Arenas (aromatic hydrocarbons)
Arenas (aromatic hydrocarbons)


#1 слайд
Arenas
(aromatic
hydrocarb
ons)
Completed: Kabylkakov
Amirzhan
Checked: Alexey
Nikolaevish
1 слайд
Arenas (aromatic hydrocarb ons) Completed: Kabylkakov Amirzhan Checked: Alexey Nikolaevish

#2 слайд
Presentation plan :
•
What are Arenas?
•
Arena structure :
•
Homologous series of arenes :
•
Arena nomenclature :
•
Arene isomerism :
•
Chemical properties of arenes :
•
Getting arenas :
2 слайд
Presentation plan : • What are Arenas? • Arena structure : • Homologous series of arenes : • Arena nomenclature : • Arene isomerism : • Chemical properties of arenes : • Getting arenas :

#3 слайд
What are Arenas?
•
Arenas are unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons, the
molecules of which contain stable cyclic groups of
atoms (benzene nuclei) with a closed system of
conjugated bonds.
•
Arenas are also called aromatic hydrocarbons. The
first member of the homologous series is benzene -
C6H6.
•
General formula: CnH2n–6 for n ≥ 6.
3 слайд
What are Arenas? • Arenas are unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons, the molecules of which contain stable cyclic groups of atoms (benzene nuclei) with a closed system of conjugated bonds. • Arenas are also called aromatic hydrocarbons. The first member of the homologous series is benzene - C6H6. • General formula: CnH2n–6 for n ≥ 6.
#4 слайд
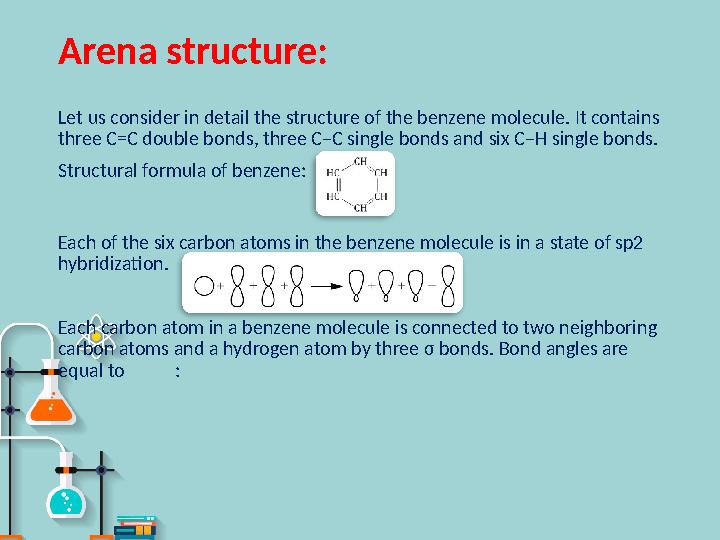
Arena structure :
Let us consider in detail the structure of the benzene molecule. It contains
three C=C double bonds, three C–C single bonds and six C–H single bonds.
Structural formula of benzene:
Each of the six carbon atoms in the benzene molecule is in a state of sp2
hybridization.
