuva dish. For him, surimi is mixed with starch and egg white, forming an even rectangular layer. Then the mass is wrapped around a thick skewer or a special pin (in production), and then fried over an open fire or steamed to obtain a kind of hollow tube. A hearty dish is sold at street fairs. It is also called "tikuwa-kamaboko", often cut along the entire length and stuffed with various fillings.
Surimi was very popular with the Japanese, but up to a certain point it was not an affordable product for everyone. Everything changed after the end of the Second World War, when new cooling and freezing technologies appeared. This allowed the start of pollock fishing in the North Pacific Ocean – the raw material for surimi. Thanks to this, another variety of kamakobo began to develop – kani-kamaboko, abbreviated "Kanikama" (Kanikama). These are the crab sticks familiar to us all. It was under this name in 1973 that they were first produced by the Japanese company Sugiyo.

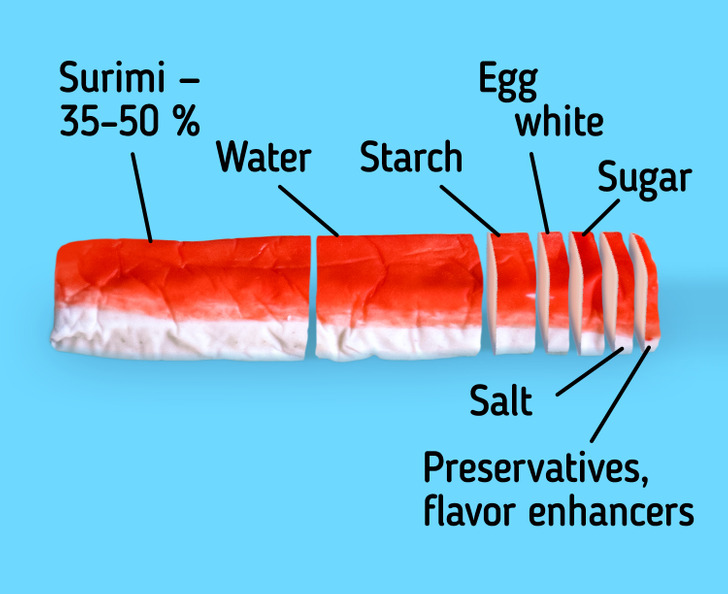
Additional ingredients for cooking crab sticks is minced fish usually makes up 35-50% of the total weight of the product, sometimes slightly above 50%.Other main ingredients of imitation crab meat:
-
Water. As a rule, this is the second most popular ingredient in crab sticks. Water is necessary to obtain the correct texture of the product.
-
Starch. Potato, corn starch or tapioca starch are often used to harden surimi and make it suitable for freezing. If you found sticky or excessively soft crab sticks on sale, it means that the product was stored incorrectly (re-frozen) or saved on starch.
-
Protein. Most often, egg white (albumin) is found in crab sticks. It improves the texture of crab sticks, their color and shine.
-
Sugar and sorbitol. These ingredients help the product withstand freezing and defrosting, plus they add a little sweetness to it.
-
Vegetable oil. Sunflower, soy or other vegetable oils are used to improve the structure, white color and increase the shelf life.
-
Salt (sodium chloride). Affects the overall taste of the product. It also participates in chemical processes, as a result of which a kind of gel is formed, forming the texture of crab sticks.
Additives included in the composition of crab sticks include:
-
Gum. The thickener and emulsifier helps the ingredients stick together, is included in the formulation to stabilize the product. Carrageenan (a natural gelling agent obtained by processing red seaweed, E407) and the polysaccharide xanthan gum (E415) can be used.
-
Red dyes. The most commonly used carmine (E120) is a red dye that is obtained from carminic acid. It is produced by females of tiny beetles called cochineal. Carmine, which gave its name to the shade of red-purple of the same name, is used, for example, for coloring different types of sausage products.
-
Glutamates. Sodium glutamate (E621) and a similar compound, sodium inosinate (E631), serve as flavor enhancers – to identify the taste of umami.
-
Flavors. Some manufacturers use real crab extract, artificial crab flavors and mirin, fermented rice wine.
-
Preservatives. To increase the shelf life, sodium benzoate (E211) and several phosphate-based additives (E339-342 or E450-452) are regularly used. Some studies show that excessive consumption of foods with added phosphates can lead to a violation
2.2. The emergence of interest in crab sticks
