Alkali metals
Alkali metals

#1 слайд
Alkali metals
Со mpleted : Kabylkakov
Amirzhan
Checked: Alexey
Nikolaevish
1 слайд
Alkali metals Со mpleted : Kabylkakov Amirzhan Checked: Alexey Nikolaevish

#2 слайд
Position in the periodic table of chemical
elements :
•
Alkali metals are located in the main
subgroup of the first group of the periodic
table of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev.
These are lithium Li, sodium Na, potassium
K, cesium Cs, rubidium Rb and francium Fr.
2 слайд
Position in the periodic table of chemical elements : • Alkali metals are located in the main subgroup of the first group of the periodic table of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev. These are lithium Li, sodium Na, potassium K, cesium Cs, rubidium Rb and francium Fr.

#3 слайд
Electronic structure of alkali metals and basic
properties :
•
Electronic configuration of the outer energy level of
alkali metals: ns1, the outer energy level contains 1
s-electron. Therefore, the typical oxidation state of
alkali metals in compounds is +1.
•
Let us consider some patterns of changes in the
properties of alkali metals.
3 слайд
Electronic structure of alkali metals and basic properties : • Electronic configuration of the outer energy level of alkali metals: ns1, the outer energy level contains 1 s-electron. Therefore, the typical oxidation state of alkali metals in compounds is +1. • Let us consider some patterns of changes in the properties of alkali metals.
#4 слайд
•
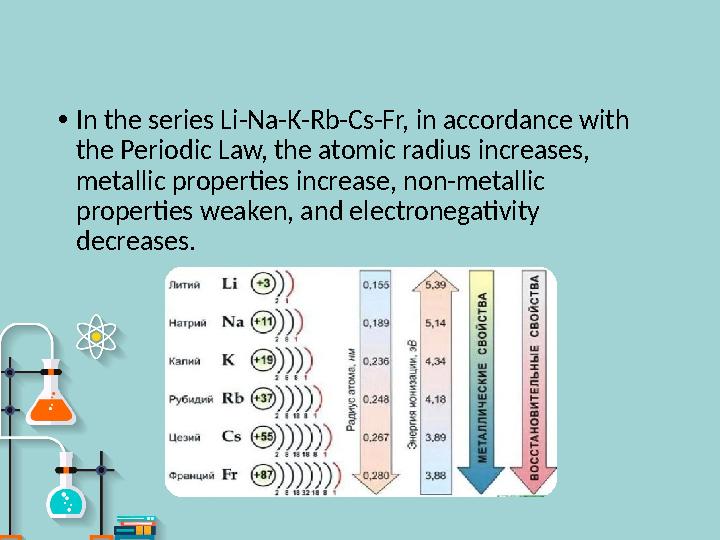
In the series Li-Na-K-Rb-Cs-Fr, in accordance with
the Periodic Law, the atomic radius increases,
metallic properties increase, non-metallic
properties weaken, and electronegativity
decreases.
4 слайд
• In the series Li-Na-K-Rb-Cs-Fr, in accordance with the Periodic Law, the atomic radius increases, metallic properties increase, non-metallic properties weaken, and electronegativity decreases.

#5 слайд
Physical properties :
•
All alkali metals are soft, silvery substances. Their
freshly cut surface has a characteristic shine.
5 слайд
Physical properties : • All alkali metals are soft, silvery substances. Their freshly cut surface has a characteristic shine.
#6 слайд
•
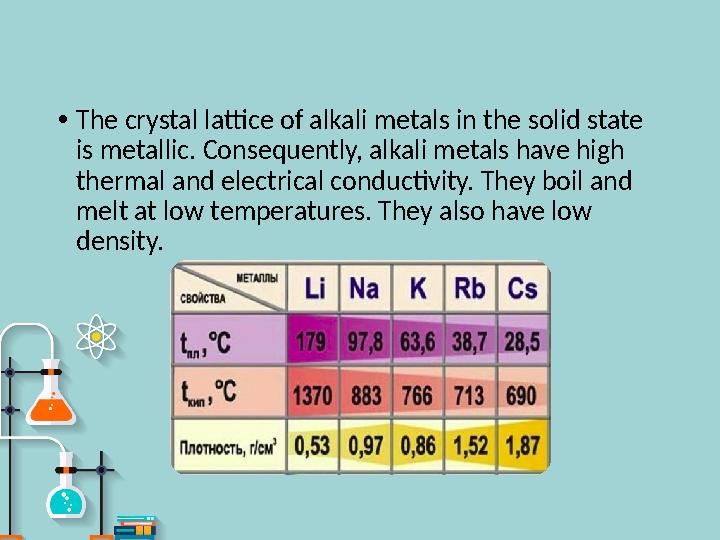
The crystal lattice of alkali metals in the solid state
is metallic. Consequently, alkali metals have high
thermal and electrical conductivity. They boil and
melt at low temperatures. They also have low
density.
6 слайд
• The crystal lattice of alkali metals in the solid state is metallic. Consequently, alkali metals have high thermal and electrical conductivity. They boil and melt at low temperatures. They also have low density.