Each carbon atom in a benzene molecule is connected to two neighboring
carbon atoms and a hydrogen atom by three σ bonds. Bond angles are
equal to :
4 слайд
Arena structure : Let us consider in detail the structure of the benzene molecule. It contains three C=C double bonds, three C–C single bonds and six C–H single bonds. Structural formula of benzene: Each of the six carbon atoms in the benzene molecule is in a state of sp2 hybridization. Each carbon atom in a benzene molecule is connected to two neighboring carbon atoms and a hydrogen atom by three σ bonds. Bond angles are equal to :
#5 слайд
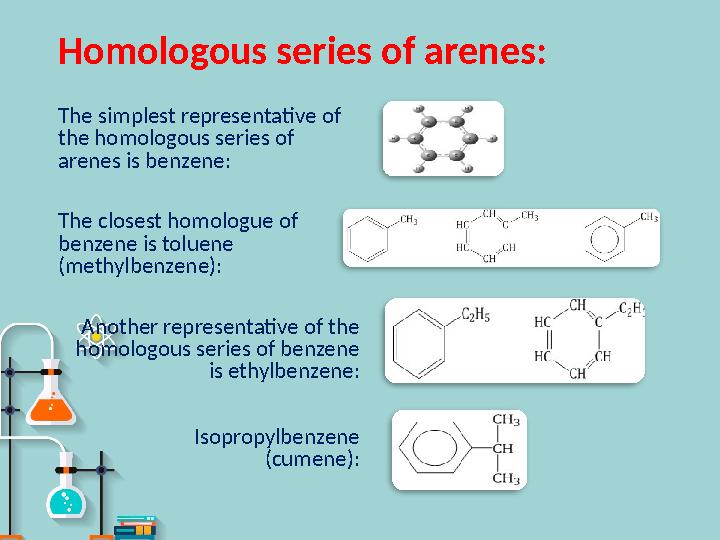
Homologous series of arenes :
The simplest representative of
the homologous series of
arenes is benzene:
The closest homologue of
benzene is toluene
(methylbenzene):
Another representative of the
homologous series of benzene
is ethylbenzene:
Isopropylbenzene
(cumene):
5 слайд
Homologous series of arenes : The simplest representative of the homologous series of arenes is benzene: The closest homologue of benzene is toluene (methylbenzene): Another representative of the homologous series of benzene is ethylbenzene: Isopropylbenzene (cumene):
#6 слайд
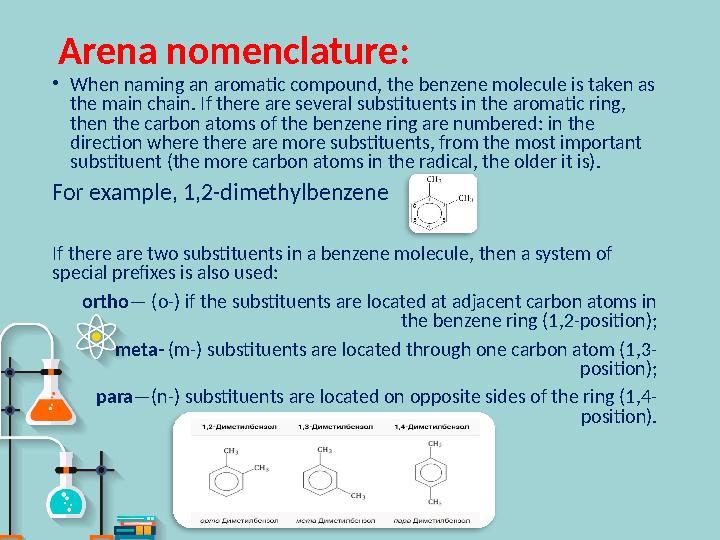
Arena nomenclature :
•
When naming an aromatic compound, the benzene molecule is taken as
the main chain. If there are several substituents in the aromatic ring,
then the carbon atoms of the benzene ring are numbered: in the
direction where there are more substituents, from the most important
substituent (the more carbon atoms in the radical, the older it is).
For example, 1,2-dimethylbenzene
If there are two substituents in a benzene molecule, then a system of
special prefixes is also used:
ortho — (o-) if the substituents are located at adjacent carbon atoms in
the benzene ring (1,2-position);
meta- (m-) substituents are located through one carbon atom (1,3-
position);
para —(n-) substituents are located on opposite sides of the ring (1,4-
position).
6 слайд
Arena nomenclature : • When naming an aromatic compound, the benzene molecule is taken as the main chain. If there are several substituents in the aromatic ring, then the carbon atoms of the benzene ring are numbered: in the direction where there are more substituents, from the most important substituent (the more carbon atoms in the radical, the older it is). For example, 1,2-dimethylbenzene If there are two substituents in a benzene molecule, then a system of special prefixes is also used: ortho — (o-) if the substituents are located at adjacent carbon atoms in the benzene ring (1,2-position); meta- (m-) substituents are located through one carbon atom (1,3- position); para —(n-) substituents are located on opposite sides of the ring (1,4- position).