In life, only a small part of people has the opportunity to eat natural delicacies. Perhaps that is why the appearance in the late nineties of the last century in the sale of crab sticks was a real sensation. They aroused great interest and instantly disappeared from the shelves of stores. This was also facilitated by the unrealistically low price of the product. Surprised customers bought fragrant pieces by the kilos and even came up with hundreds of different dishes from them. Therefore, the harm and benefits of crab sticks interested everyone who was happy to join the league of seafood lovers. In fairness, it is worth noting that apart from the name, this product has nothing more to do with crabs. Marine life has become a kind of bait or, rather, a marketing ploy of enterprising manufacturers. Why spend a lot of money to purchase live arthropods, if you can create an imitation of the product and successfully sell it on the market? Everything was simple and mutually beneficial: the buyer received a product similar to the one he dreamed of, and the manufacturer.
A little later, people began to study more closely what is written on the labels, and various questions appeared. Many were surprised to discover an unusual composition and were perplexed about the presence of some components. The basis of the product was the mysterious ingredient "surimi". Translated from Japanese, it means "minced meat". There are no secrets here. Surimi is really a minced meat made from the meat of various white fish. These are mainly herring, pollock, mackerel, whiting, hake and other representatives of the ocean expanses. The Japanese have been using this compound for more than ten centuries. and there is no doubt about it. However, the unusual way of cooking is still very interesting. The product has a fishy smell, an exceptionally white color and a slightly noticeable characteristic aroma. So, the nutritional value of crab sticks is of great interest.
2.3. Calorie content and composition
![]() Crab sticks are considered to
be a low-calorie food, containing only 95 calories per 100g
serving. The average serving size of crab sticks per person is 3 oz
or 85g. Therefore, one average serving size of crab sticks provides
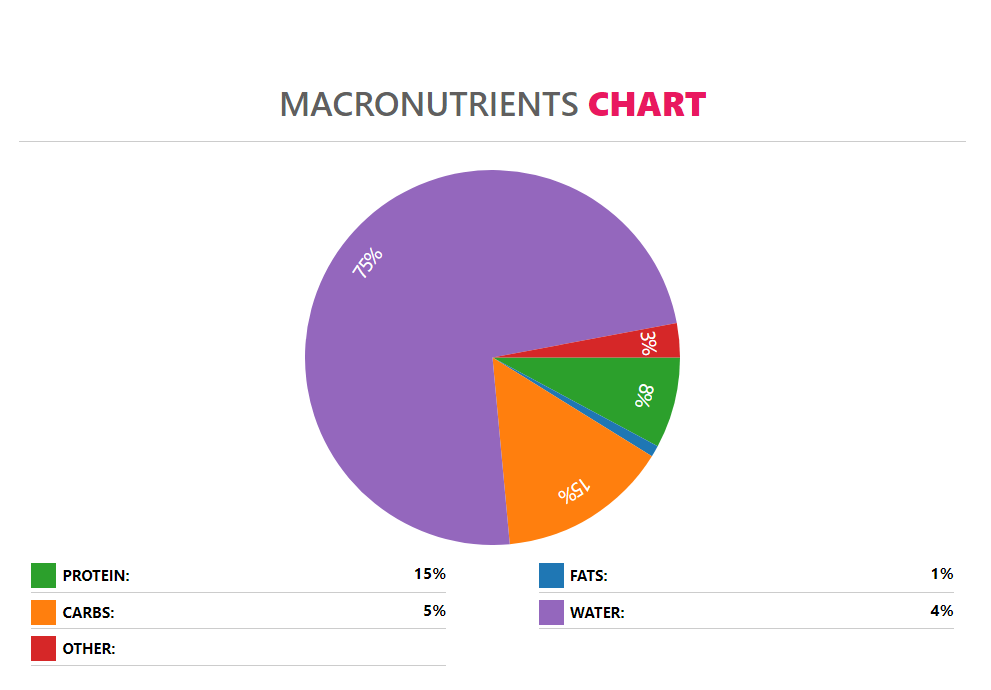
around 81 calories. Crab sticks are relatively dense in nutrients,
as they consist 75% of water and 25% of nutrients, such as
carbohydrates, protein, fats, vitamins, and minerals. In
comparison, canned real blue crab is lower in calories, containing
83 calories in every 100 g serving. However, cooked crab meat has a
very similar caloric value to imitation crab, containing 95
calories per every hundred-gram
serving.
Crab sticks are considered to
be a low-calorie food, containing only 95 calories per 100g
serving. The average serving size of crab sticks per person is 3 oz
or 85g. Therefore, one average serving size of crab sticks provides
around 81 calories. Crab sticks are relatively dense in nutrients,
as they consist 75% of water and 25% of nutrients, such as
carbohydrates, protein, fats, vitamins, and minerals. In
comparison, canned real blue crab is lower in calories, containing
83 calories in every 100 g serving. However, cooked crab meat has a
very similar caloric value to imitation crab, containing 95
calories per every hundred-gram
serving.
Carbohydrates
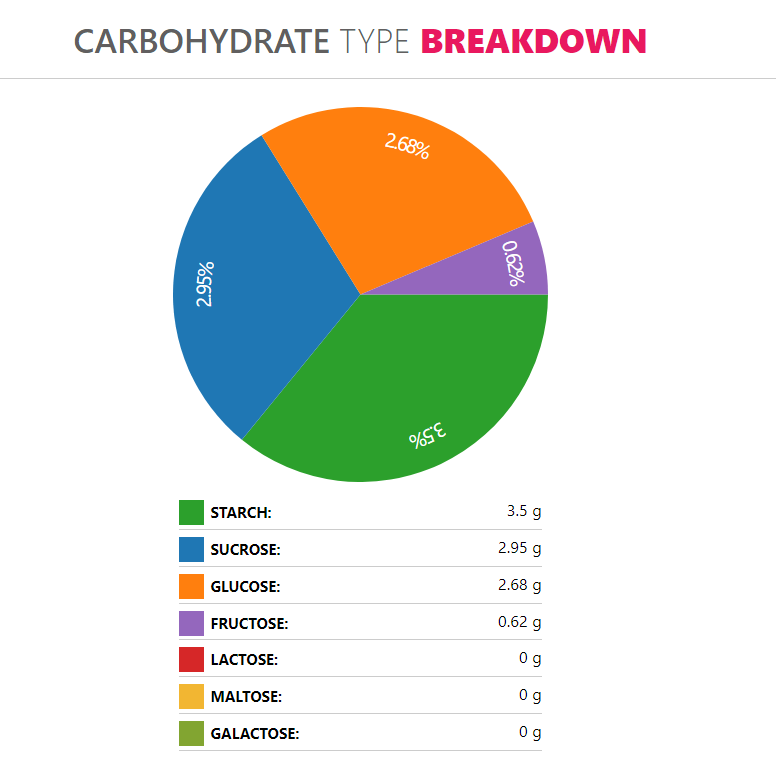
The predominant macronutrient of crab sticks is carbohydrates, consisting mainly of sugars: sucrose, glucose, and fructose. The rest of the carbohydrates are made up of mostly starch and some dietary fiber.
The sugars consist 47% of sucrose, 43% of glucose and only 10% of fructose.Crab sticks contain 3.5g of starch in every hundred-gram serving.
Unlike imitation crab, real crab meat contains no notable amount of carbohydrates, including sugars and starch.
Protein
The fish meat in crab sticks makes up the protein content, about 8g in every 100g serving. This means that one average serving size of crab sticks contains 6.4g of protein.