#7 слайд
Qualitative reactions :
•
A qualitative reaction to alkali metals is the coloring
of the flame with salts of alkali metals.
•
Flame color:
•
Li - carmine red
•
Na - yellow
•
K - purple
•
Rb - brown-red
•
Cs - violet-red
7 слайд
Qualitative reactions : • A qualitative reaction to alkali metals is the coloring of the flame with salts of alkali metals. • Flame color: • Li - carmine red • Na - yellow • K - purple • Rb - brown-red • Cs - violet-red

#8 слайд
Chemical properties :
•
1. Alkali metals are strong reducing agents. Therefore, they react with almost all
non-metals.
•
1.1. Alkali metals readily react with halogens to form halides:
2K + I2 = 2KI
•
1.2. Alkali metals react with sulfur to form sulfides:
2Na + S = Na2S
•
1.3. Alkali metals react actively with phosphorus and hydrogen (very actively). In
this case, binary compounds are formed - phosphides and hydrides:
3K + P = K3P
2Na + H2 = 2NaH
•
1.4. Lithium reacts with nitrogen at room temperature to form nitride:
6Li + N2 = 2Li3N
Other alkali metals react with nitrogen when heated.
8 слайд
Chemical properties : • 1. Alkali metals are strong reducing agents. Therefore, they react with almost all non-metals. • 1.1. Alkali metals readily react with halogens to form halides: 2K + I2 = 2KI • 1.2. Alkali metals react with sulfur to form sulfides: 2Na + S = Na2S • 1.3. Alkali metals react actively with phosphorus and hydrogen (very actively). In this case, binary compounds are formed - phosphides and hydrides: 3K + P = K3P 2Na + H2 = 2NaH • 1.4. Lithium reacts with nitrogen at room temperature to form nitride: 6Li + N2 = 2Li3N Other alkali metals react with nitrogen when heated.

#9 слайд
•
1.5. Alkali metals react with carbon to form
carbides, mainly acetylenides:
2Na + 2C = Na2C2
•
1.6. When interacting with oxygen, each alkali
metal exhibits its own individuality: when burning
in air, lithium forms an oxide, sodium - mainly
peroxide, potassium and other metals - superoxide.
4Li + O2 = 2Li2O
2Na + O2 = Na2O2
K + O2 = KO2
9 слайд
• 1.5. Alkali metals react with carbon to form carbides, mainly acetylenides: 2Na + 2C = Na2C2 • 1.6. When interacting with oxygen, each alkali metal exhibits its own individuality: when burning in air, lithium forms an oxide, sodium - mainly peroxide, potassium and other metals - superoxide. 4Li + O2 = 2Li2O 2Na + O2 = Na2O2 K + O2 = KO2

#10 слайд
•
2. Alkali metals actively interact with complex
substances:
•
2.1. Alkali metals react violently (explosively) with
water. The interaction of alkali metals with water
leads to the formation of alkali and hydrogen.
Lithium reacts violently, but without explosion.
For example, potassium reacts very violently
with water:
2K0 + H2+O = 2K+OH + H20
10 слайд
• 2. Alkali metals actively interact with complex substances: • 2.1. Alkali metals react violently (explosively) with water. The interaction of alkali metals with water leads to the formation of alkali and hydrogen. Lithium reacts violently, but without explosion. For example, potassium reacts very violently with water: 2K0 + H2+O = 2K+OH + H20

#11 слайд
•
2.2. Alkali metals react explosively with mineral acids
(hydrochloric, phosphoric and dilute sulfuric acid). This
produces salt and hydrogen.
For example, sodium reacts violently with hydrochloric
acid:
2Na + 2HCl = 2NaCl + H2↑
•
2.3. When alkali metals react with concentrated sulfuric
acid, hydrogen sulfide is released.
For example, when sodium reacts with concentrated
sulfuric acid, sodium sulfate, hydrogen sulfide and water
are formed:
8Na + 5H2SO4(conc.) → 4Na2SO4 + H2S + 4H2O
11 слайд
• 2.2. Alkali metals react explosively with mineral acids (hydrochloric, phosphoric and dilute sulfuric acid). This produces salt and hydrogen. For example, sodium reacts violently with hydrochloric acid: 2Na + 2HCl = 2NaCl + H2↑ • 2.3. When alkali metals react with concentrated sulfuric acid, hydrogen sulfide is released. For example, when sodium reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid, sodium sulfate, hydrogen sulfide and water are formed: 8Na + 5H2SO4(conc.) → 4Na2SO4 + H2S + 4H2O