#7 слайд
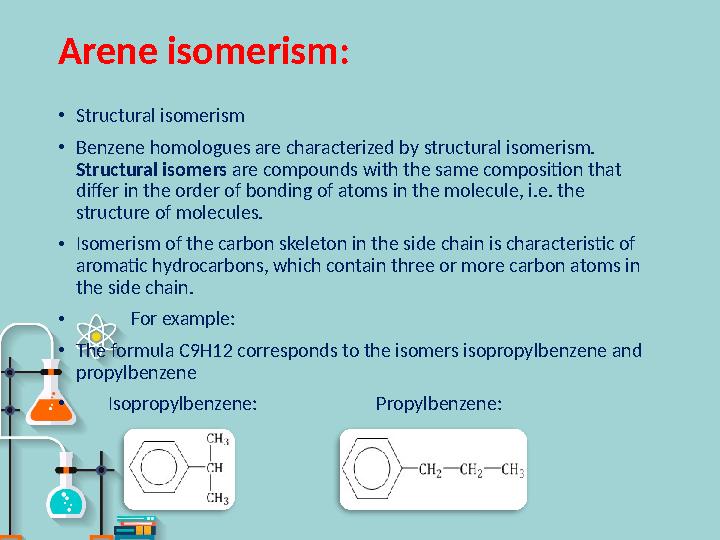
Arene isomerism :
•
Structural isomerism
•
Benzene homologues are characterized by structural isomerism.
Structural isomers are compounds with the same composition that
differ in the order of bonding of atoms in the molecule, i.e. the
structure of molecules.
•
Isomerism of the carbon skeleton in the side chain is characteristic of
aromatic hydrocarbons, which contain three or more carbon atoms in
the side chain.
•
For example :
•
The formula C9H12 corresponds to the isomers isopropylbenzene and
propylbenzene
•
Isopropylbenzene : Propylbenzene :
7 слайд
Arene isomerism : • Structural isomerism • Benzene homologues are characterized by structural isomerism. Structural isomers are compounds with the same composition that differ in the order of bonding of atoms in the molecule, i.e. the structure of molecules. • Isomerism of the carbon skeleton in the side chain is characteristic of aromatic hydrocarbons, which contain three or more carbon atoms in the side chain. • For example : • The formula C9H12 corresponds to the isomers isopropylbenzene and propylbenzene • Isopropylbenzene : Propylbenzene :
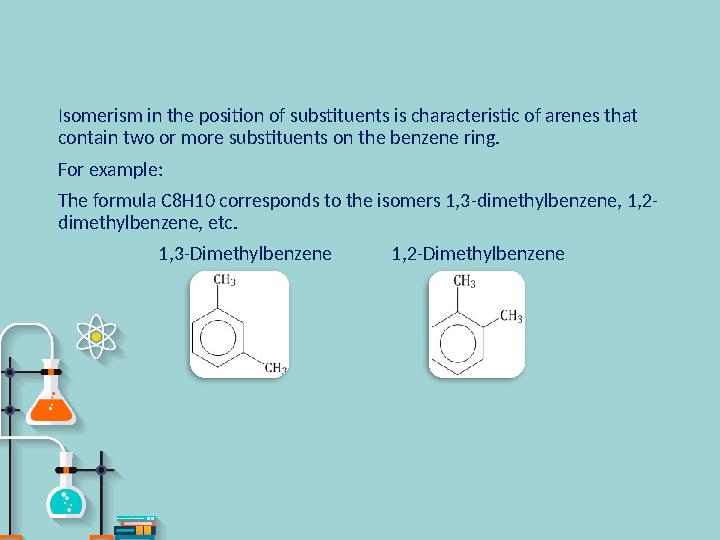
#8 слайд
Isomerism in the position of substituents is characteristic of arenes that
contain two or more substituents on the benzene ring.
For example :
The formula C8H10 corresponds to the isomers 1,3-dimethylbenzene, 1,2-
dimethylbenzene, etc.
1,3-Dimethylbenzene 1,2-Dimethylbenzene
8 слайд
Isomerism in the position of substituents is characteristic of arenes that contain two or more substituents on the benzene ring. For example : The formula C8H10 corresponds to the isomers 1,3-dimethylbenzene, 1,2- dimethylbenzene, etc. 1,3-Dimethylbenzene 1,2-Dimethylbenzene
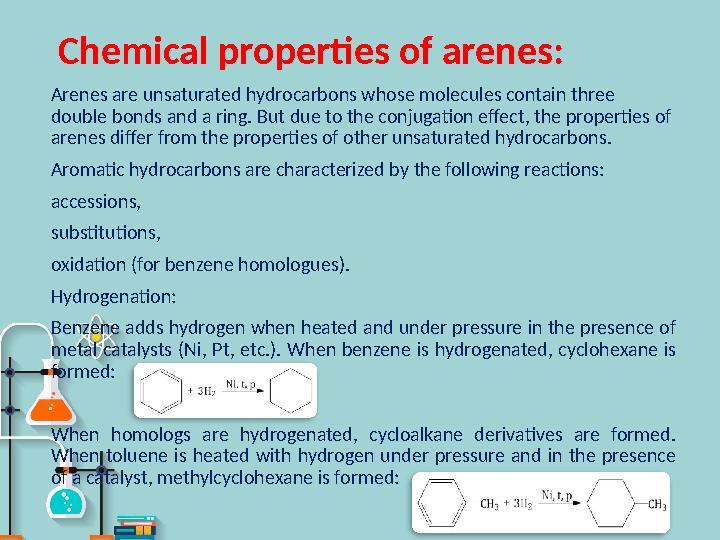
#9 слайд
Chemical properties of arenes :
Arenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons whose molecules contain three
double bonds and a ring. But due to the conjugation effect, the properties of
arenes differ from the properties of other unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Aromatic hydrocarbons are characterized by the following reactions:
accessions,
substitutions,
oxidation (for benzene homologues).