The protein found in crab sticks is of high quality as it includes some amounts of all essential amino acids. Crab stick protein is particularly rich in lysine, threonine, and tryptophan while being relatively low in valine, isoleucine, and phenylalanine. Of the non-essential amino acids, crab stick is high in aspartic and glutamic acids.Real canned crab, on the other hand, contains over two times more protein, providing 18g per every 100g serving. At the same time, cooked fresh crab meat contains 19.35g of protein in a 100g serving.
Fats
The fat composition is dominated by monounsaturated fatty acids followed by saturated fatty acids, leaving polyunsaturated fatty acids in the last place. A hundred-gram serving of crab sticks contains less than a gram of fats. However, the same serving size contains 20mg of cholesterol.
At the same time, real canned crab meat provides almost double the fats content, but 97mg of cholesterol per 100g serving. However, while containing almost 2g of fats, real cooked crab meat has 53mg of cholesterol.
Vitamins
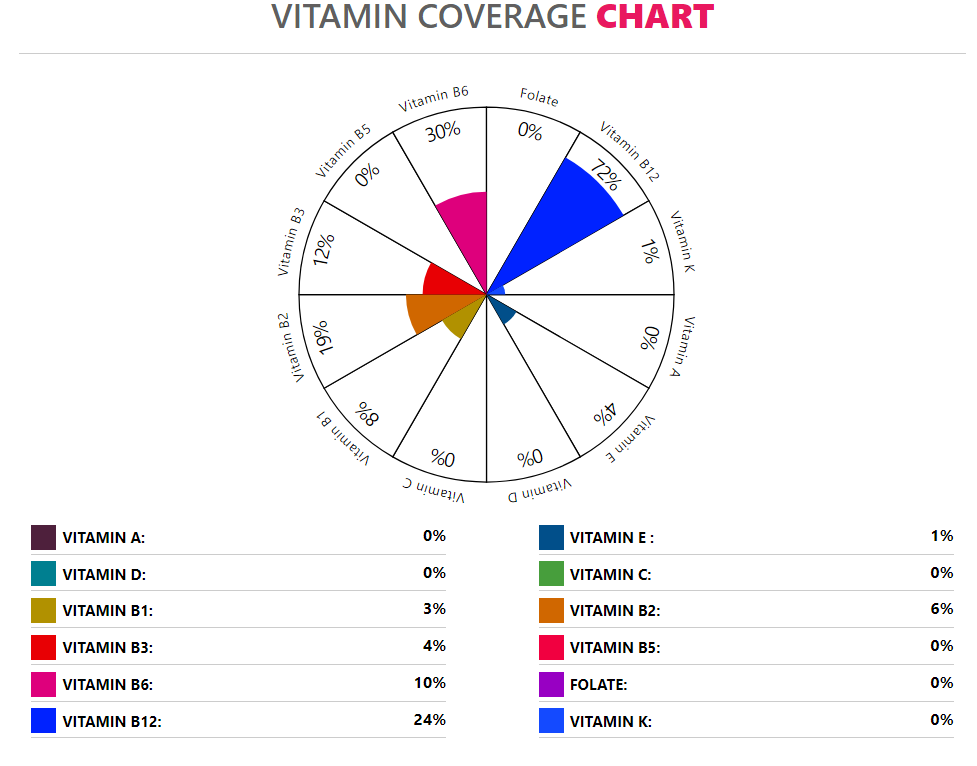
Crab sticks provide some vital vitamins, being very rich in vitamin B12 and vitamin B6. It also contains moderate amounts of vitamins B1, B2, B3, vitamin E, and vitamin K.
However, crab sticks completely lack vitamin B5 and folic acid or vitamin B9, as well as vitamin A, vitamin C, and vitamin D. Overall, imitation crab is not a great source of vitamins. On the other hand, real crab meat is richer in almost all vitamins, except for vitamin B1 and vitamin K.
2.4. Benefits and harms of crab sticks
The nutritional value of crab sticks is of great interest. Like any other seafood, they are a carbohydrate-protein food. In addition, a huge amount of vitamins (A, B6, B12, C, D) and useful macronutrients such as calcium, zinc, iron, iodine and magnesium remain unchanged for the reason that the semi-finished product is not subjected to heat treatment. All this can be attributed to the positive characteristics of the product. Here, of course, it is worth adding the fact that such a mixture is low-calorie. It does not overload the human body, because it contains about 80-90 calories per 100 grams of the finished product. This may be interesting for those who struggle with excess weight. To achieve this goal, many dieters advise people to include ordinary crab sticks in their diet. The benefits and harms of weight loss here have a fine line. On the one hand, a product with a reduced calorie content allows you to force the body to spend its own fat reserves. The benefits are obvious. But, on the other hand, frequent consumption of the product in large quantities can cause undesirable allergic reactions or disorders in the gastrointestinal tract. Both have equally detrimental effects on human health. Therefore, a measure and advice of a knowledgeable specialist are needed in everything.
The minced fish that the Japanese used more than nine centuries ago is not at all like modern crab sticks. The benefits and harms in a new generation product are side by side, which makes a person think several times before making a final decision.
It must be remembered that in addition to a unique complex of saturated fatty acids and a rich protein composition, sticks contain many chemical components, the effects of which no one can foresee on a particular organism. Of course, the absence of cholesterol and the minimum amount of fat makes such food favorable, for example, for cores. People with an enlarged thyroid gland can also include a crab simulator in their diet without fear of possible consequences. For them, this product is even useful. But because of the complex chemical composition, they still should not be given to children in large quantities. It is clear that nothing terrible will happen from a couple of pieces a day. But if the product is used with enviable constancy, then irreparable changes will not take long.