#12 слайд
•
2.4. Alkali metals react with nitric acid. When
reacting with concentrated nitric acid, nitric oxide
(I) is formed:
8Na + 10HNO3 (conc) → N2O + 8NaNO3 + 5H2O
With dilute nitric acid, molecular nitrogen is formed:
10Na + 12HNO3 (diluted)→ N2 +10NaNO3 + 6H2O
When alkali metals react with very dilute nitric
acid, ammonium nitrate is formed:
8Na + 10HNO3 = 8NaNO3 + NH4NO3 + 3H2O
12 слайд
• 2.4. Alkali metals react with nitric acid. When reacting with concentrated nitric acid, nitric oxide (I) is formed: 8Na + 10HNO3 (conc) → N2O + 8NaNO3 + 5H2O With dilute nitric acid, molecular nitrogen is formed: 10Na + 12HNO3 (diluted)→ N2 +10NaNO3 + 6H2O When alkali metals react with very dilute nitric acid, ammonium nitrate is formed: 8Na + 10HNO3 = 8NaNO3 + NH4NO3 + 3H2O

#13 слайд
•
2.5. Alkali metals can react even with substances
that exhibit very weak acidic properties. For
example, with ammonia, acetylene, alcohols,
phenol and organic acids.
For example, when lithium reacts with ammonia,
amides and hydrogen are formed:
2Li + 2NH3 = 2LiNH2 + H2 ↑
Acetylene with sodium forms sodium
acetylenide and also hydrogen:
H ─ C ≡ C ─ H + 2Na → Na ─ C≡C ─ Na + H2
13 слайд
• 2.5. Alkali metals can react even with substances that exhibit very weak acidic properties. For example, with ammonia, acetylene, alcohols, phenol and organic acids. For example, when lithium reacts with ammonia, amides and hydrogen are formed: 2Li + 2NH3 = 2LiNH2 + H2 ↑ Acetylene with sodium forms sodium acetylenide and also hydrogen: H ─ C ≡ C ─ H + 2Na → Na ─ C≡C ─ Na + H2

#14 слайд
•
Phenol reacts with sodium to form sodium phenolate and
hydrogen:
2C6H5OH + 2Na → 2C6H5ONa + H2↑
•
Methanol and sodium form sodium methoxide and
hydrogen:
2CH3OH + 2Na → 2 CH3ONa + H2↑
•
Acetic acid with lithium forms lithium acetate and
hydrogen:
2 С H3COOH + 2Li → 2CH3COOLi + H2↑
•
Alkali metals react with haloalkanes (Wurtz reaction).
For example, chloromethane with sodium forms ethane
and sodium chloride:
2CH3Cl + 2Na → C2H6 + 2NaCl
14 слайд
• Phenol reacts with sodium to form sodium phenolate and hydrogen: 2C6H5OH + 2Na → 2C6H5ONa + H2↑ • Methanol and sodium form sodium methoxide and hydrogen: 2CH3OH + 2Na → 2 CH3ONa + H2↑ • Acetic acid with lithium forms lithium acetate and hydrogen: 2 С H3COOH + 2Li → 2CH3COOLi + H2↑ • Alkali metals react with haloalkanes (Wurtz reaction). For example, chloromethane with sodium forms ethane and sodium chloride: 2CH3Cl + 2Na → C2H6 + 2NaCl

#15 слайд
•
2.6. In a melt, alkali metals can react with some
salts. Note! In solution, alkali metals will react with
water, and not with salts of other metals.
For example, sodium reacts in a melt with aluminum
chloride:
3Na + AlCl3 → 3NaCl + Al
15 слайд
• 2.6. In a melt, alkali metals can react with some salts. Note! In solution, alkali metals will react with water, and not with salts of other metals. For example, sodium reacts in a melt with aluminum chloride: 3Na + AlCl3 → 3NaCl + Al

#16 слайд
Sources used :
•
https://chemege.ru/alkalimetals/
16 слайд
Sources used : • https://chemege.ru/alkalimetals/

#17 слайд
•
Thank you for your attention !
17 слайд
• Thank you for your attention !

шағым қалдыра аласыз
