Hydrogenation :
Benzene adds hydrogen when heated and under pressure in the presence of
metal catalysts (Ni, Pt, etc.). When benzene is hydrogenated, cyclohexane is
formed:
When homologs are hydrogenated, cycloalkane derivatives are formed.
When toluene is heated with hydrogen under pressure and in the presence
of a catalyst, methylcyclohexane is formed:
9 слайд
Chemical properties of arenes : Arenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons whose molecules contain three double bonds and a ring. But due to the conjugation effect, the properties of arenes differ from the properties of other unsaturated hydrocarbons. Aromatic hydrocarbons are characterized by the following reactions: accessions, substitutions, oxidation (for benzene homologues). Hydrogenation : Benzene adds hydrogen when heated and under pressure in the presence of metal catalysts (Ni, Pt, etc.). When benzene is hydrogenated, cyclohexane is formed: When homologs are hydrogenated, cycloalkane derivatives are formed. When toluene is heated with hydrogen under pressure and in the presence of a catalyst, methylcyclohexane is formed:
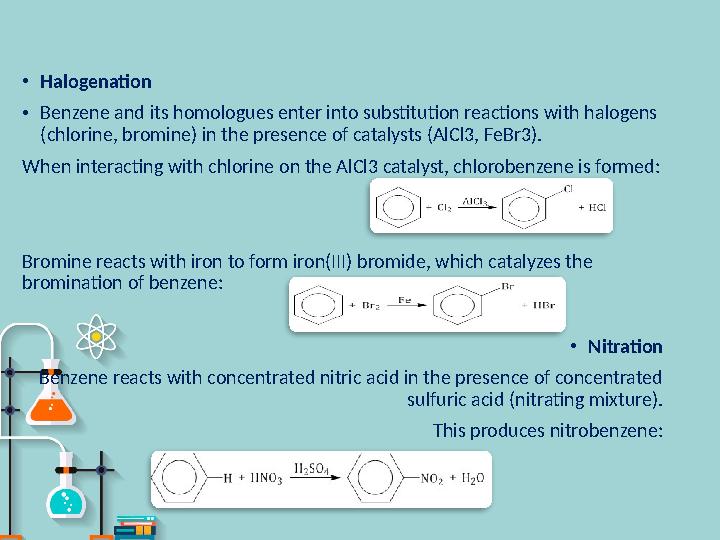
#10 слайд
•
Halogenation
•
Benzene and its homologues enter into substitution reactions with halogens
(chlorine, bromine) in the presence of catalysts (AlCl3, FeBr3).
When interacting with chlorine on the AlCl3 catalyst, chlorobenzene is formed:
Bromine reacts with iron to form iron(III) bromide, which catalyzes the
bromination of benzene:
•
Nitration
Benzene reacts with concentrated nitric acid in the presence of concentrated
sulfuric acid (nitrating mixture).