2.5. Downsides and risks of crab sticks
Allergy
Fish allergies are one of the most common allergies among adults. Even after thorough processing, surimi can retain the allergens found in the fish since approximately 75% of the fish’s original protein content remains. Therefore, consuming crab sticks can pose a severe threat to people who are allergic to certain types of fish, particularly pollock.
The codfish that surimi can be made from usually contains several allergic proteins, whereas the surimi contains only a single allergic protein. Thus, in general, surimi is less allergenic than the fish from which it has been made. The symptoms of a crab stick allergy are the same as most food allergy symptoms: oral allergy syndrome (an itching, tingling, or swelling feeling in the mouth), nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and in some rare cases, anaphylactic shock. Crab sticks do not contain crab meat; however, some added proteins may come from the aqueous extract of crabs, so for people allergic to shellfish and crab, it is better to read the label or avoid it as a whole.
In the production of crab sticks, egg whites and wheat starch are sometimes added, so it is usually not gluten-free. For people who are allergic to egg whites or are gluten intolerant, it is best to avoid crab sticks.
Diabetes
Even though imitation crab meat has a relatively low glycemic index, there is a possibility that some of its dietary proteins react with the pancreatic islet cells, among other low glycemic index seafood proteins, potentially causing an immune response harming the pancreatic beta cells. This may lead to latent autoimmune diabetes of adulthood in people predisposed to it or with prior sensitization.
Pregnancy
Imitation crab meat is cooked during production, so it is usually safe to eat for pregnant women. However, it is best to ask whether there are other raw products in foods containing crab sticks to avoid potential poisoning. There is a potential risk of Listeria monocytogenes contamination of ready-to-eat foods, especially seafood. However, the bacteria are inactivated by thermal treatment in crab stick production. The use of starfish gelatin film containing vanillin in crab stick packaging with its antimicrobial qualities also decreases the risk of Listeria monocytogenes contamination
2.5. Crab sticks in diets
Crab sticks are very low in fats and low in calories. Due to this reason, crab sticks can fit in a weight loss diet. However, crab sticks are a highly processed food with a high content of salt, starch, and sugars; therefore, they should be used with caution.
Real crab meat, although higher in fats, is a better option for healthy weight loss diets, as it is richer in beneficial nutrients and contains no carbohydrates.
|
Keto |
Imitation crab stick is not ideal for this diet due to the carbohydrates added during processing. One serving of crab sticks contains 15g of carbohydrates, while keto allows for an average of 20 to 30g of carbohydrates per day. Real crab meat is a better choice since it has no carbs. |
|
DASH |
Both imitation crab and crab meat, as most seafood products are very high in salt. For this reason, crab meat, both real and imitation, is not recommended for individuals with high blood pressure. |
|
Atkins |
During the Induction phase, you can only have 20 to 25g of carbohydrates a day, so imitation crab meat is not advised in this phase. You can add crab sticks to your diet starting from the third Fine-tuning phase and use them throughout the Maintenance phase. |
|
Mediterranean |
Seafood is a staple part of a Mediterranean diet; however, imitation crab is a highly processed food with added sugars, so if available, real crab meat is the correct alternative. |
|
Paleo |
Imitation crab meat, being a highly processed food with additives, does not fit this diet. |
|
Vegan/ Vegetarian/ Pescetarian |
Even though imitation crab doesn’t contain actual crab meat, it is still made of fish, so it does not fit a vegetarian or a vegan diet. Crab sticks also often contain eggs and a natural dye called carmine that is made using insects. Crab sticks do suit the pescetarian diet. However, in rare cases, the surimi in imitation crab can be made from deboned chicken, pork, or beef. |
|
Gluten-free |
Wheat starch is often used as a stabilizing ingredient in the production of imitation crab. Whilst wheat starch is wheat’s carbohydrate fraction and should contain no protein or gluten, it is still not considered entirely safe for people with gluten intolerance. However, gluten-free imitation crab can also be found in the market. |
|
Dukan |
Although imitation crab is rich in protein, it also contains 15g of sugars in a 100g serving. For this reason, imitation crab does not fit in the first two phases of the Dukan diet - the Attack and Cruise phases. You can start eating crab sticks starting from the Consolidation phase or the third phase, but only in strict moderation. |
|
Intermittent Fasting |
As with most foods, you can eat imitation crab during eating periods but refrain during fasting. |
|
Low Fat & Low Calorie |
Crab sticks fit a low fat and a low-calorie diet, containing only 95 calories and less than a gram of fats in a single serving. |
|
Low Carb |
Crab sticks contain 15g of carbohydrates per serving, which is not ideal for a low-carb diet. Real crab meat is the better alternative for this. |
|
Anti Inflammatory |
Real crab meat may have anti-inflammatory qualities due to its omega-3 fatty acid content. However, there is not enough research on this topic regarding imitation crab. |
|
BRAT |
Seafood products full of proteins are advised to be avoided on a BRAT diet, so imitation crab is unsuitable for this diet. |
ІІІ. PRACTICAL PART
3.1. Do students know about the benefits and harms of crab sticks?
The purpose of the survey: to determine if students know about the benefits and harmd of crab sticks
The following questions are asked:
1. Do you eat crab sticks?
Answers:
* Yes;
* No.

2. Did you know that crab sticks are not made from crab?
Answers:
* Yes;
* No.

3. Do you know about the benefits of crab sticks?
Answers:
*Yes;
* No.

4. Do you know about the harms of crab sticks?
Answers:
*Yes;
* No.

3.2. Cooking crab sticks at home
Currently, crab sticks can be cooked at home. Here is one of the easy recipes with which can use to cook delicious sticks.
Ingredients:
Hake fillet 200 g
Cream 30 g
Egg white 1 piece
Beet juice
Cooking steps:
-
Cut the hake fillet into large pieces and add cream
-
Separate the whites from the yolks, whisk the whites into a fluffy foam
-
Combine the whipped whites with the fish and interrupt it with a blender until a homogeneous consistency. Salt to taste
-
Wrap the fish mass in two layers of food film. Tie the edges well as well
-
Boil the fish "sticks" in boiling water for 10 minutes
-
Boiled fish "sticks" is tinted with beet juice and added to the salad, crumbling it into small pieces.
IV. Conclusion
Despite the fact that the original crab sticks contain really a lot of useful substances, modern manufacturers of such a product strive to save money and at the same time improve their product, so they resort to some tricks that can have a very negative impact on the health of consumers. For example, ignoring all quality standards, flavor enhancers and dyes, preservatives and stabilizers are added to crab sticks. If these substances are of appropriate quality and are used only in a small volume, they will not be able to cause serious harm to the body. During the production of high-quality crab sticks, only food dyes are used and only the outer side of them is painted, very carefully. In addition, acquired crab sticks can be carriers of harmful microbes.
LIST OF LITERATURE
1. Lee K.-Y. [и др.]. Characterization of a starfish gelatin film containing vanillin and its application in the packaging of crab stick // Food Science and Biotechnology. 2016. № 4 (25). C. 1023–1028.
2. Крабовые палочки - польза или вред | Евгения Полевская | Это просто | Дзен [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://dzen.ru/media/eto_prosto/krabovye-palochki-polza-ili-vred-5c78f17c2e9e2e00b37a9860
3. Surimi - Wikipedia [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Surimi
жүктеу мүмкіндігіне ие боласыз
Бұл материал сайт қолданушысы жариялаған. Материалдың ішінде жазылған барлық ақпаратқа жауапкершілікті жариялаған қолданушы жауап береді. Ұстаз тілегі тек ақпаратты таратуға қолдау көрсетеді. Егер материал сіздің авторлық құқығыңызды бұзған болса немесе басқа да себептермен сайттан өшіру керек деп ойласаңыз осында жазыңыз
Зерттеу жұмысы: «Crab sticks - ways of making, benefits and harms»
Зерттеу жұмысы: «Crab sticks - ways of making, benefits and harms»
ЗЕРТТЕУ ЖҰМЫСЫНЫҢ ТАҚЫРЫБЫ:
Crab sticks - ways of making, benefits and harms
Секция: ағылшын тілі, ағылшын тілі
Тақырыбы: «Crab sticks - ways of making, benefits and harms»
«Краб таяқшаларының пайдасы мен зияны»
Оқушының толық аты:
Сынып:
Жетекшісі:
АННОТАЦИЯ
Краб таяқшалары - сурими балықтарының филесінен жасалған балық өнімі. Пішіні мен түсі бойынша таяқшалар краб етіне ұқсайды, сондықтанда атауы осыдан шыққан. Краб таяқшаларында краб еті жоқ ол тек сурими атты ақ мұхиттық балықтардың ұнтақталған филесінен ақуызды өңдеу арқылы алынады. Құрамына су, май, крахмал, жұмыртқа ақтығы, қант және тұз кіреді. Краб таяқшаларды жасау идеясы Жапониядан келді. Қазір краб таяқшалары бүкіл әлемде шығарылады, оларды шикі жеуге, салаттар мен тағамдарға қосуға болады. Краб таяқшалары - бұл қол жетімді және кең таралған өнім, кез-келген тоңазытқышта бар. Краб таяқшалары - жеуге дайын өнім, ұзын тіктөртбұрышты немесе ақ түсті цилиндрлі, жоғарғы бөлігі крабтың түсіне ұқсайтын қызғылт сары немесе қызыл түске боялған. Әрбір таяқшада жұқа полиэтиленнен жасалған жеке мөлдір қаптама бар. Краб таяқшалары жұқа қабаттардан тұрады, олар ораммен тығыз оралған, оны кескенде айқын көруге болады. Өнім серпімді құрылымға ие, дәмі мен иісі бойынша шаянтәрізділерге жақын.
АННОТАЦИЯ
Крабовые палочки — рыбий продукт из филе сурими рыбы. Получил свое обманчивое такое название засчет формы и цвета палочки, которая напоминает клешню краба. Палочки получаются путем обработки белков из филе белых океанических рыб и не содержат мяса. В состав также входит вода, масло, крахмал, яичный белок, сахар и соль. Идея создания палочек позрадилась в Японии. Сейчас палочки производятся во всем мире, их можно есть сырыми, добавлять в салаты и закуски. Крабовые палочки являются доступным и распространённым продуктом, практически в каждом холодильнике найдётся упаковка, приобретённая «на всякий случай». Крабовые палочки – это готовые к употреблению полностью продукты, представляющие собой длинные прямоугольники или цилиндры белого цвета, верхняя часть окрашена в оранжевый или красный цвет, имитирующий окраску краба. Каждая палочка имеет индивидуальную прозрачную упаковку из тонкого полиэтилена. На срезе это отчётливо видно крабовые палочки состоят из тонких пластов, туго свёрнутых рулетом. Продукт имеет упругую структуру, по вкусу и запаху близок к ракообразным.
ANNOTATION
Crab sticks are a fish product made from minced fish surimi. In shape and color, the sticks vaguely resemble a crab claw for which they received their deceptive name. The sticks do not contain crab meat at all and are obtained by processing protein from minced surimi — fillet of white oceanic fish. The composition also includes water, oil, starch, egg white, sugar and salt. The idea of creating sticks came from Japan. Now chopsticks are produced all over the world, they can be eaten raw, added to salads and snacks. Crab sticks are an affordable and common product, almost every refrigerator has a package purchased "just in case". Crab sticks are a completely ready–to-use product, they are long rectangles or cylinders of white color, the upper part is painted orange or red, imitating the color of a crab. Each stick has an individual transparent packaging made of thin polyethylene. Crab sticks consist of thin layers tightly rolled into a roll, this is clearly visible on the slice. The product has an elastic structure, tastes and smells close to crustaceans.
CONTENT OF THE SCIENTIFIC PROJECT
I. INTRODUCTION..............................................................................................
II. MAIN PART.....................................................................................................
2.1. Ways of making crab sticks
2.2. The emergence of interest in crab sticks
2.3. Calorie content and composition
2.4. Benefits and harms of crab sticks
2.5. Downsides and risks of crab sticks
2.6. Crab sticks in the diet
III. PRACTICAL PART.......................................................................................
3.1. Do students know about the benefits and harms of crab sticks?
3.2. Cooking crab sticks at home
IV. Conclusion........................................................................................................
LIST OF LITERATURE .....................................................................................
І. КІРІСПЕ
This crab stand-in has become popular over the past few decades and is commonly found in seafood salad, crab cakes, California sushi rolls and crab rangoons.
In short, imitation crab is processed fish meat — in fact, it’s sometimes called “the hot dog of the sea.” However, some people may still wonder what it’s made from and whether it’s healthy.
Purpose of the project: to determine the benefits and harms of crab sticks
Relevance of the chosen topic: Сrab sticks are known all over the world. Do people know what crab sticks are made of and their benefits to the body or harms?
Object of research: Crab sticks
Hypothesis: How healthful and harmful are crab sticks?
Responsibilities:
1. To analyze data from books and other information sources;
2. To make a plan for researching my topic;
3. To ask what our school students know about crab sticks;
4. To make a conclusion on the research topic.
Research methods:
1. To study special literature;
2. To watch videos;
3. To conduct a survey;
4. To analyze received data;
5. Generalization.
II. MAIN PART.
2.1.Ways of making crab sticks
Crab sticks! In fact, the product is not made from crab meat, but from minced fish. Therefore, they differ from natural crab meat in the same way as an artificial flower from a real one. Crab sticks are a fish product made from minced fish surimi.
One of the main ingredients of quality sticks is minced fish (surimi). Its recipe was invented in Japan in the 12th century. The inhabitants of the island noticed that the mass obtained from ground and squeezed out of the water fish has good taste, various figures can be molded from this mass to decorate the dish.