This produces nitrobenzene:
10 слайд
• Halogenation • Benzene and its homologues enter into substitution reactions with halogens (chlorine, bromine) in the presence of catalysts (AlCl3, FeBr3). When interacting with chlorine on the AlCl3 catalyst, chlorobenzene is formed: Bromine reacts with iron to form iron(III) bromide, which catalyzes the bromination of benzene: • Nitration Benzene reacts with concentrated nitric acid in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid (nitrating mixture). This produces nitrobenzene:
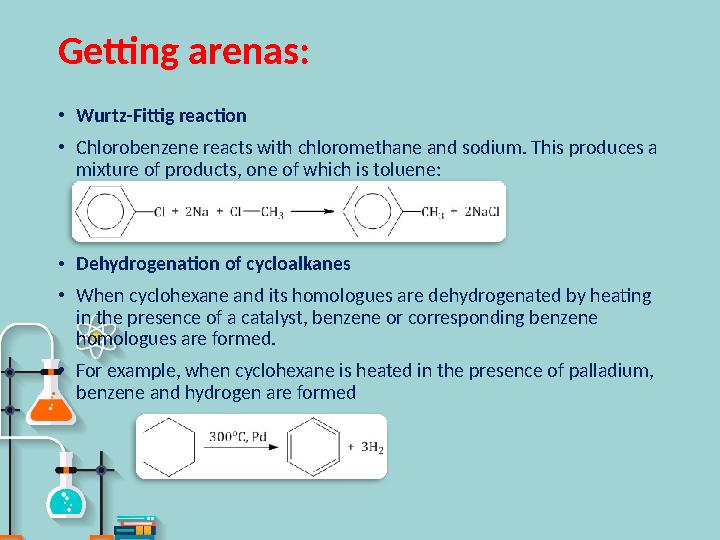
#11 слайд
Getting arenas :
•
Wurtz-Fittig reaction
•
Chlorobenzene reacts with chloromethane and sodium. This produces a
mixture of products, one of which is toluene:
•
Dehydrogenation of cycloalkanes
•
When cyclohexane and its homologues are dehydrogenated by heating
in the presence of a catalyst, benzene or corresponding benzene
homologues are formed.
•
For example, when cyclohexane is heated in the presence of palladium,
benzene and hydrogen are formed
11 слайд
Getting arenas : • Wurtz-Fittig reaction • Chlorobenzene reacts with chloromethane and sodium. This produces a mixture of products, one of which is toluene: • Dehydrogenation of cycloalkanes • When cyclohexane and its homologues are dehydrogenated by heating in the presence of a catalyst, benzene or corresponding benzene homologues are formed. • For example, when cyclohexane is heated in the presence of palladium, benzene and hydrogen are formed
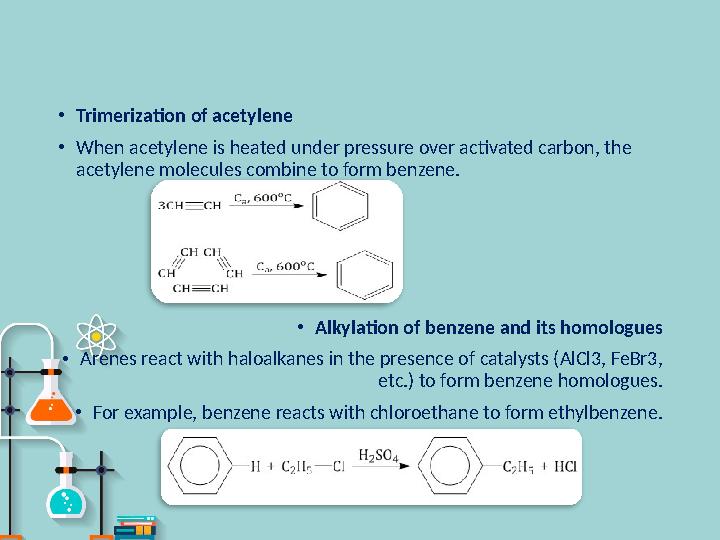
#12 слайд
•
Trimerization of acetylene
•
When acetylene is heated under pressure over activated carbon, the
acetylene molecules combine to form benzene.
•
Alkylation of benzene and its homologues
•
Arenes react with haloalkanes in the presence of catalysts (AlCl3, FeBr3,
etc.) to form benzene homologues.
•
For example, benzene reacts with chloroethane to form ethylbenzene .
12 слайд
• Trimerization of acetylene • When acetylene is heated under pressure over activated carbon, the acetylene molecules combine to form benzene. • Alkylation of benzene and its homologues • Arenes react with haloalkanes in the presence of catalysts (AlCl3, FeBr3, etc.) to form benzene homologues. • For example, benzene reacts with chloroethane to form ethylbenzene .

#13 слайд
•
Thank you for your
attention !
13 слайд
• Thank you for your attention !

шағым қалдыра аласыз
