Japanese people failed to export surimi and products made from it for a long time. Americans and Europeans were not willing to buy the product. This continued until the Japanese technologists dyed the product with food coloring, applied a red stripe to them, after which the “imitation crab meat” product went on sale. In such packaging, they quickly flooded not only European and American markets, but became popular all over the world.


Minced fish for crab sticks is made from fish fillets that live in the ocean. It can be pollock, hake, herring or mackerel. The meat is minced and washed many times with water. Then the mass is placed in a centrifuge to remove excess water. The result is an almost tasteless mixture that the Japanese love, but residents of other countries do not. Therefore, minced fish had to be seasoned with salt, sugar, flavorings, and in order for the product to be well stored, preservatives were also added. Then apply a red stripe with food coloring and the product is ready for use.

Crab sticks are low-calorie foods. It will not be difficult to independently determine the calorie content of one stick - according to the same instructions on the pack.
Surimi was invented by the Japanese in order not to throw away food waste. According to historians, minced fish mixed with starch has been known in the land of the Rising Sun for more than 900 years. The first surviving mention of Japanese products from Surimi dates back to 1115.
Starting from the XIV century. in Japan, the kamaboko dish is eaten. For him, minced white fish with the addition of several more ingredients, primarily affecting the texture of the final mass, is turned into tortillas and usually steamed. Usually kamaboko is served on New Year's Eve. There is also a tikuva dish. For him, surimi is mixed with starch and egg white, forming an even rectangular layer. Then the mass is wrapped around a thick skewer or a special pin (in production), and then fried over an open fire or steamed to obtain a kind of hollow tube. A hearty dish is sold at street fairs. It is also called "tikuwa-kamaboko", often cut along the entire length and stuffed with various fillings.
Surimi was very popular with the Japanese, but up to a certain point it was not an affordable product for everyone. Everything changed after the end of the Second World War, when new cooling and freezing technologies appeared. This allowed the start of pollock fishing in the North Pacific Ocean – the raw material for surimi. Thanks to this, another variety of kamakobo began to develop – kani-kamaboko, abbreviated "Kanikama" (Kanikama). These are the crab sticks familiar to us all. It was under this name in 1973 that they were first produced by the Japanese company Sugiyo.

Additional ingredients for cooking crab sticks is minced fish usually makes up 35-50% of the total weight of the product, sometimes slightly above 50%.Other main ingredients of imitation crab meat:
-
Water. As a rule, this is the second most popular ingredient in crab sticks. Water is necessary to obtain the correct texture of the product.
-
Starch. Potato, corn starch or tapioca starch are often used to harden surimi and make it suitable for freezing. If you found sticky or excessively soft crab sticks on sale, it means that the product was stored incorrectly (re-frozen) or saved on starch.
-
Protein. Most often, egg white (albumin) is found in crab sticks. It improves the texture of crab sticks, their color and shine.
-
Sugar and sorbitol. These ingredients help the product withstand freezing and defrosting, plus they add a little sweetness to it.
-
Vegetable oil. Sunflower, soy or other vegetable oils are used to improve the structure, white color and increase the shelf life.
-
Salt (sodium chloride). Affects the overall taste of the product. It also participates in chemical processes, as a result of which a kind of gel is formed, forming the texture of crab sticks.
Additives included in the composition of crab sticks include:
-
Gum. The thickener and emulsifier helps the ingredients stick together, is included in the formulation to stabilize the product. Carrageenan (a natural gelling agent obtained by processing red seaweed, E407) and the polysaccharide xanthan gum (E415) can be used.
-
Red dyes. The most commonly used carmine (E120) is a red dye that is obtained from carminic acid. It is produced by females of tiny beetles called cochineal. Carmine, which gave its name to the shade of red-purple of the same name, is used, for example, for coloring different types of sausage products.
-
Glutamates. Sodium glutamate (E621) and a similar compound, sodium inosinate (E631), serve as flavor enhancers – to identify the taste of umami.
-
Flavors. Some manufacturers use real crab extract, artificial crab flavors and mirin, fermented rice wine.
-
Preservatives. To increase the shelf life, sodium benzoate (E211) and several phosphate-based additives (E339-342 or E450-452) are regularly used. Some studies show that excessive consumption of foods with added phosphates can lead to a violation
2.2. The emergence of interest in crab sticks
In life, only a small part of people has the opportunity to eat natural delicacies. Perhaps that is why the appearance in the late nineties of the last century in the sale of crab sticks was a real sensation. They aroused great interest and instantly disappeared from the shelves of stores. This was also facilitated by the unrealistically low price of the product. Surprised customers bought fragrant pieces by the kilos and even came up with hundreds of different dishes from them. Therefore, the harm and benefits of crab sticks interested everyone who was happy to join the league of seafood lovers. In fairness, it is worth noting that apart from the name, this product has nothing more to do with crabs. Marine life has become a kind of bait or, rather, a marketing ploy of enterprising manufacturers. Why spend a lot of money to purchase live arthropods, if you can create an imitation of the product and successfully sell it on the market? Everything was simple and mutually beneficial: the buyer received a product similar to the one he dreamed of, and the manufacturer.
A little later, people began to study more closely what is written on the labels, and various questions appeared. Many were surprised to discover an unusual composition and were perplexed about the presence of some components. The basis of the product was the mysterious ingredient "surimi". Translated from Japanese, it means "minced meat". There are no secrets here. Surimi is really a minced meat made from the meat of various white fish. These are mainly herring, pollock, mackerel, whiting, hake and other representatives of the ocean expanses. The Japanese have been using this compound for more than ten centuries. and there is no doubt about it. However, the unusual way of cooking is still very interesting. The product has a fishy smell, an exceptionally white color and a slightly noticeable characteristic aroma. So, the nutritional value of crab sticks is of great interest.
2.3. Calorie content and composition
![]() Crab sticks are considered to
be a low-calorie food, containing only 95 calories per 100g
serving. The average serving size of crab sticks per person is 3 oz
or 85g. Therefore, one average serving size of crab sticks provides
around 81 calories. Crab sticks are relatively dense in nutrients,
as they consist 75% of water and 25% of nutrients, such as
carbohydrates, protein, fats, vitamins, and minerals. In
comparison, canned real blue crab is lower in calories, containing
83 calories in every 100 g serving. However, cooked crab meat has a
very similar caloric value to imitation crab, containing 95
calories per every hundred-gram
serving.
Crab sticks are considered to
be a low-calorie food, containing only 95 calories per 100g
serving. The average serving size of crab sticks per person is 3 oz
or 85g. Therefore, one average serving size of crab sticks provides
around 81 calories. Crab sticks are relatively dense in nutrients,
as they consist 75% of water and 25% of nutrients, such as
carbohydrates, protein, fats, vitamins, and minerals. In
comparison, canned real blue crab is lower in calories, containing
83 calories in every 100 g serving. However, cooked crab meat has a
very similar caloric value to imitation crab, containing 95
calories per every hundred-gram
serving.

Carbohydrates
The predominant macronutrient of crab sticks is carbohydrates, consisting mainly of sugars: sucrose, glucose, and fructose. The rest of the carbohydrates are made up of mostly starch and some dietary fiber.
The sugars consist 47% of sucrose, 43% of glucose and only 10% of fructose.Crab sticks contain 3.5g of starch in every hundred-gram serving.

Unlike imitation crab, real crab meat contains no notable amount of carbohydrates, including sugars and starch.
Protein
The fish meat in crab sticks makes up the protein content, about 8g in every 100g serving. This means that one average serving size of crab sticks contains 6.4g of protein.
The protein found in crab sticks is of high quality as it includes some amounts of all essential amino acids. Crab stick protein is particularly rich in lysine, threonine, and tryptophan while being relatively low in valine, isoleucine, and phenylalanine. Of the non-essential amino acids, crab stick is high in aspartic and glutamic acids.Real canned crab, on the other hand, contains over two times more protein, providing 18g per every 100g serving. At the same time, cooked fresh crab meat contains 19.35g of protein in a 100g serving.
Fats
The fat composition is dominated by monounsaturated fatty acids followed by saturated fatty acids, leaving polyunsaturated fatty acids in the last place. A hundred-gram serving of crab sticks contains less than a gram of fats. However, the same serving size contains 20mg of cholesterol.
At the same time, real canned crab meat provides almost double the fats content, but 97mg of cholesterol per 100g serving. However, while containing almost 2g of fats, real cooked crab meat has 53mg of cholesterol.
Vitamins
Crab sticks provide some vital vitamins, being very rich in vitamin B12 and vitamin B6. It also contains moderate amounts of vitamins B1, B2, B3, vitamin E, and vitamin K.
However, crab sticks completely lack vitamin B5 and folic acid or vitamin B9, as well as vitamin A, vitamin C, and vitamin D. Overall, imitation crab is not a great source of vitamins. On the other hand, real crab meat is richer in almost all vitamins, except for vitamin B1 and vitamin K.

2.4. Benefits and harms of crab sticks
The nutritional value of crab sticks is of great interest. Like any other seafood, they are a carbohydrate-protein food. In addition, a huge amount of vitamins (A, B6, B12, C, D) and useful macronutrients such as calcium, zinc, iron, iodine and magnesium remain unchanged for the reason that the semi-finished product is not subjected to heat treatment. All this can be attributed to the positive characteristics of the product. Here, of course, it is worth adding the fact that such a mixture is low-calorie. It does not overload the human body, because it contains about 80-90 calories per 100 grams of the finished product. This may be interesting for those who struggle with excess weight. To achieve this goal, many dieters advise people to include ordinary crab sticks in their diet. The benefits and harms of weight loss here have a fine line. On the one hand, a product with a reduced calorie content allows you to force the body to spend its own fat reserves. The benefits are obvious. But, on the other hand, frequent consumption of the product in large quantities can cause undesirable allergic reactions or disorders in the gastrointestinal tract. Both have equally detrimental effects on human health. Therefore, a measure and advice of a knowledgeable specialist are needed in everything.
The minced fish that the Japanese used more than nine centuries ago is not at all like modern crab sticks. The benefits and harms in a new generation product are side by side, which makes a person think several times before making a final decision.
It must be remembered that in addition to a unique complex of saturated fatty acids and a rich protein composition, sticks contain many chemical components, the effects of which no one can foresee on a particular organism. Of course, the absence of cholesterol and the minimum amount of fat makes such food favorable, for example, for cores. People with an enlarged thyroid gland can also include a crab simulator in their diet without fear of possible consequences. For them, this product is even useful. But because of the complex chemical composition, they still should not be given to children in large quantities. It is clear that nothing terrible will happen from a couple of pieces a day. But if the product is used with enviable constancy, then irreparable changes will not take long.

2.5. Downsides and risks of crab sticks
Allergy
Fish allergies are one of the most common allergies among adults. Even after thorough processing, surimi can retain the allergens found in the fish since approximately 75% of the fish’s original protein content remains. Therefore, consuming crab sticks can pose a severe threat to people who are allergic to certain types of fish, particularly pollock.
The codfish that surimi can be made from usually contains several allergic proteins, whereas the surimi contains only a single allergic protein. Thus, in general, surimi is less allergenic than the fish from which it has been made. The symptoms of a crab stick allergy are the same as most food allergy symptoms: oral allergy syndrome (an itching, tingling, or swelling feeling in the mouth), nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and in some rare cases, anaphylactic shock. Crab sticks do not contain crab meat; however, some added proteins may come from the aqueous extract of crabs, so for people allergic to shellfish and crab, it is better to read the label or avoid it as a whole.
In the production of crab sticks, egg whites and wheat starch are sometimes added, so it is usually not gluten-free. For people who are allergic to egg whites or are gluten intolerant, it is best to avoid crab sticks.
Diabetes
Even though imitation crab meat has a relatively low glycemic index, there is a possibility that some of its dietary proteins react with the pancreatic islet cells, among other low glycemic index seafood proteins, potentially causing an immune response harming the pancreatic beta cells. This may lead to latent autoimmune diabetes of adulthood in people predisposed to it or with prior sensitization.
Pregnancy
Imitation crab meat is cooked during production, so it is usually safe to eat for pregnant women. However, it is best to ask whether there are other raw products in foods containing crab sticks to avoid potential poisoning. There is a potential risk of Listeria monocytogenes contamination of ready-to-eat foods, especially seafood. However, the bacteria are inactivated by thermal treatment in crab stick production. The use of starfish gelatin film containing vanillin in crab stick packaging with its antimicrobial qualities also decreases the risk of Listeria monocytogenes contamination
2.5. Crab sticks in diets
Crab sticks are very low in fats and low in calories. Due to this reason, crab sticks can fit in a weight loss diet. However, crab sticks are a highly processed food with a high content of salt, starch, and sugars; therefore, they should be used with caution.
Real crab meat, although higher in fats, is a better option for healthy weight loss diets, as it is richer in beneficial nutrients and contains no carbohydrates.
|
Keto |
Imitation crab stick is not ideal for this diet due to the carbohydrates added during processing. One serving of crab sticks contains 15g of carbohydrates, while keto allows for an average of 20 to 30g of carbohydrates per day. Real crab meat is a better choice since it has no carbs. |
|
DASH |
Both imitation crab and crab meat, as most seafood products are very high in salt. For this reason, crab meat, both real and imitation, is not recommended for individuals with high blood pressure. |
|
Atkins |
During the Induction phase, you can only have 20 to 25g of carbohydrates a day, so imitation crab meat is not advised in this phase. You can add crab sticks to your diet starting from the third Fine-tuning phase and use them throughout the Maintenance phase. |
|
Mediterranean |
Seafood is a staple part of a Mediterranean diet; however, imitation crab is a highly processed food with added sugars, so if available, real crab meat is the correct alternative. |
|
Paleo |
Imitation crab meat, being a highly processed food with additives, does not fit this diet. |
|
Vegan/ Vegetarian/ Pescetarian |
Even though imitation crab doesn’t contain actual crab meat, it is still made of fish, so it does not fit a vegetarian or a vegan diet. Crab sticks also often contain eggs and a natural dye called carmine that is made using insects. Crab sticks do suit the pescetarian diet. However, in rare cases, the surimi in imitation crab can be made from deboned chicken, pork, or beef. |
|
Gluten-free |
Wheat starch is often used as a stabilizing ingredient in the production of imitation crab. Whilst wheat starch is wheat’s carbohydrate fraction and should contain no protein or gluten, it is still not considered entirely safe for people with gluten intolerance. However, gluten-free imitation crab can also be found in the market. |
|
Dukan |
Although imitation crab is rich in protein, it also contains 15g of sugars in a 100g serving. For this reason, imitation crab does not fit in the first two phases of the Dukan diet - the Attack and Cruise phases. You can start eating crab sticks starting from the Consolidation phase or the third phase, but only in strict moderation. |
|
Intermittent Fasting |
As with most foods, you can eat imitation crab during eating periods but refrain during fasting. |
|
Low Fat & Low Calorie |
Crab sticks fit a low fat and a low-calorie diet, containing only 95 calories and less than a gram of fats in a single serving. |
|
Low Carb |
Crab sticks contain 15g of carbohydrates per serving, which is not ideal for a low-carb diet. Real crab meat is the better alternative for this. |
|
Anti Inflammatory |
Real crab meat may have anti-inflammatory qualities due to its omega-3 fatty acid content. However, there is not enough research on this topic regarding imitation crab. |
|
BRAT |
Seafood products full of proteins are advised to be avoided on a BRAT diet, so imitation crab is unsuitable for this diet. |
ІІІ. PRACTICAL PART
3.1. Do students know about the benefits and harms of crab sticks?
The purpose of the survey: to determine if students know about the benefits and harmd of crab sticks
The following questions are asked:
1. Do you eat crab sticks?
Answers:
* Yes;
* No.

2. Did you know that crab sticks are not made from crab?
Answers:
* Yes;
* No.

3. Do you know about the benefits of crab sticks?
Answers:
*Yes;
* No.

4. Do you know about the harms of crab sticks?
Answers:
*Yes;
* No.

3.2. Cooking crab sticks at home
Currently, crab sticks can be cooked at home. Here is one of the easy recipes with which can use to cook delicious sticks.
Ingredients:
Hake fillet 200 g
Cream 30 g
Egg white 1 piece
Beet juice
Cooking steps:
-
Cut the hake fillet into large pieces and add cream
-
Separate the whites from the yolks, whisk the whites into a fluffy foam
-
Combine the whipped whites with the fish and interrupt it with a blender until a homogeneous consistency. Salt to taste
-
Wrap the fish mass in two layers of food film. Tie the edges well as well
-
Boil the fish "sticks" in boiling water for 10 minutes
-
Boiled fish "sticks" is tinted with beet juice and added to the salad, crumbling it into small pieces.
IV. Conclusion
Despite the fact that the original crab sticks contain really a lot of useful substances, modern manufacturers of such a product strive to save money and at the same time improve their product, so they resort to some tricks that can have a very negative impact on the health of consumers. For example, ignoring all quality standards, flavor enhancers and dyes, preservatives and stabilizers are added to crab sticks. If these substances are of appropriate quality and are used only in a small volume, they will not be able to cause serious harm to the body. During the production of high-quality crab sticks, only food dyes are used and only the outer side of them is painted, very carefully. In addition, acquired crab sticks can be carriers of harmful microbes.
LIST OF LITERATURE
1. Lee K.-Y. [и др.]. Characterization of a starfish gelatin film containing vanillin and its application in the packaging of crab stick // Food Science and Biotechnology. 2016. № 4 (25). C. 1023–1028.
2. Крабовые палочки - польза или вред | Евгения Полевская | Это просто | Дзен [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://dzen.ru/media/eto_prosto/krabovye-palochki-polza-ili-vred-5c78f17c2e9e2e00b37a9860
3. Surimi - Wikipedia [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Surimi

шағым қалдыра аласыз















